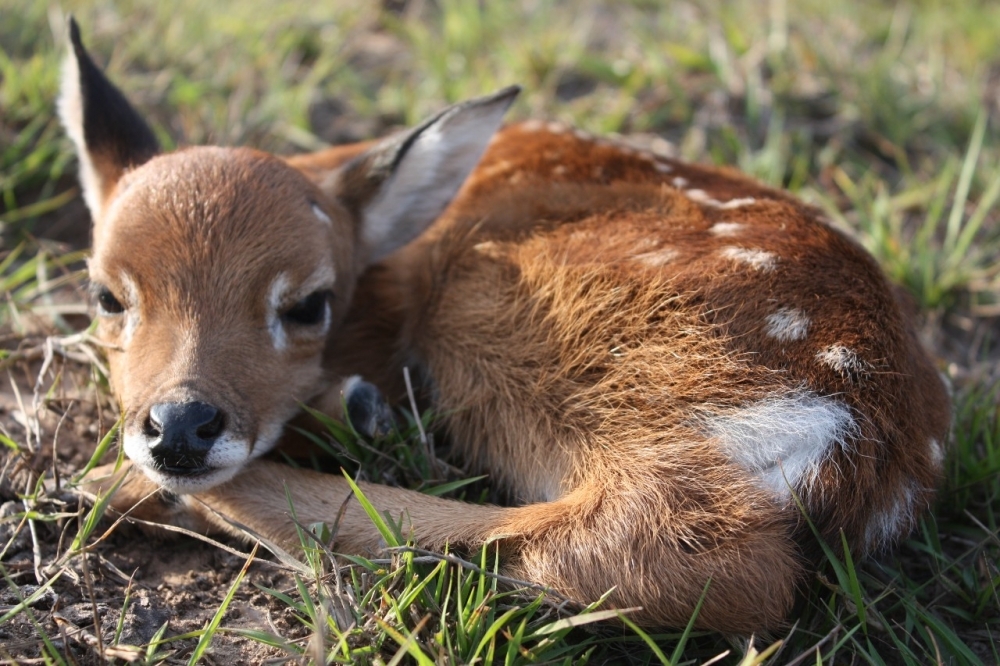



An analysis of the management plans for 118 protected areas in all parts of Brazil shows that 60% use methodologies that may yield an incorrect diagnosis of the threat to the various species of deer, especially those living in forests. The researchers have produced an illustrated guide to help identify species in future stocktaking exercises.
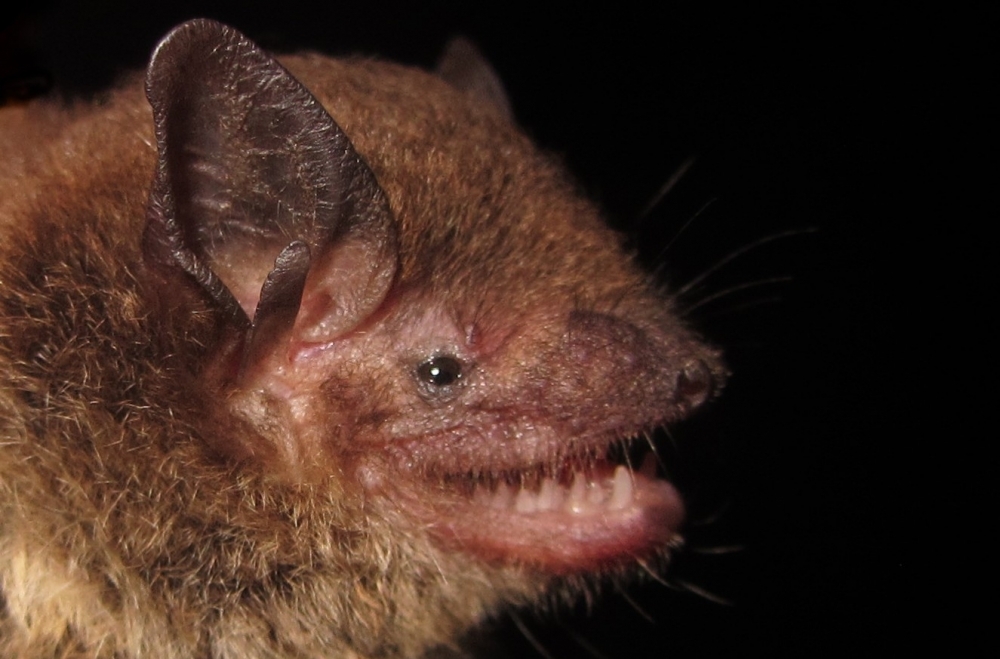

A Brazilian study that reconstructs the evolutionary history of flying mammals suggests expenditure of resources to gestate two young simultaneously results in a shorter lifespan.
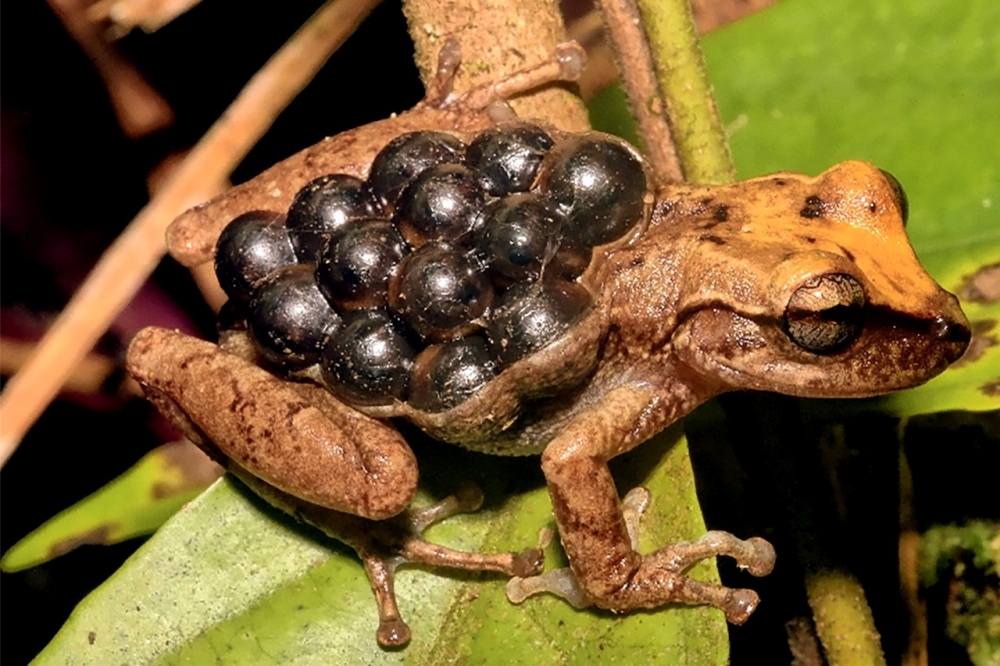

Carrying eggs on their back, laying them in bromeliads or depositing them on leaves are some of the strategies cataloged by Brazilian researchers in a study that will help scientists understand the evolution of vertebrates and contribute to conservation policy.
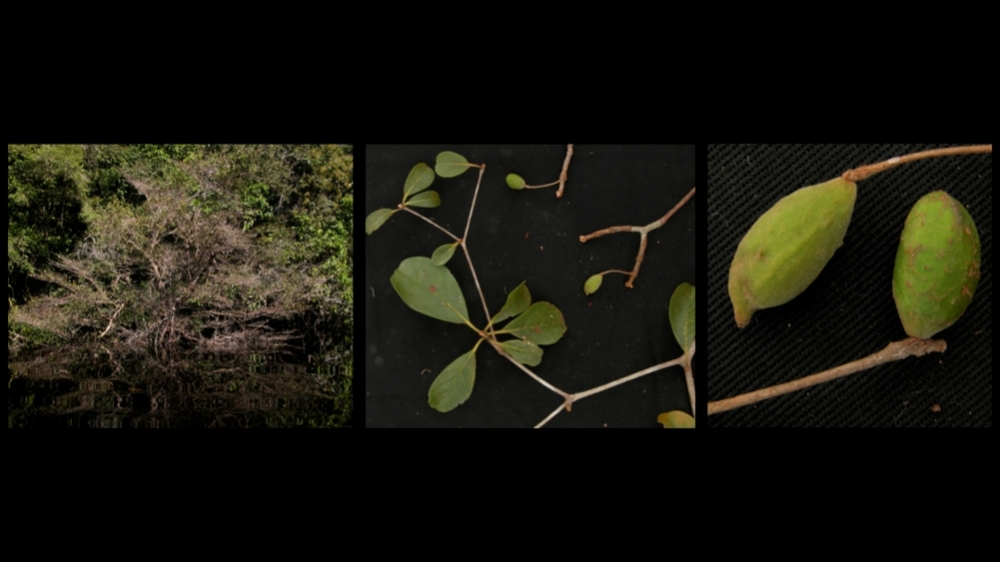

A study by the University of São Paulo shows that where the Negro River is very wide certain plants found on one bank are not found on the other. Overall, however, the extraordinary variety of species is due more to ecology than geography.
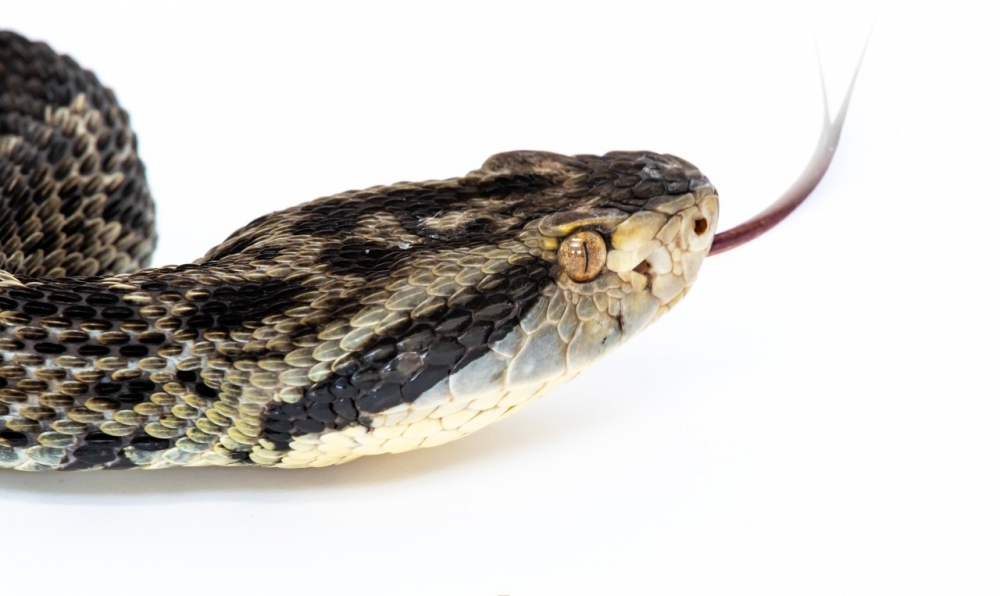

In an article published in PNAS, researchers affiliated with Butantan Institute describe the genome of Bothrops jararaca and suggest the origin of genes responsible for toxins in its venom.

A study conducted at the University of São Paulo and published in Science correlates birds and plants in seed dispersal networks.
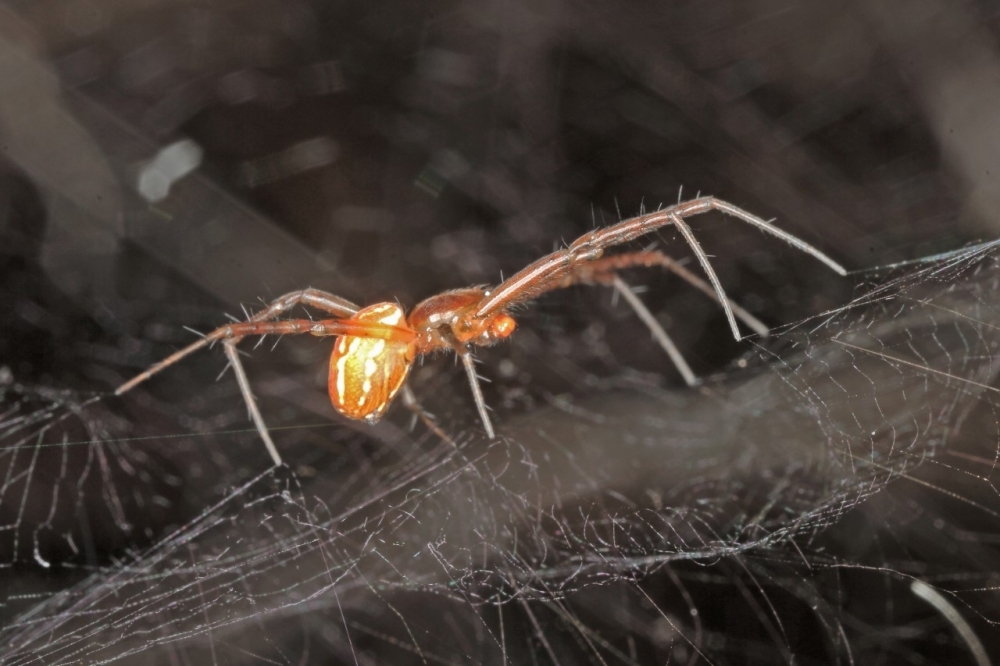

Study shows that males of the species Manogea porracea protect spiderlings and eggs against predators even if they cannot be sure of their paternity.
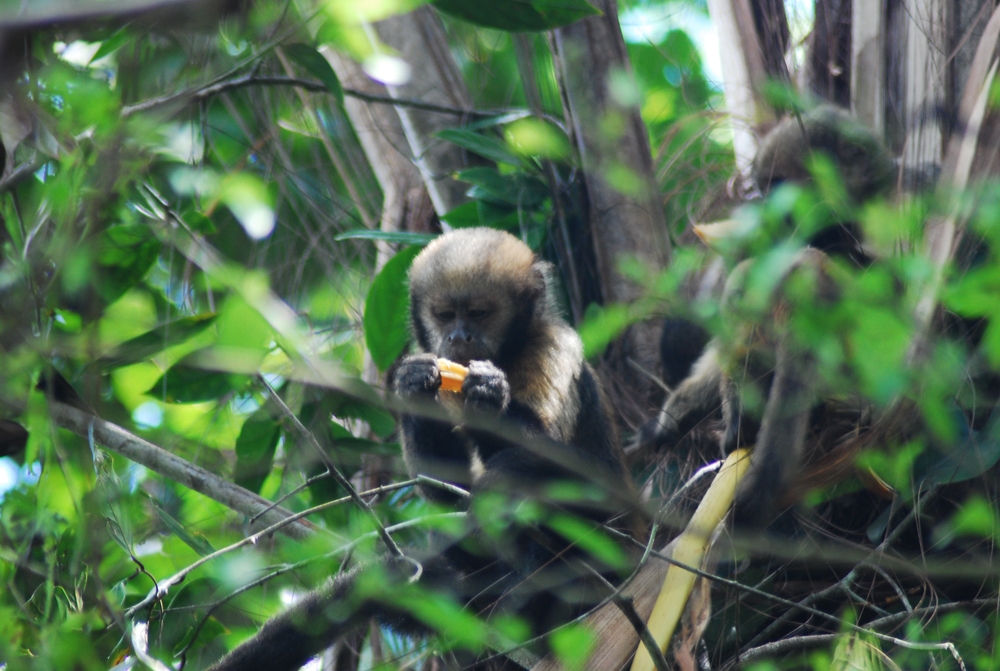

Contradicting theories of primatologists, a study led by Brazilian scientists shows that in a habitat with high hunting pressure, the risk of predation influences the habits of these monkeys more than the availability of food. They spend less time in areas they perceive as ‘more dangerous’ even if plant biomass and invertebrates are more abundant there.
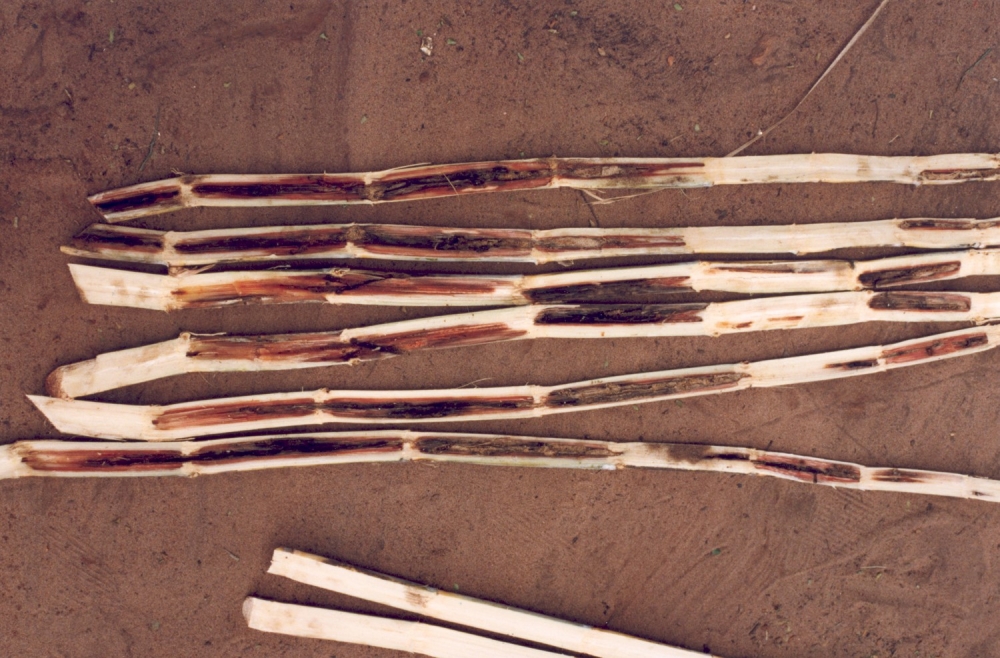

Researchers at the University of São Paulo discover that the fungus Fusarium verticillioides uses volatile compounds to manipulate insects and plants, promoting its own dissemination.

The device was used for the first time to culture two maternal endometrial cell types, revealing the effects of alterations in glucose and insulin levels in the uterine environment. It can also be converted into a model for study of pregnancy in humans and endometriosis.
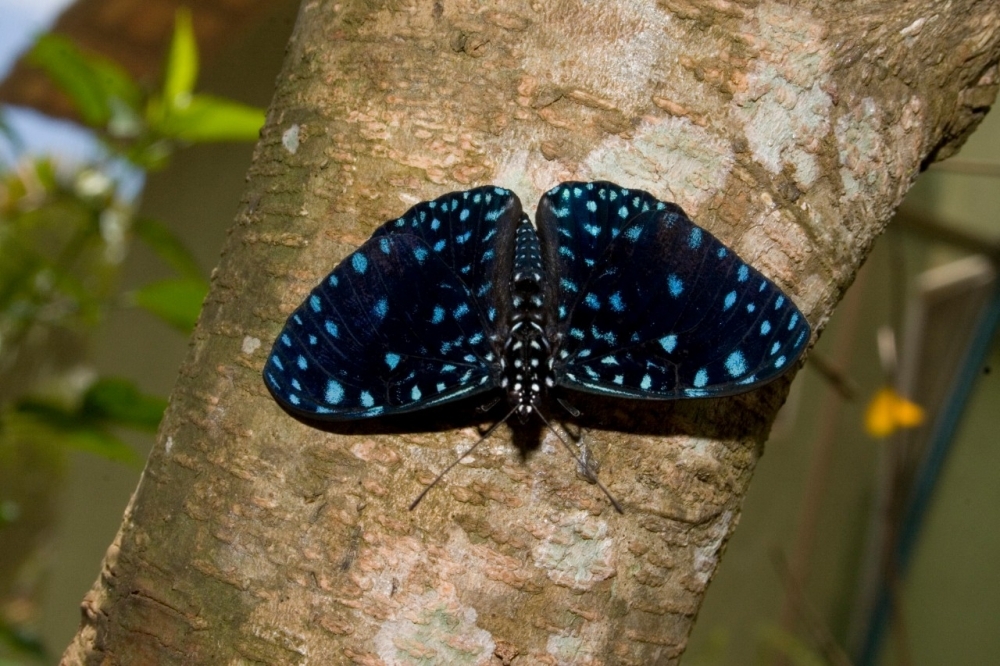

Butterflies are considered a key biological indicator of trends in the biome. The study quantified the contributions of landscape and climate variables to current species distribution patterns.
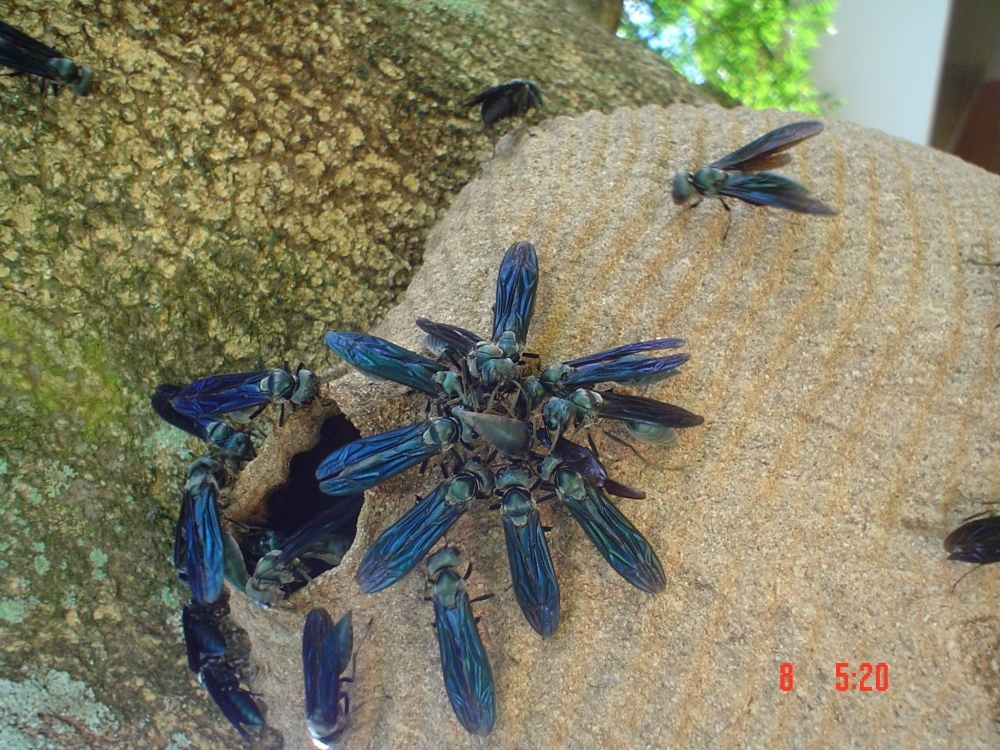

A study by researchers at São Paulo State University reinforces the idea that environmental and climate-related changes resulting from the Andean uplift triggered a revolution in the caste system of these paper wasps.

Researchers in Brazil, Argentina, Chile, and the UK are participating in the initiative. Results are published in the journal BioScience.
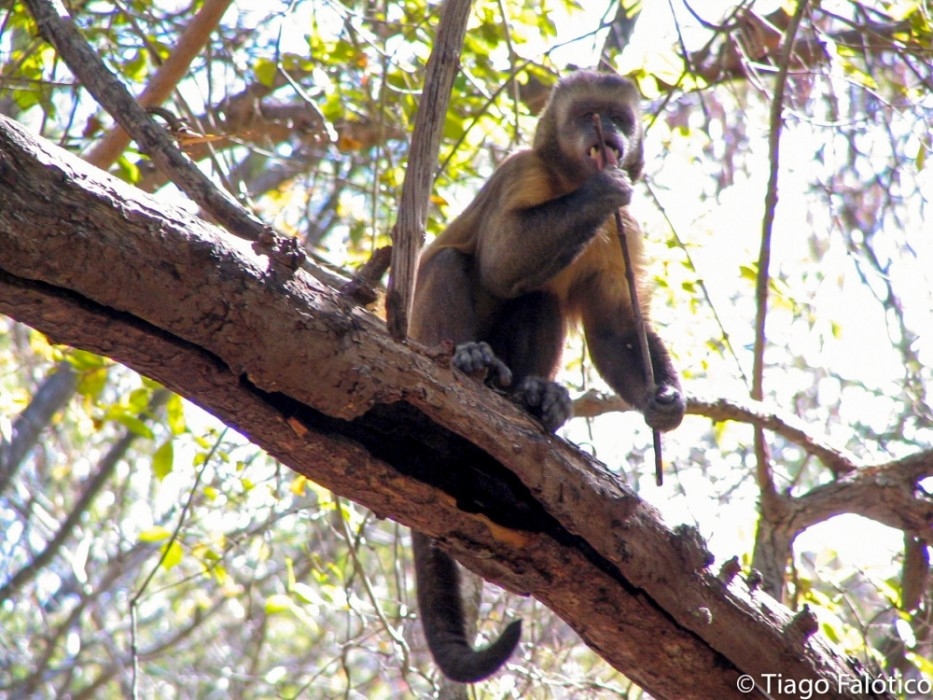

Scientists who study capuchin monkeys on a nature reserve in Brazil found that stone tools are used for digging, seed pounding, and stone-on-stone percussion. The monkeys can serve as a model to help understand how humans evolved to use tools.
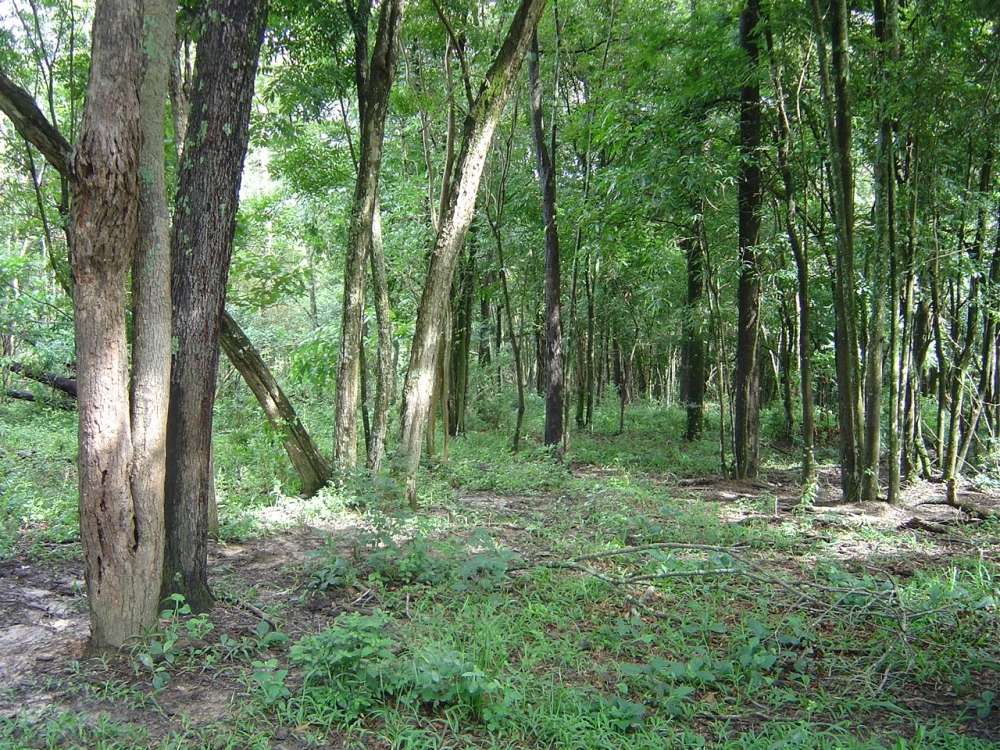

Researchers at the University of São Paulo estimated biodiversity and biomass losses in the biome using data from 1,819 forest inventories. In terms of carbon storage, the losses correspond to the destruction of 70,000 km² of forest, representing some USD 2.6 billion in carbon credits.
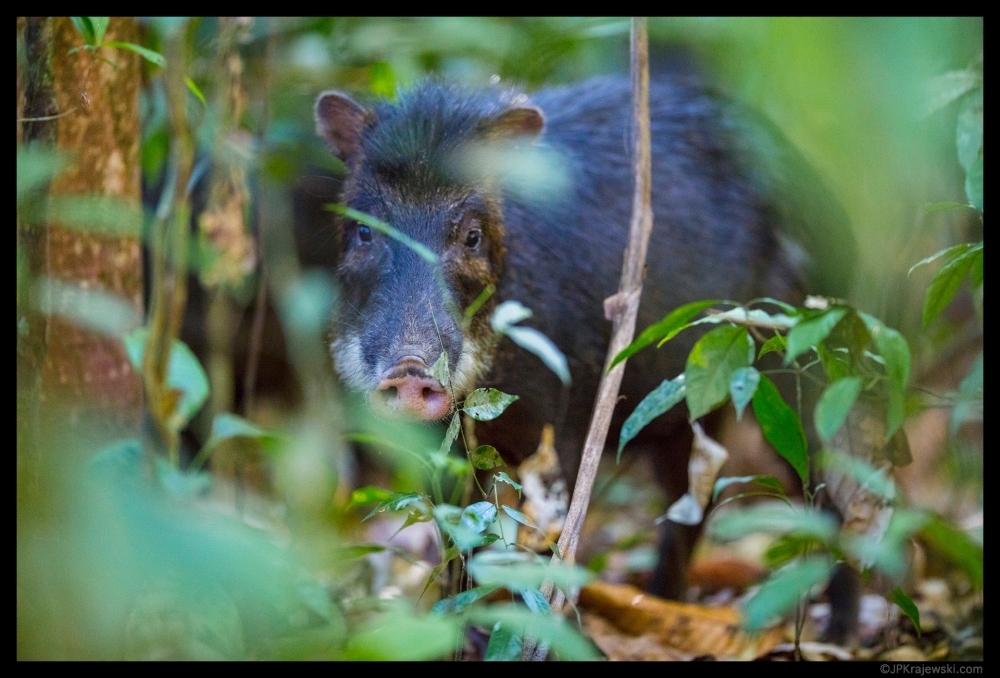

A study conducted by scientists at São Paulo State University demonstrates that animals like peccaries and tapirs boost soil levels of nitrogen, an essential element to plant growth.
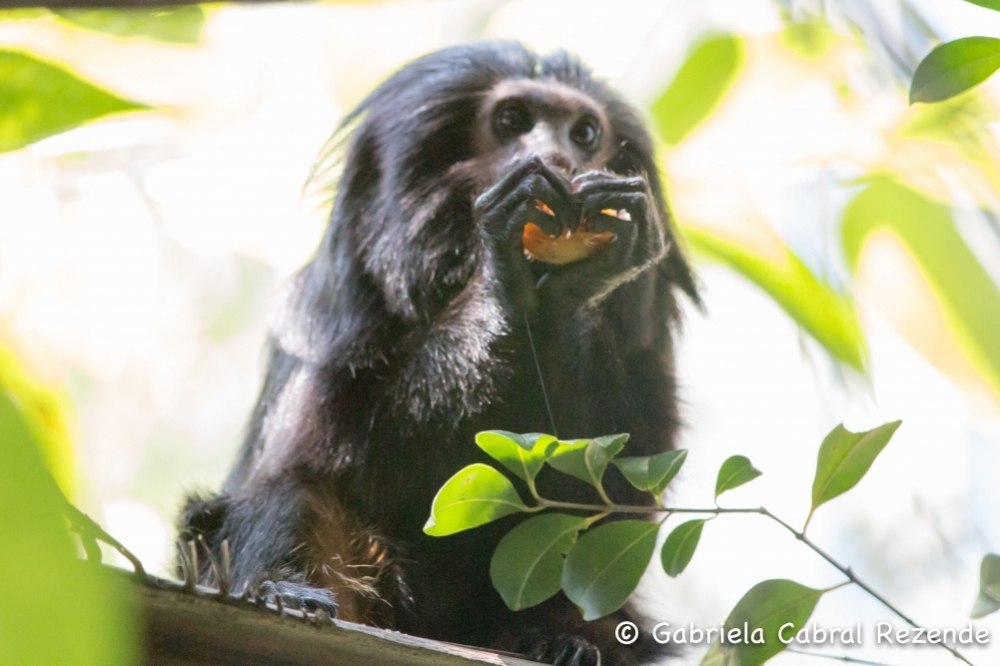

The researchers used modeling to show which areas are suitable in terms of forest cover and climate for occupation by the endangered species, which is endemic to the state of São Paulo. Their study is a contribution to translocation initiatives that move groups of these animals to areas from which the species has disappeared.
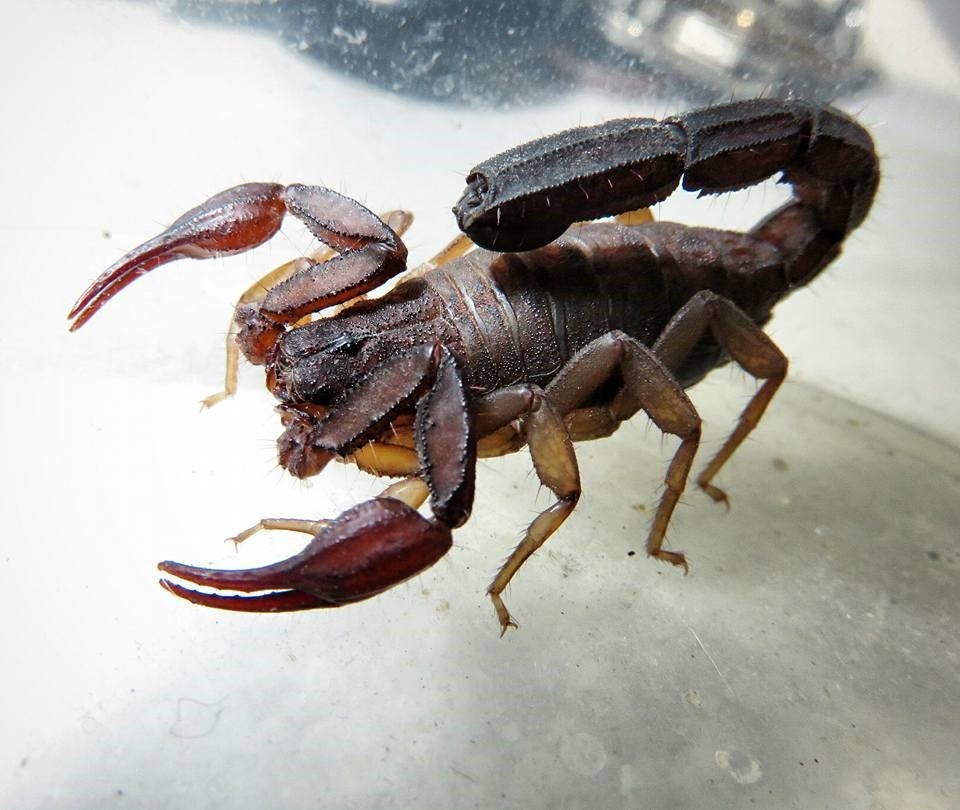

Brazilian researchers tested the antichagasic properties of VmCT1, obtained from the venom of Vaejovis mexicanus, a scorpion harmless to humans, and synthesized novel analogs to redesign the native molecule.
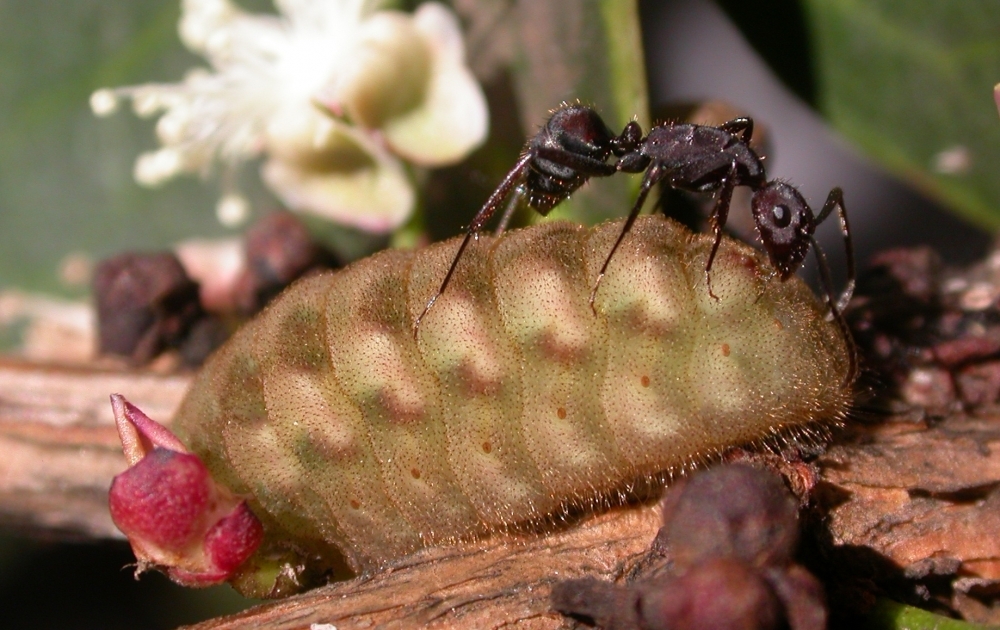

Study reveals different forms of interaction between insect groups: while some caterpillar species have bodies covered with molecules identical to those of the plants they inhabit and are ‘invisible’ to ants, others offer ants nectar in exchange for protection from predators.
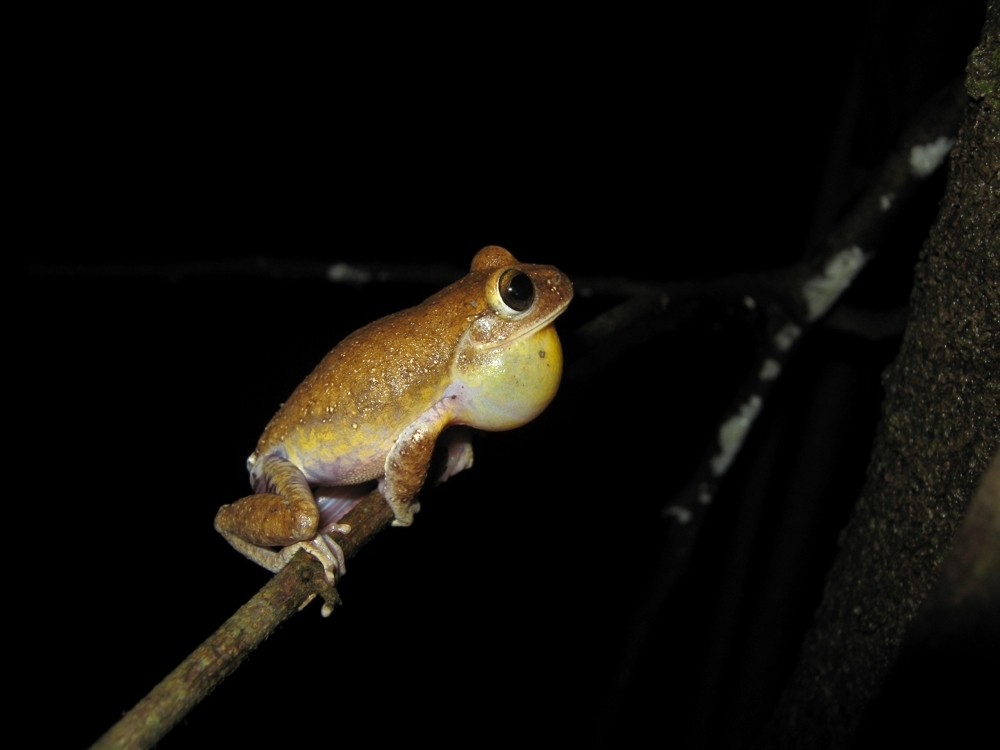

Study shows that a tree frog endemic to a mountainous region of the Brazilian savanna is unable to disperse and find genetically closer mates when the terrain is rugged, potentially endangering survival of the species. The findings show that topography is an important factor for conservation policy.
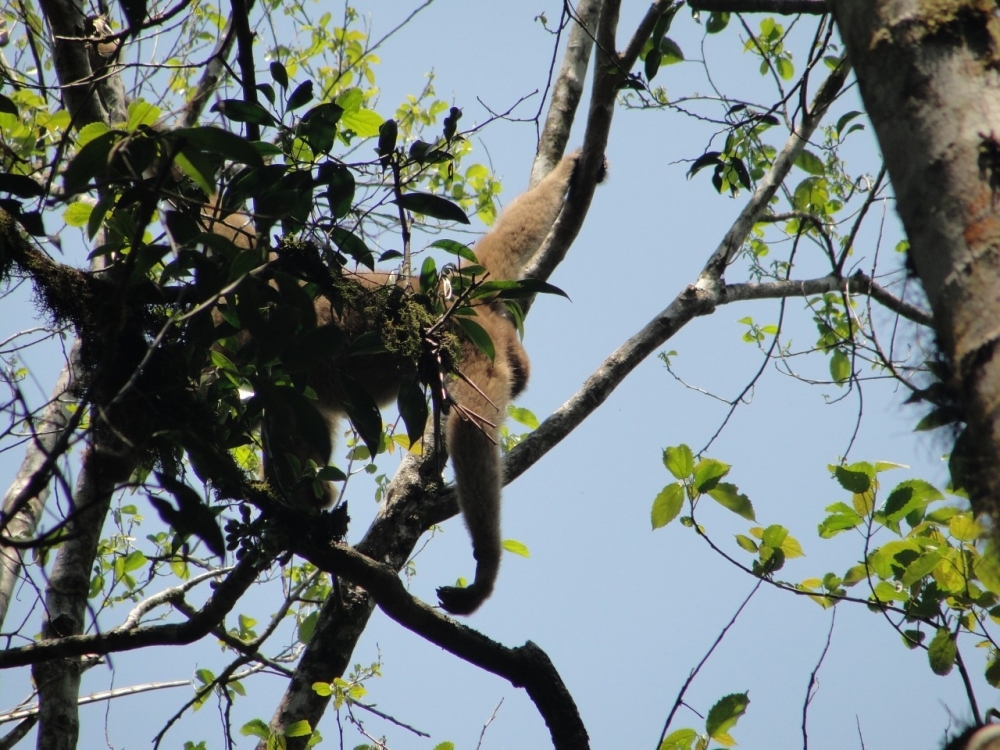

Group led by Brazilian ecologist shows defaunation wiped out 40% of the ecosystem services provided or supported by mammals, such as ecotourism, disease control and soil formation. Large-bodied mammals are disappearing fastest.
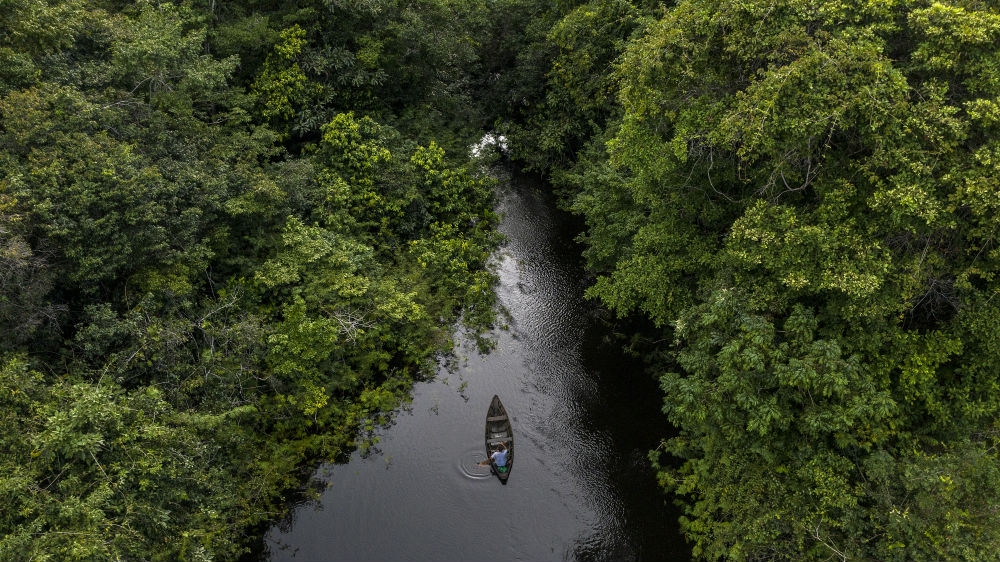

Simulations using field data suggest focusing on the protection of species that live in rivers and lakes can be more efficient than the approach most used now, which focuses on terrestrial biodiversity. An article at Science is based on the findings.
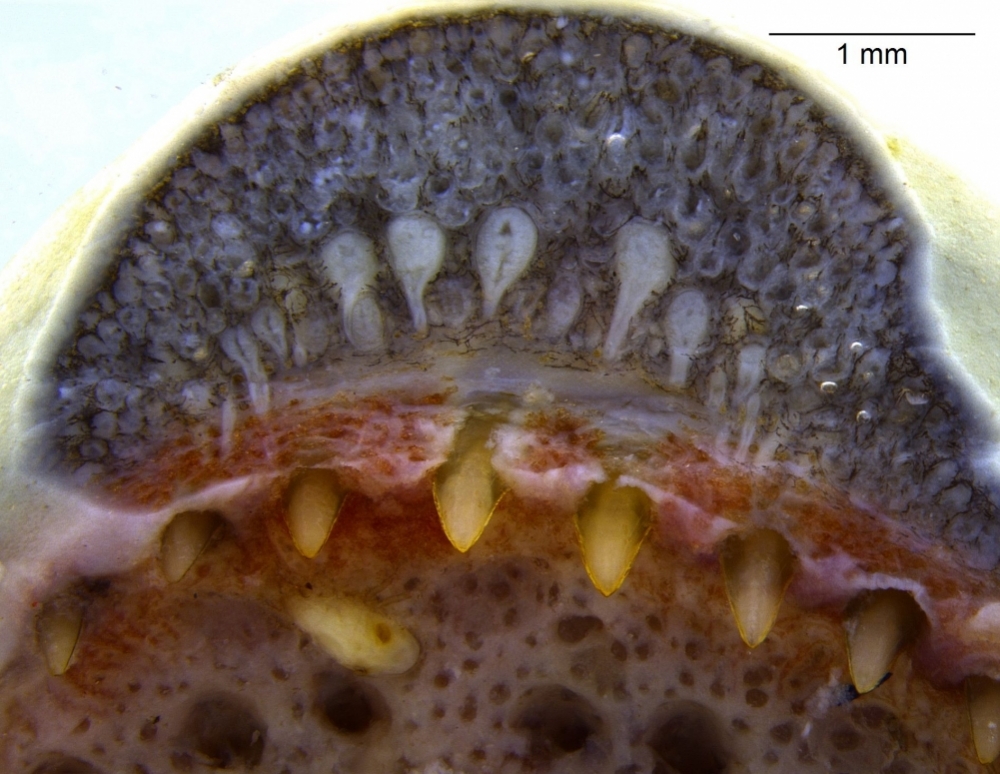
Brazilian researchers discover that caecilians, limbless amphibians resembling worms or snakes that emerged some 150 million years before the latter, can probably inject venom into their prey while biting.

Dozens of scientists from several countries calculated upper limits to global and local temperatures if tropical forests are to survive.
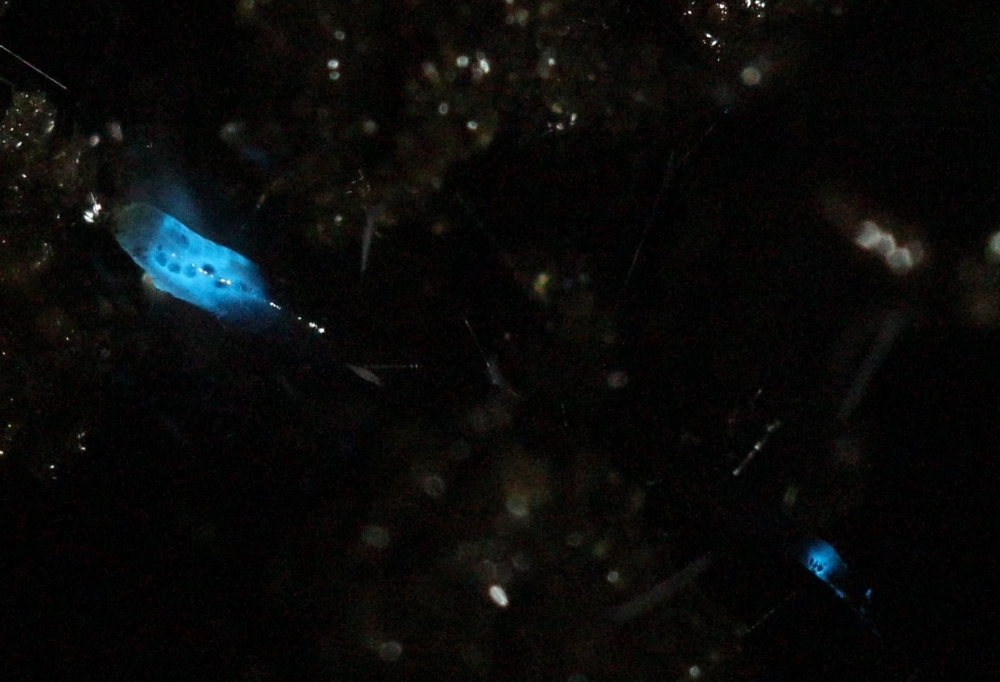
Researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) isolated molecules present in the larvae of a blue light-emitting fungus gnat that inhabits the Appalachians. The study will help elucidate human diseases and could lead to novel biotech applications.