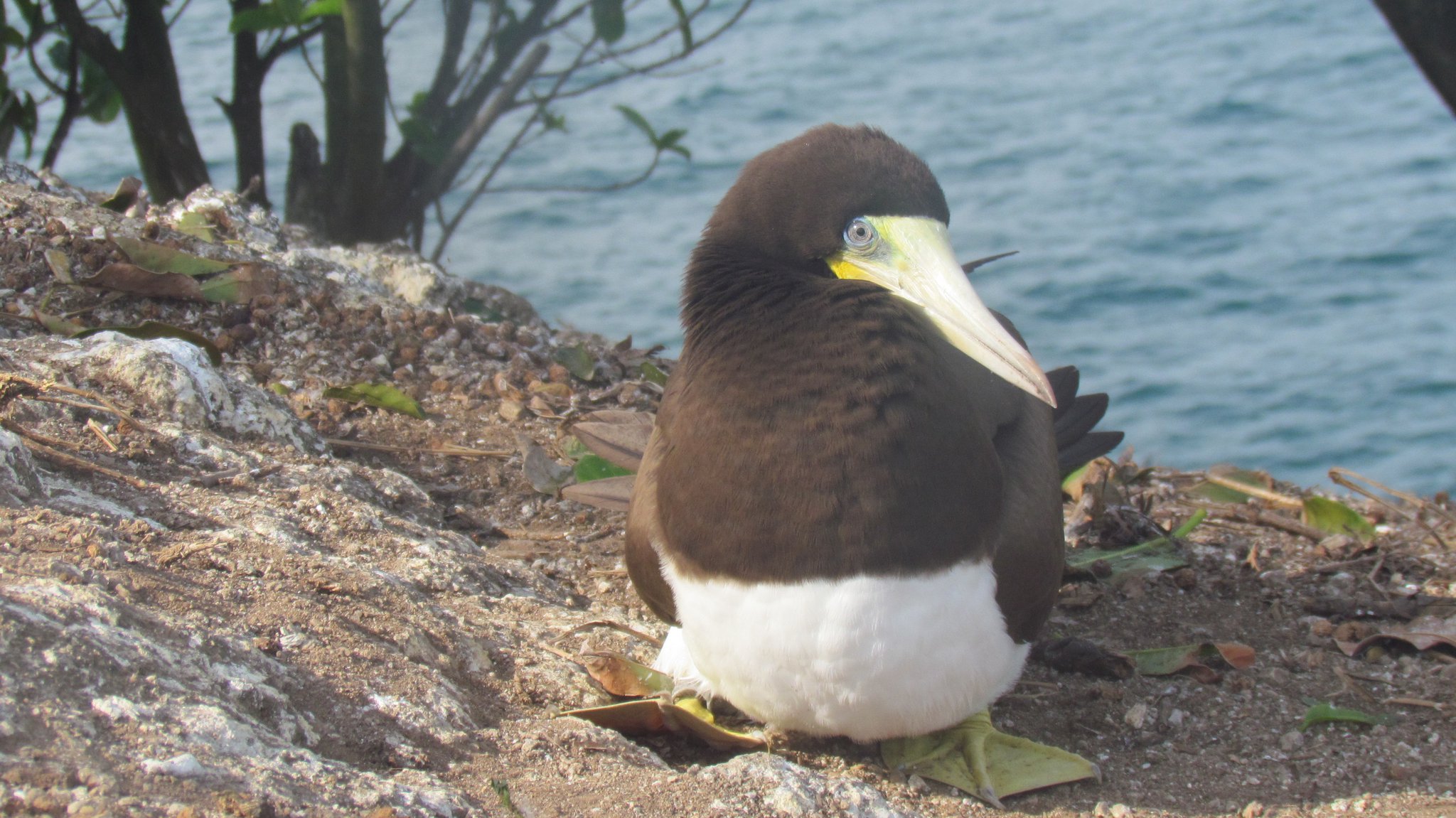



Analyses of biological material from six migratory and one resident species in Brazil indicate similar concentrations of some persistent organic pollutants (POPs), including DDT and the formicide mirex, even in birds with different feeding habits.

Analyses of biological material from six migratory and one resident species in Brazil indicate similar concentrations of some persistent organic pollutants (POPs), including DDT and the formicide mirex, even in birds with different feeding habits.
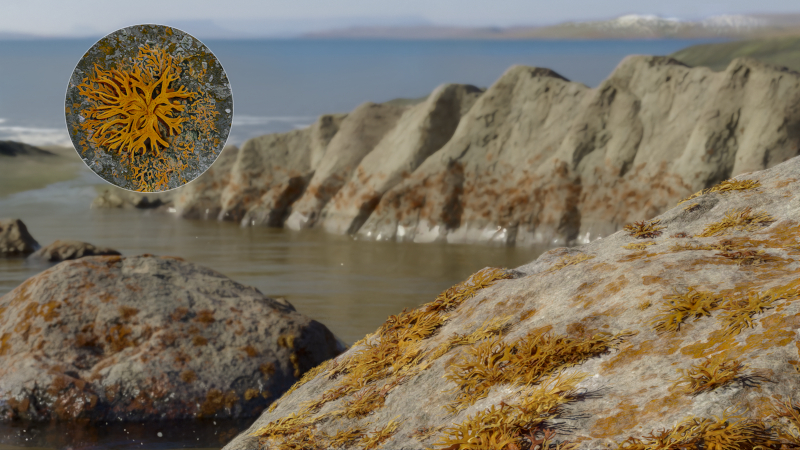

Study confirms that the symbiosis between fungi and algae that dissolves rocks and was widely distributed across Earth 410 million years ago helped form the first soils.

Study confirms that the symbiosis between fungi and algae that dissolves rocks and was widely distributed across Earth 410 million years ago helped form the first soils.
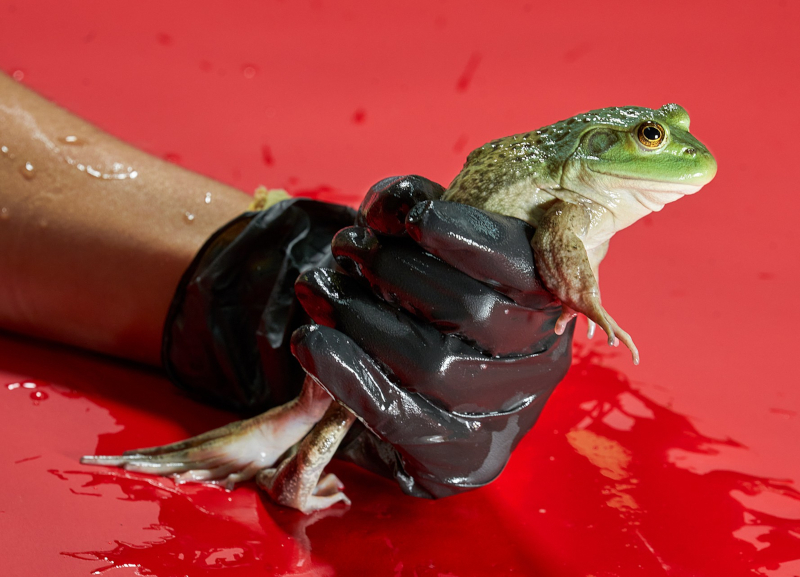

Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis is responsible for the decline of toad and frog populations across the globe. The origin of the fungal strain was the subject of a study led by researchers at the State University of Campinas.
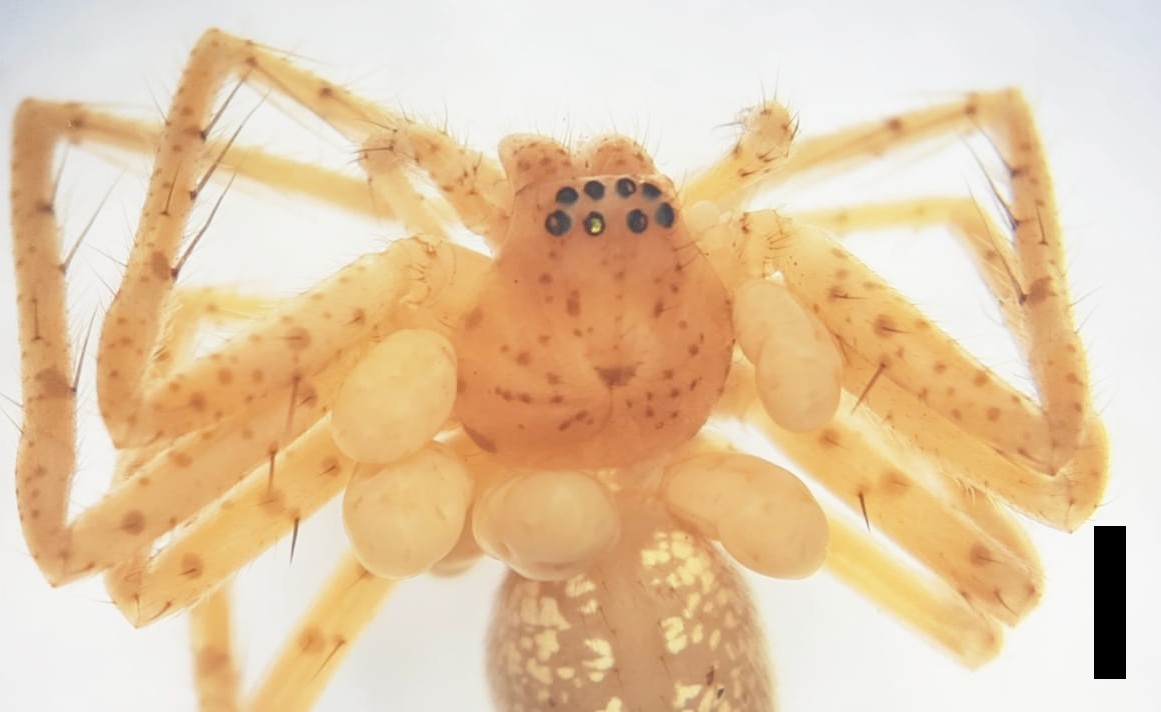

The parasitic mites were found on juvenile arachnids in the Butantan Institute collection. The larvae of Araneothrombium brasiliensis were collected in Rio de Janeiro. Previously, the genus had only one known species in Costa Rica.
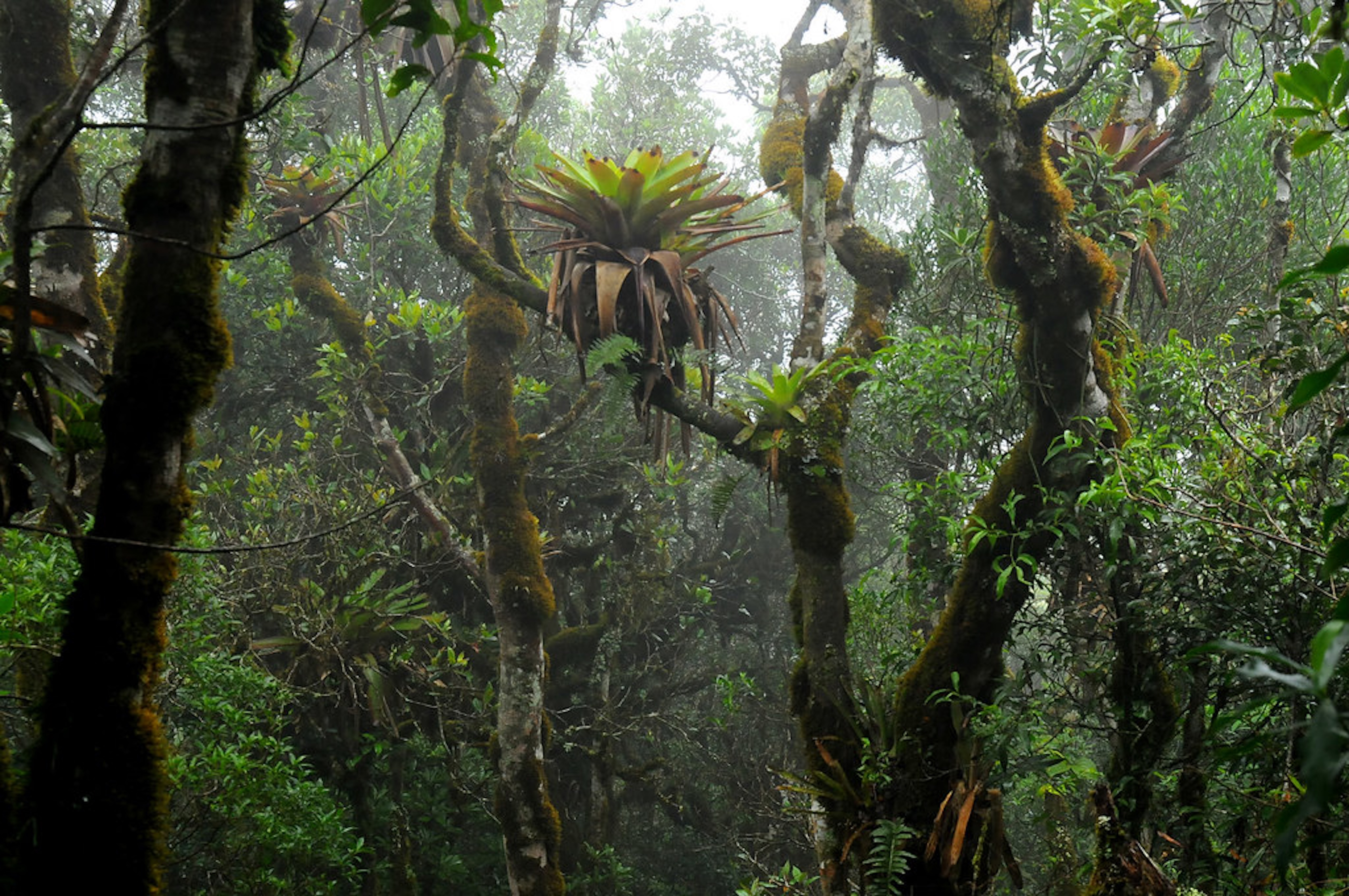

Water accumulated in the tanks of these plants living high up in trees has much higher concentrations of nitrogen, phosphorus, calcium, potassium, magnesium, sulfur, and iron than rainwater. Plants irrigated with this nutrient-rich water produced almost twice as many leaves.

Water accumulated in the tanks of these plants living high up in trees has much higher concentrations of nitrogen, phosphorus, calcium, potassium, magnesium, sulfur, and iron than rainwater. Plants irrigated with this nutrient-rich water produced almost twice as many leaves.
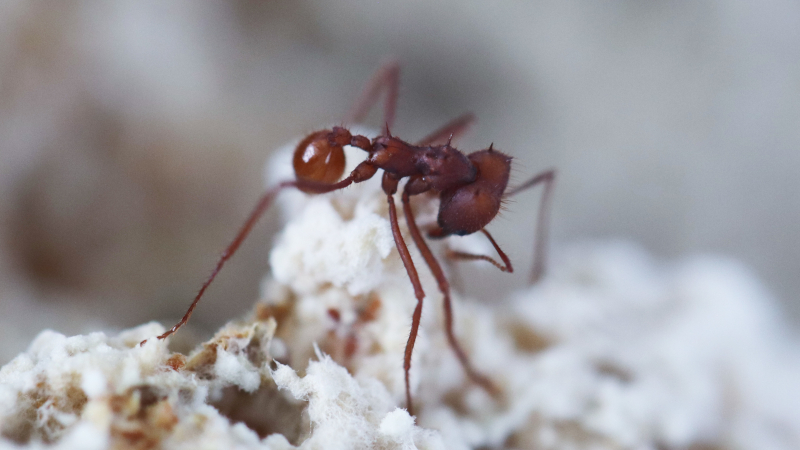

Analysis of 309 strains collected in eight countries indicates that the genus Escovopsis emerged 56.9 million years ago, but only began interacting with today’s mutualistic ants 38 million years ago, challenging the theory that they all emerged at the same time.

Analysis of 309 strains collected in eight countries indicates that the genus Escovopsis emerged 56.9 million years ago, but only began interacting with today’s mutualistic ants 38 million years ago, challenging the theory that they all emerged at the same time.
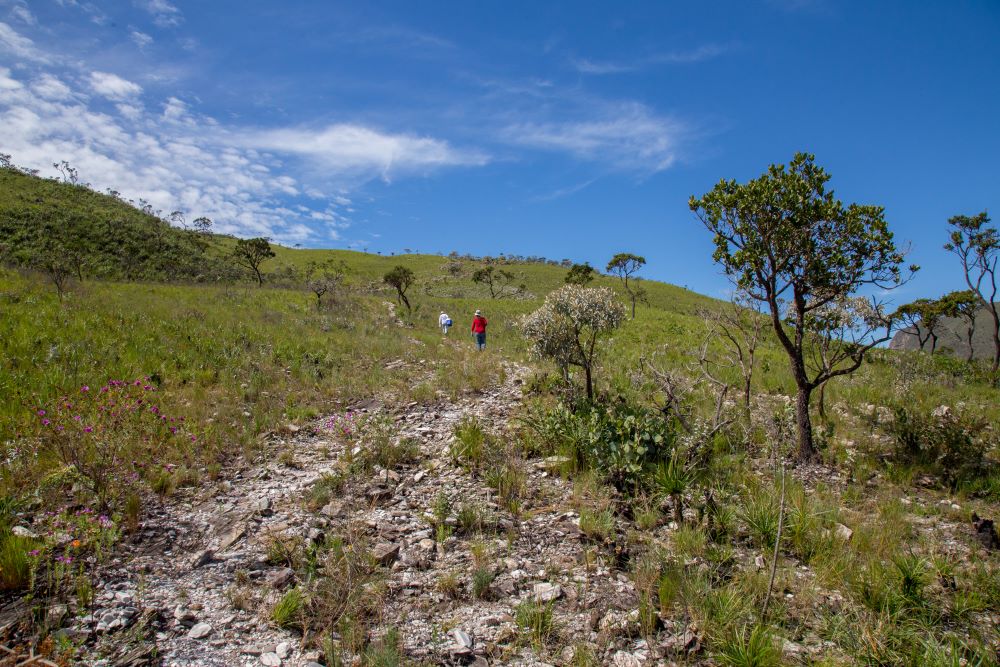

A study has identified more than 257,000 species of bacteria and archaea in velozias, which are plants that thrive in extreme environments of drought, heat, and poor soil, such as this mountainous savannah ecoregion. The results could guide conservation initiatives and biotechnological solutions for soil management in arid conditions.
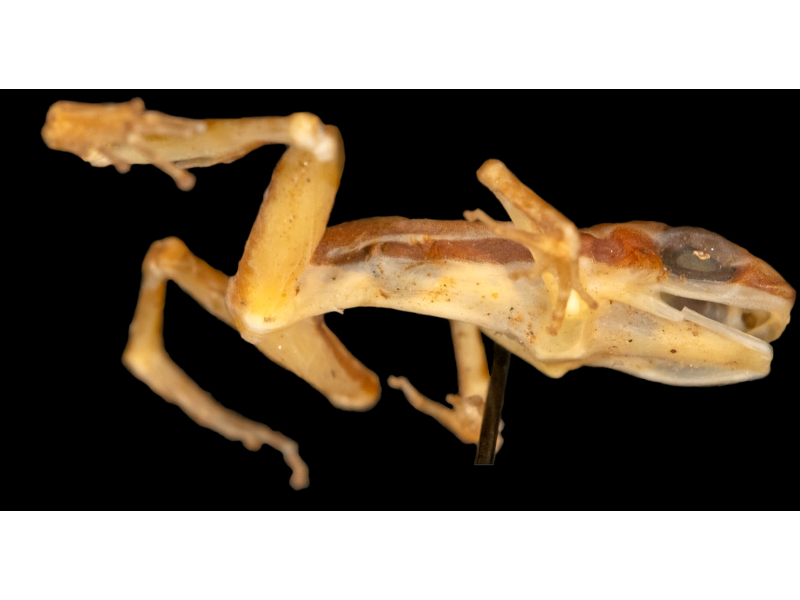

The dried specimen of the amphibian, collected by herpetologist Doris Cochran in 1963 in what is now a residential neighborhood of Curitiba, Brazil, is stored in the collection of the Smithsonian Institution’s National Museum of Natural History in the United States.

The dried specimen of the amphibian, collected by herpetologist Doris Cochran in 1963 in what is now a residential neighborhood of Curitiba, Brazil, is stored in the collection of the Smithsonian Institution’s National Museum of Natural History in the United States.

The research used network theory to analyze the ecological connectivity of 28 areas in the northwest of the state of São Paulo, Brazil.
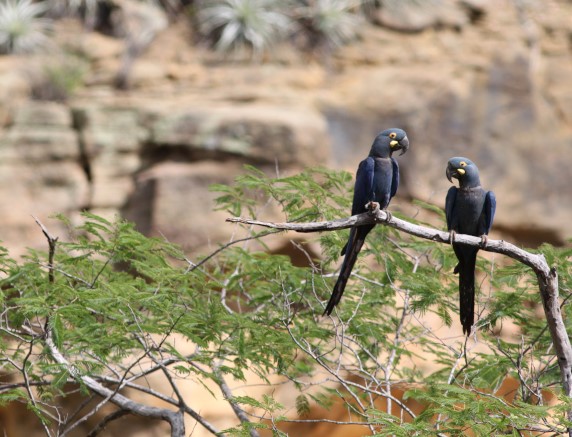

At least 35 individuals of the endangered Lear's macaw have been killed by electrocution in the semi-arid region of Bahia, Brazil, in 2025. Replacing 10% of the riskiest poles could prevent 80% of these deaths.
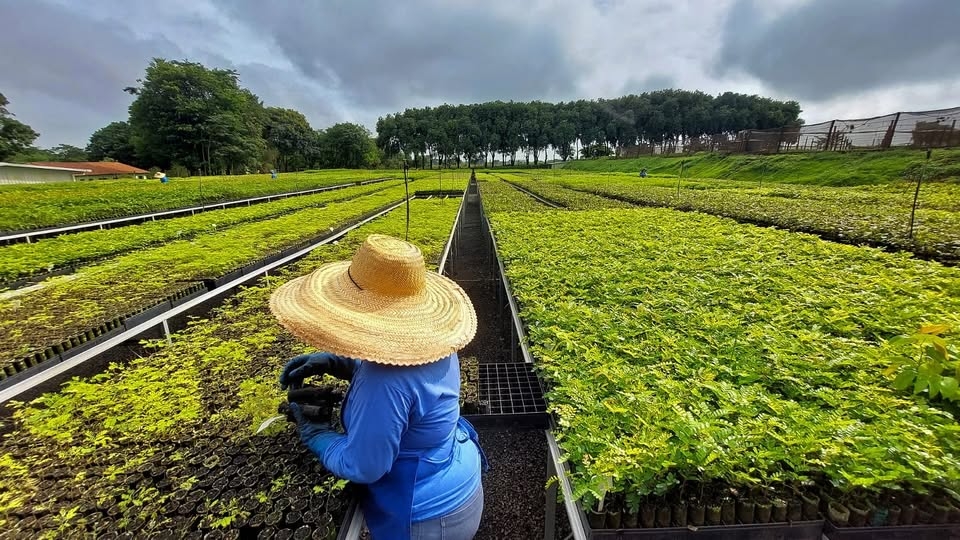

One way Re.green compensates its investors is by selling carbon credits sequestered by restored areas. The calculation methodology is based on the results of a project supported by FAPESP.
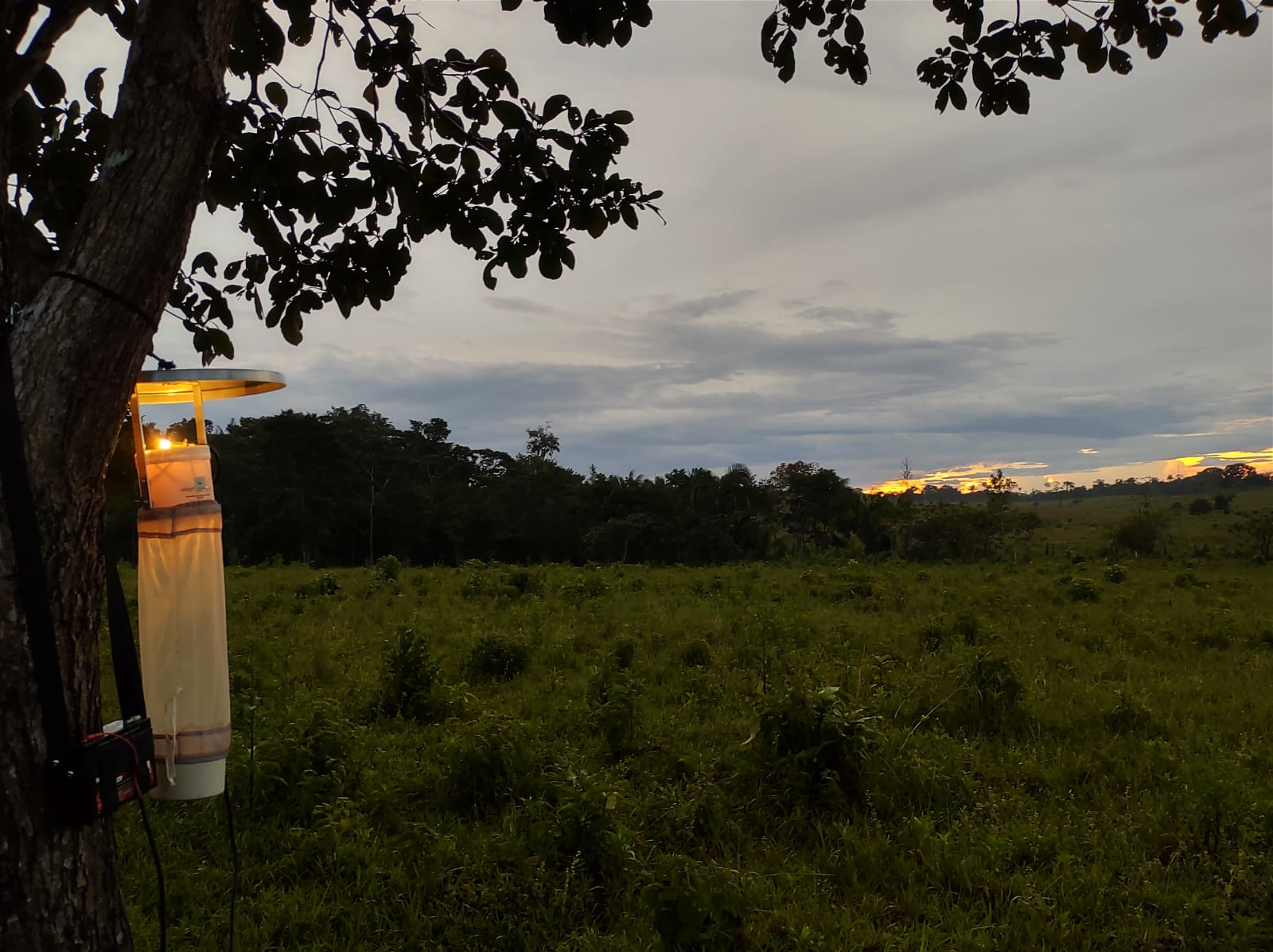

Research shows that areas with 50% deforestation near residential areas or fragmented vegetation allow greater contact between mosquitoes and humans. Amid the discussions for COP30, the study helps us understand the link between forest destruction and the spread of the disease.
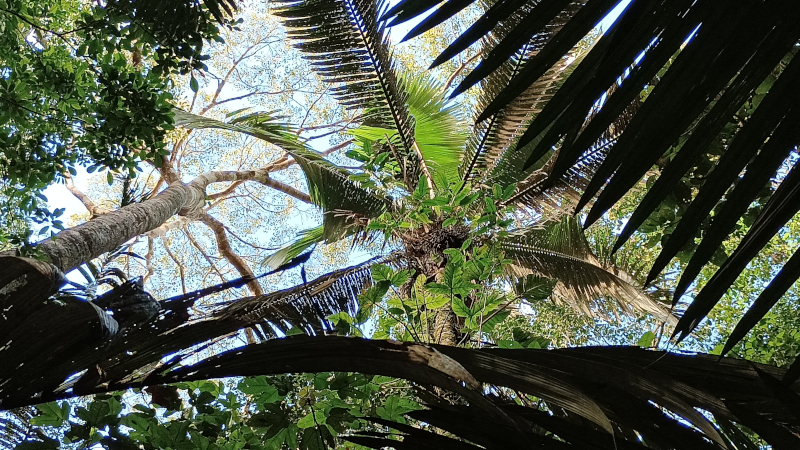

The plant family can store twice as much water as trees such as ipê, mahogany, and eucalyptus, according to a study conducted at São Paulo State University. Preliminary results were presented during the Brazil-France 2025 Forum “Forests, Biodiversity, and Human Societies”.
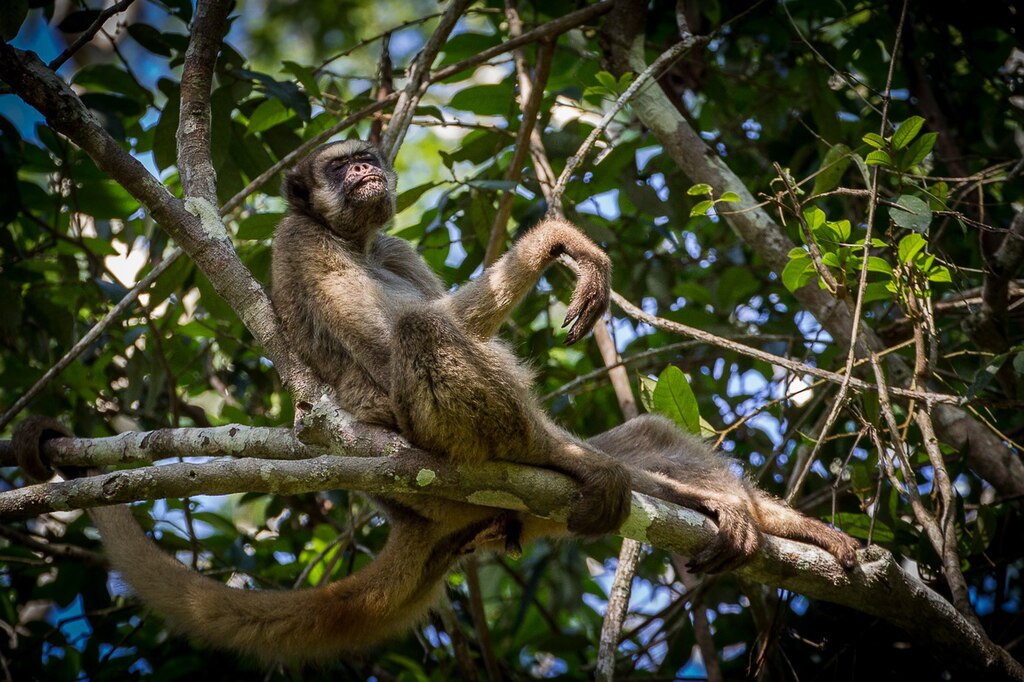

Study predicts that the two species of muriquis will be restricted mainly to coastal regions of the Atlantic Forest, leaving populations in the interior seriously at risk.

Analysis of the interaction between ants, plants that secrete sweet substances to attract them, “interested” in defending themselves from leaf-eating animals, and bees indicates that the ants may scare away pollinators. Butterflies, on the other hand, are not bothered.

Non-compliance with the law, facilitated by errors in the technical language used in environmental licensing, has already led to the loss of over 580,000 hectares of native vegetation, 61% of which has been converted for agricultural use.
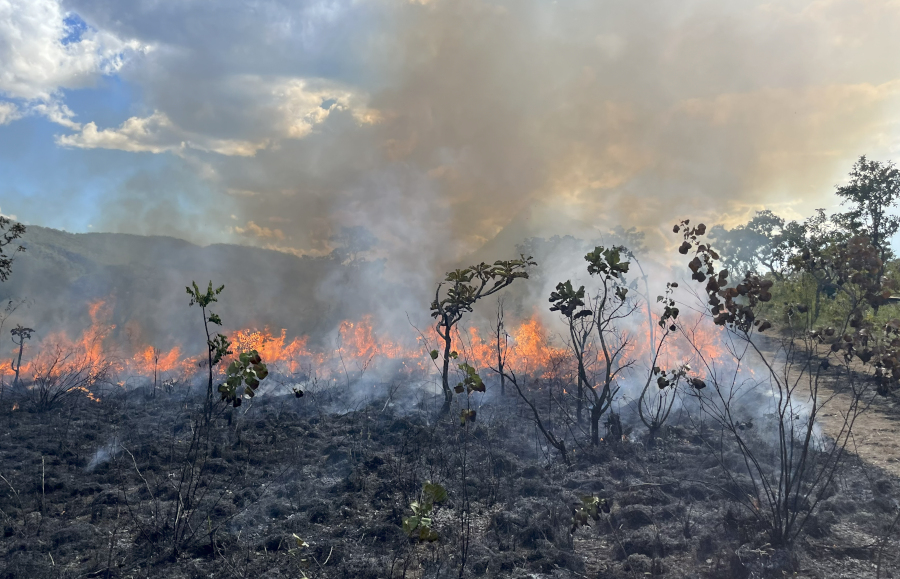

Unpublished work organized by researchers from São Paulo State University and the University of São Paulo discusses the influence of fires on the ecological dynamics of nine large South American biomes.
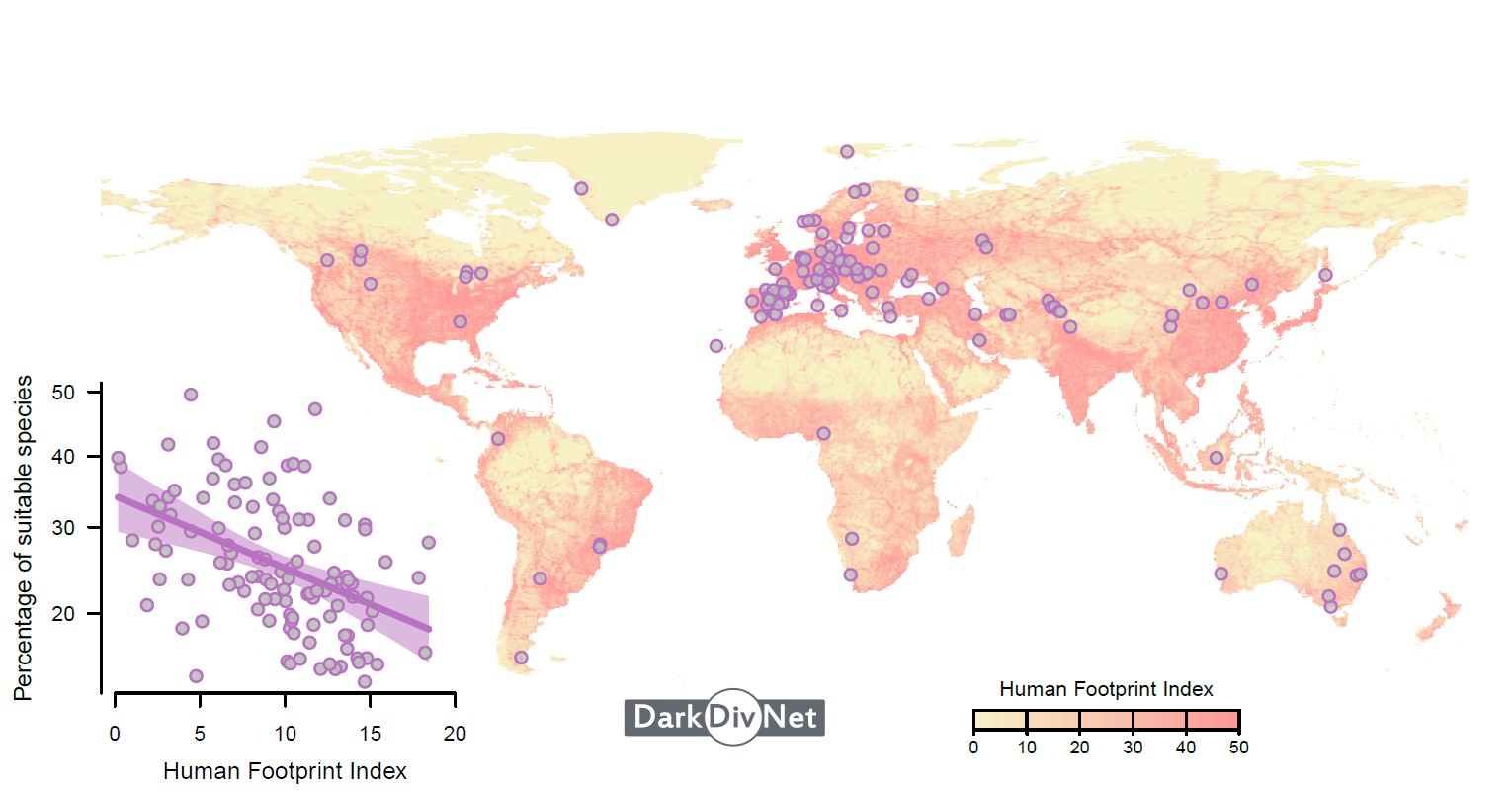
A survey of 119 regions around the world investigated “missing diversity,” or native species that could be present in a given area but were absent. The results were published in the journal Nature.
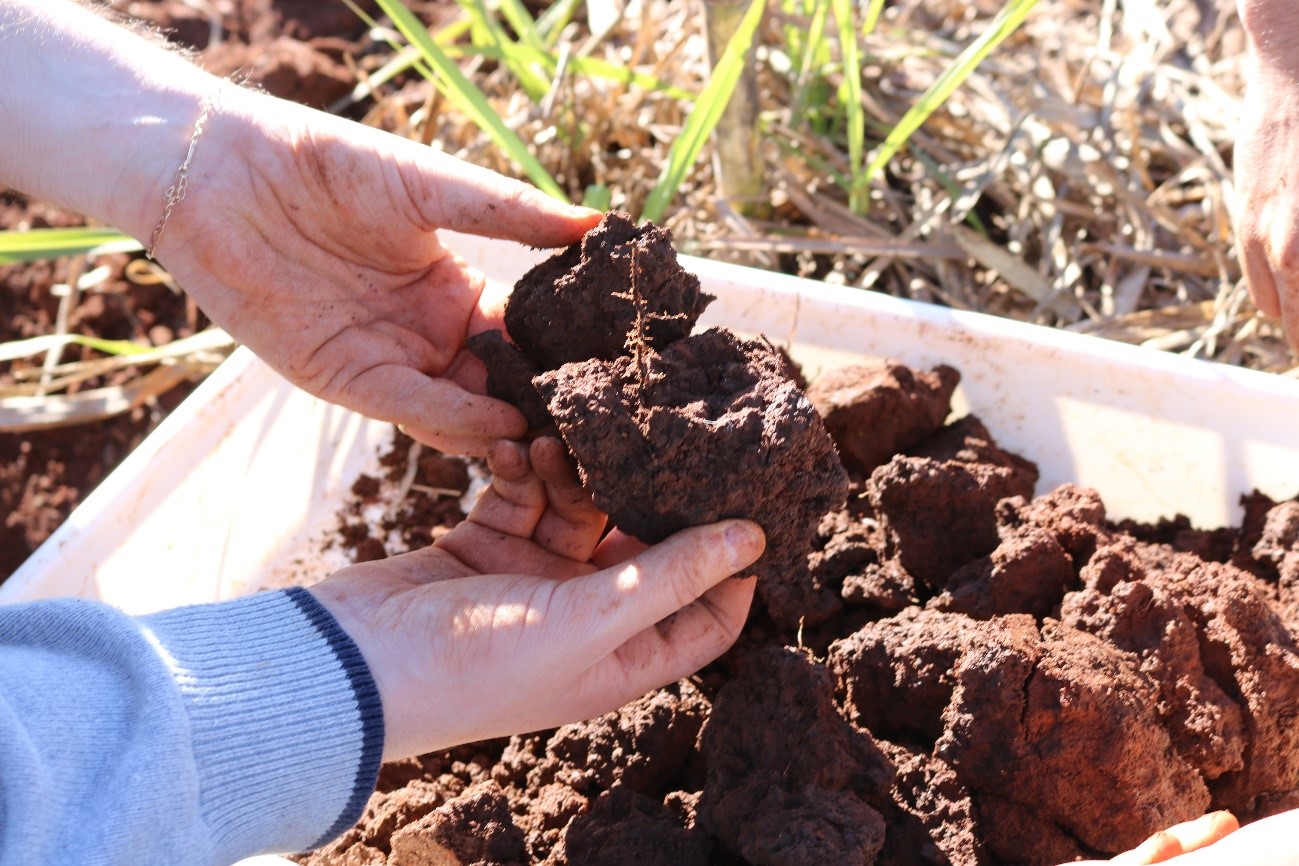

Countries such as Colombia and Venezuela lead the way in terms of the extent of healthy soils, while regions such as the Brazilian Northeast, northern Mexico and parts of Chile and Argentina face the greatest challenges. The data can guide public policies for conservation.
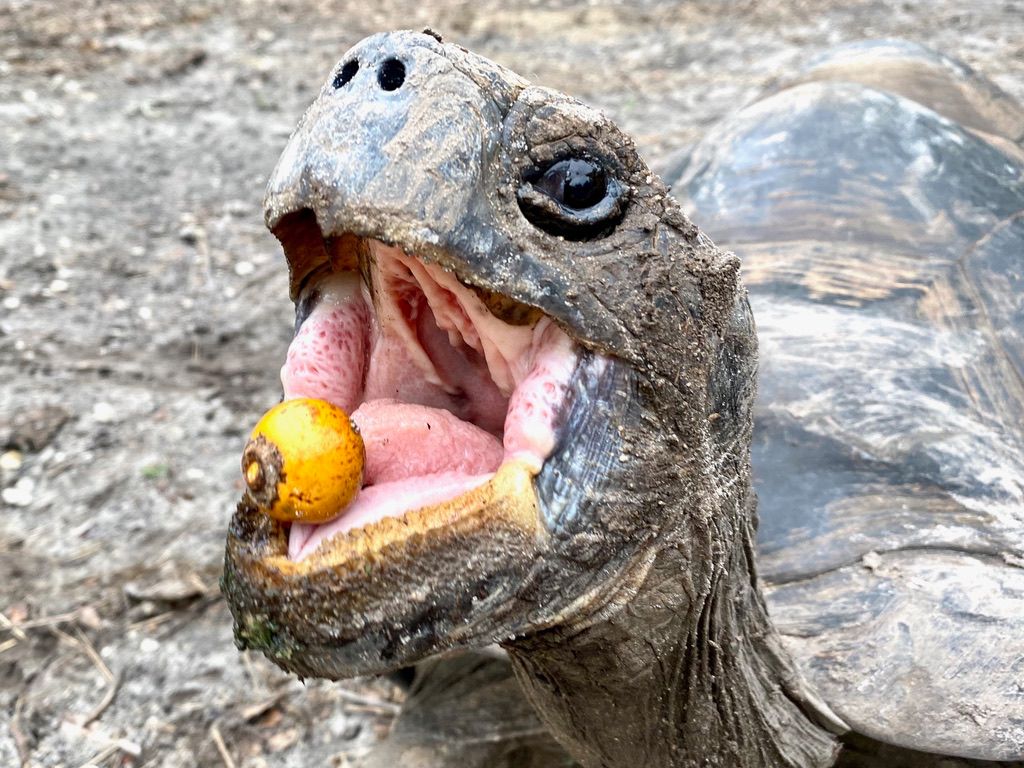

International team of researchers issues global warning about the need to include frugivores in conservation, forest restoration, and climate change mitigation strategies.