

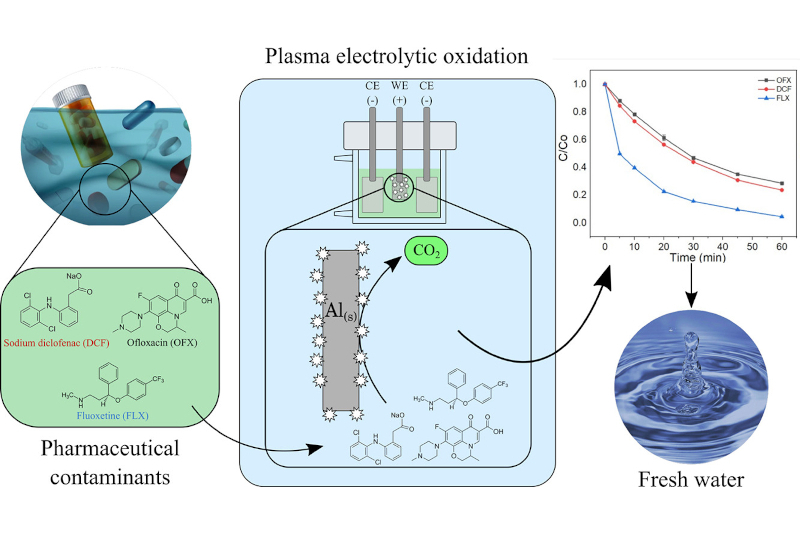
A study supported by FAPESP tested using high-energy sparks to degrade pollutants without generating waste.

A study supported by FAPESP tested using high-energy sparks to degrade pollutants without generating waste.
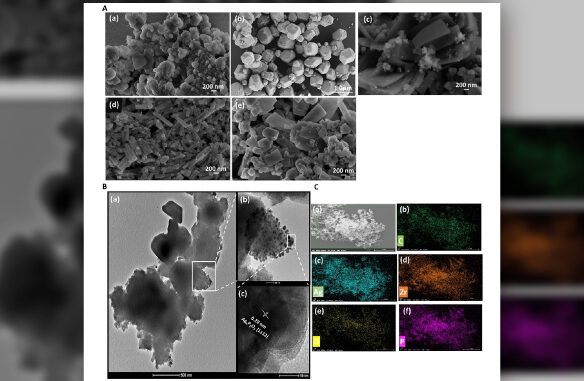
Study involving researchers from a FAPESP-supported center presents a new molecular architecture based on zirconium metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) designed for efficiently degrading emerging water contaminants.

Researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo found that the toxicological effects of the drug on marine animals may be greater than those of cocaine. Preliminary results of the study were presented during the São Paulo School of Advanced Science on Emerging Pollutants.

Study shows that most of the country’s underground reservoirs will lose their capacity for renewal, increasing the risk of water shortages in several regions, especially the Southeast and South. One strategy to address the problem is “managed recharge,” which includes techniques that promote the infiltration of rainwater or even treated sewage.

Non-compliance with the law, facilitated by errors in the technical language used in environmental licensing, has already led to the loss of over 580,000 hectares of native vegetation, 61% of which has been converted for agricultural use.

In addition to the scarcity and unequal distribution of water, quality is being strongly affected by agricultural pesticides, industrial waste, and the disposal of medicines and hygiene products.
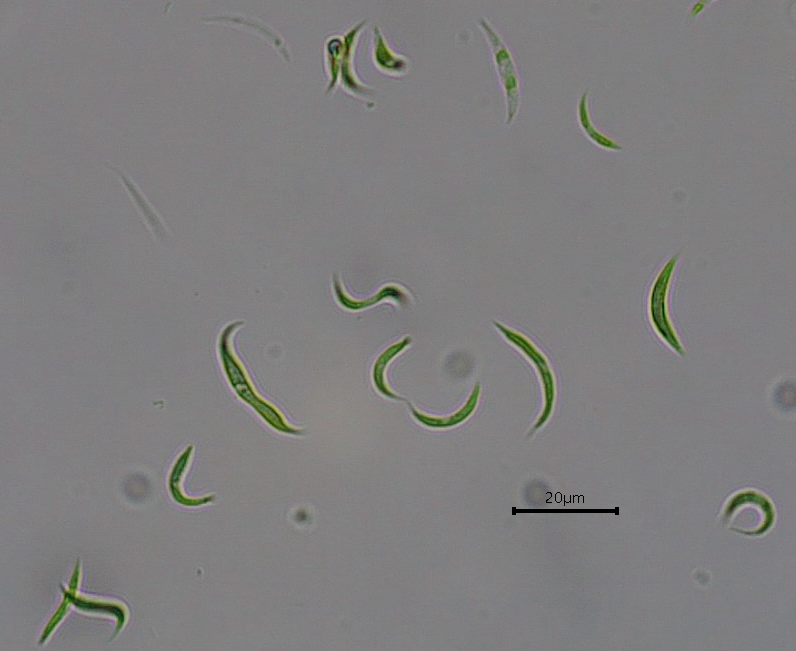
In the laboratory, the species Monoraphidium contortum removed some of the drugs added to the liquid and produced biomass with potential commercial value.

In a ceremony at the University of São Paulo, which hosts the Center of Excellence in Ocean Innovation and Transformative Technologies, researchers and high officials celebrated a partnership set to foster research on ocean sustainability and fuel public policy.

For Elena Fernandez de la Iglesia, from the Faculty of Law at the Complutense University of Madrid, taxing producers and consumers according to the amount and type of material used is one of the best tools for promoting the circular economy. The topic was discussed during FAPESP Week Spain.

The Guarani Aquifer is the source of drinking water for some 90 million people and is being overused in several areas of São Paulo state (Brazil). The researchers deployed stable isotopes to estimate the relative contributions of rainwater and groundwater to the maintenance of springs in the region.
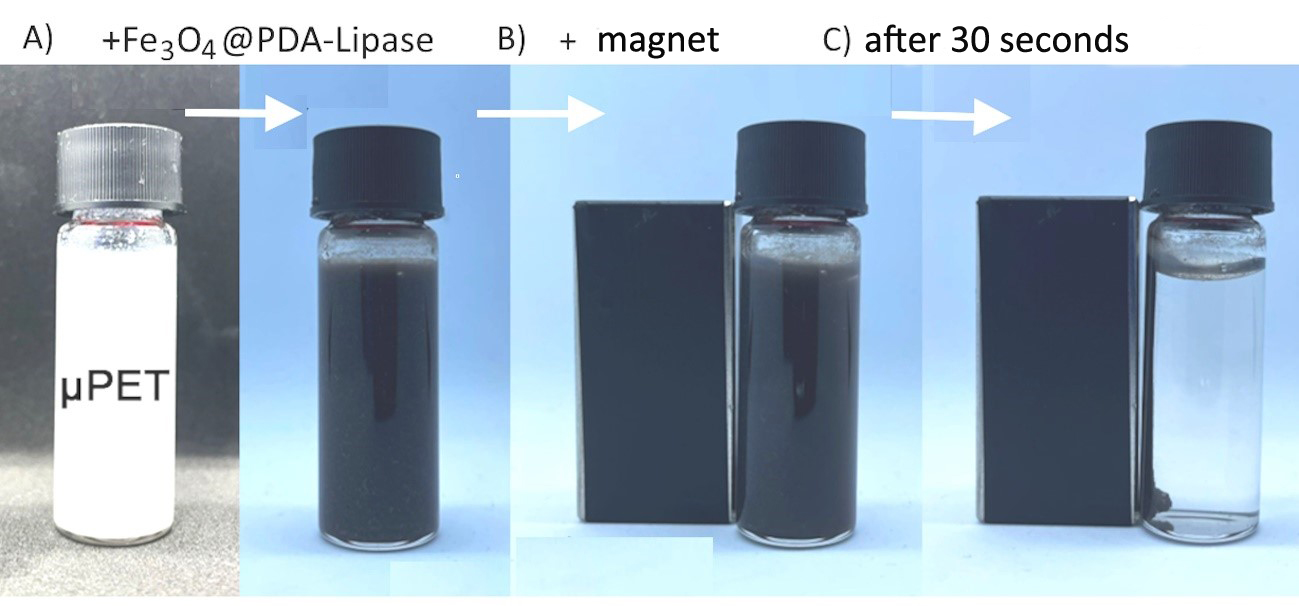
The strategy developed at the University of São Paulo uses magnetic nanoparticles that bind to tiny plastic particles and permit their removal with the aid of a magnet.

The solution, developed by a startup supported by FAPESP, enables farmers to forecast water availability for a six-month horizon.
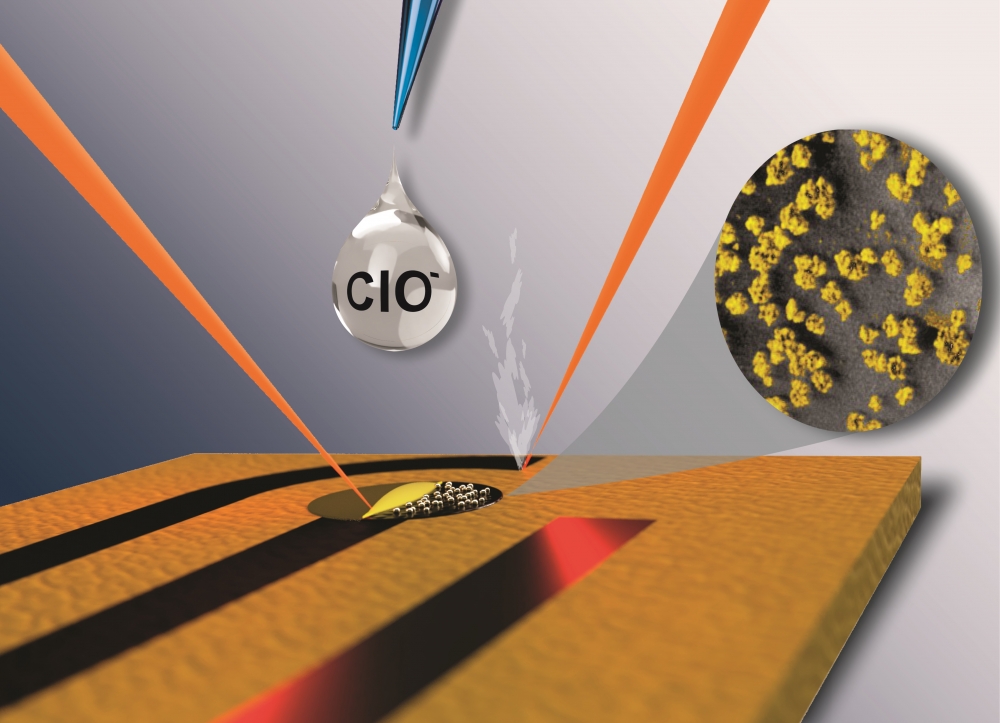
The device developed at the University of São Paulo is inexpensive, environmentally friendly and easy to use. A patent application has been filed.

The drug accumulates not only in water, but also in sediments and marine organisms, and poses a high ecological risk, said Camilo Seabra, a professor at the Federal University of São Paulo, during FAPESP Week Illinois.
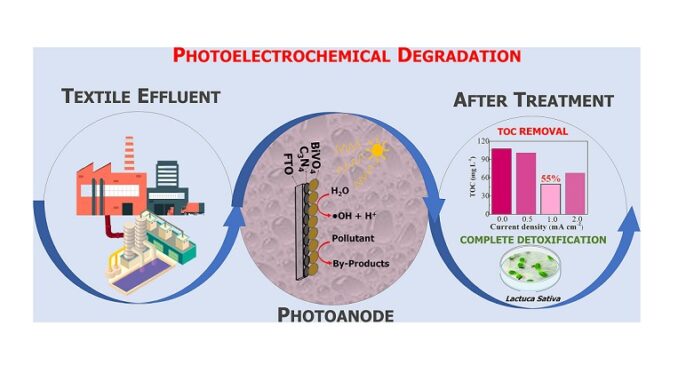
Investigators affiliated with two FAPESP-supported research centers conducted an experiment using actual effluent from the textile industry. The results are detailed in the journal Chemosphere.
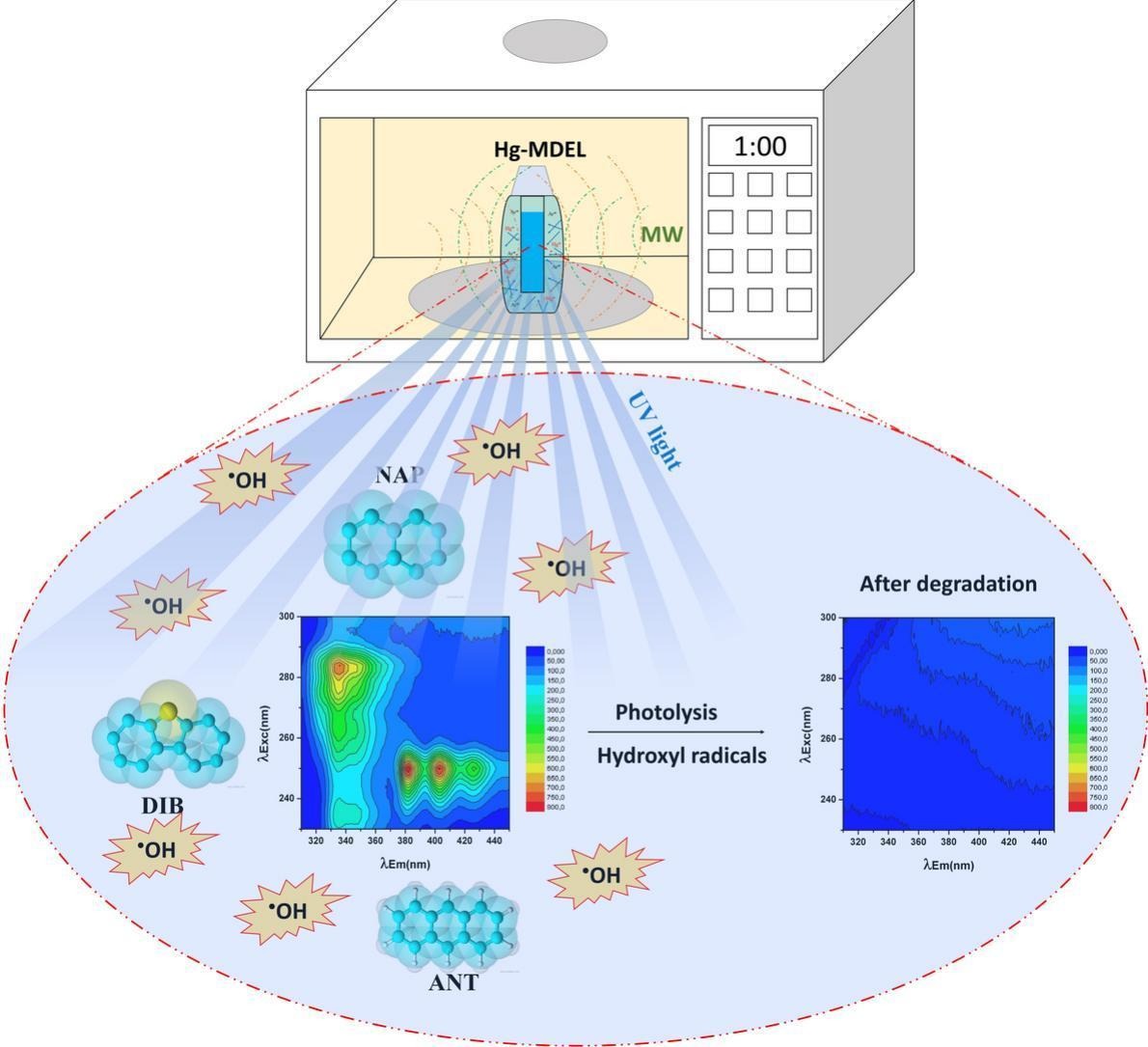
Brazilian scientists tested a simple and sustainable method for monitoring and degrading a mixture of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, compounds present in fossil fuels and industrial waste.
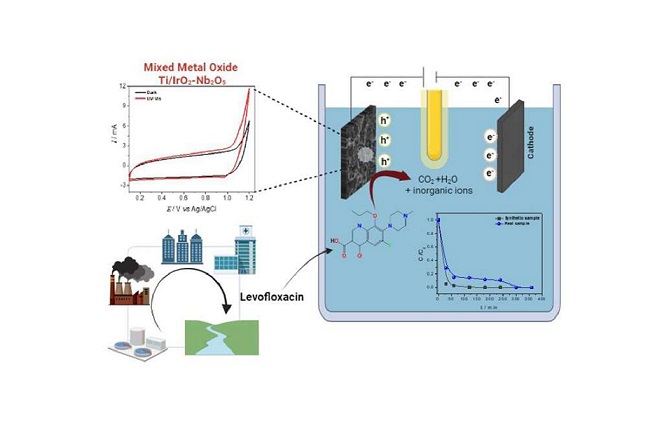
An electrode with films of iridium dioxide and niobium oxide on a titanium substrate removed molecules of the drug levofloxacin, considered an emerging pollutant.

Brazilian researchers tested a photocatalyst based on zinc oxide and found it to perform well in degrading sertraline, an emerging pollutant.
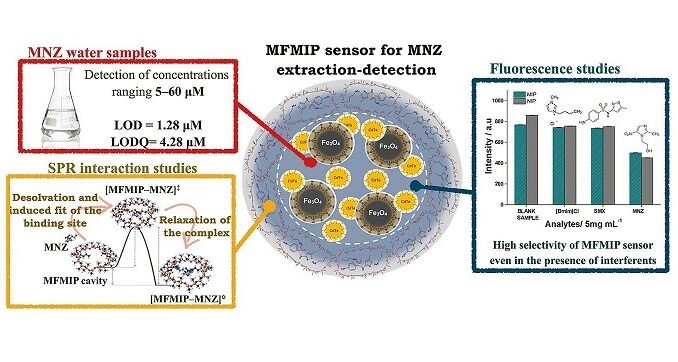
The device, which combines magnetic fluorescent nanoparticles, was designed at the Center for Development of Functional Materials, a research center supported by FAPESP and hosted by the Federal University of São Carlos.

Scientists at the State University of Campinas analyzed samples taken at 15 points in the basin comprising the Piracicaba, Capivari and Jundiaí Rivers, and detected 45 contaminants, including compounds from agricultural, industrial and household effluents not yet regulated by Brazilian legislation.
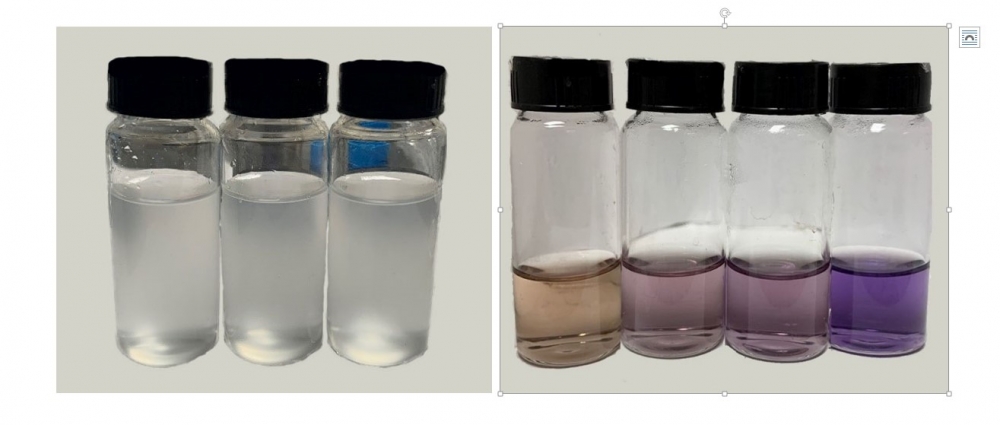

The technique uses functionalized cellulose fibers from sugarcane bagasse to remove residues of the herbicide from an aqueous medium.
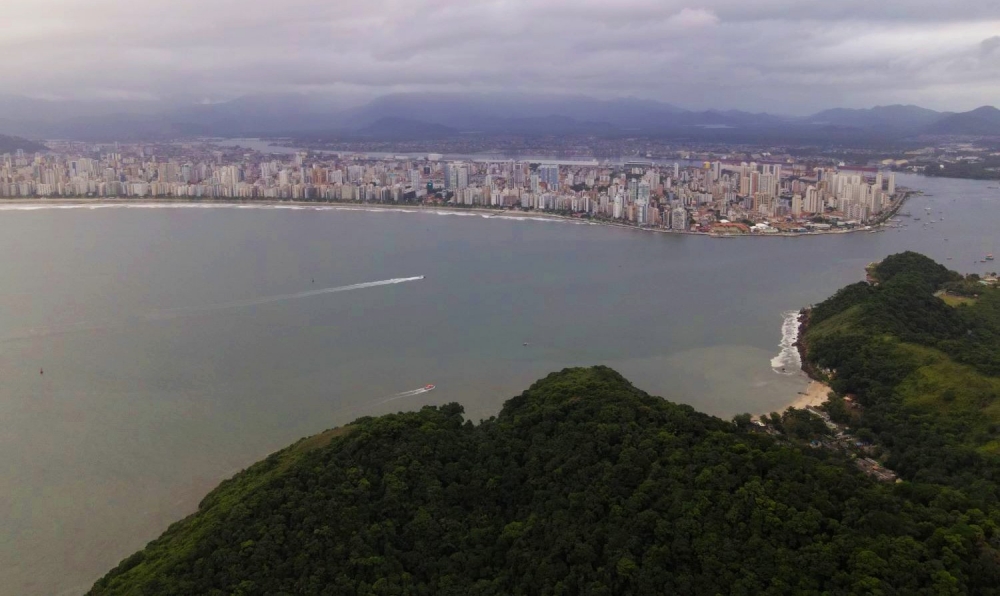

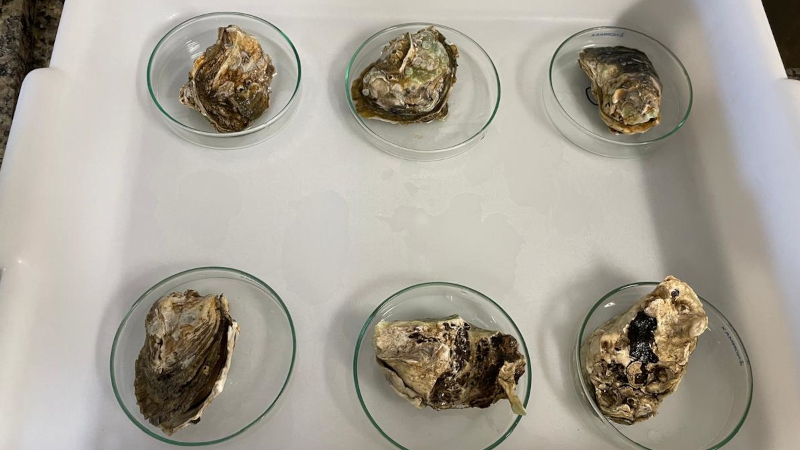
Researchers sampled oysters and mussels at three locations between the port of Santos and the nearby city of Guarujá. Their aims included assembling data as a basis for public policy on basic sanitation. The law does not currently require removal of microplastic particles from sewage.
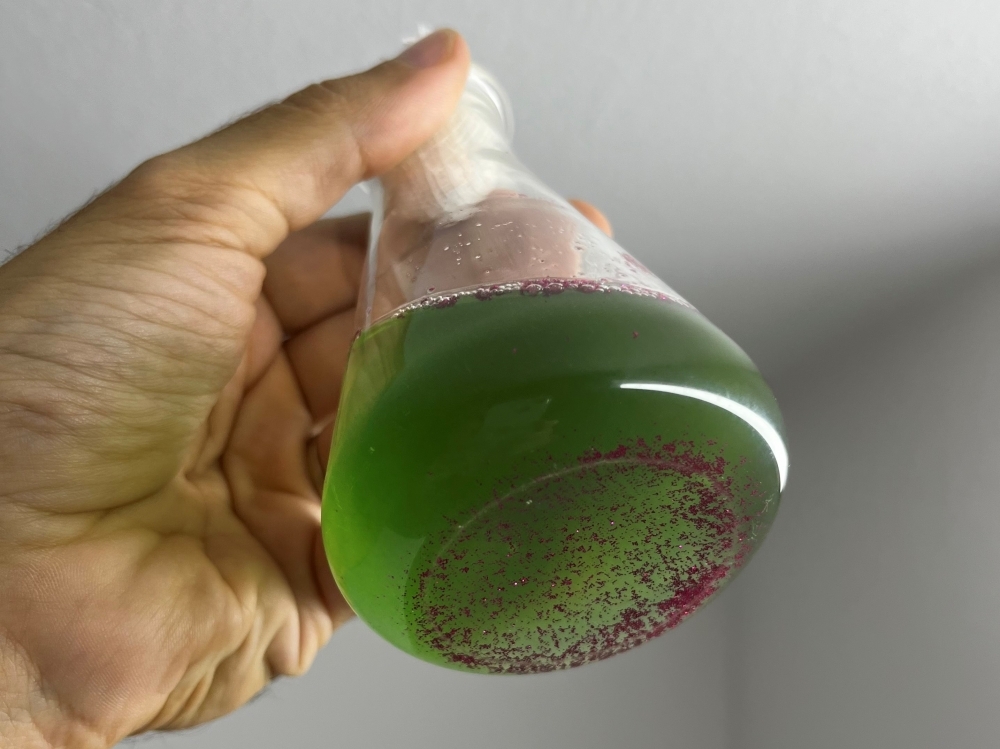

Researchers at the University of São Paulo investigated the effects of five concentrations of glitter on two strains of cyanobacteria. Use of the material in makeup, party costumes and decorations should be reconsidered, they argue.
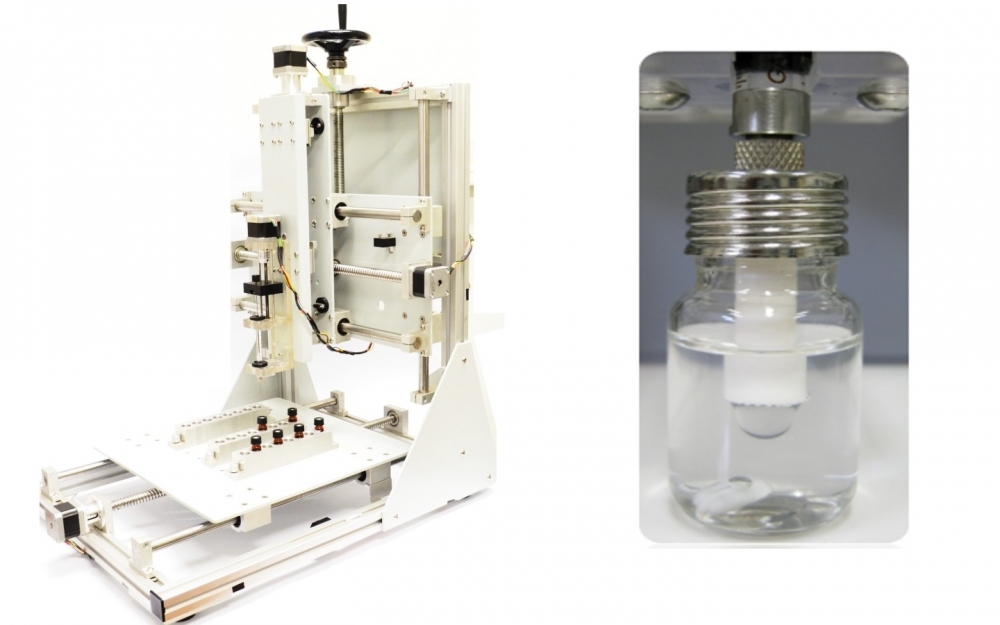

Technology developed at the University of São Paulo increases the precision of chemical analysis and reduces the use of expensive toxic solvents. The immediate focus was on parabens, potentially carcinogenic compounds used in industry as preservatives.