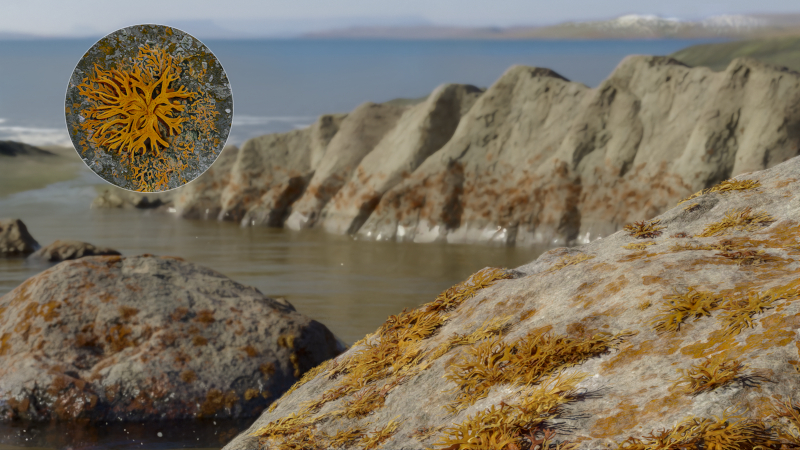



Study confirms that the symbiosis between fungi and algae that dissolves rocks and was widely distributed across Earth 410 million years ago helped form the first soils.

Study confirms that the symbiosis between fungi and algae that dissolves rocks and was widely distributed across Earth 410 million years ago helped form the first soils.
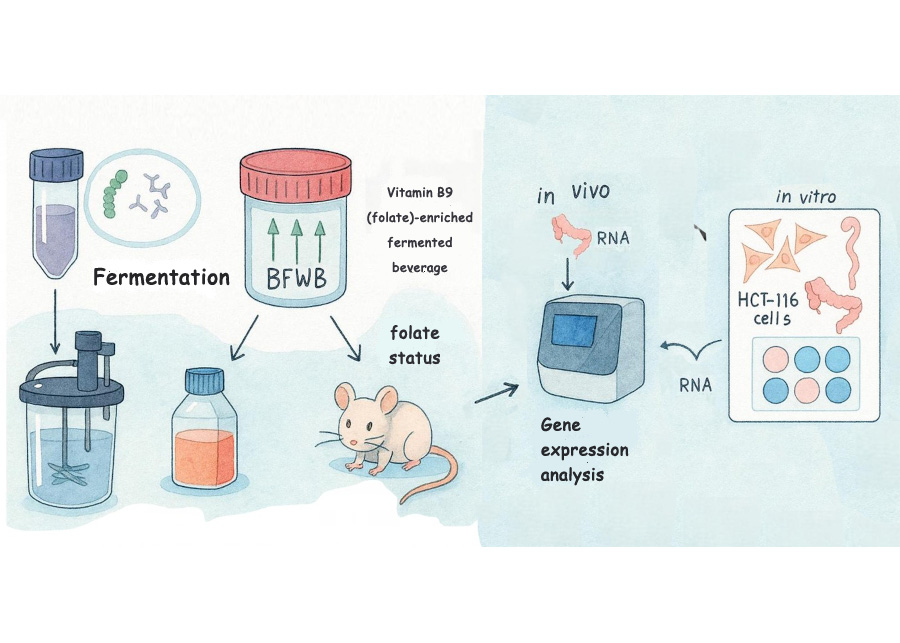
Formula containing whey and grape by-product extract was developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo and tested in partnership with a center in Argentina.

A study by the Federal University of São Carlos and University College London examined 2,815 older adults and identified an indicator of loss of mobility.
Discovery increased the number of known variations of the HER2 protein, the target of advanced drugs against the disease, from 13 to 90; diversity may explain resistance to therapies.
The multicenter Titan Trial project is investigating a method to treat unilateral spatial neglect, a sequela of stroke that affects perception of the side opposite to the affected cerebral hemisphere.

Using biofeedback and gamification, the solution teaches emotional self-regulation strategies to child patients with disorders such as ADHD and ASD.
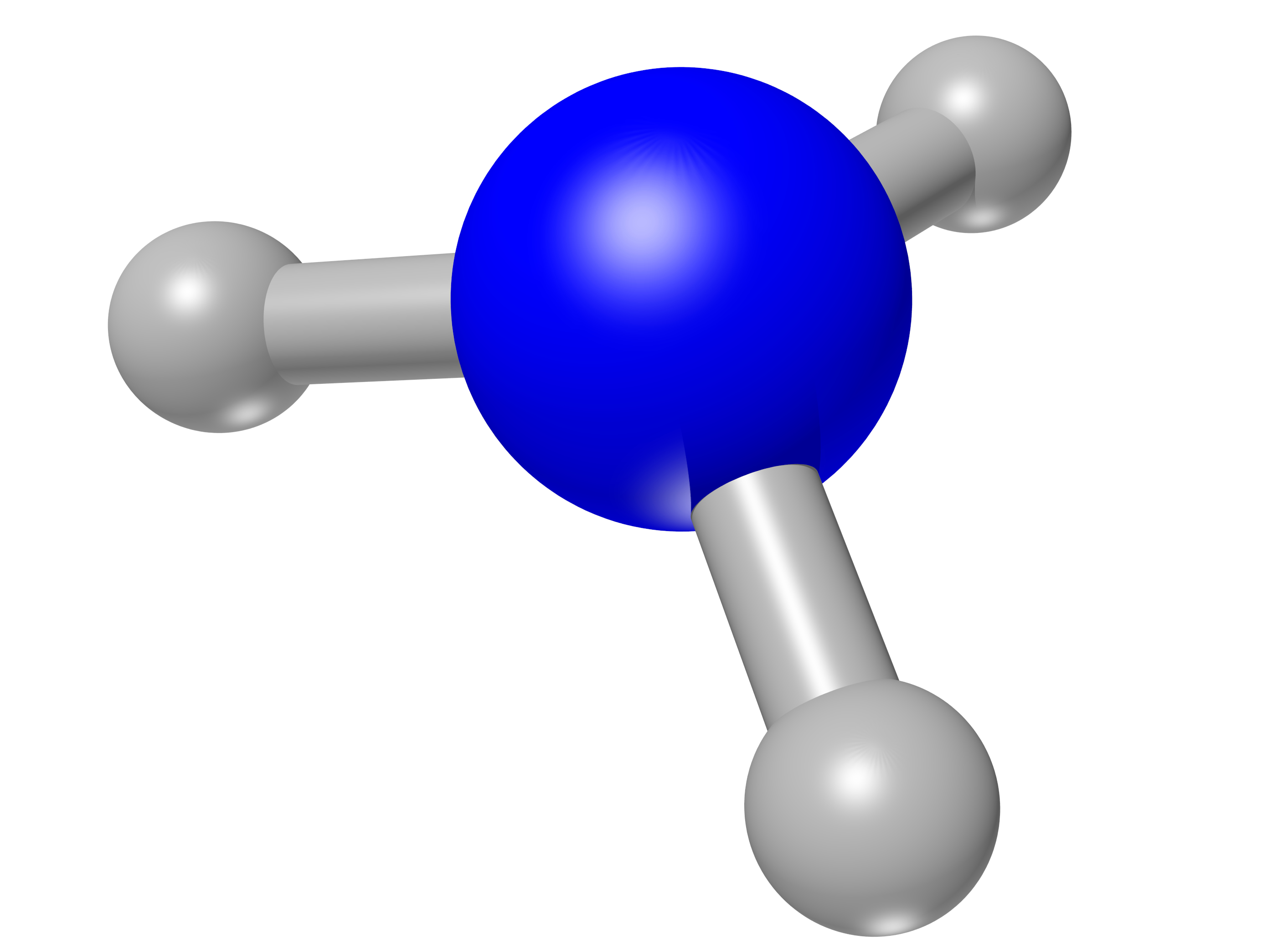
The chemical compound is used in various industrial processes, but its synthesis is highly polluting. Research involving scientists from the Center for Development of Functional Materials and the Center for Innovation on New Energies, supported by FAPESP, indicates clean ways of obtaining the input.
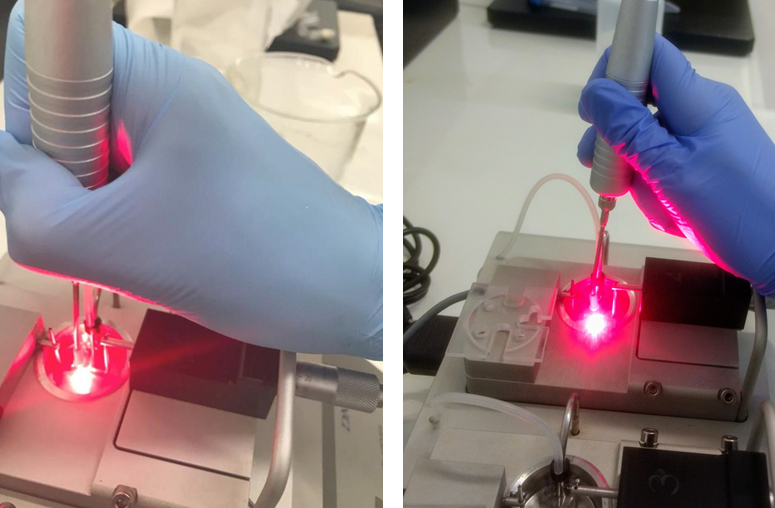
An experiment conducted at the Federal University of São Carlos demonstrated that applying low-intensity light had a hypotensive effect on rats that became hypertensive due to a reduction in hormones, a process characteristic of aging in the female reproductive system.
Researchers compared the repertoire of long non-coding RNAs in humans with those of rhesus monkeys, mice, and chickens and noted that these structures played a role in functional specialization throughout evolution.

Preliminary data suggest that the population in this area of southwestern Pará state is more exposed to infection than average due to a lack of access to healthcare and greater contact with sex workers.
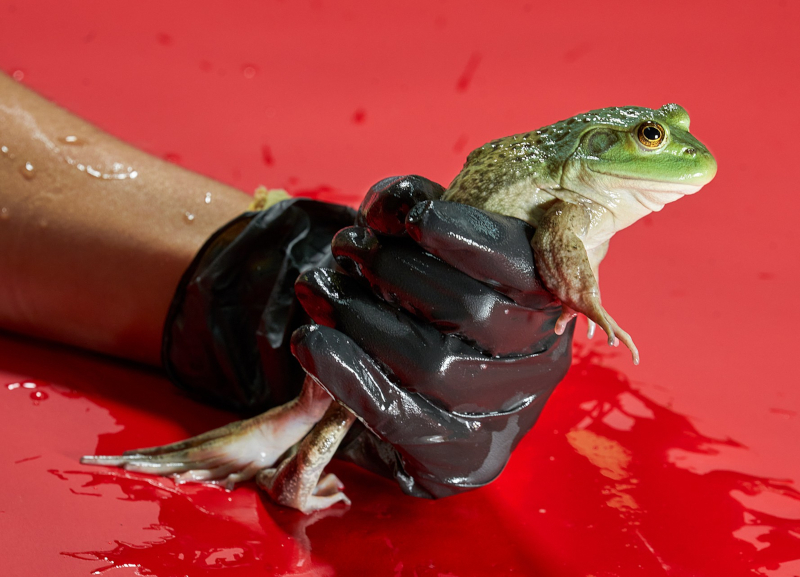

Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis is responsible for the decline of toad and frog populations across the globe. The origin of the fungal strain was the subject of a study led by researchers at the State University of Campinas.

Brazilian research shows that stellate pancreatic cells produce periostin, remodeling tissue and facilitating tumor infiltration, a key mechanism of the aggressiveness and high mortality of the disease.

Real-time monitoring reduces medication waste and increases treatment effectiveness.

Results indicate that the innate immune response remains activated even with immunosuppressant use, paving the way for new therapies to prevent organ rejection.
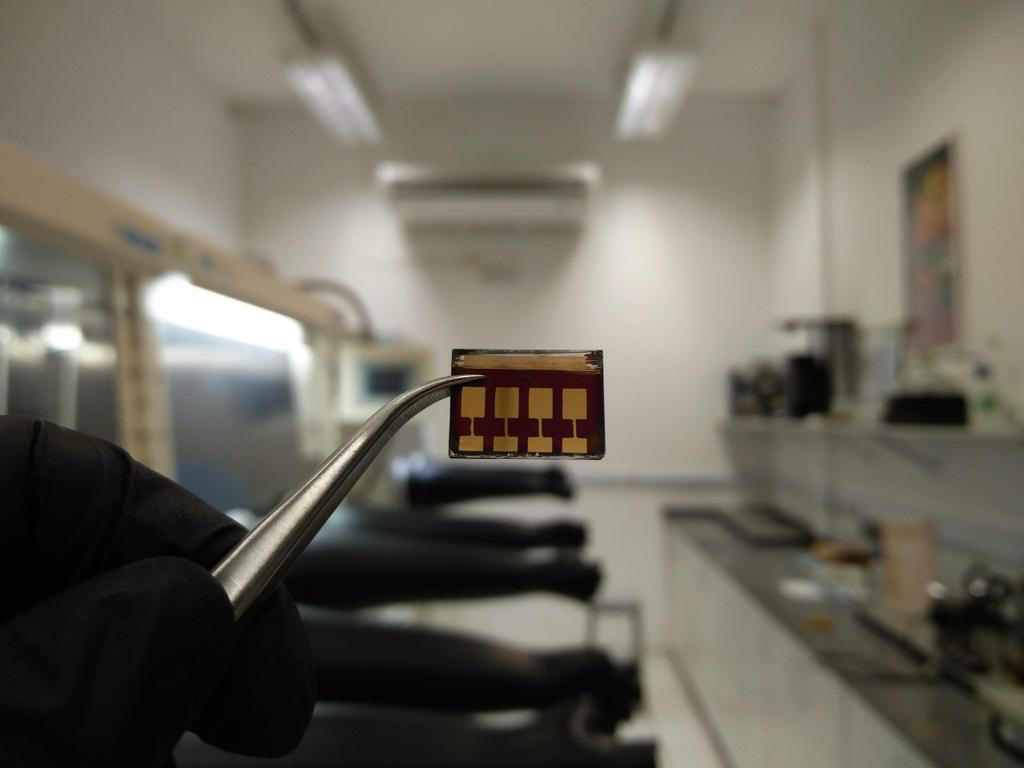

Films made from these photosensitive semiconductors promise to be the stars of the next generation due to their ability to convert sunlight into electricity. However, the stability of the material under heat and humidity still needs improvement.

Films made from these photosensitive semiconductors promise to be the stars of the next generation due to their ability to convert sunlight into electricity. However, the stability of the material under heat and humidity still needs improvement.
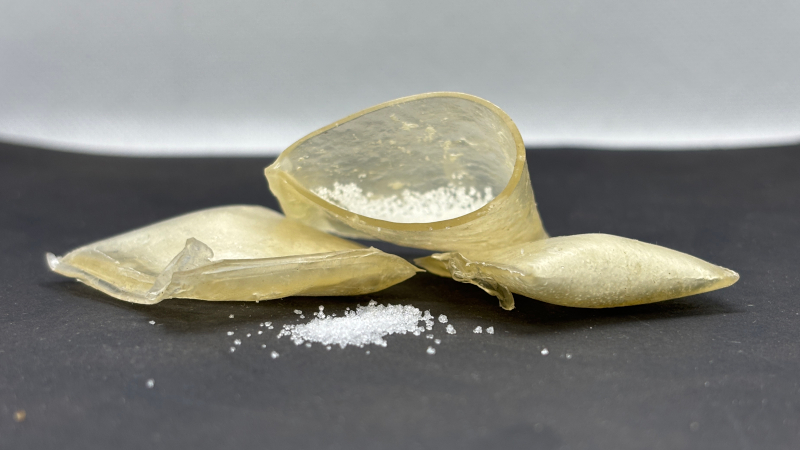

Nanoparticle-reinforced wrappers can be filled with various formulations of the granular products needed for crops, a versatility that facilitates application by agribusiness.
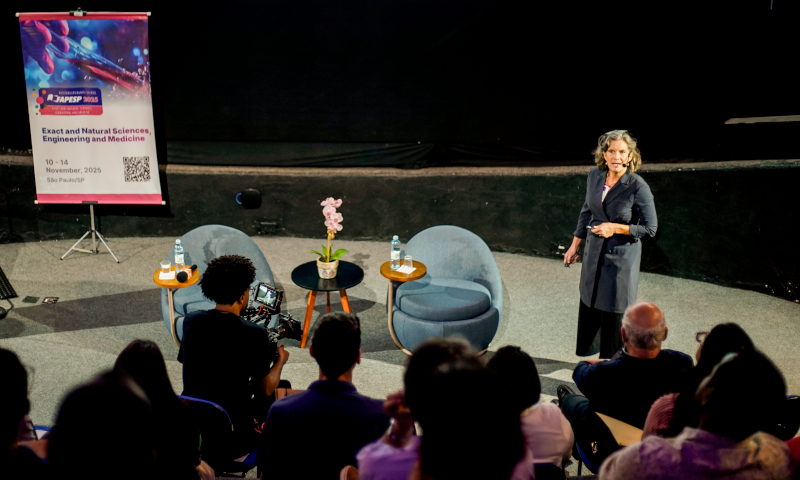

Conservation of natural areas should be a major factor in preventing new pandemics, said Felicia Keesing of Bard College during the first day of the FAPESP Interdisciplinary School.
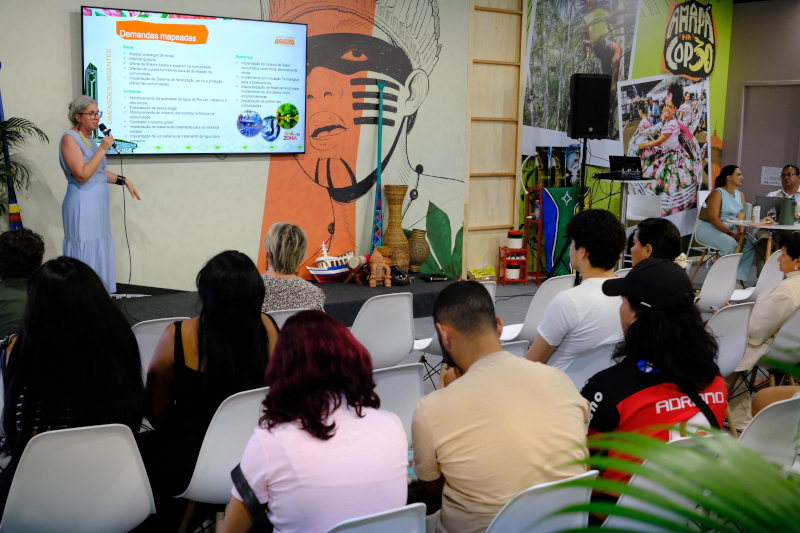

Researchers from the Amazon+10 Initiative begin presenting their initial findings in the social, environmental, and economic areas.
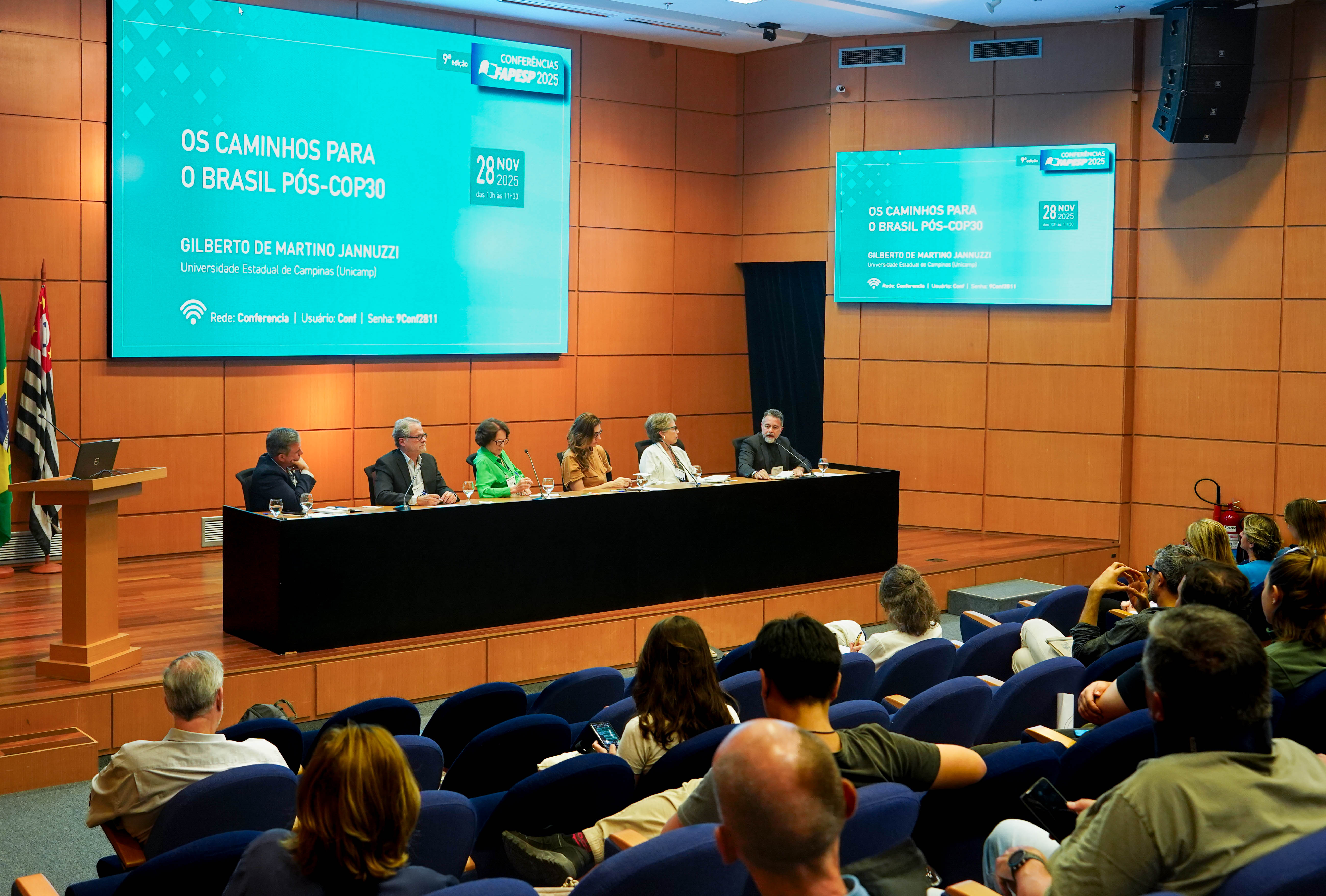

São Paulo needs to drive the process of gradually replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy sources in Brazil, said Gilberto Jannuzzi at a conference organized by FAPESP to discuss the path forward for the country after COP30.
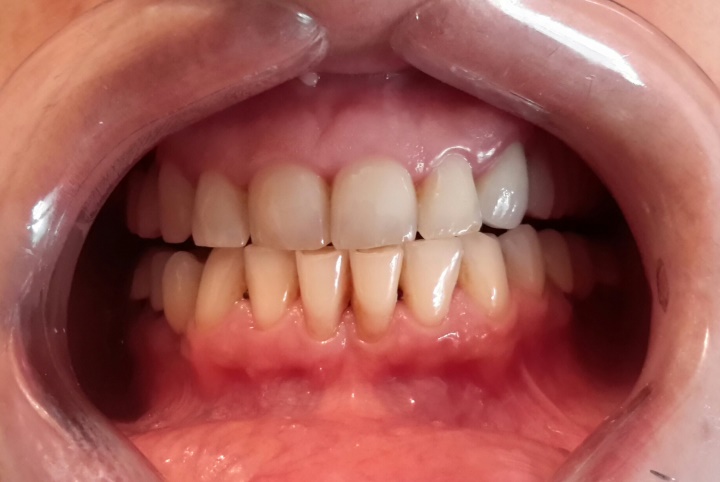
According to a study by the University of São Paulo, the effects are intensified when the molecule is applied in conjunction with fluoride and xylitol.
Test results in two days. A study supported by FAPESP contributes to improving disease monitoring, but the high cost remains a barrier.
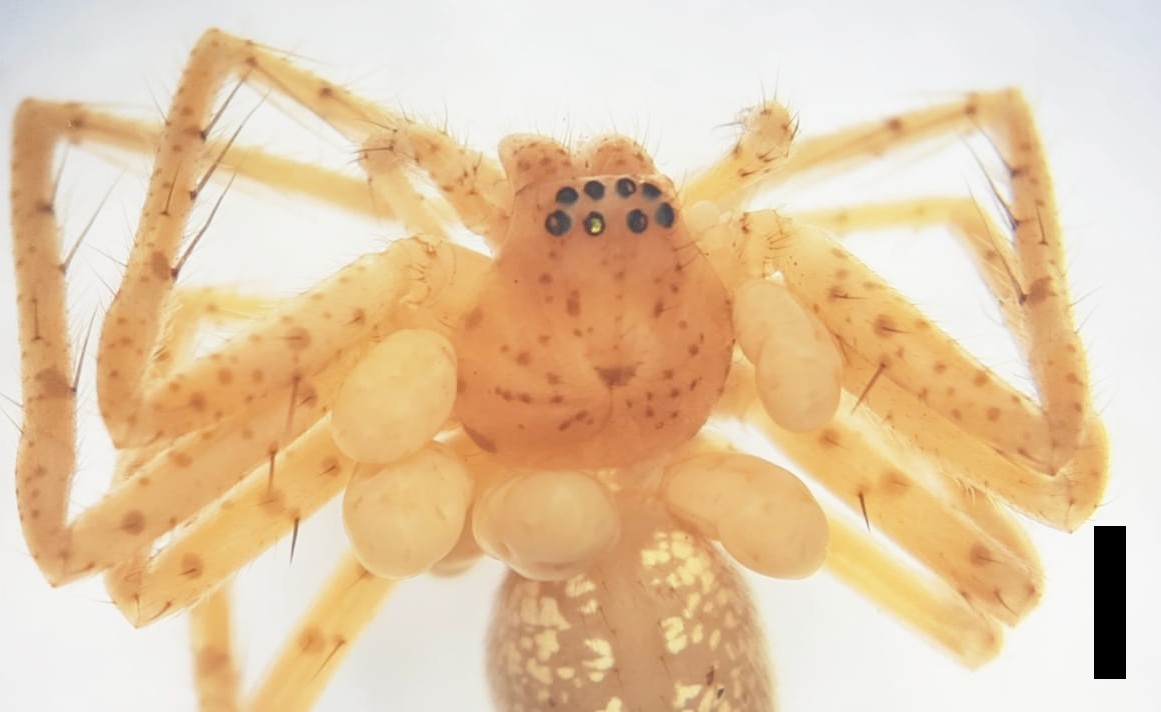

The parasitic mites were found on juvenile arachnids in the Butantan Institute collection. The larvae of Araneothrombium brasiliensis were collected in Rio de Janeiro. Previously, the genus had only one known species in Costa Rica.

Brazilian technology from Nanox is recognized for its solution to reduce food loss and waste. The Center for Development of Functional Materials is a FAPESP Research, Innovation, and Dissemination Center based at UFSCar.