


The finding was based on questionnaires applied to 313 Brazilian women in their 30s. The results indicate that, although the reported discomforts negatively affect the participants’ quality of life and sexual health, they tend to normalize them.

The study conducted at the University of São Paulo evaluated data from 54 women who were newly diagnosed with early-stage disease.
In animal tests, researchers from the University of São Paulo observed that changes in insulin signaling in the brain affected both memory and the frequency and severity of seizures. The findings support clinical evidence and point the way to new therapeutic approaches.
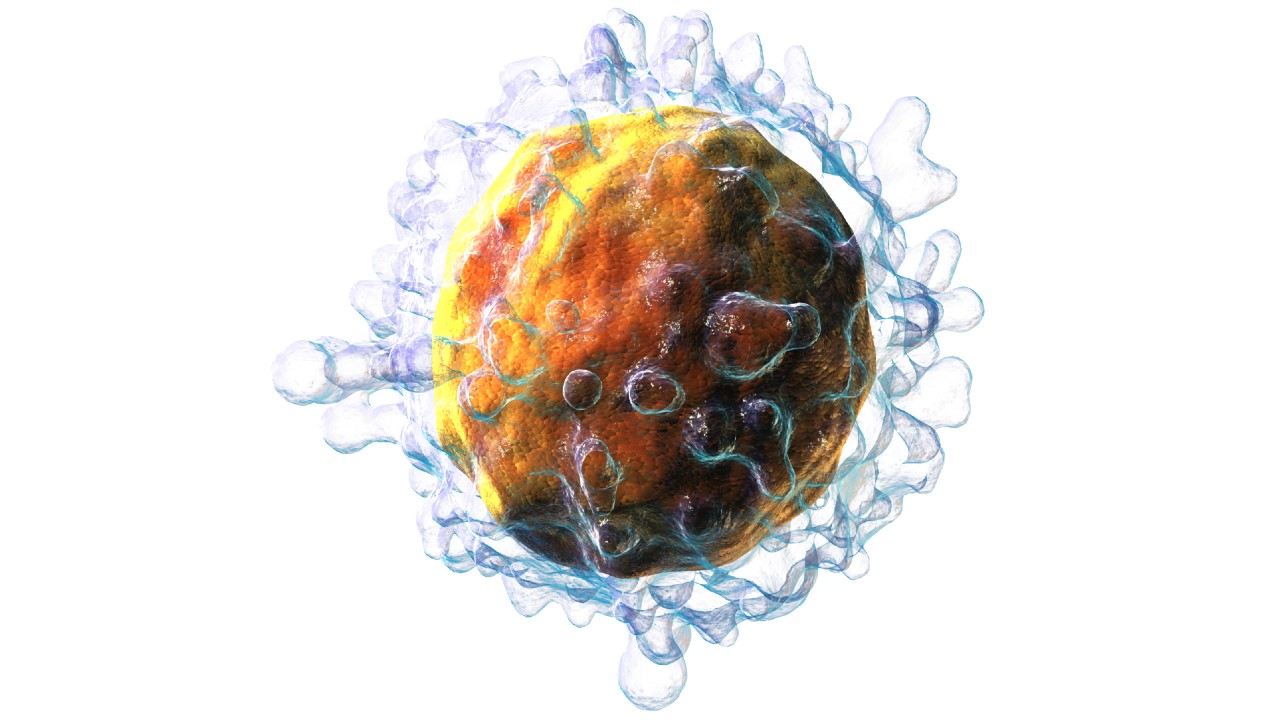
A group led by researchers at the A.C.Camargo Cancer Center has succeeded in improving CAR-T cells, making them more effective in treating refractory types of lymphoma and leukemia.

The conclusion comes from a study conducted at the University of São Paulo with 595 participants between the ages of 18 and 59. The analysis shows a link between insomnia and high levels of neuroticism, and points to anxiety as part of the problem.

The project developed by Food Research Center takes into account the eating habits and biodiversity of each country in the region.
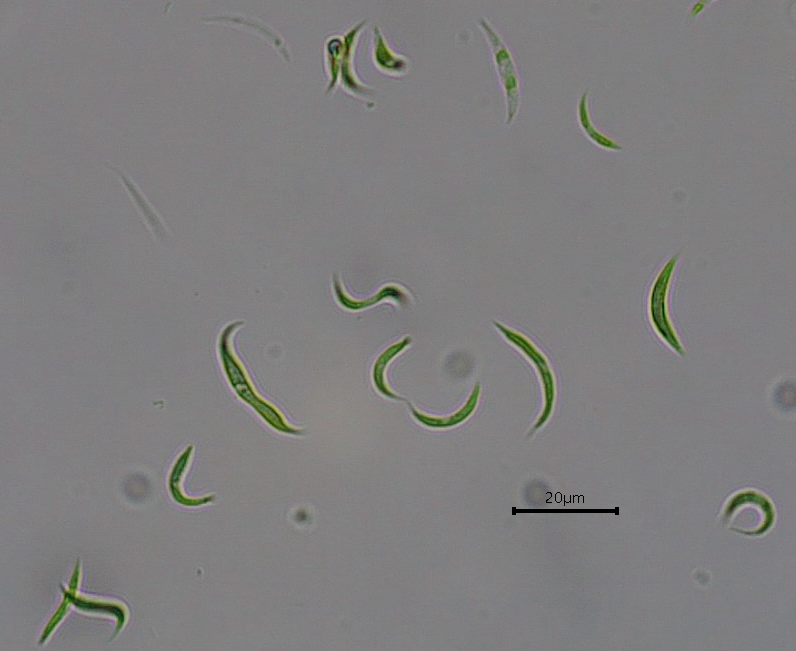
In the laboratory, the species Monoraphidium contortum removed some of the drugs added to the liquid and produced biomass with potential commercial value.

Praziquantel, usually administered in large tablets, is the only anthelmintic available on the market. New form of presentation uses nanotechnology and facilitates use by children and pets.
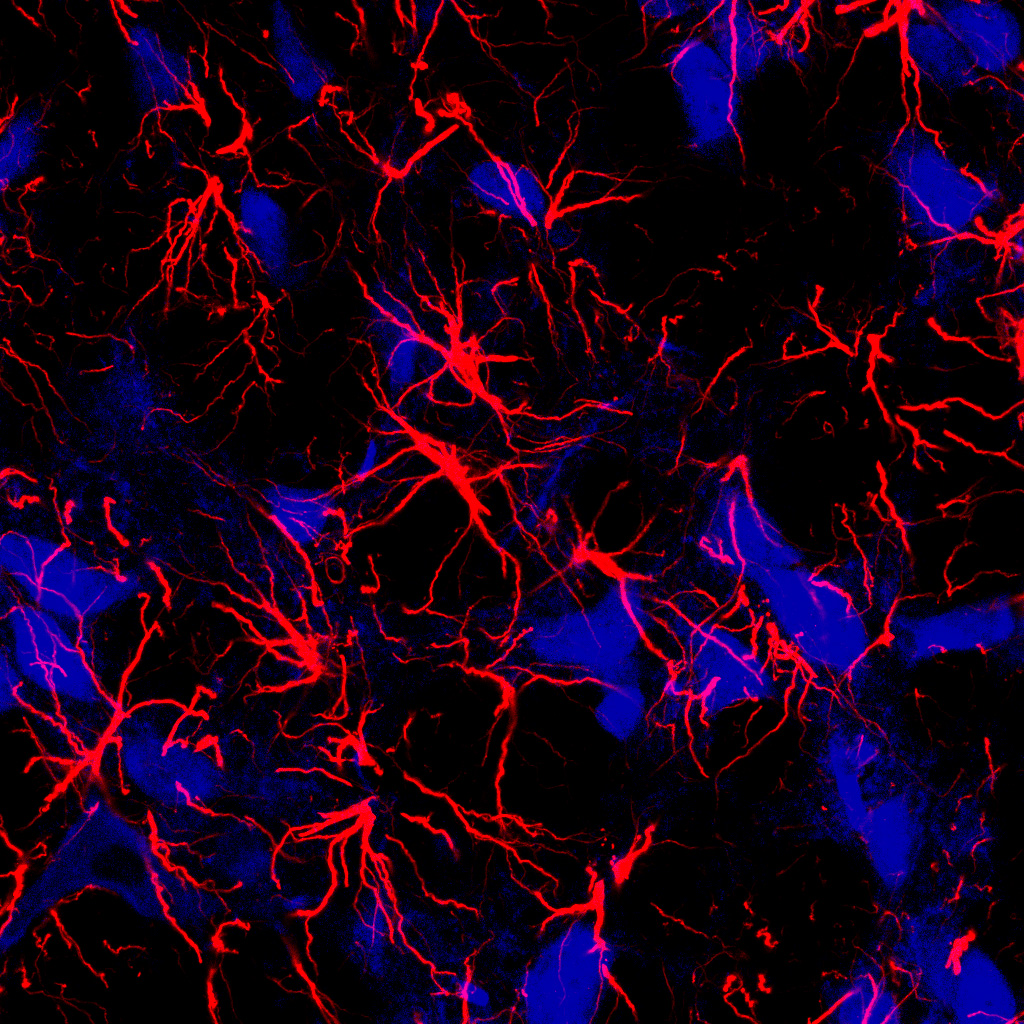
Brazilian researchers observed increased connections between neurons in rodents after inducing an increase in the synthesis of hevin – a glycoprotein naturally produced by astrocytes.
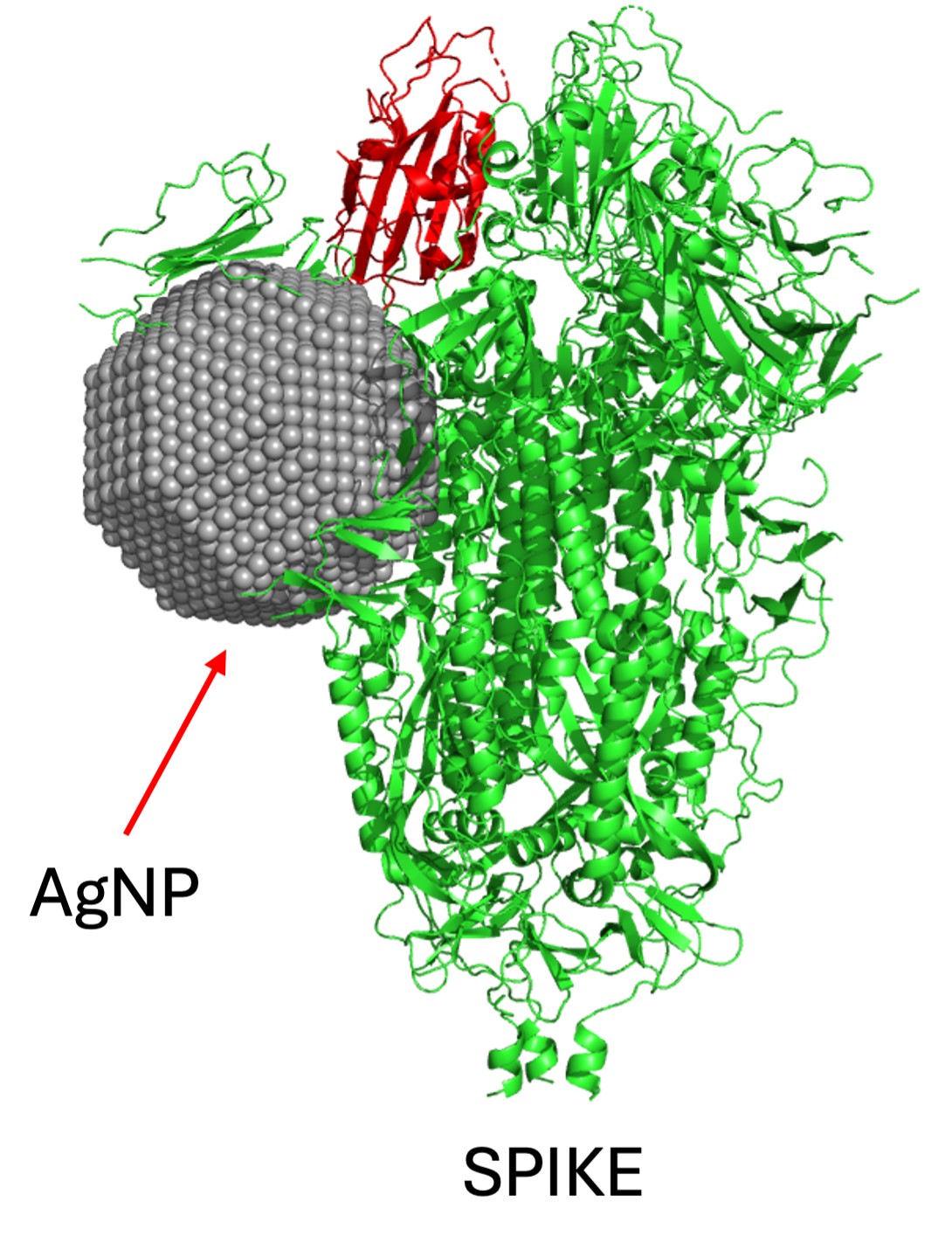
Study in hamsters paves way for development of nasal sprays and other products to fight several viral diseases, including HIV/AIDS, shingles and influenza.

The conclusion comes from a study that followed 805 Brazilians in their 50s for eight years. The results underscore the need for increased attention to hearing health as a way to prevent dementia.
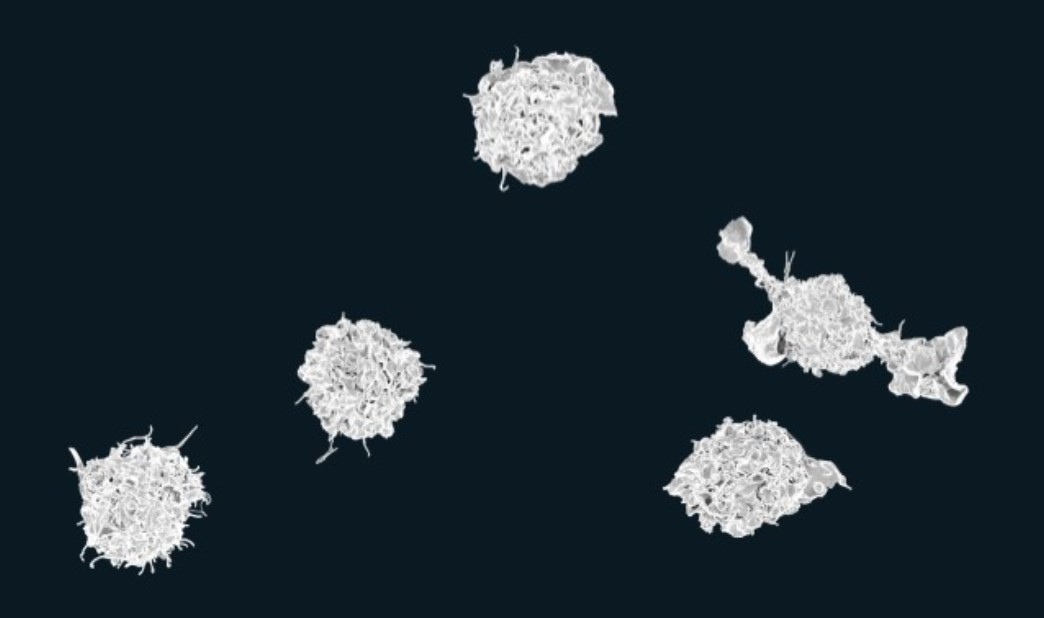
Through experiments with mice, scientists from the State University of Campinas have shown that physical activity induces immune cells involved in the inflammatory process to acquire an anti-inflammatory profile. The finding opens the way to new therapeutic approaches.

A study conducted at the Federal University of São Paulo compared the performance of people diagnosed with primary progressive aphasia and healthy individuals, identifying the main tasks that can signal the presence of the syndrome.

Analysis of the gut microbiota of more than 700 babies also showed that breastfeeding was a protective factor, mitigating the problem in those who consumed industrialized products. The study underscores the importance of breastfeeding and avoiding foods high in sugar, saturated fat, salt and chemical additives.

This is the finding of a study that followed 352 pairs of newborns and their mothers in the cities of Guarulhos and São Paulo (Brazil). Changes observed in the first two months of life may increase future risk of obesity and diabetes.
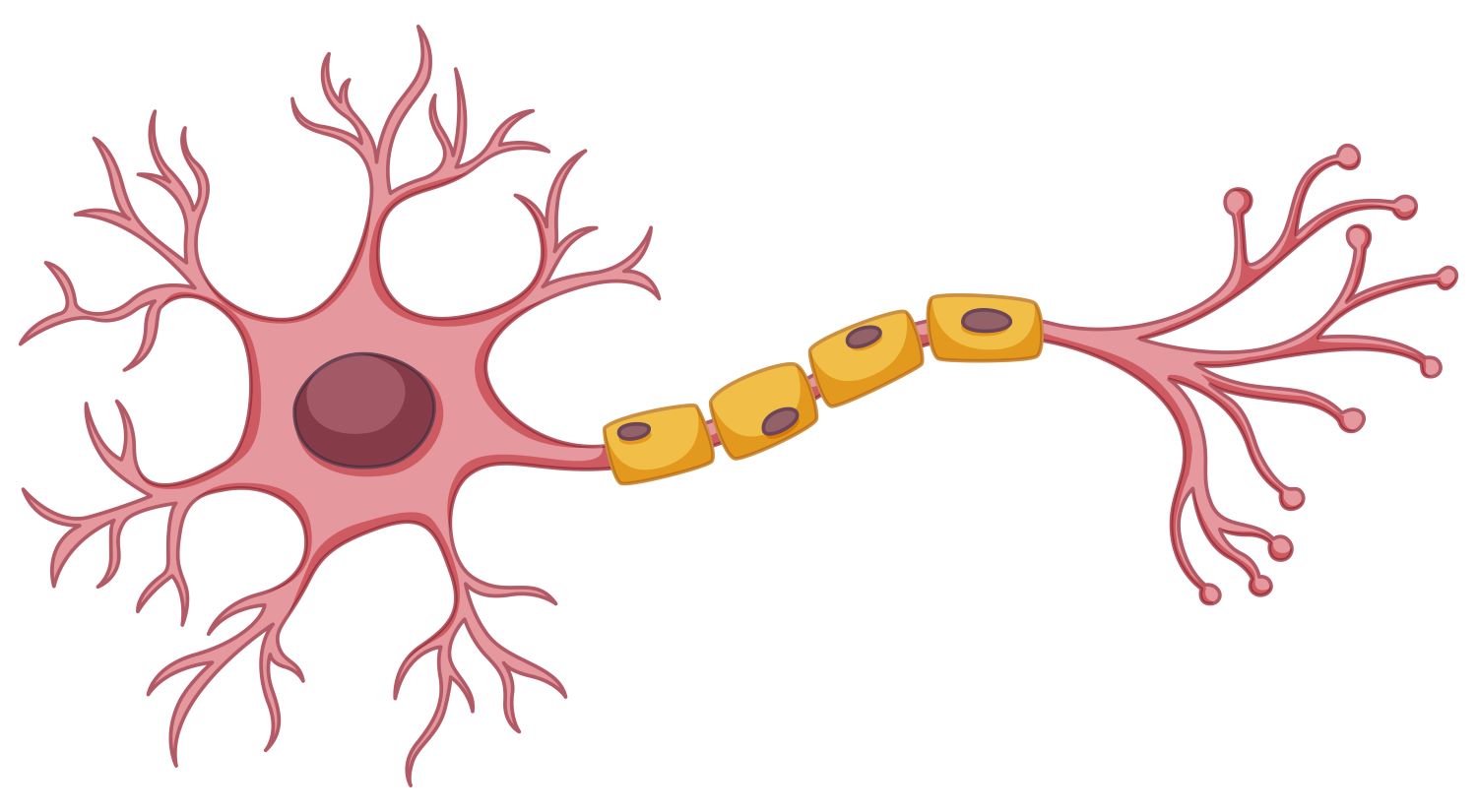
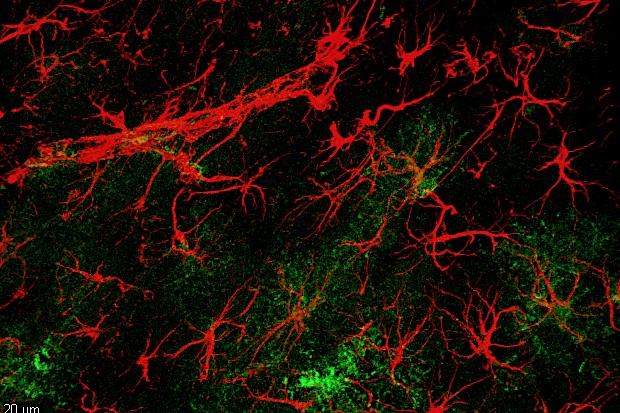
The rodent experiment, conducted at the State University of Campinas, highlighted the involvement of the hnRNP A1 molecule in maintaining the integrity of the myelin sheath – a fatty layer that protects neurons and facilitates communication between them. The findings pave the way for potential therapies.
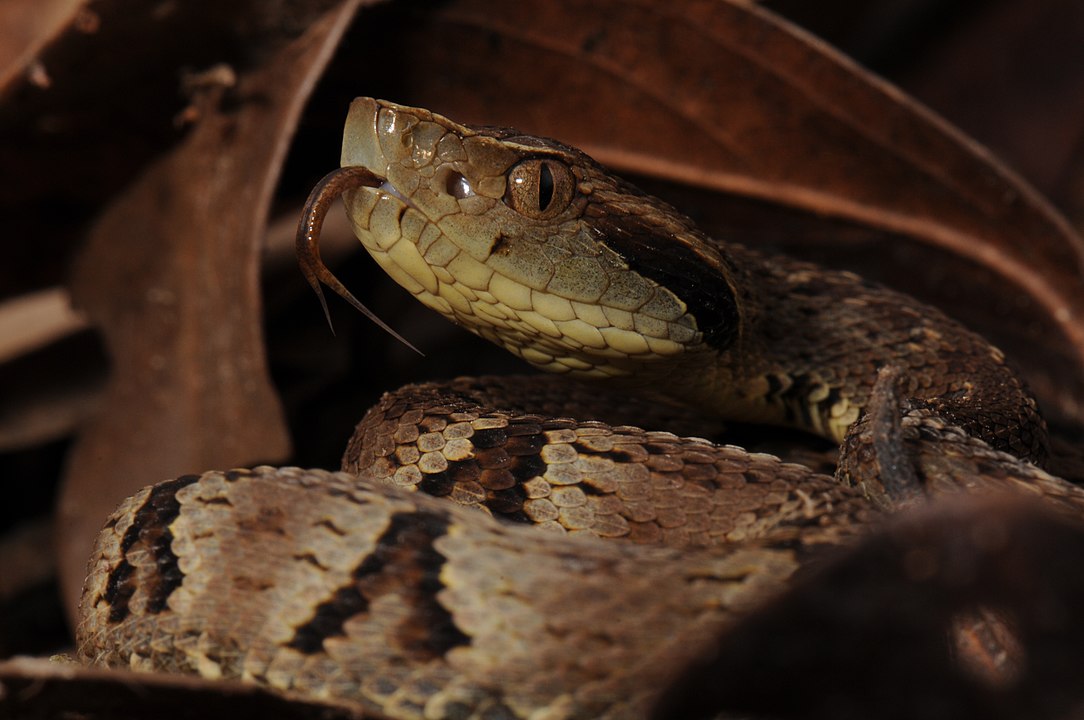

Researchers from the Federal University of São Paulo and the Butantan Institute are working on an improved version of the antibothropic serum, with more neutralizing antibodies and fewer proteins associated with side effects.
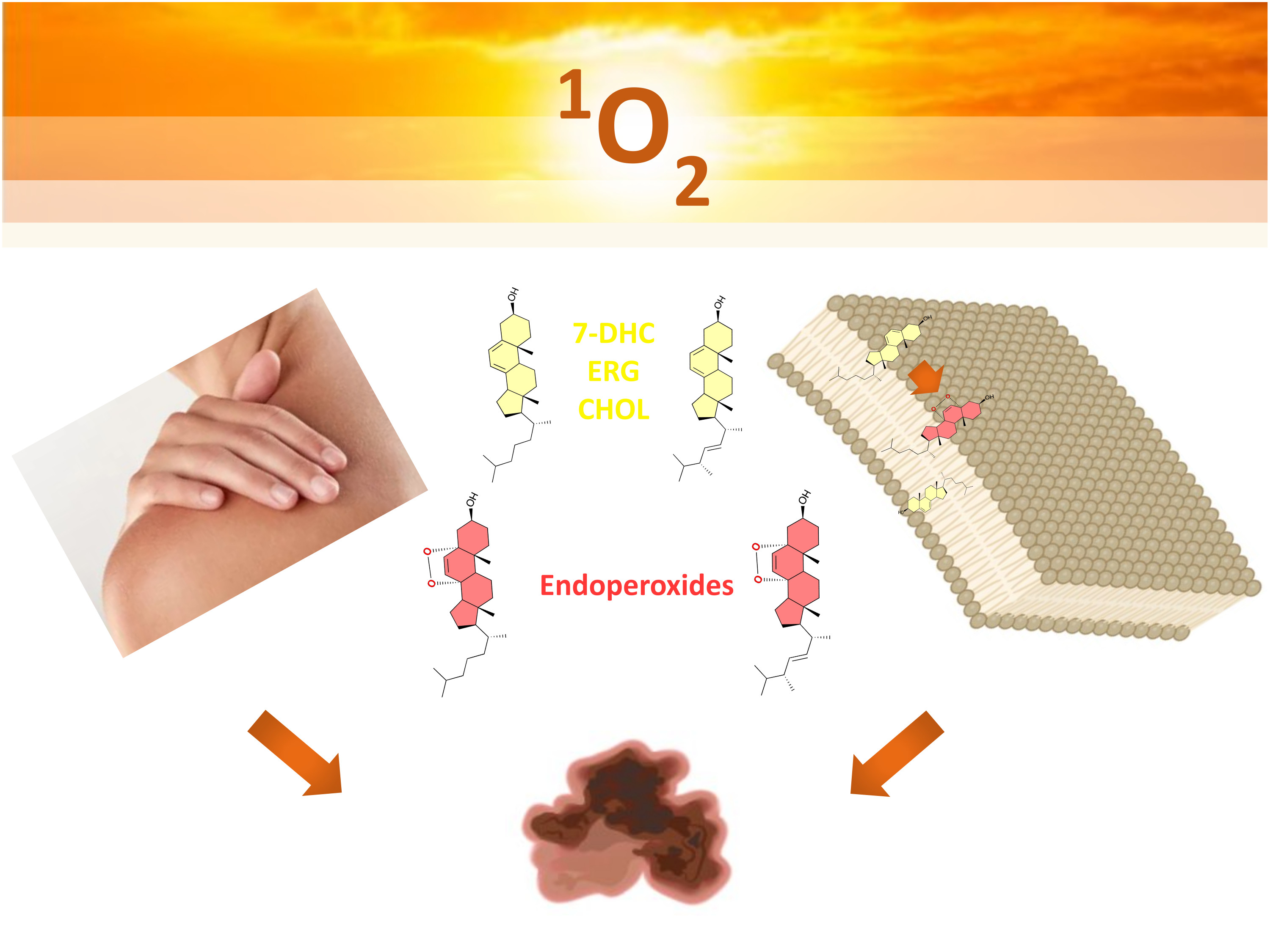
Results from a FAPESP-supported research center pave the way for expanding the use of photodynamic therapy in the fight against skin cancer.

While cognitive-behavioral therapy showed faster results, the effect of acceptance and commitment therapy was more lasting, shows a study conducted at the University of São Paulo with 227 volunteers.
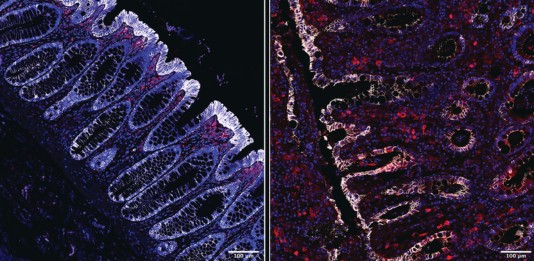
Rodents fed a diet rich in soluble fiber coped better with a microorganism that causes diarrhea and can lead to death in debilitated patients. Researchers observed that acetate – a compound produced by the gut microbiota when fiber is digested – helps modulate the immune response.
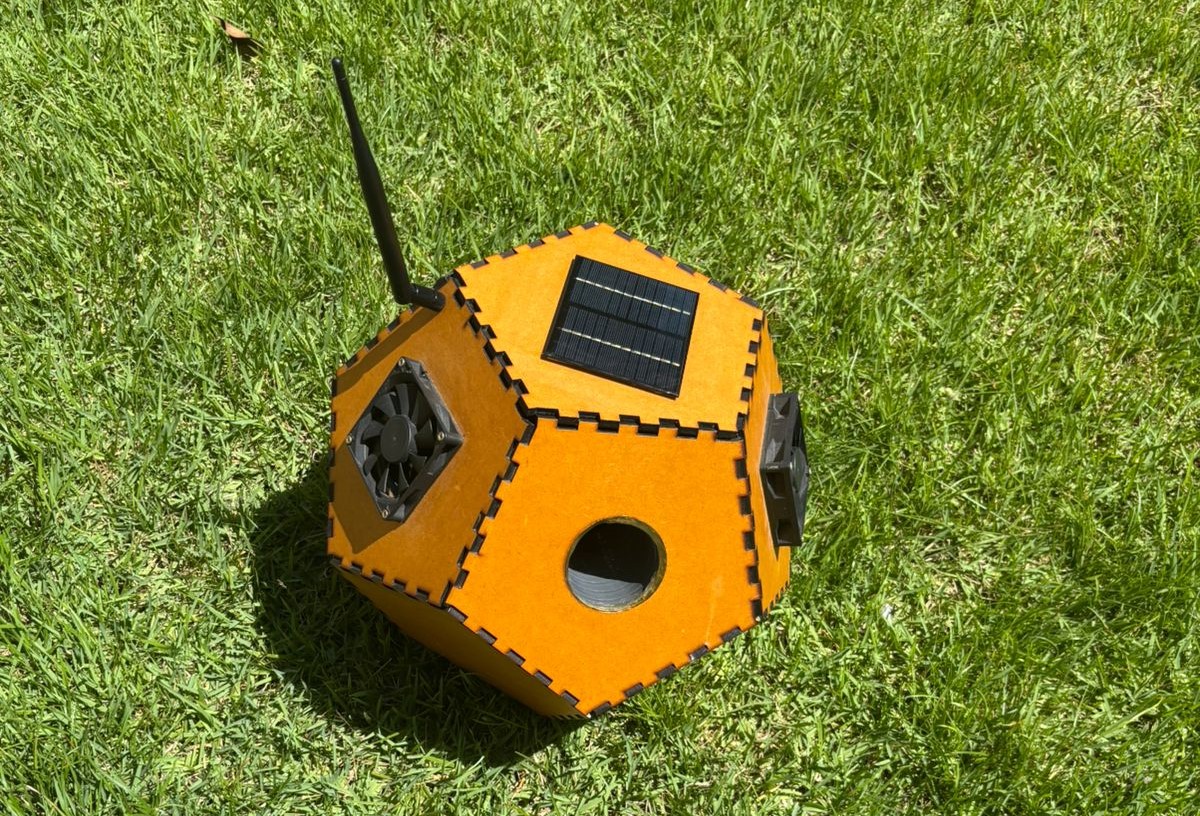

Equipment developed in Brazil by researchers at the National Telecommunications Institute combines Internet of Things devices, high-resolution cameras, and artificial intelligence algorithms to capture and identify female Aedes aegypti without harming other insects.

Device developed with the support of FAPESP is more accurate than assessments made by doctors using a dermatoscope.

Researchers from São Paulo State University and collaborators studied 50 young people with an average age of between 26 and 27. The goal was to find biomarkers that allow early detection of health changes.

An enzyme cloned from an insect found by Brazilian researchers – and genetically modified – makes it possible to monitor intracellular acidity and could be used to study diseases and drugs.

The study, conducted at the State University of Campinas, involved 44 people with mild cognitive impairment. After six months, the volunteers who practiced strength training showed improvements in memory and brain anatomy, while the others showed a decline in the parameters evaluated.