


Researchers from Brazil and Germany study the mechanism of action of phytochemicals from papaya, passion fruit and medicinal plant extracts; results were presented at FAPESP Week Germany.

This is the conclusion of a study conducted at the University of São Paulo with 23 volunteers. The data show that only evening workouts regulated so-called baroreflex sensitivity – a mechanism that compensates for sudden changes in blood pressure.
In a study of 130 volunteers conducted at the Federal University of São Carlos, a drastic decrease in heart rate variability, i.e. the heart’s ability to adapt to environmental and physiological demands, was observed – up to six weeks after infection.
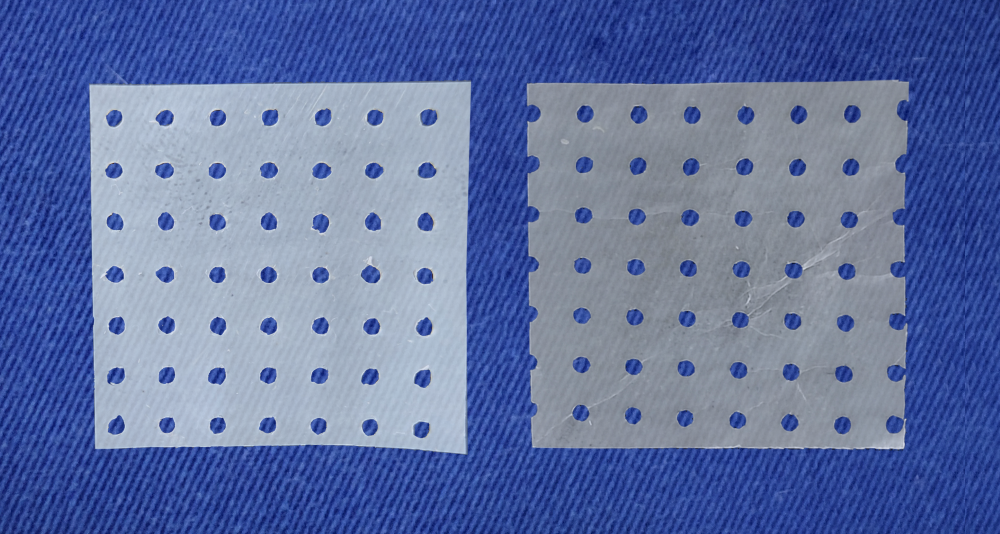
In rodent experiments, a cellulose product with silver nanoparticles was able to reduce microbial colonies in skin lesions, speeding up healing; treatment could benefit people with diabetic foot, burns, and bedridden patients with pressure ulcers.
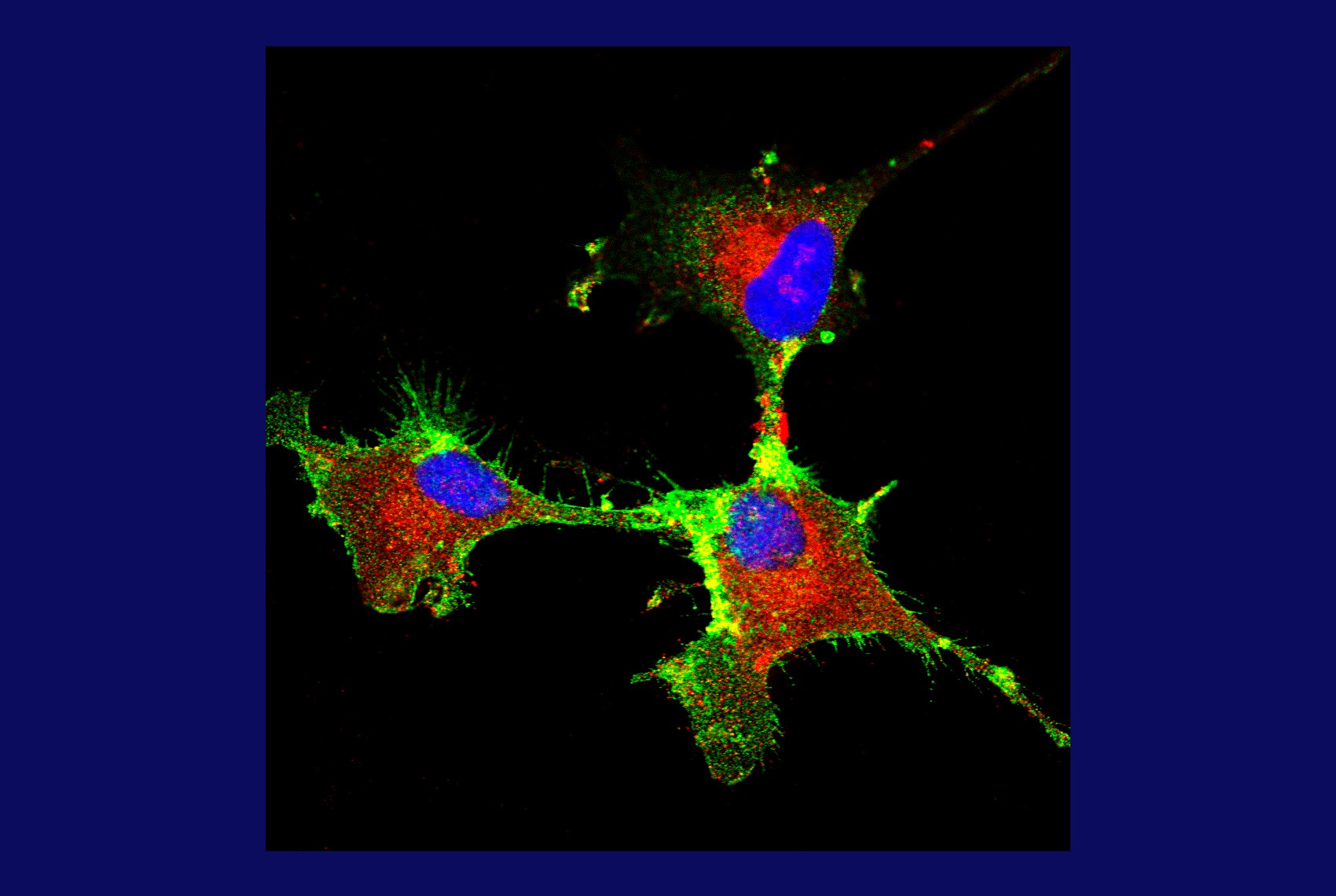
In experiments conducted at the University of São Paulo, tumor stem cells became less able to proliferate and invade tissues when the production of the prion protein was blocked by gene editing; the results suggest that the molecule could be a therapeutic target.

Researchers tested different concentrations of the substance on dental pulp cells. Results show promise for dental tissue repair.
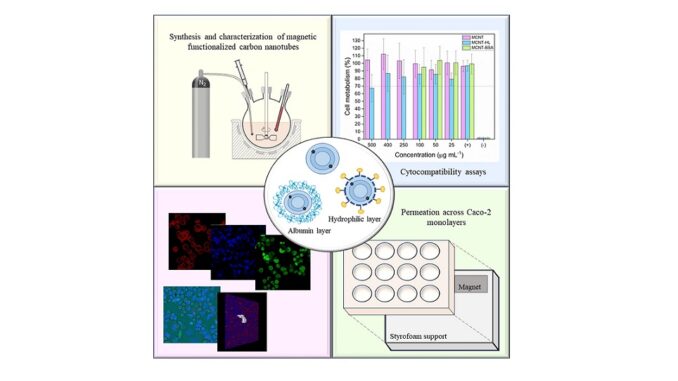
Material shows potential for use in drug delivery and tissue support systems in the human body.

Brazilian researchers have conducted a comprehensive study of the effects of seizures during development. The findings could lead to new treatments for autism, attention deficit disorder, schizophrenia and epilepsy.

Research conducted at the Butantan Institute seeks to identify a compound that can be used in both the prevention and treatment of arboviruses.
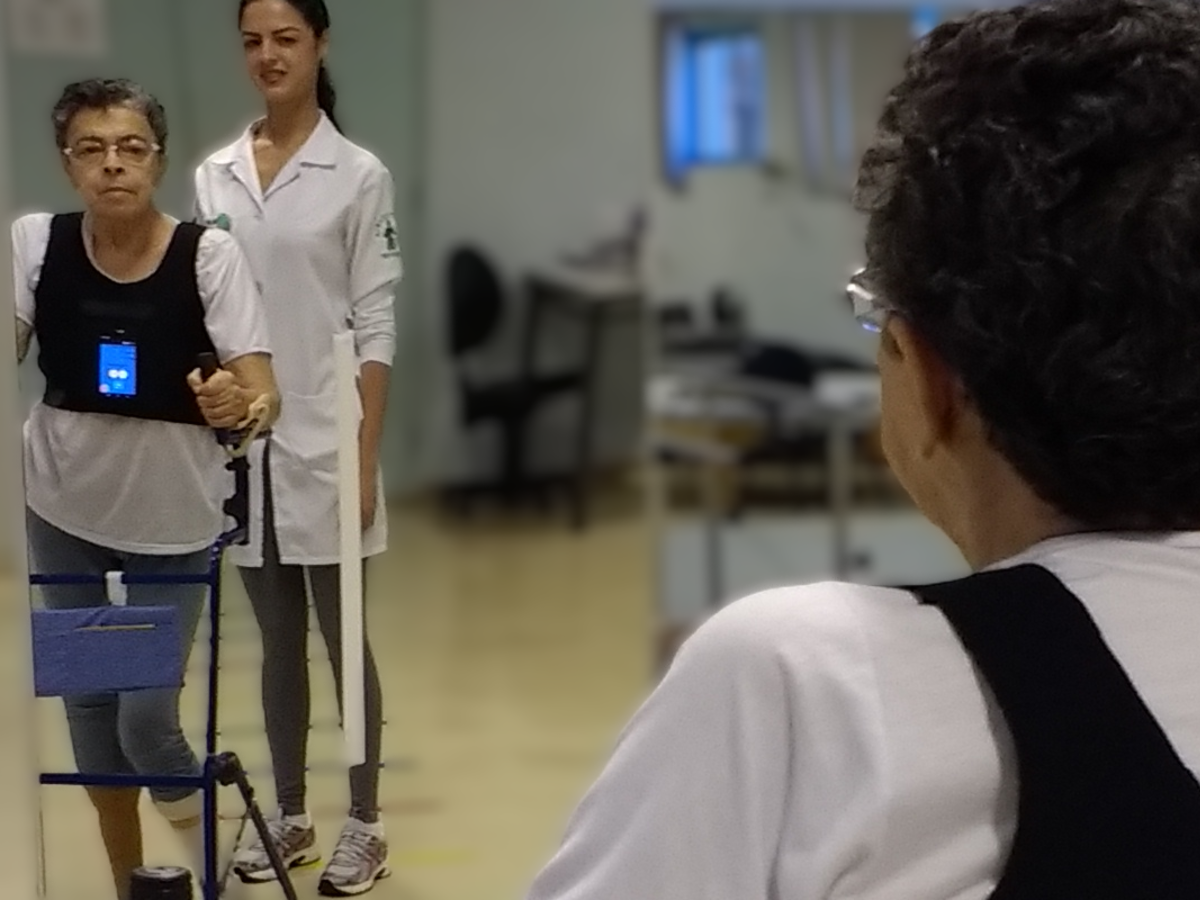

Assistive technology developed at the University of São Paulo helps patients with reduced muscle strength or unilateral paralysis perform daily activities and regain lost body awareness.
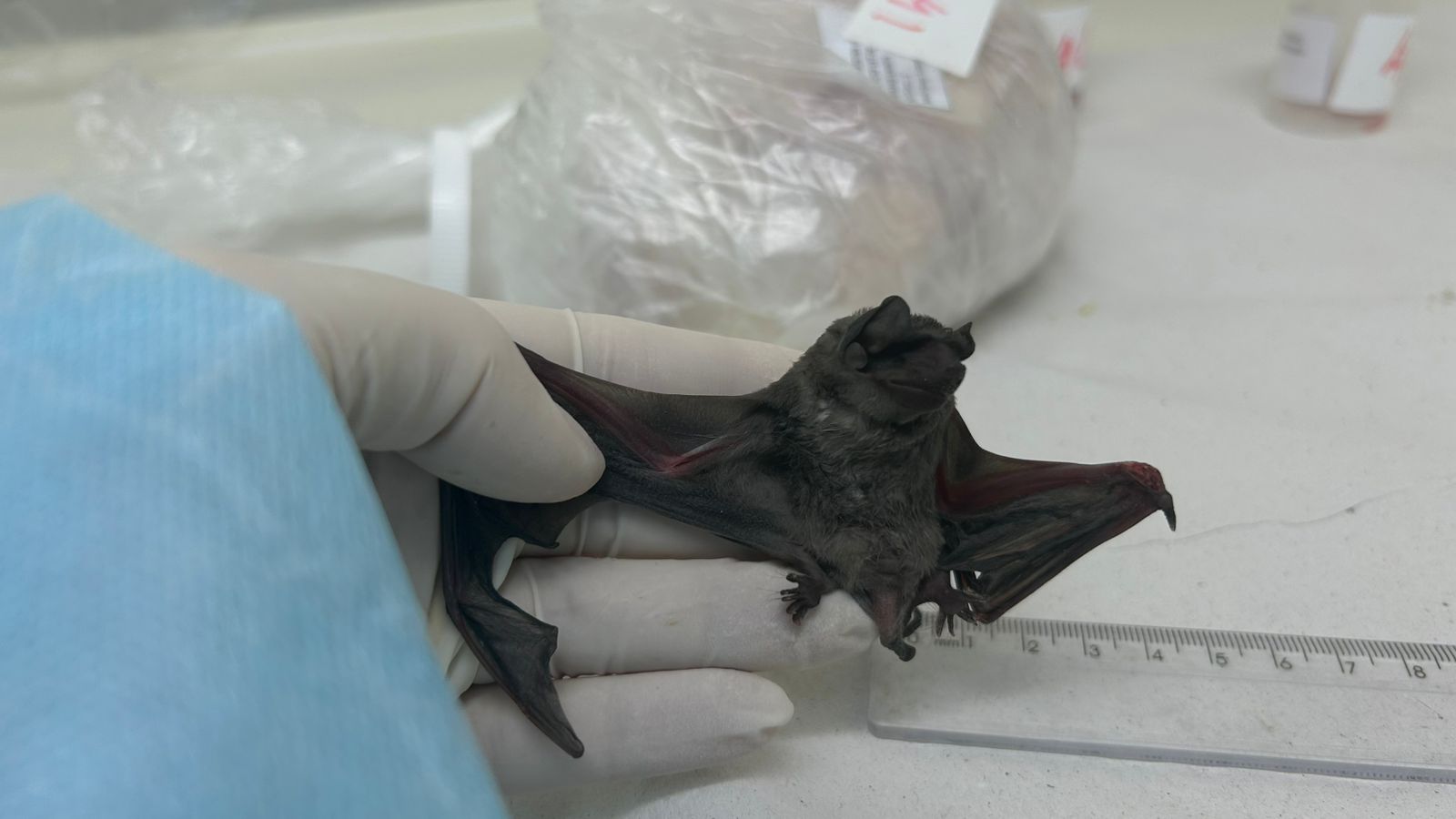

Detected in the state of Ceará, Brazil, the novel coronavirus has similarities with the coronavirus that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome, first identified in 2012. Experiments to find out whether it can infect humans are set to take place during 2025.

Already provided by the UK’s National Health Service, the approach, called PACT, aims to improve communication and interaction by focusing on the child’s interests.

Fish oil supplementation altered the profile of defense cells, which switched from a pro-inflammatory to an anti-inflammatory state, reversing a condition similar to type 2 diabetes.
The method developed at the University of São Paulo detects and distinguishes between antibodies induced by the pathogens in blood samples. The strategy can be used to orient public policy in health and to evaluate the efficacy of dengue vaccines.

Researchers used an innovative approach and analyzed data from a large sample involving residents of four state capitals in different regions of Brazil; study contributes to preventive strategies for this type of tumor.
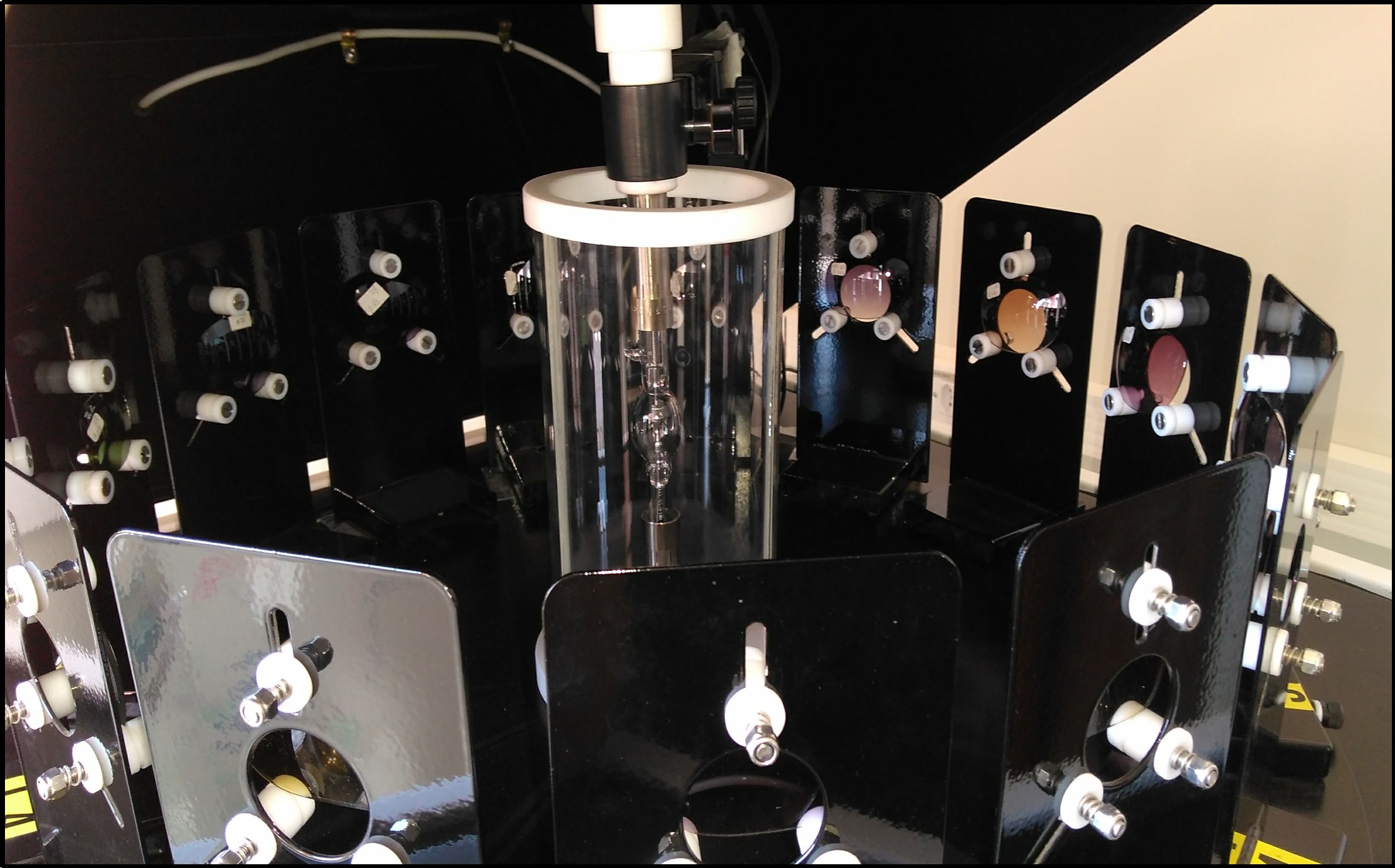

A study conducted at the University of São Paulo analyzed the effectiveness of 12 models and showed that only one met the safety limits set by an international organization.

The conclusion comes from a study that analyzed data from more than 3,600 adolescents aged 14 to 17. Moderate screen time spent on educational activities was associated with less psychological distress.

The world’s largest study of the impact of dietary polyphenol intake on the risk of cardiometabolic problems tracked more than 6,000 Brazilians for eight years.

A study involving 173 pregnant women reached this conclusion. The findings expand scientific knowledge of the preeclampsia and the mechanisms whereby damage to the kidneys, lungs, liver and brain may occur.

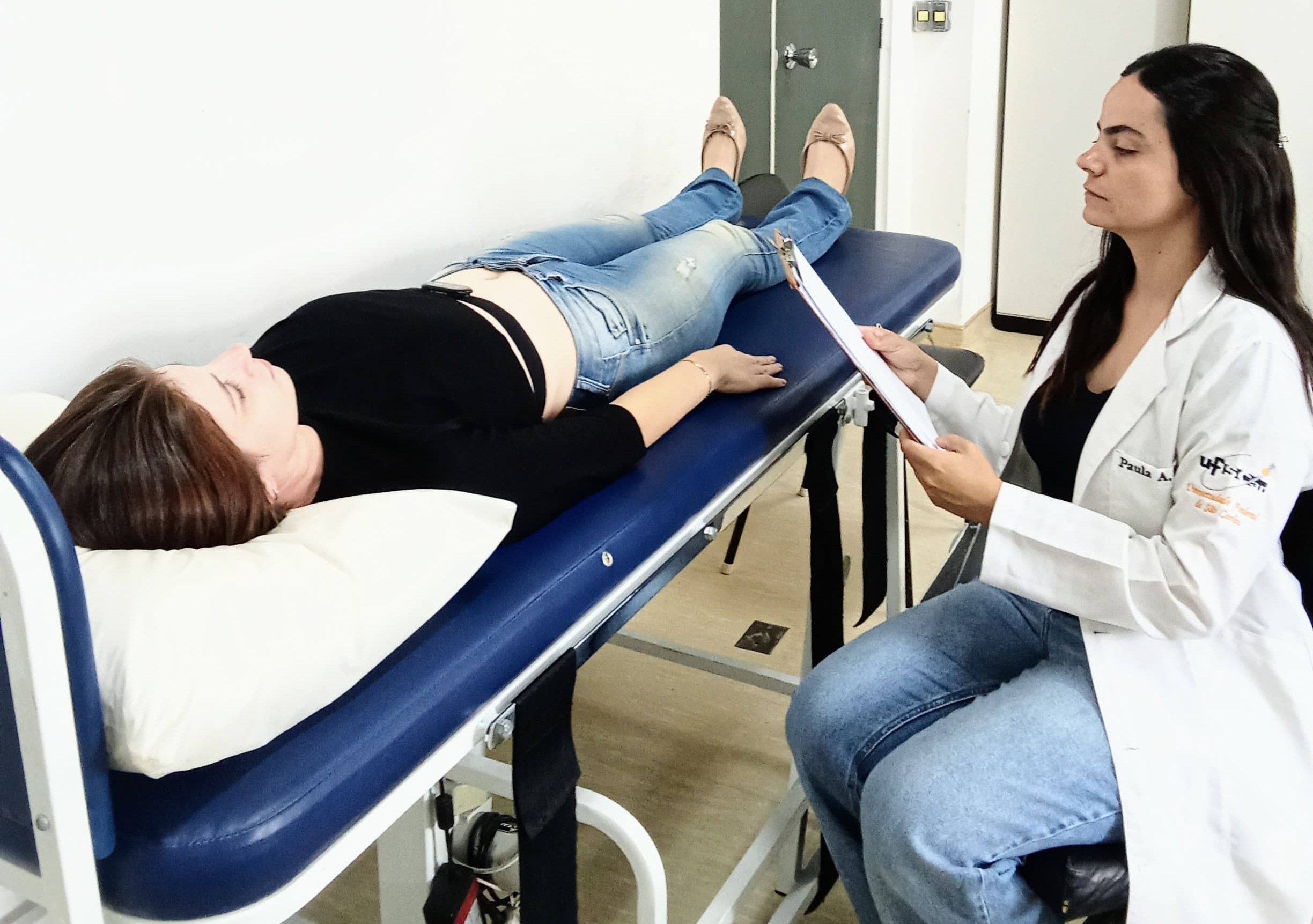
A study of 153 people between the ages of 60 and 89 suggests modifications to a well-established clinical test for assessing balance in the elderly to make it more efficient, accessible, and predictive.
By creating a new metric, researchers envision the possibility of diagnostic and treatment advances for the disease, which is estimated to affect about 4 million people worldwide.

The population is not immunized against DENV-3. Meanwhile, DENV-1 and -2 continue to circulate, experts warn.
Researchers at a FAPESP-supported research center have identified the key role of the GenB2 enzyme in the formation of gentamicin components. The findings make it possible to develop safer and more selective versions of the drug.

The phase 3 clinical trial showed that Butantan-DV is effective against dengue virus types 1 and 2, which were circulating at the time. The results can be extrapolated for types 3 and 4 based on additional in vitro testing, according to the researchers.
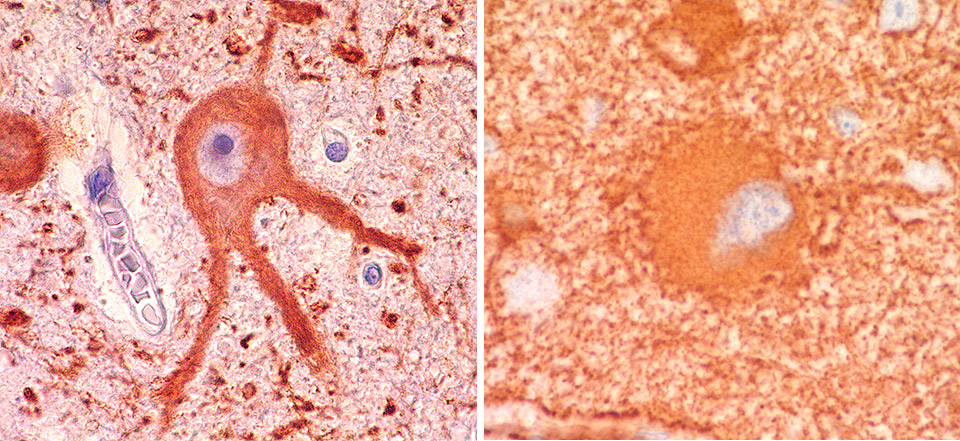
Using a single-cell sequencing technique, it was possible to characterize the different cell types present in the brain lesion. The result paves the way for specific treatments against focal cortical dysplasia.