

Scientists at the University of São Paulo analyzed blood samples donated by six serodiscordant couples where female partners were resistant to SARS-CoV-2 despite intense contact with their infected male partners. Overexpression of the gene IFIT3 in these asymptomatic women suggests it affords protection and could be a target for novel antiviral therapies.

Studies conducted at the State University of Campinas have shown that physical training, combining strength training and aerobic exercise, improves lipid metabolism, reduces inflammation and reverses early immunosenescence in obese and diabetic individuals.
Study involved 242 couples living in the Metropolitan Region of São Paulo (Brazil); men showed higher levels of work-family conflict, while women were more affected by stress.

Researchers isolated a strain of Pseudomonas alcaligenes that can withstand temperatures as high as 44 °C from a hot spring in Chile, and characterized the substances produced by the bacterium that help it survive extreme conditions.

The ‘Best Oral Presentation’ award at an event promoted by the Hospital de Amor in Barretos (São Paulo state) was given to doctoral student Mariane Tirapelle, who is part of the Cell Therapy Center and the Nucleus of Cellular Therapy teams.
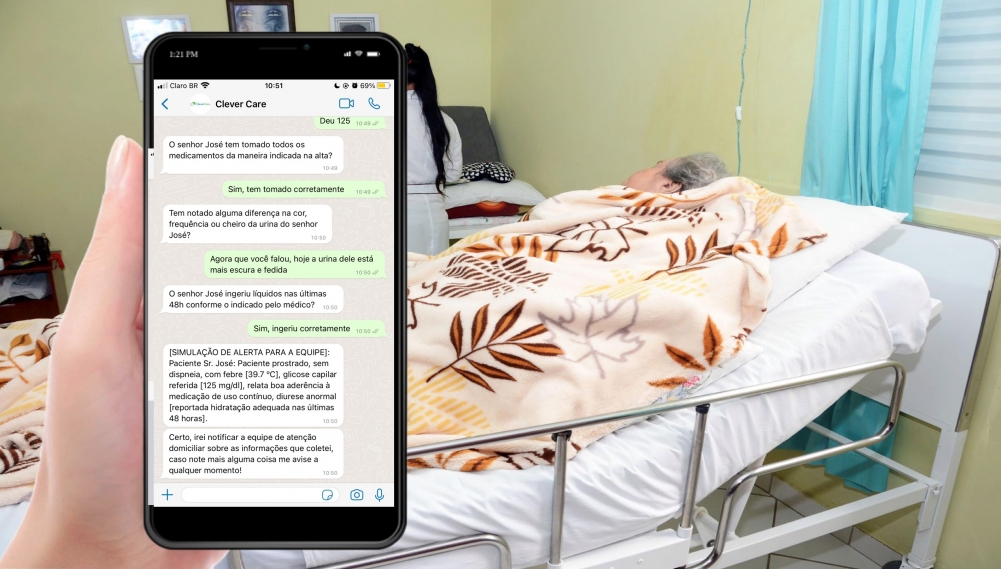
System developed by FAPESP-supported startup provides information and guidance after hospital discharge.
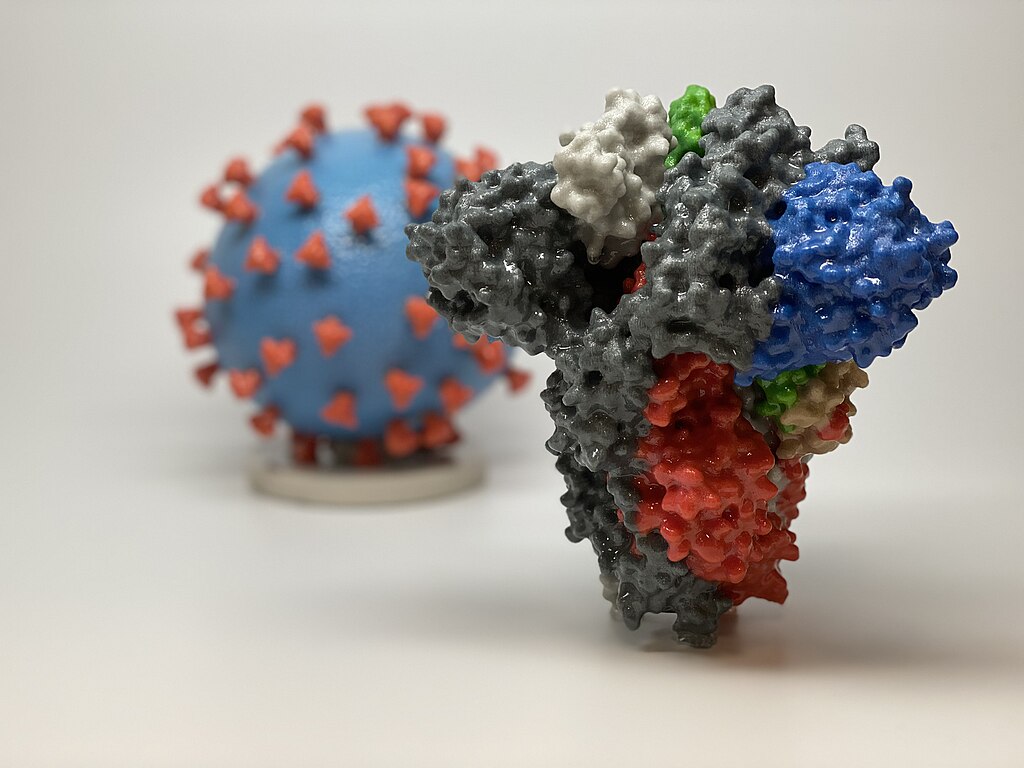
The vaccine formulation has proved to be highly protective, safe and versatile. Moreover, it can serve as a basis for the development of zika and dengue vaccines, for example.
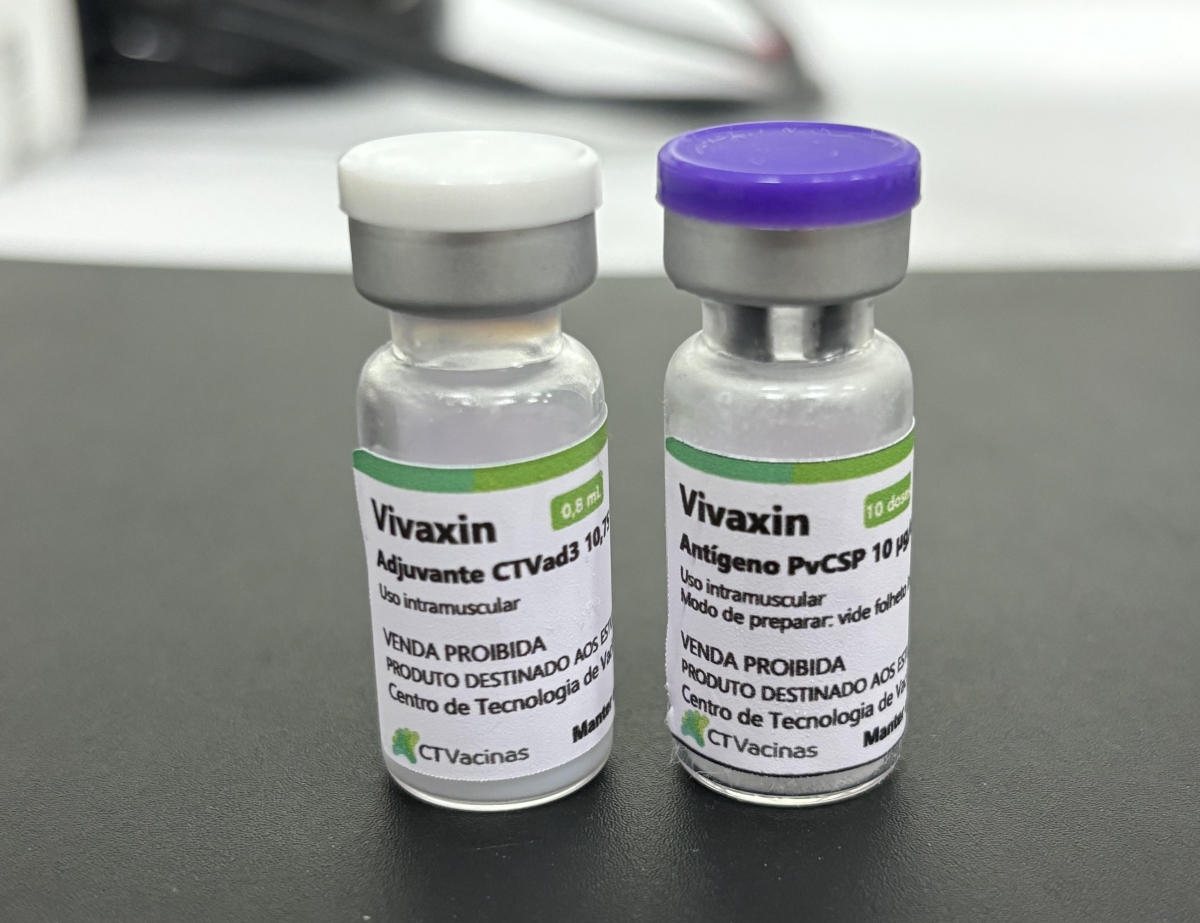
USP is developing the vaccine in partnership with the Vaccine Technology Center at the Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG). Permission to conduct a clinical trial is due before the end of this month.
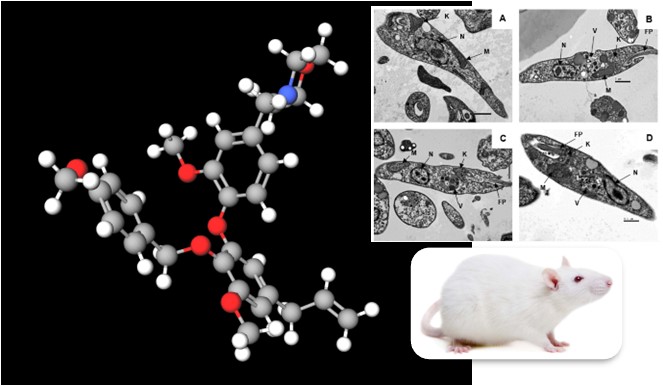
The researchers synthesized a molecule inspired by a substance present in Nectandra leucantha (canela-seca or canela-branca). Animal trials have produced promising results.

Researchers tested the effects of the plant’s methanolic extract and an isolated alkaloid substance, palmatine, on mice. The results were promising.
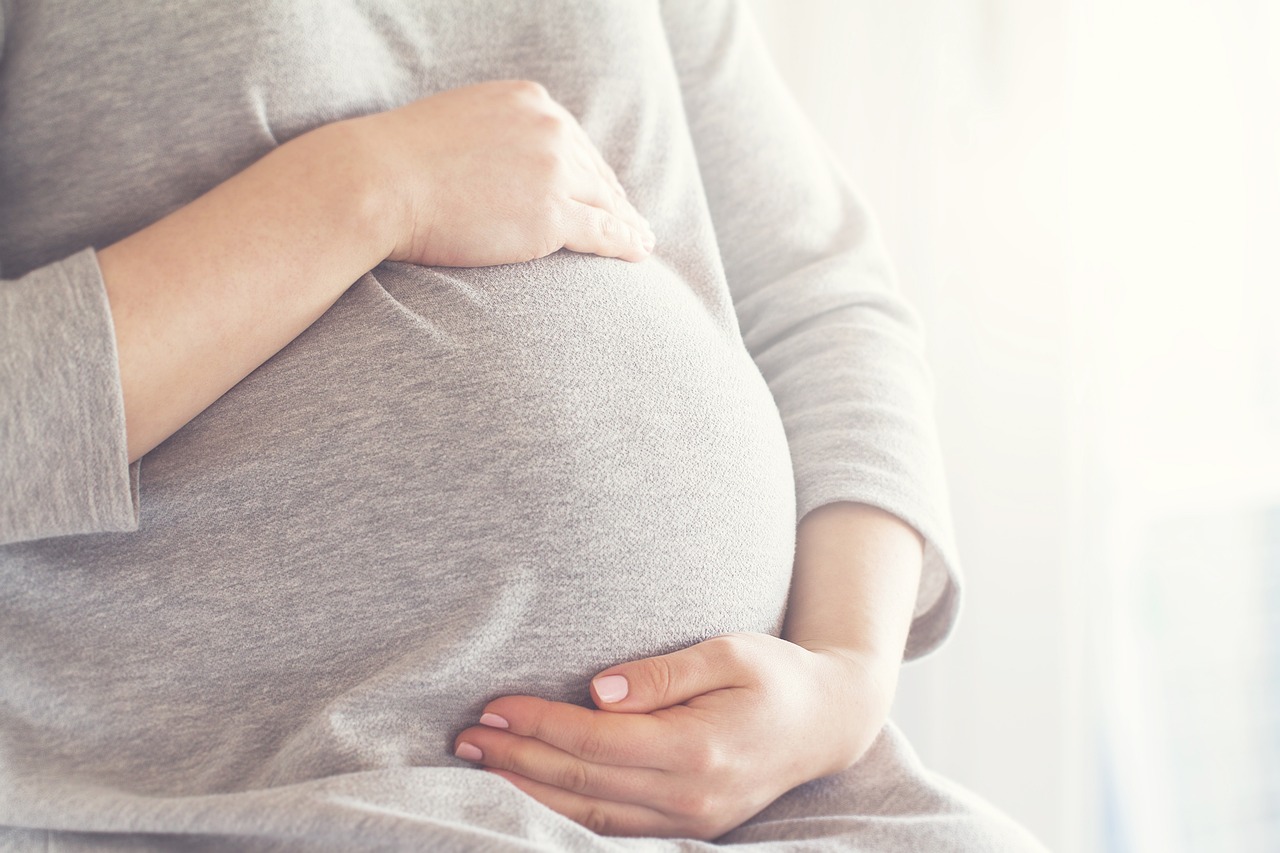

The study was conducted at the University of São Paulo. As the pregnant women were treated and their symptoms of depression improved, the proportion of “good” bacteria in their gut microbiome increased.
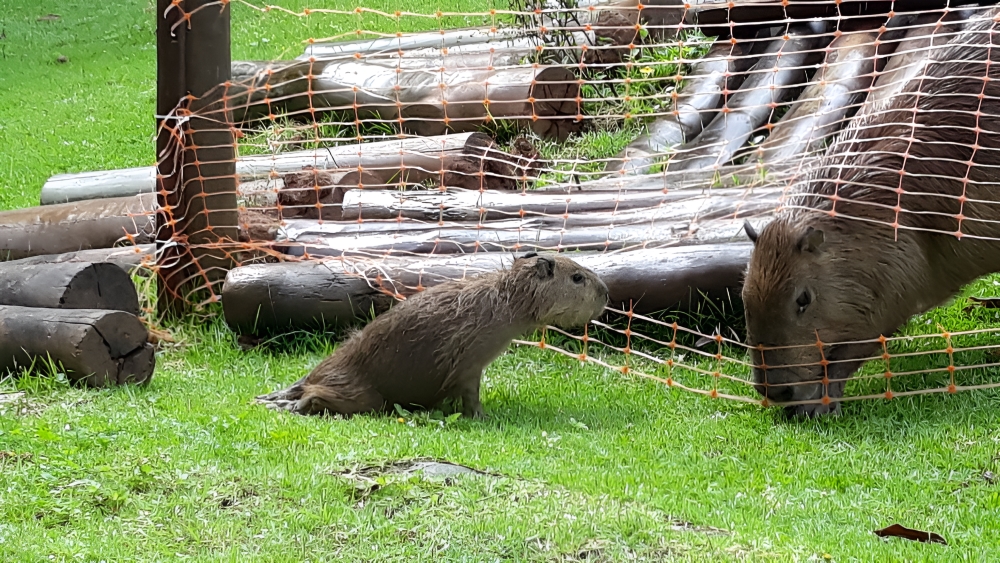

The viral strain found in the dead animals on Anchieta Island in Ubatuba was the variant transmitted by vampire bats, which probably fed on the capybaras’ blood at a time of habitat disturbance.
A study conducted by a Brazilian researcher at Harvard shows that serotonin – a hormone known for regulating mood – plays a central role in the development of postprandial hypoglycemia in up to 30% of people who have undergone surgery; the findings suggest avenues for possible treatments.
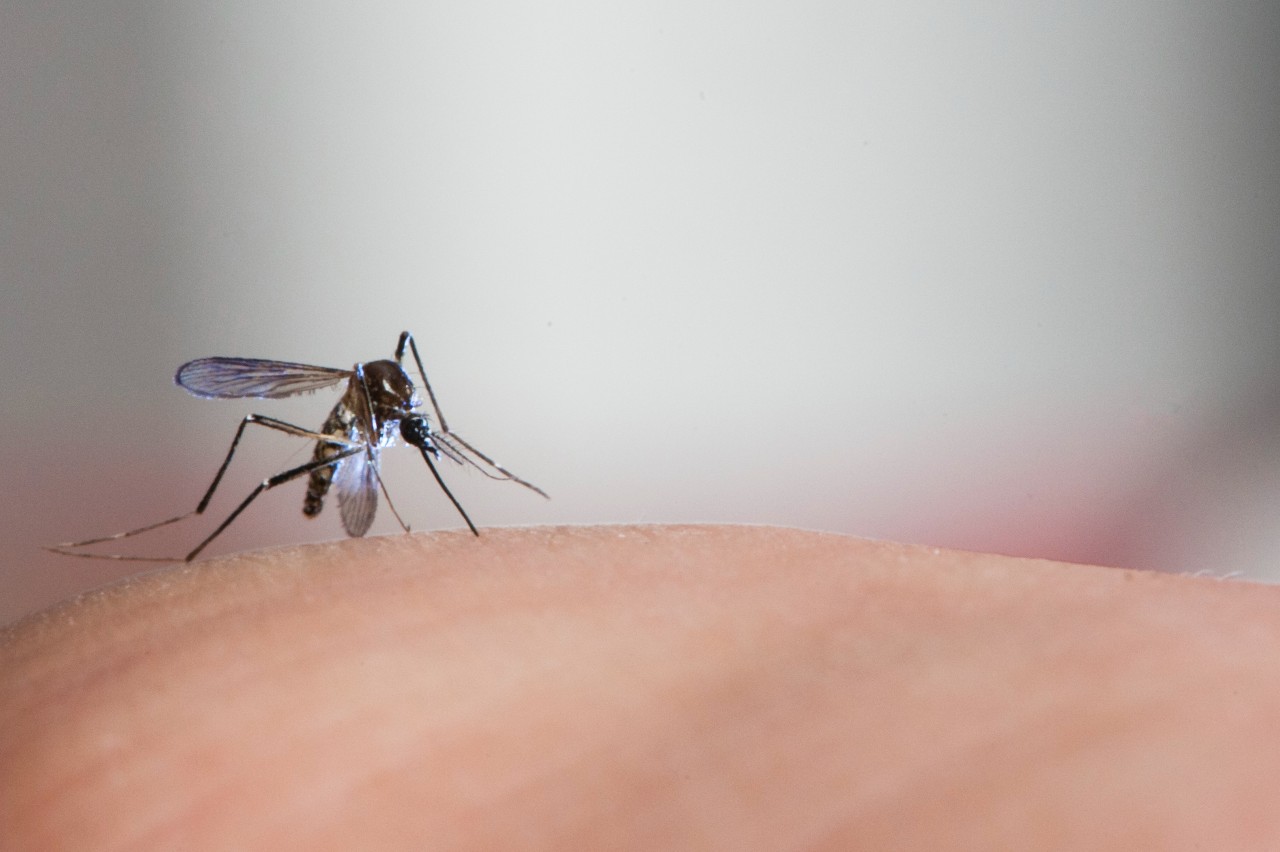

A study by a group of scientists shows that larval infestations of Aedes aegypti in open-air disused containers increased in response to the effects of the weather phenomenon, especially mean seasonal temperature and rainfall above 23.3 °C and 153 mm respectively.
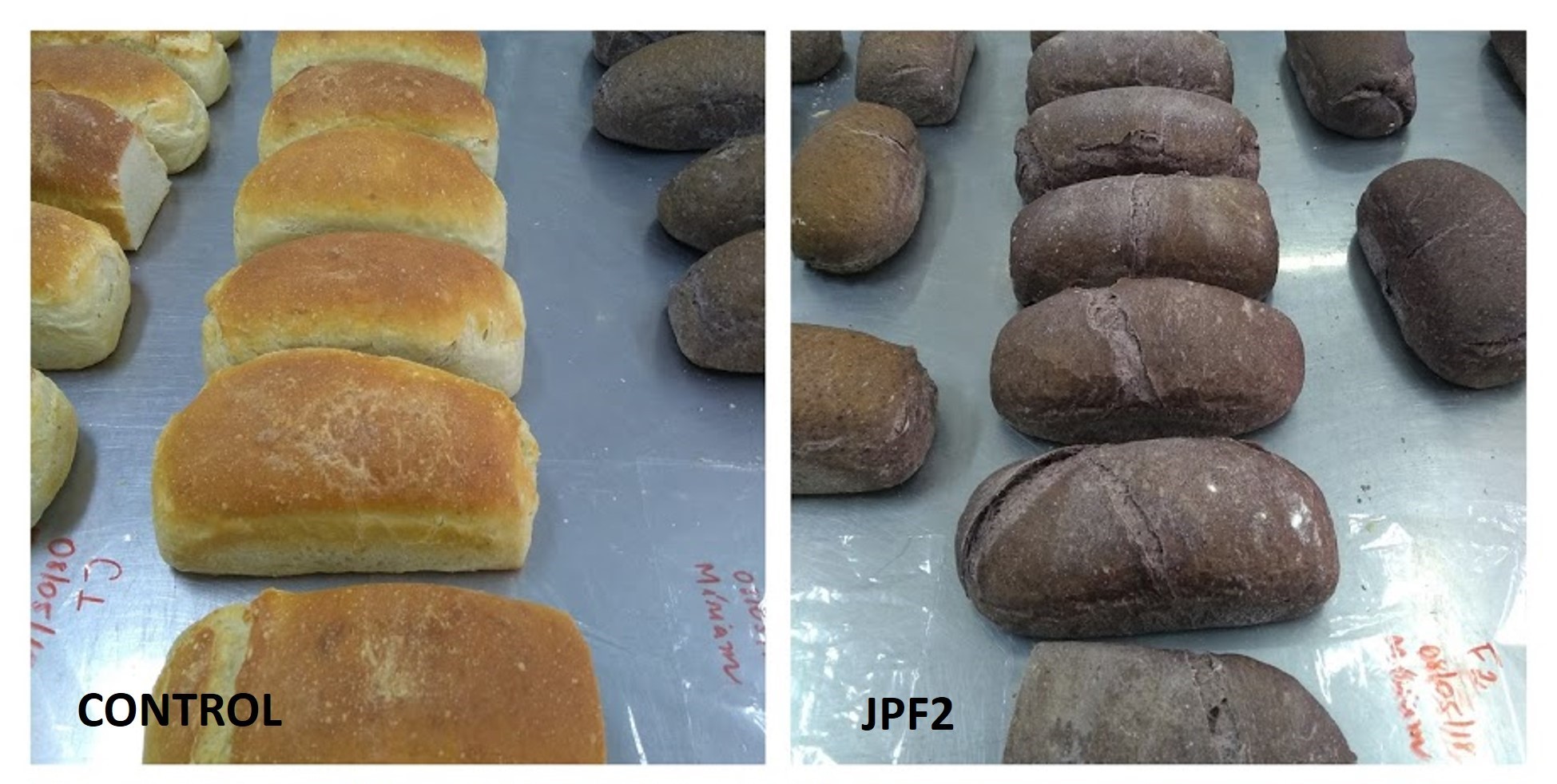

Consumption of bread supplemented with jabuticaba peel flour, which is rich in fiber and antioxidants, lowers glycemic peaks and prolongs satiety.
The pioneering initiative by scientists at the University of São Paulo aimed to promote early diagnosis and improve treatment of the disease, which is relatively infrequent but one of the leading causes of death from cancer in Brazil.

In vitro model has all three layers of the organ, simulates diseases and injuries more accurately, and could replace animals in toxicological studies of medicines and cosmetics; innovation was presented at FAPESP Week Spain.

Researchers at the University of São Paulo analyzed data from 89 mother-father-baby triads and concluded that the higher the father’s body mass index, the smaller the baby, and that this can influence the baby’s health far into adulthood.

The strategy developed at the State University of Campinas consists of submitting the ingredient to heat treatment and combining it with guarana extract and vitamin D. The result could become an alternative to animal products.

WHO advisory group publishes first article in scientific journal outlining challenges and actions that can help make the field more equitable and promote progress in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of various diseases, including rare ones.
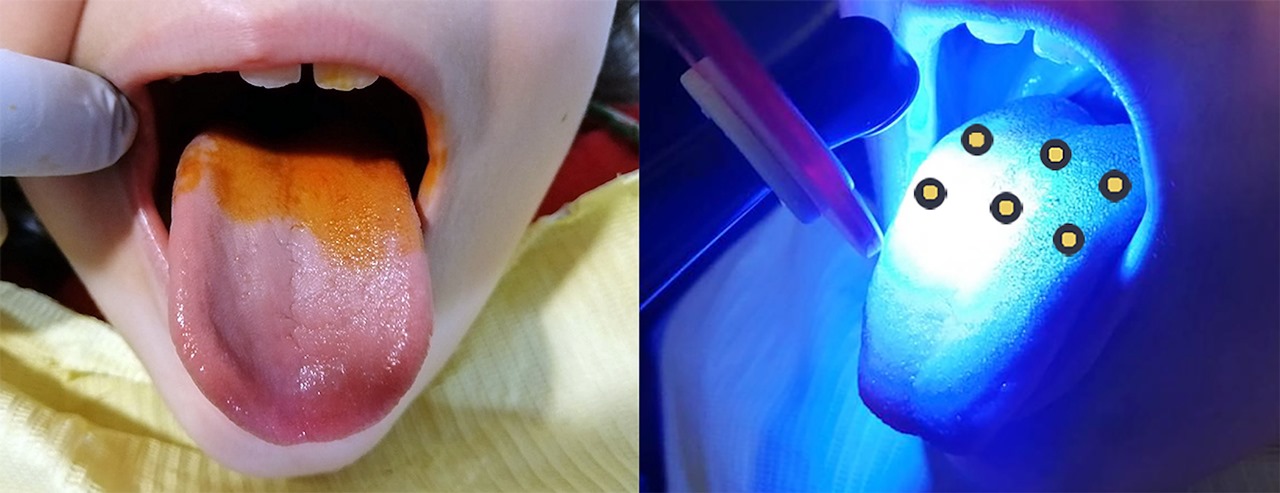
The study involved 52 mouth-breathing children aged 6-12 with halitosis. The results are published in PLOS ONE.
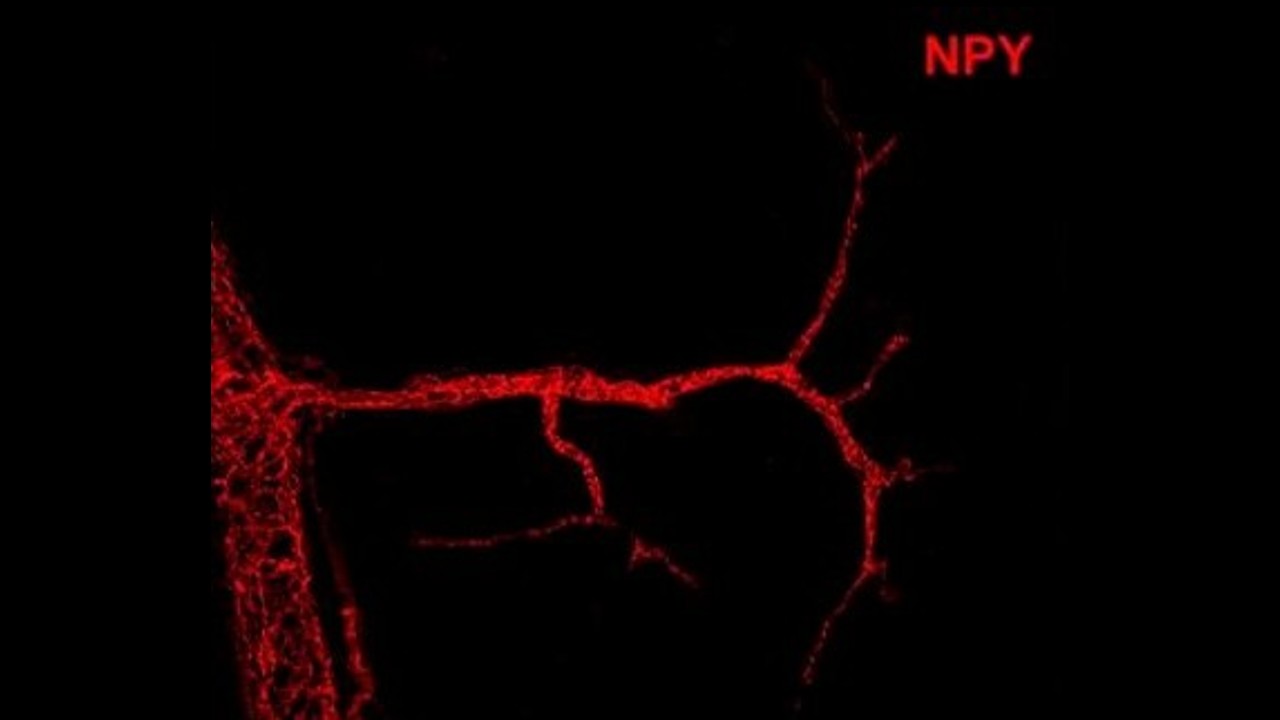
Researchers from the University of Oxford and the State University of Campinas have discovered a neuropeptide that acts on the peripheral nervous system, outside the brain, to speed up metabolism. The finding opens the way to more efficient and cheaper treatments for obesity.
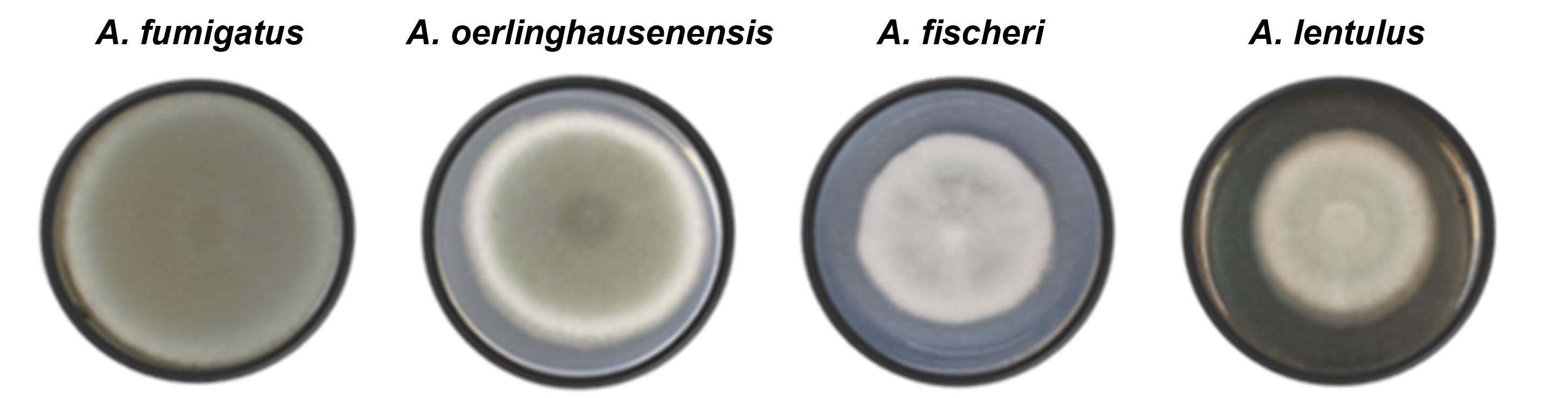
Researchers at the University of São Paulo found 62 proteins specific to spores of Aspergillus fumigatus, a fungal species that causes lung disease. The study, published in Nature Microbiology, showed that at least one of these proteins inhibits human defense mechanisms.

São Paulo-based startup supported by FAPESP develops cheaper and more sensitive alternative to imported test kits.

Conclusion comes from study that followed more than 4,000 people aged 50 or older for 12 years; damage is mainly in brain areas associated with memory.