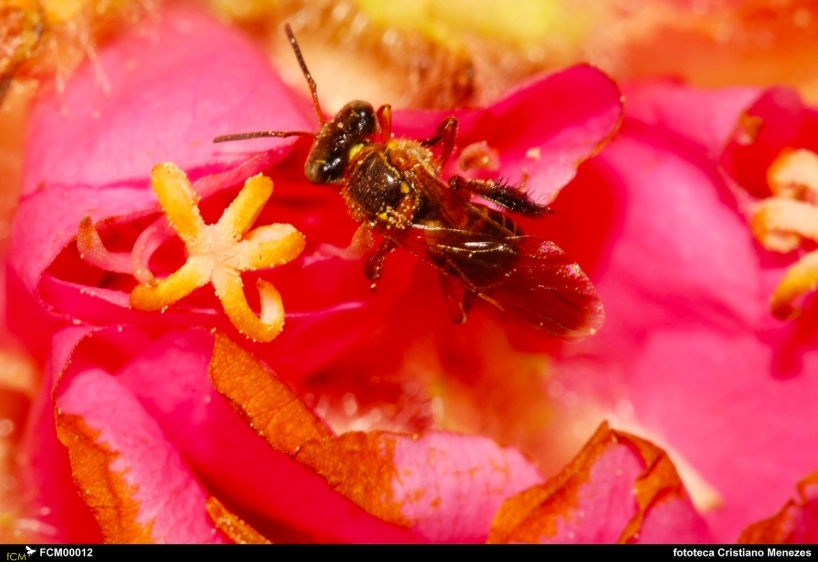



Frieseomelitta varia is a docile species of economic interest as a pollinator. Its workers are sterile, and some of its genetic sequences are identical to those found in other eusocial bees, pointing to the conservation of ancestral traits.
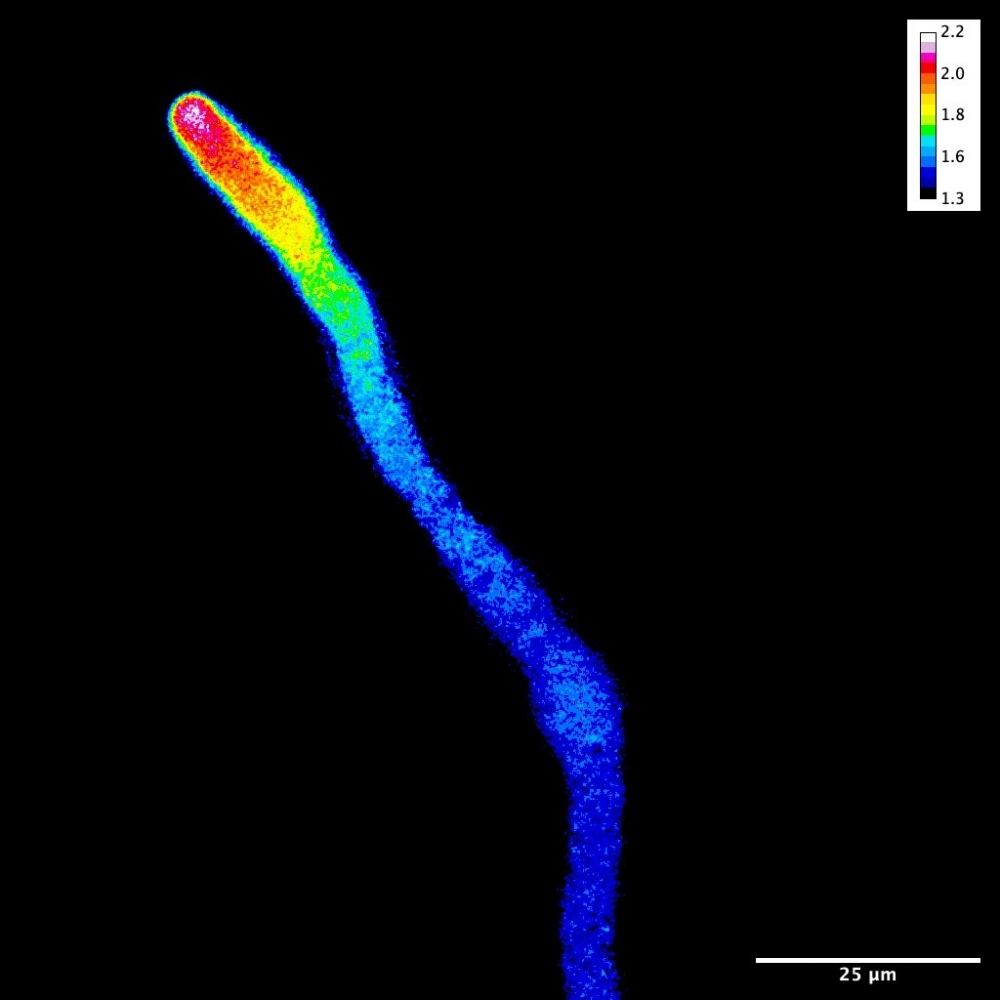
A study showing how pollen tubes grow into flowers to reach the ovule paves the way for the improvement of food crop varieties as well as a deeper understanding of the growth of fungi and neurons.
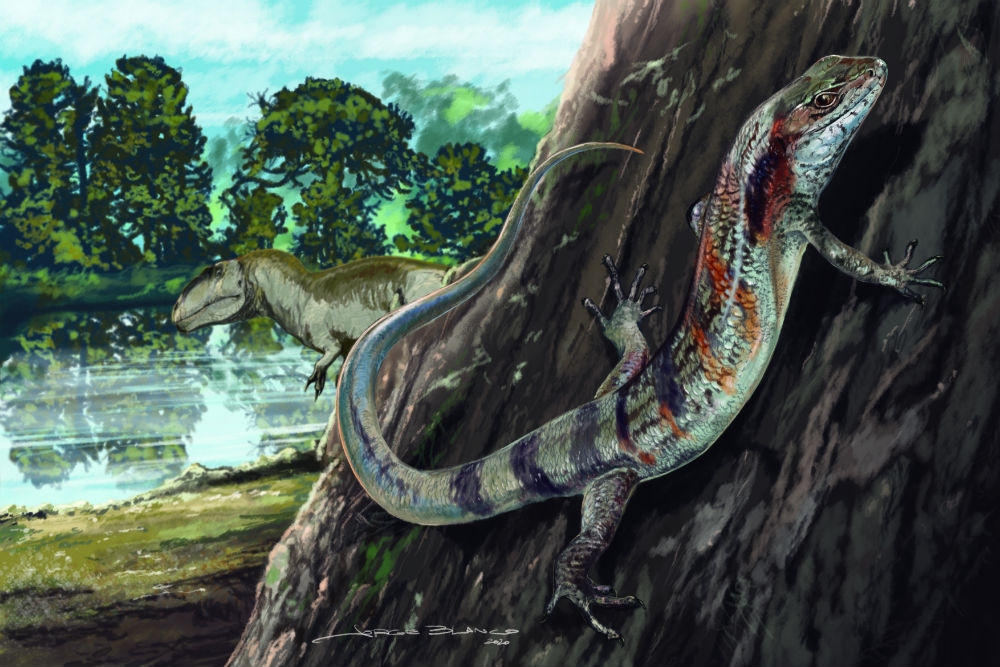

The animal was approximately 10 cm long and lived more than 130 million years ago in what is now the state of Minas Gerais. Its morphology differs from that of all other known lizard species.
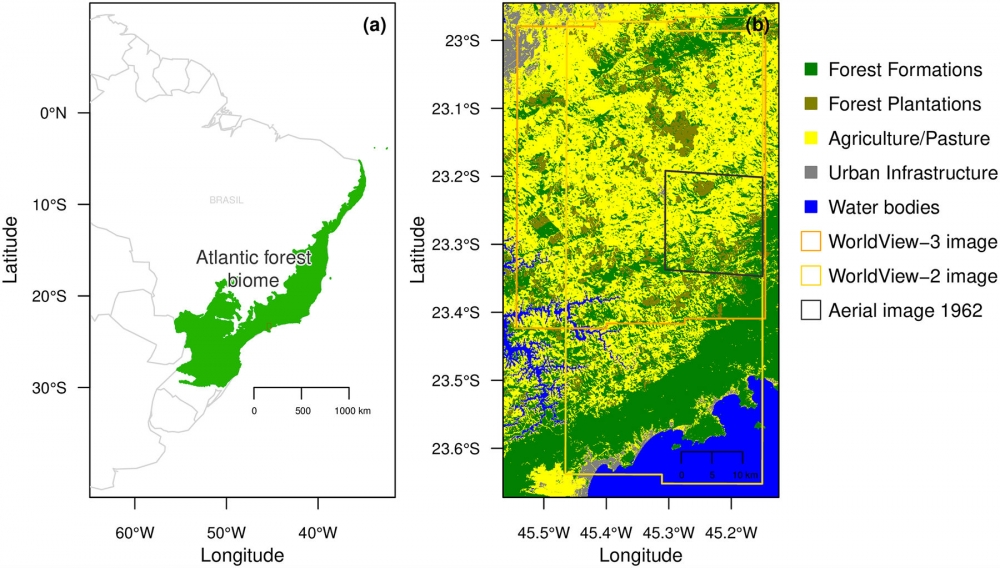
On average, more than 4% of the studied forest fragments have regenerated naturally in the past 50 years. In certain forests near the Serra do Mar ridge, regeneration has reached 50%. The study used artificial intelligence to compare satellite images and aerial photographs taken in 1962.
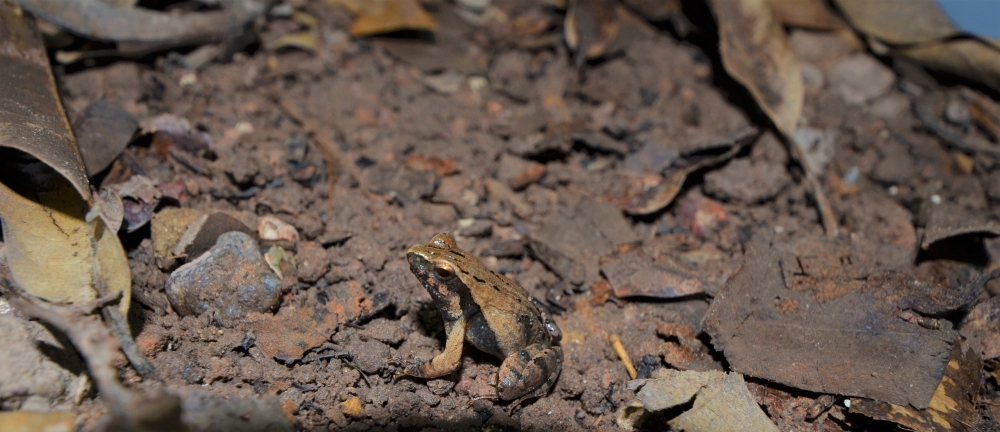

Using advanced molecular biology techniques, researchers discover that two frog species widely distributed in Brazil may actually be as many as seven, some exclusive to the Amazon. The change in classification could require new conservation actions.

Agreement between São Paulo State University and American Chemical Society facilitates the compilation of information dispersed across more than 30,000 scientific articles.
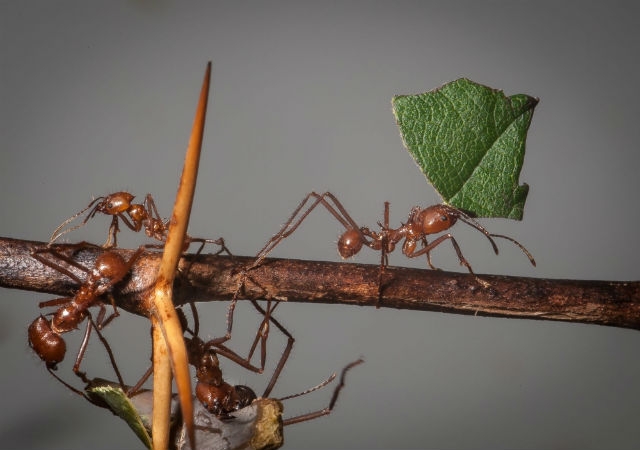

Leafcutter ants speed up foraging to collect as much food as possible when they sense a decrease in atmospheric pressure according to a study by researchers at the University of São Paulo in Brazil
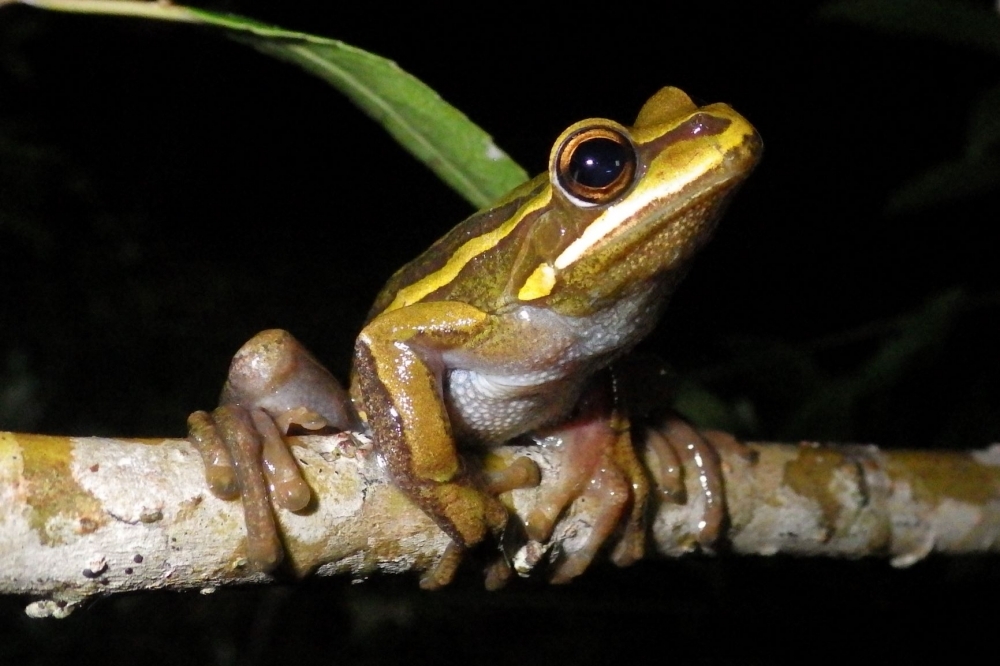

Updated survey of anuran amphibians that live in South America was led by a Brazilian researcher. Results are published in a book with maps of species diversity, ecological functions and endemic species.
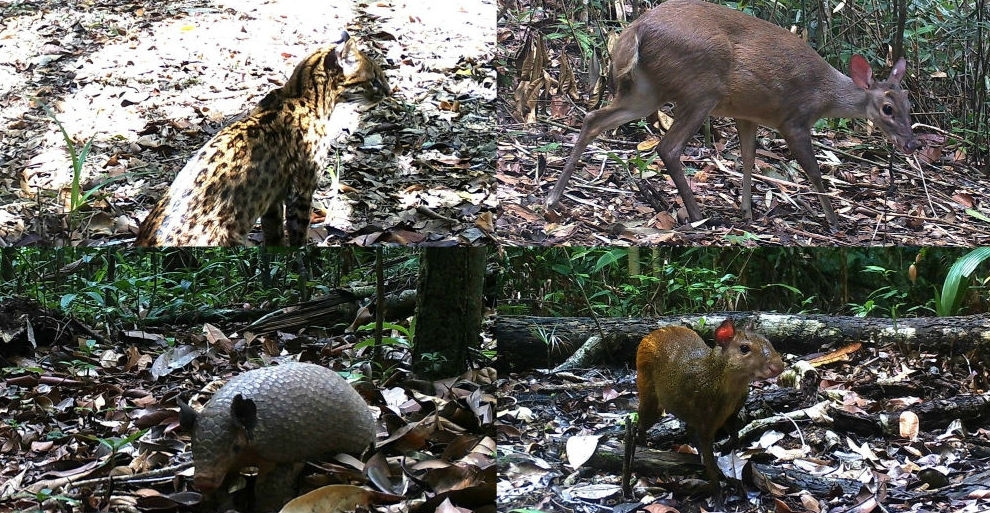

In an article published in PNAS, Brazilian researchers stress the need for agricultural management that favors the maintenance of wildlife.
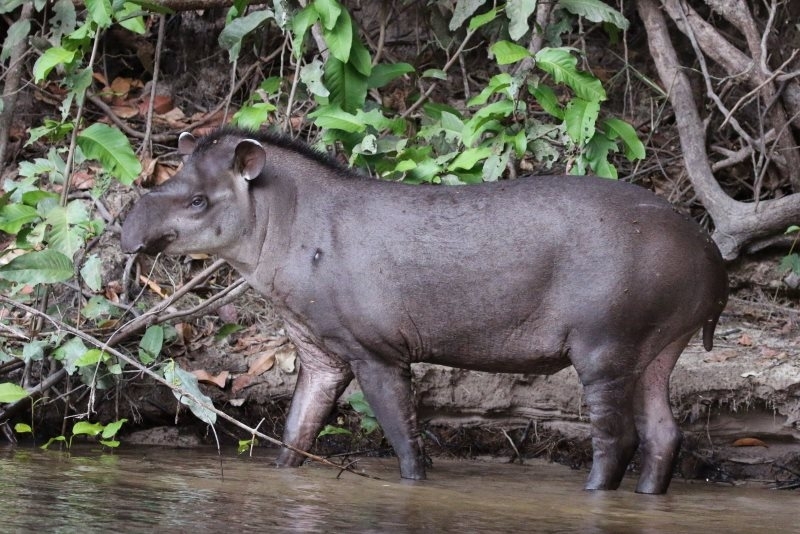

Study suggests these two species of large herbivores have complementary ecological functions, favoring seed dispersal and growth of adult trees.
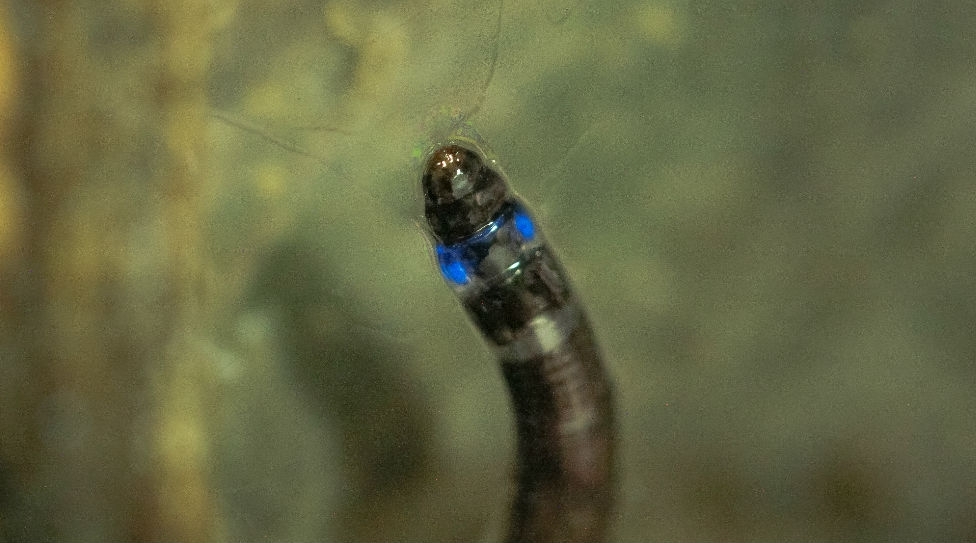

Larvae of a fungus gnat found in Iporanga, São Paulo State, Brazil, have bioluminescent properties previously observed only in species native to North America, New Zealand and Asia. This study paves the way for new biotech applications.
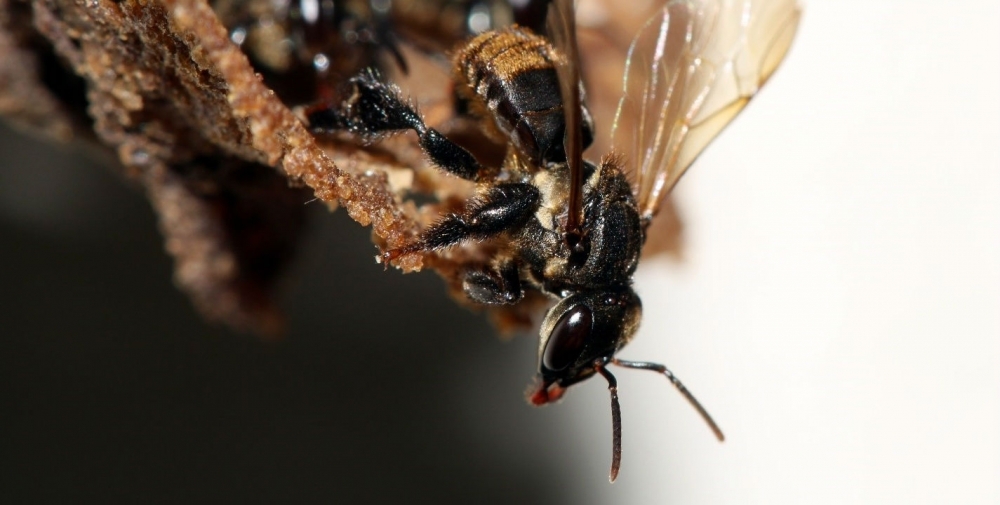

A report published in PLOS ONE describes key roles of various microorganisms in the development of the larvae of Scaptotrigona depilis. Researchers warn that this symbiotic relationship is threatened by the indiscriminate use of pesticides.
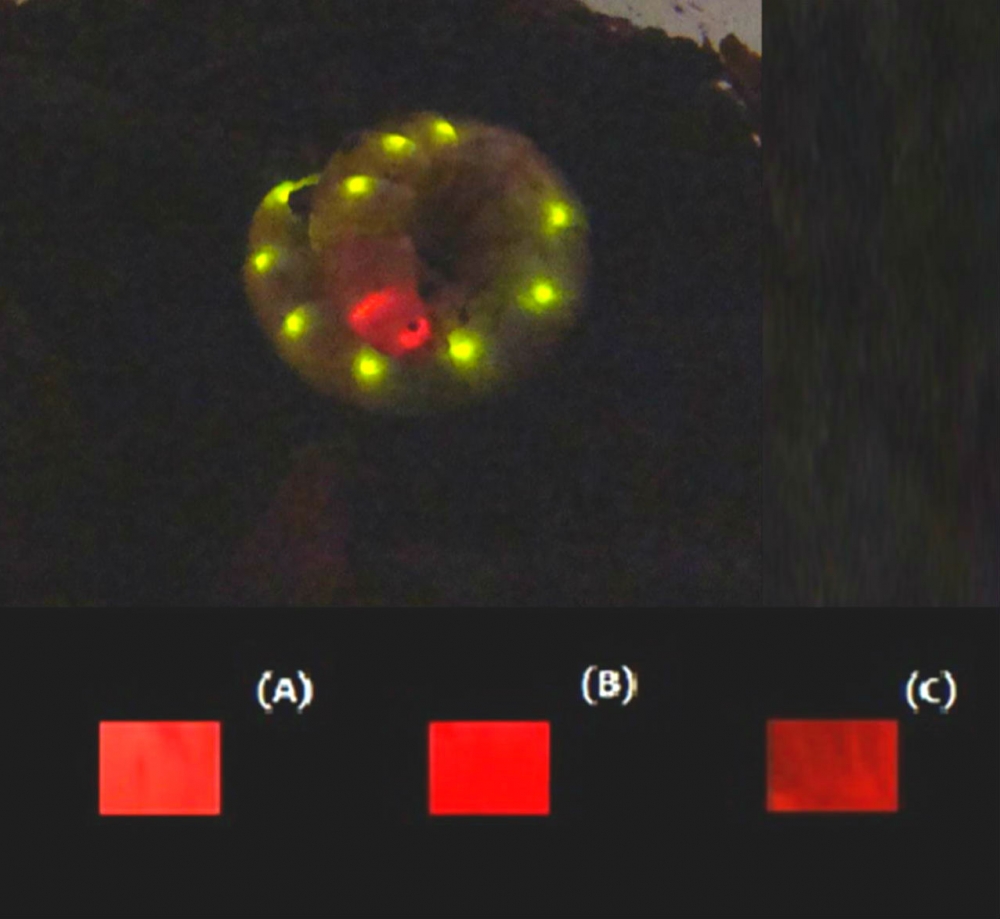
Color differences in the light produced by the larviform beetle are known to be caused by two enzymes with minor structural differences, but the details were hitherto unknown. This discovery has potential for applications in biotechnology.

A study conducted as part of a Thematic Project by Brazilian and US researchers investigates how plants and animals in the Atlantic Rainforest biome have reacted to climate change in past millennia.

An international study with key contributions from Brazilian researchers shows that an endangered species, famed as a “forest gardener,” influences African forest composition in terms of tree species and increases the aboveground biomass over the long term.
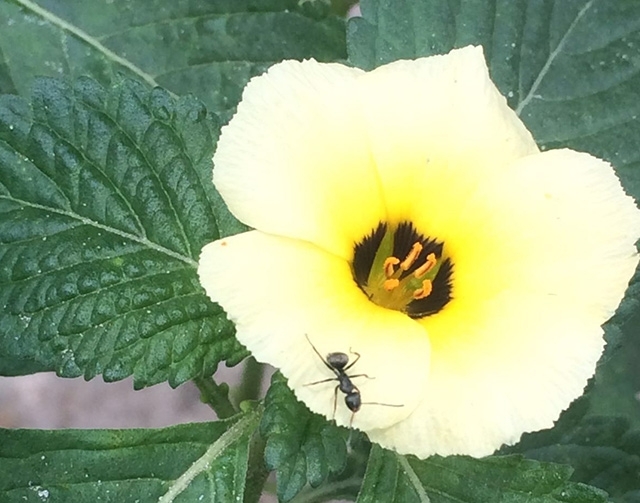

The aggressiveness of ants in arid environments with scarce food supply helps protect plants against herbivorous arthropods.
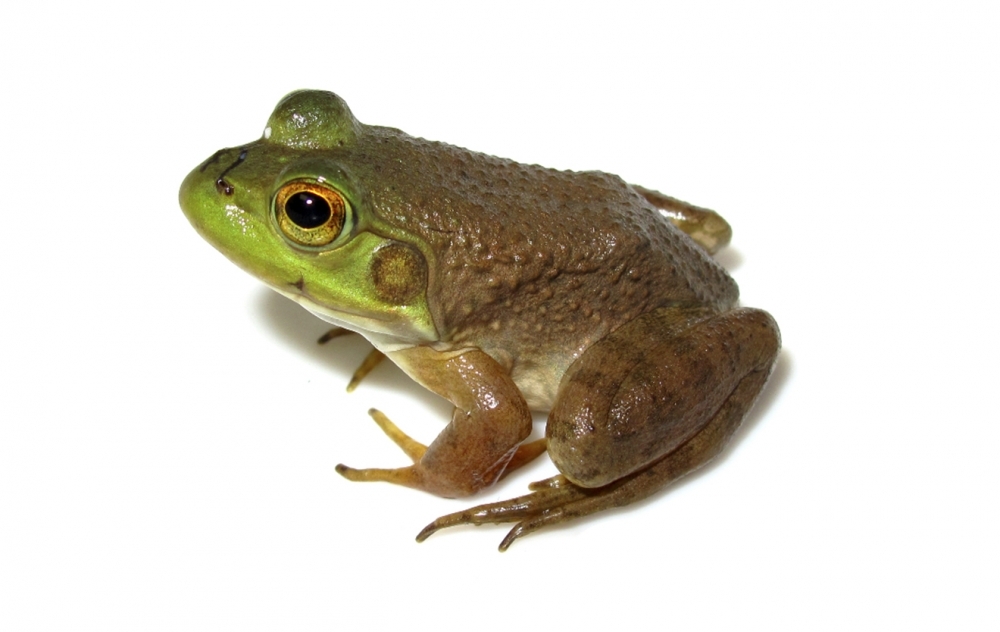

Ranavirus is linked to amphibian decline or extinction in other parts of the world, but in Brazil, it has been reported only in captive animals.
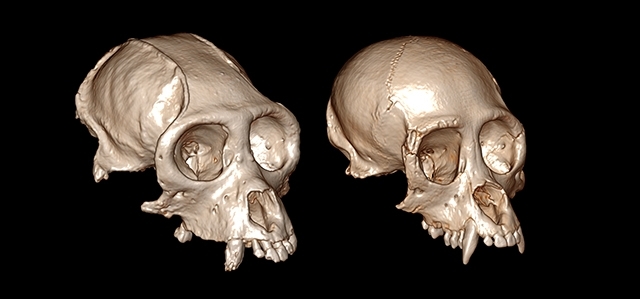
Computed tomography scans of fossils from two extinct species point to evolutionary adaptations and kinship with extant howler, spider and woolly monkeys.

A nonlethal dose of insecticide clothianidin can reduce honeybees’ life span by half; once combined with the fungicide pyraclostrobin, it alters the behavior of worker bees to the point of endangering the whole colony.

The decline in biodiversity is a direct result of human activity and represents a grave threat to human well-being according to the first global assessment of the state of nature.

Rapid resprouting and flowering of Bulbostylis paradoxa is proof of the Cerrado biome’s superb resilience and its capacity to evolve through fire.
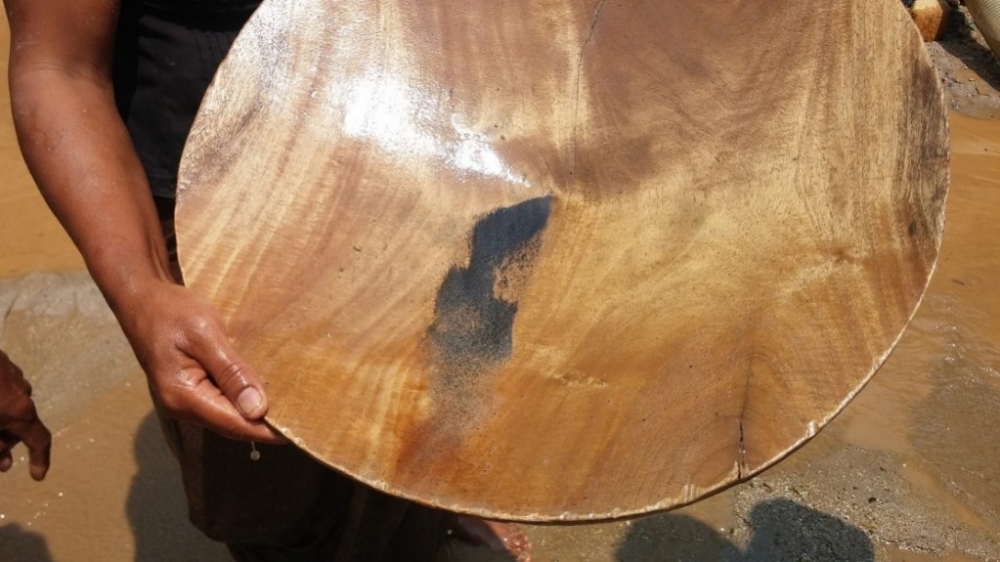

Although artisanal mining has declined in the region, it continues to account for high levels of mercury in the largest tributary of the Amazon, according to a study supported by FAPESP’s SPRINT program.
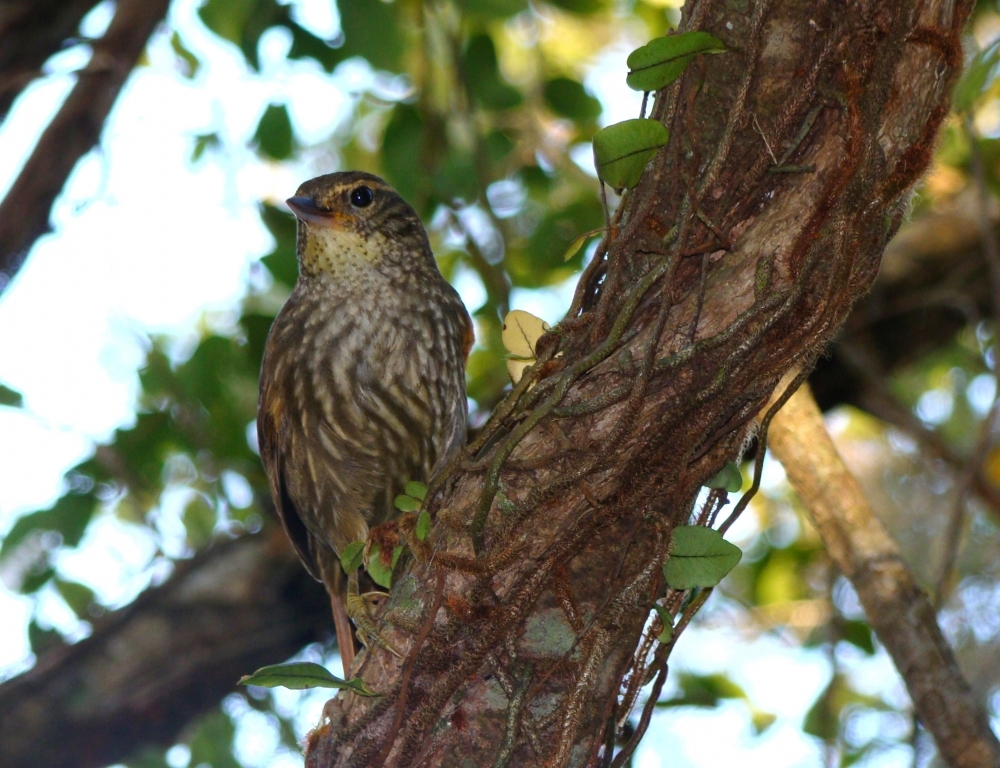

A genetic and computational analysis of birds suggests that the Andean and Atlantic tropical forests, which are now almost a thousand kilometers apart, were connected via the Cerrado in the distant past.
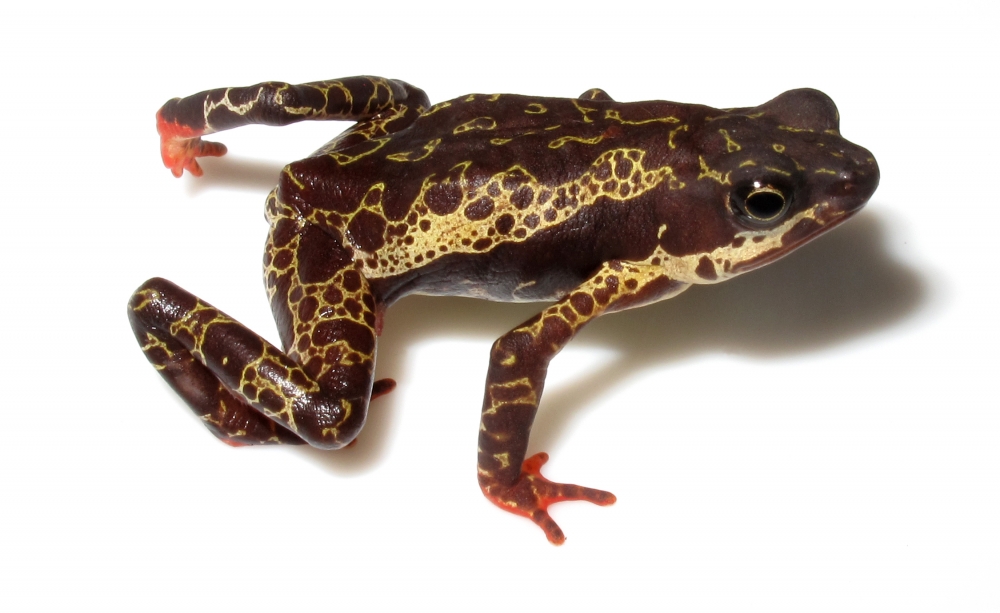

Survey by researchers in 16 countries is published in Science. Authors say chytrid fungus is responsible for heaviest biodiversity loss ever caused by a single pathogen.

The role played by symbiotic microorganisms isolated from the skin of anurans has been discovered by researchers in Brazil. The study is published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.