


Study observed accumulation of plastic on Trindade Island, Brazil’s easternmost territory, precisely in the depressions where turtles lay their eggs and hatchlings are born.

Study observed accumulation of plastic on Trindade Island, Brazil’s easternmost territory, precisely in the depressions where turtles lay their eggs and hatchlings are born.
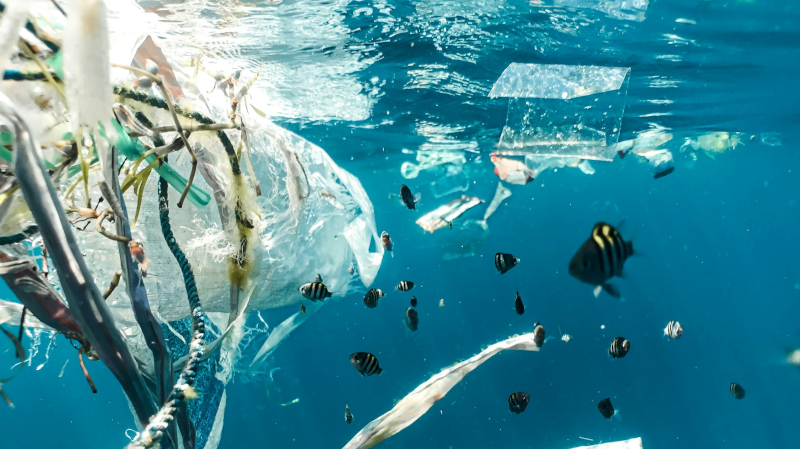

A study by researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo synthesized data from 6,049 contamination records on all continents over the last decade.

A study by researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo synthesized data from 6,049 contamination records on all continents over the last decade.

Unprecedented footage of jaguar cichlid being preyed upon was captured after heavy rains caused the overflow of freshwater into Sueste Bay, the species’ feeding ground.

Coastal ecosystems are being affected by the rising sea level associated with the expansion of real estate development; Marine scientist Omar Defeo, a professor at Uruguay’s University of the Republic, addressed this topic during the FAPESP Day Uruguay symposium.

Researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo found that the toxicological effects of the drug on marine animals may be greater than those of cocaine. Preliminary results of the study were presented during the São Paulo School of Advanced Science on Emerging Pollutants.
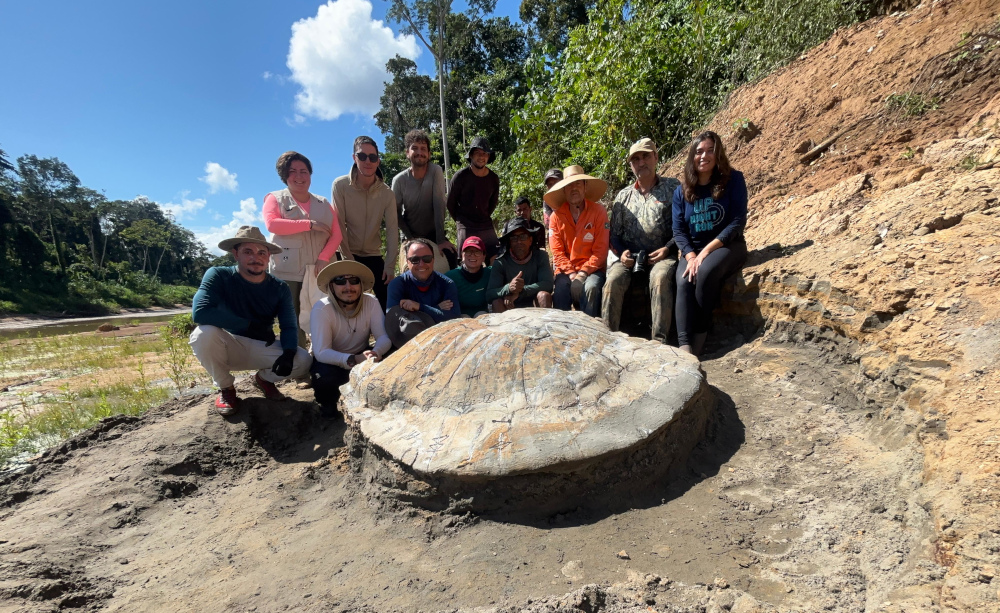

On its first expedition, a project funded by the Amazon+10 Initiative reveals clues about the Amazon millions of years ago.
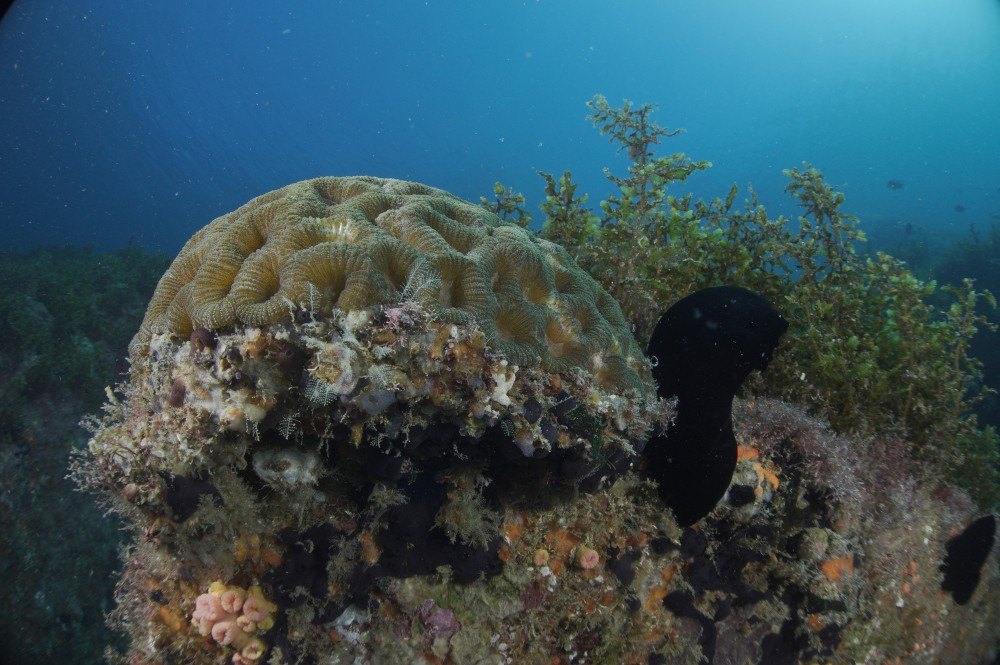

A single species found in the Alcatrazes Archipelago, brain coral, produces around 170 tons of calcium carbonate annually. This represents the retention of approximately 20 tons of carbon in mineral form, which can last for centuries or millennia. A study by the Federal University of São Paulo highlights the potential ecosystem services provided by subtropical corals.
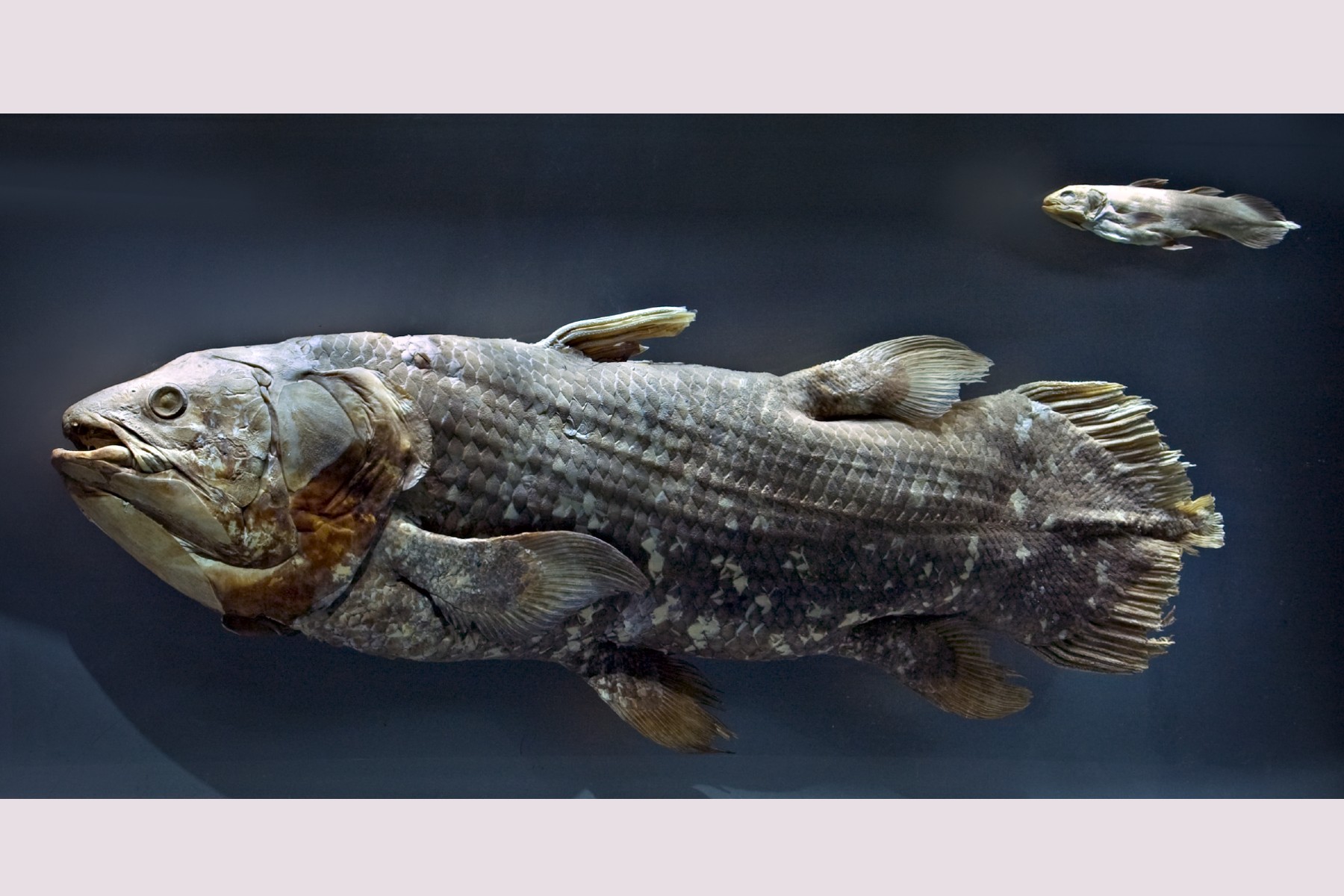

Researchers reanalyzed the skull musculature of coelacanths, a group of fish that has existed for 400 million years, and concluded that many structures had been incorrectly described. The study was published in Science Advances by researchers from the University of São Paulo and the Smithsonian Institution.
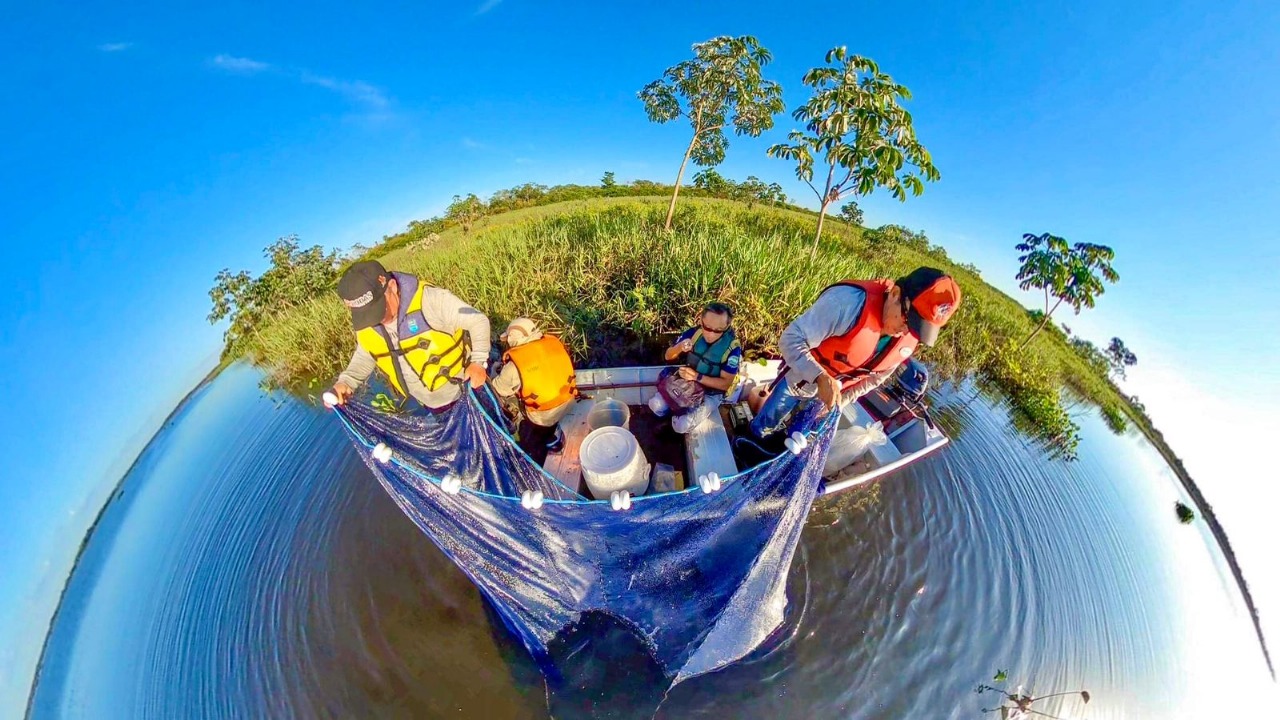

An analysis of data collected over 20 years in the upper stretch of the river shows a 50% loss in economic gains from fishing. Native fish have become smaller and smaller. Conversely, invasive species, which have a lower market value, are becoming more abundant. The phenomenon has been accompanied by a loss of vegetation cover on the riverbanks.

Event will be promoted by the Institute of Marine Science of the Federal University of São Paulo between August 19th and September 1st.

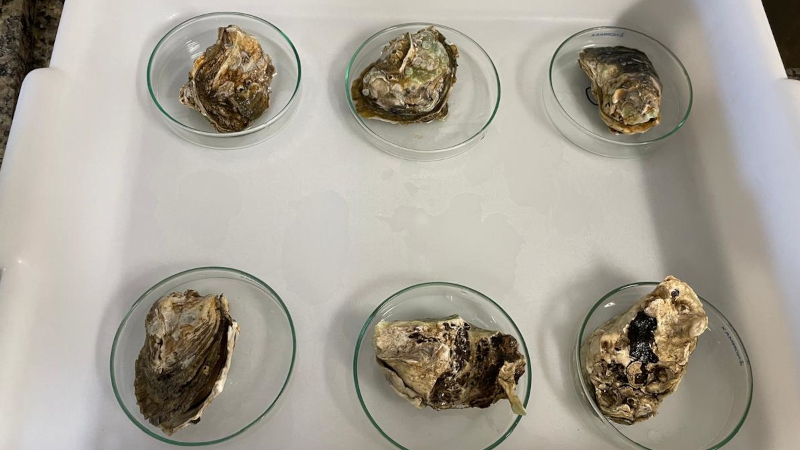
Researchers from the Federal University of São Paulo used oysters and mussels as sentinel organisms to assess the presence of these pollutants. The results show that even the most restrictive sites for human presence have significant contamination.

Among the 36 authors, André Morandini, director of the Center for Marine Biology of the University of São Paulo, presents the results of studies supported by FAPESP.

Coordinators of the FAPESP Program for the South Atlantic and Antarctica begin mapping São Paulo’s ocean science at an event in Santos.

In three recent articles, scientists associated with the Center for Development of Functional Materials warn of the synergistic effect of substances when mixed together.

Brazilian and British researchers have observed that a small crustacean that changes color according to the marine vegetation is able to disguise itself in exotic algae that did not evolve together with the species. However, the long-term effects of this interaction are unknown.
UN recognition will enhance the visibility of FAPESP’s initiative to establish a new strategy for funding research on the southern portion of the Atlantic Ocean and the planet’s coldest continent.
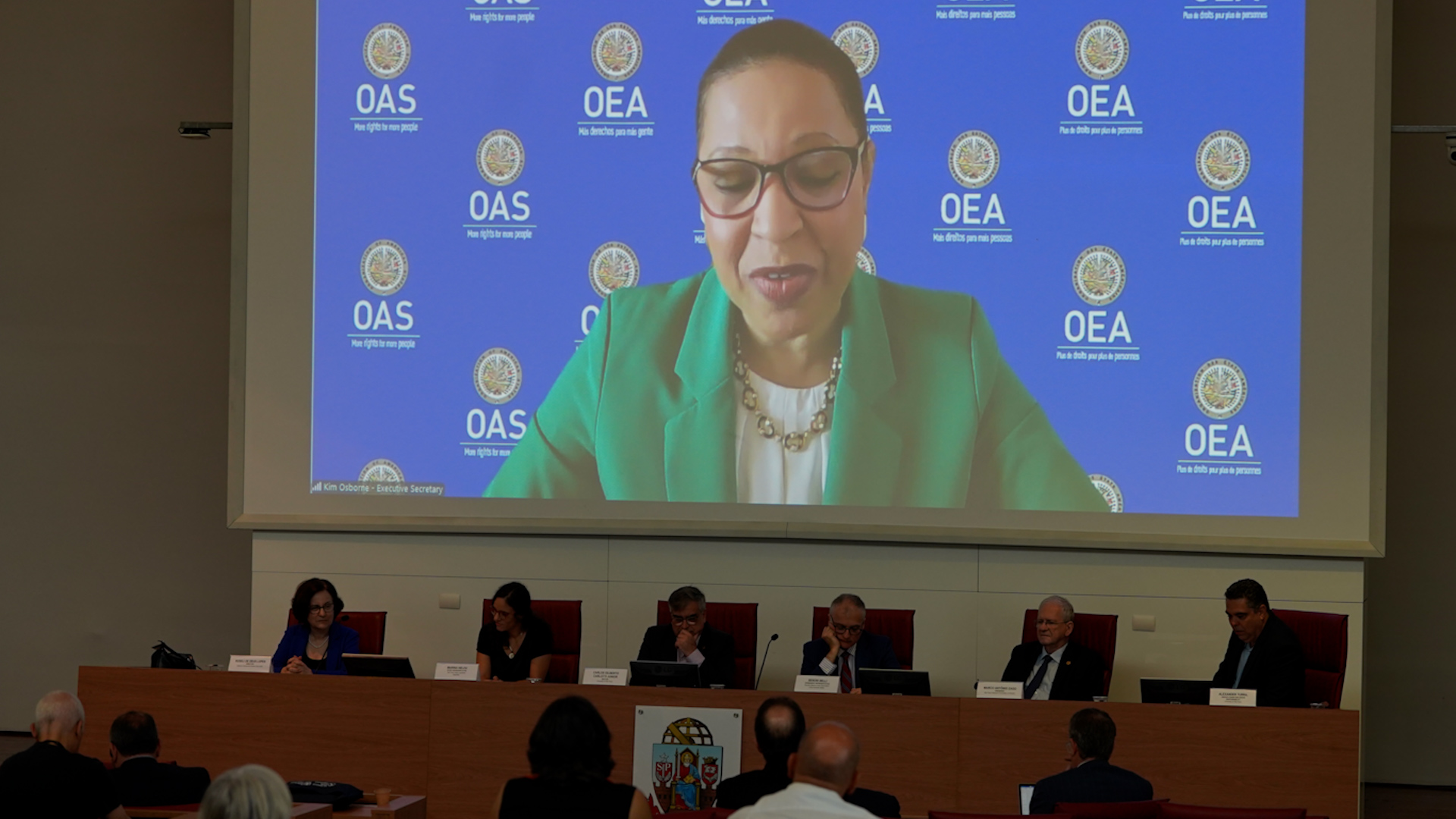

In a ceremony at the University of São Paulo, which hosts the Center of Excellence in Ocean Innovation and Transformative Technologies, researchers and high officials celebrated a partnership set to foster research on ocean sustainability and fuel public policy.
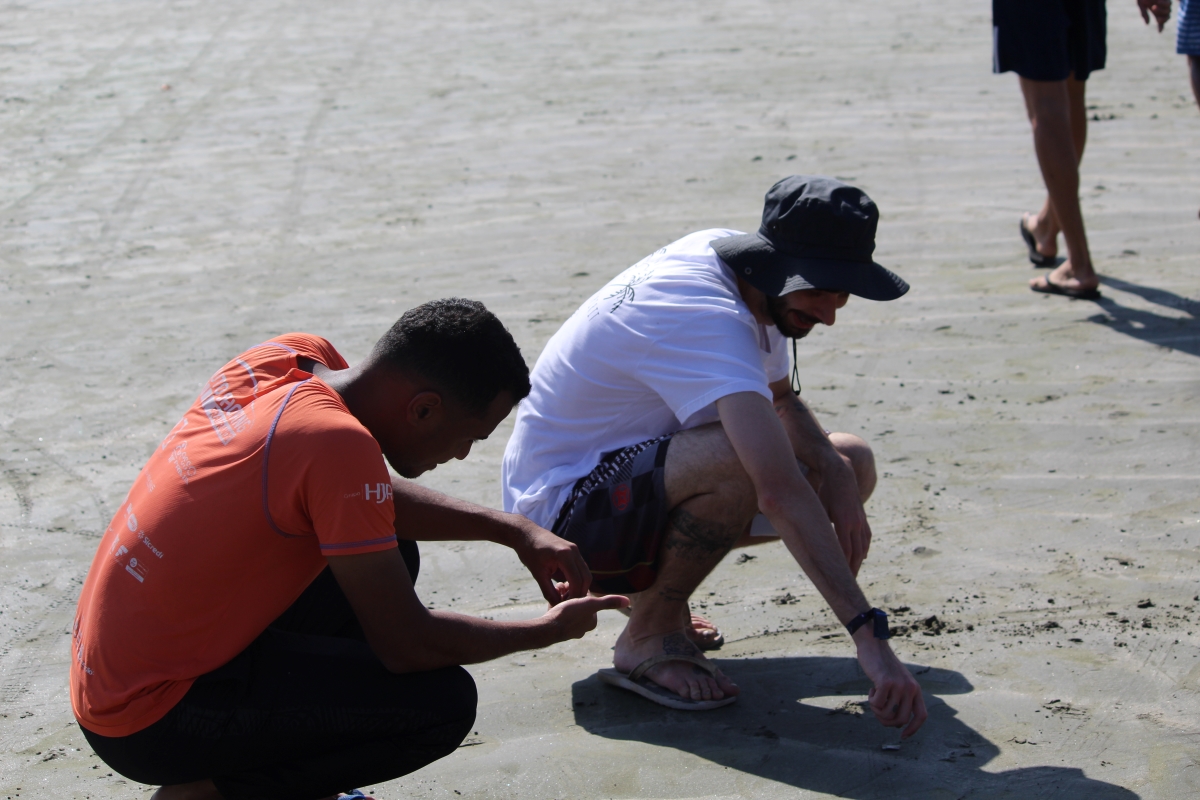

Researchers partnering with the City of Guarujá (São Paulo state) conducted a study that found a high level of contamination on Perequê Beach, with plastics and cigarette butts predominating. The results will be useful for policymakers to implement measures that can mitigate the problem.
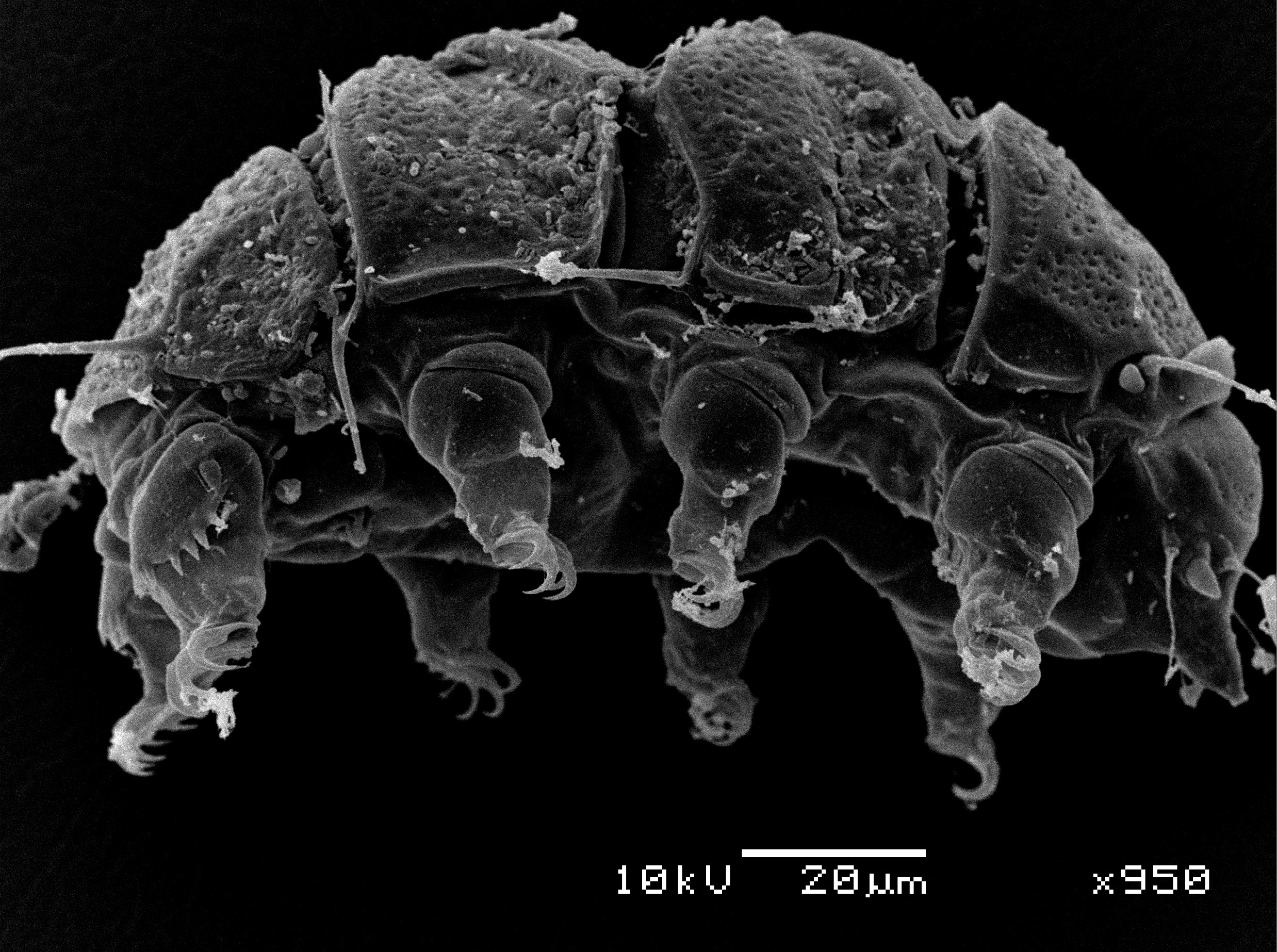

A study conducted by researchers at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP) suggests that species thought to be distributed worldwide probably do not exist in Central and South America. At the same time, a wide array of environments and few specimens from the region point to the likelihood of vast species richness.
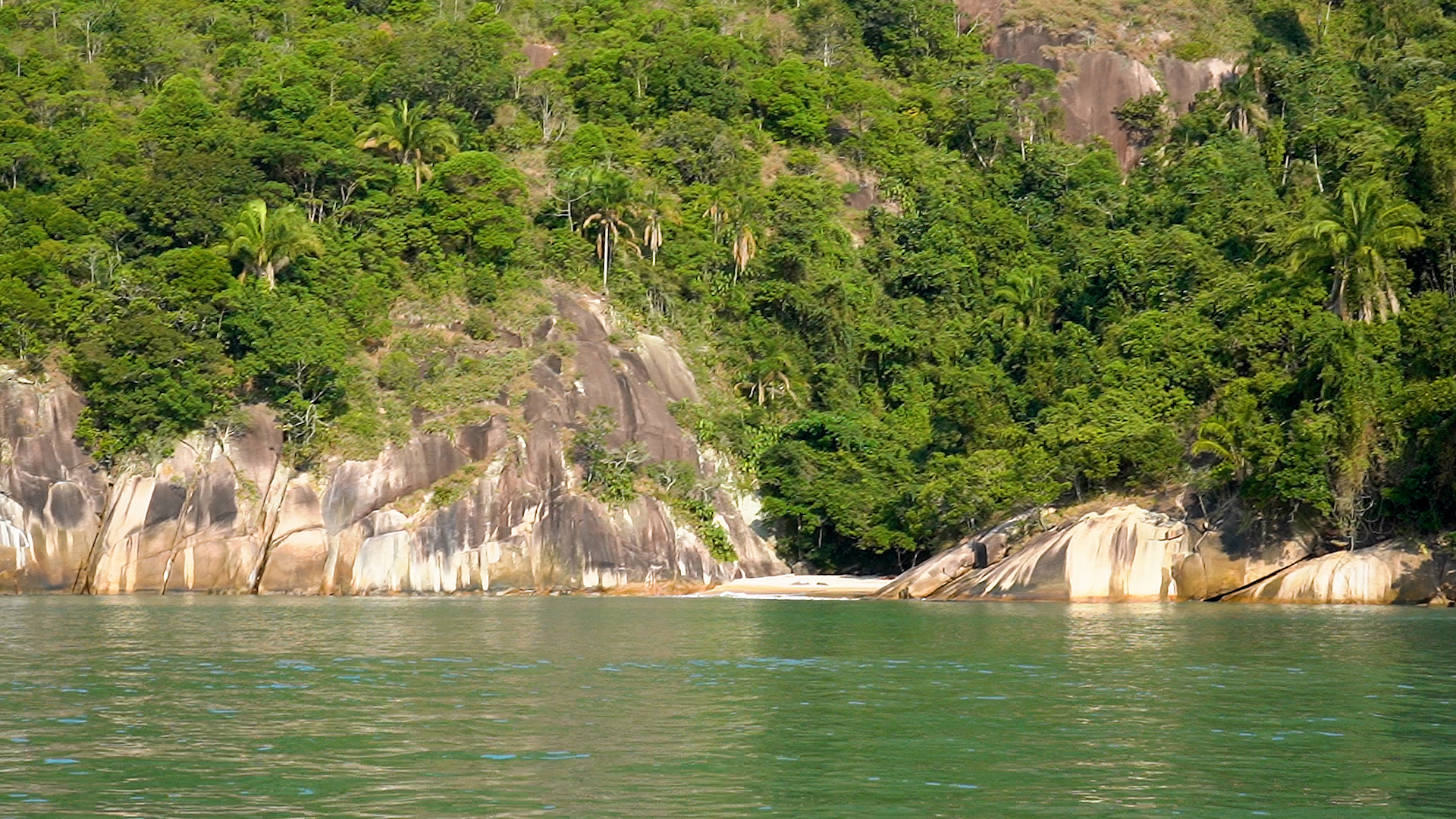

Marine organisms in areas influenced by lower sea surface temperatures, such as the Lakes Region in Rio de Janeiro state, are between 25% and 100% larger than those inhabiting warmer water along the coast of São Paulo state, the study shows.
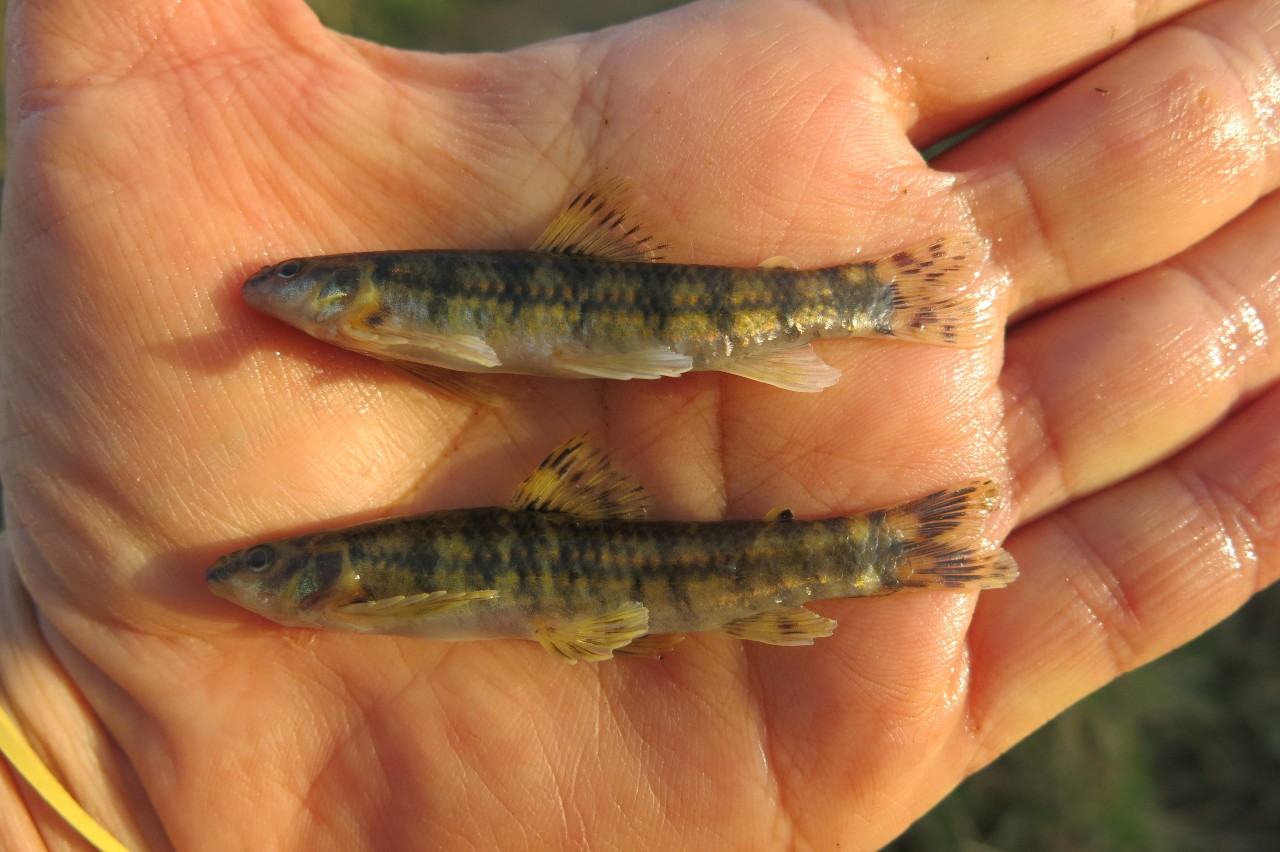

Through morphological and molecular analysis of material collected from rivers in Brazil's Northeast region, the researchers are extending their knowledge of the evolutionary history of South American darters in the genus Characidium.

Researchers affiliated with the FAPESP Research Program on Global Climate Change met at the State University of Campinas in Brazil to discuss current research priorities in the effort to understand and combat the consequences of the extreme events caused by global warming.
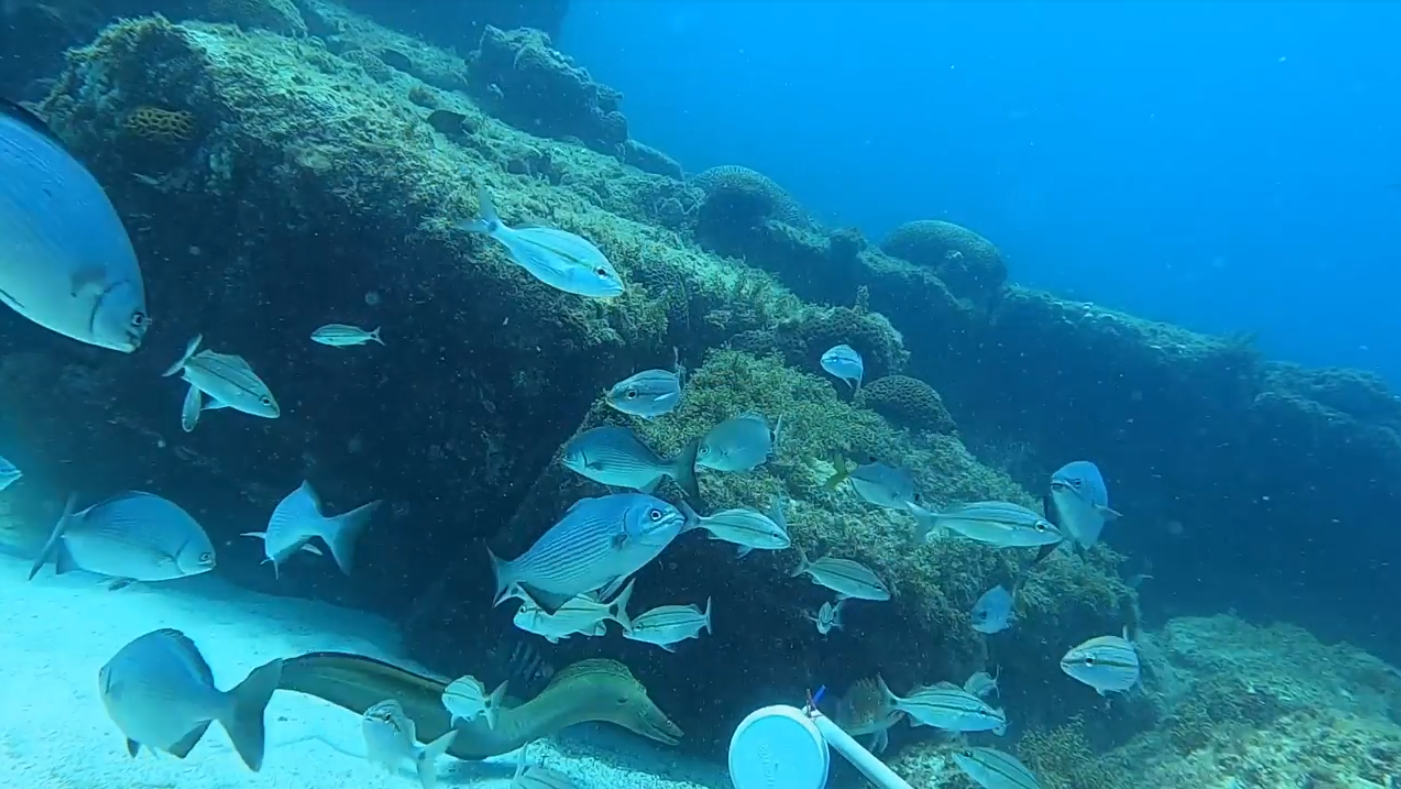

Researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo determined for the first time the vertical limits of the subtropical ocean region off the South American coast. They found that the upper limit of the mesotrophic zone, previously assumed to be 30 meters below the surface, was in fact in much shallower waters.