

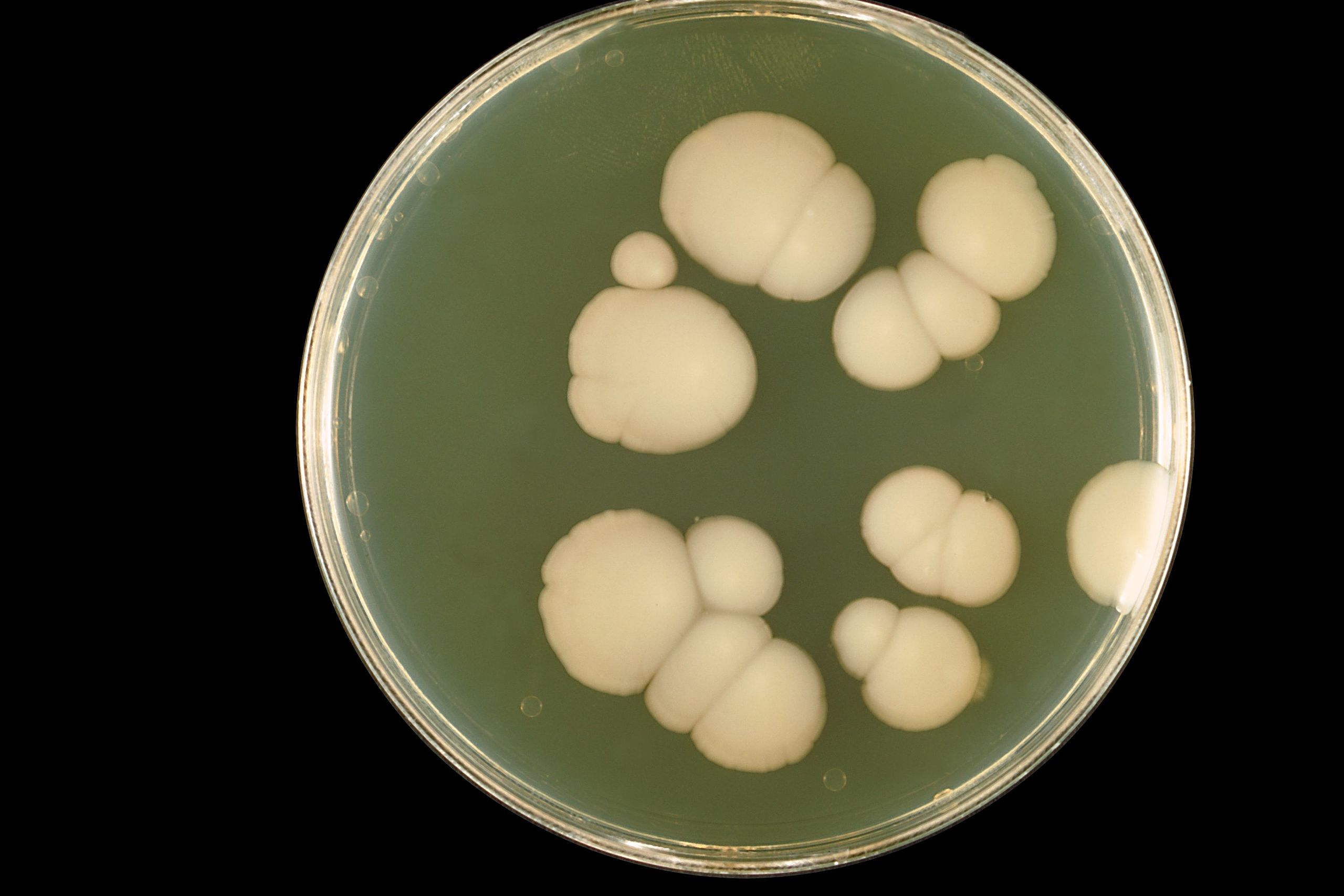
Researchers at a FAPESP-supported research center have managed to reduce Candida albicans’ resistance to fungicides by incorporating photodynamic inactivation techniques into the treatment. The results of the study indicate that the technology can be used in both human healthcare and the prevention of food contamination.
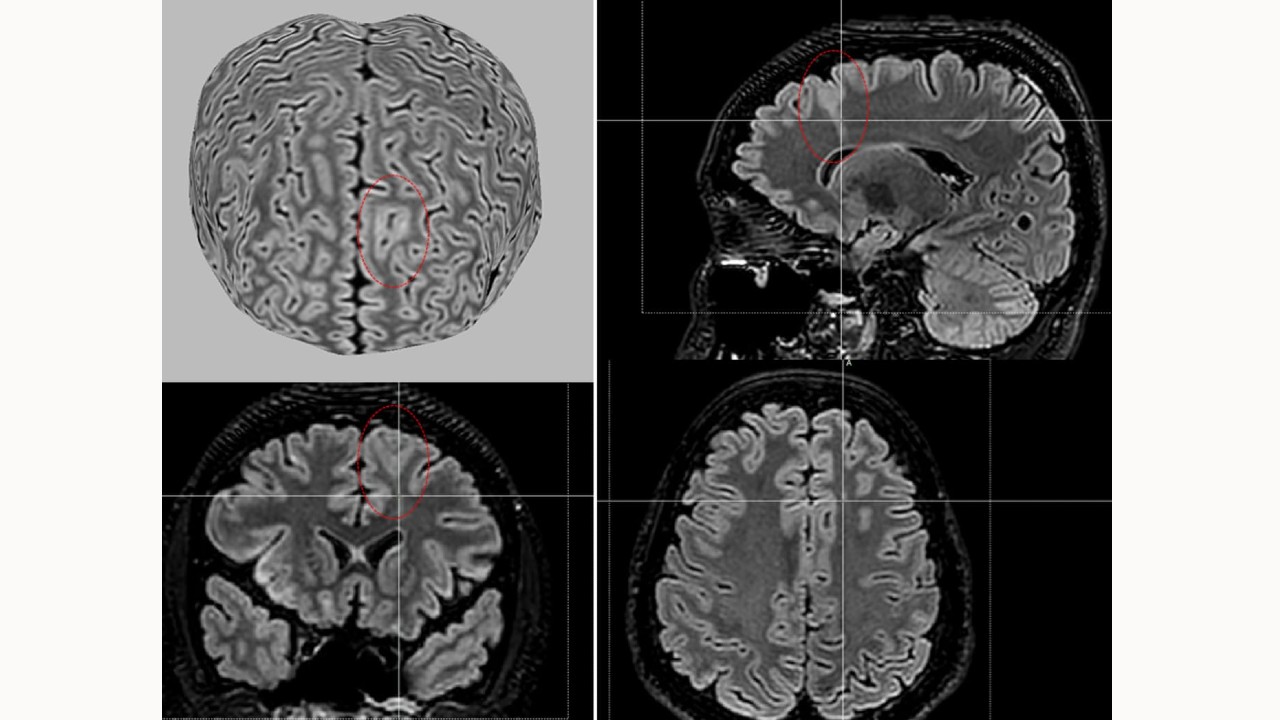
Publicly available algorithm facilitates lesion identification and surgical planning for patients with focal cortical dysplasia, a malformation associated with a drug-refractory form of the disease.

In a study of 141 patients, researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo and collaborators evaluated different models to predict which patients would benefit from risperidone treatment.

In mice, researchers observed increased intestinal stem cell proliferation and organ regeneration in the post-fasting period. However, depending on the diet and genetic profile, this can increase the risk of tumors.
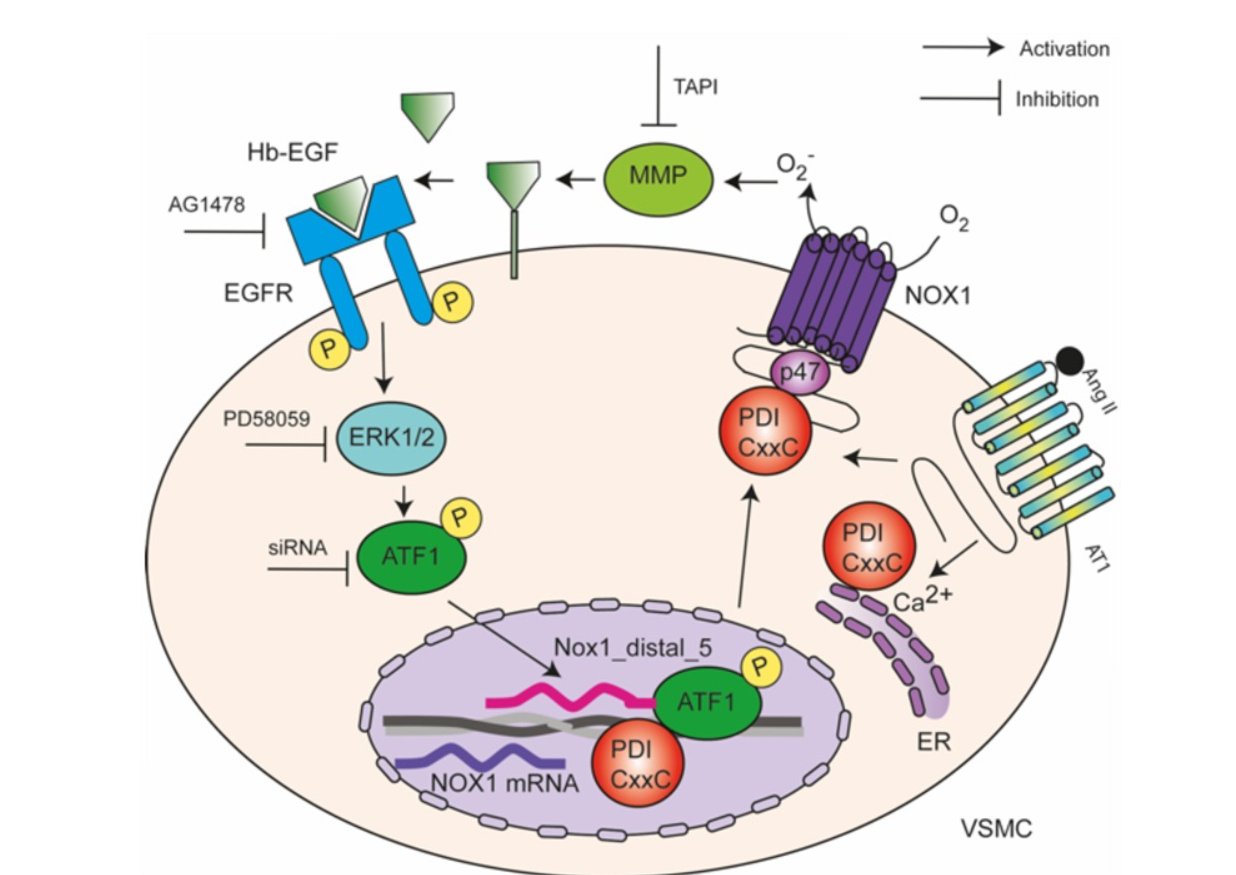
Discovery at the Center for Redox Processes in Biomedicine showed positive results in hypertensive rats and therapeutic potential.
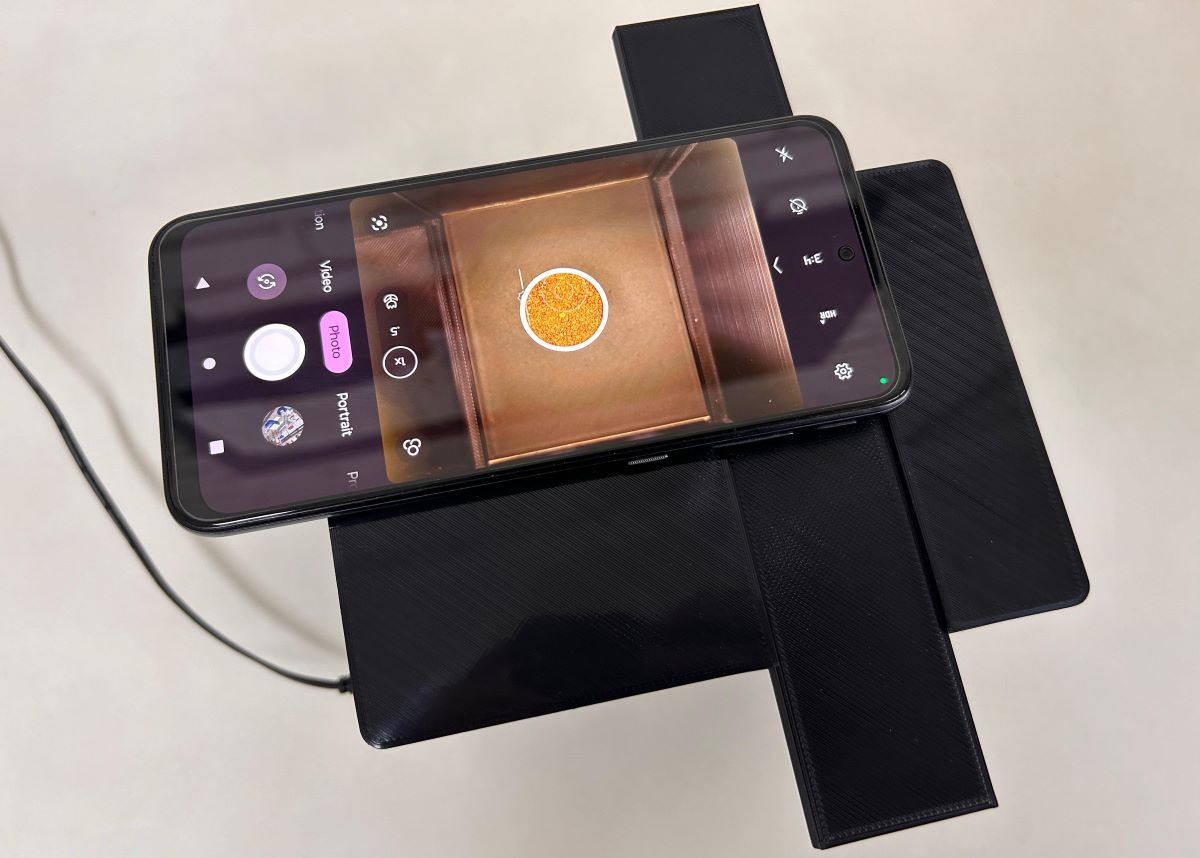

The method is part of a series of international studies on the Canephora species published by Brazilians and can be adapted to identify “fake coffees”.
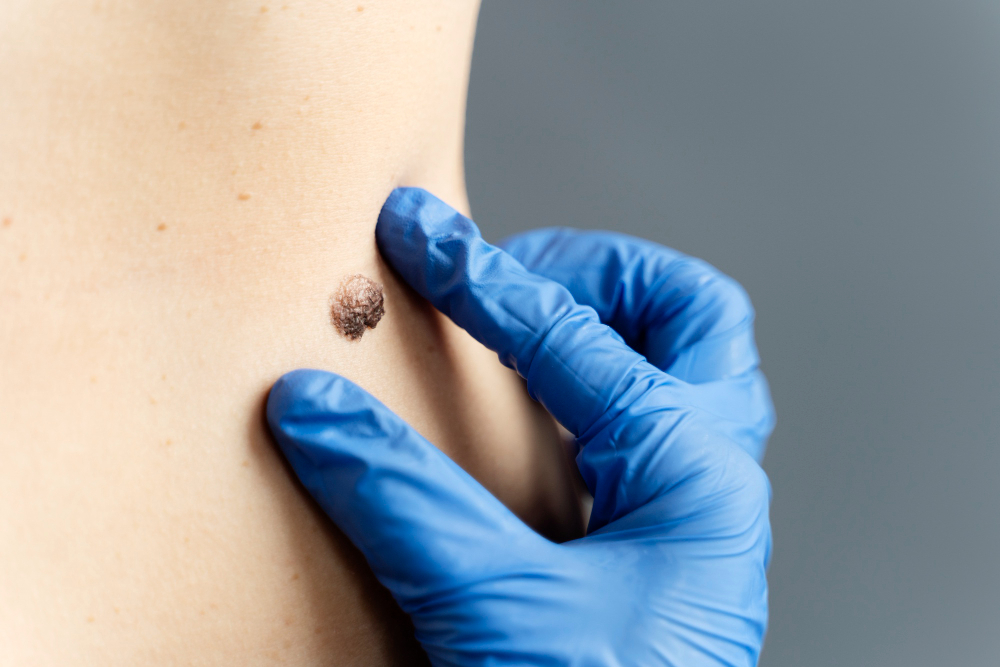
Brazilian researchers develop precision tool that can predict immunotherapy treatment failure, with the potential to personalize therapies and reduce healthcare costs.
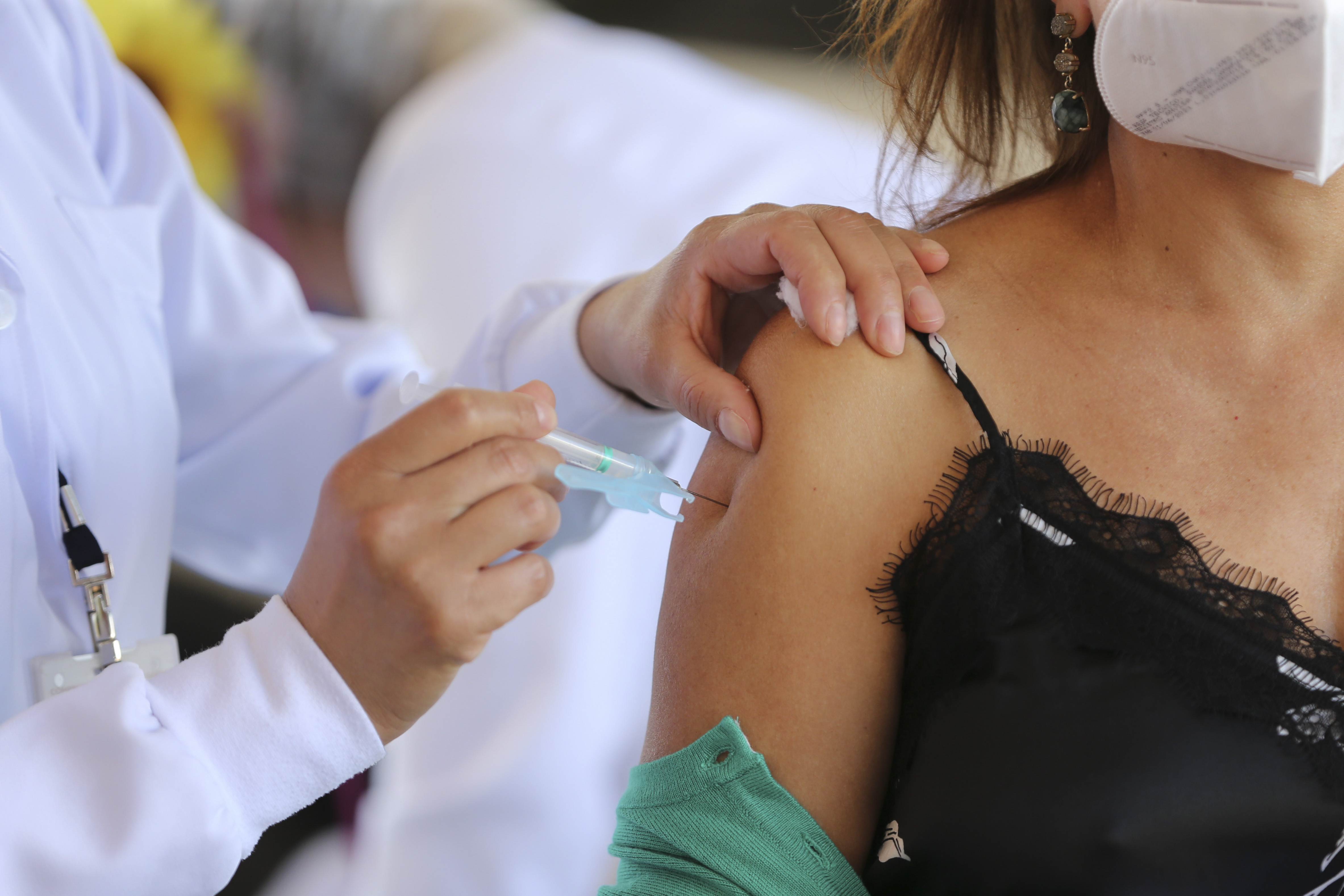
During the pandemic, a preference for domestic vaccines or those from countries such as the United States, Germany, and the United Kingdom was observed for the first time. This phenomenon, known in marketing as the country of origin effect, is usually associated with products that require consumer research before purchase or that have a long tradition in certain countries, such as Swiss chocolates. However, it had never been linked to free vaccines.
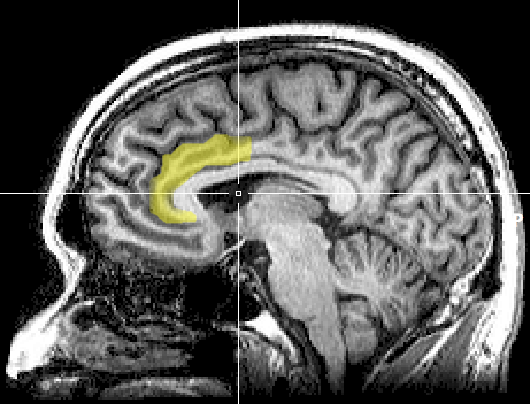
Three promising brain stimulation methods used in medical practice and academic research.

Developed at the University of São Paulo, the model uses protein expression to create a stemness index that analyzes the similarity of tumors to pluripotent stem cells. The article was published in Cell Genomics.
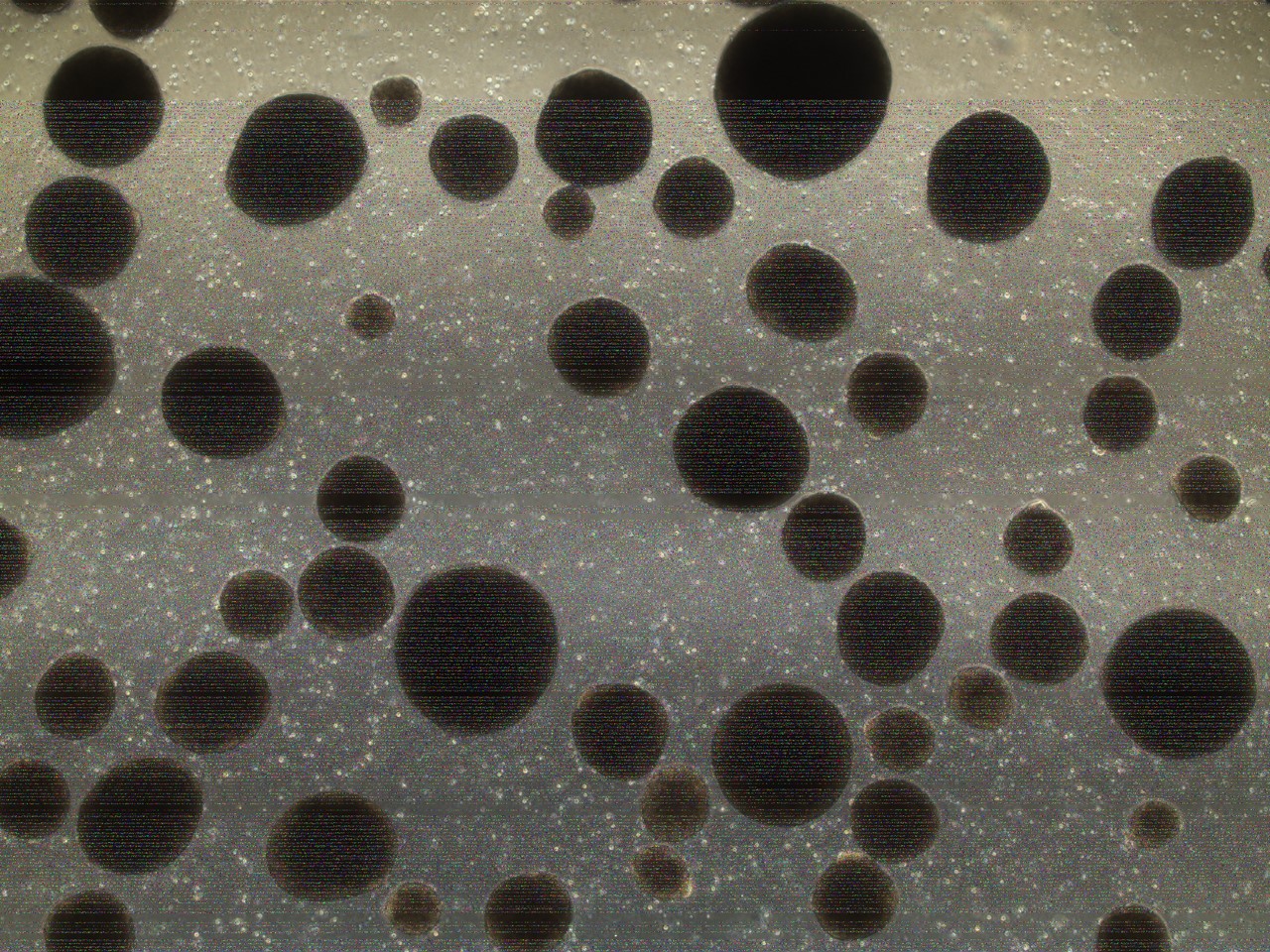
Organoids were developed from the blood cells of centenarians who are part of a project conducted at the Human Genome and Stem Cell Research Center to discover genes that protect the brain from the effects of aging.

Based on the analysis of the genotypes of 500 volunteers, the research project aims to develop a panel of prognostic biomarkers and differentiate Alzheimer’s disease from other types of dementia using blood tests.
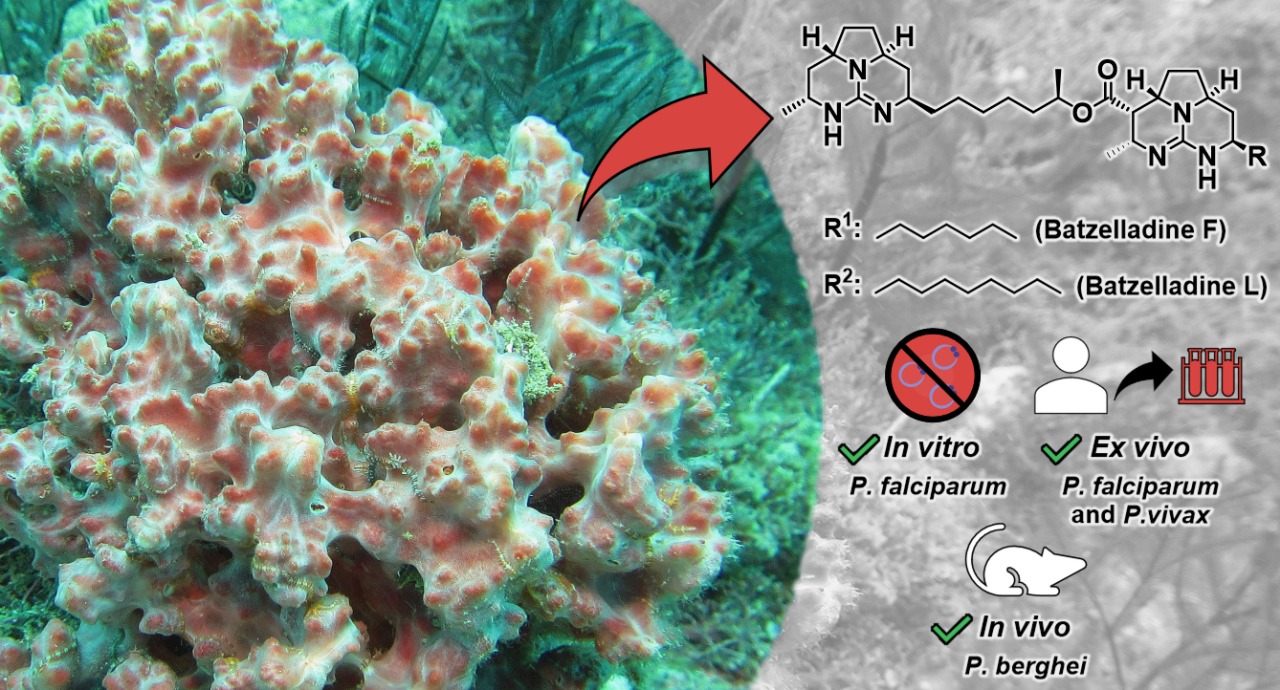
In pre-clinical tests conducted at the University of São Paulo, compounds called batzelladins were effective even against strains of Plasmodium that are resistant to conventional antimalarial drugs.
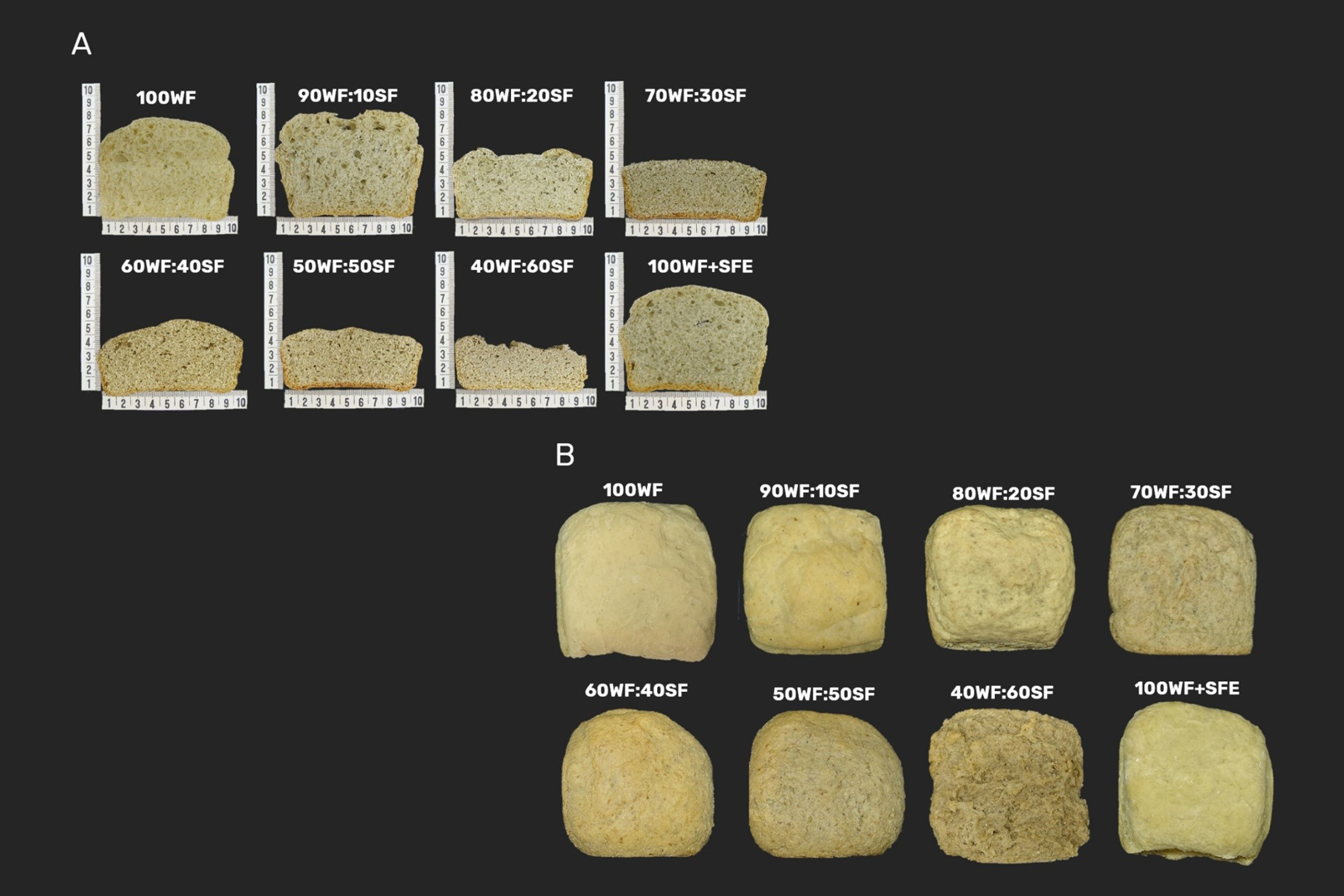

A study by Brazilian scientists shows that a by-product of industrial sunflower oil extraction can be used to produce functional breads with high nutritional value.
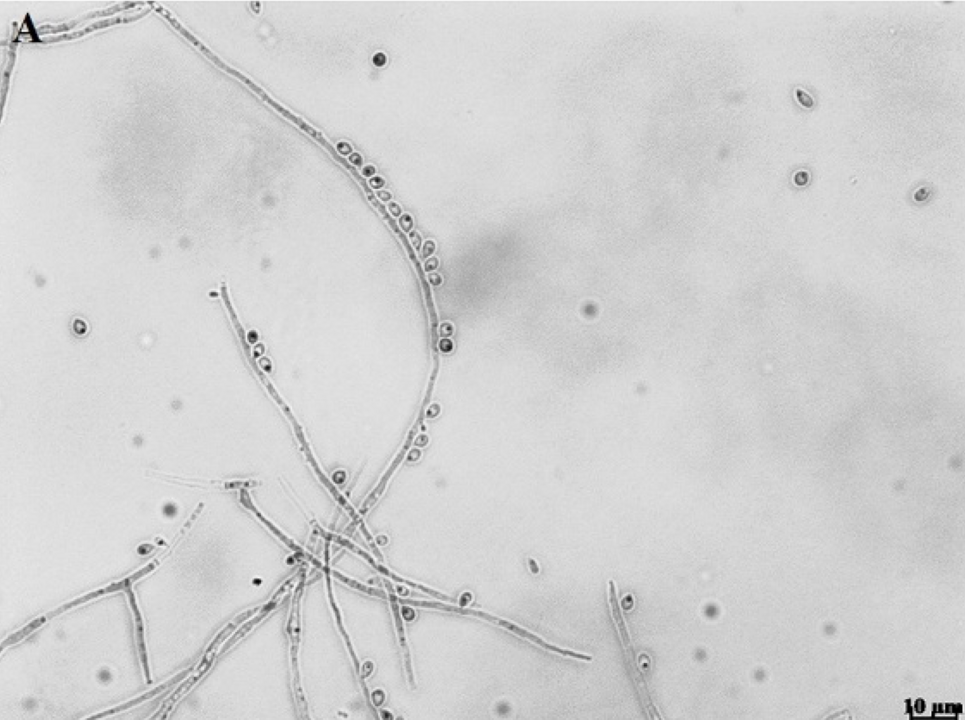
FAPESP will begin supporting the Latin American Center for Medical Mycology, a global network of laboratories led by the University of Exeter in the United Kingdom, which also has a unit in South Africa and will soon open another in Asia. Over five years, the foundation will contribute approximately £ 750,000, while the British institution will invest an additional £ 1 million.
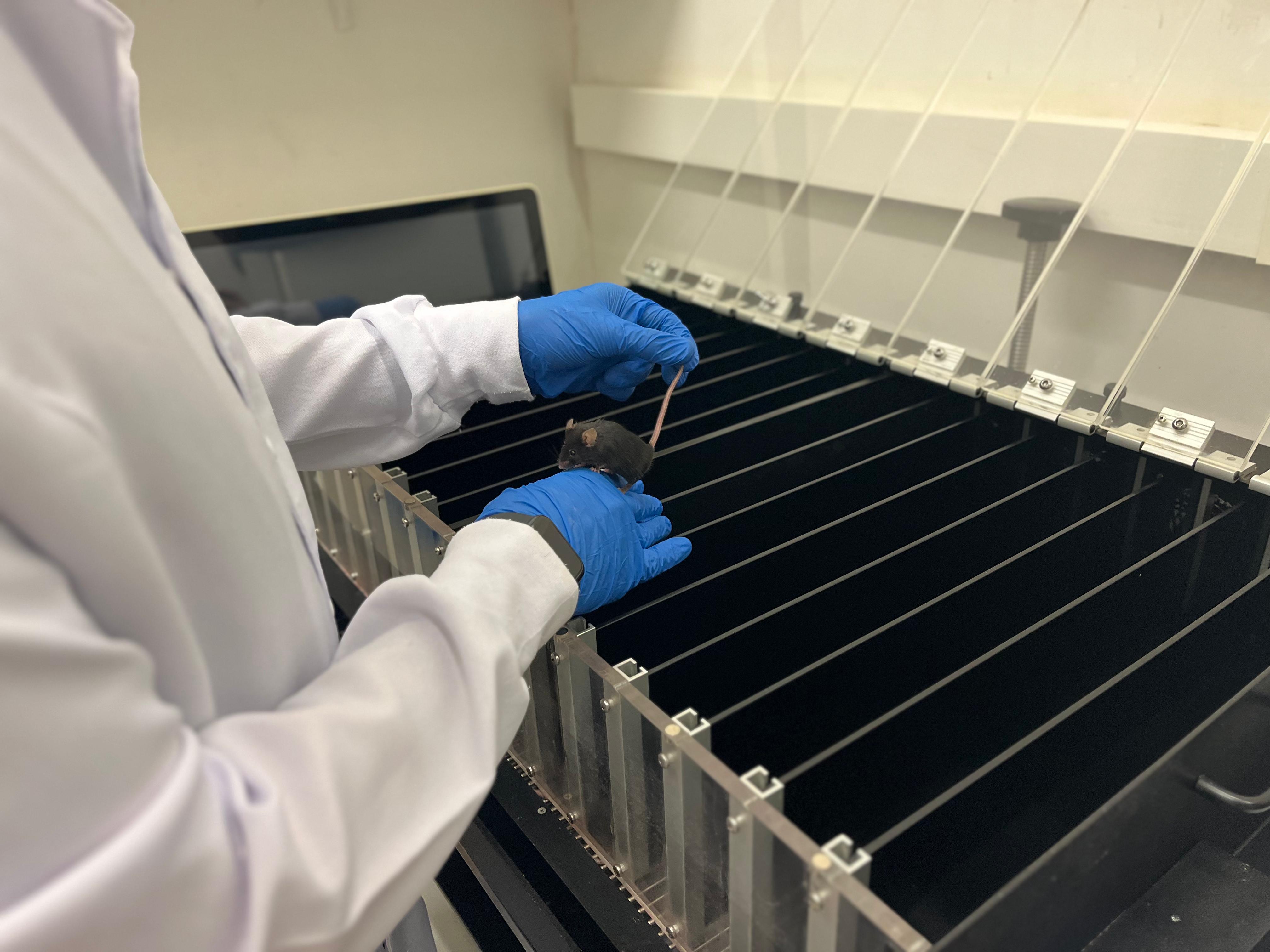
In tests with rodents, researchers from the State University of Campinas and their collaborators found that hyperactivation of the PARP1 protein after exhaustive training was associated with decreased performance, fatigue, and behavioral symptoms of overtraining. Animals treated with a drug that inhibits the molecule’s activity did not exhibit the condition.

A pilot intervention project involving playful activities that engaged motor skills and cognition showed promising results in improving eye movements and reading speed in eleven children with dyslexia.

Blood and urine analyses of the population living in the Mundaú lagoon complex revealed a greater presence of chemical contaminants and metabolic alterations that can exacerbate chronic diseases, such as diabetes and hypertension. These results underscore the need to monitor the health of the inhabitants and control the sources of contamination.
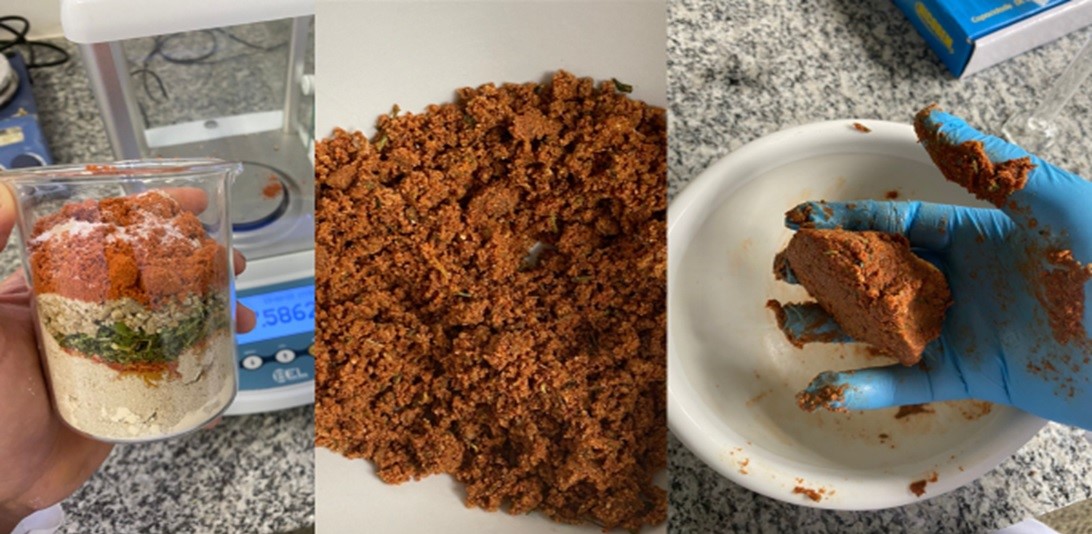

The ingredient, extracted from the plant’s seeds, is a good source of protein and has a neutral flavor and aroma, making it easy to use in food products.
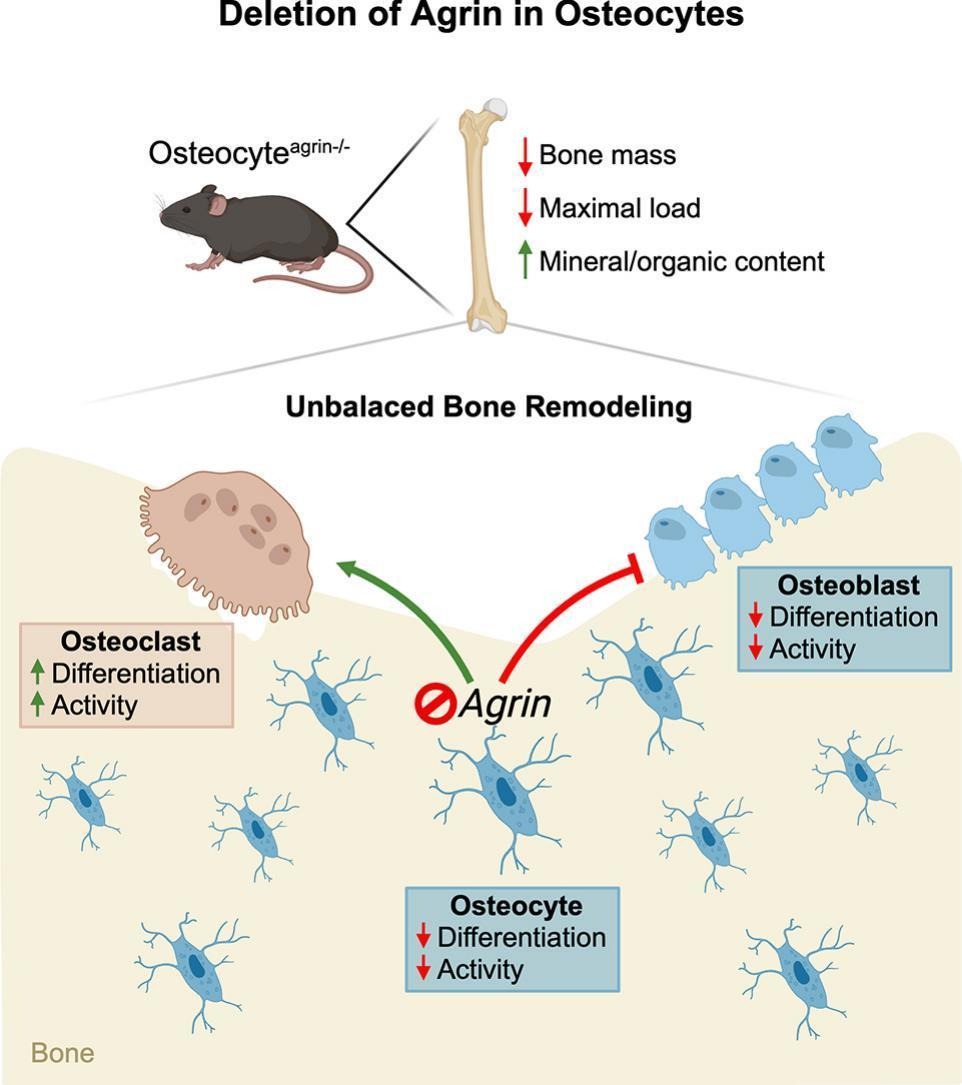
Findings published in the International Journal of Biological Macromolecules could guide studies aimed at treating diseases such as osteoporosis.
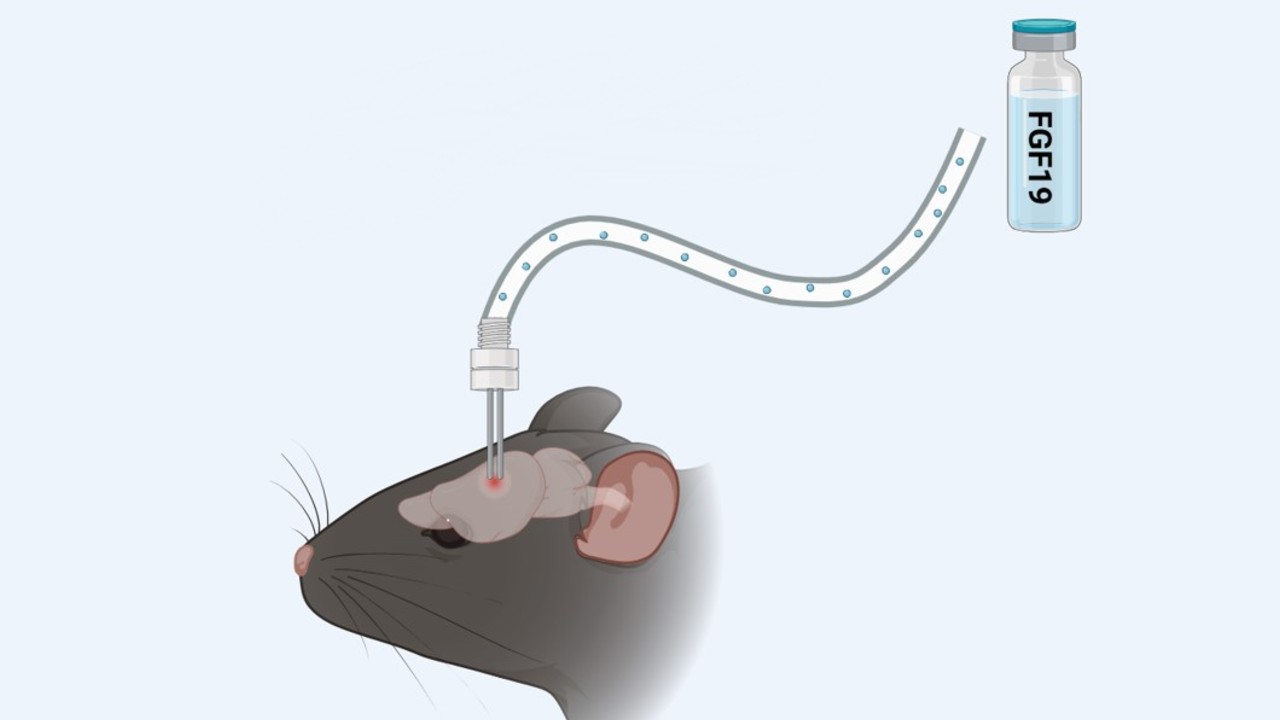
An experiment conducted at the State University of Campinas showed that FGF19, produced in the intestine, acts on specific regions of the brain, causing the body to burn energy to produce heat; the discovery paves the way for new drugs.
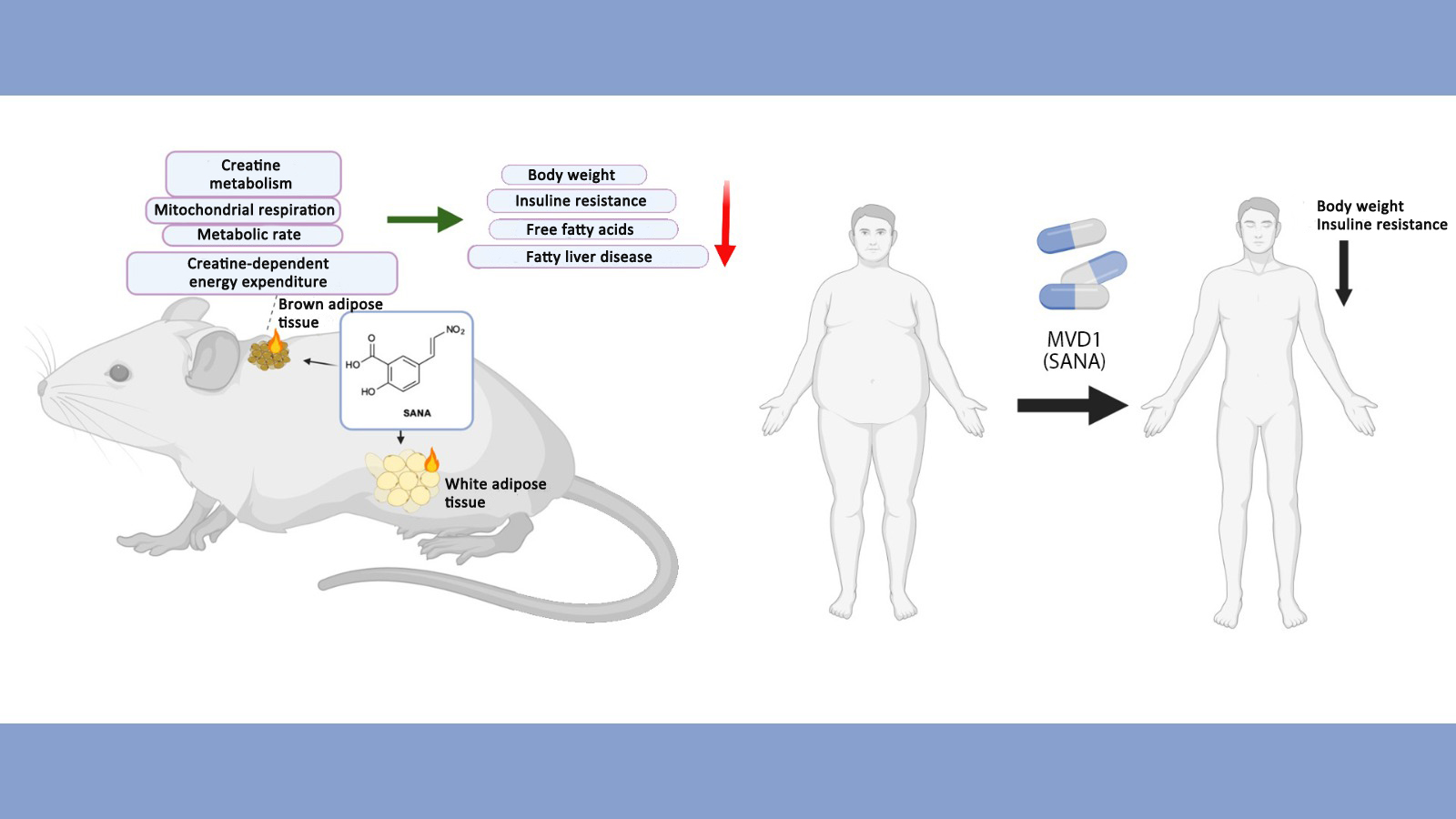
In animal tests, the molecule developed in South America has been shown to prevent fat accumulation and treat existing obesity and associated metabolic disorders. Initial human studies have confirmed the safety of the compound.
The study compared data from patients and healthy individuals from Brazil, Canada, and the United States. The results help paint a clearer picture of how genetics influences the development of OCD.
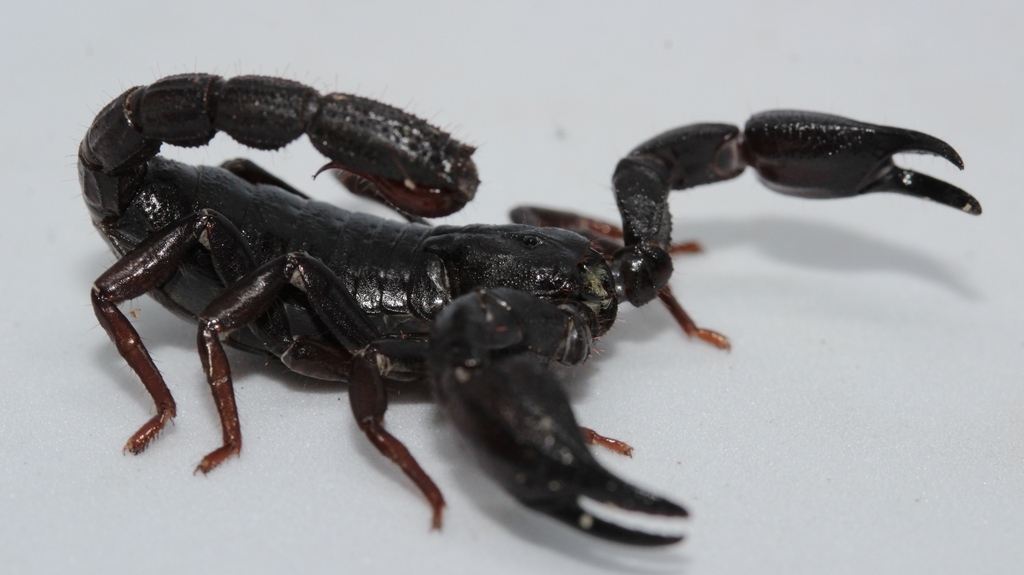

Researchers from the University of São Paulo have identified a molecule in arachnid venom that acts similarly to a commonly used chemotherapy drug for treating the disease; preliminary results of the study were presented at FAPESP Week France.
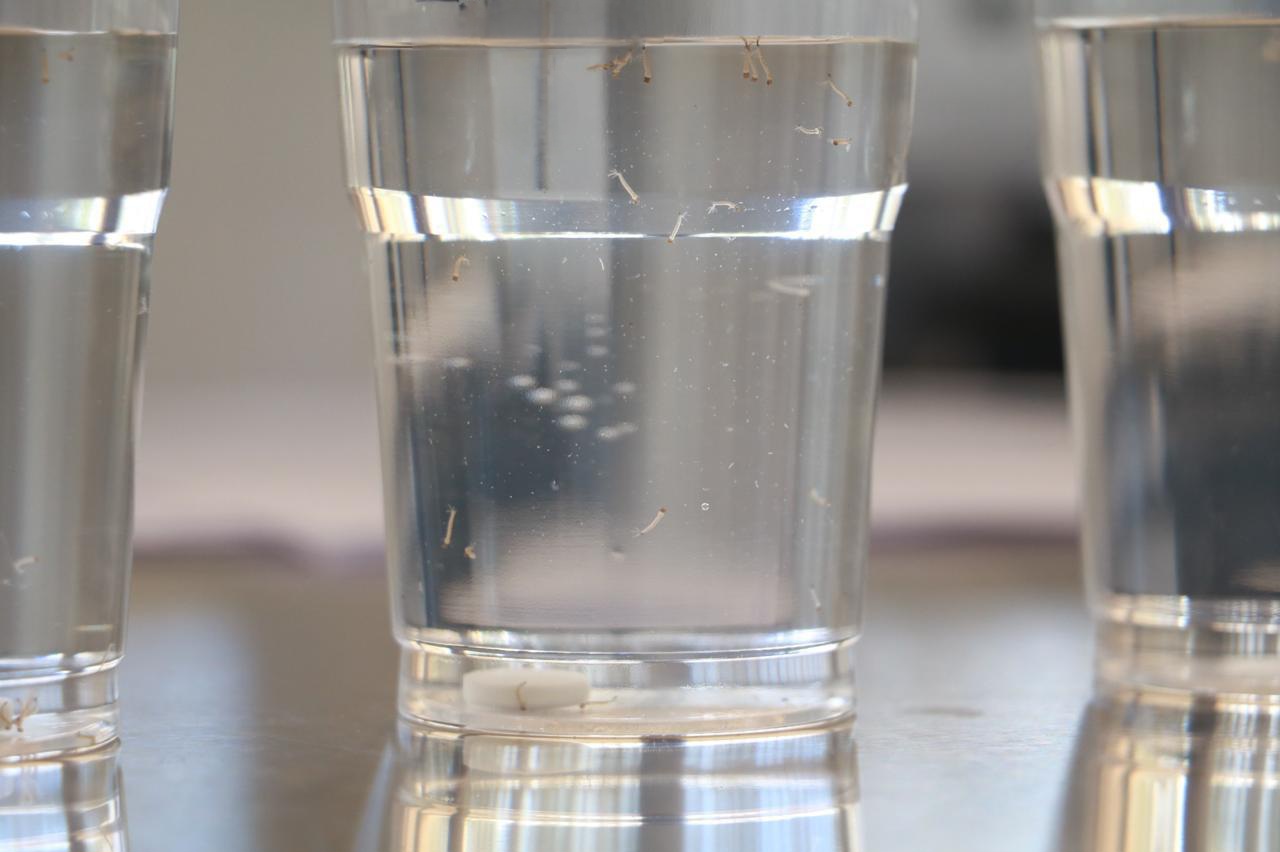

Researchers have found a substance in propolis from bees native to Brazil that kills 90% to 100% of Aedes aegypti larvae. The compound, found in pine sap, is likely enhanced by insect processing and has the potential to help combat mosquitoes that transmit arboviruses.