


Experiments with mice at the University of São Paulo used cutting-edge techniques to investigate the neural circuits behind aversive behavior and fear memory. The findings are reported in Current Biology.

Brazilian researchers publish preliminary data showing that the pathogen has undergone mutations making it more aggressive and contributing to resurgence of the disease in Brazil since 2023.

The analysis was conducted by researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP), showing that when the patients took the drug, the number of times they woke up during the night fell by 25% and the amount of time they remained awake fell 30% on average.

The protocol was designed at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar). Trained carers help patients take standard tests used by geriatricians and physical therapists, performing them in their own homes with remote assistance from health workers. The goal is to facilitate access to treatment for older people with dementia.
Trials conducted at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP) confirm that the isolate of Leishmania amazonensis from a 46-year-old patient is resistant to amphotericin B.

Produced by a startup supported by FAPESP, the bean protein concentrate is designed to appeal to flexitarians – consumers who want to increase their intake of plant-based foods and decrease that of animal products.
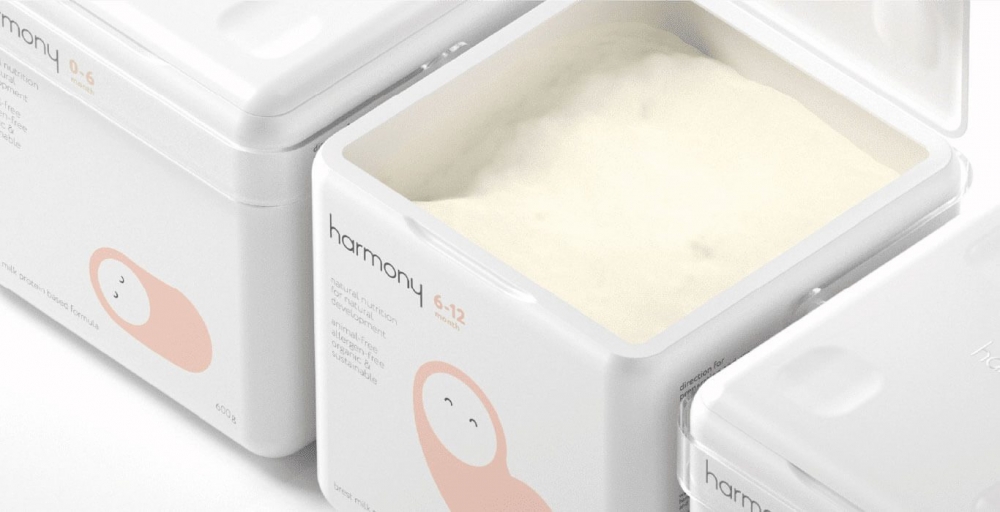

The biotech based at MIT is developing bioactive versions of the product using the same technique as breweries and pharmaceuticals that produce biologics.

Mice that did not produce interleukin 22 binding protein (IL-22BP) had stronger defenses, according to an article published in PNAS. Understanding the protein’s role in intestinal health can pave the way to novel therapeutic strategies.

A study involving 302 volunteers showed that although the damage caused by SARS-CoV-2 was most intense among those who had severe COVID-19, some exhibited memory loss and attention deficit more than 18 months after being infected, even though they had not needed to be hospitalized.

Brazilian researchers innovated by stimulating tumor cells so much that they became stressed and could survive only by behaving like healthy cells. The results of the study were so promising that the researchers plan to hold clinical trials with patients, to be conducted in the Netherlands before the end of 2024.

Researchers at the University of São Paulo conducted in vitro experiments with bone cells to confirm the properties of the novel biomaterial. Their findings suggest it can replace natural bone in grafting procedures to remedy defects or injuries.
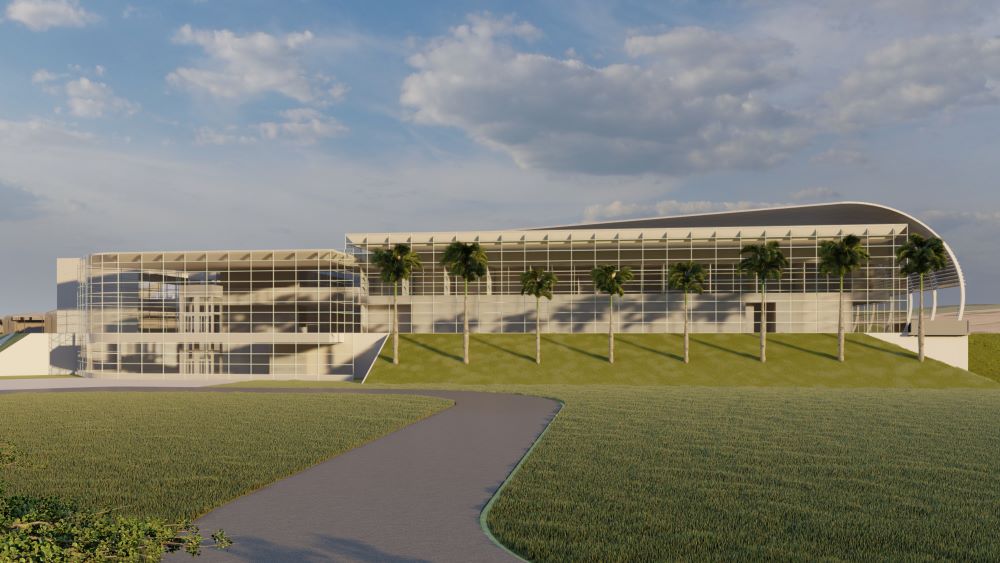

Scheduled to start operating in 2028 at the Brazilian Center for Research on Energy and Materials (CNPEM) in Campinas (São Paulo state), the lab will enable researchers for the first time in Latin America to study viruses classified as class 4, the highest category of biological risk.

Discovery of a new viral evasion mechanism, and of a monoclonal antibody that subverts it, is an advance in immunotherapy offering the prospect of effective host-directed treatment to combat infections.
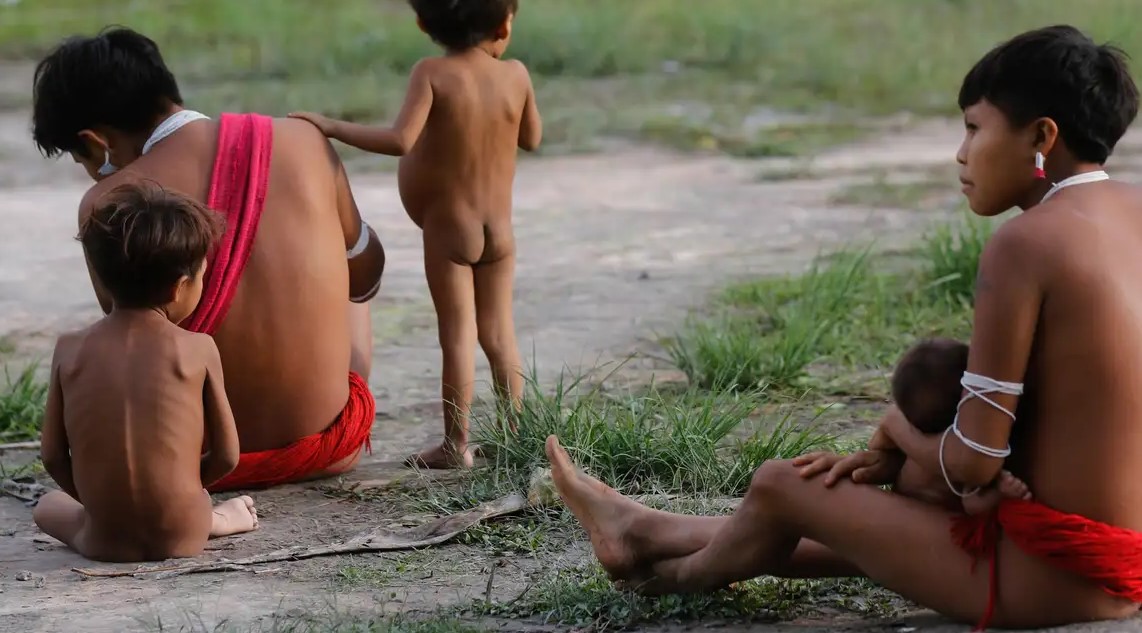

In an article published in Nature Medicine, a group at the State University of Campinas stresses that Yanomami children are suffering the most severe nutritional deficit of any Indigenous community in the Americas and warns of long-term consequences for health.
According to the authors of the study, infection by one virus was expected to afford protection against the other, preventing co-circulation. They warn of the risk of transmission of Mayaro in urban areas owing to deforestation and advocate more effective epidemiological surveillance.
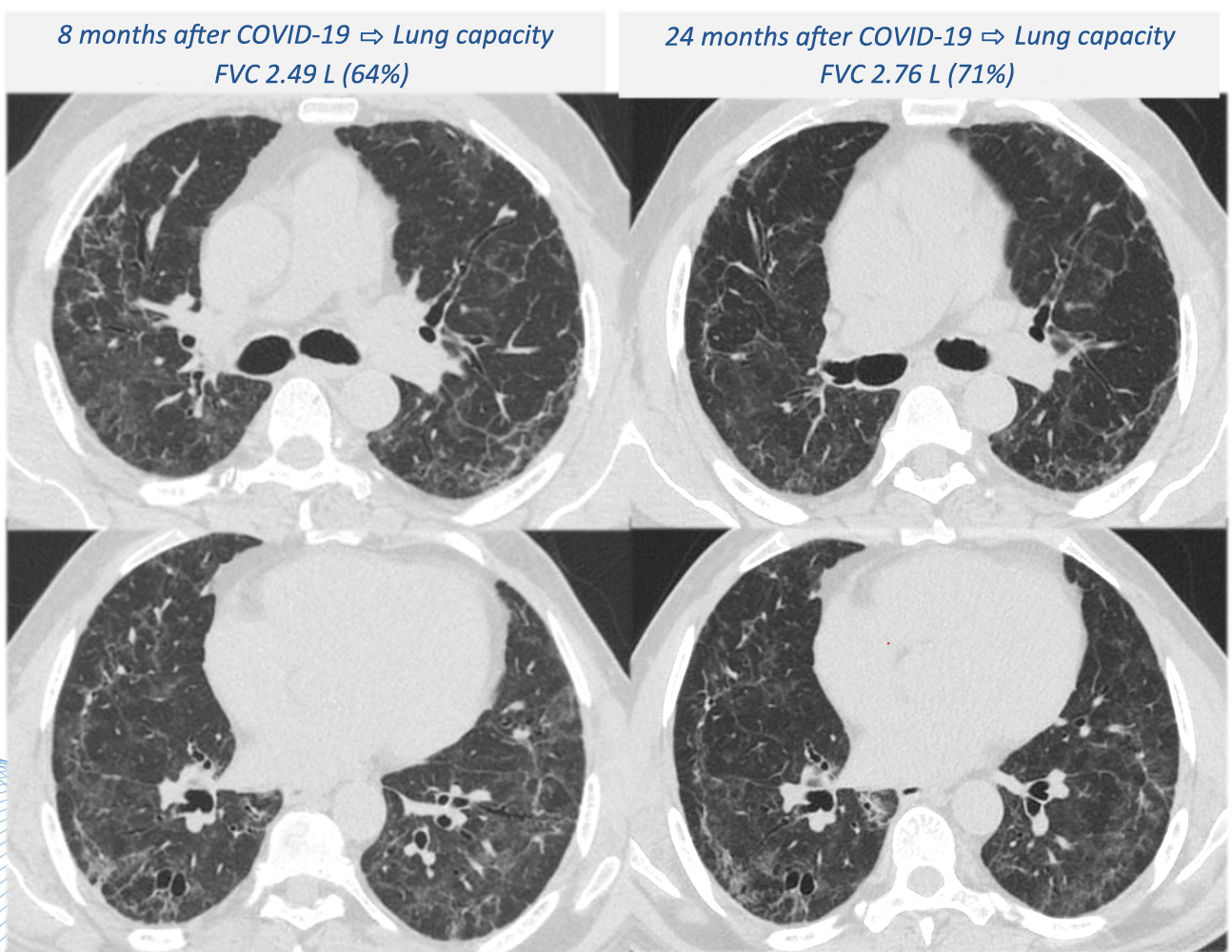
A Brazilian study assessed 237 patients treated at the University of São Paulo’s general and teaching hospital. The researchers found that 92% still had lung damage two years after discharge, with fibrosis (33% of cases) arousing most concern.
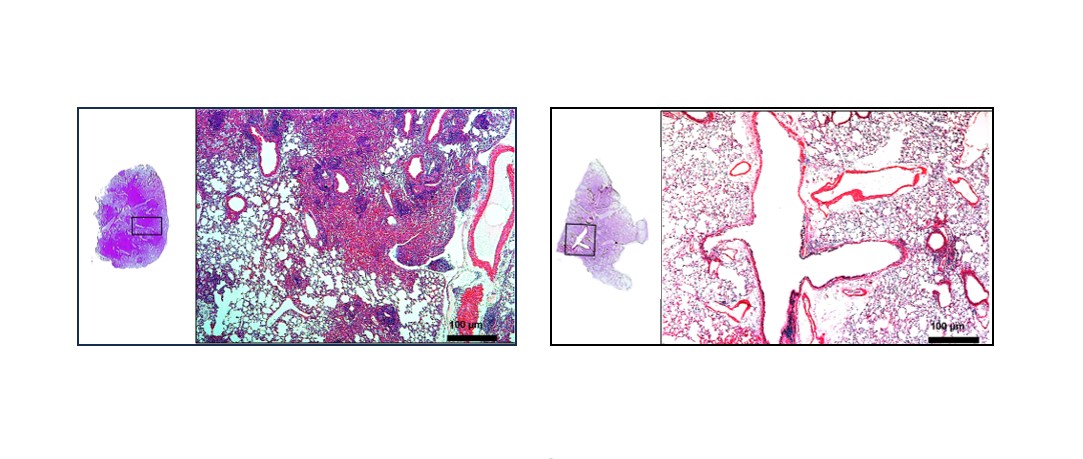
Researchers from the Butantan Institute and collaborators reveal why recombinant BCG induces a stronger and longer-lasting response than the conventional vaccine.
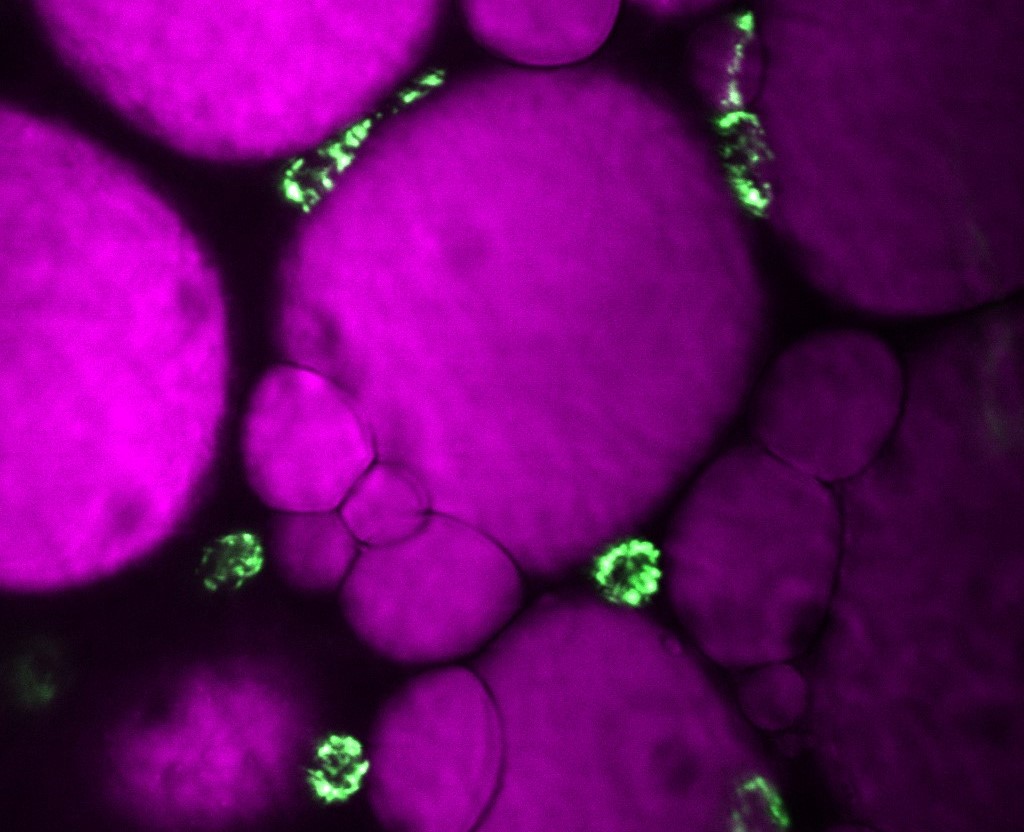
By analyzing samples from obese non-diabetics, researchers from the State University of Campinas found that high blood levels of saturated fatty acids cause pre-activation of innate immune cells that, when infected with SARS-CoV-2, produce elevated levels of inflammatory molecules. Results were presented during FAPESP Week China.
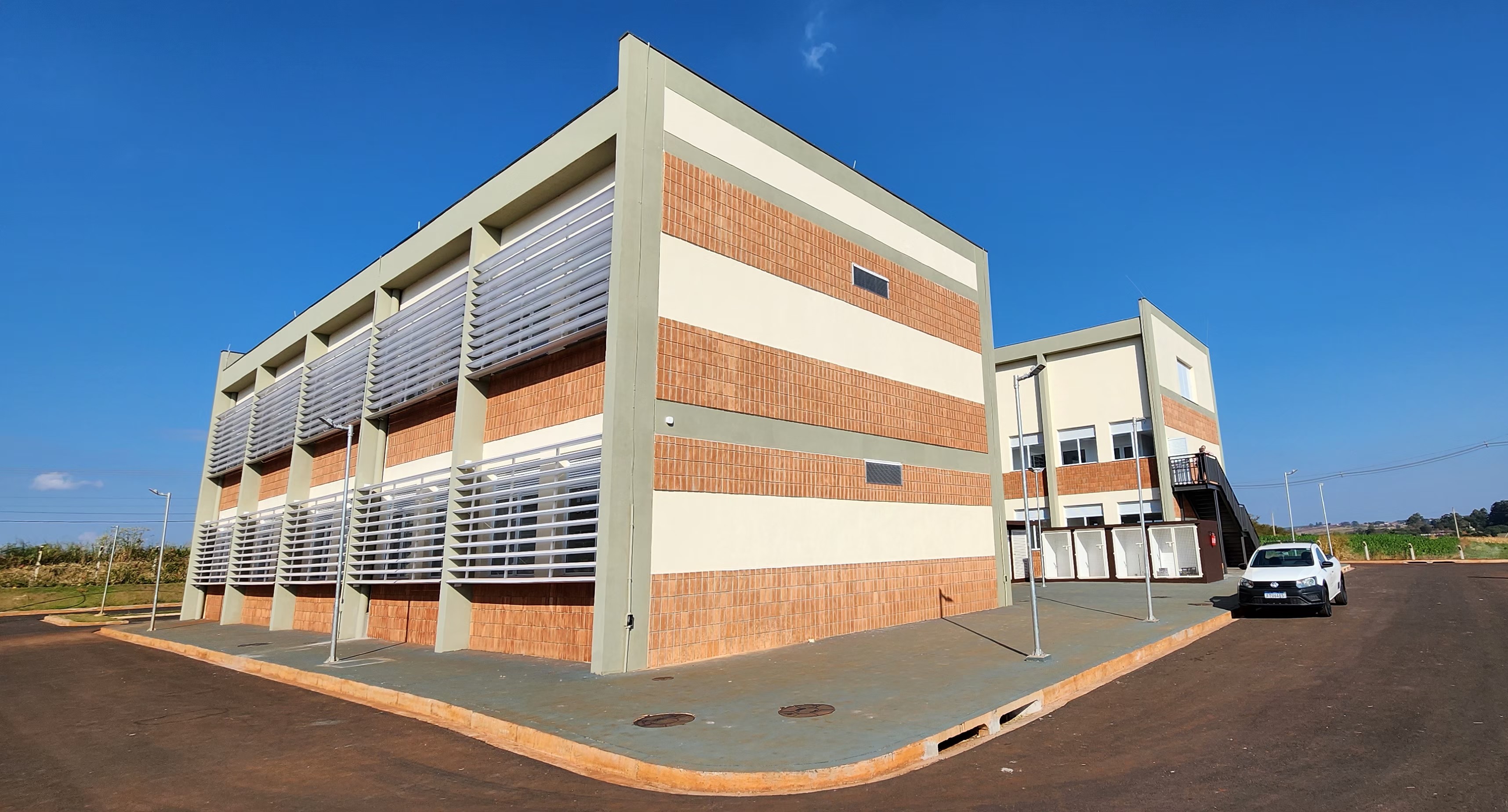

Located in Botucatu, the plant will perform outsourced medical drug development and production services for pharmaceutical companies, biotechs and other research institutions, complying with best manufacturing practices.
In a study conducted by Brazilian researchers, blood levels of an amino acid called homocysteine correlated with the development of a disease that affects a third of the inhabitants of São Paulo city.
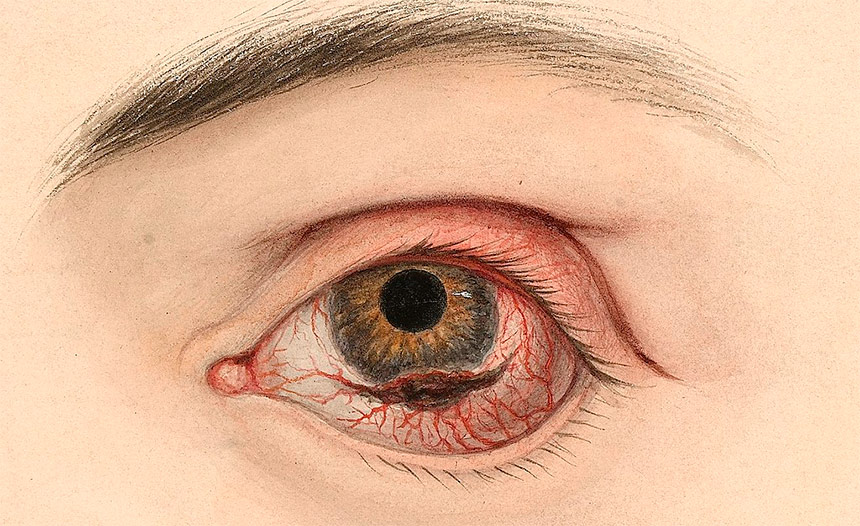
The study is the first to show that femtosecond pulsed laser irradiation is effective and safe in mice with induced ocular melanoma, paving the way for minimally invasive targeted treatment of the disease in future.
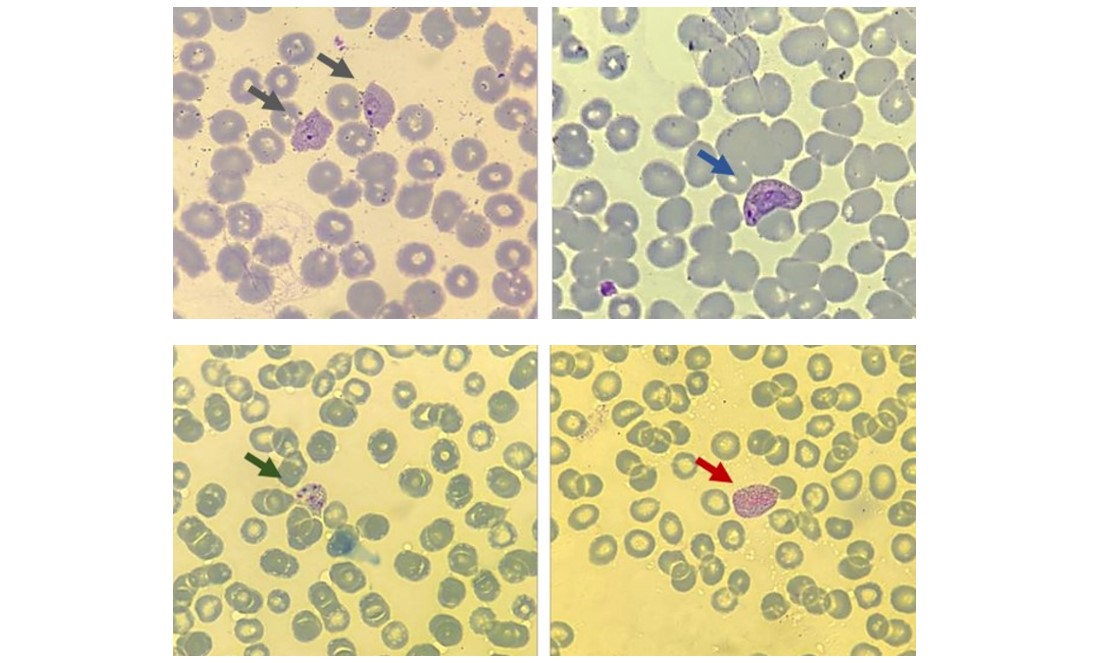
As described in Scientific Reports, the study involved analysis of blood samples from volunteers infected by Plasmodium vivax, which produces forms that lie dormant in the host and can be reactivated months after treatment. The findings will help detect and diagnose these forms, with significant potential to enhance control and treatment of the disease in future.
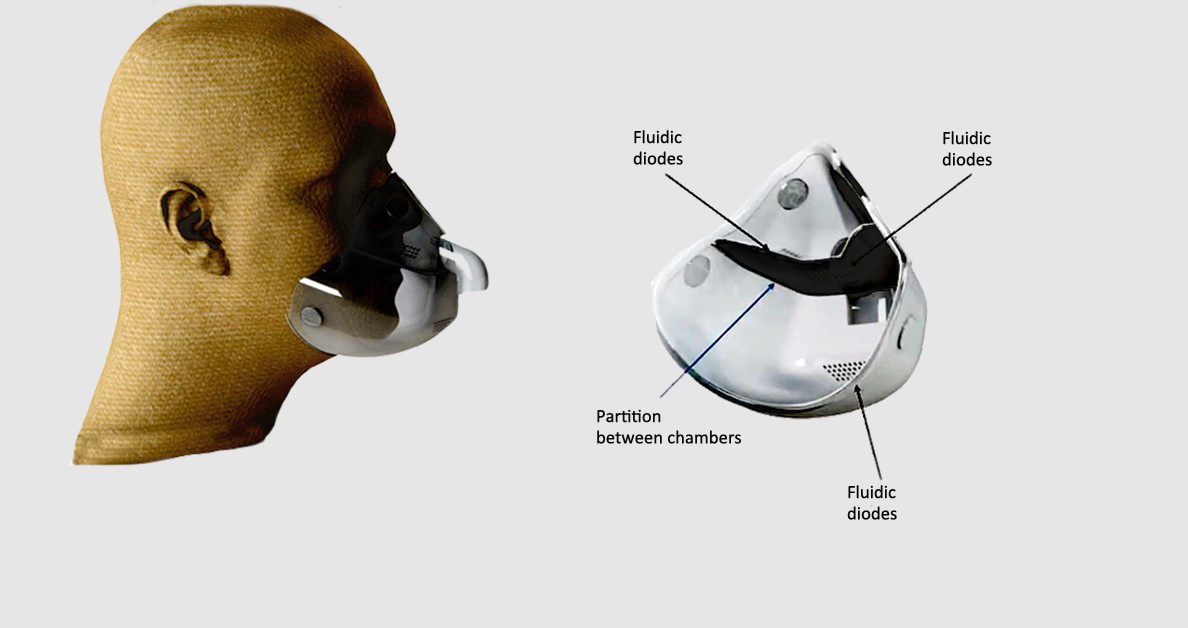
Innovation stems from a project on gas turbines conducted at the Engineering School and could make the use of CPAP more comfortable.
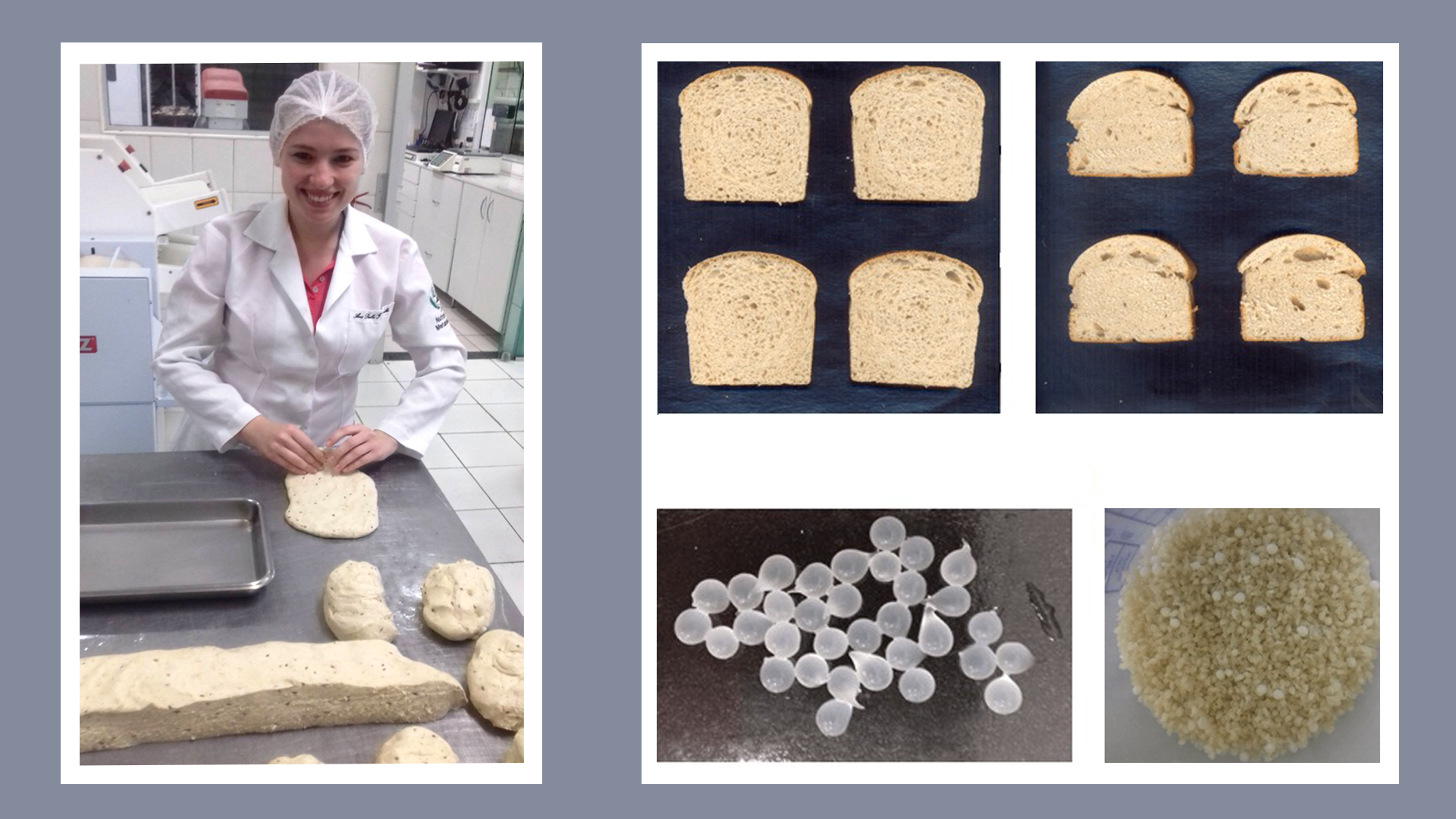

Bread produced with probiotic yeast performed well in experiments with mice, showing potential to combat asthma, which affects 20 million Brazilians.
A systematic review of 14 scientific articles on studies conducted in seven countries detected a statistically significant improvement in mental health after treatment with mindfulness.