

A study conducted at São Paulo State University indicates that the non-invasive technique provides lasting benefits by reducing the risk of falls.

A study of more than 5,000 people over 12 years showed that simple measures to assess the two conditions can facilitate the diagnosis of sarcopenic obesity without complex tests, such as MRI and CT scans. This finding expands access to treatment for older adults.

A study of more than 5,000 people over 12 years showed that simple measures to assess the two conditions can facilitate the diagnosis of sarcopenic obesity without complex tests, such as MRI and CT scans. This finding expands access to treatment for older adults.
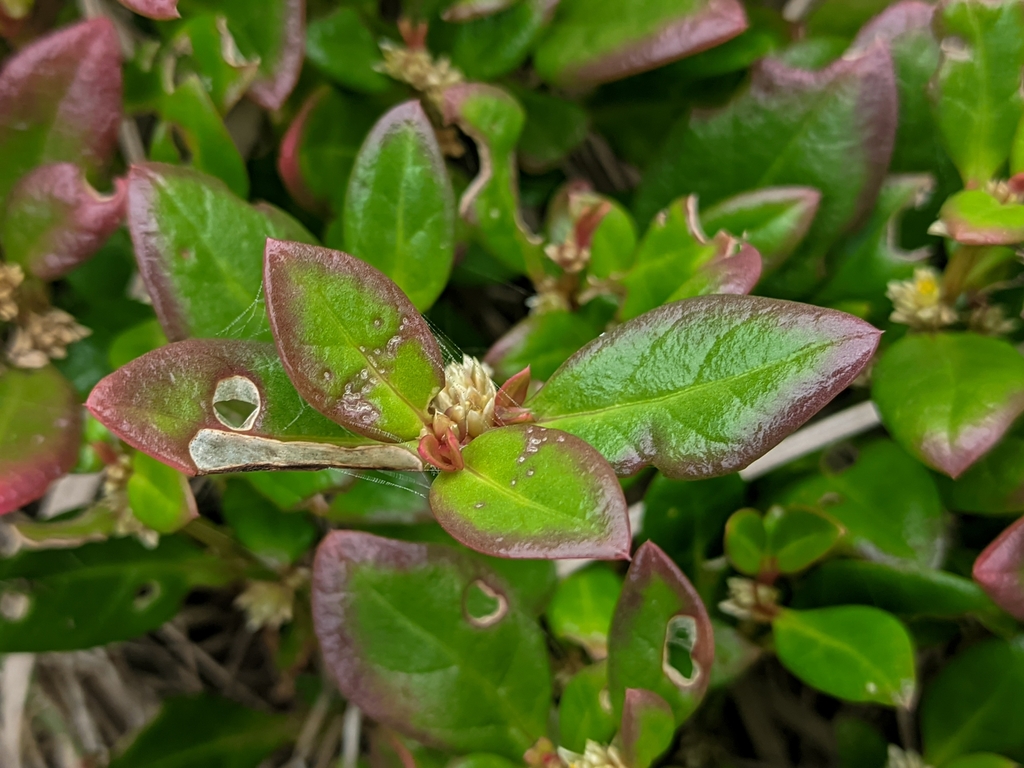

Alternanthera littoralis, also known as Joseph’s Coat, is native to the Brazilian coast and has traditionally been used to combat microbial infections and parasitic diseases.

Alternanthera littoralis, also known as Joseph’s Coat, is native to the Brazilian coast and has traditionally been used to combat microbial infections and parasitic diseases.

A review of 467 studies also points out that, instead of alleviating feelings of fear and anxiety, weapons increase them, as well as exacerbating controlling behaviors and causing domestic violence.

Researchers at São Paulo State University are investigating how hormonal fluctuations throughout a woman’s life influence the immune system and how physical exercise can mitigate these effects.
Study shows that the liver receives and sends a series of metabolism-related products derived from the gut microbiome to the heart.

Work carried out at the State University of Campinas used environmentally friendly solvents and ultrasonic waves to remove the substance and increase its absorption by the body.

In an article published in a scientific journal, the group emphasizes that Brazil must align its domestic policies with international commitments.

In an article published in a scientific journal, the group emphasizes that Brazil must align its domestic policies with international commitments.
Led by scientists from the University of São Paulo, the studies help clarify the roles of STIP1 and Maspin in vital cell processes and pave the way for advances related to cancer and applications in regenerative medicine.

Led by scientists from the University of São Paulo, the studies help clarify the roles of STIP1 and Maspin in vital cell processes and pave the way for advances related to cancer and applications in regenerative medicine.

Bacteriophages, or phages for short, can kill bacteria and may be used to combat hospital infections and food contamination.
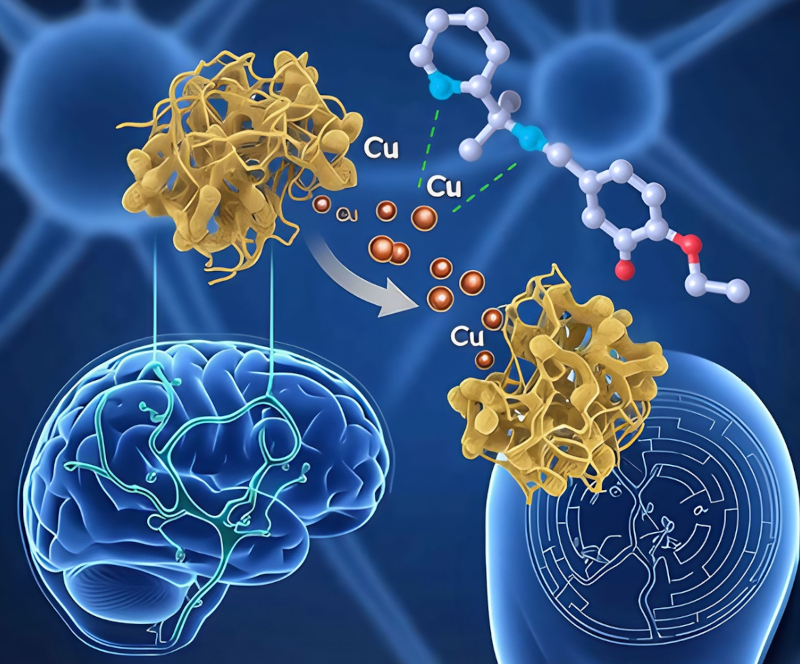
A group from the Federal University of the ABC tested the substance on rats and obtained positive results. The group is now seeking partnerships with pharmaceutical companies to conduct clinical trials.

An analysis of 70 plastic children’s products sold in Brazil revealed chemical contamination in most samples, with levels up to 15 times higher than permitted. Barium, lead, chromium, and antimony were the most commonly found toxic elements.
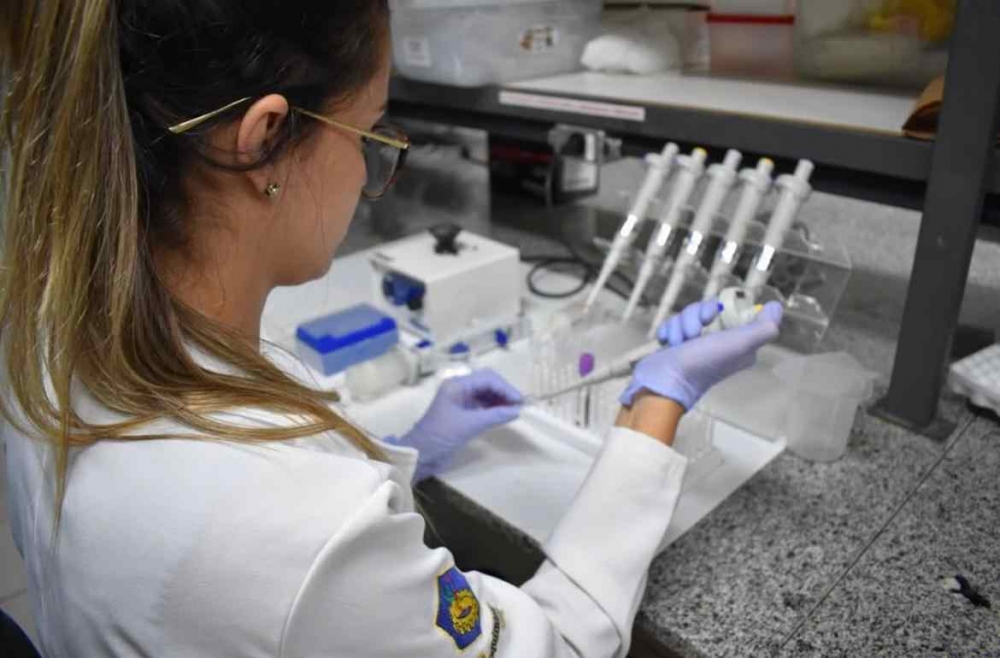

The formulation seeks to block the transmission of canine visceral leishmaniasis in order to protect both animals and humans.
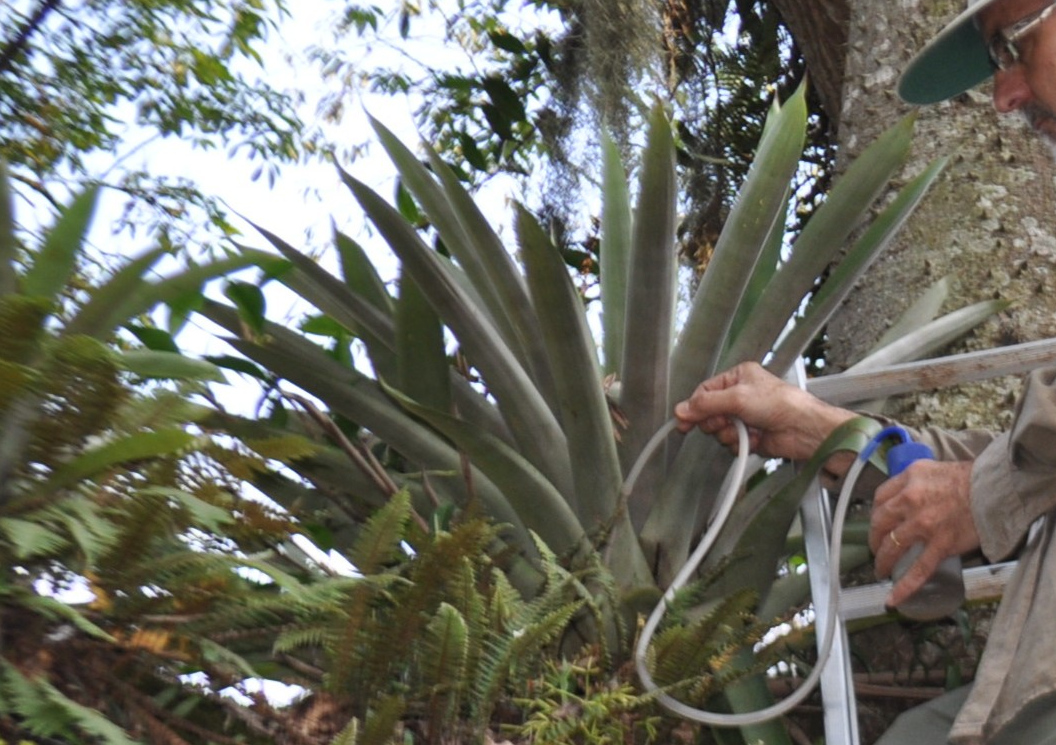

Results from a study conducted in a natural area in the municipality of São Paulo (Brazil) may help estimate the effects of climate change on disease transmission risk in the biome.
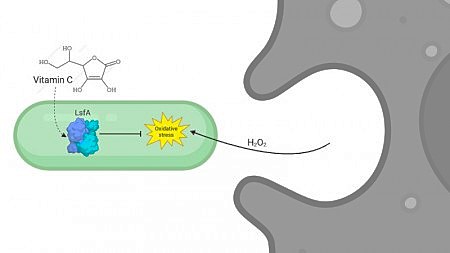
Findings contribute to the search for new targets against hospital infections.

With COP30 in Belém approaching, the ideas of the former French Minister of Justice are gaining momentum, inviting us to rethink multilateralism and the structure of the institutions that shape the world.
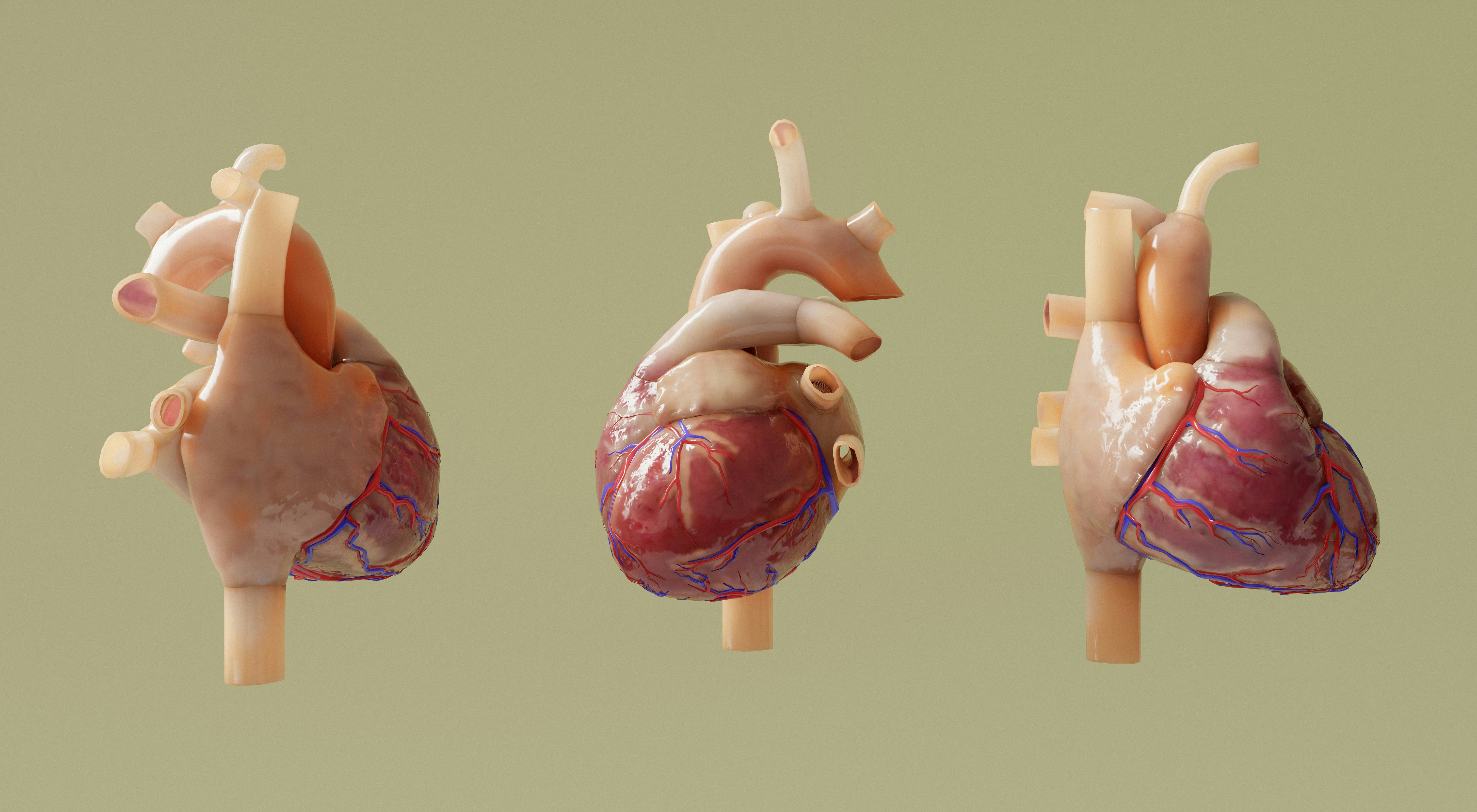
A three-year study of 77 people showed that analyzing myocardial deformation during contraction can predict the risk of death.

Technology created by a startup supported by FAPESP accelerates patient recovery and improves biological integration.
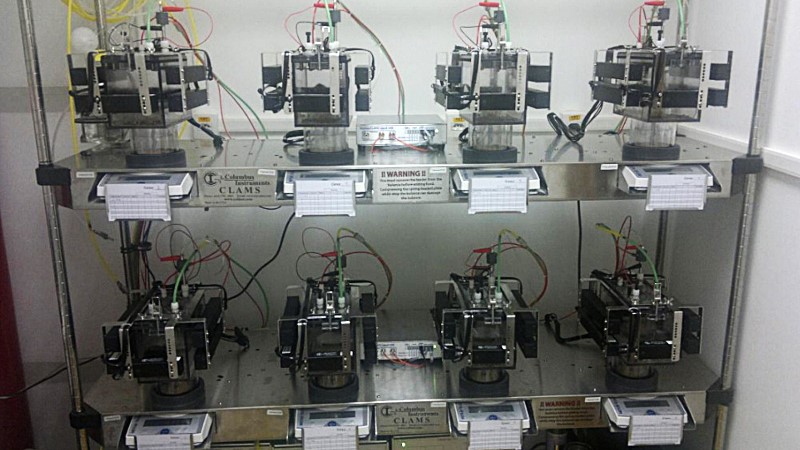

Standardization opens up possibilities for developing preclinical trials of new drug classes that focus on calorie burning.
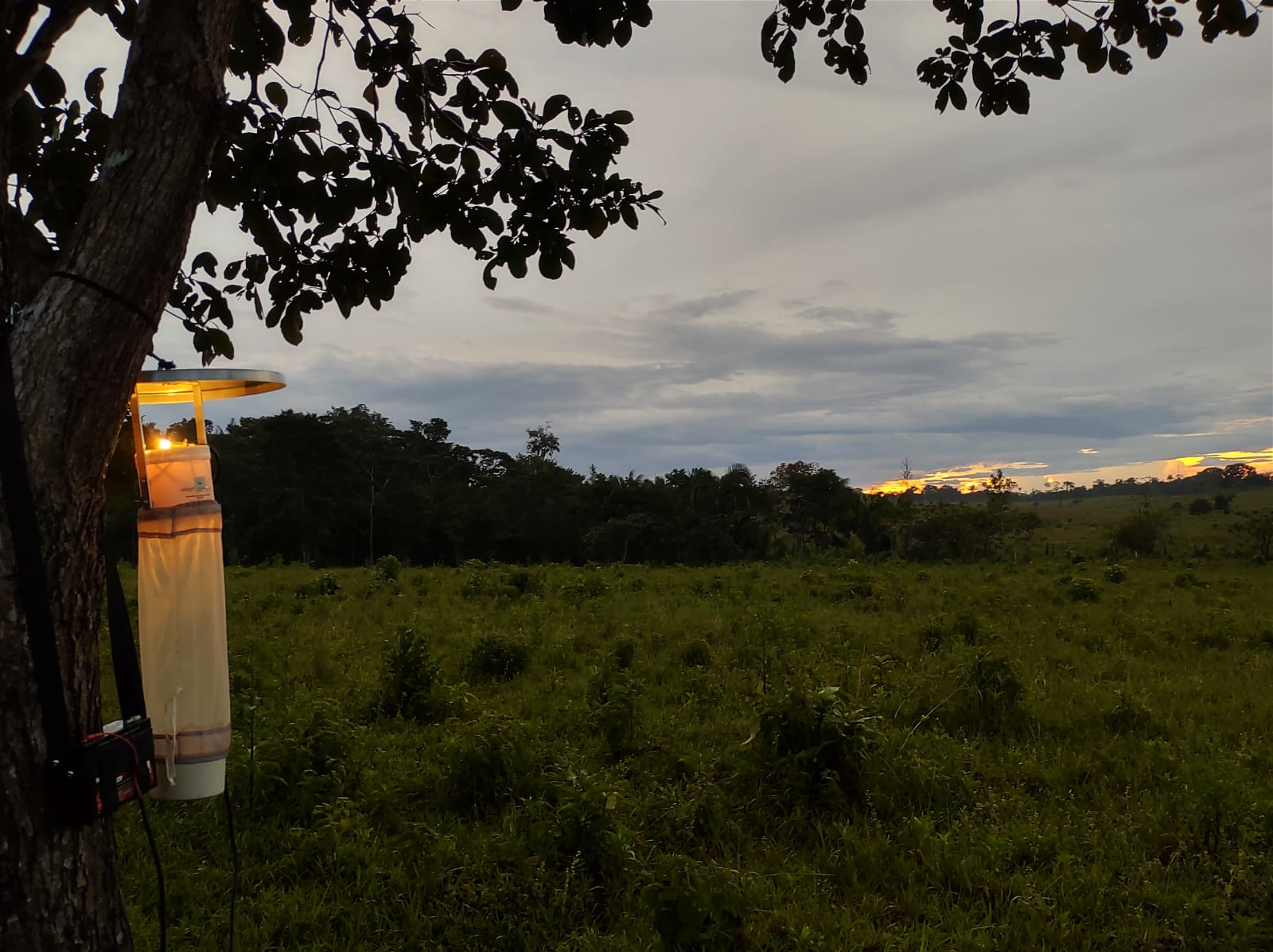

Research shows that areas with 50% deforestation near residential areas or fragmented vegetation allow greater contact between mosquitoes and humans. Amid the discussions for COP30, the study helps us understand the link between forest destruction and the spread of the disease.
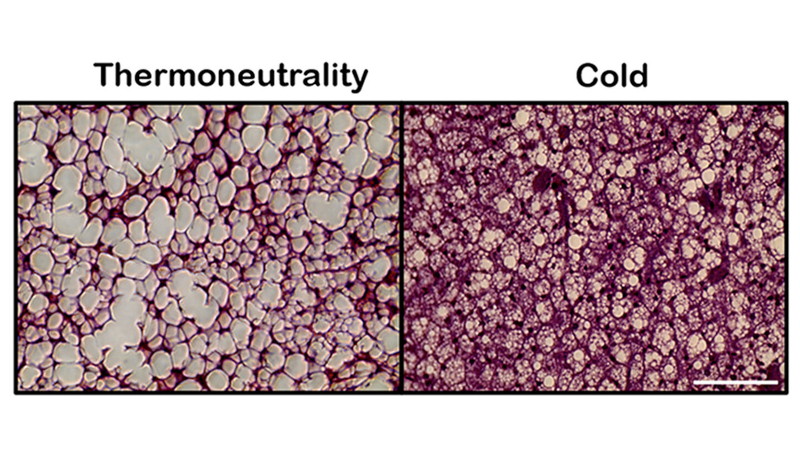
Research conducted by Redoxoma, a FAPESP Research, Innovation, and Dissemination Center, found that mitochondrial potassium channels regulate heat production in brown adipose tissue.