

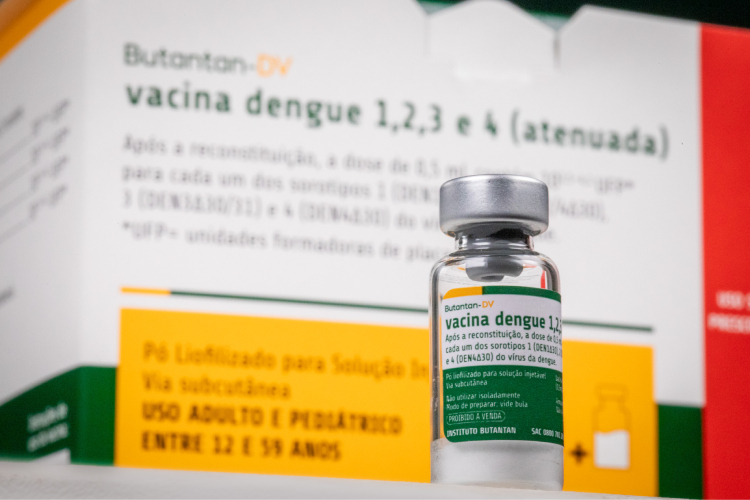
Study published in Nature Medicine confirms that Butantan-DV protects against hospitalizations.
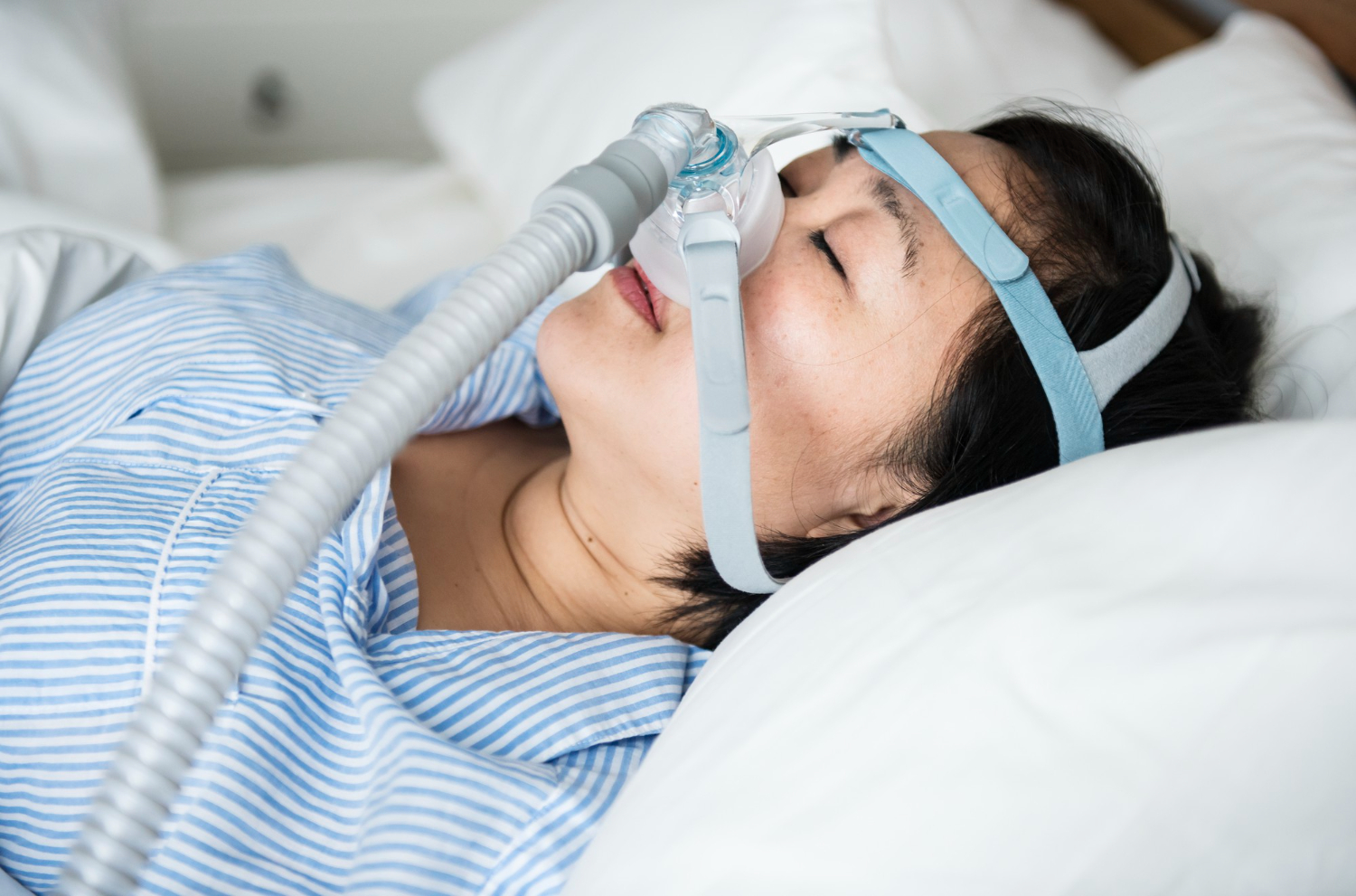
A study of 44 patients shows that the combination of the two diseases reduces strength and physical performance, directly impacting quality of life.
National solution detects billions in waste by measuring patients’ quality of life and cross-referencing the data with the actual cost of treatments.

After comparing data from over one million diagnosed individuals, an international consortium of researchers grouped the disorders into five major categories.
Biopharmaceutical developed at São Paulo State University with support from FAPESP receives financial support from the Ministry of Health for final phase of clinical trials.

Biopharmaceutical developed at São Paulo State University with support from FAPESP receives financial support from the Ministry of Health for final phase of clinical trials.

A network of genes linked to the nervous and immune systems can predict cancer risk and even explain symptoms such as fatigue and depression resulting from viral hepatitis infection.

A network of genes linked to the nervous and immune systems can predict cancer risk and even explain symptoms such as fatigue and depression resulting from viral hepatitis infection.

A study by the São José do Rio Preto School of Medicine could increase the use of the most sought-after organ in Brazil. There are almost 30,000 people on the waiting list.

A study by the São José do Rio Preto School of Medicine could increase the use of the most sought-after organ in Brazil. There are almost 30,000 people on the waiting list.

Researchers at the University of São Paulo and the University of Wisconsin-Madison found that bleeding in the intestine during severe cases of the disease causes systemic infection and worsens the viral infection.

Researchers at the University of São Paulo and the University of Wisconsin-Madison found that bleeding in the intestine during severe cases of the disease causes systemic infection and worsens the viral infection.

Analyses conducted by researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos showed that the condition can be easily reversed through simple stimuli and strategies, reinforcing the need for programs aimed at this population.

Analyses conducted by researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos showed that the condition can be easily reversed through simple stimuli and strategies, reinforcing the need for programs aimed at this population.
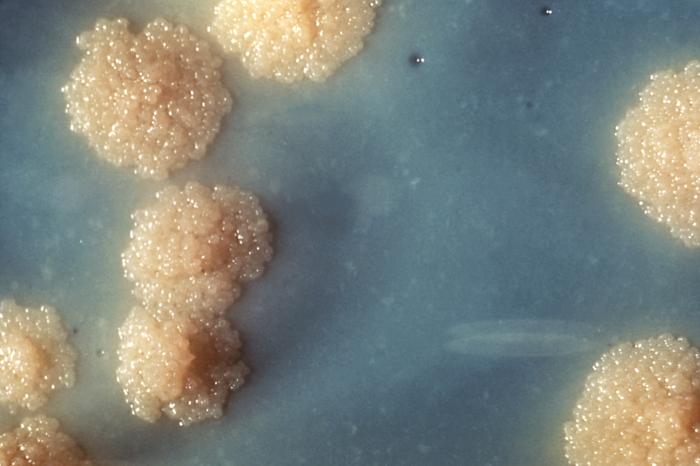
Research from São Paulo State University shows that an inexpensive, easy-to-produce substance eliminated lung infection in 30 days. The compound has the potential to reduce the time and toxicity of current therapies.

Research from São Paulo State University shows that an inexpensive, easy-to-produce substance eliminated lung infection in 30 days. The compound has the potential to reduce the time and toxicity of current therapies.

In a preliminary study conducted on human cells, two commonly used osteoporosis drugs bound to excess iron, preventing cell damage.

In a preliminary study conducted on human cells, two commonly used osteoporosis drugs bound to excess iron, preventing cell damage.
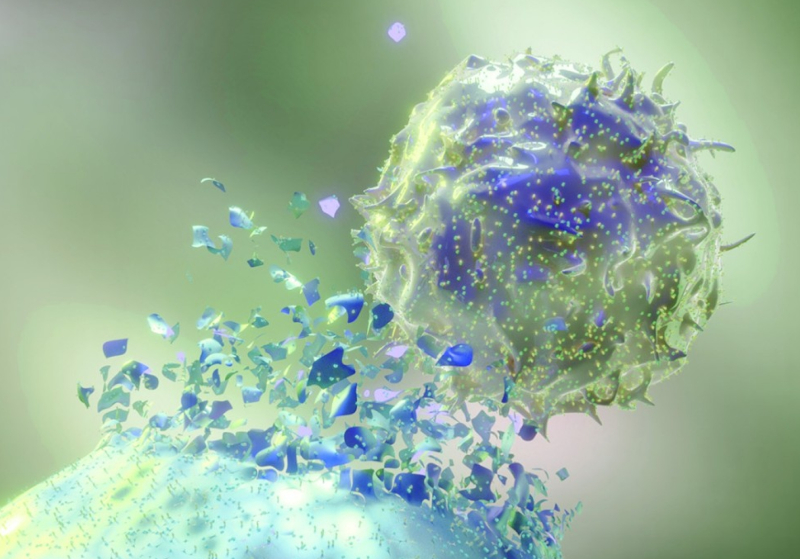
A study by FAPESP-supported center used the NK-92 cell line to test new chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) models. Tests demonstrated an increased ability of the cells to destroy tumors.

Combining acceptance and monitoring in the education of young people reduces the risk of repeating consumption patterns, even in families where parents also use these substances, including cigarettes, vapes, and marijuana.

Research conducted with 130 children between the ages of six and 11 showed that inflammation associated with obesity and being overweight affects the functioning of the endothelium – the layer that lines blood vessels – paving the way for diseases such as atherosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke.

Research from São Paulo State University shows that carbetocin, when administered before social stress situations, prevents anxiety in laboratory rats without having direct anxiolytic effects.

Research conducted on rats reinforces the idea that proton pump inhibitors, which are widely used to treat stomach problems, can affect mineral absorption and compromise bone health.

Research conducted on rats reinforces the idea that proton pump inhibitors, which are widely used to treat stomach problems, can affect mineral absorption and compromise bone health.
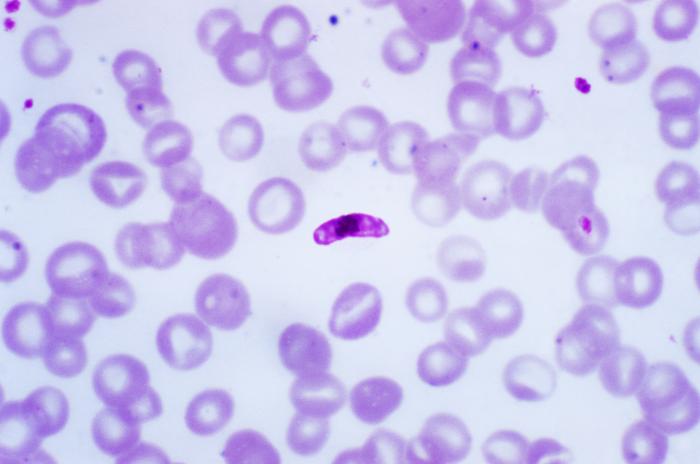
Tests on cell cultures and rodents have shown that the new molecule acts on all three stages of the disease cycle, eliminating the parasite from human blood and liver and preventing transmission to mosquitoes.