


Tool can support managers in setting conservation priorities for these ecosystems, called “blue carbon forests.” Brazil has the second largest mangrove area on the planet, behind only Indonesia.

After comparing data from over one million diagnosed individuals, an international consortium of researchers grouped the disorders into five major categories.

A network of genes linked to the nervous and immune systems can predict cancer risk and even explain symptoms such as fatigue and depression resulting from viral hepatitis infection.

A study by the São José do Rio Preto School of Medicine could increase the use of the most sought-after organ in Brazil. There are almost 30,000 people on the waiting list.

A study by the São José do Rio Preto School of Medicine could increase the use of the most sought-after organ in Brazil. There are almost 30,000 people on the waiting list.

Researchers at the University of São Paulo and the University of Wisconsin-Madison found that bleeding in the intestine during severe cases of the disease causes systemic infection and worsens the viral infection.

Researchers at the University of São Paulo and the University of Wisconsin-Madison found that bleeding in the intestine during severe cases of the disease causes systemic infection and worsens the viral infection.

A red extract made from Talaromyces amestolkiae was tested in the bases of potential products, including face cream, shampoo, and gel sticks, for its antioxidant and antibacterial properties.

A red extract made from Talaromyces amestolkiae was tested in the bases of potential products, including face cream, shampoo, and gel sticks, for its antioxidant and antibacterial properties.

Study reveals that evolutionary divergence occurred before ecological divergence, enabling these insects to feed on both wood and soil. Future discoveries may be applied to the production of biofuels.

Study reveals that evolutionary divergence occurred before ecological divergence, enabling these insects to feed on both wood and soil. Future discoveries may be applied to the production of biofuels.

The manufacturing strategy allows for the production of single and entangled photon emitters with low density, high symmetry, and wavelengths that are more suitable for integrated photonics.

The manufacturing strategy allows for the production of single and entangled photon emitters with low density, high symmetry, and wavelengths that are more suitable for integrated photonics.

Analyses conducted by researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos showed that the condition can be easily reversed through simple stimuli and strategies, reinforcing the need for programs aimed at this population.

Analyses conducted by researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos showed that the condition can be easily reversed through simple stimuli and strategies, reinforcing the need for programs aimed at this population.
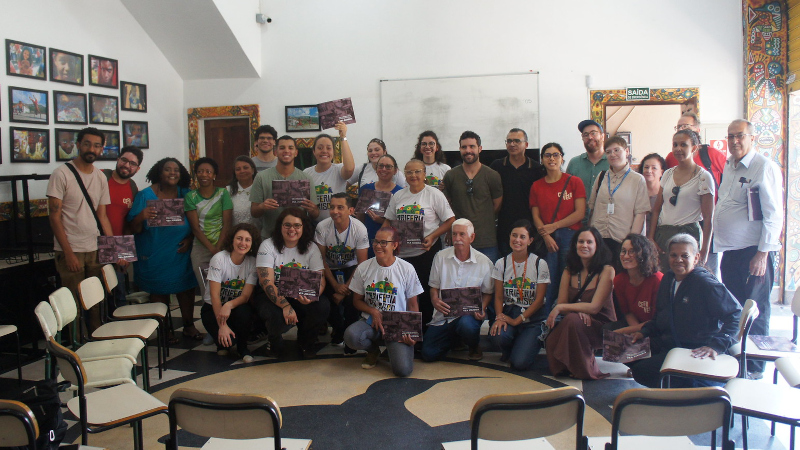

For 11 months, researchers from the FAPESP-funded Center for Favela Studies provided support to the community in the municipality of Diadema.

For 11 months, researchers from the FAPESP-funded Center for Favela Studies provided support to the community in the municipality of Diadema.
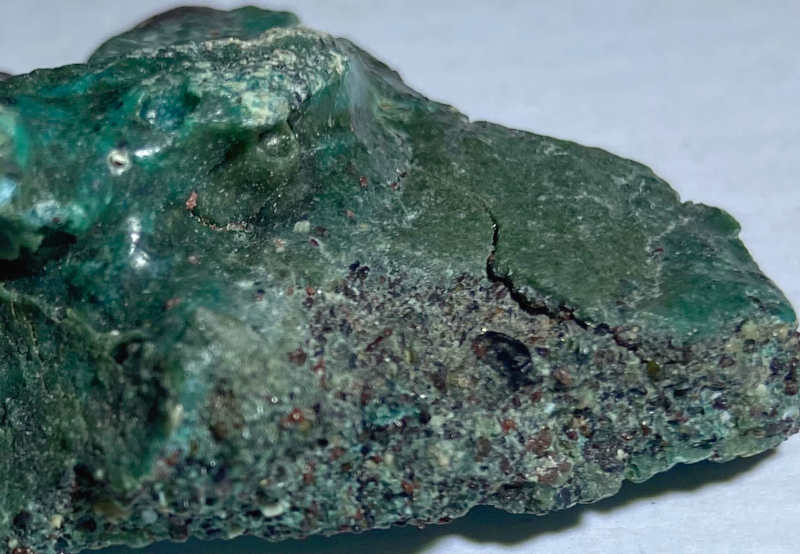

Study observed accumulation of plastic on Trindade Island, Brazil’s easternmost territory, precisely in the depressions where turtles lay their eggs and hatchlings are born.

Study observed accumulation of plastic on Trindade Island, Brazil’s easternmost territory, precisely in the depressions where turtles lay their eggs and hatchlings are born.
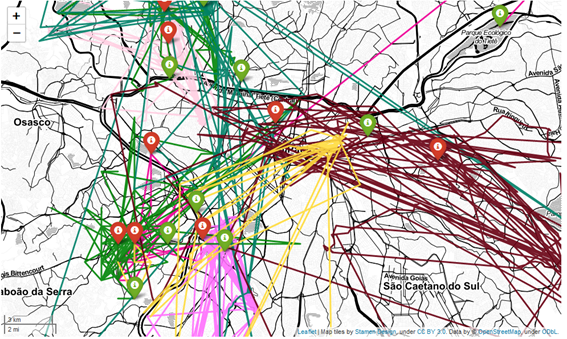
Research using mobile phone data indicates that the living condition reduces the variability of daily movements.

Research using mobile phone data indicates that the living condition reduces the variability of daily movements.
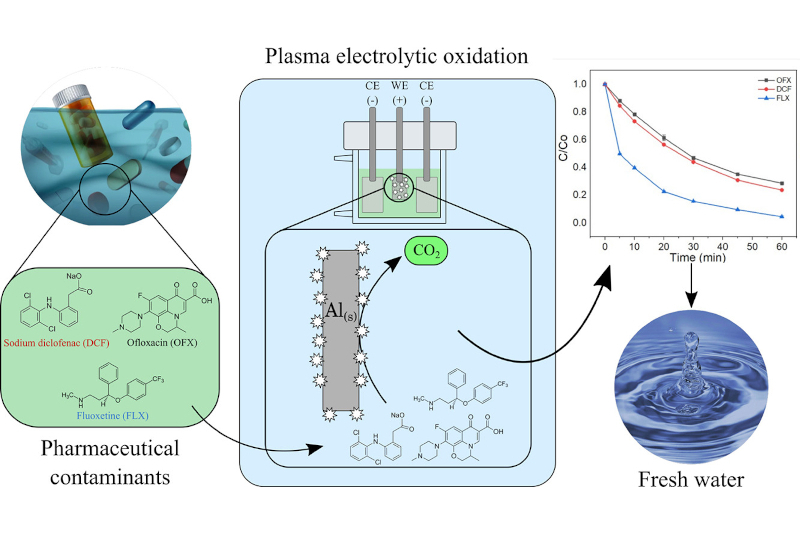
A study supported by FAPESP tested using high-energy sparks to degrade pollutants without generating waste.

A study supported by FAPESP tested using high-energy sparks to degrade pollutants without generating waste.
Research from São Paulo State University shows that an inexpensive, easy-to-produce substance eliminated lung infection in 30 days. The compound has the potential to reduce the time and toxicity of current therapies.

Research from São Paulo State University shows that an inexpensive, easy-to-produce substance eliminated lung infection in 30 days. The compound has the potential to reduce the time and toxicity of current therapies.