

Test results in two days. A study supported by FAPESP contributes to improving disease monitoring, but the high cost remains a barrier.
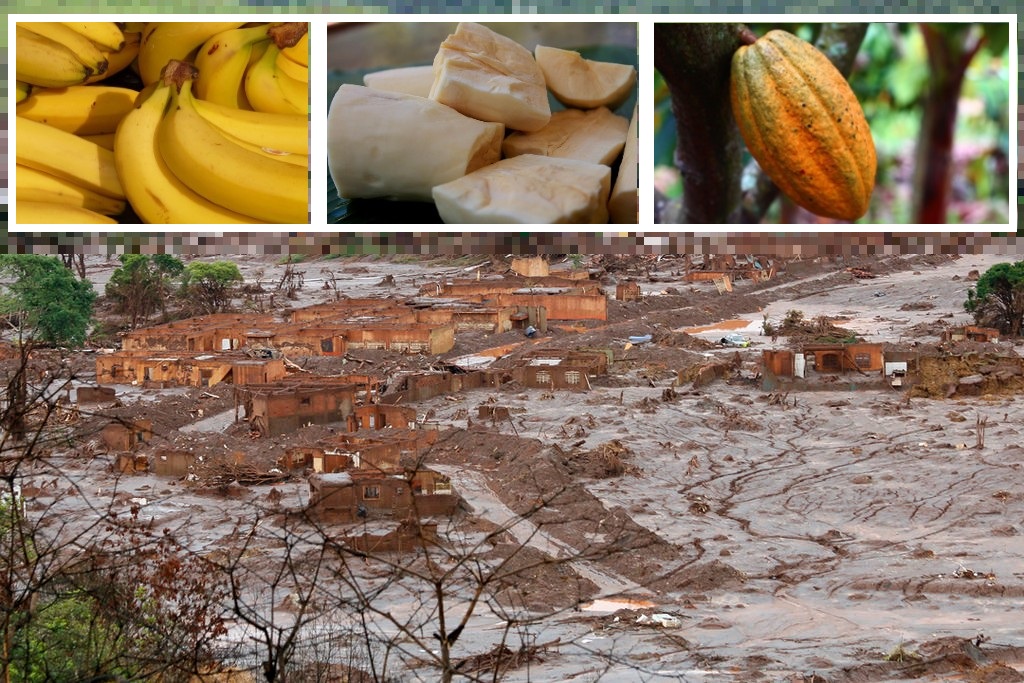

The study also assessed the risks of consuming cocoa and cassava grown in Linhares, a municipality in an area affected by the Fundão dam collapse in Minas Gerais, Brazil, ten years ago.

The study also assessed the risks of consuming cocoa and cassava grown in Linhares, a municipality in an area affected by the Fundão dam collapse in Minas Gerais, Brazil, ten years ago.
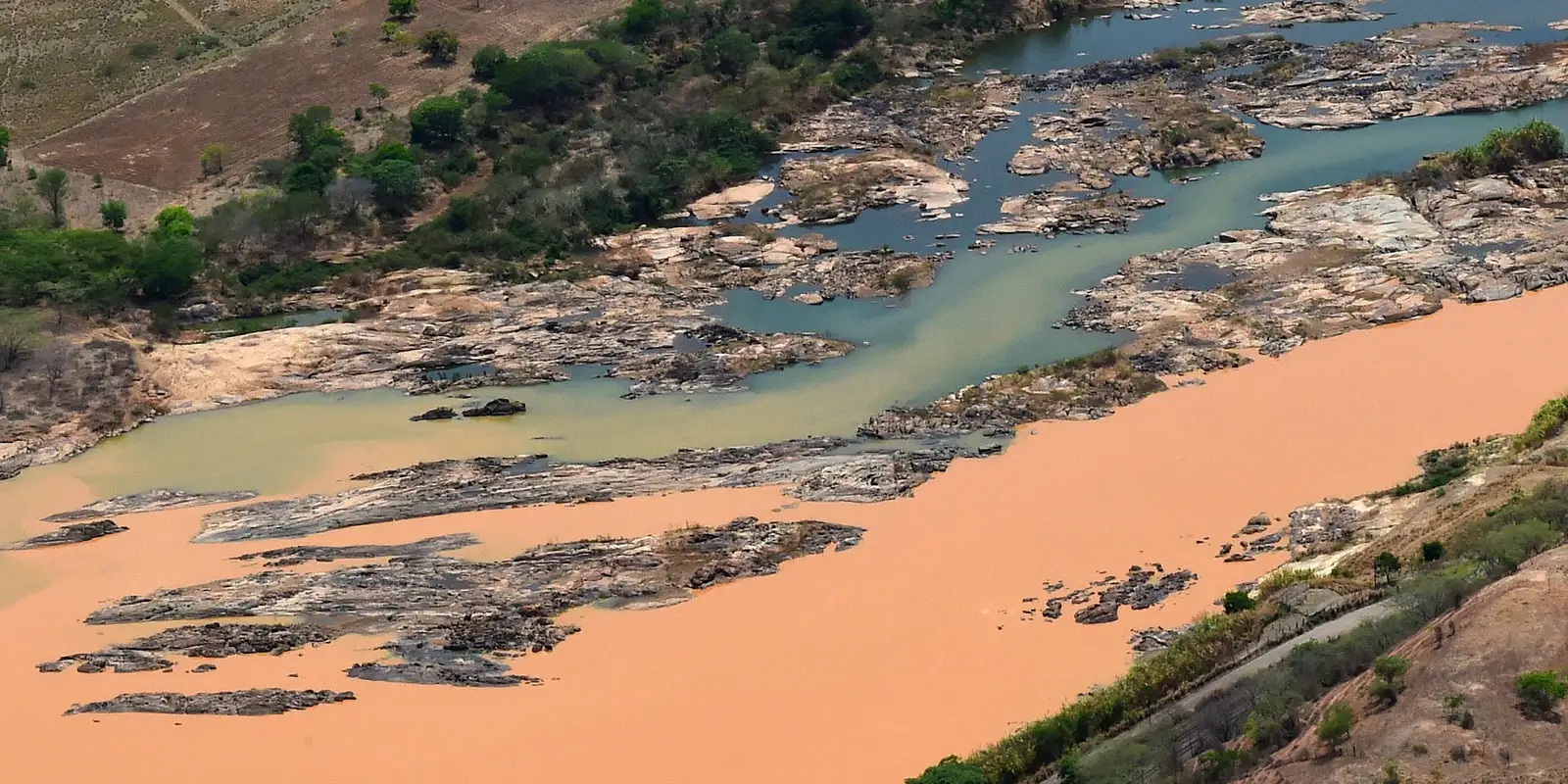

A comprehensive analysis conducted in 2019 detected the accumulation of 13 heavy metals and other toxic substances, advising against consumption due to risks to human health.

A comprehensive analysis conducted in 2019 detected the accumulation of 13 heavy metals and other toxic substances, advising against consumption due to risks to human health.
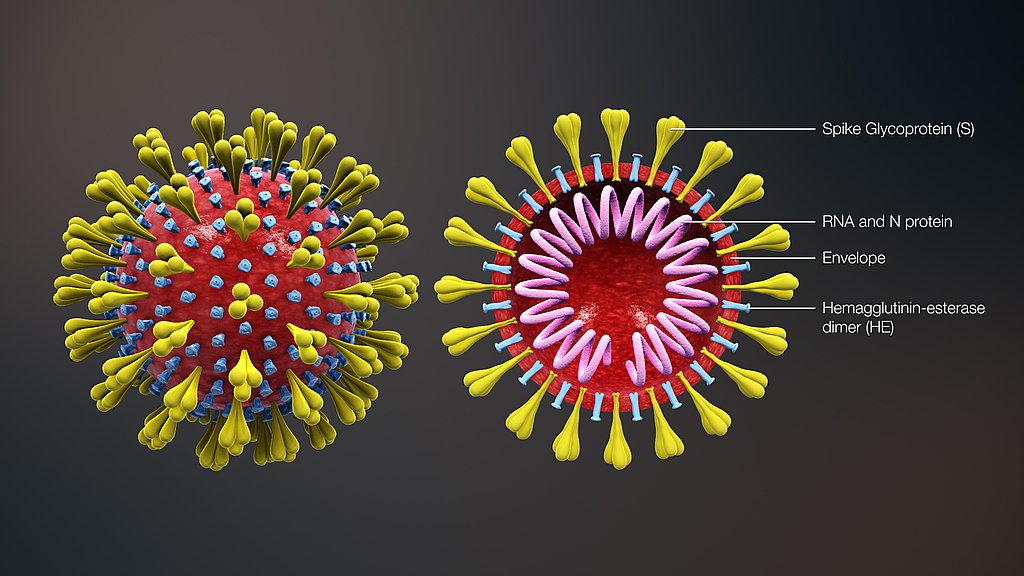
A study by the Federal University of São Paulo describes how SARS-CoV-2 interacts with the RNA of infected lung cells in an unprecedented way. The results may guide the search for new treatments and vaccines.

A study by the Federal University of São Paulo describes how SARS-CoV-2 interacts with the RNA of infected lung cells in an unprecedented way. The results may guide the search for new treatments and vaccines.
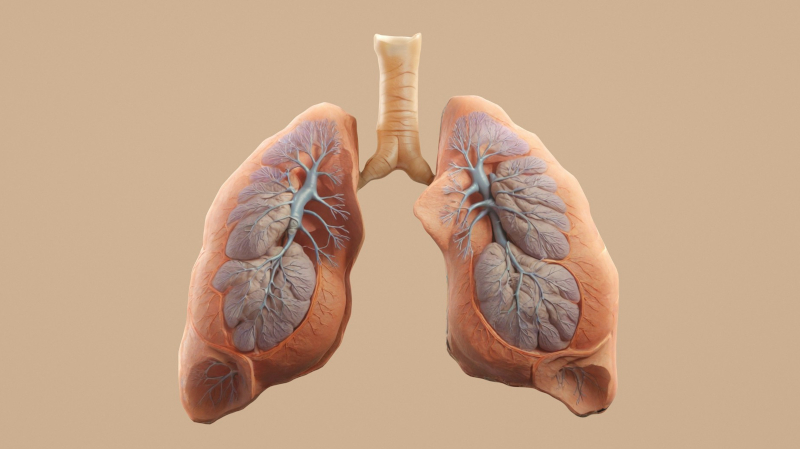
A study of nearly 900 adults indicates that although smoking is still the main risk factor for lung function loss, systemic inflammation and obesity also increase the risk of developing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.

A study of nearly 900 adults indicates that although smoking is still the main risk factor for lung function loss, systemic inflammation and obesity also increase the risk of developing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.

After analyzing over 1,400 cases of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, the study found that more aggressive histopathological variants occur at a rate of 4.6%. Previous estimates pointed to a rate of up to 15%.

After analyzing over 1,400 cases of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, the study found that more aggressive histopathological variants occur at a rate of 4.6%. Previous estimates pointed to a rate of up to 15%.
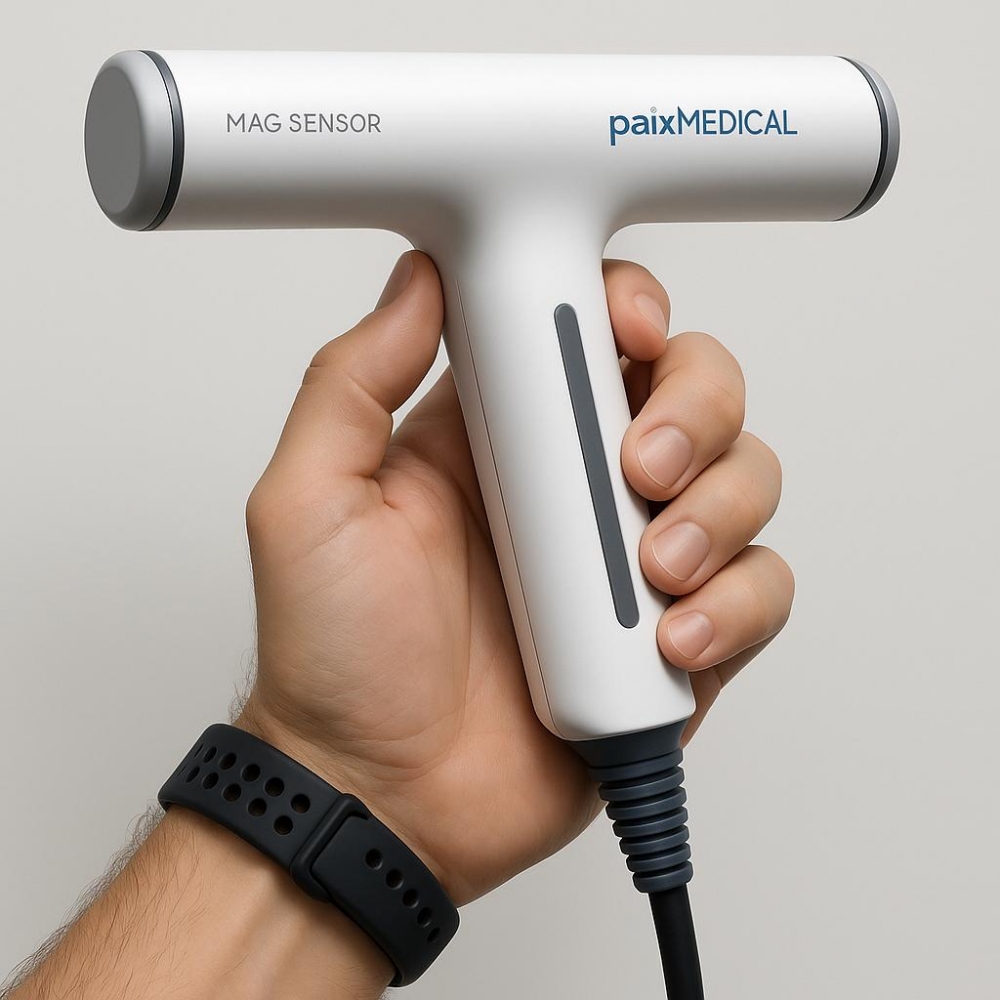
FAPESP-supported startup develops unprecedented technology to democratize digestive system exams with a simple, fast, and accessible procedure.

FAPESP-supported startup develops unprecedented technology to democratize digestive system exams with a simple, fast, and accessible procedure.
A study conducted at São Paulo State University indicates that the non-invasive technique provides lasting benefits by reducing the risk of falls.

A study conducted at São Paulo State University indicates that the non-invasive technique provides lasting benefits by reducing the risk of falls.
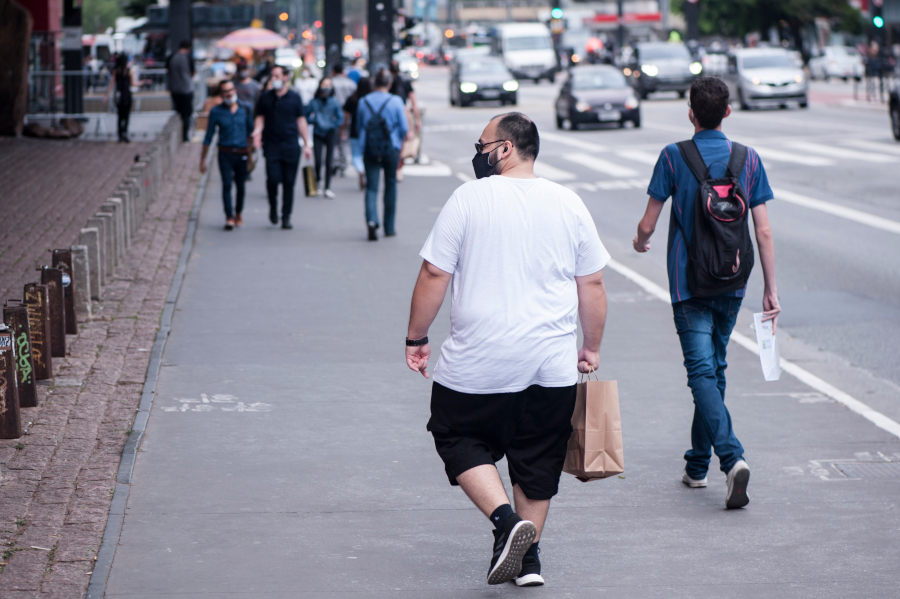

A study of more than 5,000 people over 12 years showed that simple measures to assess the two conditions can facilitate the diagnosis of sarcopenic obesity without complex tests, such as MRI and CT scans. This finding expands access to treatment for older adults.

A study of more than 5,000 people over 12 years showed that simple measures to assess the two conditions can facilitate the diagnosis of sarcopenic obesity without complex tests, such as MRI and CT scans. This finding expands access to treatment for older adults.
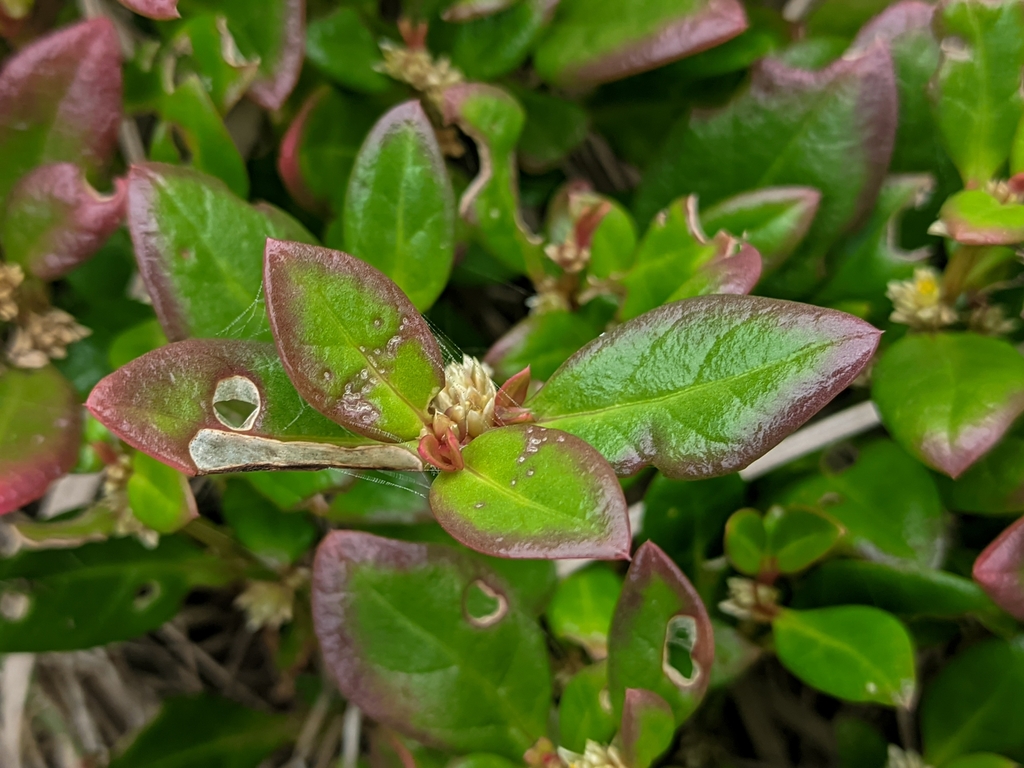

Alternanthera littoralis, also known as Joseph’s Coat, is native to the Brazilian coast and has traditionally been used to combat microbial infections and parasitic diseases.

Alternanthera littoralis, also known as Joseph’s Coat, is native to the Brazilian coast and has traditionally been used to combat microbial infections and parasitic diseases.

A review of 467 studies also points out that, instead of alleviating feelings of fear and anxiety, weapons increase them, as well as exacerbating controlling behaviors and causing domestic violence.

Researchers at São Paulo State University are investigating how hormonal fluctuations throughout a woman’s life influence the immune system and how physical exercise can mitigate these effects.
Study shows that the liver receives and sends a series of metabolism-related products derived from the gut microbiome to the heart.
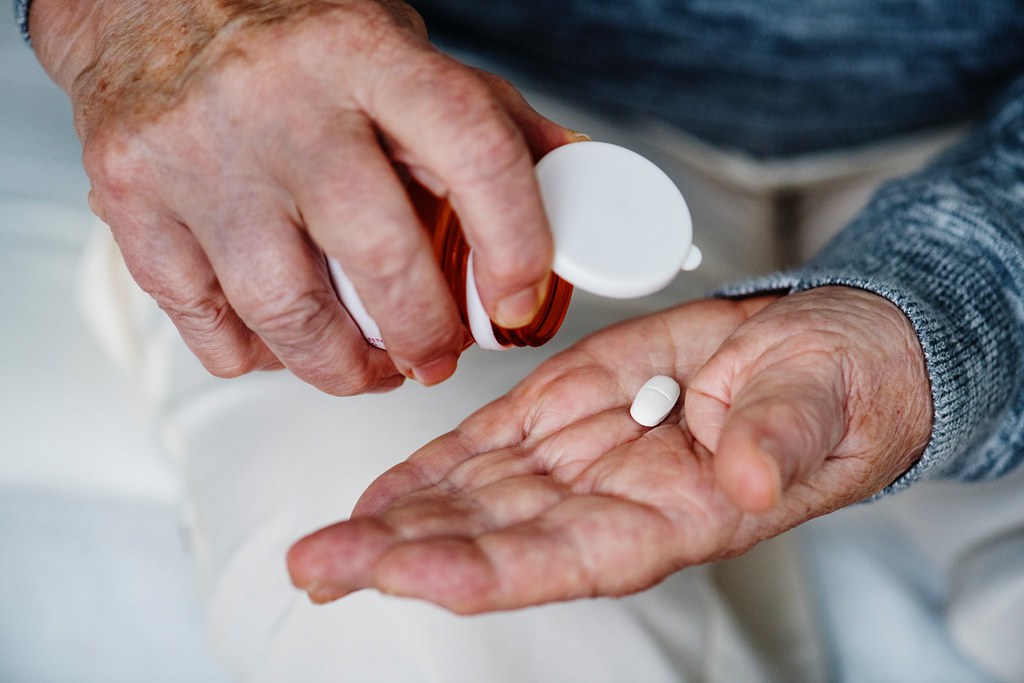

Work carried out at the State University of Campinas used environmentally friendly solvents and ultrasonic waves to remove the substance and increase its absorption by the body.
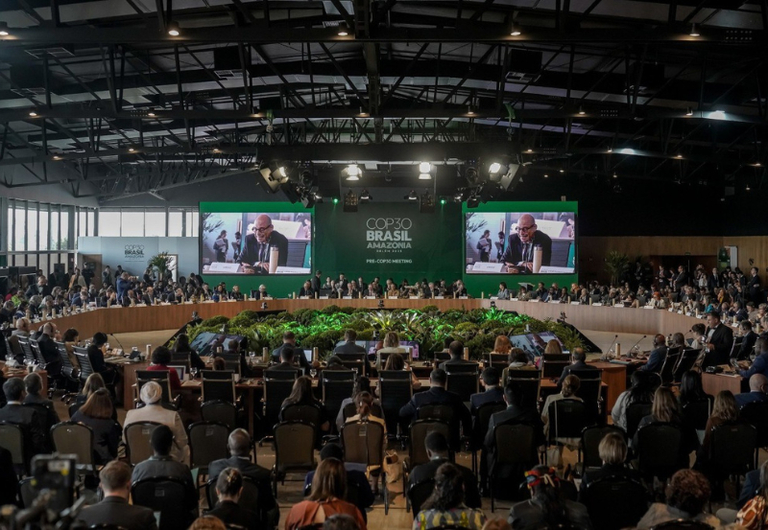

In an article published in a scientific journal, the group emphasizes that Brazil must align its domestic policies with international commitments.

In an article published in a scientific journal, the group emphasizes that Brazil must align its domestic policies with international commitments.