

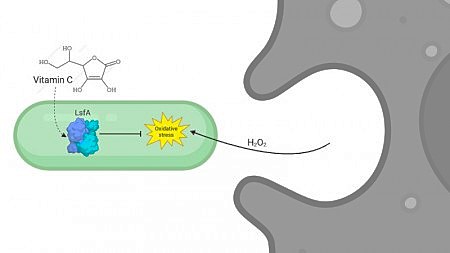
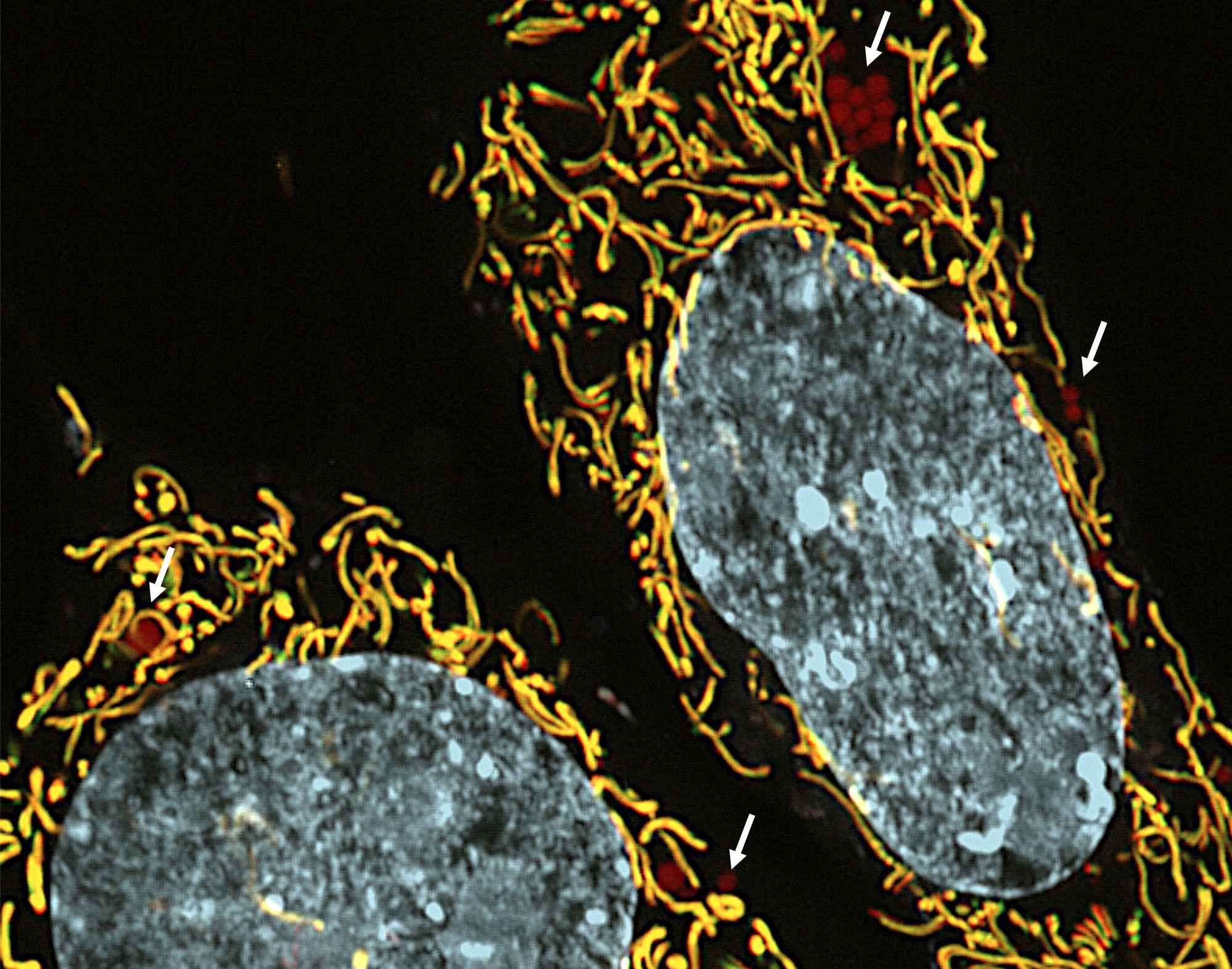
Findings contribute to the search for new targets against hospital infections.

With COP30 in Belém approaching, the ideas of the former French Minister of Justice are gaining momentum, inviting us to rethink multilateralism and the structure of the institutions that shape the world.
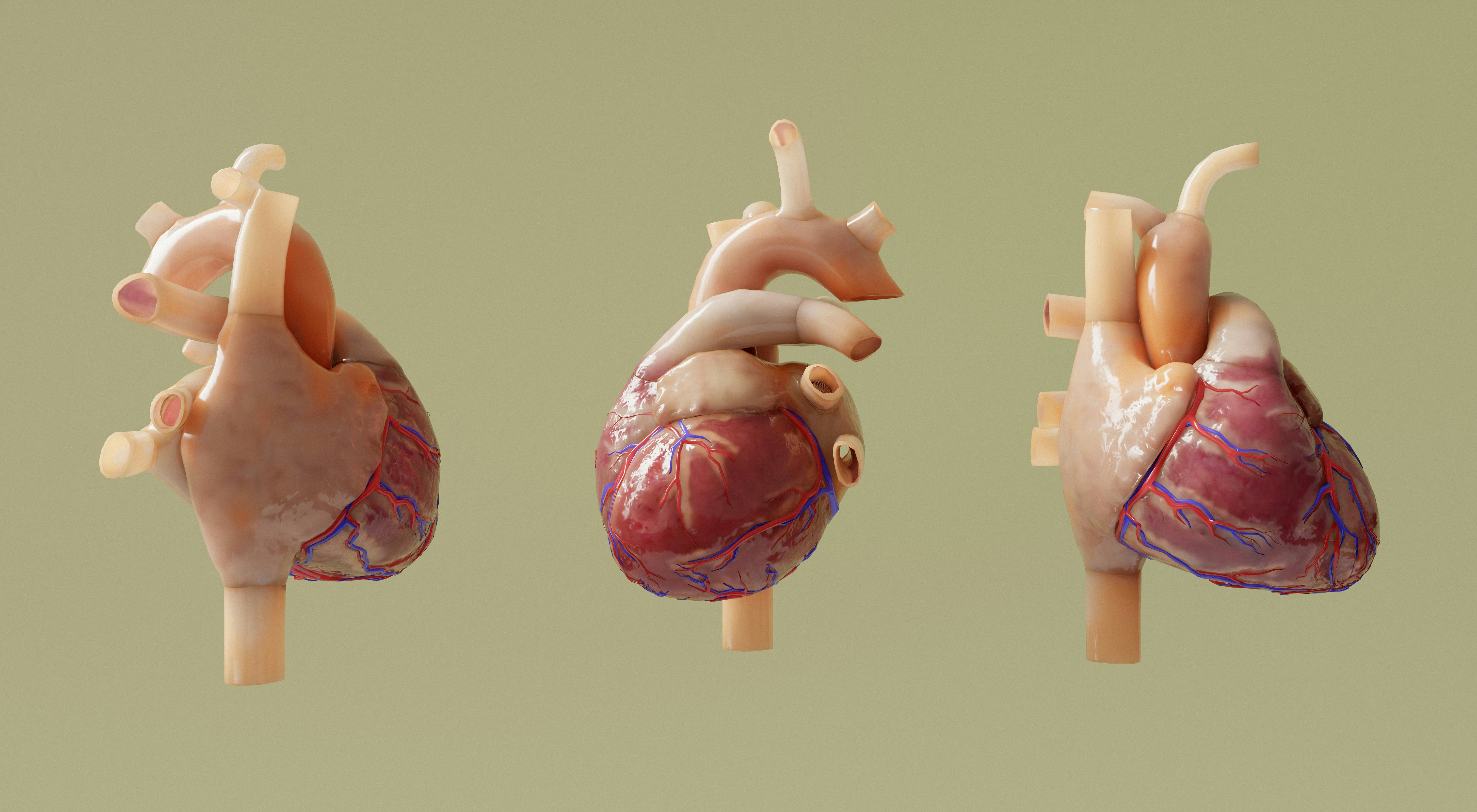
A three-year study of 77 people showed that analyzing myocardial deformation during contraction can predict the risk of death.

Technology created by a startup supported by FAPESP accelerates patient recovery and improves biological integration.
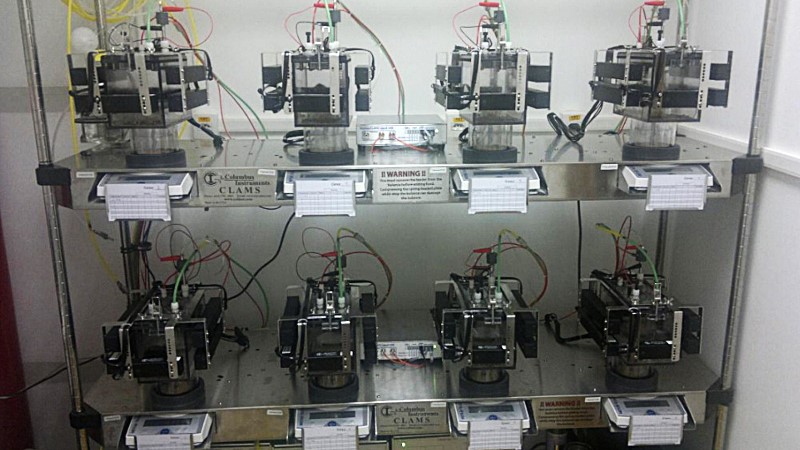

Standardization opens up possibilities for developing preclinical trials of new drug classes that focus on calorie burning.
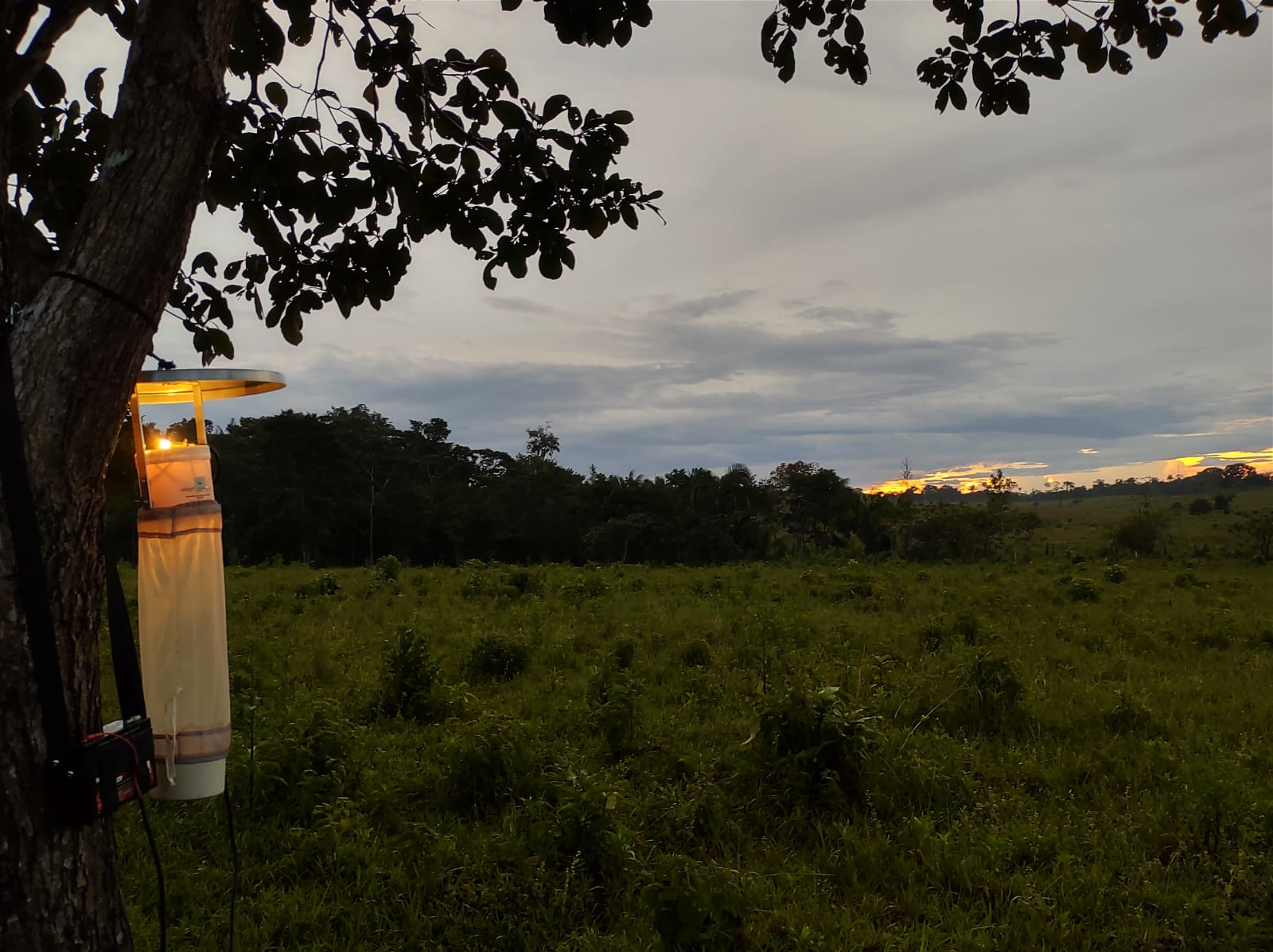

Research shows that areas with 50% deforestation near residential areas or fragmented vegetation allow greater contact between mosquitoes and humans. Amid the discussions for COP30, the study helps us understand the link between forest destruction and the spread of the disease.
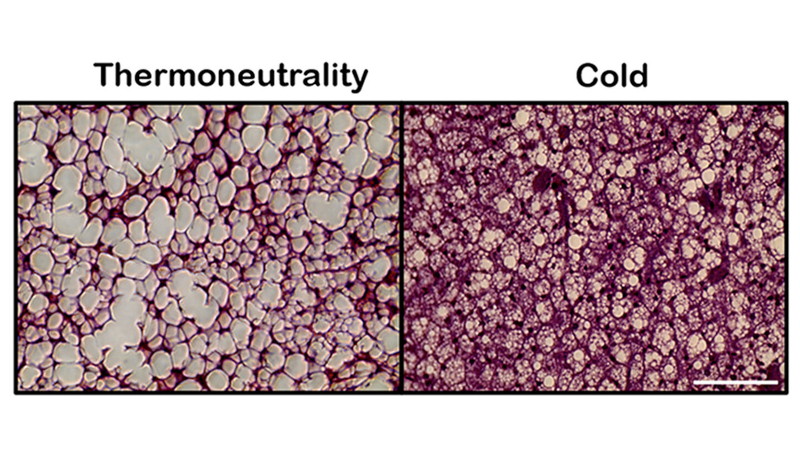
Research conducted by Redoxoma, a FAPESP Research, Innovation, and Dissemination Center, found that mitochondrial potassium channels regulate heat production in brown adipose tissue.

In the nearly three years since its creation, the Fish for Health Research Center has achieved significant results in understanding the nutritional value and consumption habits of fish in the state of São Paulo, received new investments, and is preparing to expand its network of associated researchers.
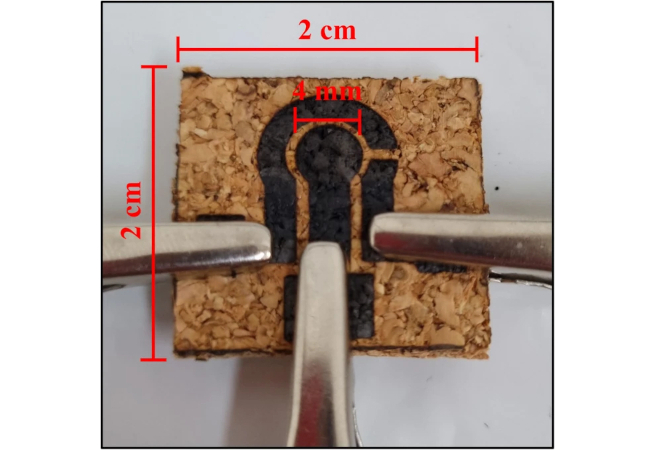
Sodium nitrate is used as a preservative and to add color to products such as ham and sausages, but is potentially carcinogenic and cannot be applied in beverages; researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos used pieces of cork and lasers to develop a sensor.

The substance is essential for the survival of microbes in extreme environments and has been shown to have antioxidant, emulsifying, and stabilizing properties.
A study published in Science and involving a Brazilian researcher unveils a cellular mechanism involved in transmitting mutations in mitochondrial DNA. These mutations can cause serious, incurable diseases.
In tests with rodents, researchers observed that the immune system attempts to mitigate damage to the hypothalamus caused by food, which can lead to obesity in the long term. Animals whose migration of these cells was inhibited experienced greater weight gain, increased fat accumulation, and worsened metabolic markers.

In an article published in the journal Scientific Reports, an international team of researchers describes how the defense cells of older adults with a history of endurance training are more effective against inflammation.
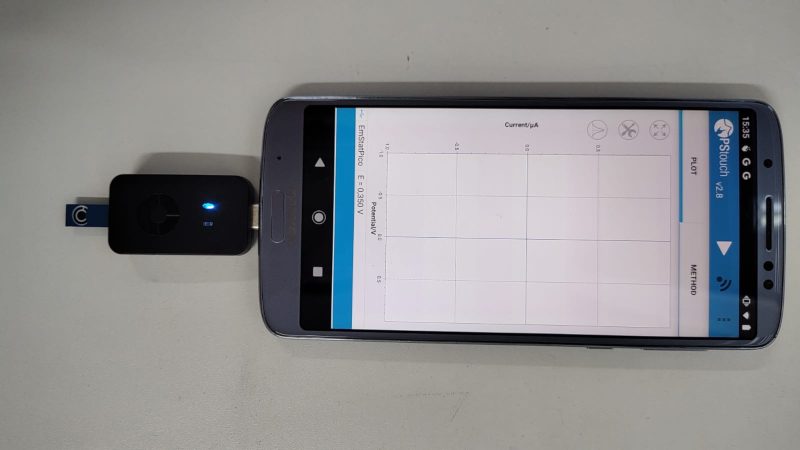
Researchers develop technology that identifies highly potent and dangerous psychoactive substances. The device can be used in emergency medical facilities and to help inform users and reduce the harm associated with consumption.
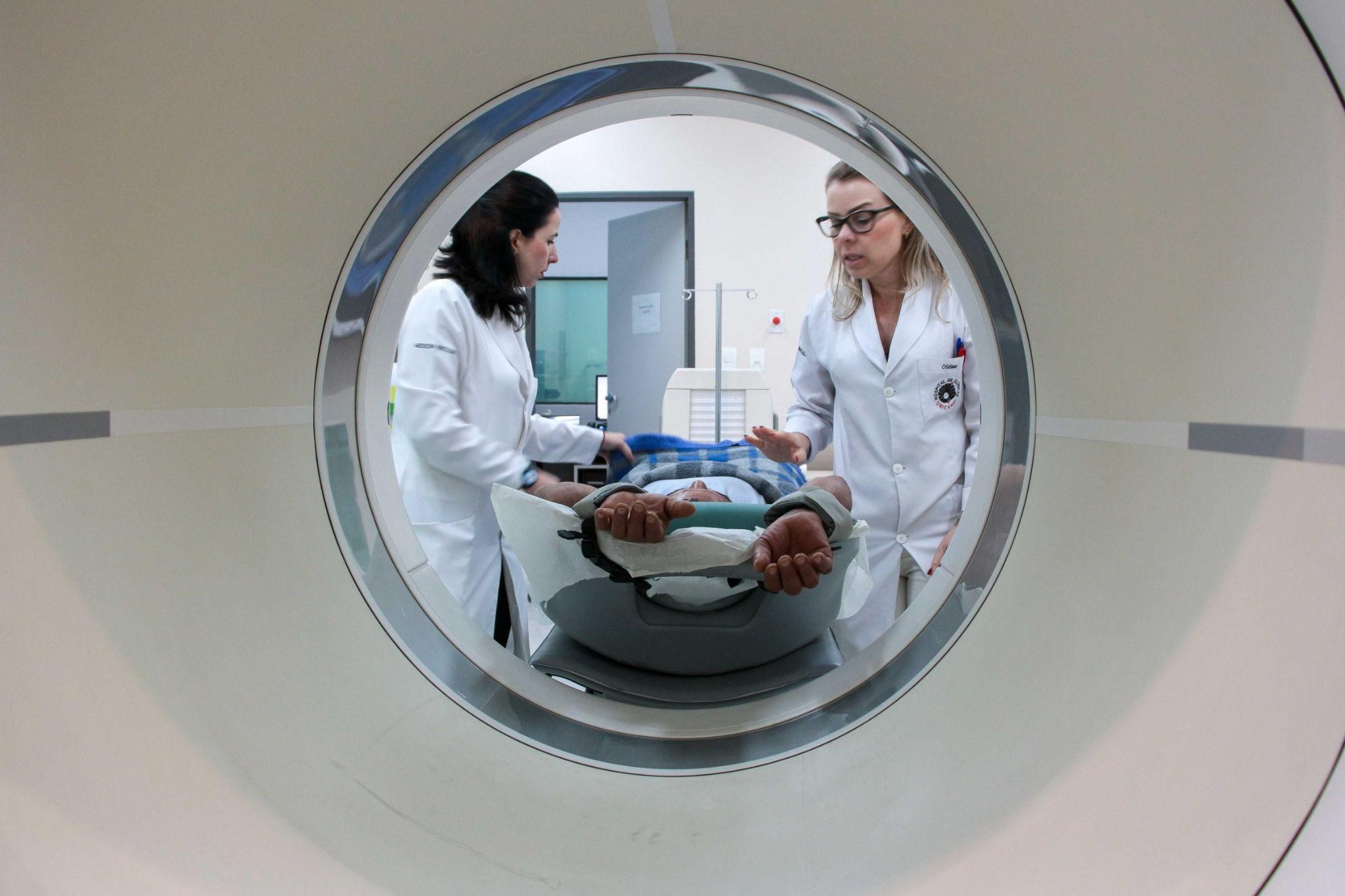
The new functionalities allow the Cancer Theranostics Innovation Center to generate dynamic, more detailed images and provide more accurate diagnoses. The device is available to the scientific community in the state of São Paulo.
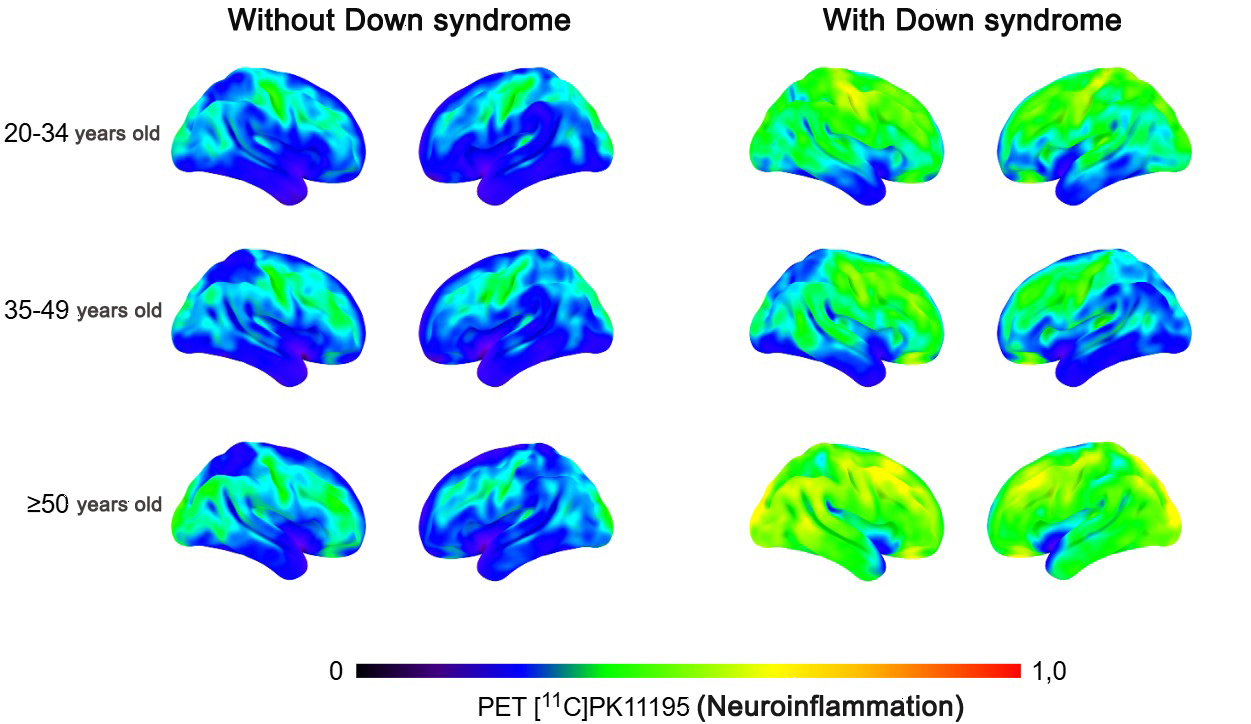
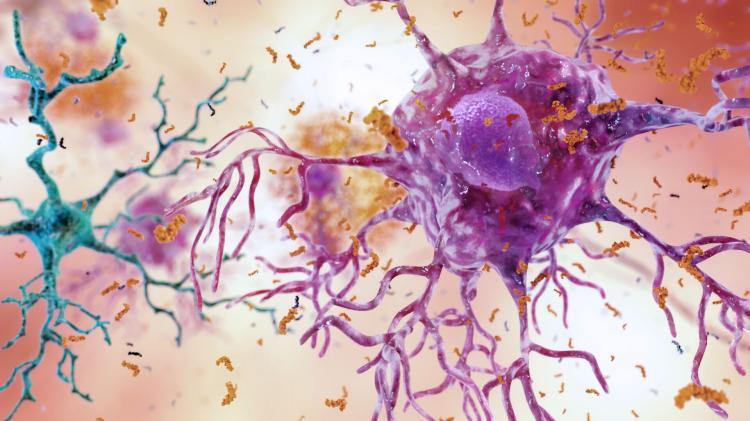
Researchers at the University of São Paulo identify a new factor that explains the high prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease in older people with Down syndrome. The discovery paves the way for disease prevention strategies in this population.
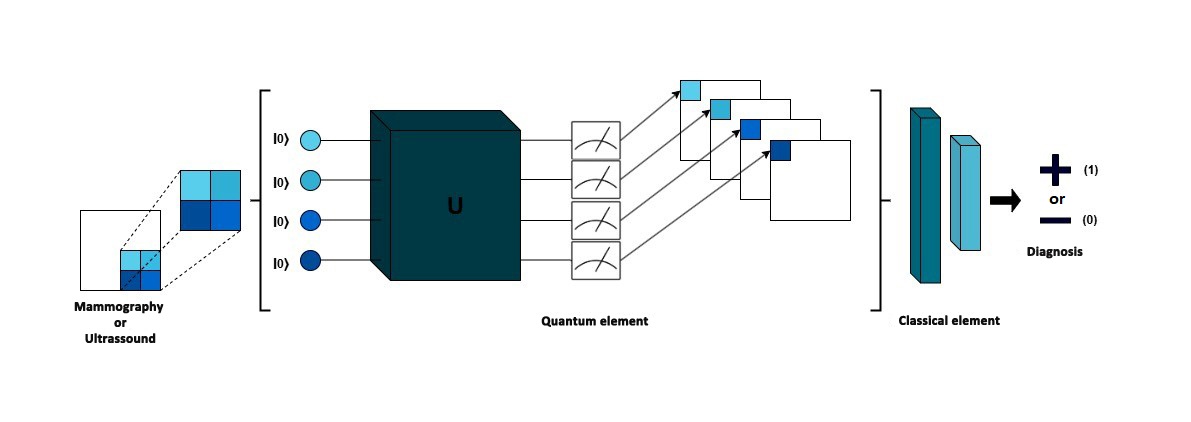
Simple quantum-classical neural networks achieve good results in classifying lesions with fewer computational parameters. Scientists from São Paulo State University demonstrated a hybrid model at an international symposium.

Article published in Nature Medicine points to the risk of setbacks in research focused on this population. Experts question new rules in Brazil and other countries.

To reach this conclusion, Brazilian researchers cross-referenced data obtained from the local public health network with data from an indicator of variations in the Earth’s geomagnetic field. The study was published in the journal Communications Medicine.
Brazilian researchers, in partnership with French institutions, combine advanced cell image analysis technology and machine learning and discover a morphological marker linked to individuals who do not respond to natalizumab.
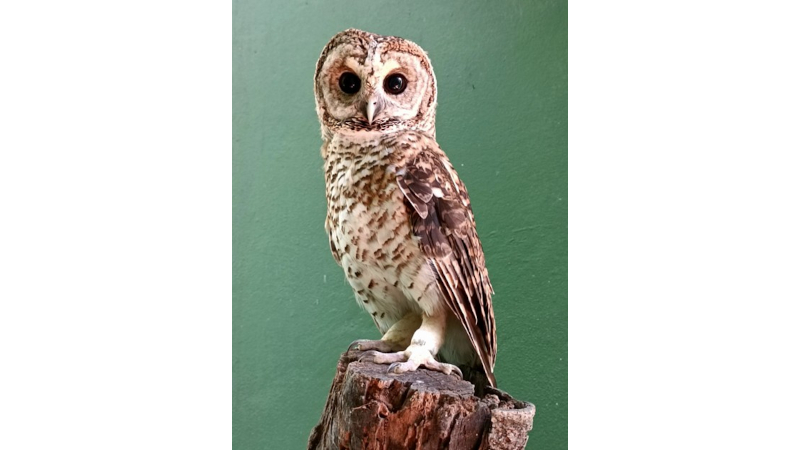

A vulture recently arrived at the Santos Municipal Orchid Garden and an owl living in captivity for ten years were colonized by antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli.

Pioneering research conducted in São Paulo state (Brazil) shows how the immune system reacts to rare types of childhood cancer.

Morin-based powder, extracted from guava leaves, apple peel, and figs, can be slowly released with the help of polymers and serve as an alternative to antibiotics.

Brazilian researchers analyzed over 60 scientific articles on the subject and found that the materials negatively affect bone tissue.

A summary of published studies on the risk of emerging diseases shows that only 7.4% simultaneously consider hazard, exposure, and vulnerability to infection. These three components are essential for reliably and accurately assessing the risk of these diseases in the context of environmental change.