


Subnational funding agencies and Brazil’s National Scientific Council will partner to allocate almost BRL 60 million to research projects that explore little-known areas of the world’s largest tropical forest.

The researchers correlated data on the animal’s ecological niche and connectivity among populations with existing and planned hydropower development sites in Brazil’s South region. They estimated that 30% of its habitat could be lost, heightening the risk of extinction.
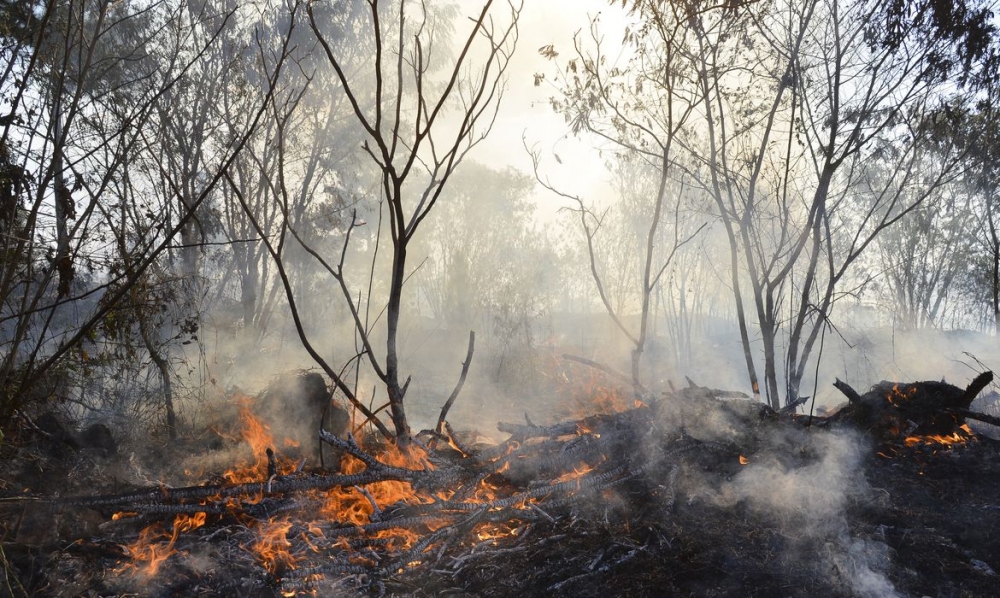

Available free of charge on the internet, the platform simulates fire propagation in the savanna biome three times a day and is in use in nine conservation units.
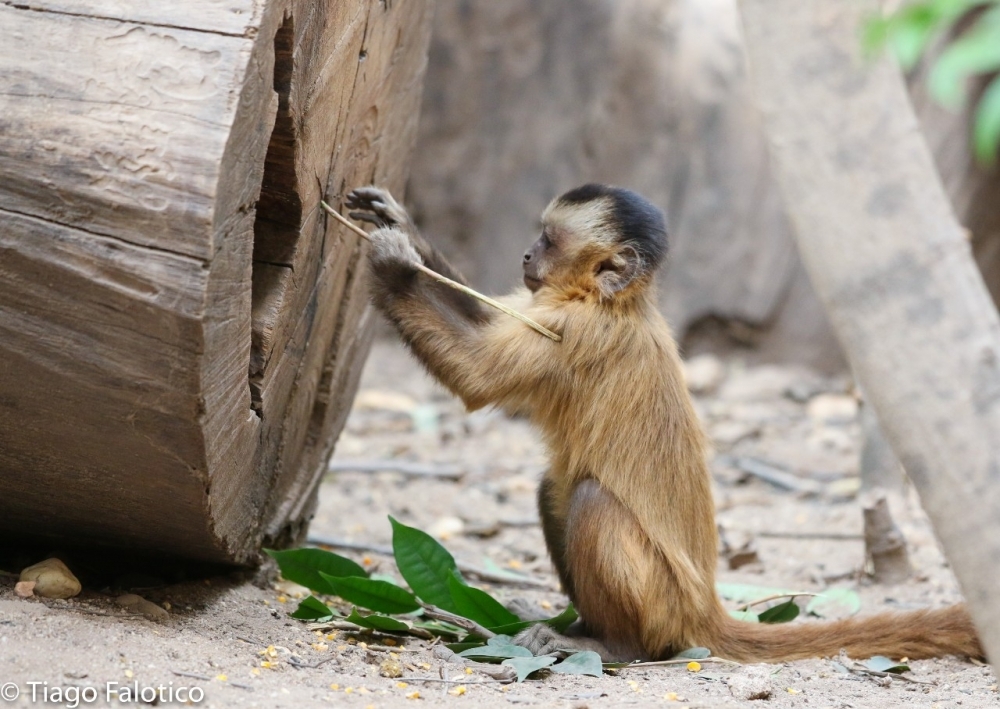

Primates in a Brazilian national park spend 41% of their time on the ground. Territoriality influences stone tool use, the behavior of females while on heat, and care of disabled individuals.

An article in Science by 35 researchers affiliated with institutions in Brazil and elsewhere shows that carbon emissions resulting from forest degradation are equivalent to emissions from deforestation. The authors analyzed degradation due to fire, edge effects, illegal logging and extreme drought.
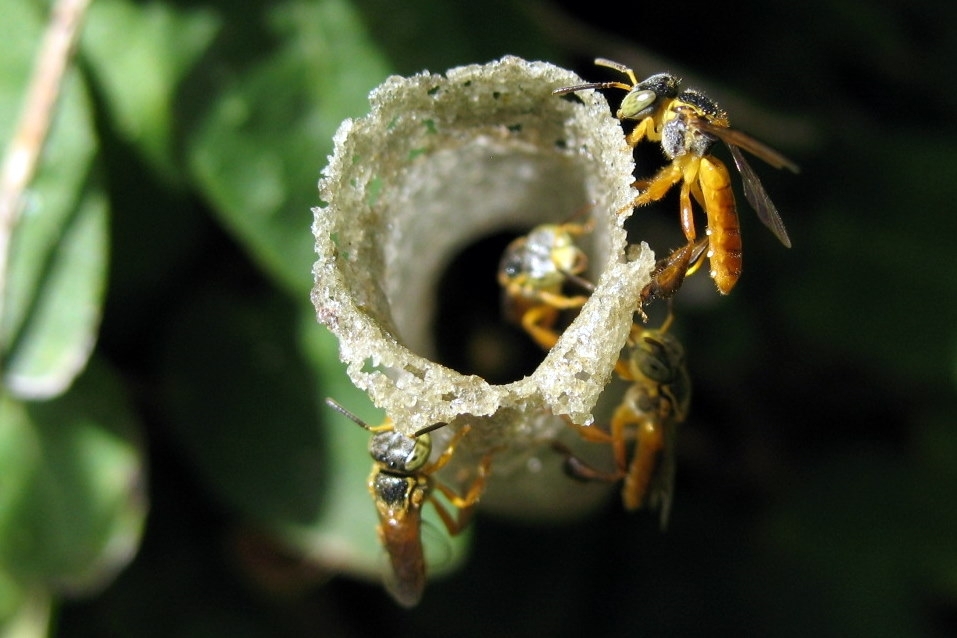

The study by Brazilian researchers showed that the microscopic arachnids rid stingless bee colonies of excessive fungi and serve as food for the larvae of these honey-making insects.

The mechanism has resulted from evolution over millions of years to protect the buds that enable plants to survive fire. A study conducted in an environmental protection unit in São Paulo state (Brazil) can contribute to strategies for mitigating the effects of climate change.

A review of the literature shows that 15% of articles published between 1960 and 2021 focused on only ten species, while no articles at all were published on almost 40% of all species. Research efforts tend to be biased toward large-bodied animals and species native to wealthier countries, among other factors that should be taken into consideration when planning future studies, according to the authors.
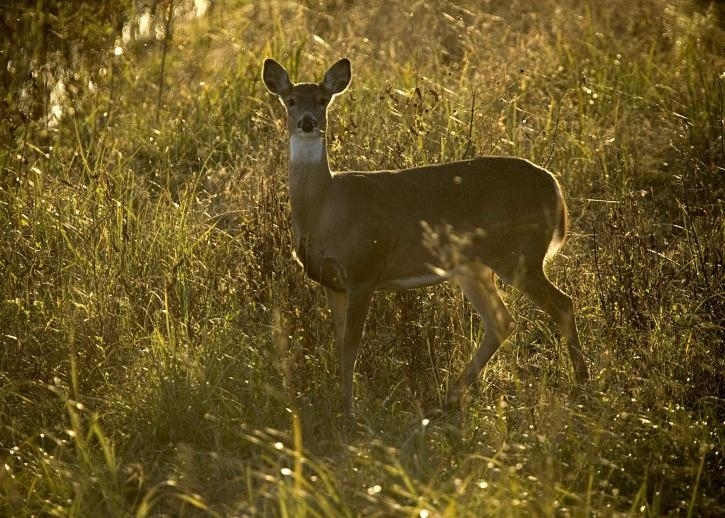

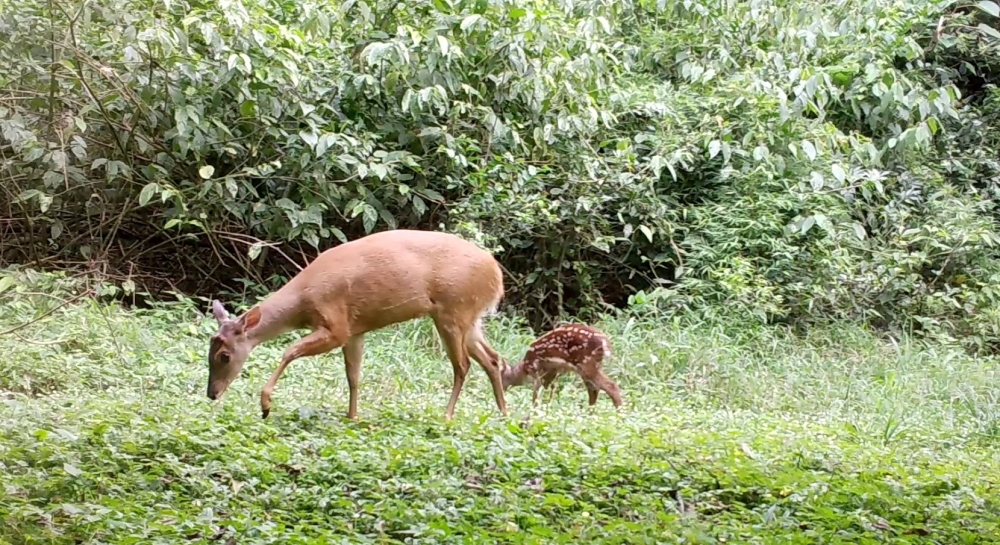
A survey of news items on Brazilian deer published between 2011 and 2021 shows that most referred to habitat loss and poaching, but diseases transmitted by cattle and low reproductive efficiency were ignored as factors that can lead to species extinction. Lack of the right information can hinder conservation efforts.
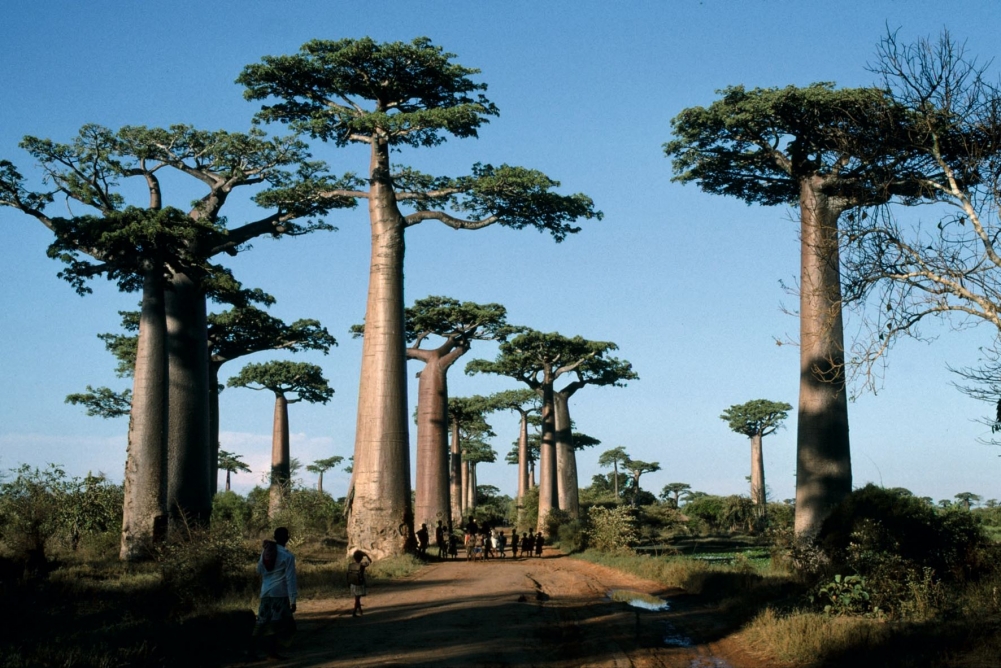

Two articles published in the journal Science by an international group of researchers that includes Brazilians present an up-to-date review of existing knowledge of the island’s rich biodiversity and how it is protected. Maintaining harmony between the species found on this tropical island off the coast of Africa and its human population is a daunting challenge.

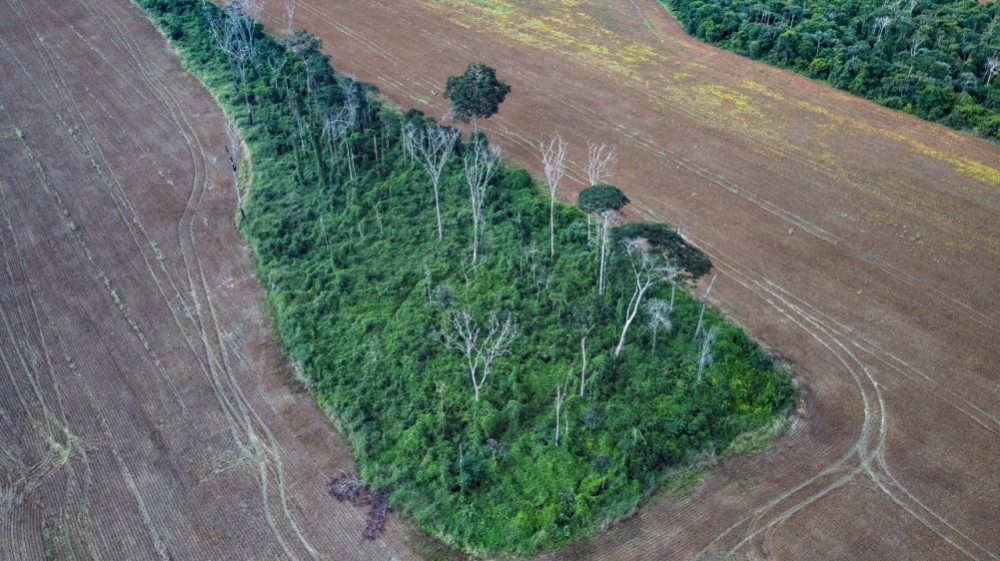
According to a mapping exercise by a group of Brazilian researchers, 56.8% of the areas that should be priorities for conservation are not legally protected. They identified 21 large forests that could be converted into new conservation units.
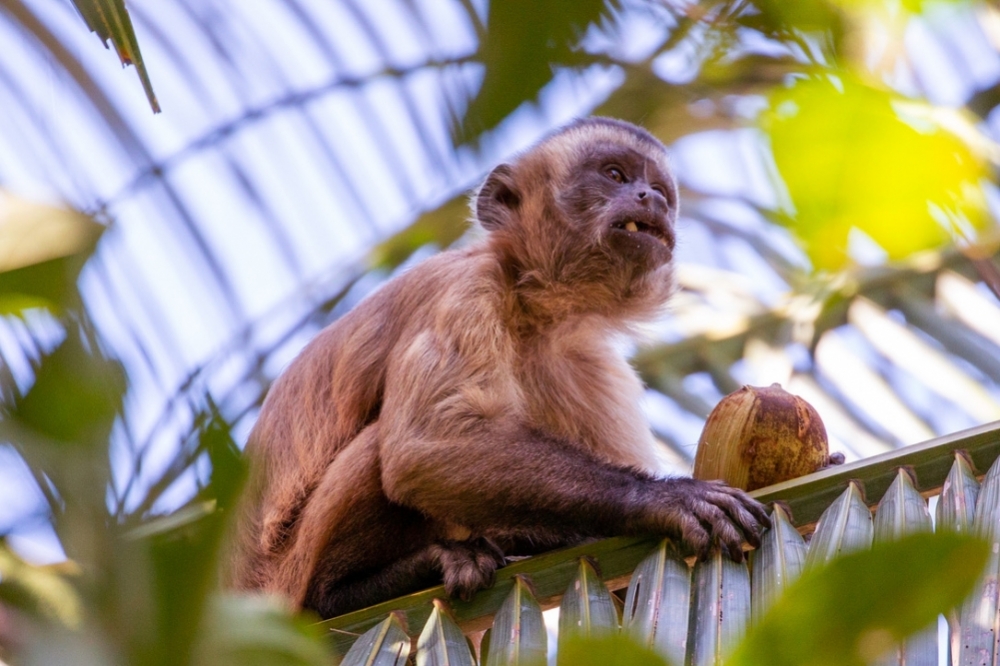

Researchers documented the size and weight of the stones used as tools by three populations of these primates living in Central Brazil, as well as the hardness of the nuts and seeds the tools were used on. Even when more suitable tools were available, some animals preferred the heaviest stones, possibly as a result of cultural learning.
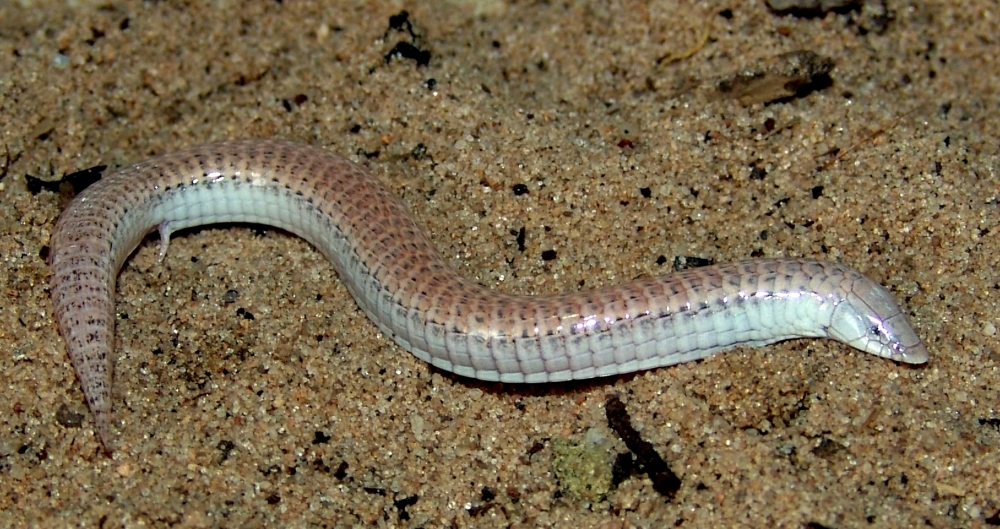

Genomic analyses performed by researchers in Brazil and Germany suggest that different groups of reptiles submitted to similar environmental conditions developed convergent adaptations independently.

In a special issue of the journal Science, some of the leading experts on the subject argue that rehabilitating degraded areas requires more complex solutions that take the biome’s specificities into account.
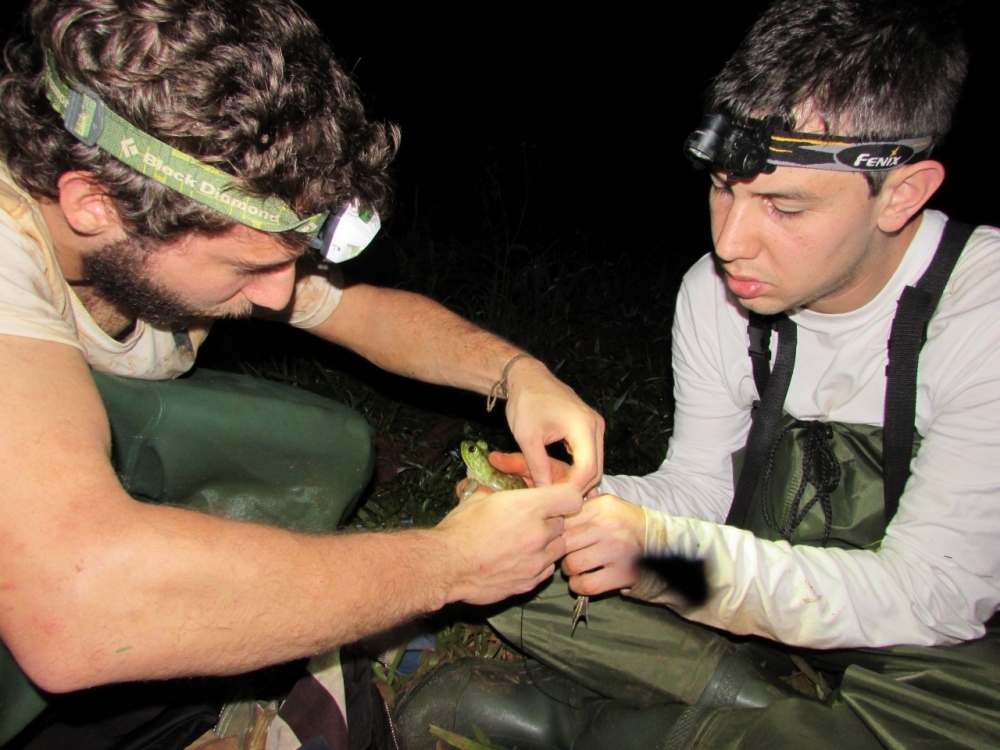

Genetic analysis of Aquarana catesbeiana, a species that originally came from North America and is now found in nine Brazilian states, shows that the lineage introduced in 1935 prevails in both captive and feral bullfrogs. Law enforcement to maintain sanitary standards is difficult. The invaders prey on native amphibians and transmit diseases to them.

The system is being developed by a Brazilian startup supported by FAPESP and can be used by biologists in scientific research, by NGOs to track endangered species, and by environmental consultants.
In a webinar held to present the third chapter of the book published by the São Paulo State Academy of Sciences to commemorate FAPESP’s sixtieth anniversary, specialists showed that protection of terrestrial and marine environments contributes to food production and job creation, among other benefits.
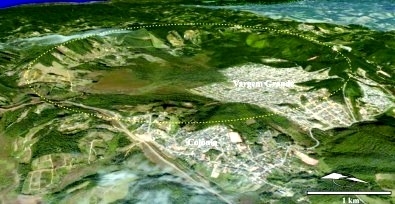
Spherules were discovered in the sediments present at depths of 180-224 m inside the crater located in São Paulo, Brazil. Their shape suggests local rock was pulverized, nebulized, and expelled upward by the collision.
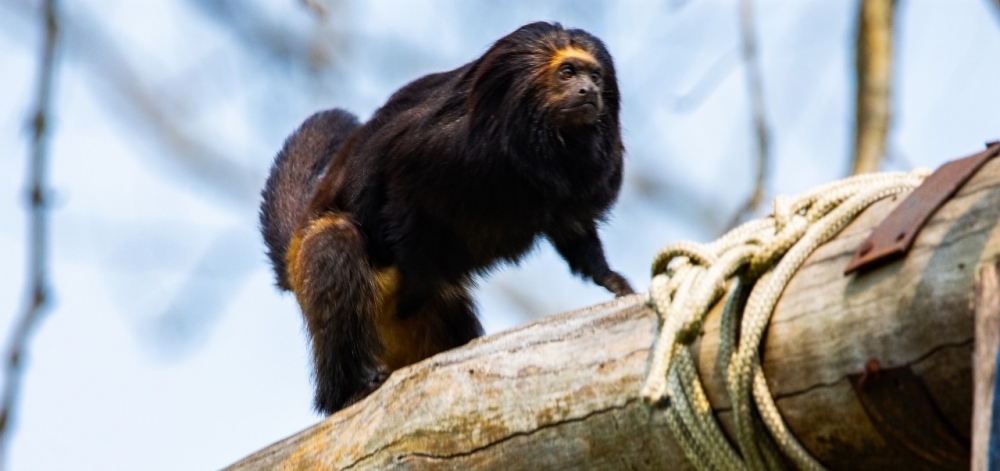

A project supported by environmental agencies, local government and private enterprise, as well as FAPESP, compared the use of a wooden pole bridge and a rope ladder bridge between tree canopies over a local road for three years in a municipality with an Atlantic Rainforest conservation unit. Monitoring focused on the Black lion tamarin, an environmental heritage species symbolizing wildlife conservation in the state of São Paulo.
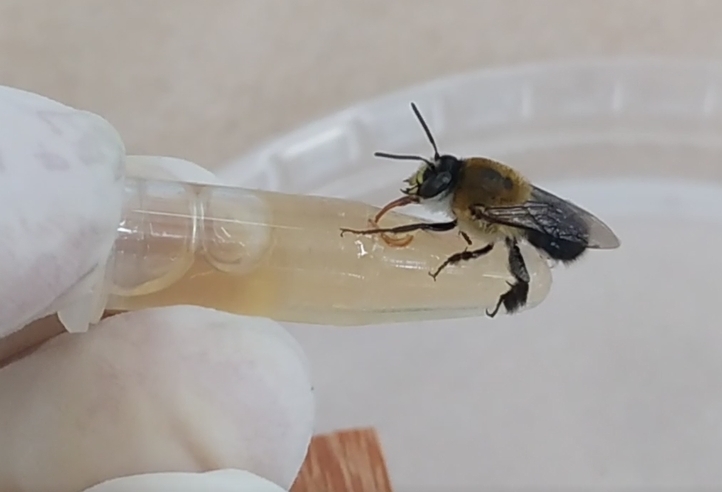

Preliminary results of trials conducted by Brazilian scientists show that the existing regulatory framework based on a protocol referenced to the Western honeybee, Apis mellifera, is too Eurocentric and may not be sufficient to guarantee the protection of native bees, which are important pollinators.

The new species of beetle in the family Buprestidae was found in the state of Bahia and described by researchers at the University of São Paulo and collaborators. The group discovered how the insect contributes to production of red propolis by honey bees.
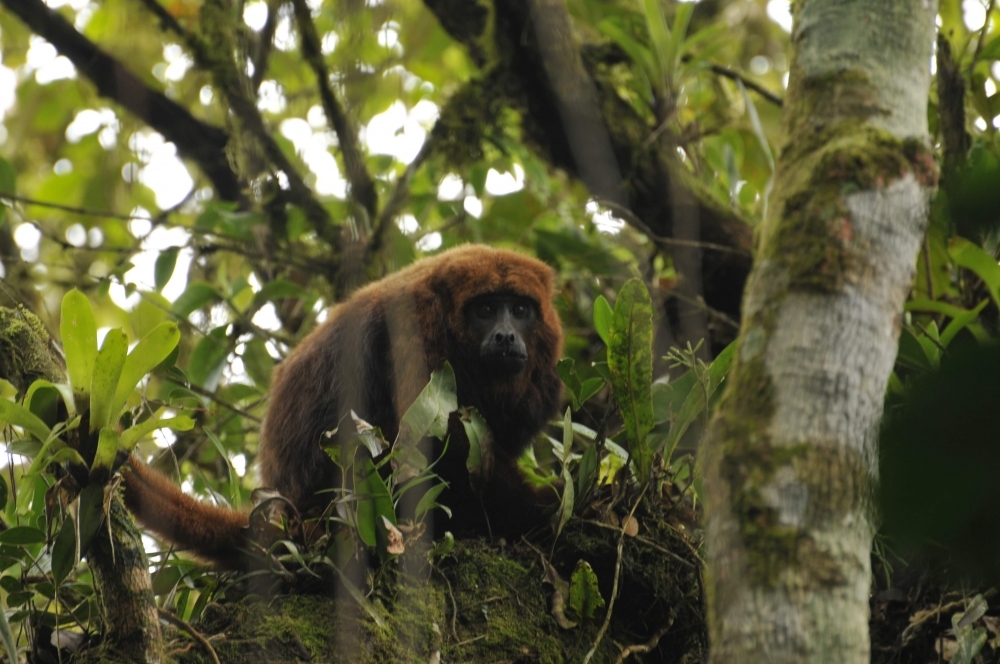

Large mammals and birds that can swallow fruit of different sizes are crucial to assure rich animal-plant interactions, thanks to which forests thrive, according to a study conducted at São Paulo State University.
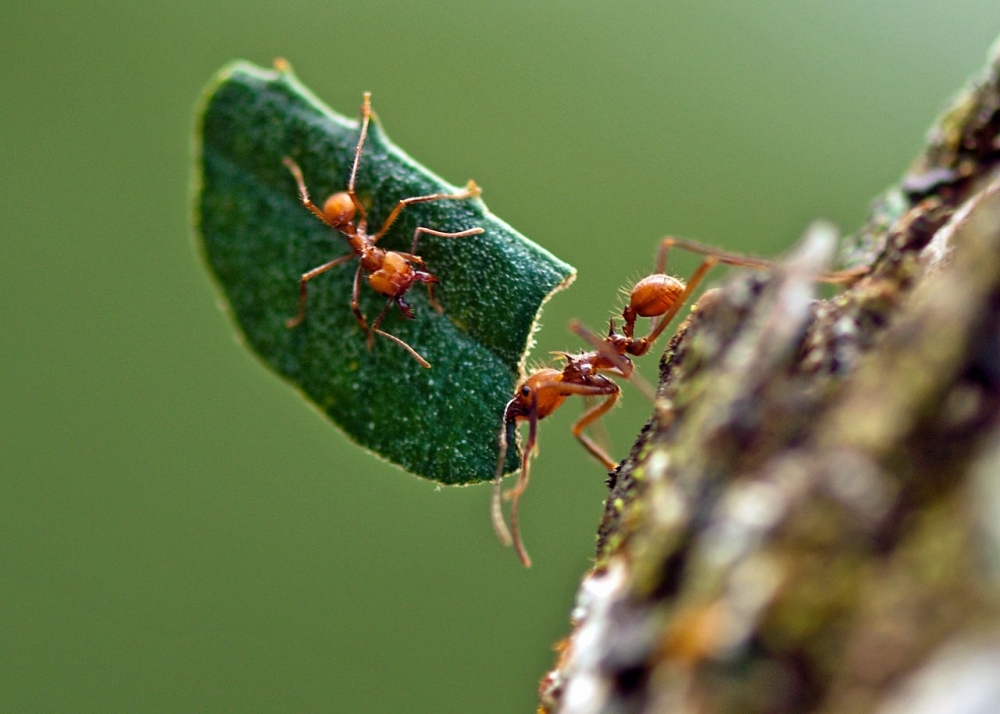

These ants emerged some 8.5 million years ago and underwent an intense speciation process between 1 million and 3 million years ago, when the Brazilian savanna was expanding. The recent advance of agriculture in the region, however, appears to be reducing this biodiversity and selecting species that damage crops.

A study led by Brazilian researchers measured species numbers and attributes, as well as carbon dynamics, in two areas of the Brazilian savanna – one is regularly burned and no fires have occurred in the other for 16 years.

Innovative, artificial intelligence-based methodology detects occurrences of Pleroma by identifying blooms, and maps distribution in biome.