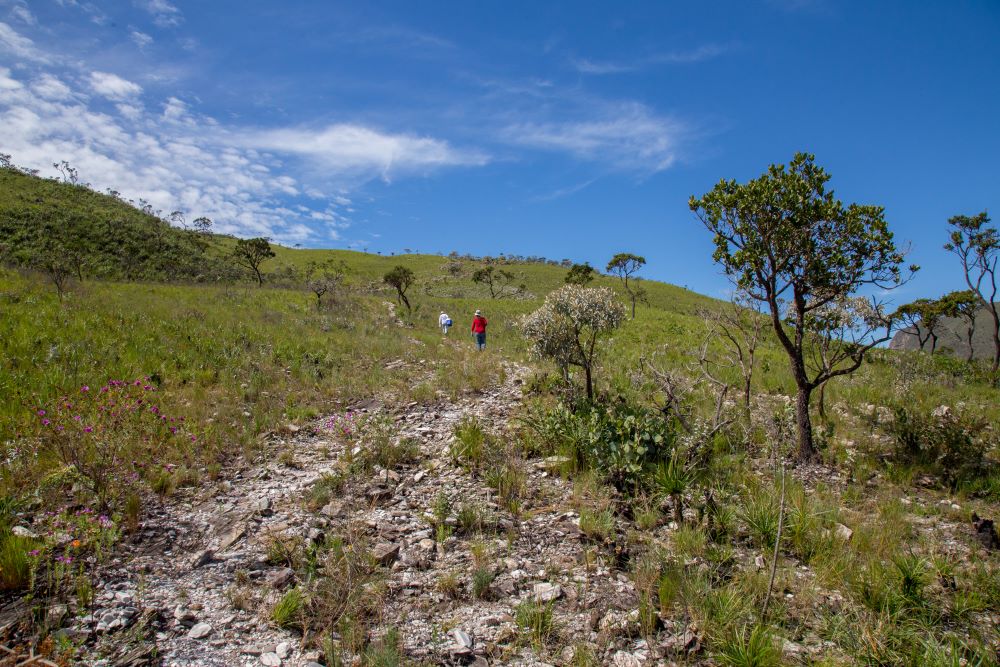



A study has identified more than 257,000 species of bacteria and archaea in velozias, which are plants that thrive in extreme environments of drought, heat, and poor soil, such as this mountainous savannah ecoregion. The results could guide conservation initiatives and biotechnological solutions for soil management in arid conditions.

In an article published in a scientific journal, the group emphasizes that Brazil must align its domestic policies with international commitments.

In an article published in a scientific journal, the group emphasizes that Brazil must align its domestic policies with international commitments.

The margin must be defined as a reference point in the COP30 negotiations, assess members of the Scientific Council of the climate conference presidency.
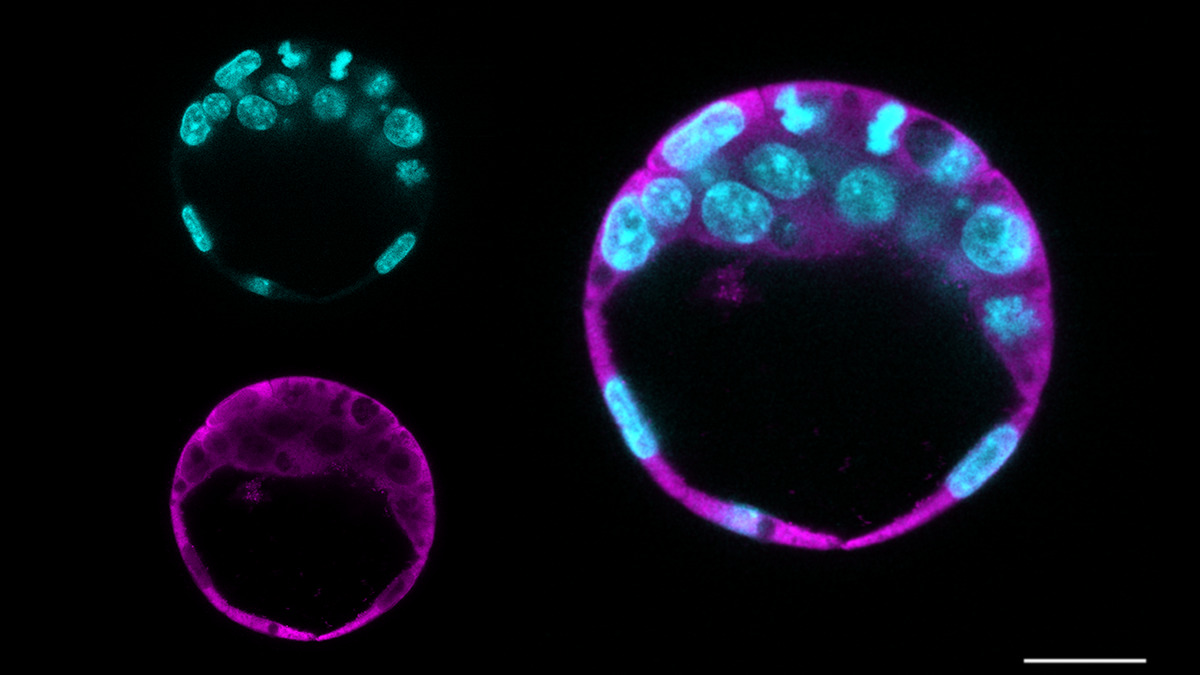
Led by scientists from the University of São Paulo, the studies help clarify the roles of STIP1 and Maspin in vital cell processes and pave the way for advances related to cancer and applications in regenerative medicine.

Led by scientists from the University of São Paulo, the studies help clarify the roles of STIP1 and Maspin in vital cell processes and pave the way for advances related to cancer and applications in regenerative medicine.
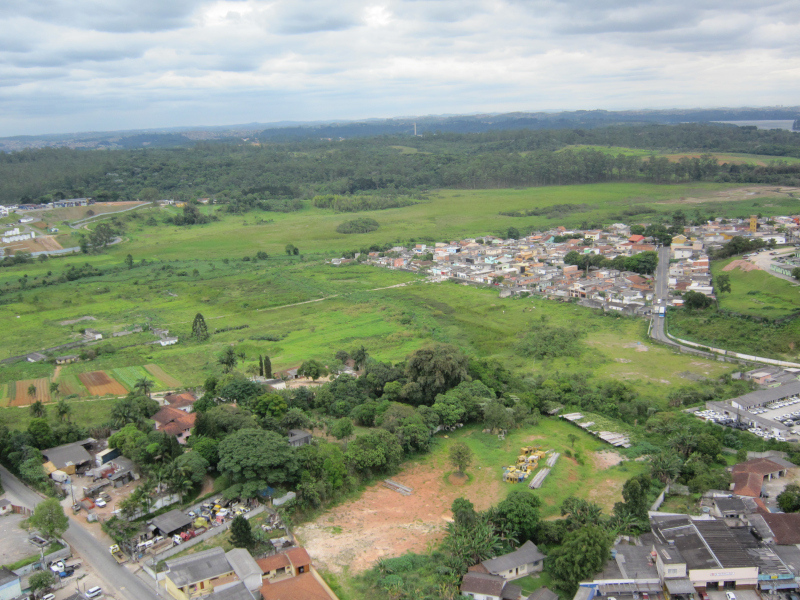

Researchers from a FAPESP-supported research center point to 410,000 hectares of land in cities that could be regenerated.

Researchers from a FAPESP-supported research center point to 410,000 hectares of land in cities that could be regenerated.
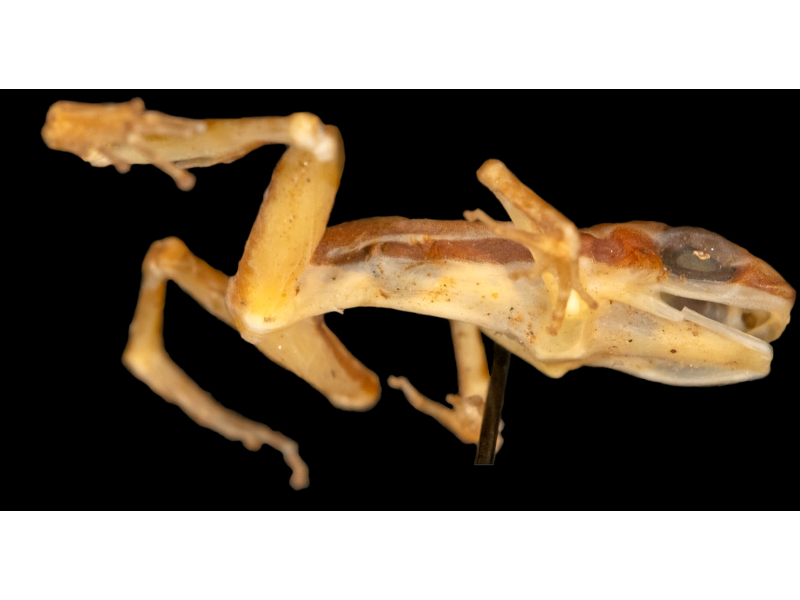

The dried specimen of the amphibian, collected by herpetologist Doris Cochran in 1963 in what is now a residential neighborhood of Curitiba, Brazil, is stored in the collection of the Smithsonian Institution’s National Museum of Natural History in the United States.

The dried specimen of the amphibian, collected by herpetologist Doris Cochran in 1963 in what is now a residential neighborhood of Curitiba, Brazil, is stored in the collection of the Smithsonian Institution’s National Museum of Natural History in the United States.
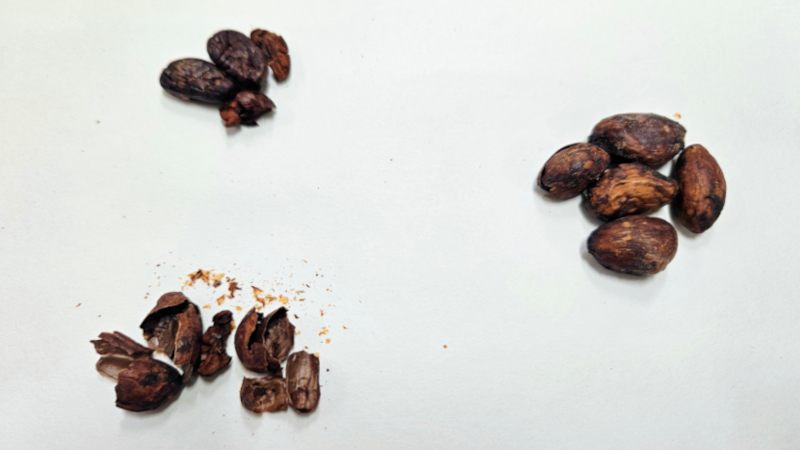

Researchers at the State University of Campinas used a product from native stingless bees to extract bioactive compounds, such as caffeine, from chocolate manufacturing waste. This process adds nutritional and commercial value to an ingredient that is usually discarded.

Researchers at the State University of Campinas used a product from native stingless bees to extract bioactive compounds, such as caffeine, from chocolate manufacturing waste. This process adds nutritional and commercial value to an ingredient that is usually discarded.

Mathematical tool aims to minimize total capital and operating costs while ensuring robust performance in the face of instabilities in the supply of renewable energy, since the sun and wind are intermittent sources.

Mathematical tool aims to minimize total capital and operating costs while ensuring robust performance in the face of instabilities in the supply of renewable energy, since the sun and wind are intermittent sources.
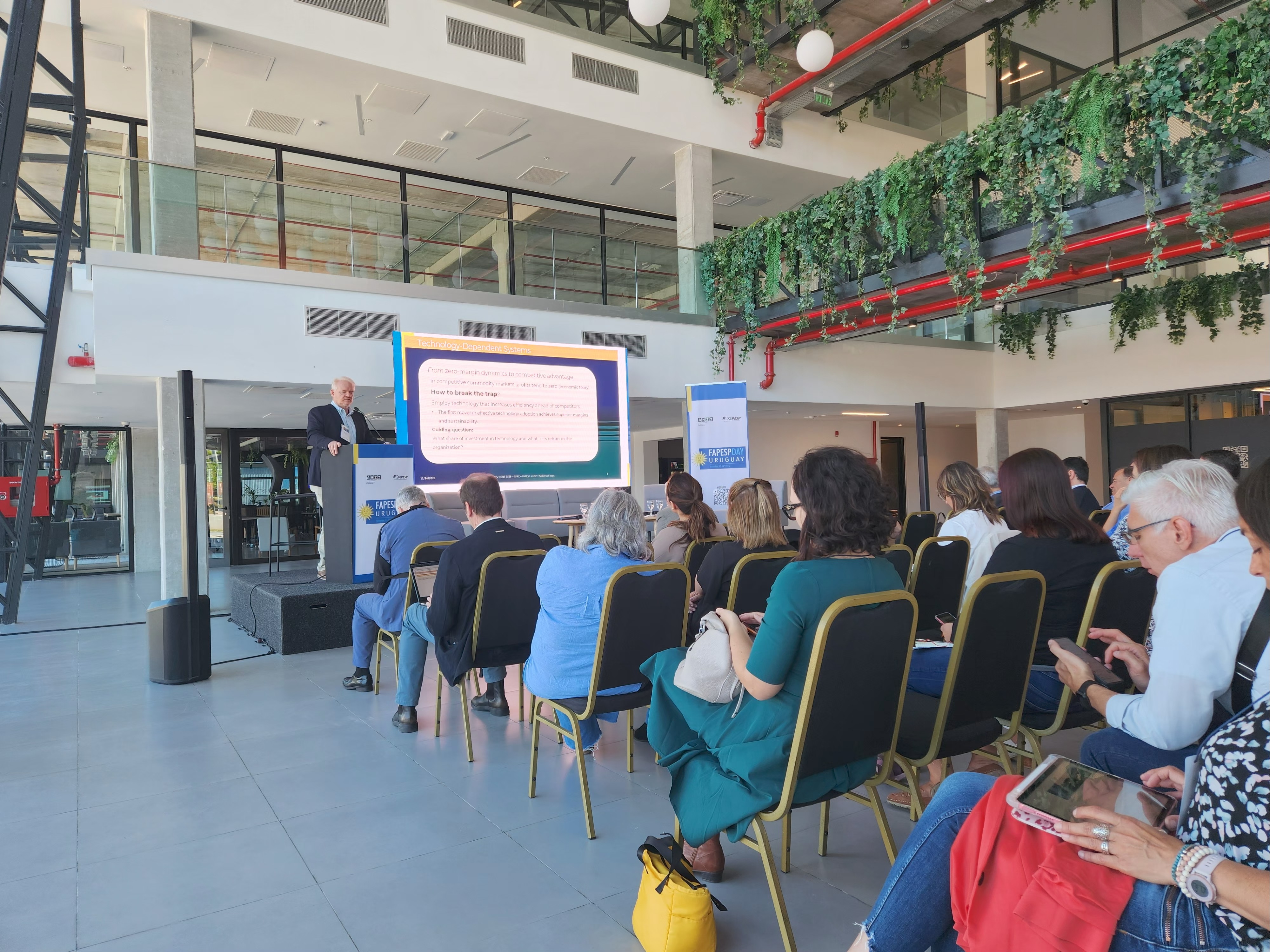

Professor Sérgio de Zen presented the project during the FAPESP Day Uruguay symposium. An investment of USD 20 million over five years is planned.

Professor Sérgio de Zen presented the project during the FAPESP Day Uruguay symposium. An investment of USD 20 million over five years is planned.

One of the main objectives is to encourage collaboration between researchers from the Uruguayan institution and their counterparts at the Pasteur Institute of São Paulo.

One of the main objectives is to encourage collaboration between researchers from the Uruguayan institution and their counterparts at the Pasteur Institute of São Paulo.

Coastal ecosystems are being affected by the rising sea level associated with the expansion of real estate development; Marine scientist Omar Defeo, a professor at Uruguay’s University of the Republic, addressed this topic during the FAPESP Day Uruguay symposium.

Bacteriophages, or phages for short, can kill bacteria and may be used to combat hospital infections and food contamination.
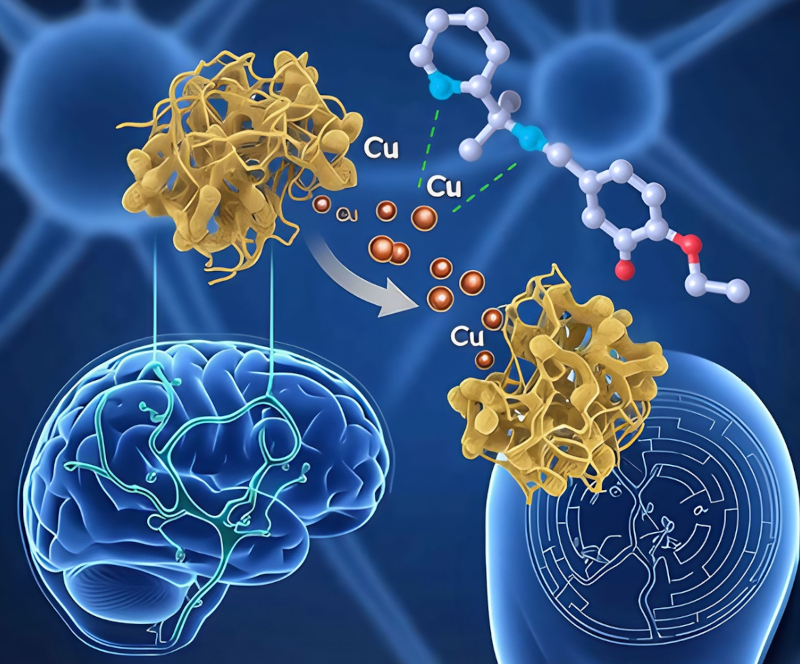
A group from the Federal University of the ABC tested the substance on rats and obtained positive results. The group is now seeking partnerships with pharmaceutical companies to conduct clinical trials.
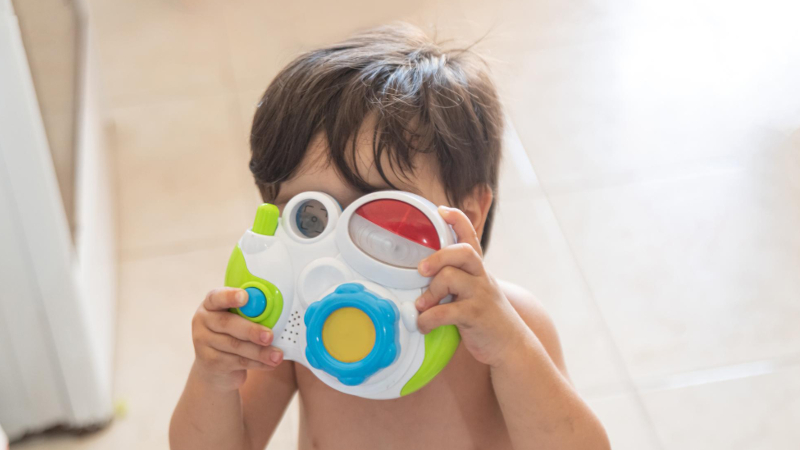

An analysis of 70 plastic children’s products sold in Brazil revealed chemical contamination in most samples, with levels up to 15 times higher than permitted. Barium, lead, chromium, and antimony were the most commonly found toxic elements.

The formulation seeks to block the transmission of canine visceral leishmaniasis in order to protect both animals and humans.

Results from a study conducted in a natural area in the municipality of São Paulo (Brazil) may help estimate the effects of climate change on disease transmission risk in the biome.
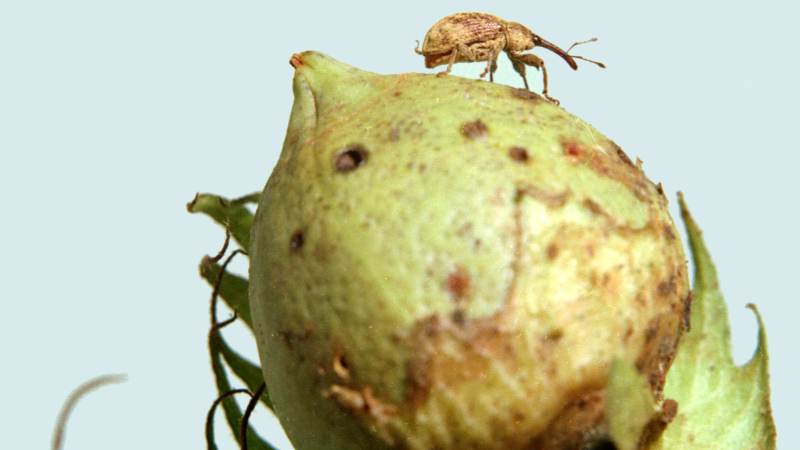

Researchers revisit advances in generating genetically modified plants that prevent bedbugs, beetles, weevils, and woodworms from digesting starch.