


The drug accumulates not only in water, but also in sediments and marine organisms, and poses a high ecological risk, said Camilo Seabra, a professor at the Federal University of São Paulo, during FAPESP Week Illinois.
Brazilian scientists conducted the first research project to evaluate the immunity induced in an actual group of vaccinated subjects. Their findings are reported in the Journal of Medical Virology.
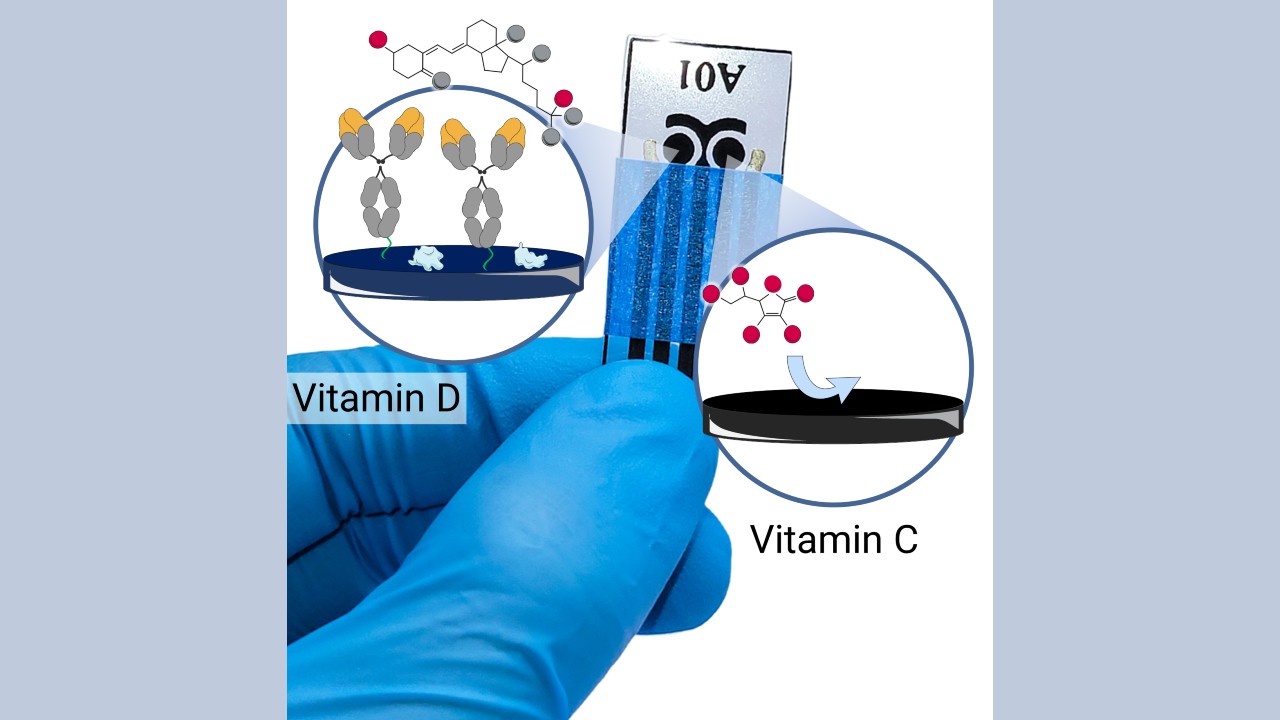
The device was developed at the University of São Paulo and can be used for self-monitoring of micronutrients, assistance with personalized diets, and prevention of deficiencies and toxicity.

The vaccine is being developed by researchers in Brazil. The results of preclinical trials are published in the journal Frontiers in Immunology.

The technology used to sequence the first infections by SARS-CoV-2 at record speed has been successfully tested as a technique to monitor viruses transmitted by mosquitoes, such as dengue, zika, chikungunya and yellow fever.

Researchers supported by FAPESP have created a drug using antibodies for direct application to the skin.

Group from the University of Illinois in Chicago creates program to stimulate math learning through physical activity; results of the work were presented at FAPESP Week Illinois.

Brazilian researchers analyzed more than 200 articles on the subject and identified the types of training most indicated for these cases. Their findings are reported in the journal Psychiatry Research.

In Brazil, researchers analyzed data for 8,384 clinical appointments that took place in a two-year period at Hospital de Base in São José do Rio Preto (São Paulo state) and found the situation to be similar to those in publicly-funded psychiatric outpatient clinics elsewhere in the country. The results, reported in Frontiers in Psychiatry, list the most common mental health problems and most frequently prescribed drugs.
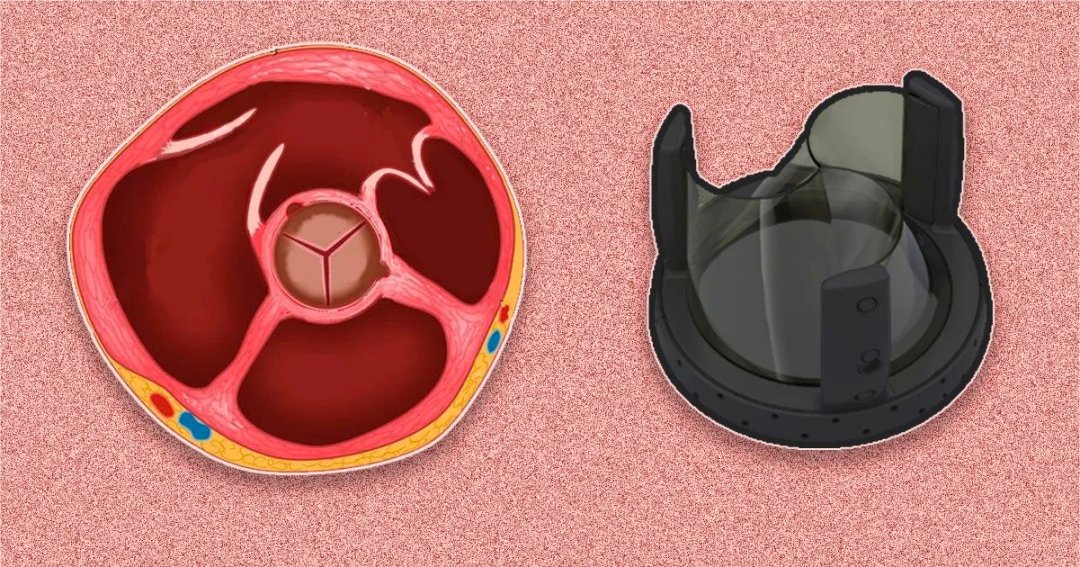
Study developed at Center for Mathematical Sciences Applied to Industry aims to perfect device for cardiovascular treatments.
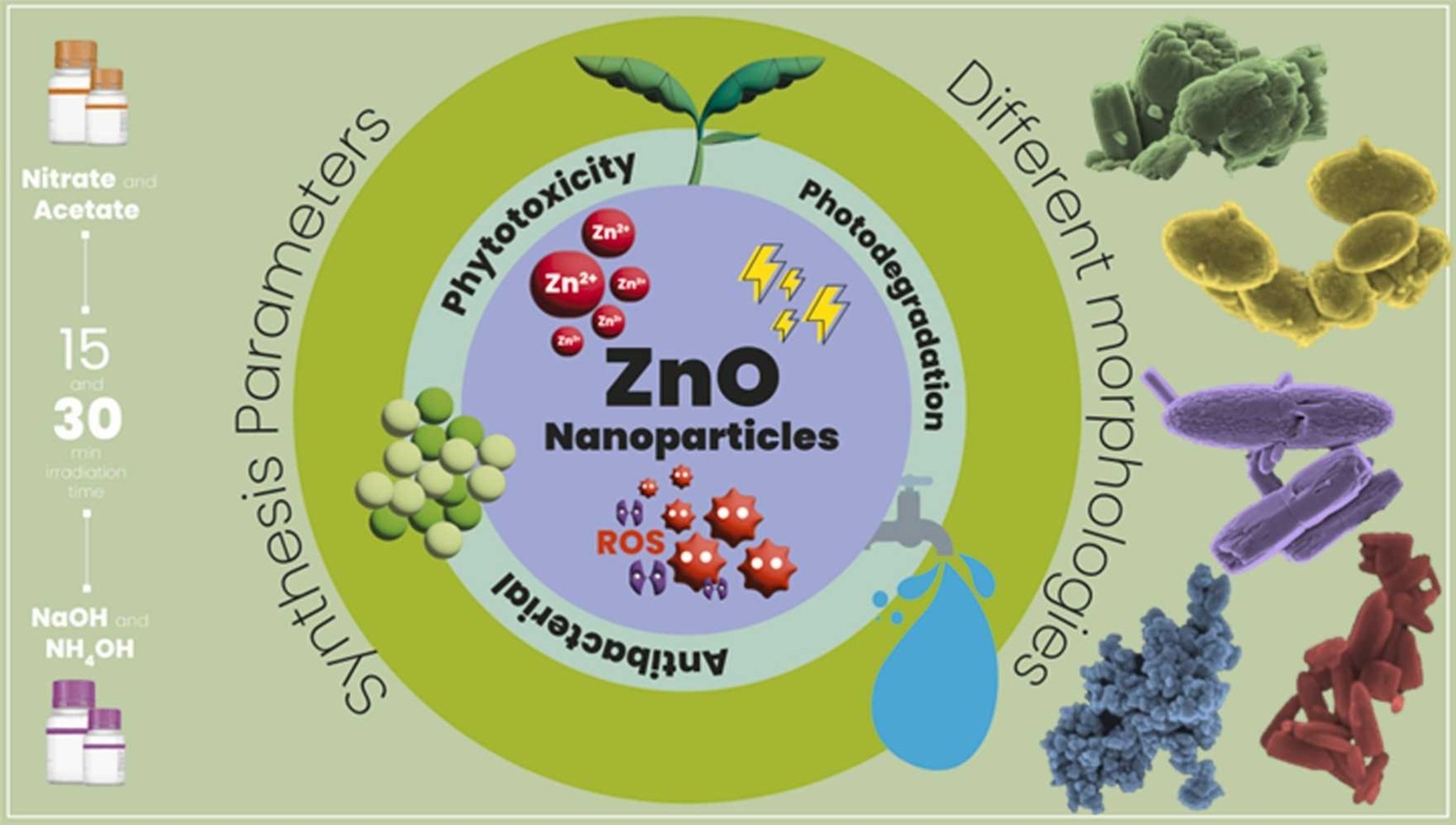
Zinc oxide nanoparticles with varying morphologies were tested against microorganisms isolated from patients. The results are reported in the Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.
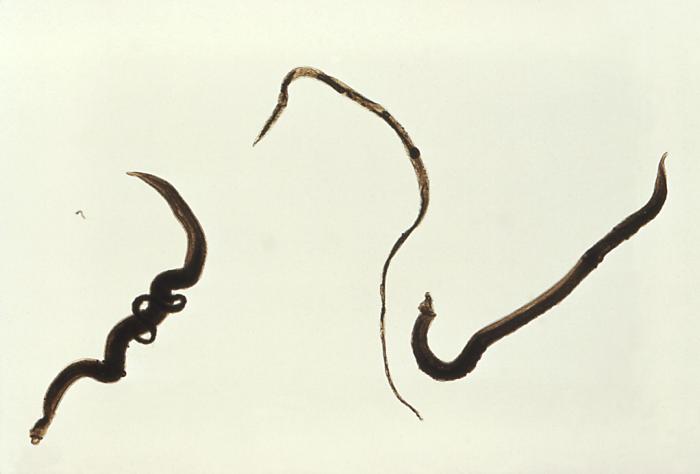

Experiments conducted at Butantan Institute in São Paulo used phage display to screen 12,000 proteins found in Schistosoma mansoni, the worm that causes the disease. The method deployed bacteriophages, viruses that infect bacteria, to identify key parasite peptides.
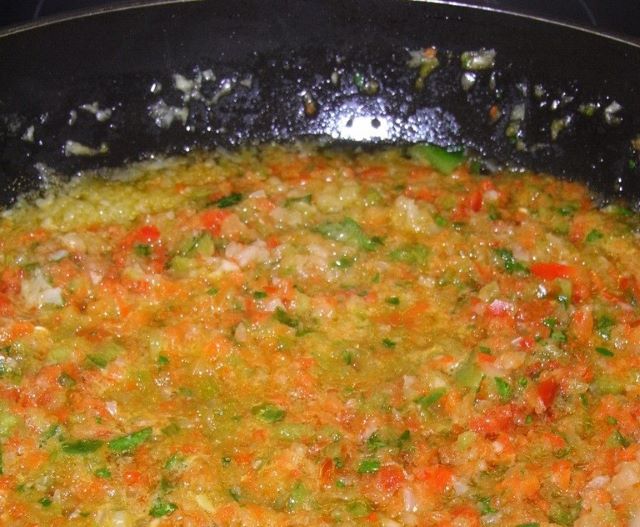

The health benefits of the so-called “sofrito” were observed in experiments with rats conducted by scientists from the Food Research Center and collaborators. The effect may be linked to a compound identified in the animals’ livers called butanediol.
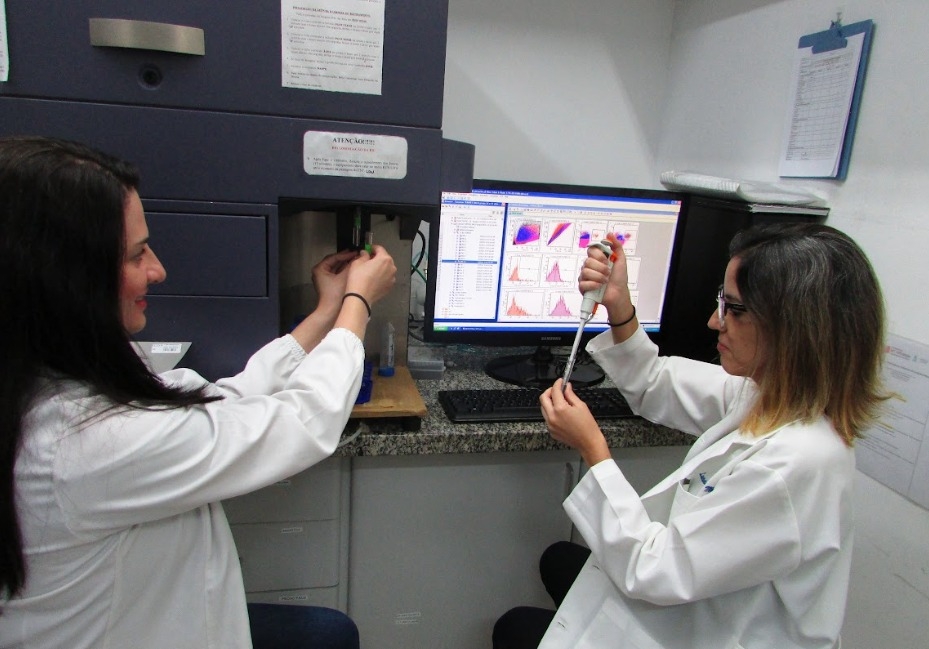

Developed by ImunoTera as part of a project supported by FAPESP, the molecule triggers the immune system’s response to infected cells and helps combat the disease.
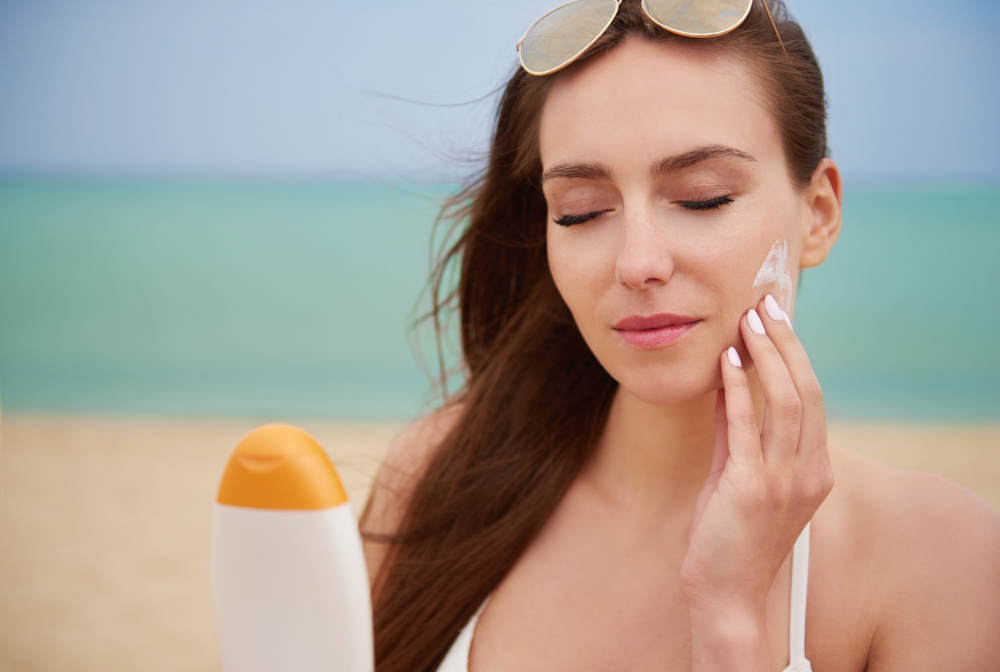

Developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo, the process proposes using silica particles coated with melanin in formulations to protect the skin not only from UVA and UVB rays, but also from visible light.
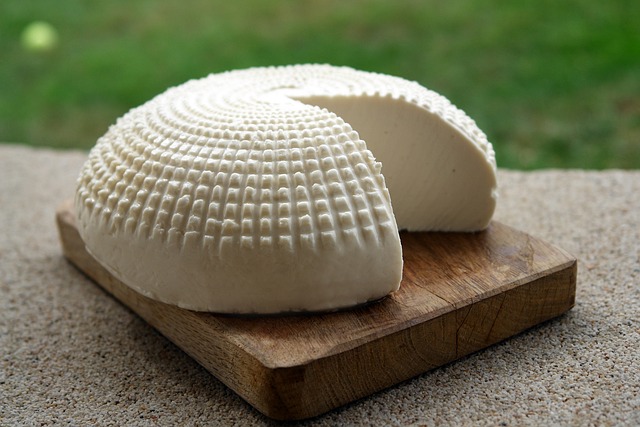

The proposal is being analyzed by an inspection body in the state of São Paulo. In this region alone, there are more than 1,200 informal producers of milk and dairy products with the potential to be regularized.
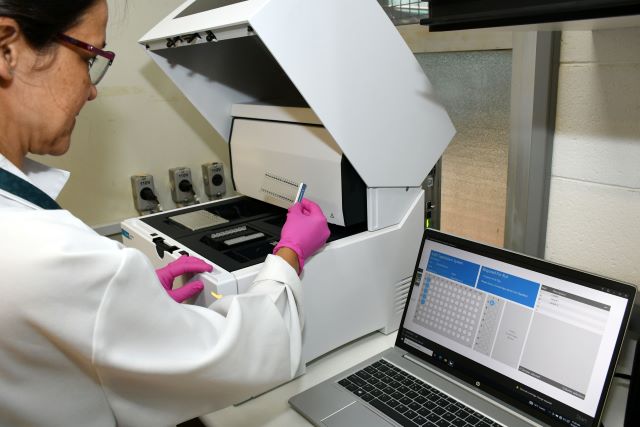

More than 29 thousand patients were analyzed and 26 areas of the genome associated with the disorder were identified; Brazil was the only Latin American representative through the Brazilian Institute of Neuroscience and Neurotechnology of the State University of Campinas.
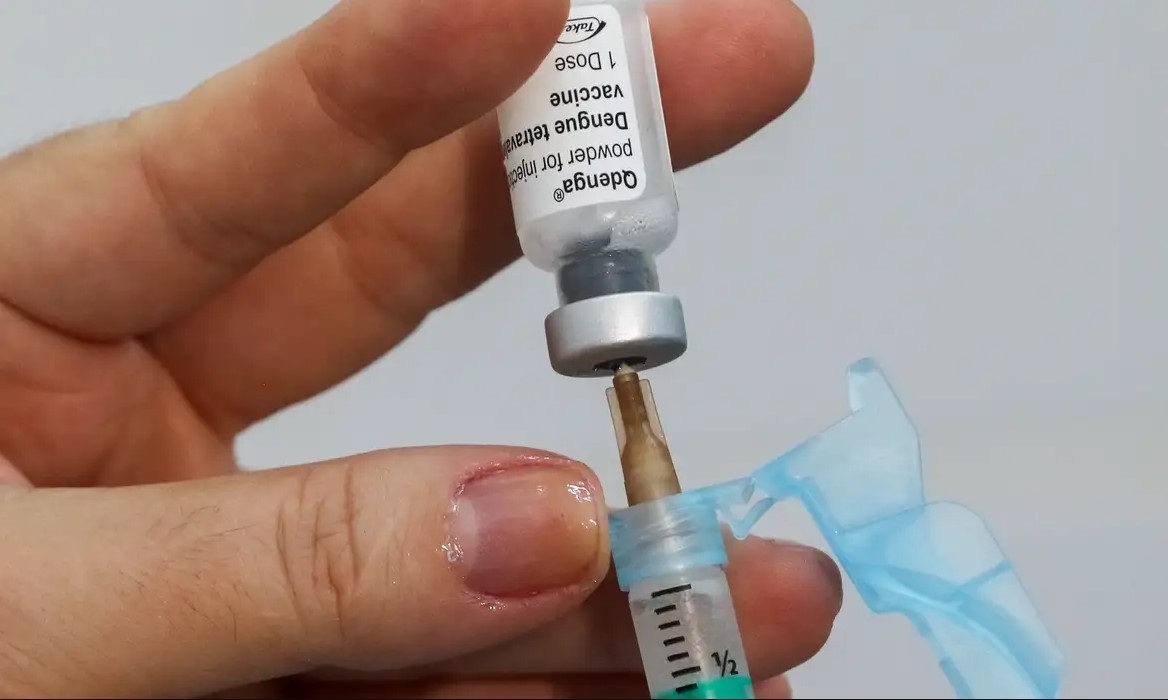
Researchers at the University of São Paulo in Brazil compared data for the immune response induced by natural infection and vaccines. They identified the key factors in the development of long-lasting immunity. Their findings can be used to develop novel vaccines and antiviral therapies.
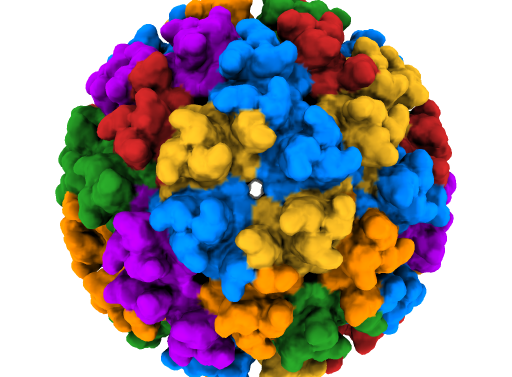
An international team including virologists, physicians, epidemiologists, clinicians, physicists and statisticians has discovered new mechanisms related to central nervous system infection in fatal cases of the infection. The results were published in the journal Cell Host & Microbe.

The findings, published in Psychiatry Research, are an important contribution to both the understanding of mental disorders and suicide prevention.

After inducing mutations in the genotypes of mice and analyzing their effects on several generations of descendants, Brazilian and American researchers mapped the genetic determinants essential to an understanding of cardiovascular disease. Their findings are published in the journal Science Advances.

A formulation developed by Brazilian researchers proved effective in tests involving mice.

The correlation between these two symptoms of the disease was observed by researchers affiliated with institutions in Brazil and France in a systematic review of 20 studies.

Patricia LoRusso, President of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR), gave Agência FAPESP an exclusive interview during a visit to Brazil. She spoke about the importance of attracting early-career researchers to oncology, the future of clinical cancer research, and potential new discoveries in the field.
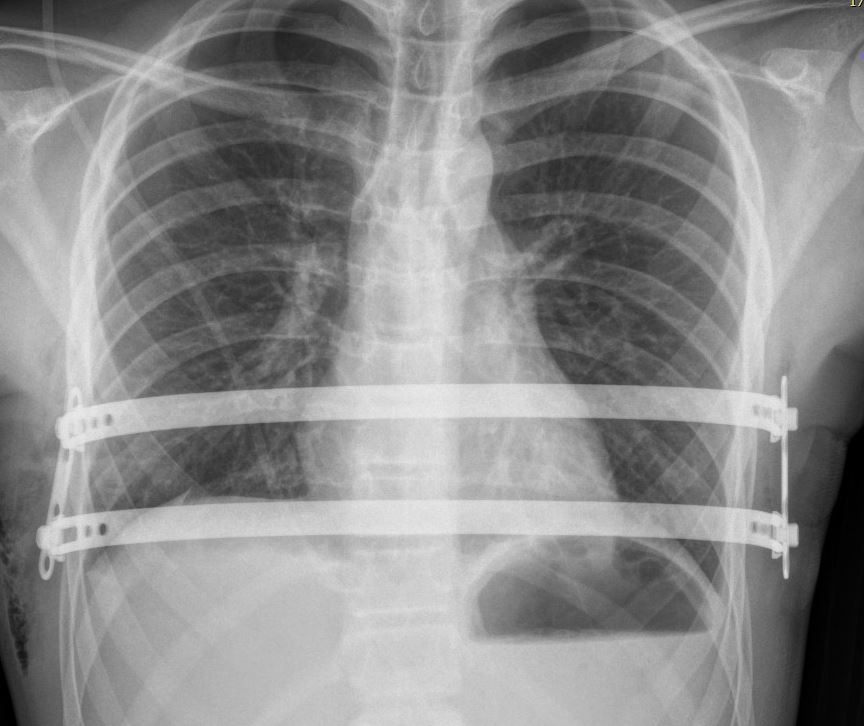
The device was developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo’s Heart Institute (INCOR) and a Brazilian company with FAPESP’s support. It is biocompatible and offers other advantages over the imported product used hitherto.