


The initiative brings together documents, photos, and interviews with scientists who, since 1962, have advanced knowledge on topics including biodiversity, climate change, and traditional communities through their research.
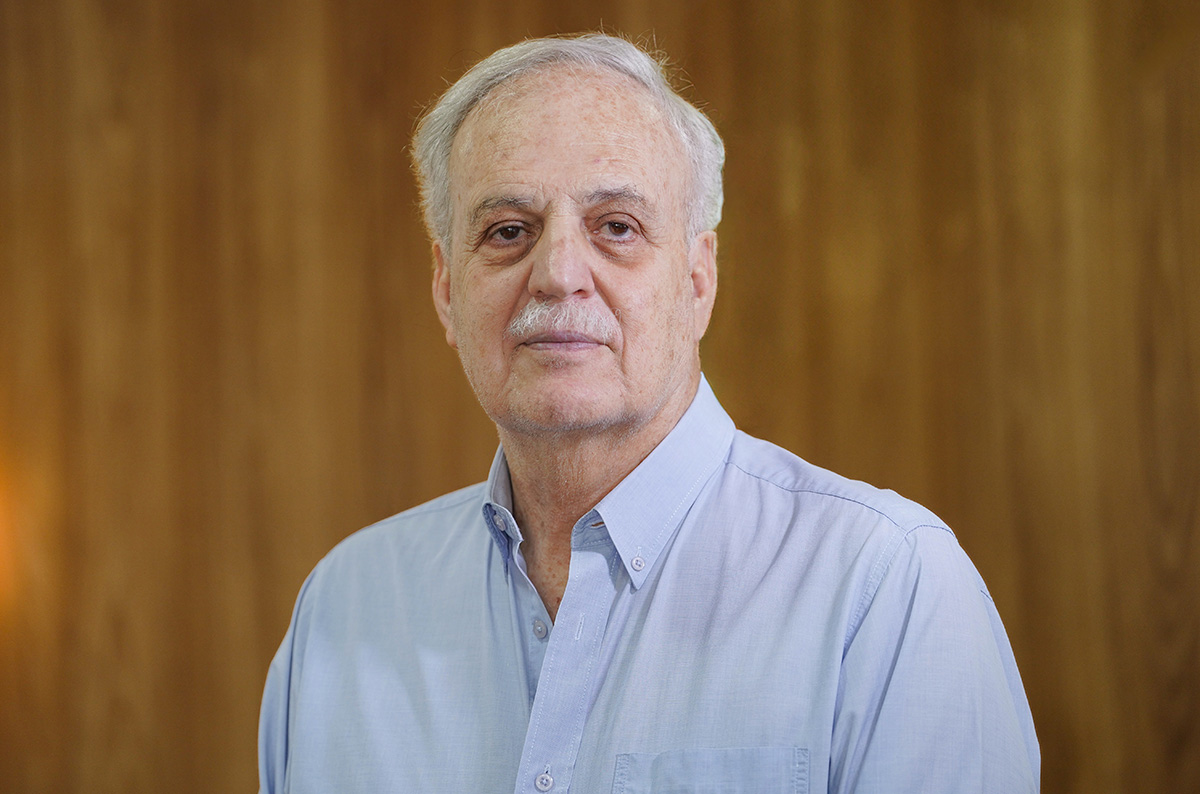

The climate scientist was the first scientific coordinator of the Large-Scale Biosphere-Atmosphere Experiment in the Amazon (LBA).
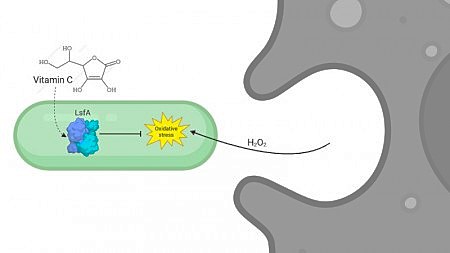
Findings contribute to the search for new targets against hospital infections.

With COP30 in Belém approaching, the ideas of the former French Minister of Justice are gaining momentum, inviting us to rethink multilateralism and the structure of the institutions that shape the world.
A three-year study of 77 people showed that analyzing myocardial deformation during contraction can predict the risk of death.

The research used network theory to analyze the ecological connectivity of 28 areas in the northwest of the state of São Paulo, Brazil.

Technology created by a startup supported by FAPESP accelerates patient recovery and improves biological integration.
Regions most vulnerable to climate change and environmental degradation produce the least local knowledge on the subject.

The study investigated compounds that can be used as electrolytes in sodium-ion devices. Sodium is an abundant and widely distributed element. The equipment shows great promise for storing surplus energy from solar and wind farms.
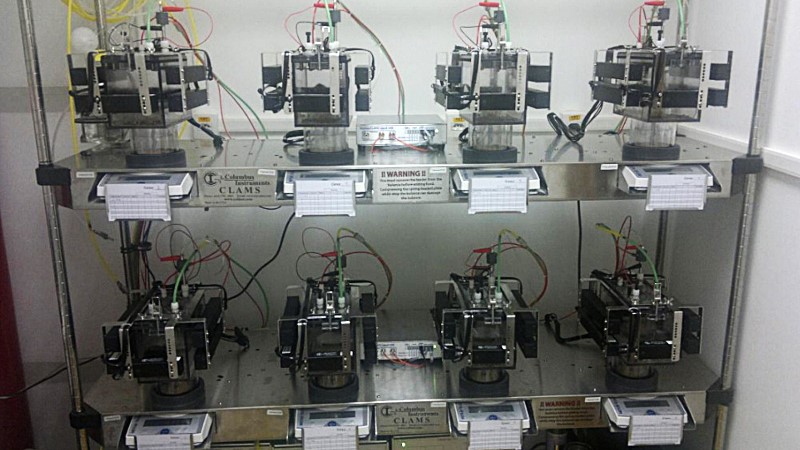

Standardization opens up possibilities for developing preclinical trials of new drug classes that focus on calorie burning.
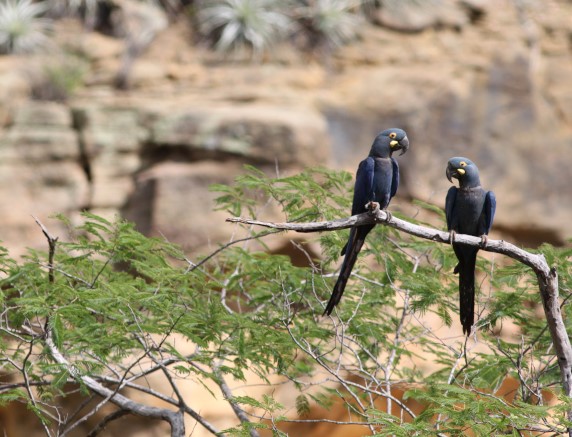

At least 35 individuals of the endangered Lear's macaw have been killed by electrocution in the semi-arid region of Bahia, Brazil, in 2025. Replacing 10% of the riskiest poles could prevent 80% of these deaths.
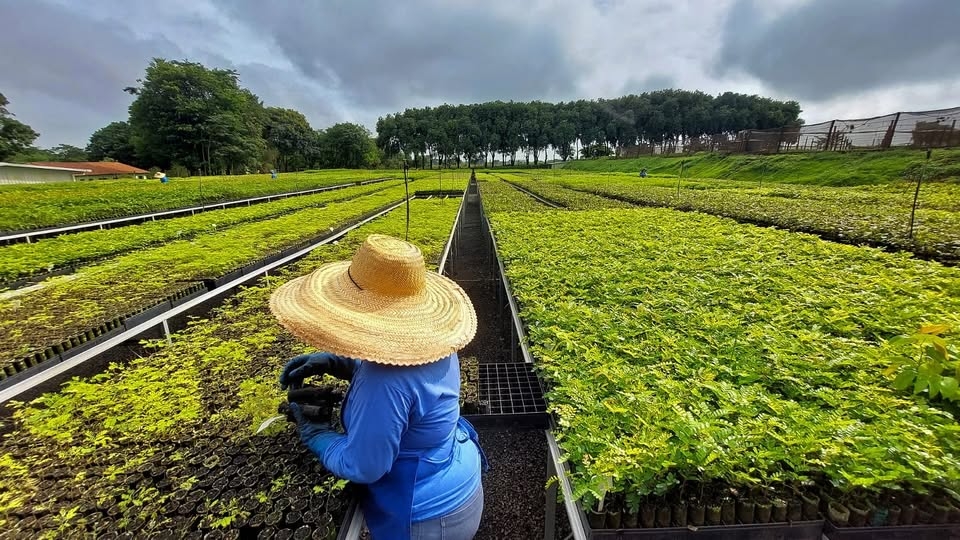

One way Re.green compensates its investors is by selling carbon credits sequestered by restored areas. The calculation methodology is based on the results of a project supported by FAPESP.

Often treated as waste from the pulp and paper industry, lignin, a polymer responsible for the rigidity of plant cell walls, has increased the stability and effectiveness of herbicide nanoparticles.

Research shows that areas with 50% deforestation near residential areas or fragmented vegetation allow greater contact between mosquitoes and humans. Amid the discussions for COP30, the study helps us understand the link between forest destruction and the spread of the disease.
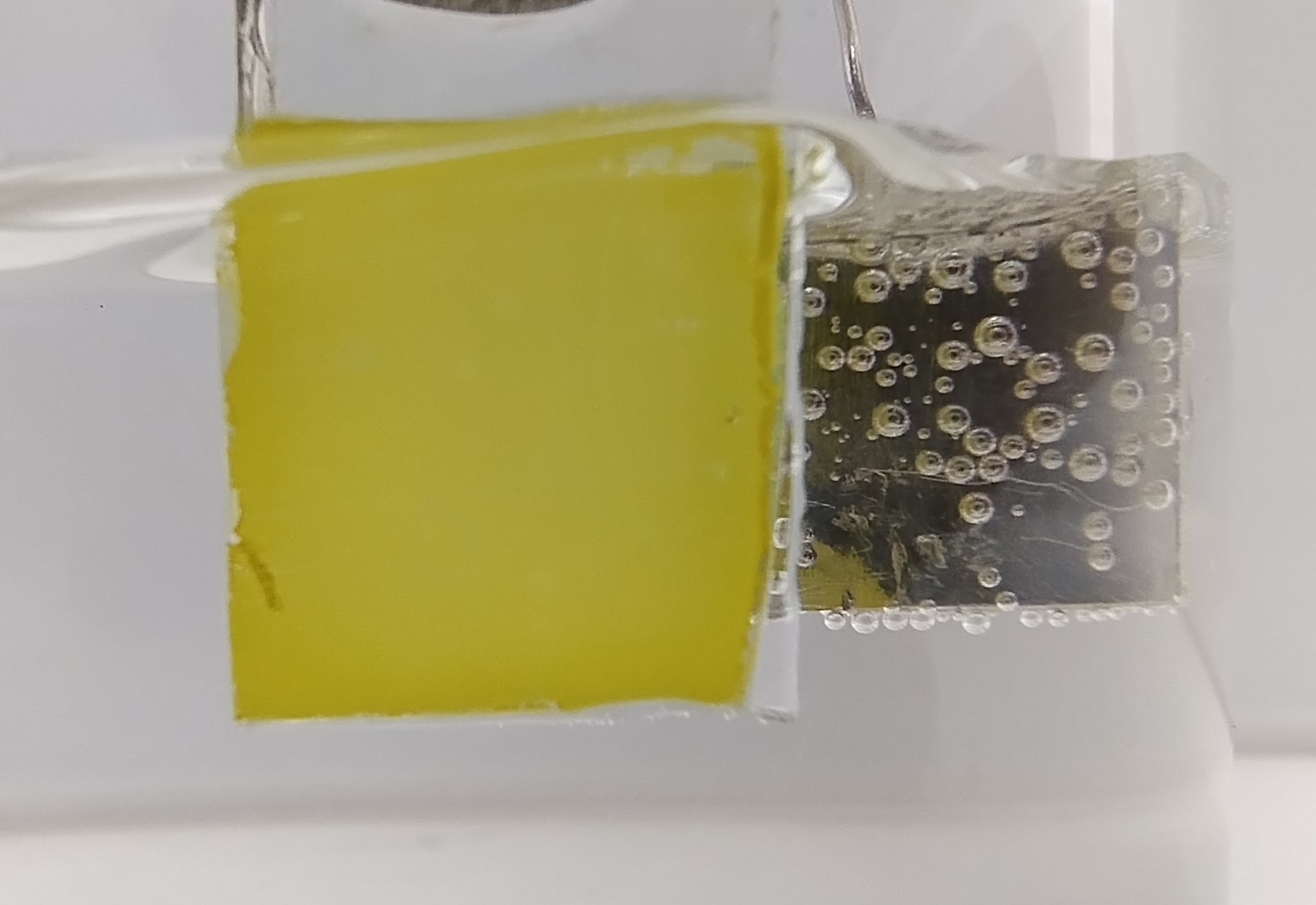
According to a study led by researchers from the Center for Innovation in New Energies, the abundant biodiesel by-product increases the efficiency of photoelectrochemical cells since water oxidation is slow and inefficient.
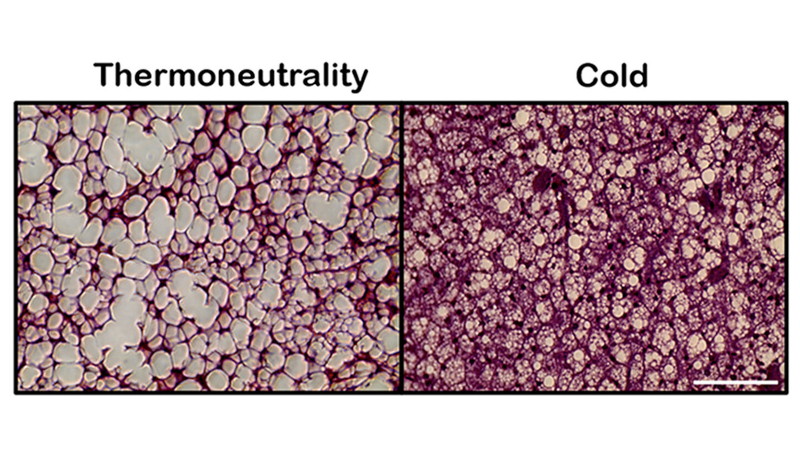
Research conducted by Redoxoma, a FAPESP Research, Innovation, and Dissemination Center, found that mitochondrial potassium channels regulate heat production in brown adipose tissue.

The plant family can store twice as much water as trees such as ipê, mahogany, and eucalyptus, according to a study conducted at São Paulo State University. Preliminary results were presented during the Brazil-France 2025 Forum “Forests, Biodiversity, and Human Societies”.

Spin-off of startup supported by FAPESP develops technology based on artificial intelligence to create individualized beauty products.
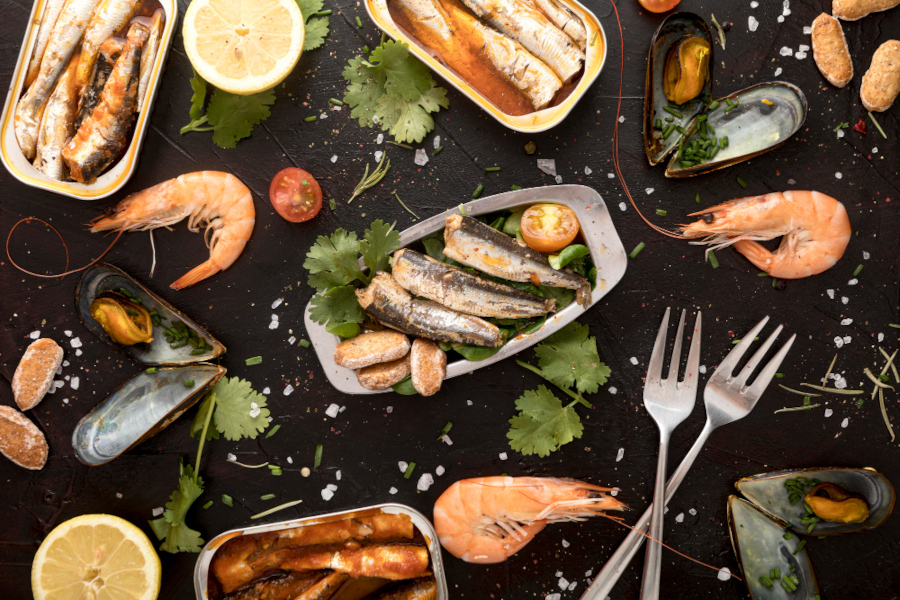

In the nearly three years since its creation, the Fish for Health Research Center has achieved significant results in understanding the nutritional value and consumption habits of fish in the state of São Paulo, received new investments, and is preparing to expand its network of associated researchers.
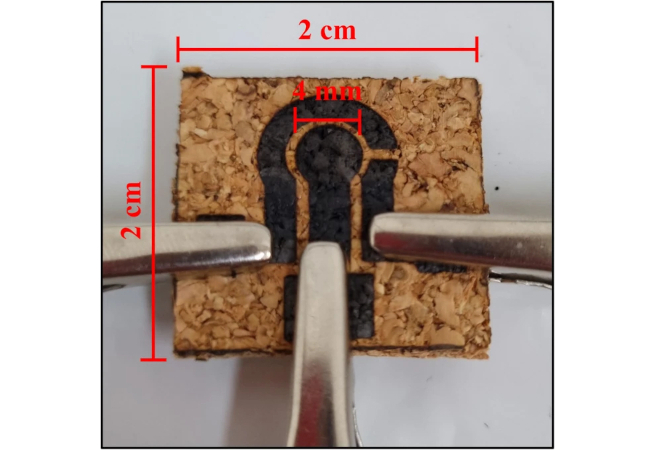
Sodium nitrate is used as a preservative and to add color to products such as ham and sausages, but is potentially carcinogenic and cannot be applied in beverages; researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos used pieces of cork and lasers to develop a sensor.
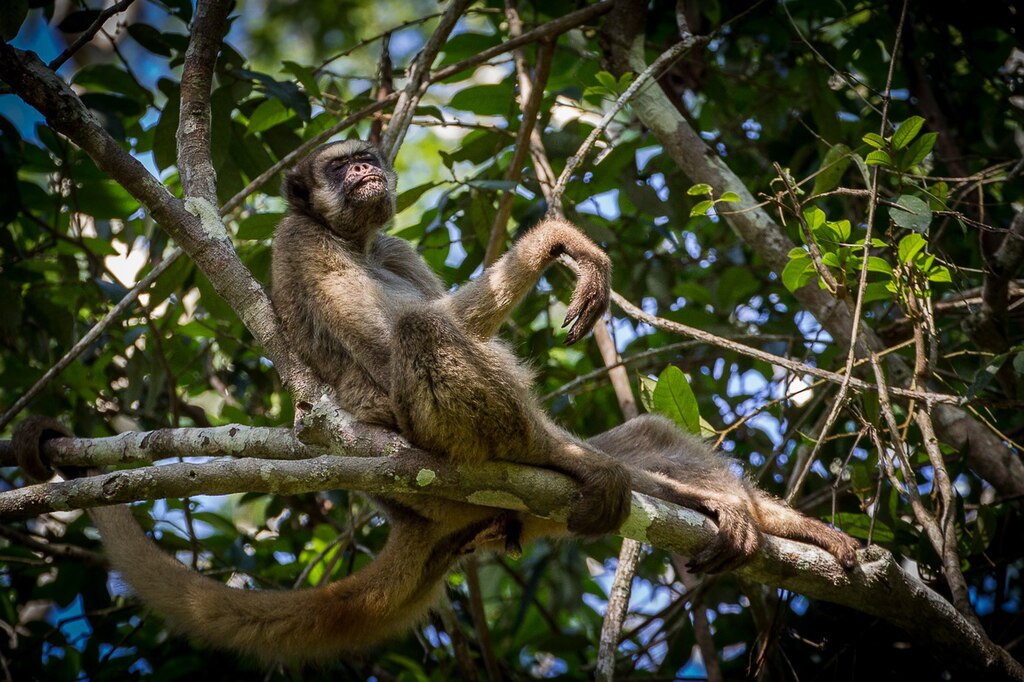

Study predicts that the two species of muriquis will be restricted mainly to coastal regions of the Atlantic Forest, leaving populations in the interior seriously at risk.
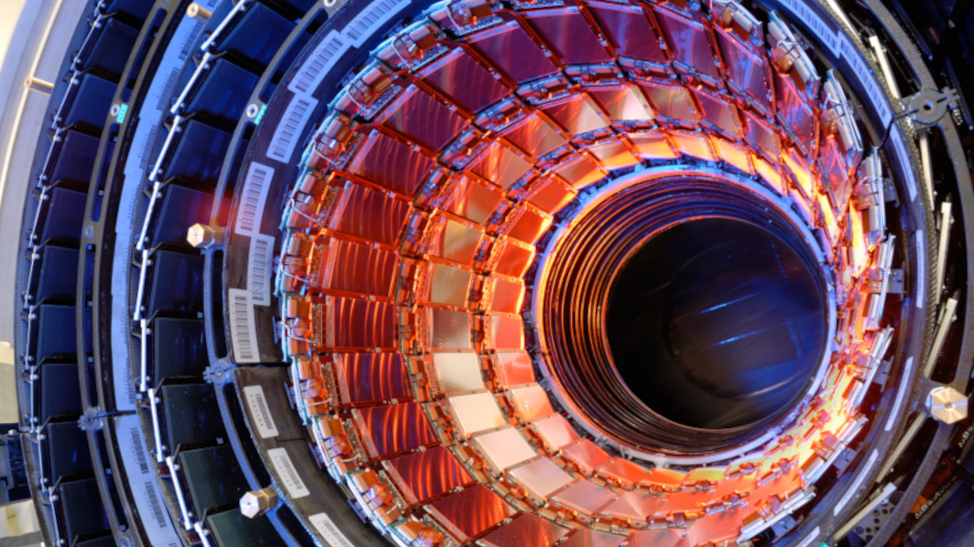
OpenIPMC ensures reliable data collection from the Large Hadron Collider’s detectors.
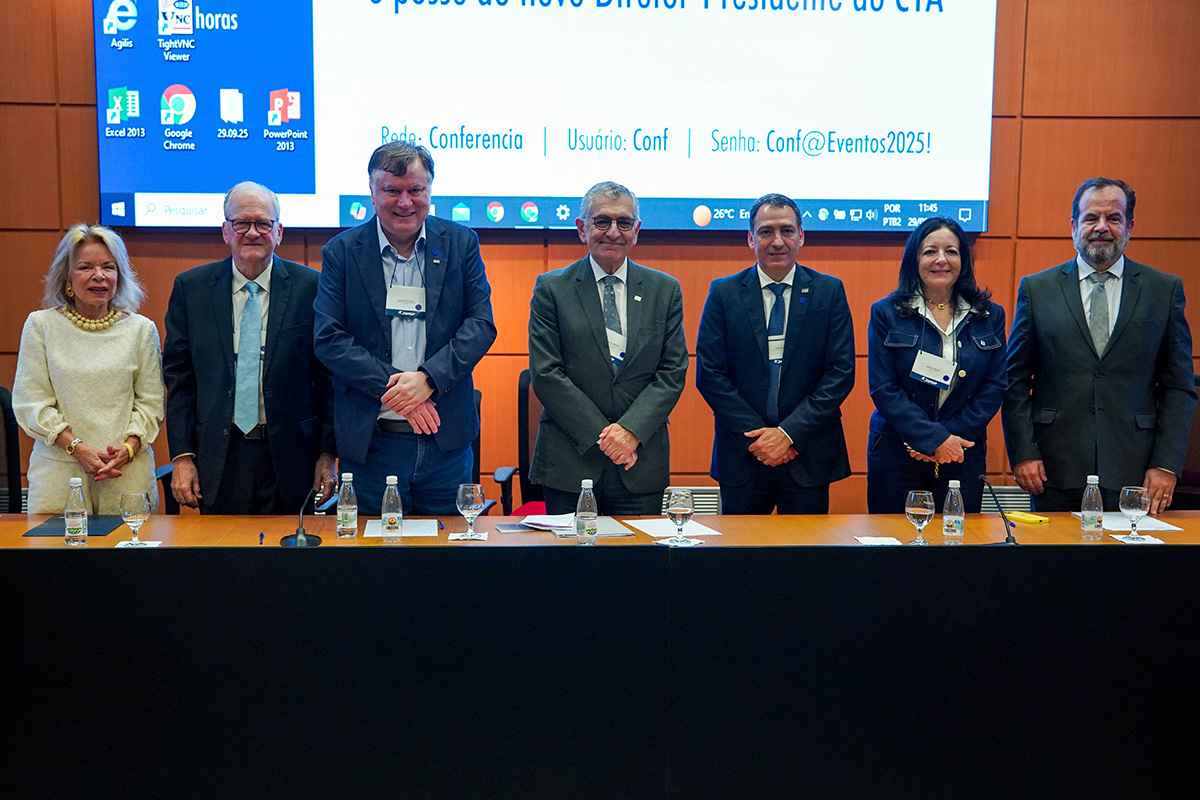

The fourth call for proposals for the program provides for investments of BRL 256 million. The announcement was made at a ceremony that also marked the start of Carlos Graeff’s term as the new CEO of the Executive Board.

The substance is essential for the survival of microbes in extreme environments and has been shown to have antioxidant, emulsifying, and stabilizing properties.
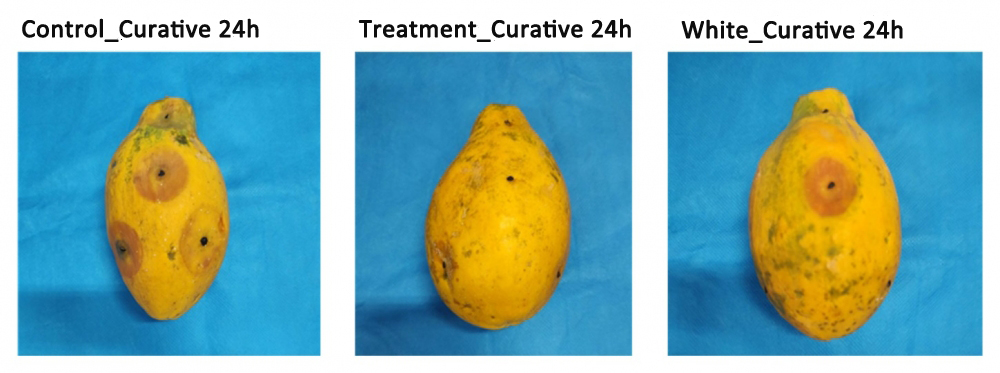
FAPESP-supported startup develops formulations based on bio-inputs to combat fungal infections and reduce the use of pesticides in fruit growing.