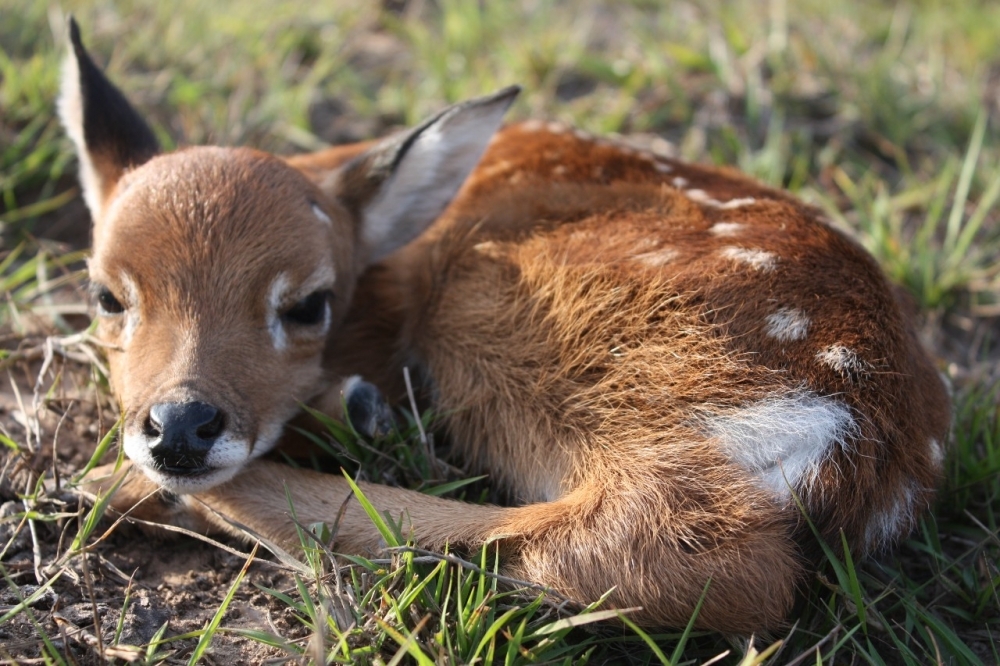



An analysis of the management plans for 118 protected areas in all parts of Brazil shows that 60% use methodologies that may yield an incorrect diagnosis of the threat to the various species of deer, especially those living in forests. The researchers have produced an illustrated guide to help identify species in future stocktaking exercises.
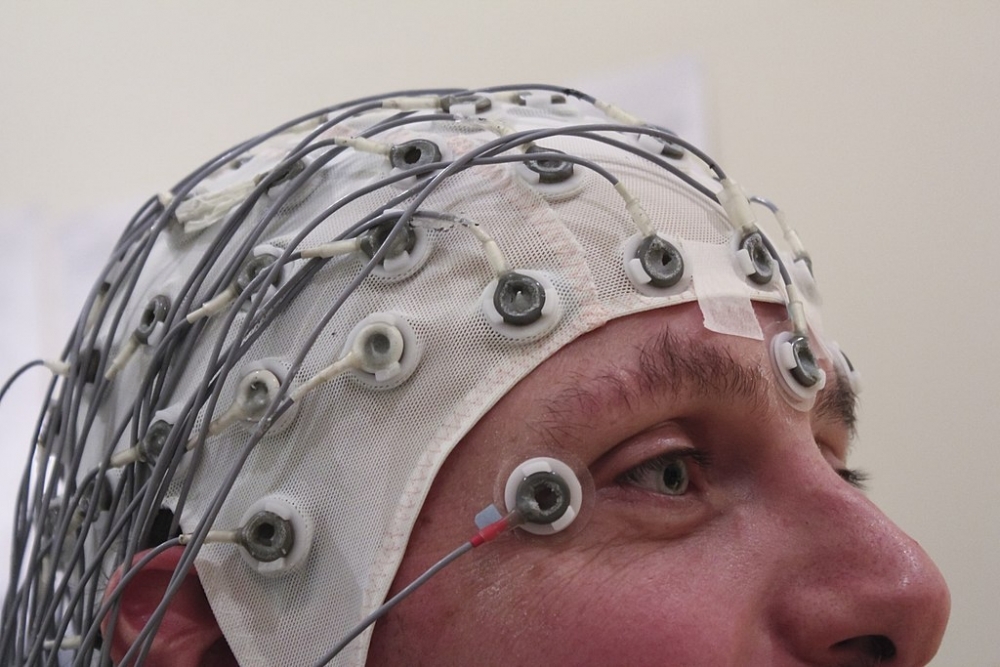
Using two low-cost techniques, researchers in Brazil differentiate patients with the disease from healthy subjects. Next steps include refining the approach to diagnose the disease in its early stages.
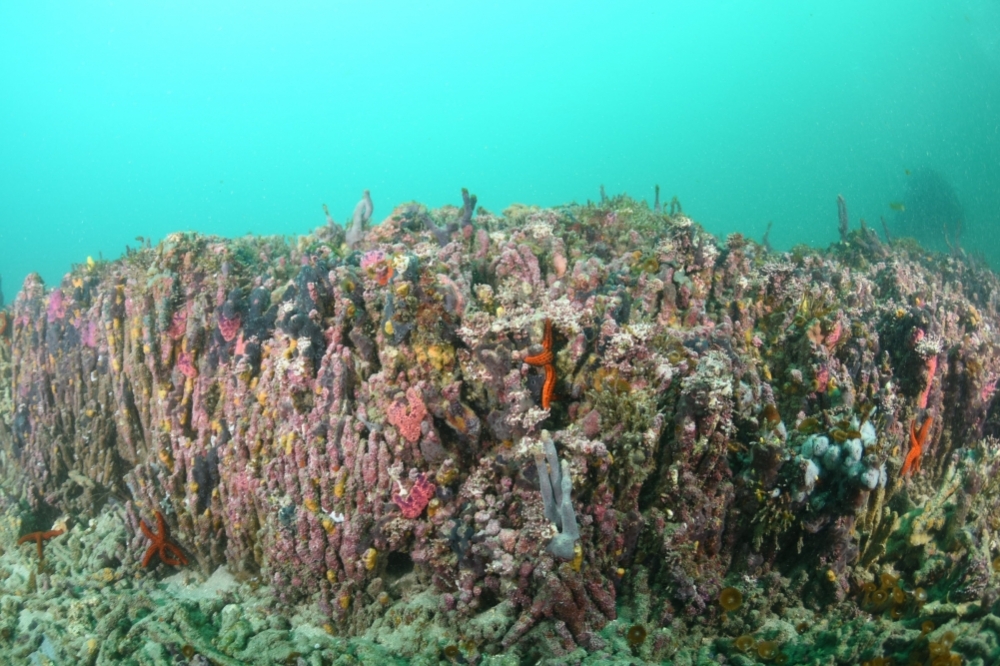

Described in 2019, the Queimada Grande coral reef off the coast of São Paulo state arose when the ocean was warmer and stopped growing when cooler sea surface temperatures influenced the climate in the region, according to a study led by researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo.
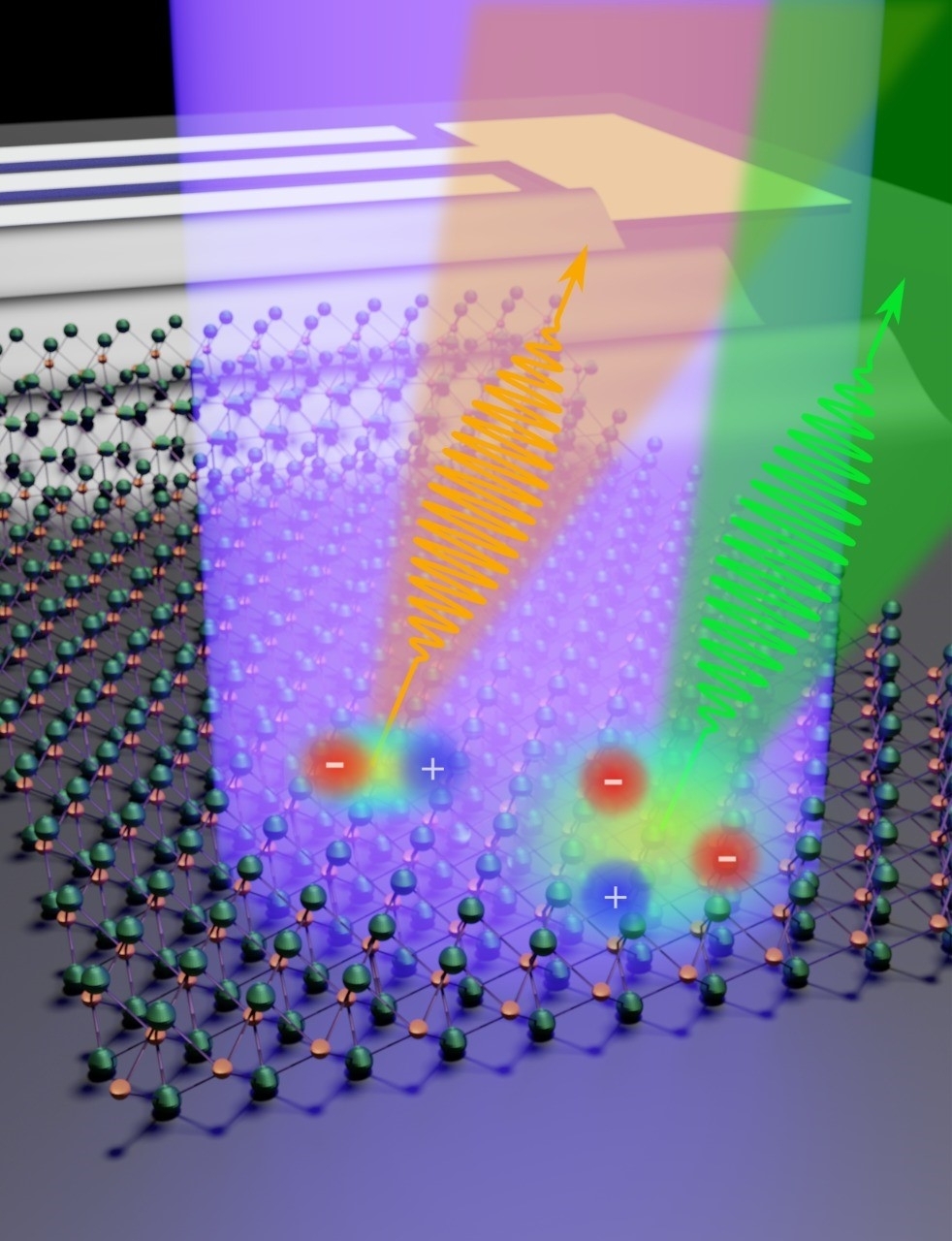
The result permits external control of the light emission from quantum states in two-dimensional semiconductors.

The automotive giant resulting from the PSA-Fiat Chrysler merger is partnering with FAPESP in this ERC, which is integrated with Stellantis’s global network of science labs.

Experiments conducted at Butantan Institute (Brazil) show how the primate’s immune system prevents multiplication of the parasite in the organism. The discovery will facilitate the identification of targets for novel therapies and vaccines.
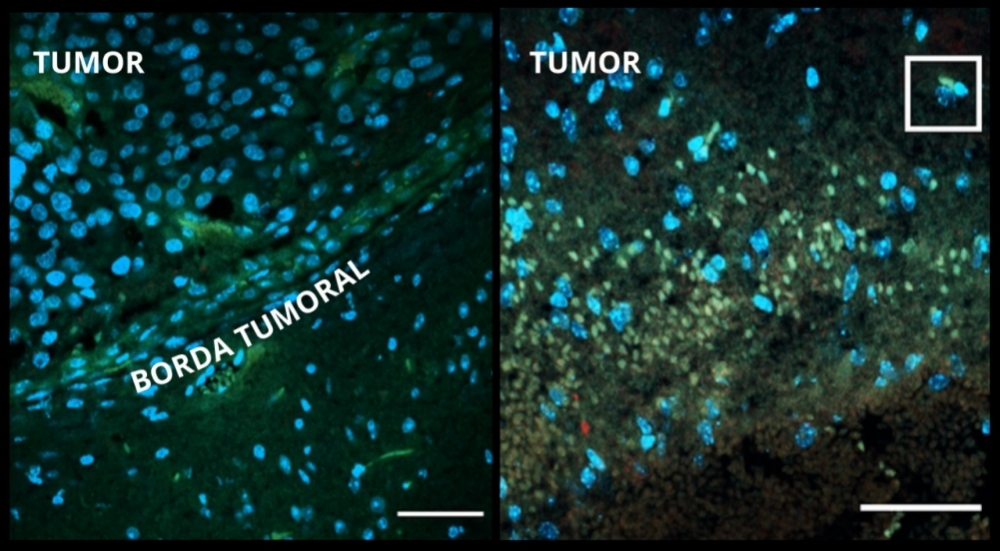
Experiments conducted at a FAPESP-supported research center showed that besides directly combating tumor cells, zika alerted the immune system to the presence of cancer. The study opens up prospects for the use of virotherapy for central nervous system tumors.
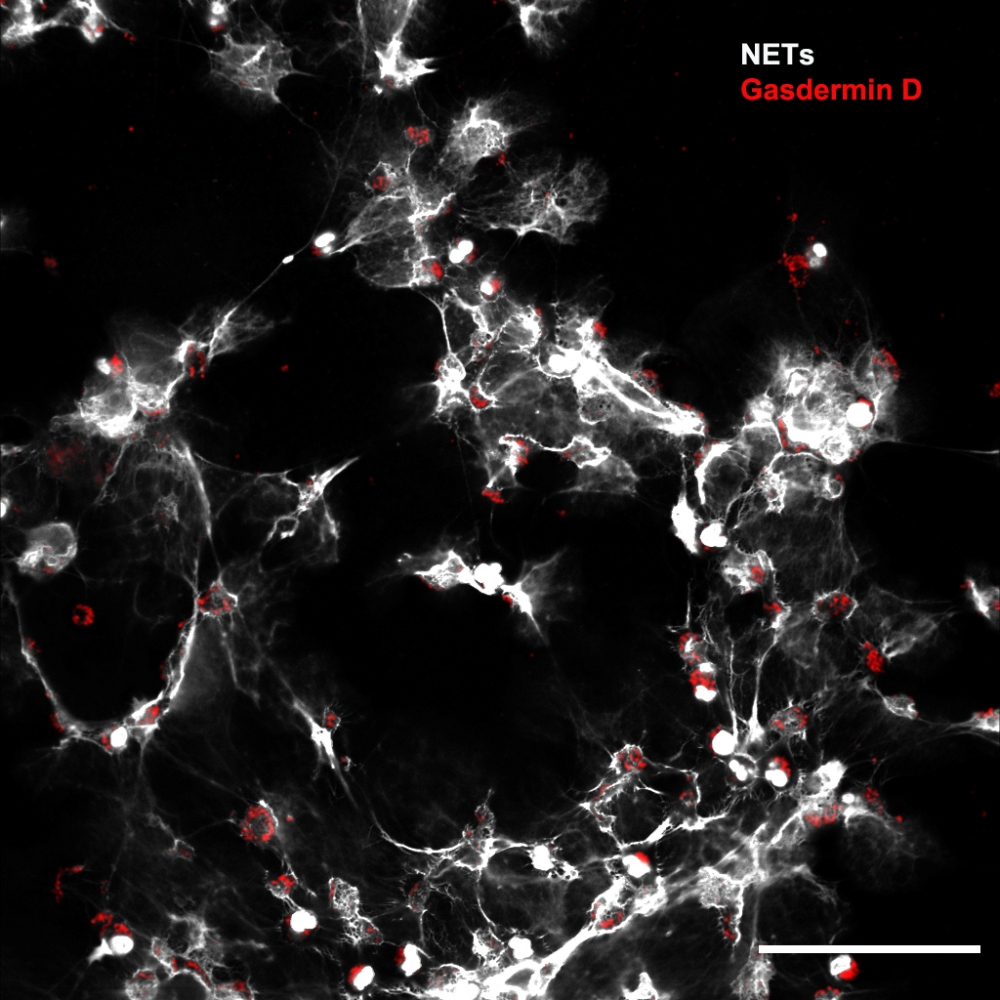
Researchers affiliated with a FAPESP-funded research center showed that a protein called gasdermin D is involved in septic patients’ organ lesions. The study also proved that a drug originally indicated to treat alcohol dependence can inhibit the molecule’s action and prevent complications.

With 50 million hectares of reforestable land, Brazil can make a decisive contribution to efforts to achieve the world’s climate change mitigation targets, while earning substantial income from carbon credit trading, according to participants in a webinar hosted by BIOTA-FAPESP.
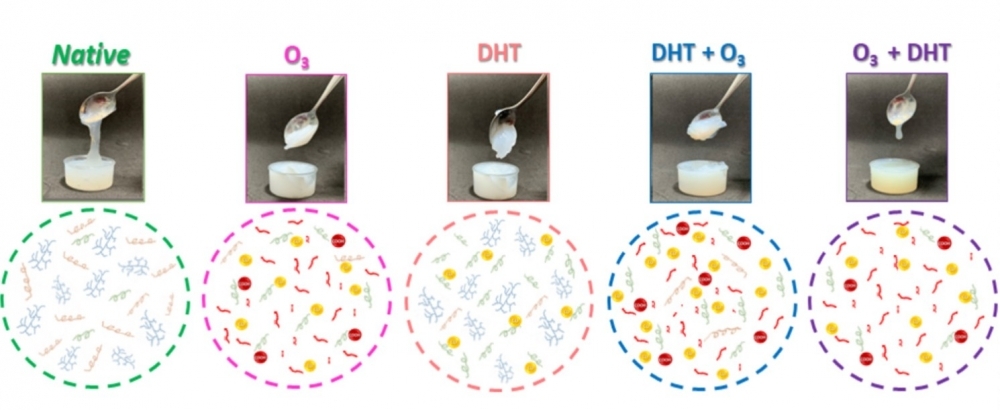
Methods considered emerging are environment-friendly and can be implemented now by industry in various segments.
Scientists at the University of Campinas investigated the electronic and optical properties of boron nitride, currently used as an electrical insulator. One of the possible applications is in high-efficiency devices to sterilize spaces, surfaces and water.
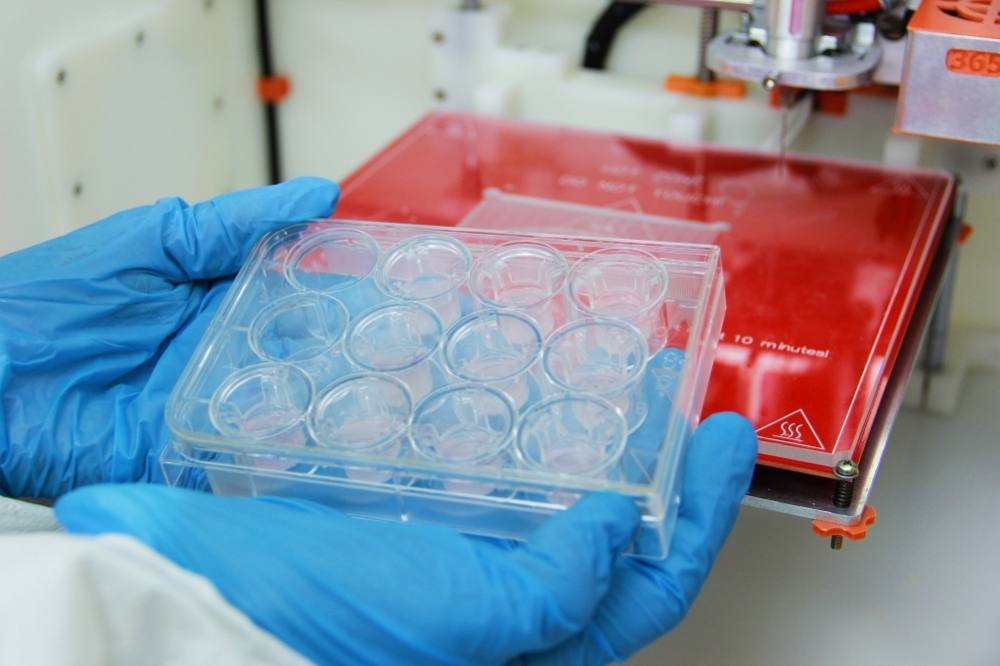

FAPESP has funded development of the solution, which can in future be used to bioprint human organs using cells from the recipient.

FAPESP signed an extension of its scientific cooperation agreement with CNRS and another agreement to fund young researchers’ projects in biomedical sciences conducted at the Pasteur-USP Science Platform.

Participants in an online seminar presented the results of research projects approved under a fast-track call issued by FAPESP at the start of the pandemic. The projects led to important discoveries on the mechanisms of the disease, development of vaccine and diagnostic technologies, and a deeper understanding of the role of governments in public health emergencies.

The topic was discussed during the 7th FAPESP 60 Years Conference. The speakers presented proposals that could help institutions surmount the longstanding problem of lack of funds in Brazil.
A workshop held by FAPESP and NNSFC featured scientists from China and São Paulo presenting research projects with potential for partnership.

A study conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo estimated the likelihood of politicians’ future conviction for corruption and other financial crimes by analyzing networks pointing to similarity of voting histories.
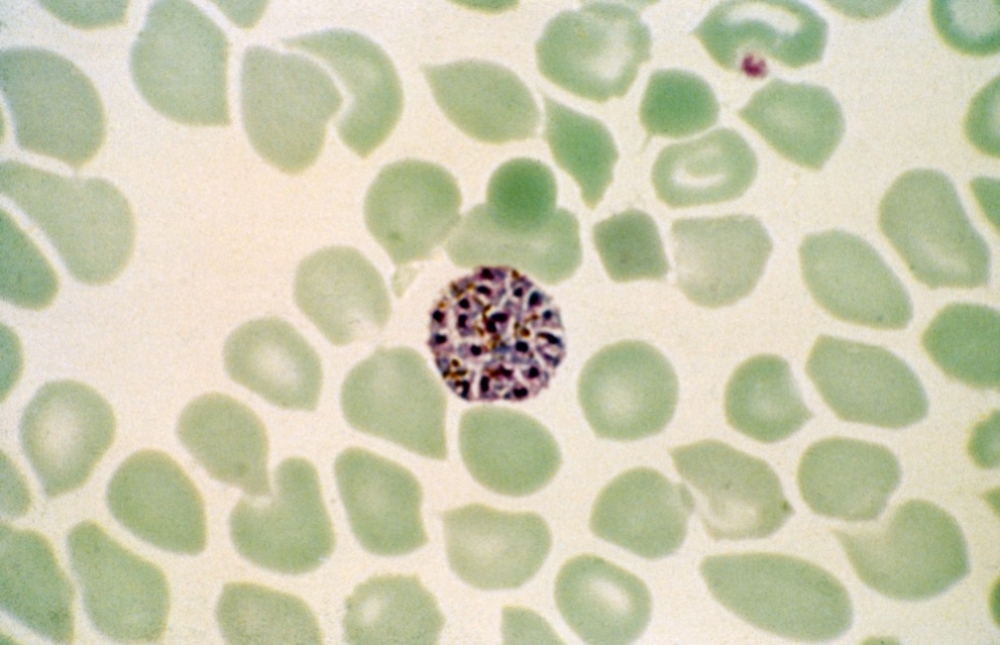
A research group led by scientists at the University of Campinas in Brazil found total parasite biomass to be a better predictor of complications from malaria than parasite burden in the bloodstream. The discovery can help develop treatment and a Plasmodium vivax vaccine.
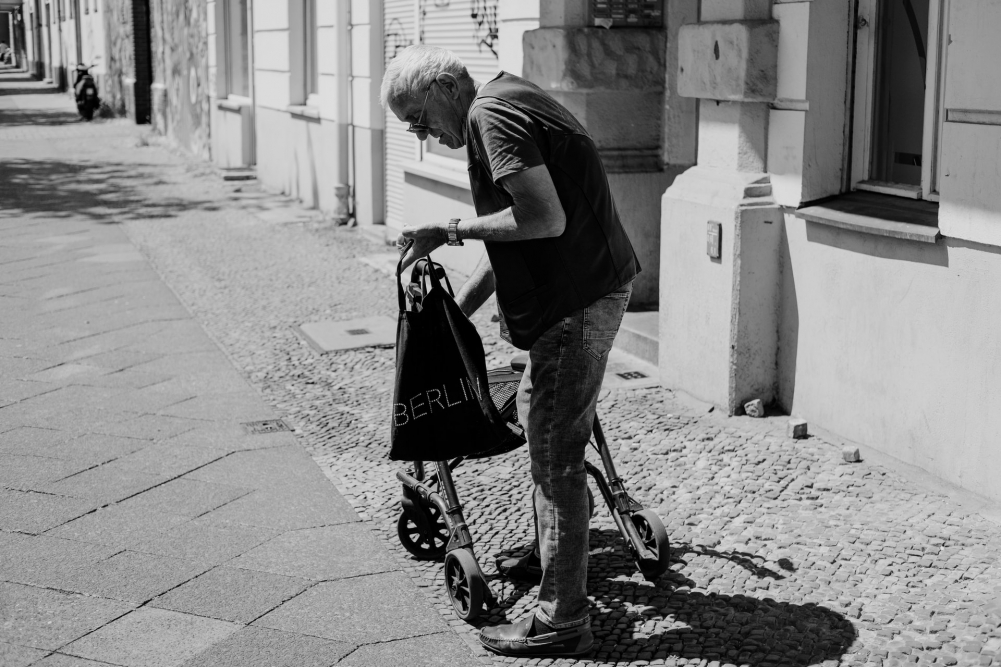

The finding is reported in an article in the Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle by researchers in Brazil and the UK, who analyzed data for more than 3,000 people aged 60 and over.
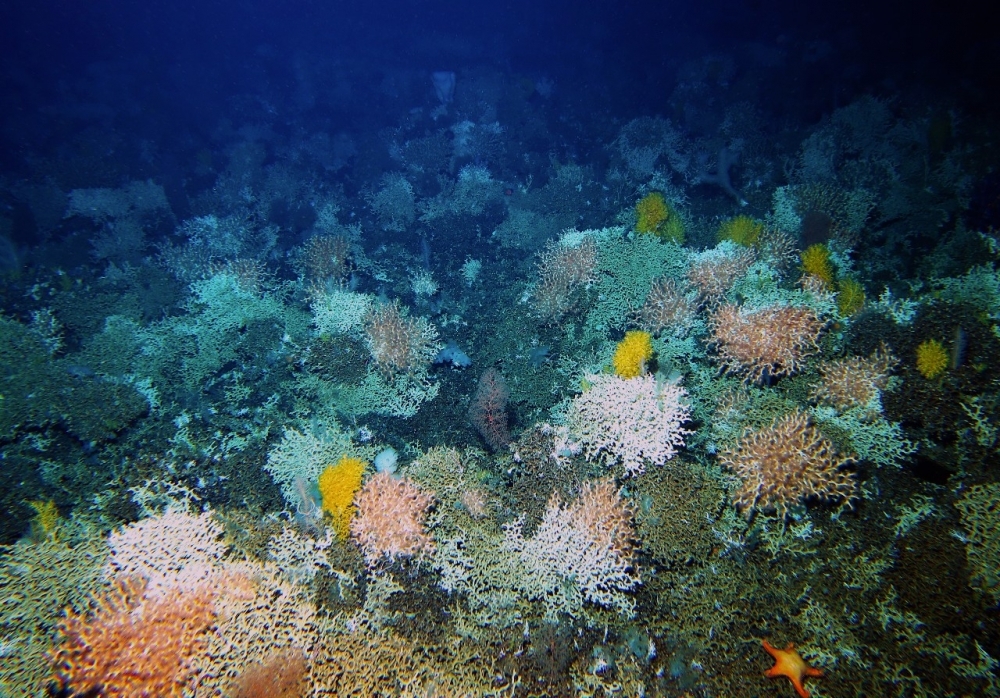

A book with a Brazilian co-author documents 267 species in the archipelago, 47 of which had never been described before. It resulted from 37 scientific expeditions conducted between 1978 and 2016 by France’s National Museum of Natural History.
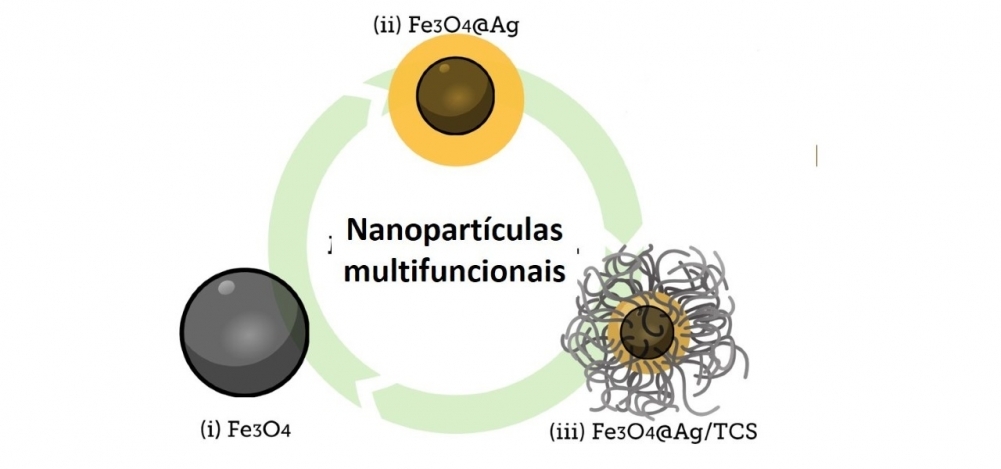
The proposition is to use nanoparticles that can be guided by applying an external magnetic field to attack solid tumors resistant to conventional treatment.
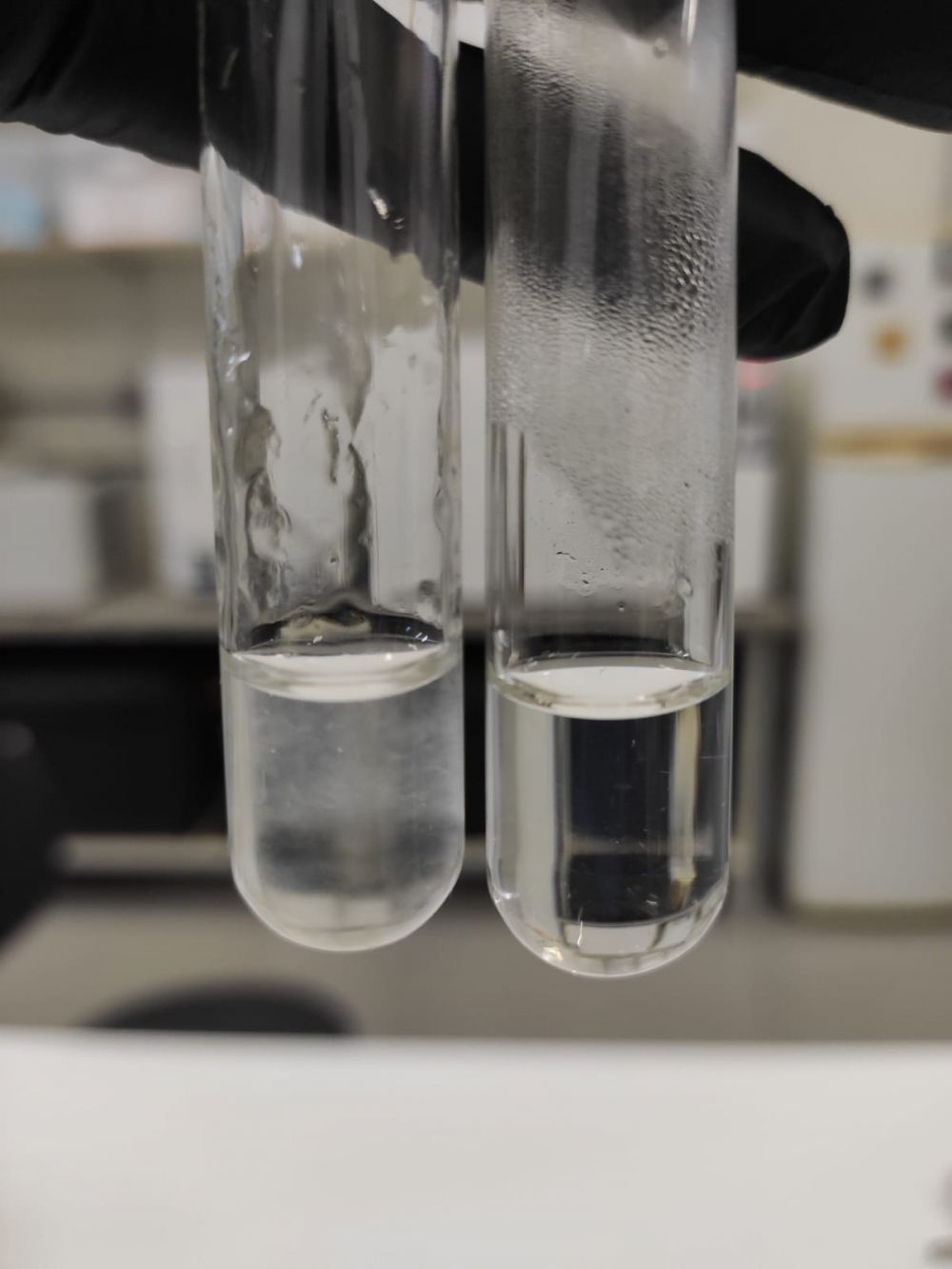

The global market for dermal fillers is expected to reach USD 9.4 billion by 2028. The technique consists of injecting hyaluronic acid into the region to be treated.
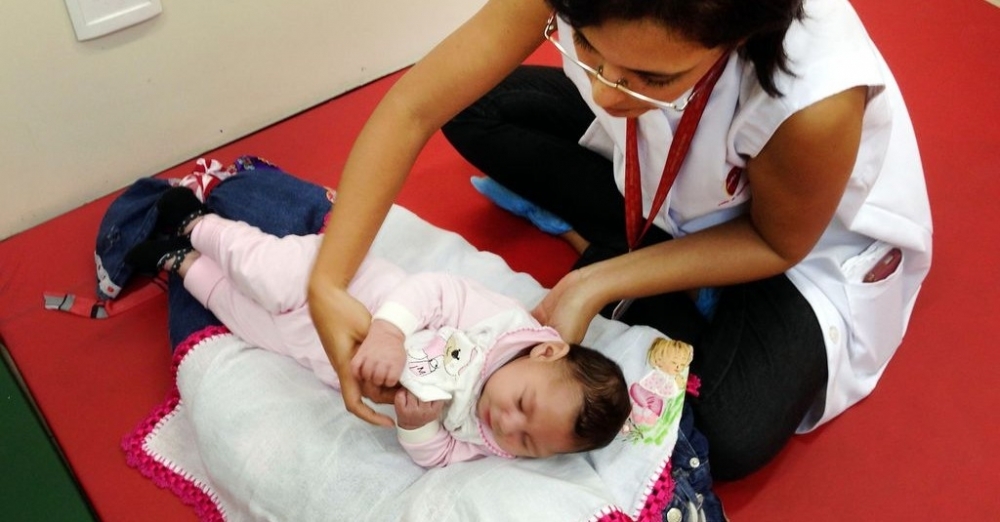
Assessment of two- and three-year-olds can help health professionals design personalized treatment. The study involved scientists in Brazil and the United States, and is published in PLOS ONE.
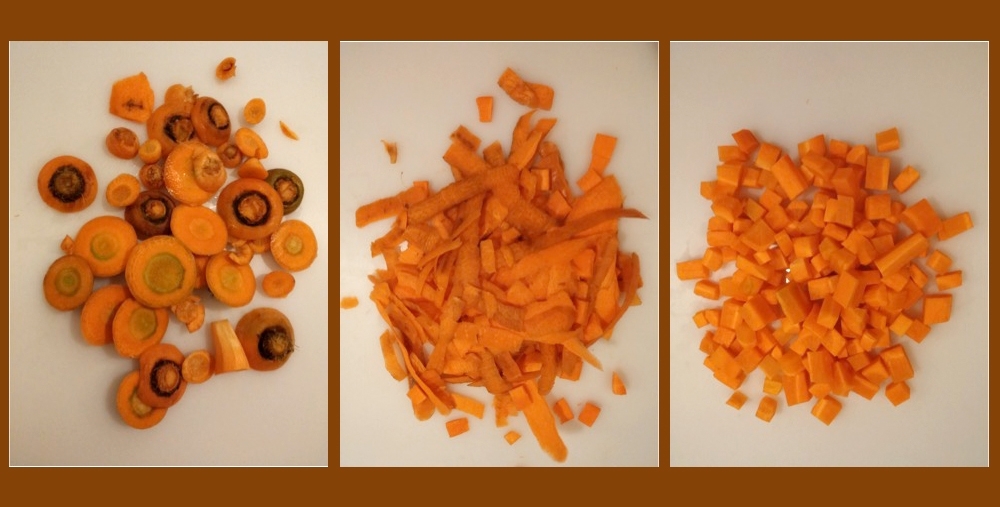

A paper by a research group including Brazilian scientists and international collaborators shows that low-cost waste biomass can be upcycled to make bioplastic, electronic devices, equipment for power generation, storage and transmission, and other high added-value products.
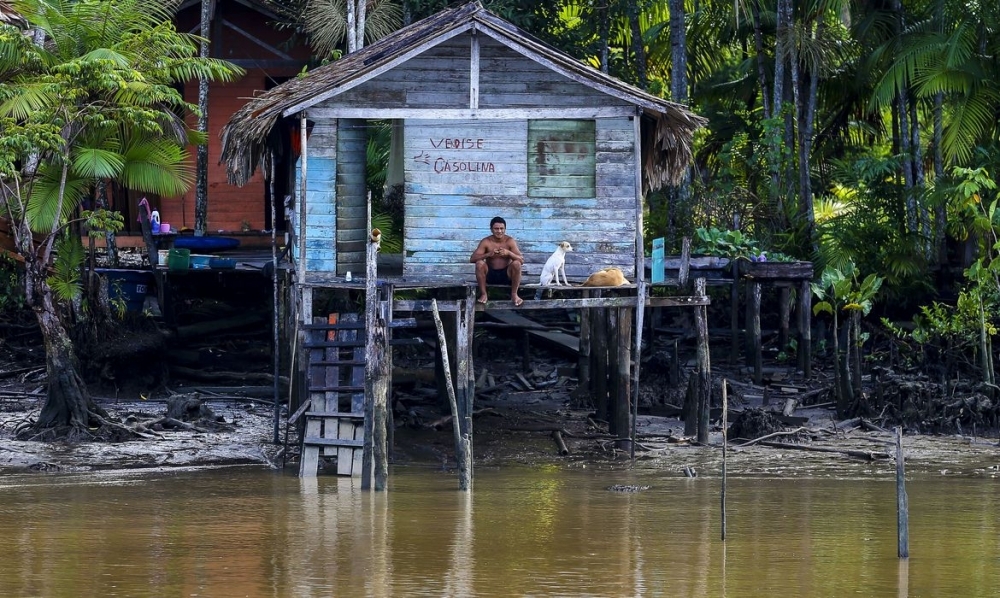

The launch was announced during COP26 at an event attended by São Paulo State Governor João Doria.