

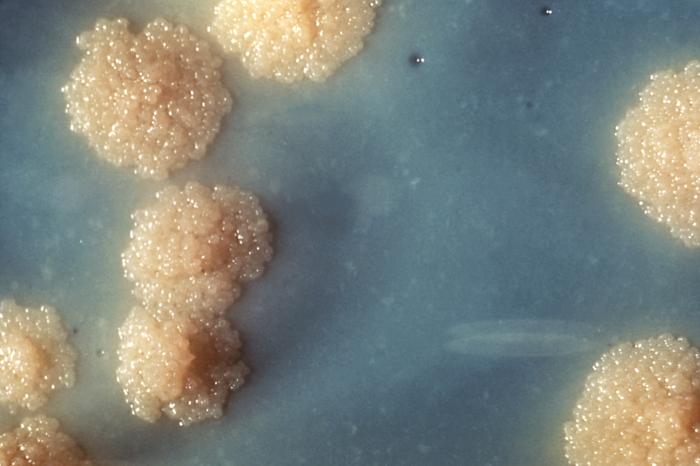
Research from São Paulo State University shows that an inexpensive, easy-to-produce substance eliminated lung infection in 30 days. The compound has the potential to reduce the time and toxicity of current therapies.

Research from São Paulo State University shows that an inexpensive, easy-to-produce substance eliminated lung infection in 30 days. The compound has the potential to reduce the time and toxicity of current therapies.

In a preliminary study conducted on human cells, two commonly used osteoporosis drugs bound to excess iron, preventing cell damage.

In a preliminary study conducted on human cells, two commonly used osteoporosis drugs bound to excess iron, preventing cell damage.
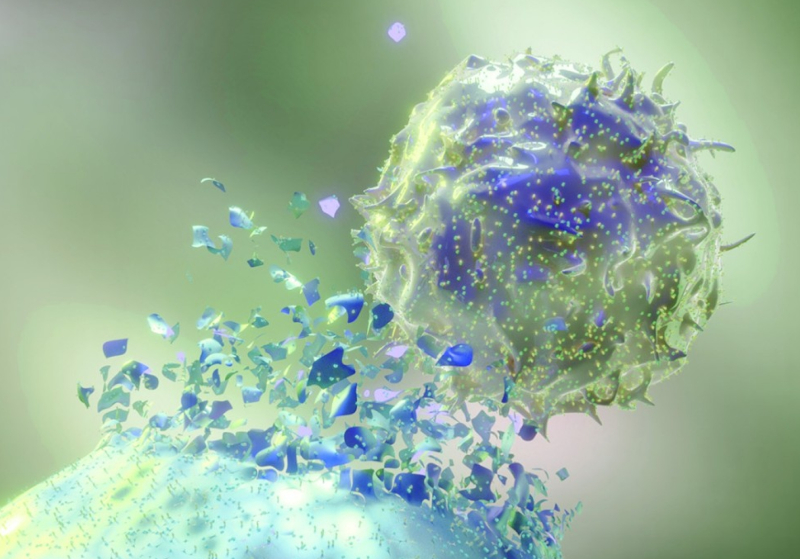
A study by FAPESP-supported center used the NK-92 cell line to test new chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) models. Tests demonstrated an increased ability of the cells to destroy tumors.

Combining acceptance and monitoring in the education of young people reduces the risk of repeating consumption patterns, even in families where parents also use these substances, including cigarettes, vapes, and marijuana.
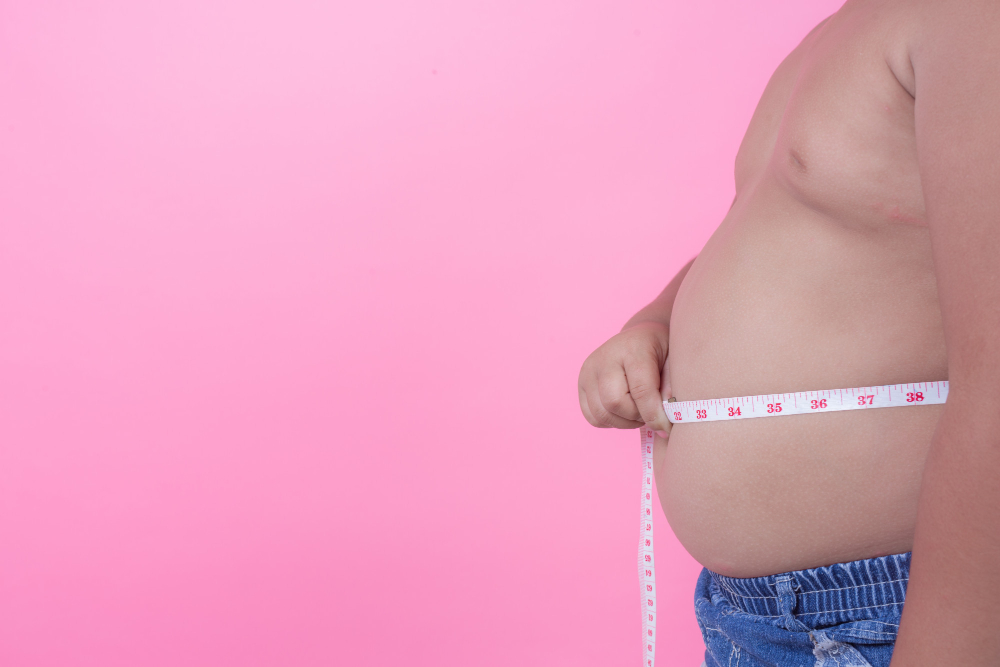

Research conducted with 130 children between the ages of six and 11 showed that inflammation associated with obesity and being overweight affects the functioning of the endothelium – the layer that lines blood vessels – paving the way for diseases such as atherosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke.

Research from São Paulo State University shows that carbetocin, when administered before social stress situations, prevents anxiety in laboratory rats without having direct anxiolytic effects.

Research conducted on rats reinforces the idea that proton pump inhibitors, which are widely used to treat stomach problems, can affect mineral absorption and compromise bone health.

Research conducted on rats reinforces the idea that proton pump inhibitors, which are widely used to treat stomach problems, can affect mineral absorption and compromise bone health.
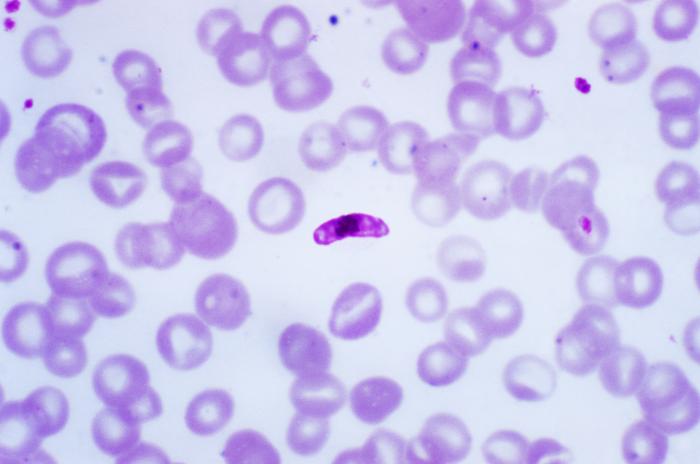
Tests on cell cultures and rodents have shown that the new molecule acts on all three stages of the disease cycle, eliminating the parasite from human blood and liver and preventing transmission to mosquitoes.
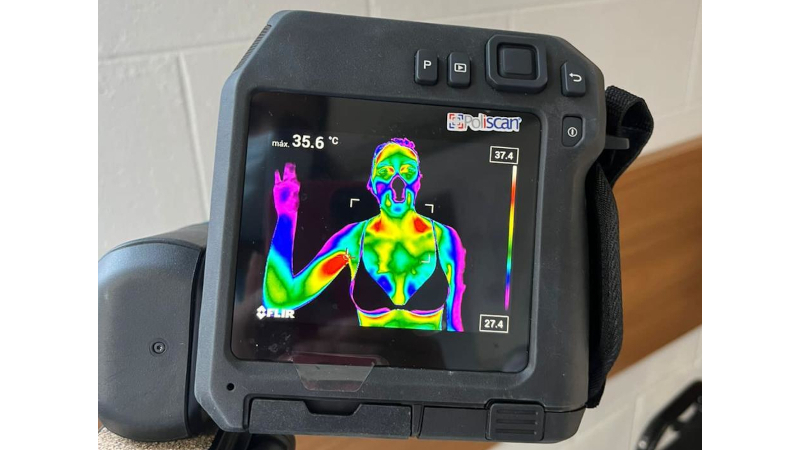

Research from the State University of Campinas reveals that cycles of weight loss and weight regain affect more than just the numbers on the scale.

Research from the Federal University of São Carlos emphasizes the need for health and education professionals to consider sensory processing to expand support strategies for childhood dyspraxia.

Research from the Federal University of São Carlos emphasizes the need for health and education professionals to consider sensory processing to expand support strategies for childhood dyspraxia.

In an opinion piece in the British Medical Journal, researchers propose incorporating local knowledge as a strategy for adapting to extreme events and food insecurity.

In an opinion piece in the British Medical Journal, researchers propose incorporating local knowledge as a strategy for adapting to extreme events and food insecurity.
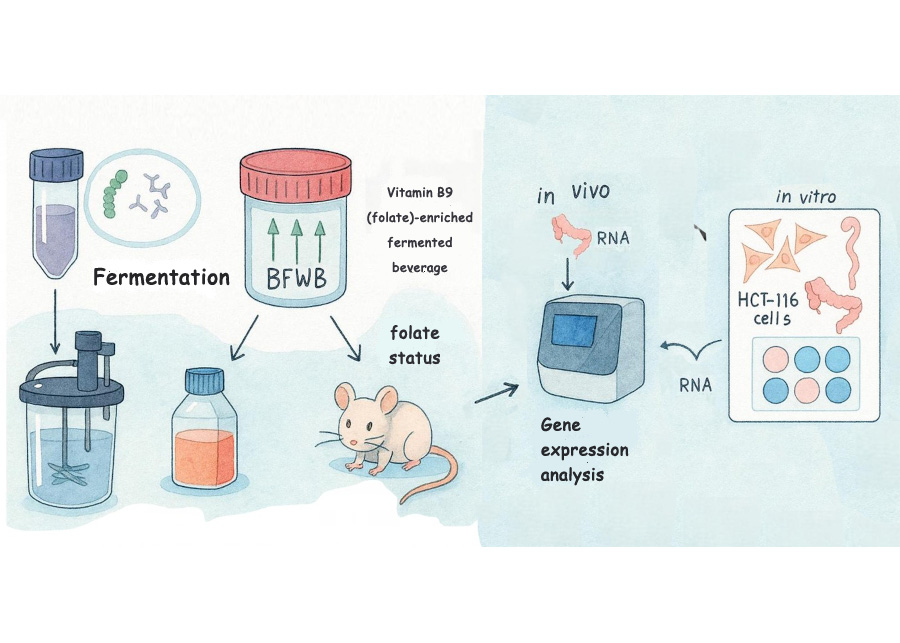
Formula containing whey and grape by-product extract was developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo and tested in partnership with a center in Argentina.

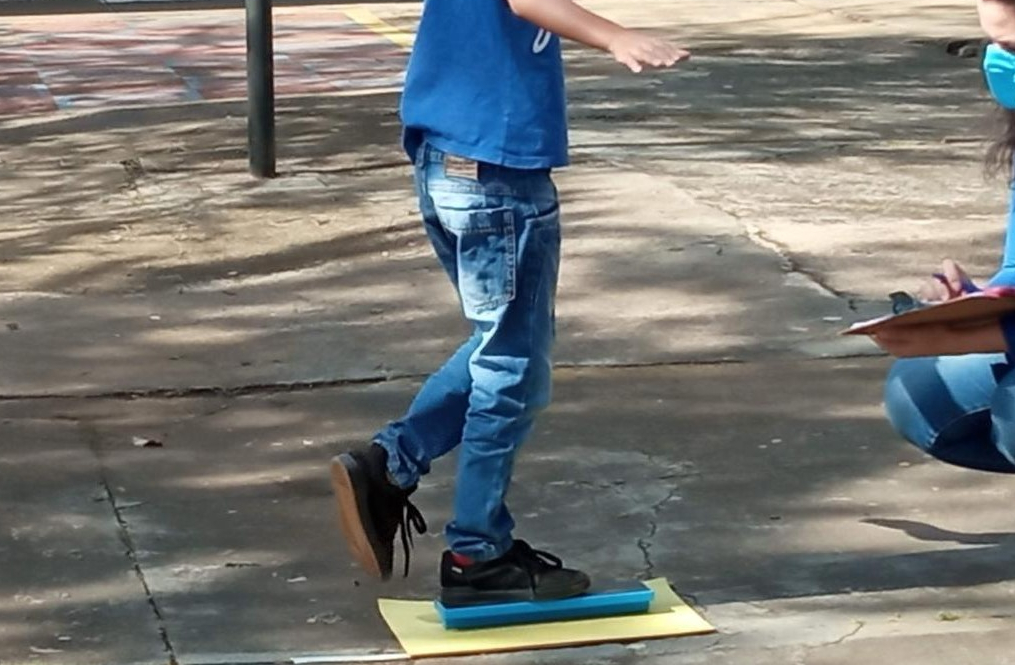
A study by the Federal University of São Carlos and University College London examined 2,815 older adults and identified an indicator of loss of mobility.
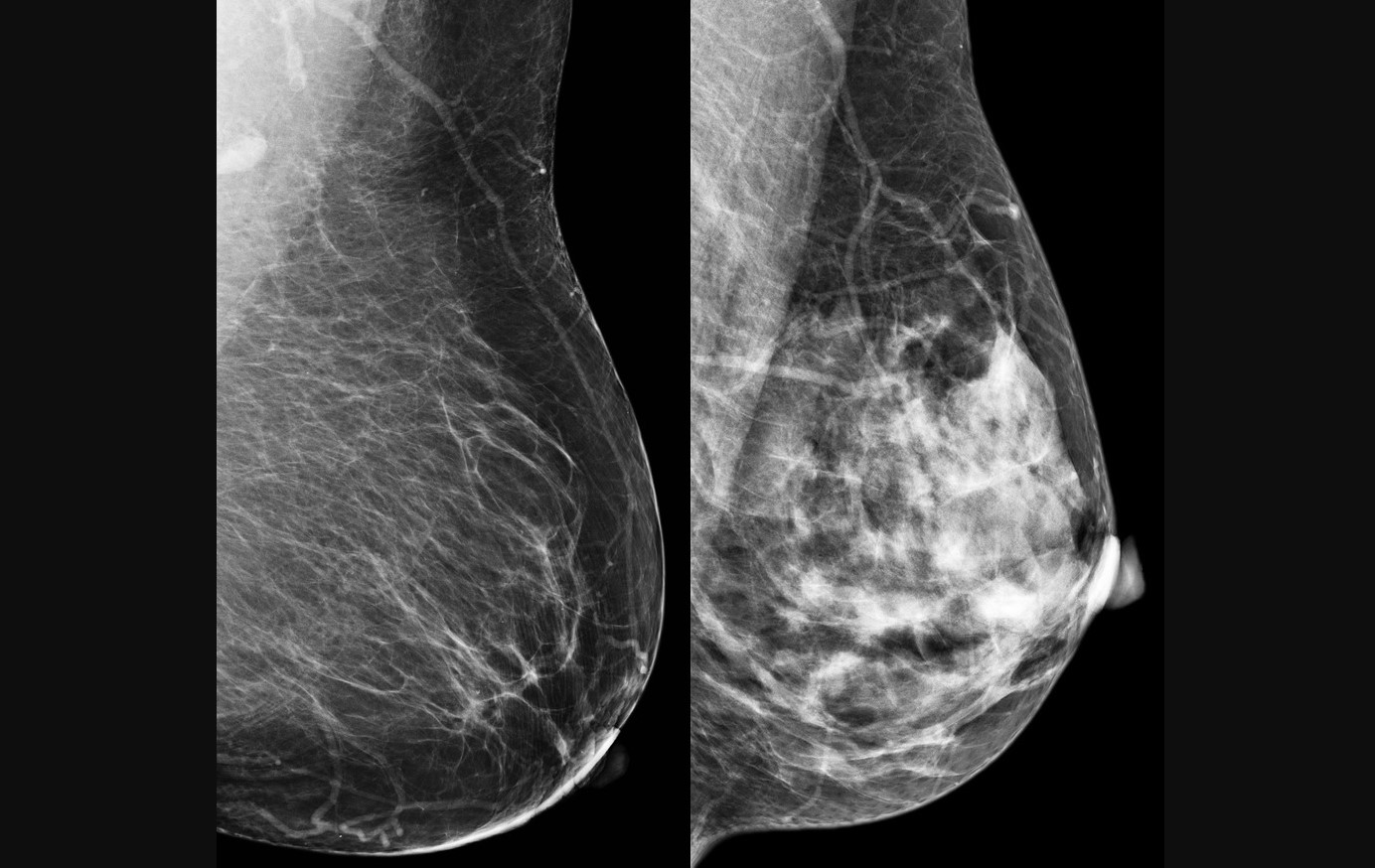
Discovery increased the number of known variations of the HER2 protein, the target of advanced drugs against the disease, from 13 to 90; diversity may explain resistance to therapies.
The multicenter Titan Trial project is investigating a method to treat unilateral spatial neglect, a sequela of stroke that affects perception of the side opposite to the affected cerebral hemisphere.

Using biofeedback and gamification, the solution teaches emotional self-regulation strategies to child patients with disorders such as ADHD and ASD.
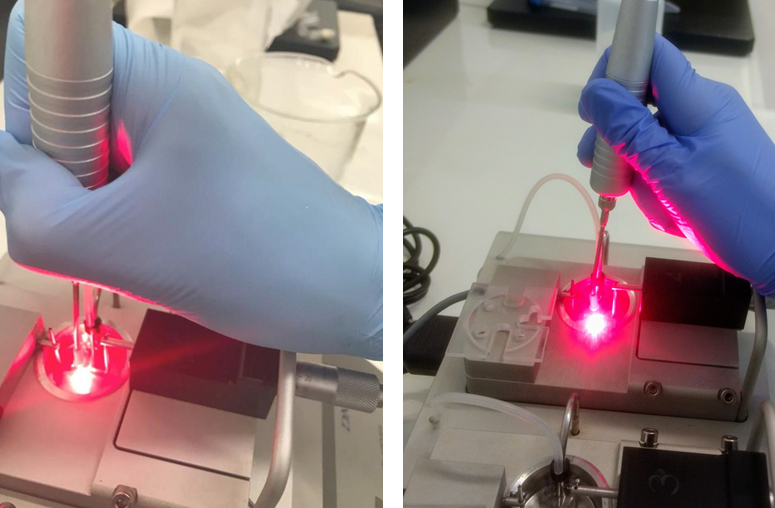
An experiment conducted at the Federal University of São Carlos demonstrated that applying low-intensity light had a hypotensive effect on rats that became hypertensive due to a reduction in hormones, a process characteristic of aging in the female reproductive system.
Researchers compared the repertoire of long non-coding RNAs in humans with those of rhesus monkeys, mice, and chickens and noted that these structures played a role in functional specialization throughout evolution.

Preliminary data suggest that the population in this area of southwestern Pará state is more exposed to infection than average due to a lack of access to healthcare and greater contact with sex workers.

Brazilian research shows that stellate pancreatic cells produce periostin, remodeling tissue and facilitating tumor infiltration, a key mechanism of the aggressiveness and high mortality of the disease.