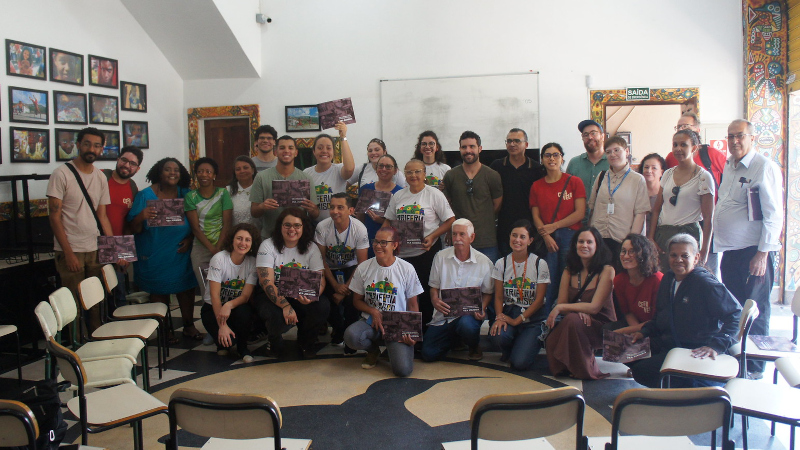



For 11 months, researchers from the FAPESP-funded Center for Favela Studies provided support to the community in the municipality of Diadema.

Study observed accumulation of plastic on Trindade Island, Brazil’s easternmost territory, precisely in the depressions where turtles lay their eggs and hatchlings are born.

Study observed accumulation of plastic on Trindade Island, Brazil’s easternmost territory, precisely in the depressions where turtles lay their eggs and hatchlings are born.
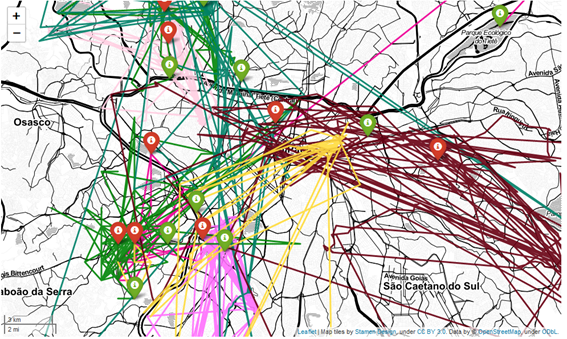
Research using mobile phone data indicates that the living condition reduces the variability of daily movements.

Research using mobile phone data indicates that the living condition reduces the variability of daily movements.
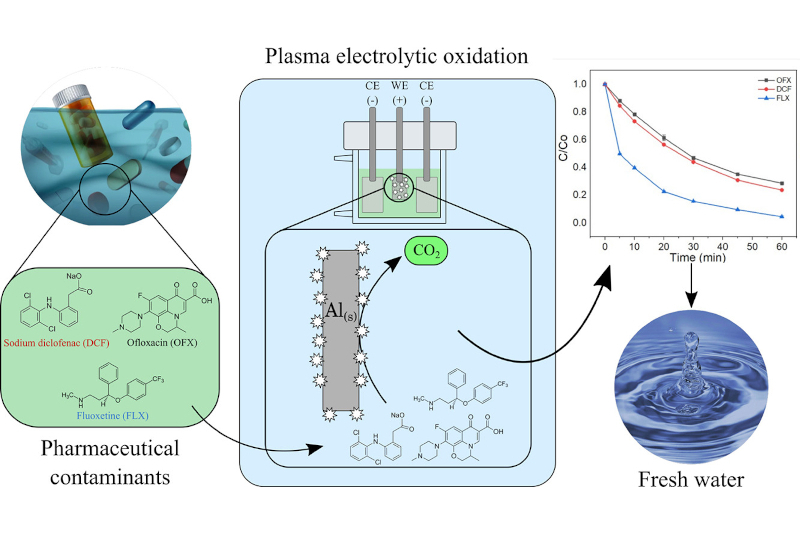
A study supported by FAPESP tested using high-energy sparks to degrade pollutants without generating waste.

A study supported by FAPESP tested using high-energy sparks to degrade pollutants without generating waste.
Research from São Paulo State University shows that an inexpensive, easy-to-produce substance eliminated lung infection in 30 days. The compound has the potential to reduce the time and toxicity of current therapies.

Research from São Paulo State University shows that an inexpensive, easy-to-produce substance eliminated lung infection in 30 days. The compound has the potential to reduce the time and toxicity of current therapies.
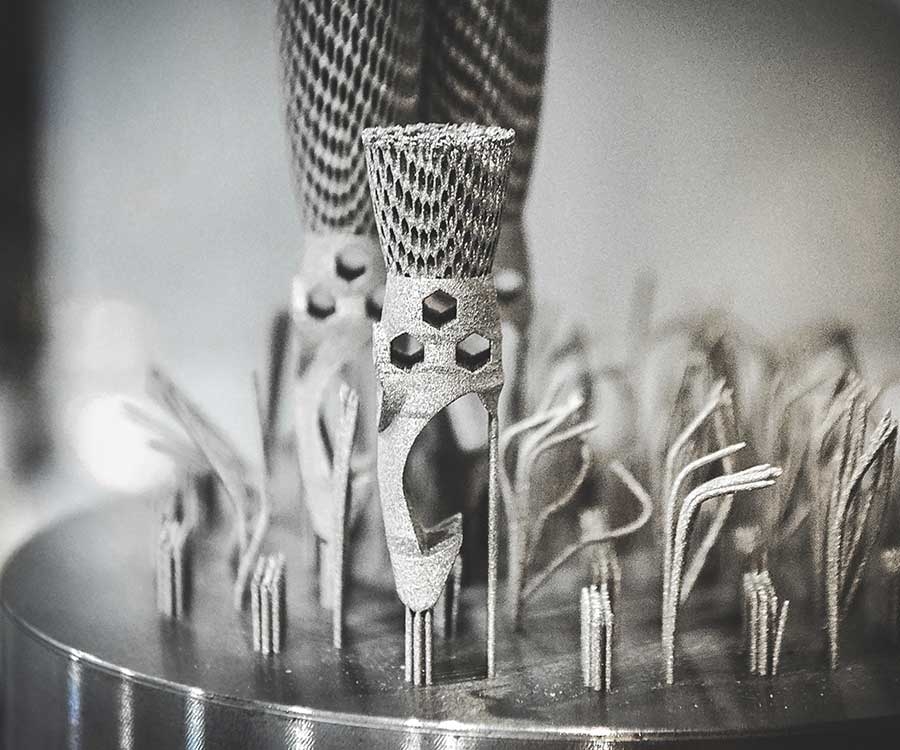

Software developed by a FAPESP-supported startup simulates complex industrial processes and promises to reduce costs in sectors ranging from aviation to wind energy.

Software developed by a FAPESP-supported startup simulates complex industrial processes and promises to reduce costs in sectors ranging from aviation to wind energy.
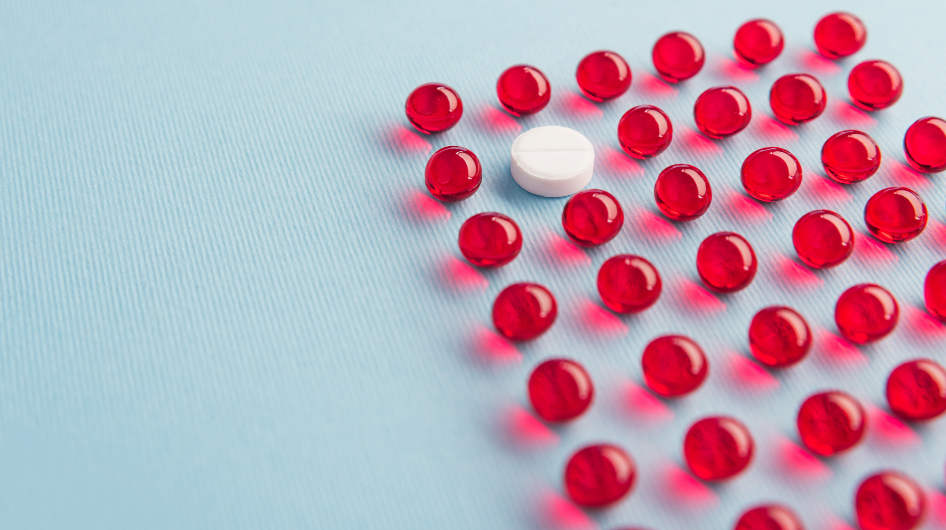

In a preliminary study conducted on human cells, two commonly used osteoporosis drugs bound to excess iron, preventing cell damage.

In a preliminary study conducted on human cells, two commonly used osteoporosis drugs bound to excess iron, preventing cell damage.
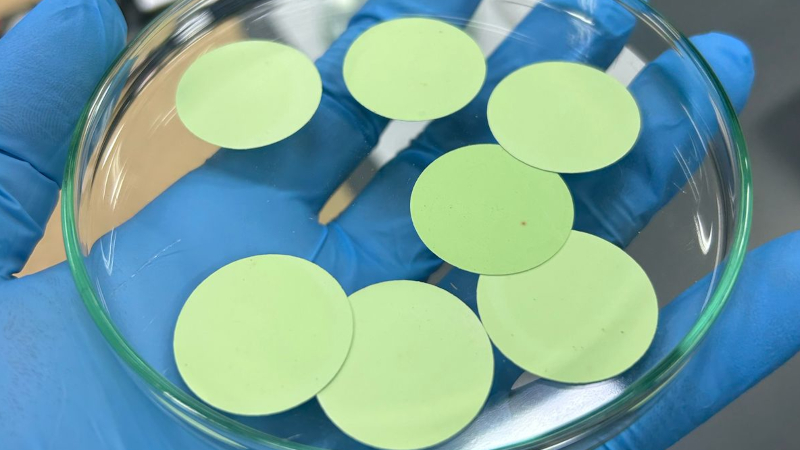

Funded by FAPESP, the Center for Innovation on New Energies has already produced 100% Brazilian prototypes, reducing dependence on foreign suppliers.

Funded by FAPESP, the Center for Innovation on New Energies has already produced 100% Brazilian prototypes, reducing dependence on foreign suppliers.
A study by FAPESP-supported center used the NK-92 cell line to test new chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) models. Tests demonstrated an increased ability of the cells to destroy tumors.
FAPESP-supported startup uses artificial intelligence to connect government data and reveal a complete picture of innovation ecosystems in all Brazilian municipalities.
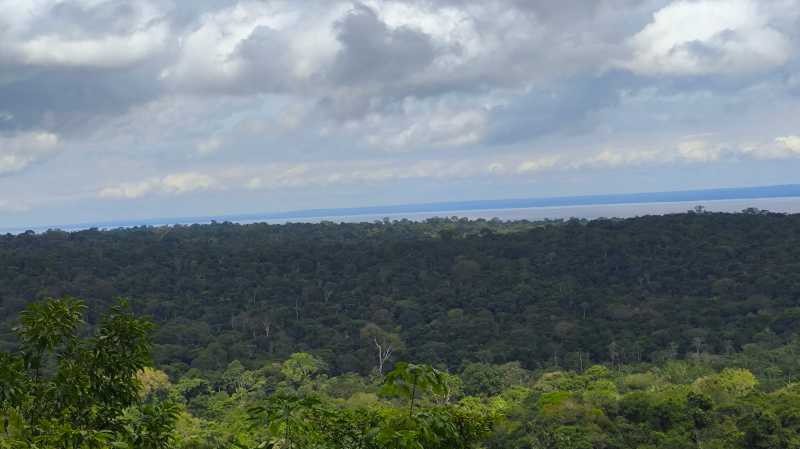

Satellite data also shows 25% less rainfall compared to regions with high forest cover.

Combining acceptance and monitoring in the education of young people reduces the risk of repeating consumption patterns, even in families where parents also use these substances, including cigarettes, vapes, and marijuana.
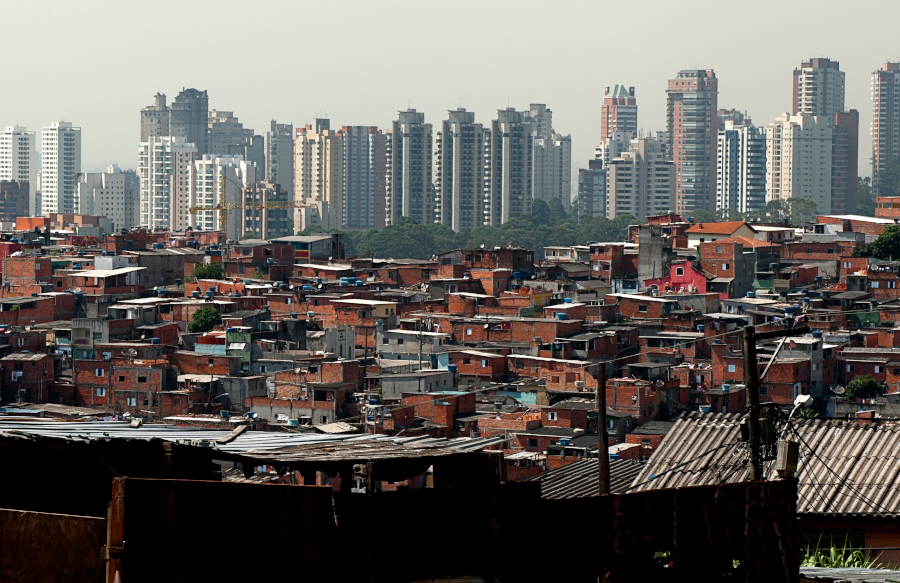

Research by a FAPESP-supported center indicates that the favela formation process is ongoing but slowing down.
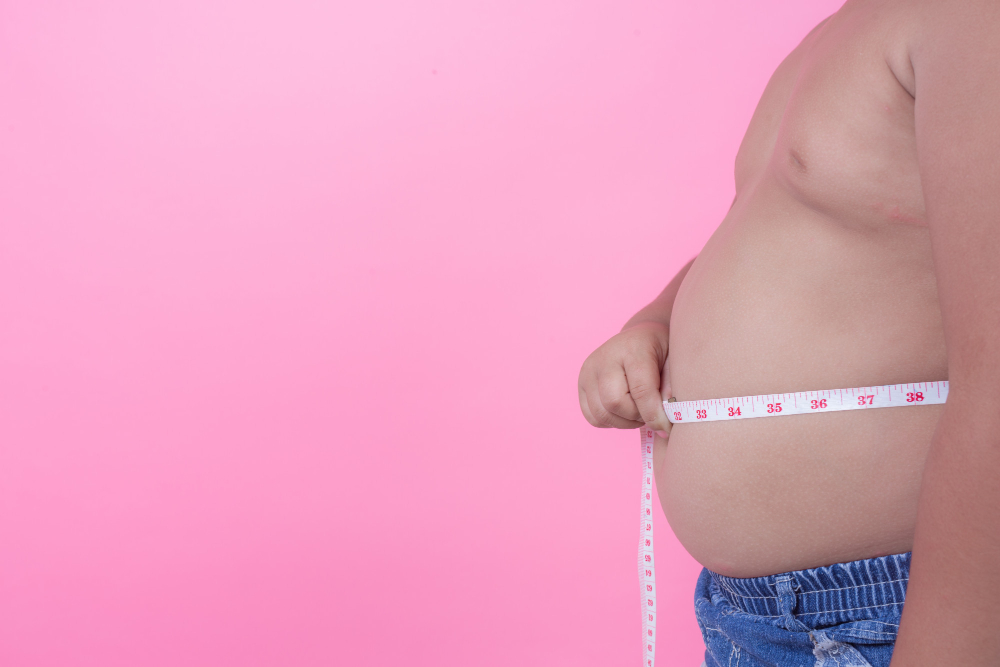

Research conducted with 130 children between the ages of six and 11 showed that inflammation associated with obesity and being overweight affects the functioning of the endothelium – the layer that lines blood vessels – paving the way for diseases such as atherosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke.
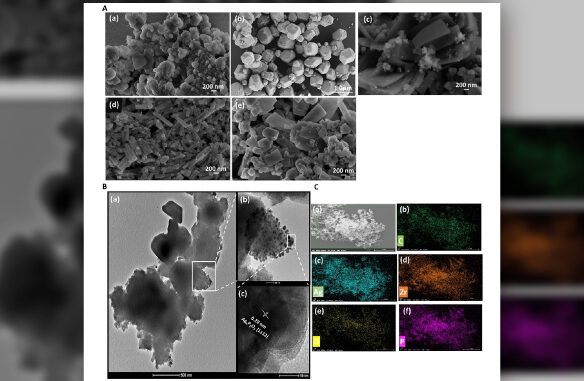
Study involving researchers from a FAPESP-supported center presents a new molecular architecture based on zirconium metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) designed for efficiently degrading emerging water contaminants.
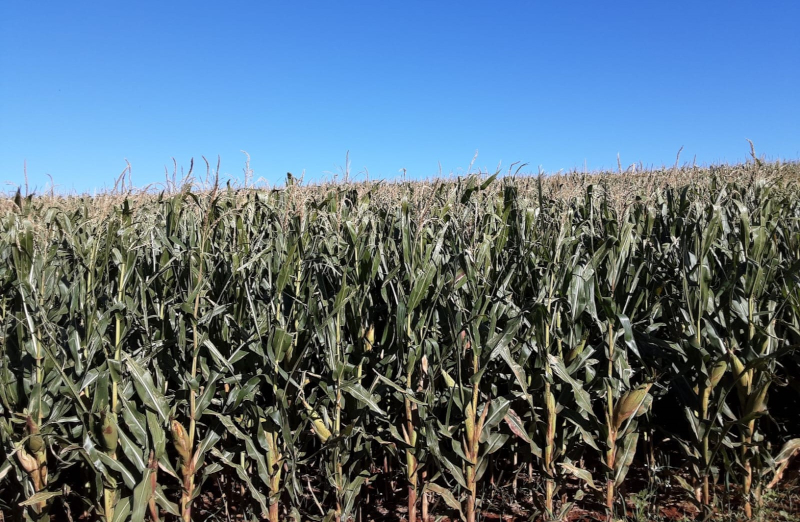

Tool uses remote sensing to reduce uncertainties regarding agricultural losses, contributing to public policy.
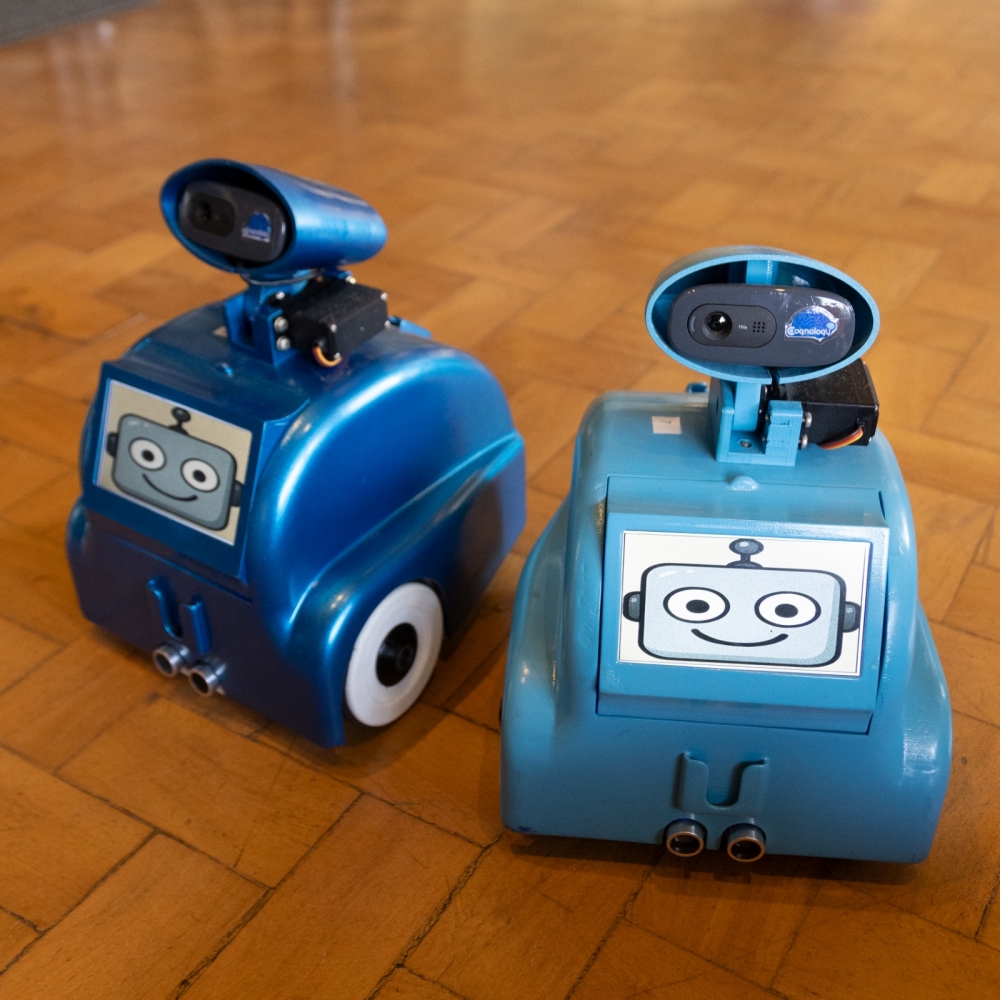

Brazilian startup supported by FAPESP develops technology to support teachers and identify individual student difficulties.
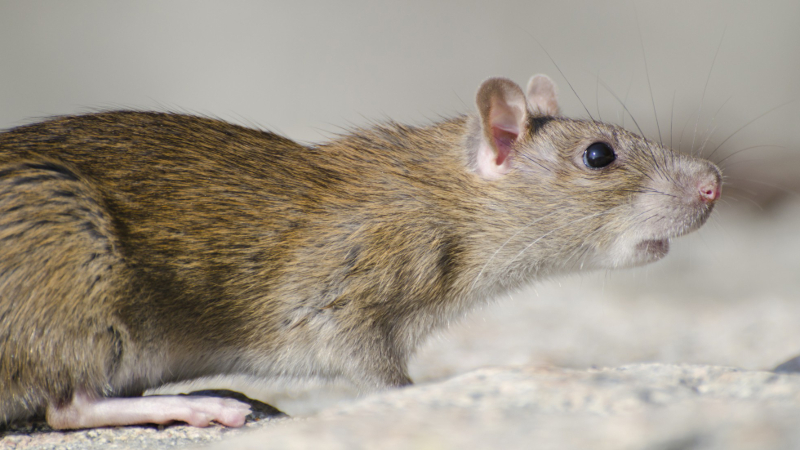

Research from São Paulo State University shows that carbetocin, when administered before social stress situations, prevents anxiety in laboratory rats without having direct anxiolytic effects.