


Film based on algae and nanocellulose created at the Federal University of São Carlos is safe for the environment, reduces nutrient loss, and could replace microplastics in agriculture.
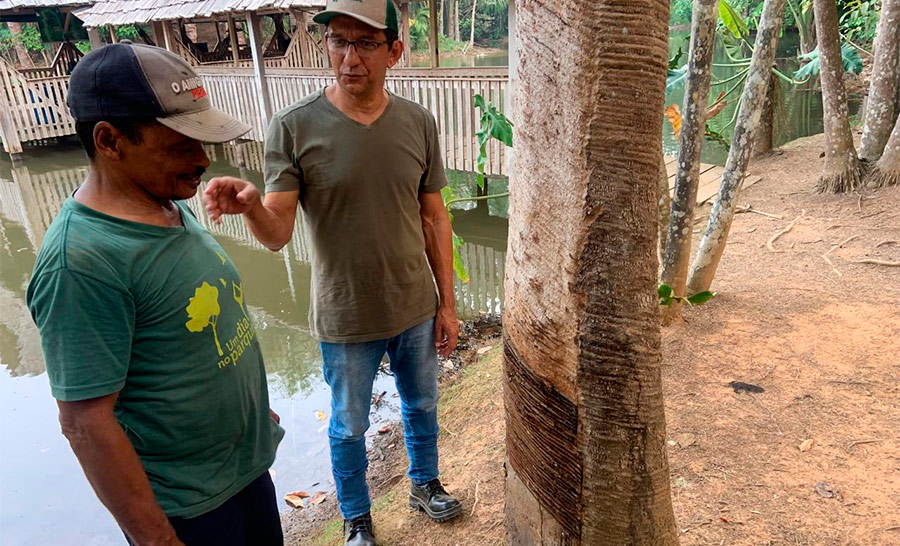

A project in the Chico Mendes Extractive Reserve shows that rubber provides adequate income to sustain livelihoods and conserve the forest. However, nut collection yields low pay, which contributes to the adoption of unsustainable practices such as extensive cattle ranching.
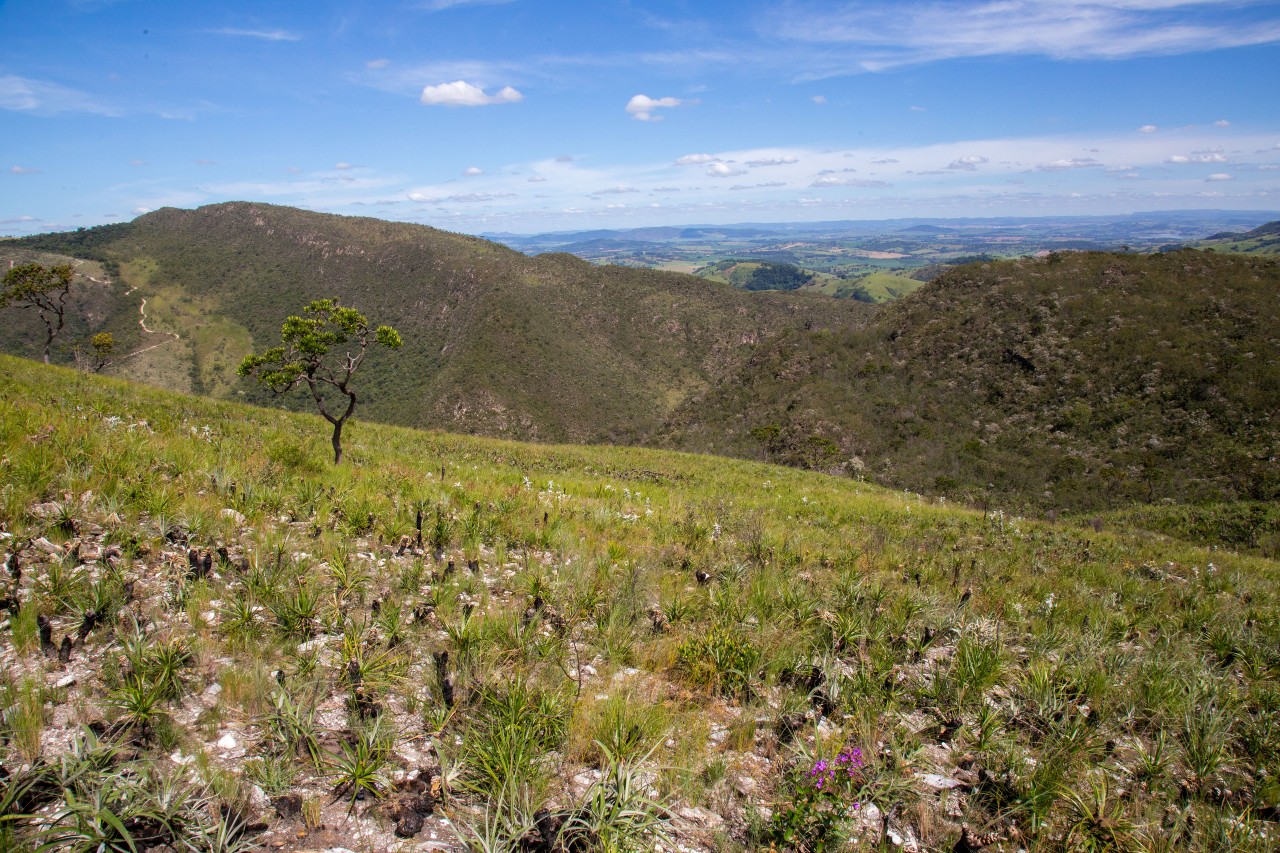

Researchers at a FAPESP-supported research center have combined innovative techniques to determine the chromosome number of species of the genus Vellozia, typical of this montane savannah ecoregion. The result provides support for conservation programs and biotechnological applications.
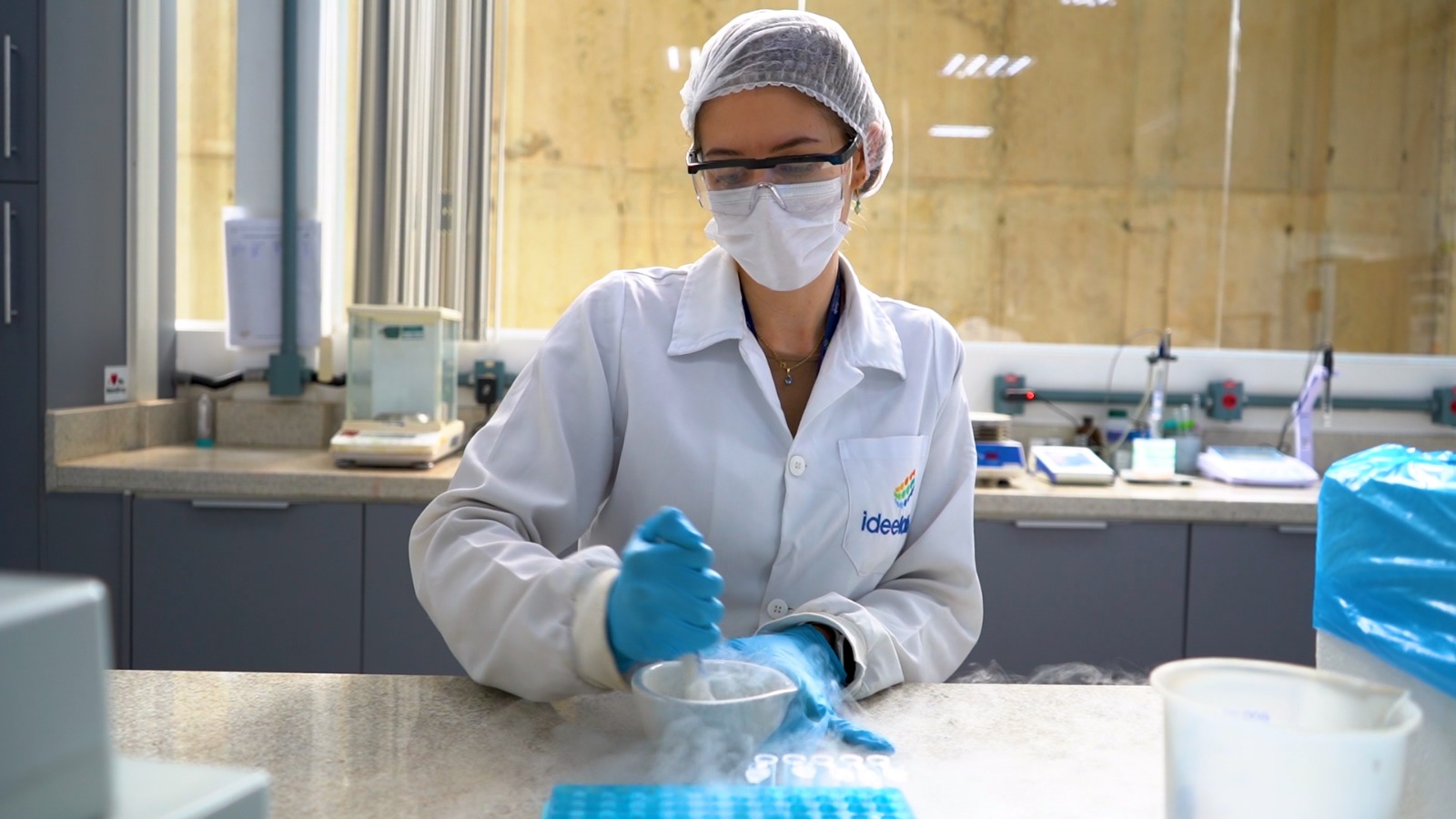

With support from FAPESP, the São Paulo startup is developing more efficient strategies to combat pathogens that threaten citrus farming; the technology will be presented at VivaTech in France.

Researchers from the University of São Paulo and collaborators conducted a comprehensive review of the available literature on the subject, which included more than 13,000 articles.
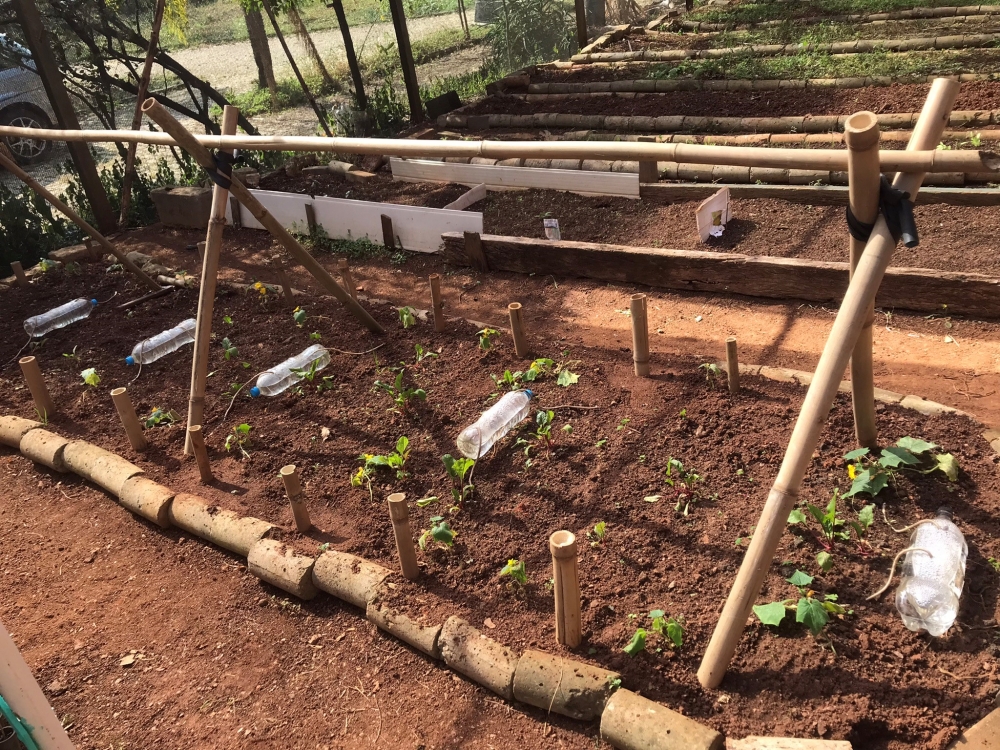

With the support of FAPESP, Santa Food Tech has developed a model to transform urban areas into laboratories of sustainability; the initiative is already implemented in four micro-regions of the state capital and in Guarulhos.

In an article published in Environmental Science and Pollution Research, researchers from the Federal University of São Paulo discuss the need for the production chain to adopt emission reduction practices.

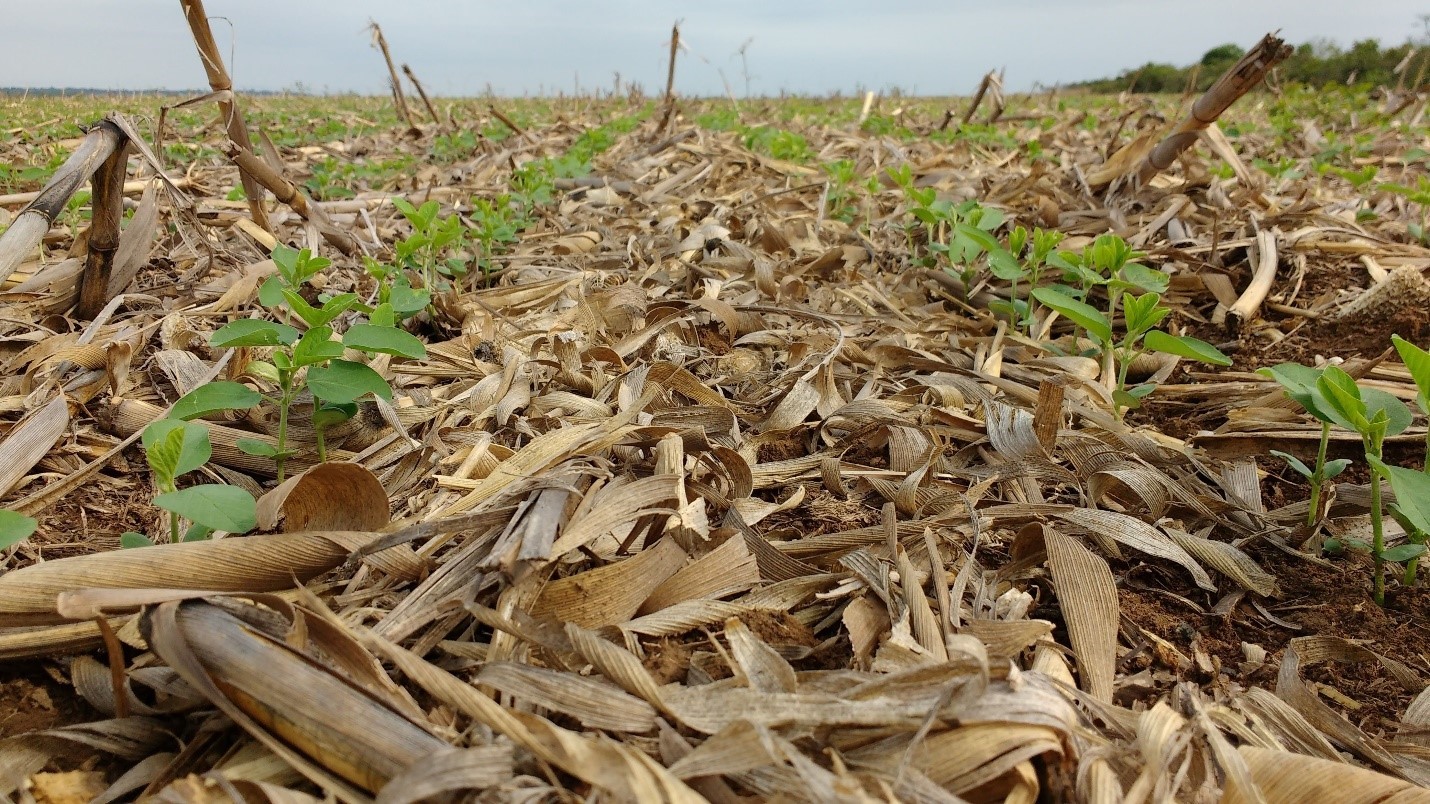
A group of scientists supported by FAPESP is studying a new strain of bacteria in consortium with rhizobia, microorganisms that biologically fix nitrogen, an essential nutrient for crops.

Images taken from an unmanned aerial vehicle, processed with free software, help assess water stress parameters in corn experiments and select varieties that are better adapted to water shortages.
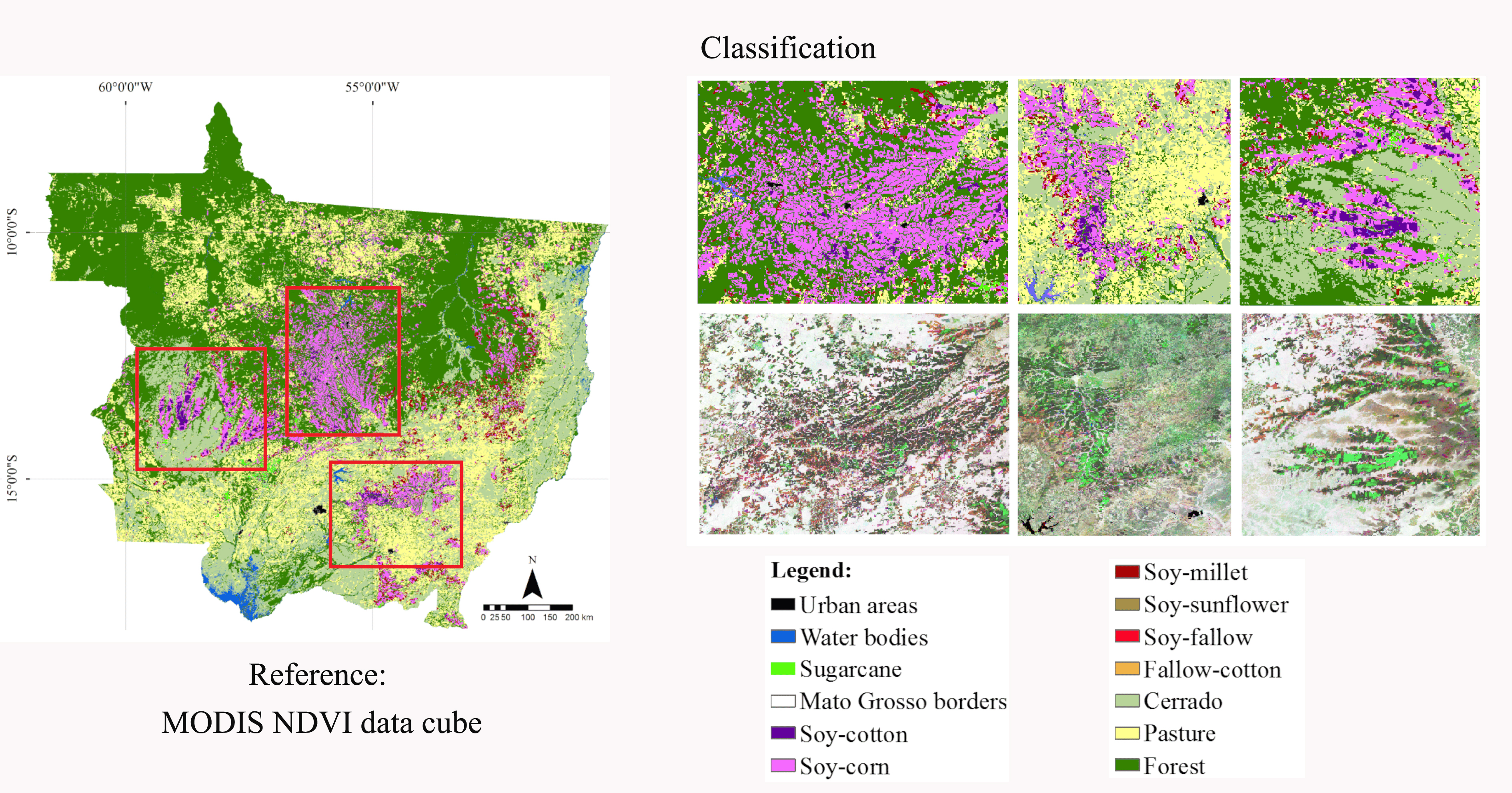
A technique developed by researchers at São Paulo State University was tested in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso and more accurately delineated areas of natural vegetation and agricultural production by crop type; the results showed 95% accuracy in mapping.

Practical guide prepared by researchers from the University of São Paulo gets extended version, accessible for free on the Internet.

The Agrotechnological District of Breves, in the Brazilian state of Pará, was created as part of Semear Digital, a Science Center for Development led by EMBRAPA Digital Agriculture and supported by FAPESP.
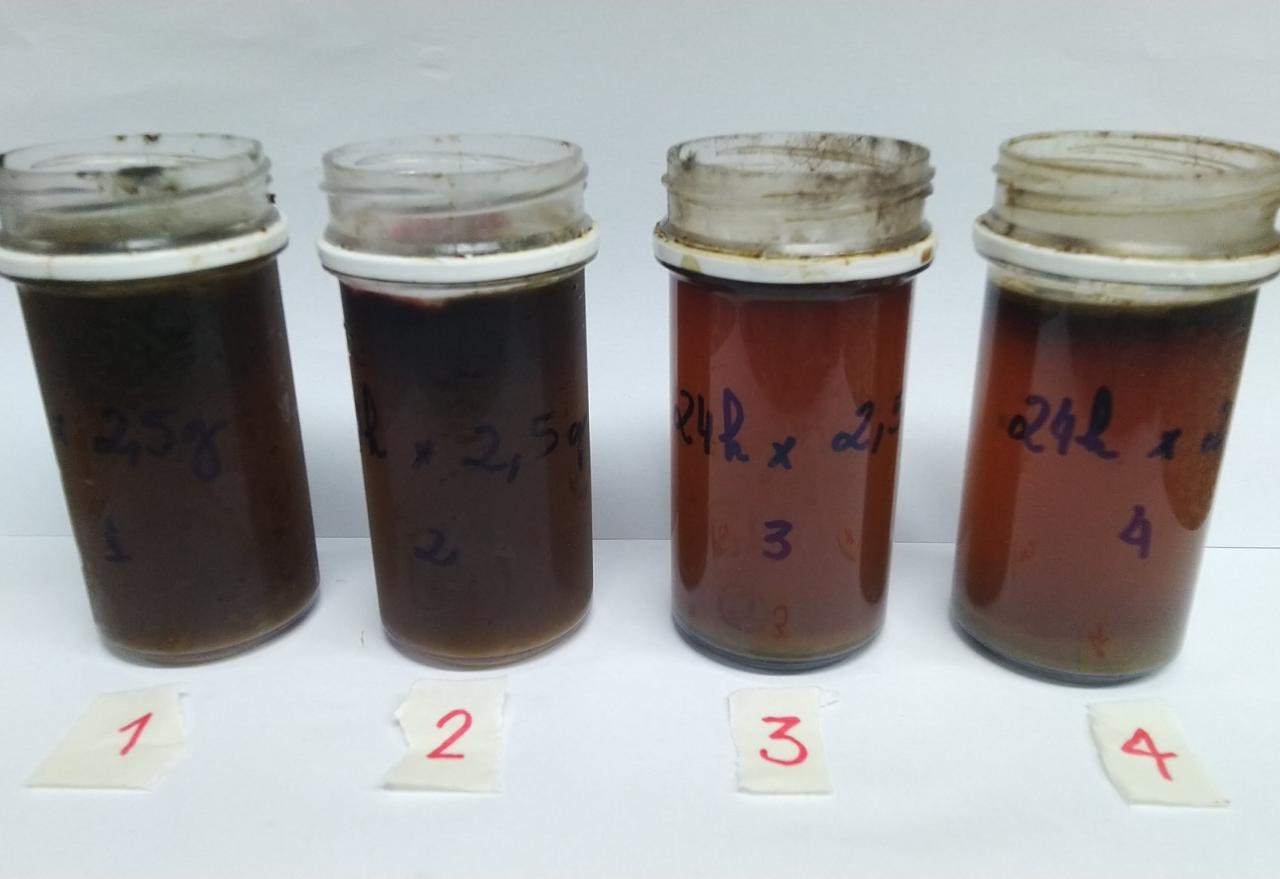

The method converts the vinasse left over from ethanol production into a potassium- and nitrogen-rich fertilizer. The groundbreaking study was conducted at the Federal University of São Carlos and published in the Journal of Environmental Management.

The solution developed at the Plasticulture Engineering Center, supported by FAPESP, uses machine learning on time series of satellite images to detect agricultural areas where the material is used with almost 100% accuracy.
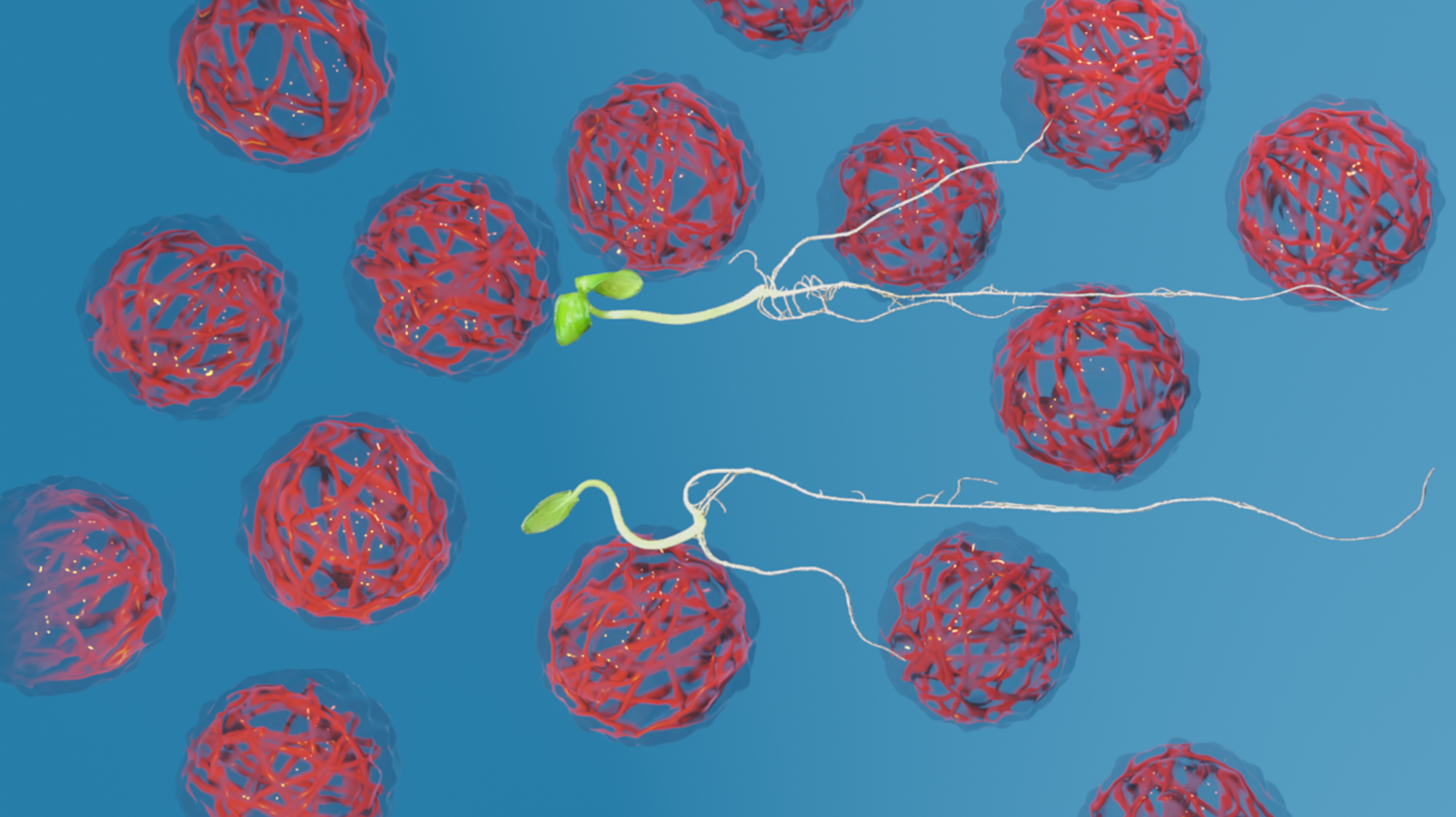
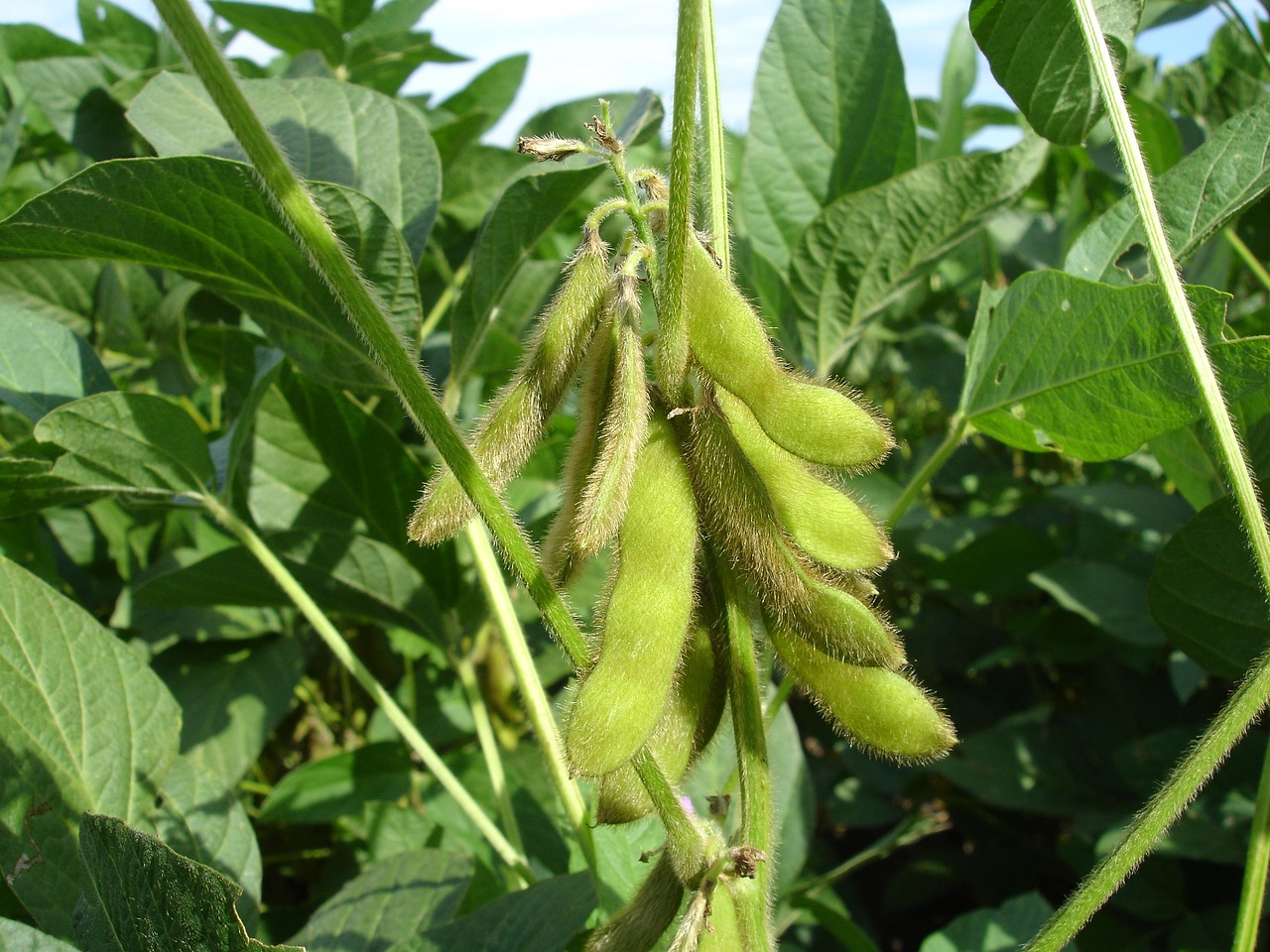
A study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry shows that this type of polymer may in future optimize production of this crop in terms of time, space and cost, favoring sustainable food production.
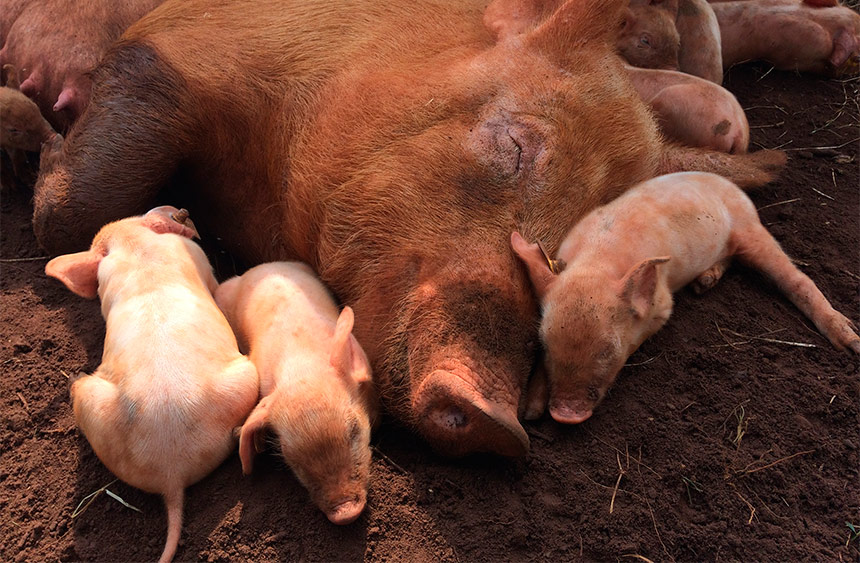

Without having had any contact with their parents, piglets fathered by boars housed in cramped conditions for four weeks exhibited elevated levels of cortisol, among other indicators of stress. Offspring of pigs housed in roomier pens and given showers and tactile stimuli coped better with stressful situations.

Cutting-edge technologies and systems promise to contribute to more sustainable practices but need academics, scientists, processors and farmers to join forces, according to speakers at the São Paulo School of Advanced Science held on the Jaboticabal campus of São Paulo State University.
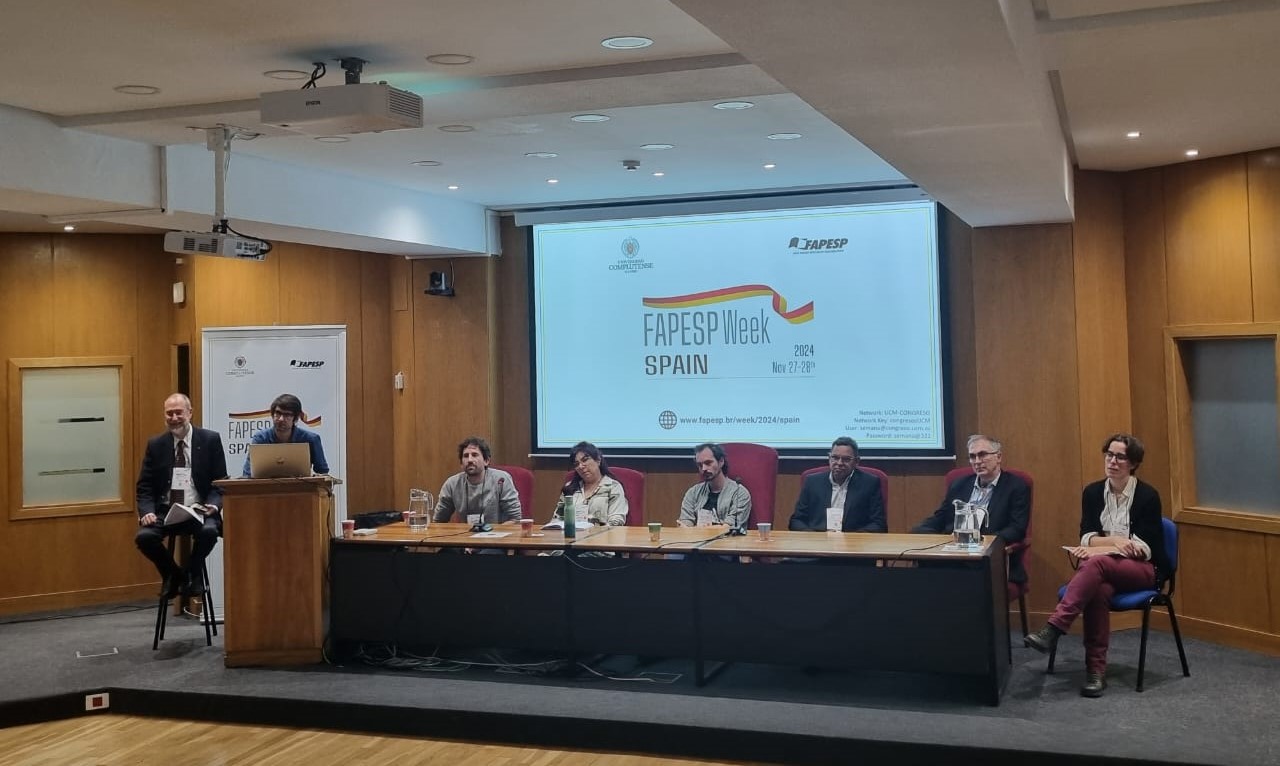

Scientists from Brazil and Spain use sensors embedded in drones and agricultural machinery, as well as satellite imagery, to predict the ideal time to harvest, reduce CO2 emissions, and manage water use in plantations; work was presented at FAPESP Week Spain.
While studying a region of vineyards in the interior of the state of São Paulo, researchers observed that the most preserved sites had a greater diversity of birds and the ecological functions they perform.
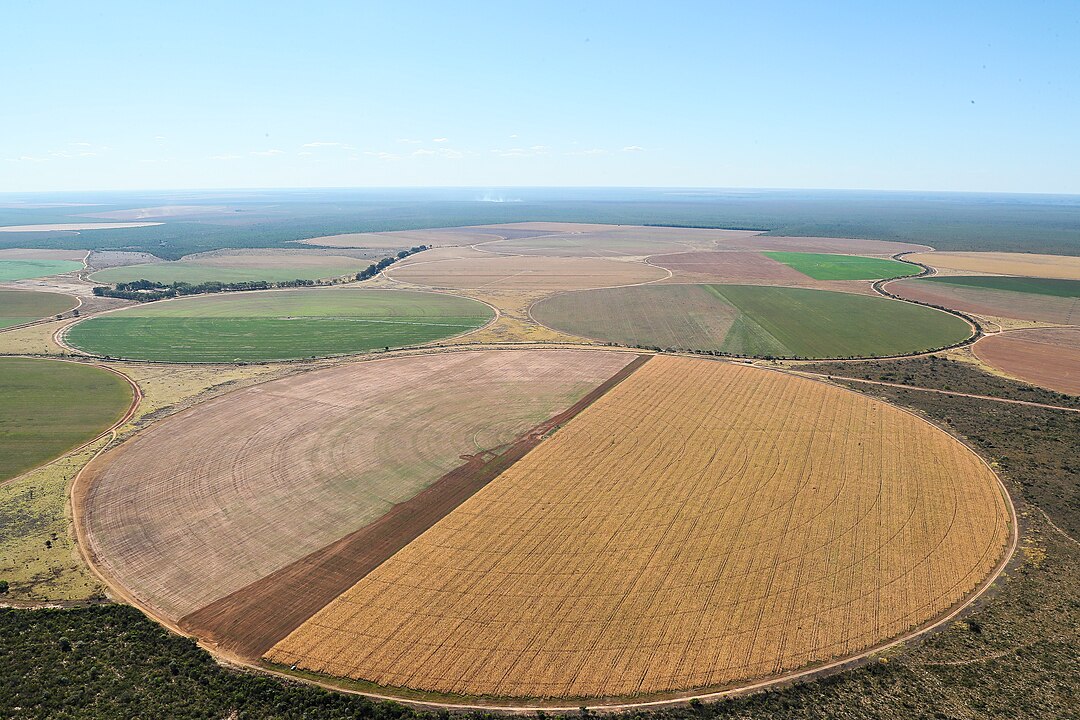

Overuse of water resources in Brazil’s main agricultural frontier region, in conjunction with climate change, is reducing replenishment of the Urucuia aquifer and surface water bodies in the basin of a tributary of the São Francisco, the largest river in the Northeast.

Experiments conducted at the Federal University of the ABC showed that nitrogen-fixing bacteria play a key role in the reproduction of a legume native to Brazil.

Scientists at the University of São Paulo present this conclusion based on a systematic review of the literature in a paper published in the Journal of Cleaner Production.
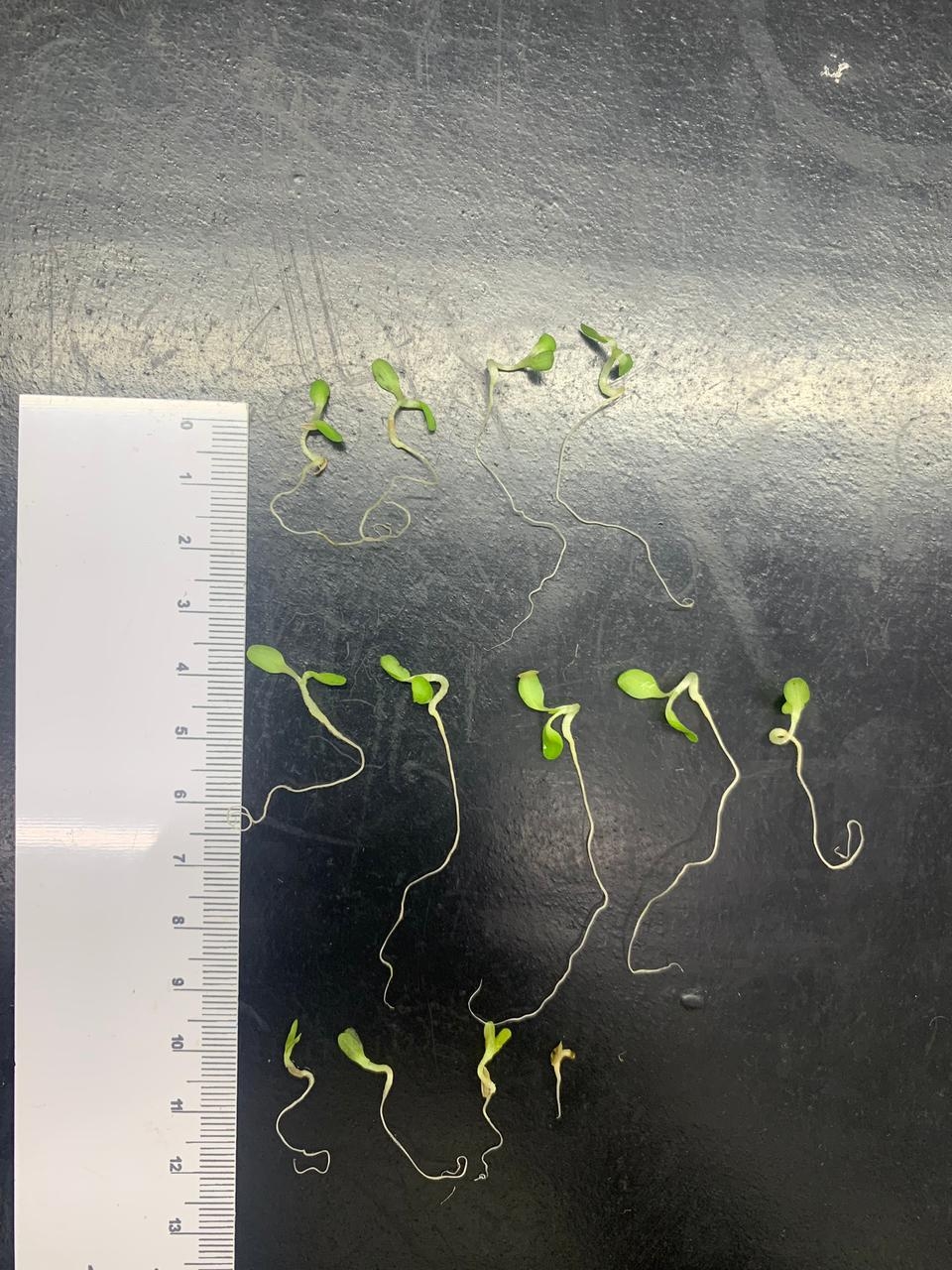

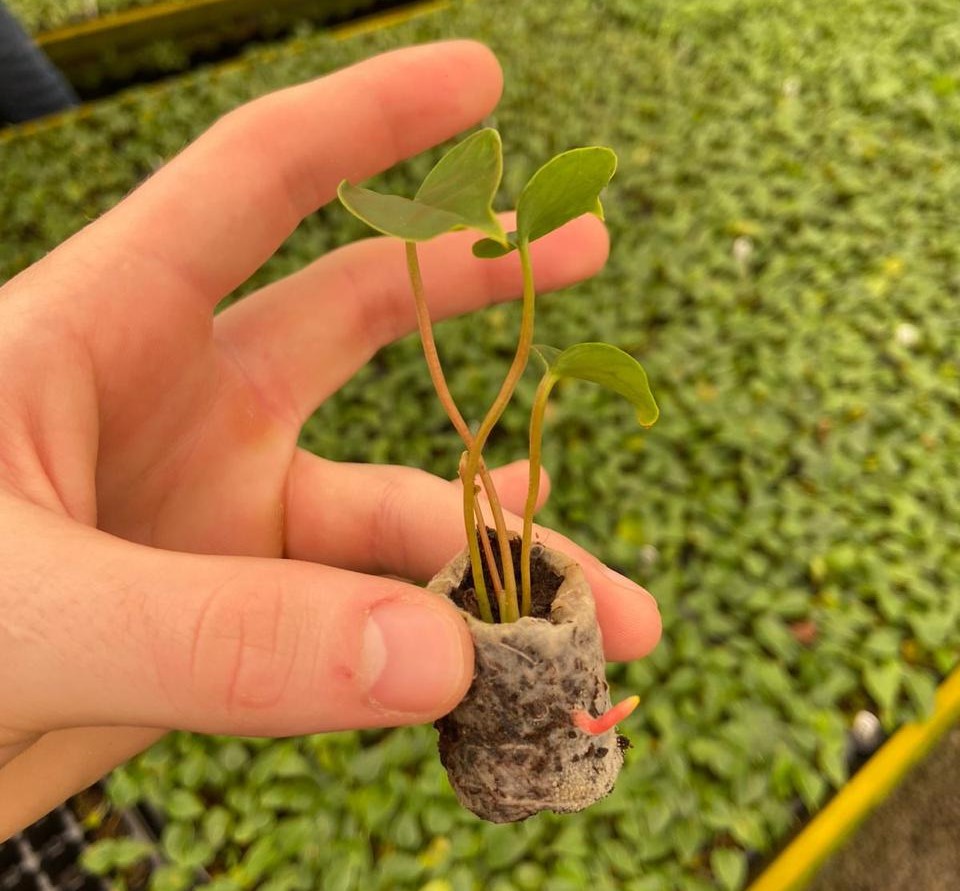
A startup supported by FAPESP has created a solution that promotes development and growth of the roots and aerial part of plants.
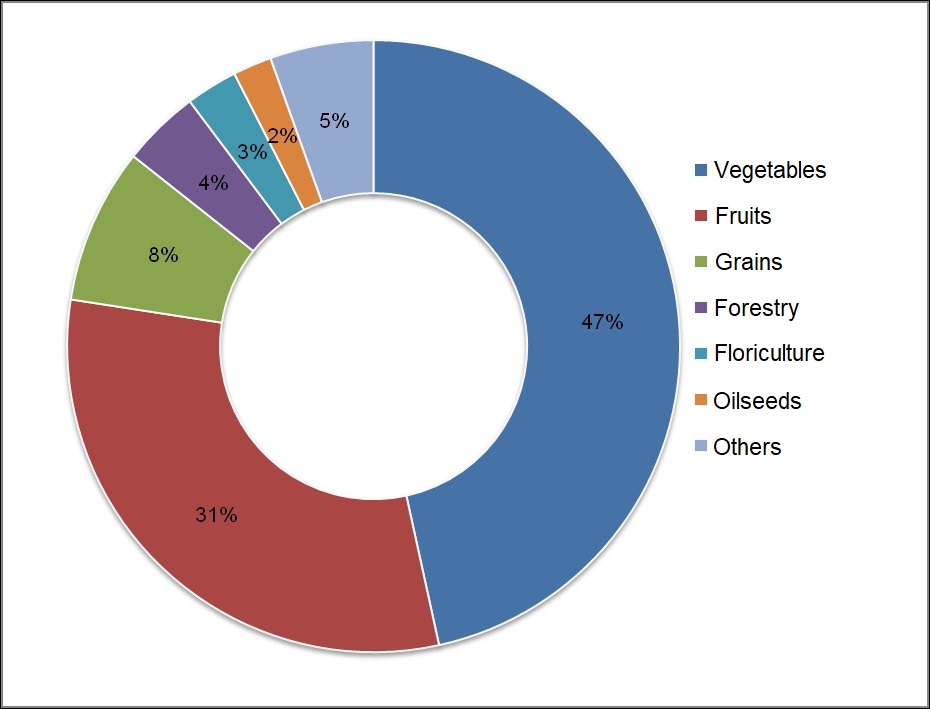
A study conducted in São Paulo state (Brazil) showed that farms with peer-to-peer certification had 58.8 organic items on average, while farms conventionally certified by third parties had 22.2.