


The researchers correlated data on the animal’s ecological niche and connectivity among populations with existing and planned hydropower development sites in Brazil’s South region. They estimated that 30% of its habitat could be lost, heightening the risk of extinction.

Researchers sampled oysters and mussels at three locations between the port of Santos and the nearby city of Guarujá. Their aims included assembling data as a basis for public policy on basic sanitation. The law does not currently require removal of microplastic particles from sewage.
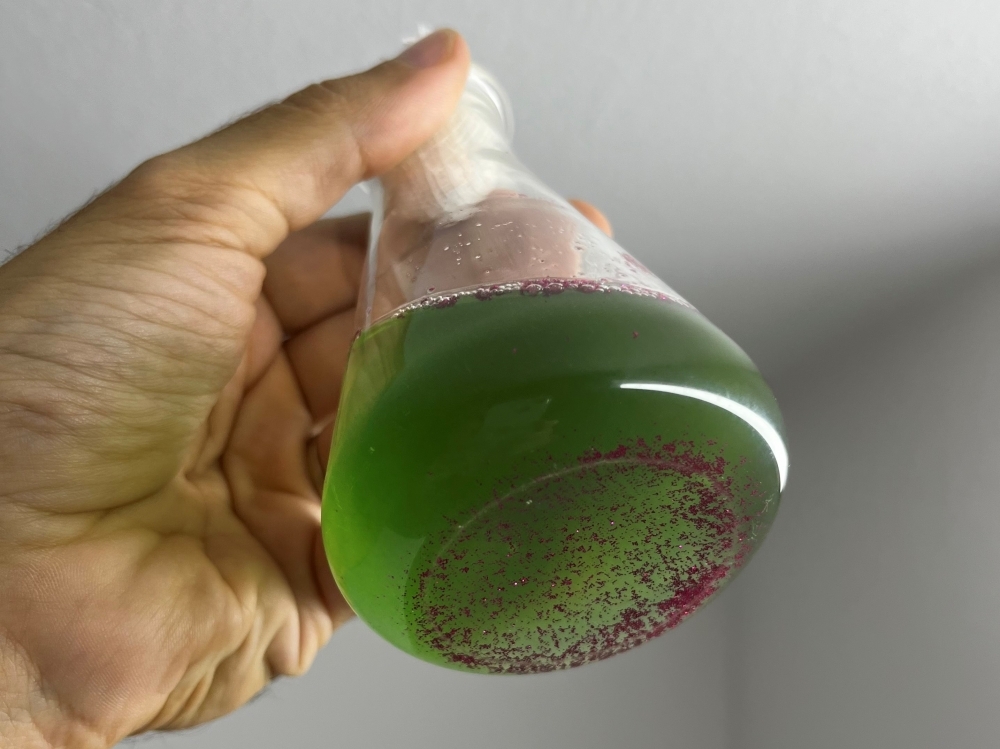

Researchers at the University of São Paulo investigated the effects of five concentrations of glitter on two strains of cyanobacteria. Use of the material in makeup, party costumes and decorations should be reconsidered, they argue.
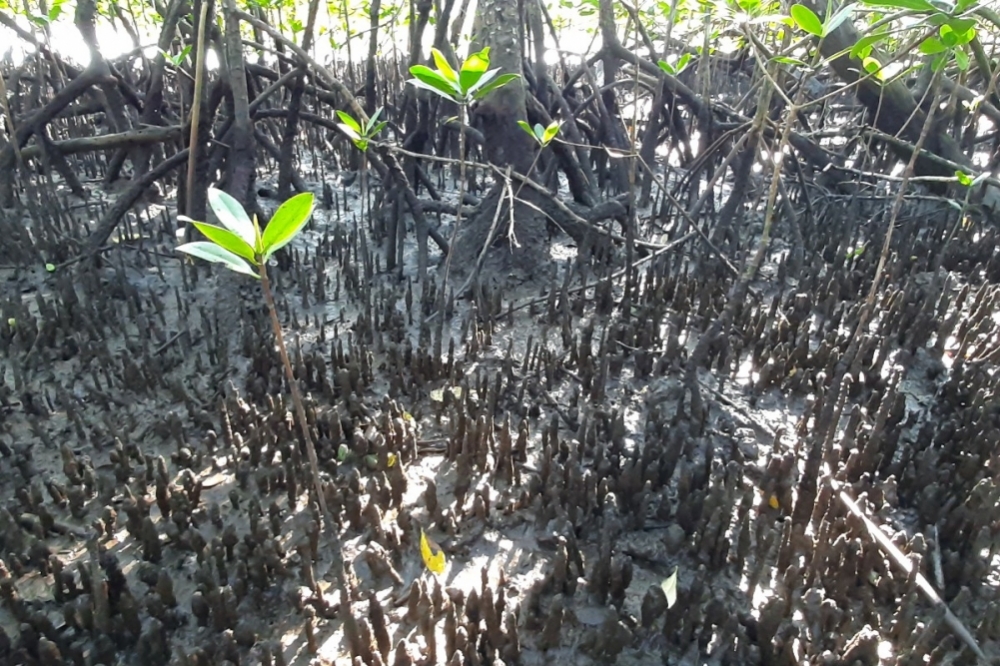

A study combining genetic analysis and oceanographic simulations showed that a species of mangrove rarely disperses very far, so that North and South Brazil have two distinct populations. The results can help prioritize conservation units and understand global patterns in mangrove forest formation.
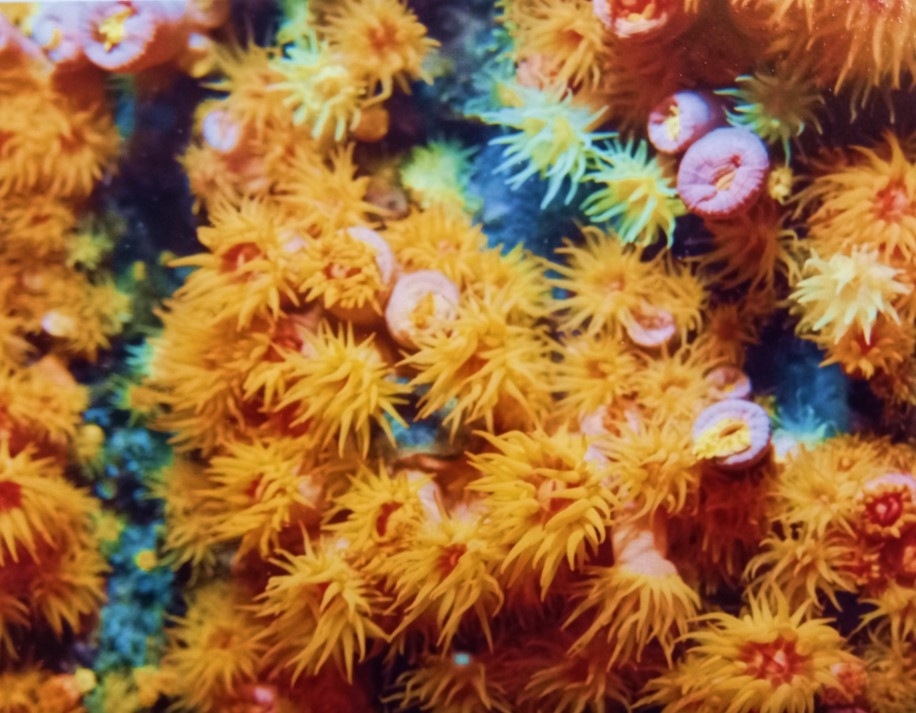

Trials involving mammalian cells were conducted by researchers in São Paulo state, Brazil. Although it endangers biodiversity along much of the coast, sun coral could be an ally in combating Chagas disease, which affects 7 million people worldwide and lacks effective treatment.

Soon to be officially launched, IPOS is a coalition of 16 research institutions, research funders and universities. Its mission will be to bridge the science-policy divide and help protect the world’s ocean environment.
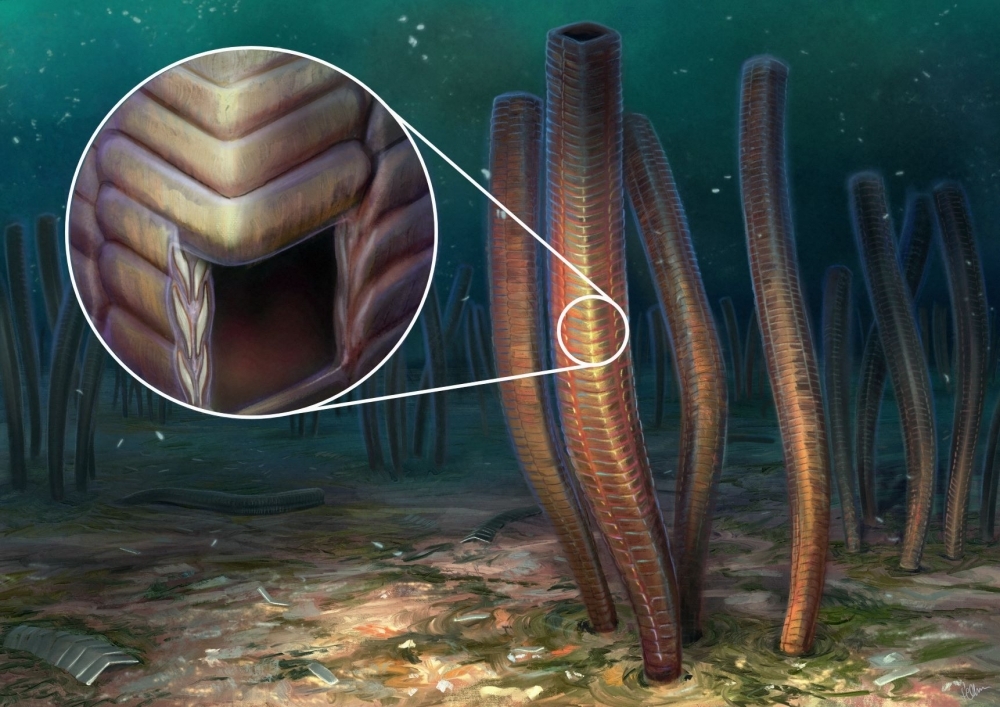
Carapace resembling scaled armor used by medieval knights appears to be first evidence of defense against predators and linked to origin of large group of animals with bilateral symmetry, which includes humans. Advanced techniques including electron microscopy and tomography applied to rocks found in Brazil in the 1970s enabled scientists to reconstruct this animal’s morphology.
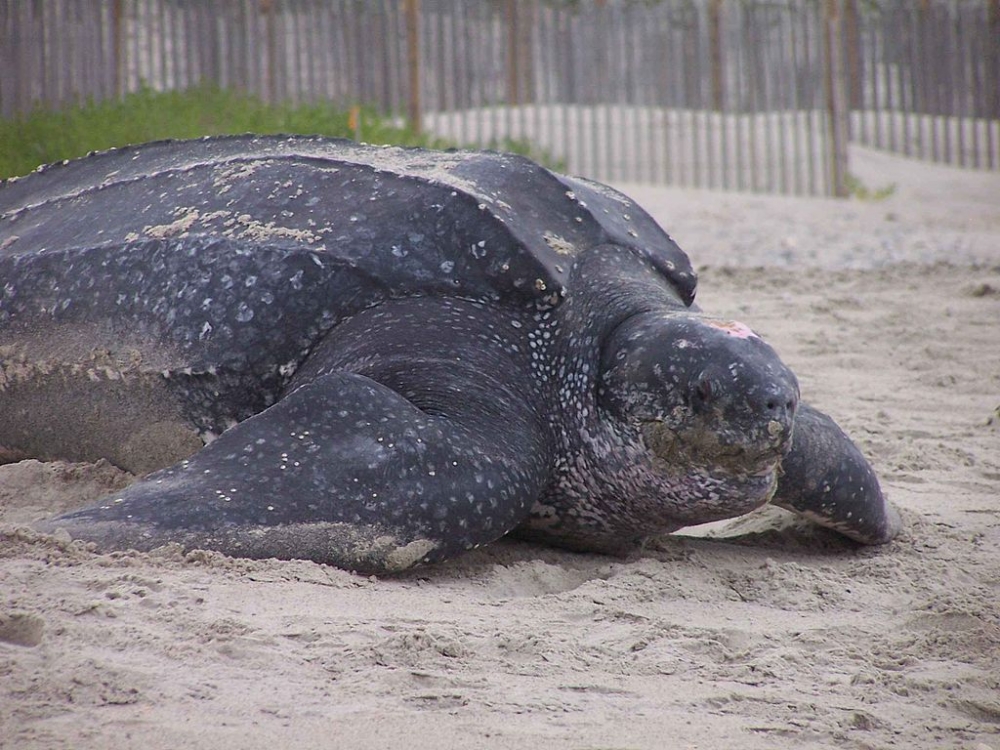

The most comprehensive sequencing to date of the genomes of the Leatherback and Green sea turtles shows they are mostly identical. An article in PNAS helps scientists understand how the group has evolved and provides ideas for conservation strategies.
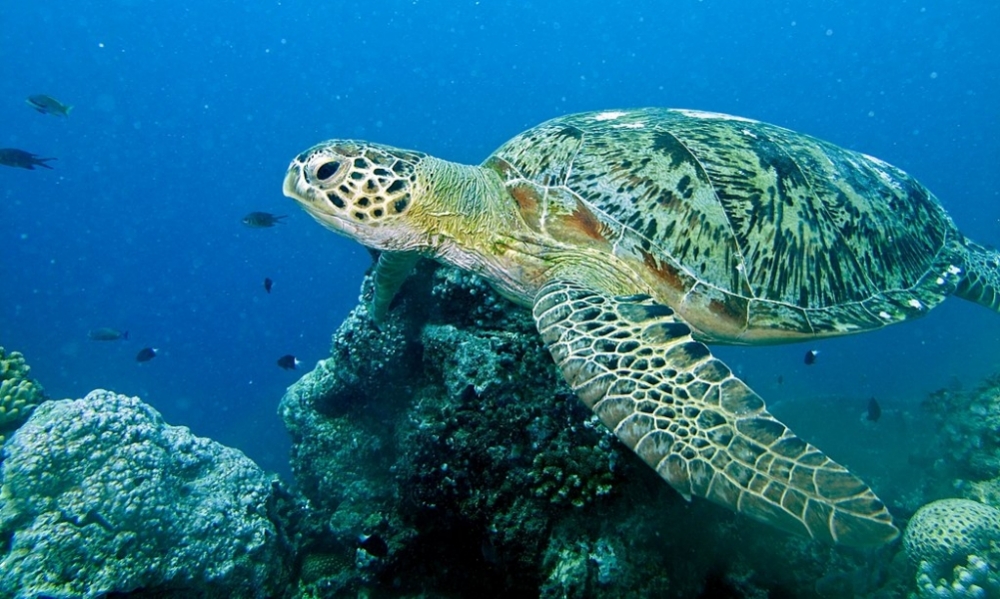

A review of the literature shows that 15% of articles published between 1960 and 2021 focused on only ten species, while no articles at all were published on almost 40% of all species. Research efforts tend to be biased toward large-bodied animals and species native to wealthier countries, among other factors that should be taken into consideration when planning future studies, according to the authors.

A review of 300 projects funded by FAPESP since 1972 highlights its contributions to the understanding of marine life, especially after the launch of BIOTA, its biodiversity program, in 1999. One of the challenges for the future is expanding deep-sea research.
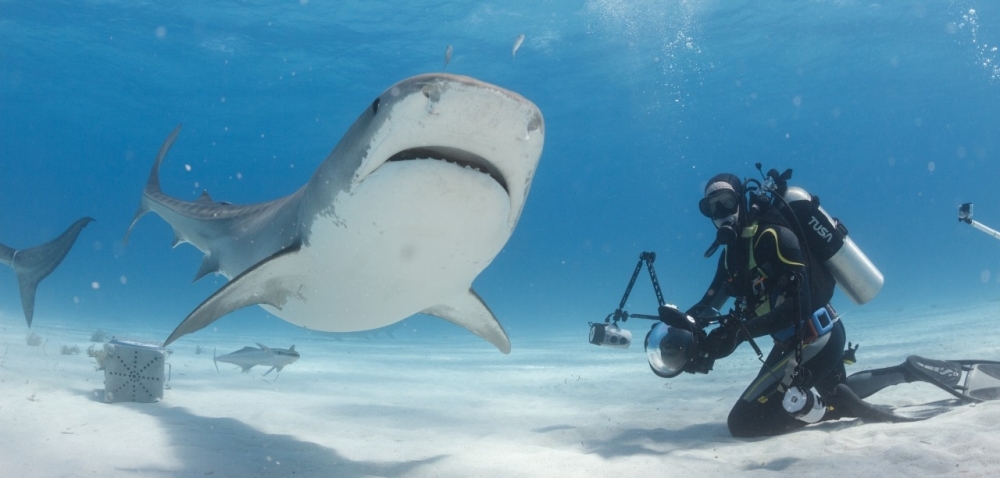

Sharks that frequent diving tourism sites where food is provided have higher levels of testosterone and corticosteroids than others that spend less time in these areas, as well as a better nutritional state. The effects of shark-human interaction are poorly understood.
In a webinar held to present the third chapter of the book published by the São Paulo State Academy of Sciences to commemorate FAPESP’s sixtieth anniversary, specialists showed that protection of terrestrial and marine environments contributes to food production and job creation, among other benefits.

Several substances that killed antibiotic-resistant bacteria were found by Brazilian researchers in a marine sponge native to Fernando de Noronha, an archipelago off the coast of the Northeast.
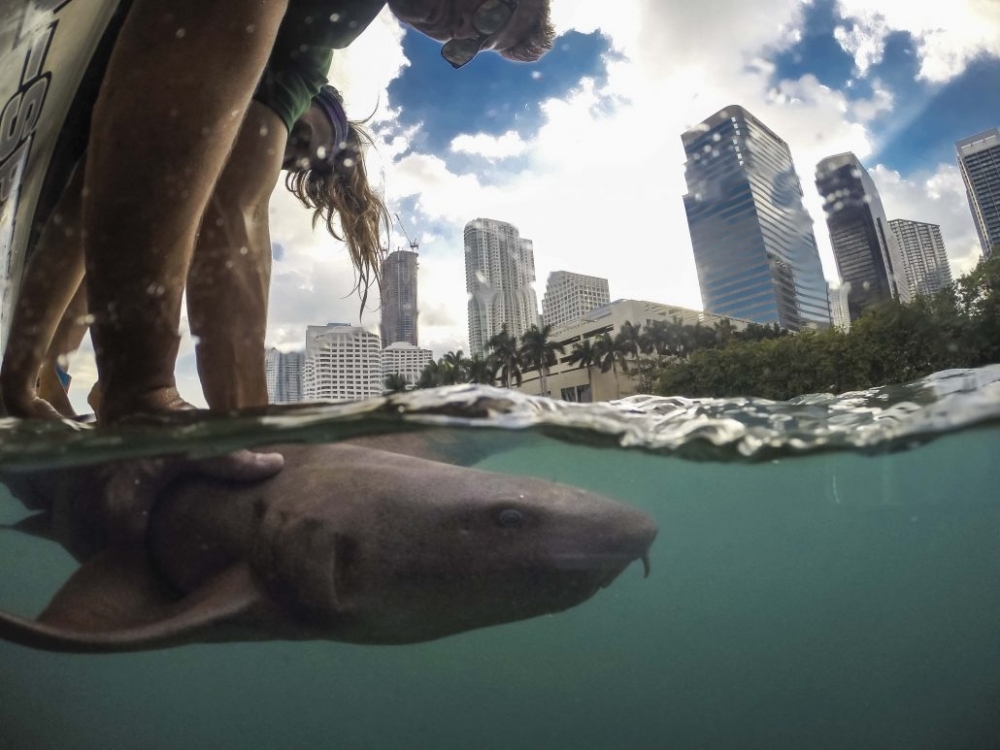

Analysis of blood samples showed that sharks living near urban areas have a lower-quality diet than those living in wilderness areas. Dietary imbalances can impair important physiological processes, such as cardiovascular tone, inflammatory response and reproduction.

Species sensitive to habitat change are gradually being replaced by more resistant species, according to a study conducted in Brazil. The trend is leading to a loss of the ecological functions performed by the vanishing species.
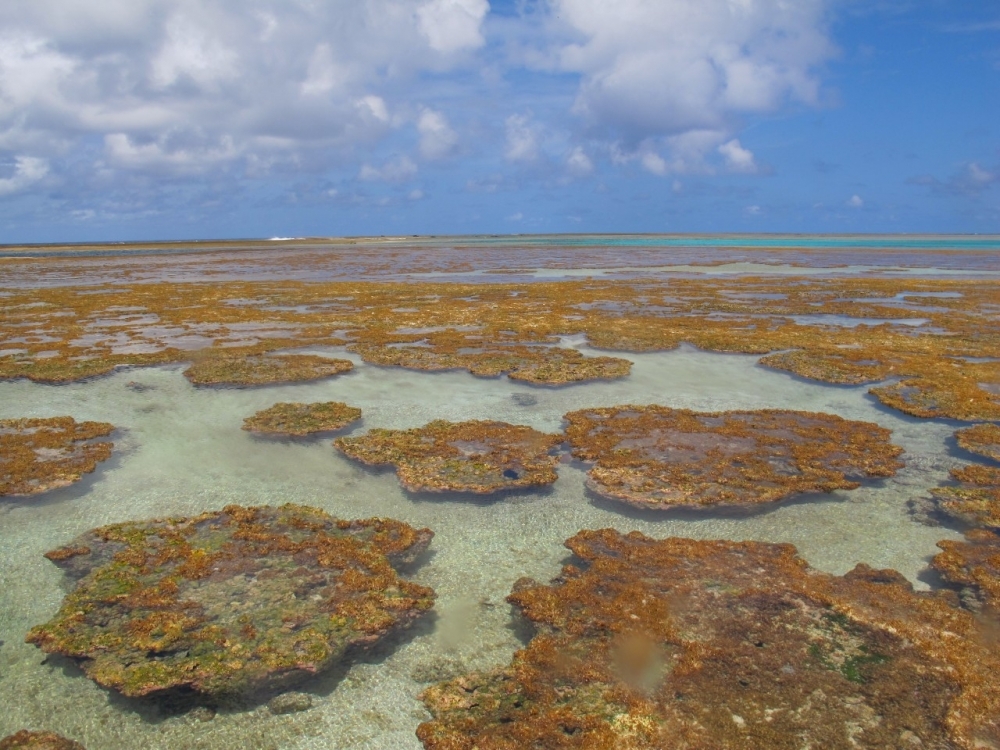

Genetic sequencing enables scientists to identify 79 different species of coralline algae serving as a habitat for countless marine organisms on the Brazilian coast, with many yet to be explored in deep waters.
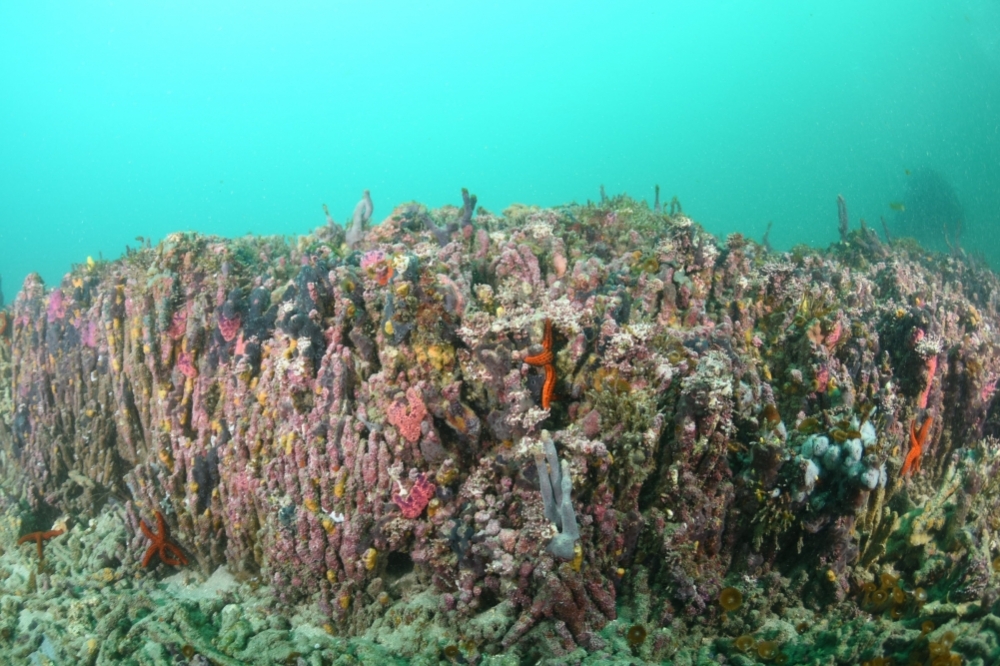

Described in 2019, the Queimada Grande coral reef off the coast of São Paulo state arose when the ocean was warmer and stopped growing when cooler sea surface temperatures influenced the climate in the region, according to a study led by researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo.
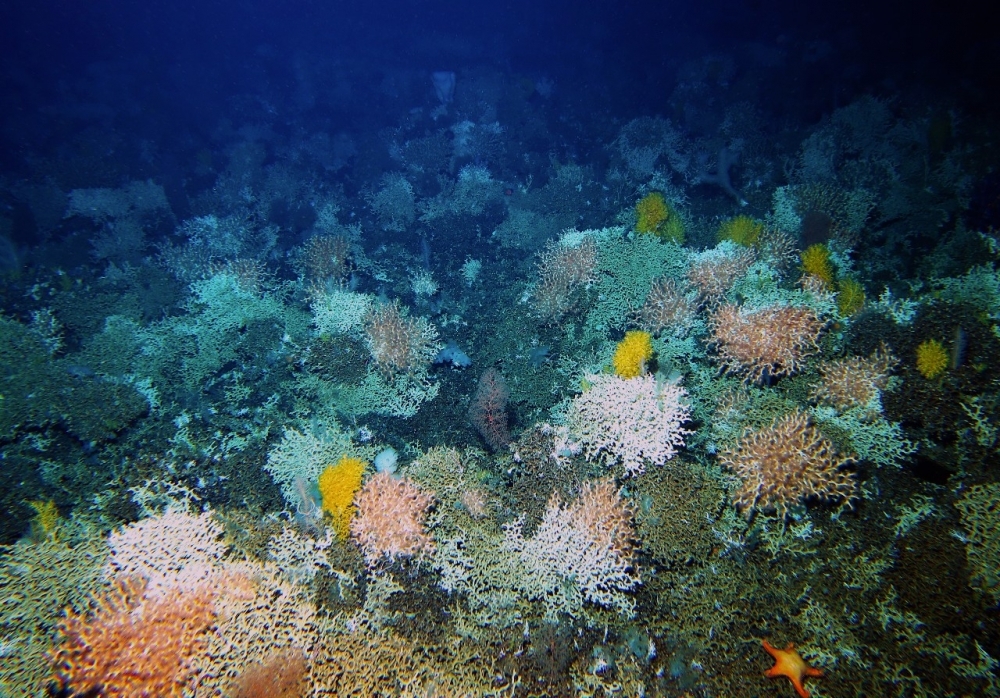

A book with a Brazilian co-author documents 267 species in the archipelago, 47 of which had never been described before. It resulted from 37 scientific expeditions conducted between 1978 and 2016 by France’s National Museum of Natural History.
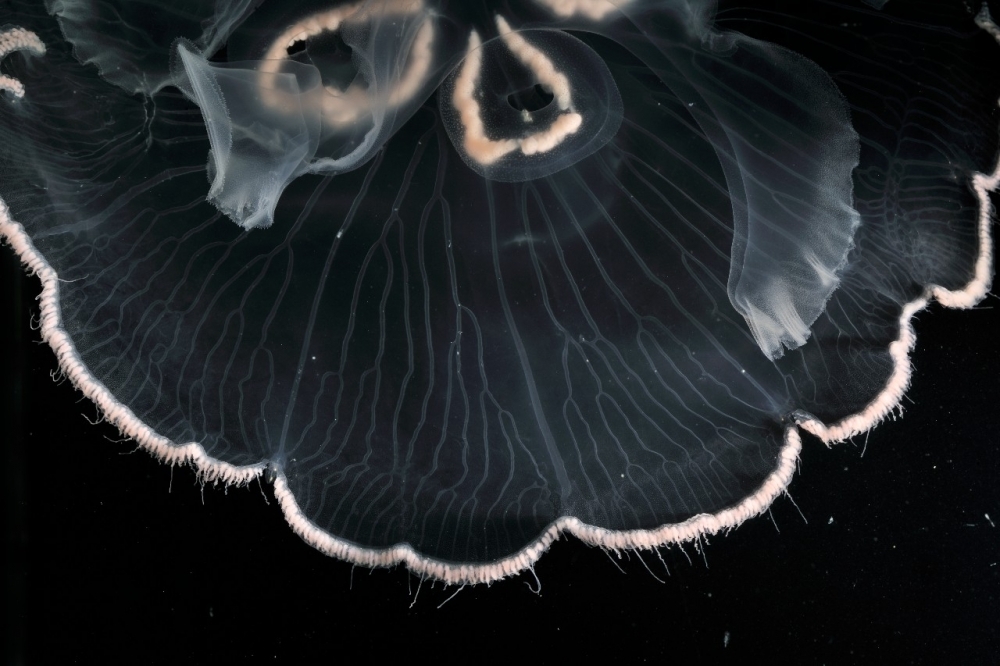
On the basis of genetic analysis of jellyfish specimens held in collections around the world, researchers have reclassified these species in the genus Aurelia, many of which are highly similar. Painstaking descriptions of species are key to conservation strategies.
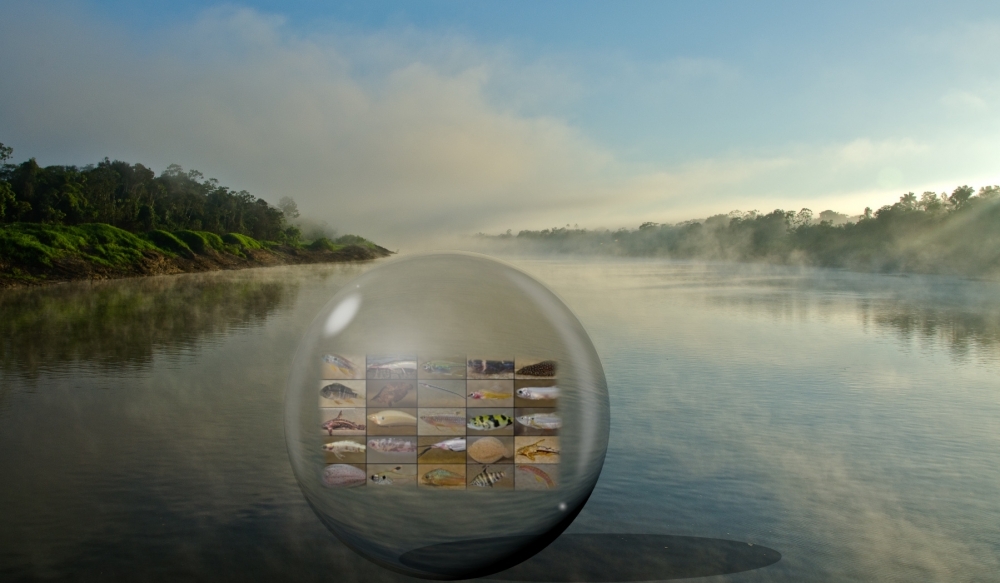

Scientists identified fish orders present in the Javari River basin by sequencing DNA molecules in water samples. To make the method more sensitive and capable of differentiating species, however, reference libraries of genetic material must be created.
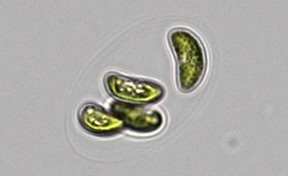
The discovery resulted in phylogenetic reclassification of microalgae in the genus Nephrocytium. An article on the research is in Taxon.
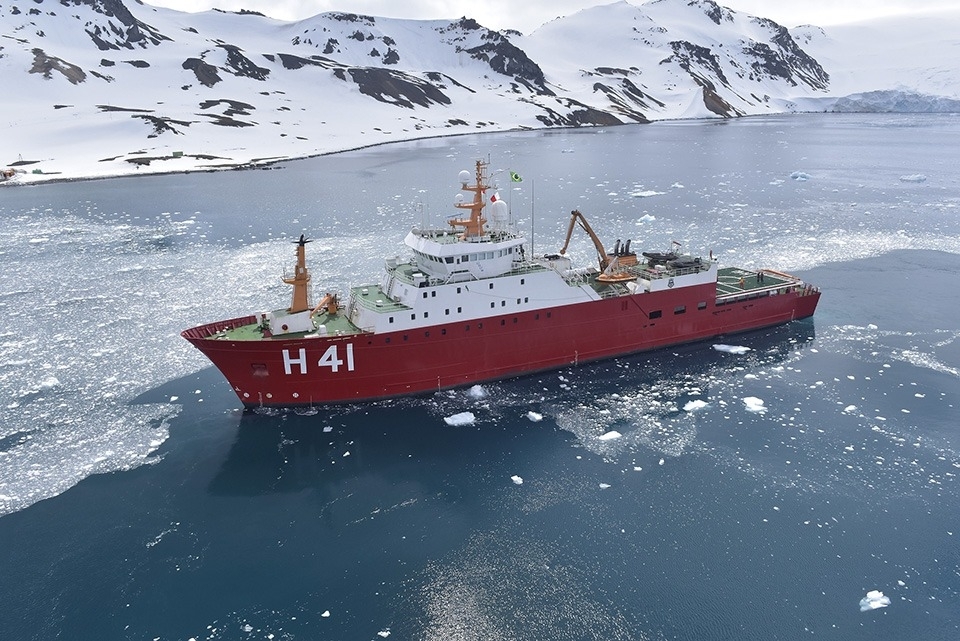

A study published in Frontiers in Marine Science is the first to predict the impact of long-term changes in sea surface temperature on local microbial diversity. The methodology is also innovative.
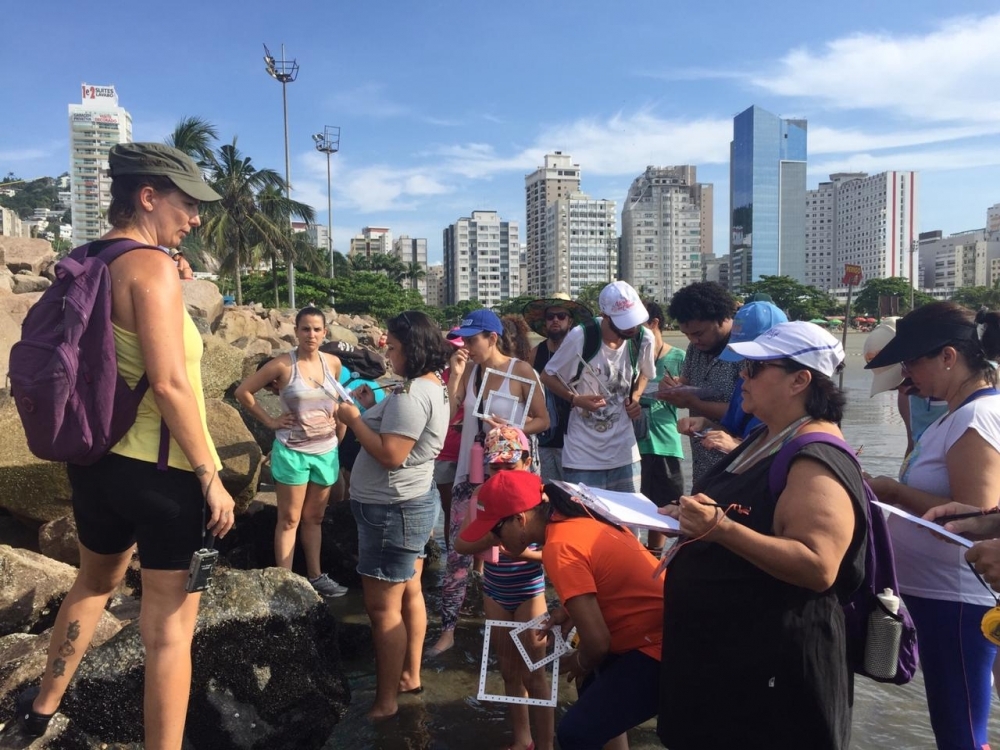

A study conducted in the port city of Santos (Brazil) by researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo shows collaboration between civil society and academia achieving progress toward the goals of the UN Ocean Decade.
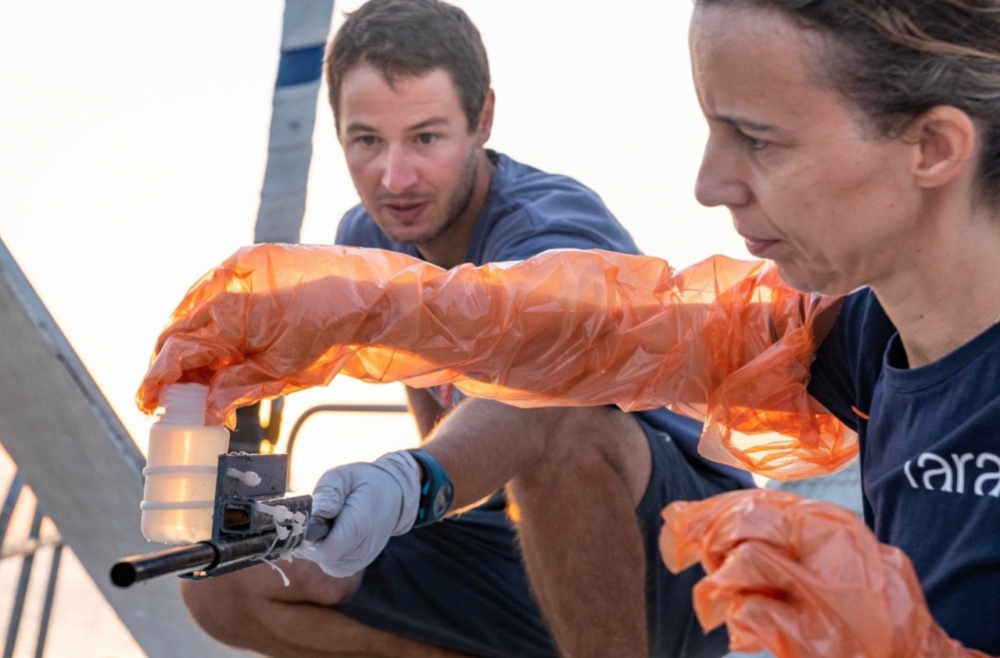

Plankton are the foundation of life in the oceans and produce half the world’s oxygen. These marine microorganisms will suffer from rising temperatures at the poles, rising salinity in the tropics, and a reduction in the flow of nutrients in the temperate zone, according to simulations based on data collected from all oceans around the globe.
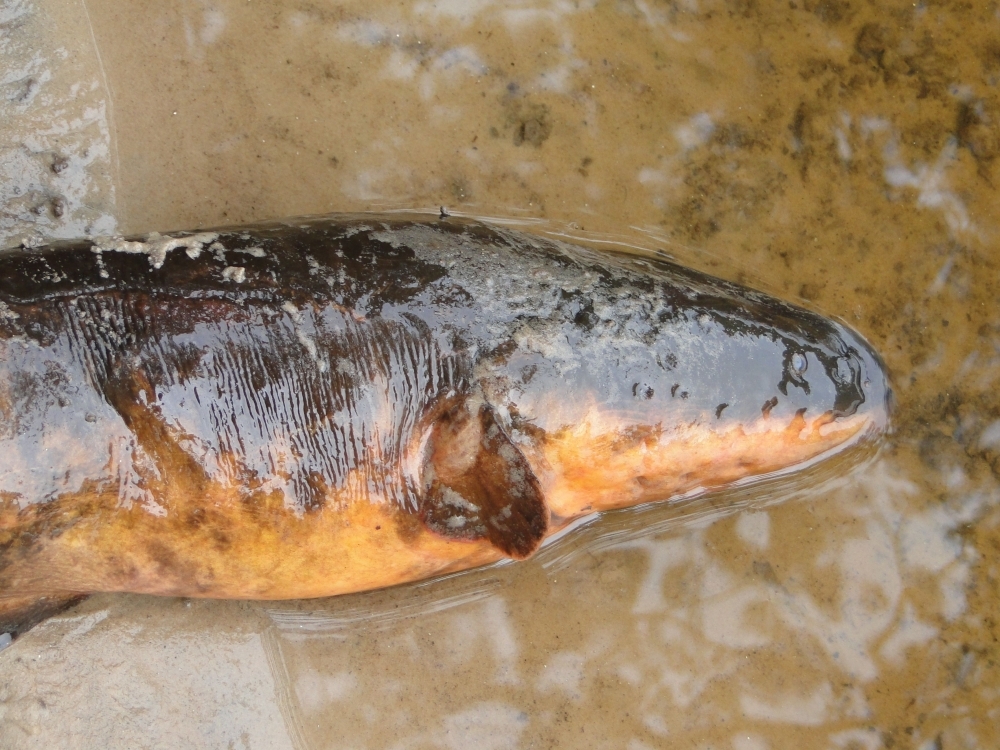

Electric eels of the species Electrophorus varii feed on other fish, especially those habitually hunted by larger predators such as caimans and giant river otters. Hunting tactics enable them to maintain the same diet in the wet and dry seasons alike.