


A study by a FAPESP-supported research center showed that the surfaces change when an electron beam is applied. The material has potential for applications in semiconductors, antibacterial agents, gas sensors, and more.
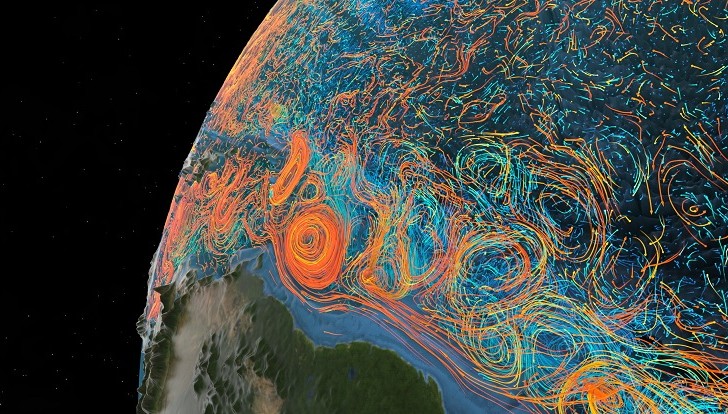

Combining field research data with climate model projections, a study has reconstructed the activity of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation – one of the main drivers of the Earth’s climate – throughout the Holocene. Projected scenarios for the future are unlike anything seen in the last 6,500 years.
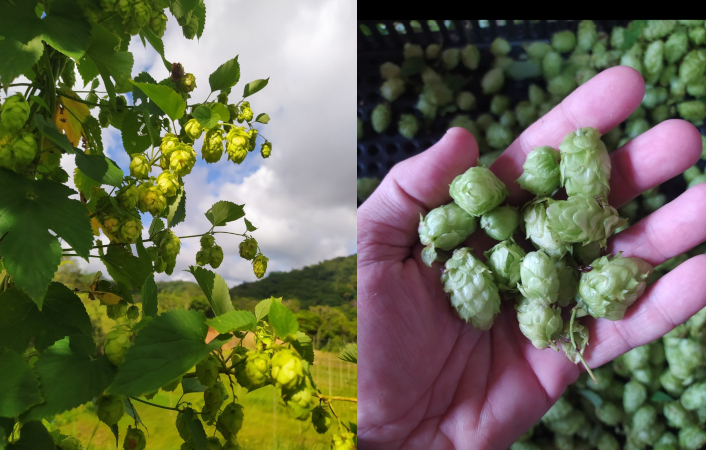

Project developed in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, allows for the highly efficient extraction of aromatic and bioactive compounds, reducing logistics costs and increasing beer quality.
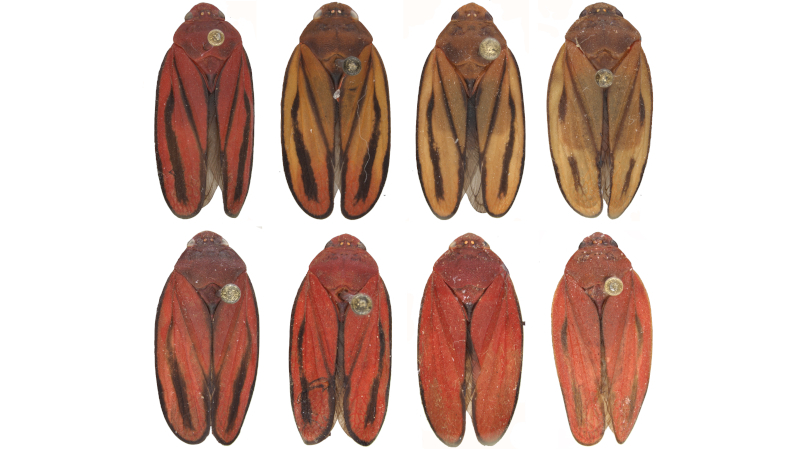

Analyses show that a sugarcane spittlebug, found in the Southeast and South of Brazil since the 1960s, was mistaken for other species that are similar to the naked eye.

The topic was addressed in a workshop organized by the project “Democlites – Democracy, Climate, and Ecological and Social Transition,” a joint initiative of Université Paris 1 Panthéon-Sorbonne and USP supported by FAPESP.
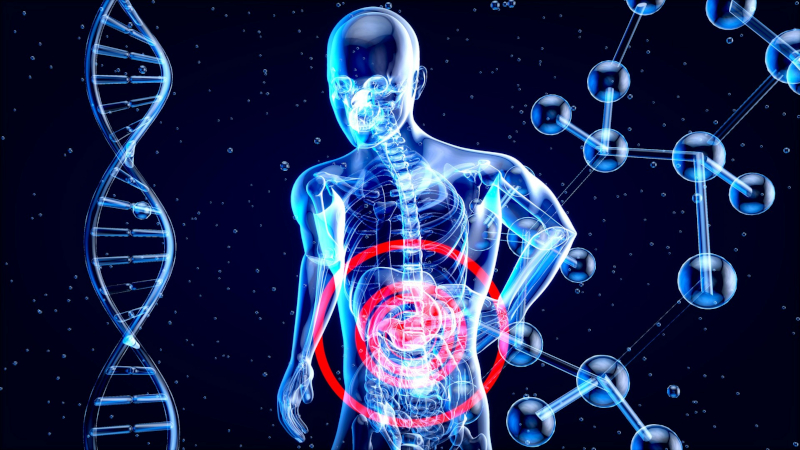
Study shows that the liver receives and sends a series of metabolism-related products derived from the gut microbiome to the heart.

FAPESP-supported startup creates immersive educational solutions ranging from academic laboratories to team training in industries.
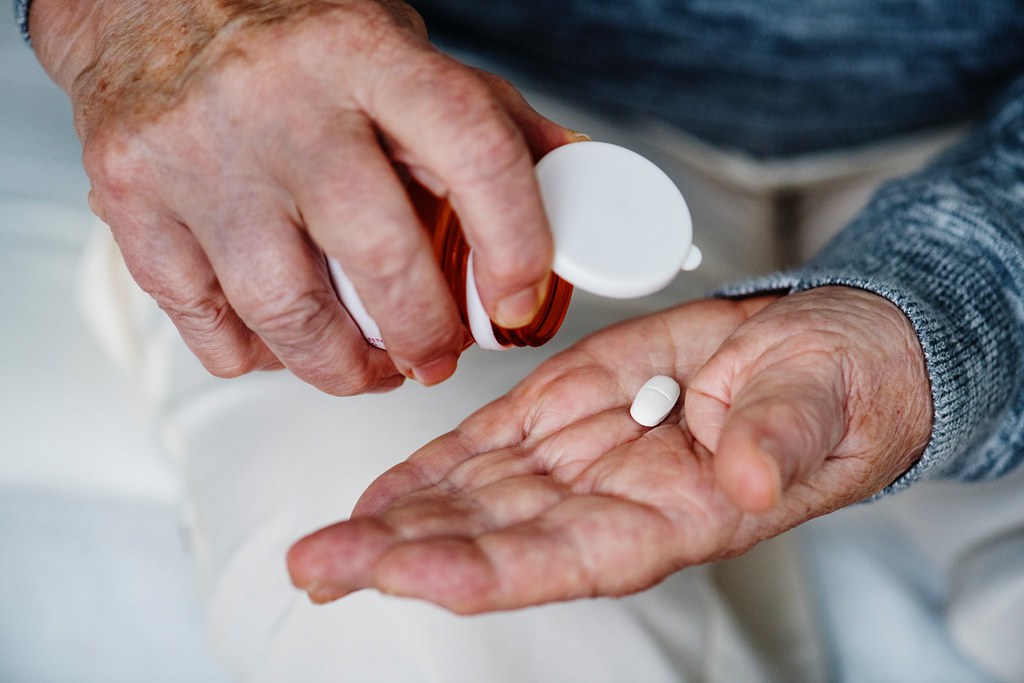

Work carried out at the State University of Campinas used environmentally friendly solvents and ultrasonic waves to remove the substance and increase its absorption by the body.
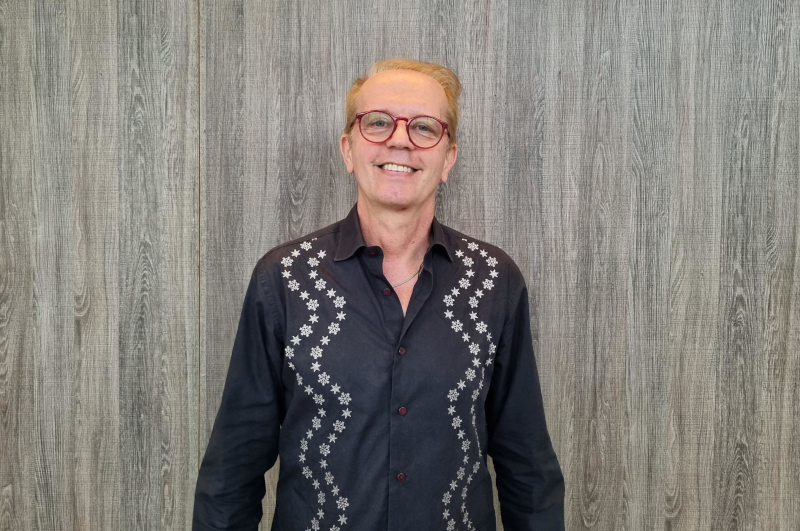

One of the world’s leading experts on the fruit, Hervé Rogez, a professor at the Federal University of Pará, warns about the social, environmental, and economic impacts of “açaízation” in the Amazon.
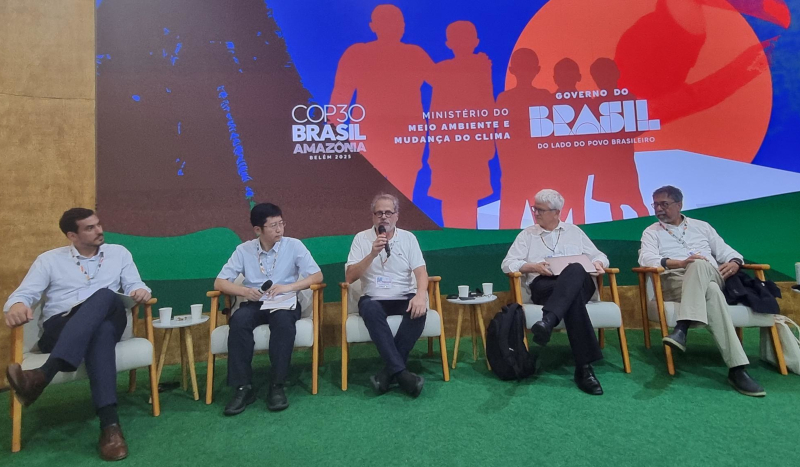

Developing nations hold most of the mineral reserves essential for clean energy and already have experience and a pioneering spirit in creating new markets, such as bioenergy and electric cars, according to participants in a panel discussion promoted by FAPESP at COP30.
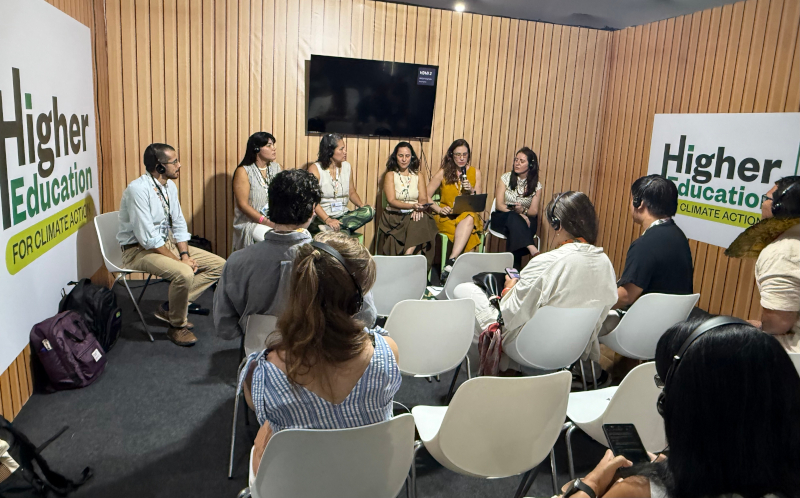

In a panel discussion held in the Blue Zone of the conference, a Brazilian IPCC researcher said that discussions on the subject must reach society through accessible communication without losing scientific rigor.
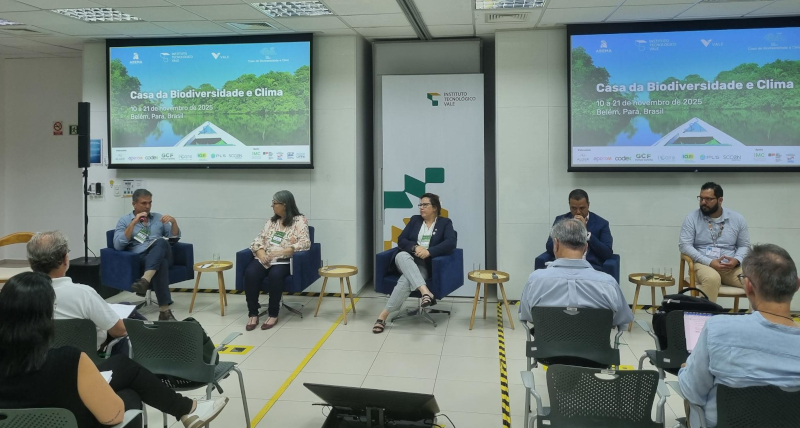

This assessment was made by participants at an event promoted by FAPESP, the Brazilian Association of State Environmental Agencies, and the Vale Technological Institute during COP30.
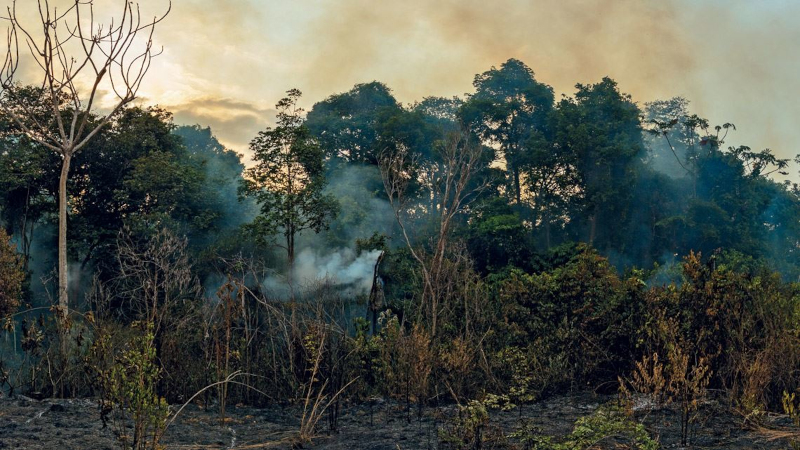

At an event in the Blue Zone at COP30, the physicist and climatologist stated that the world is close to surpassing the 1.5 °C average warming limit and is heading towards 2.8 °C.
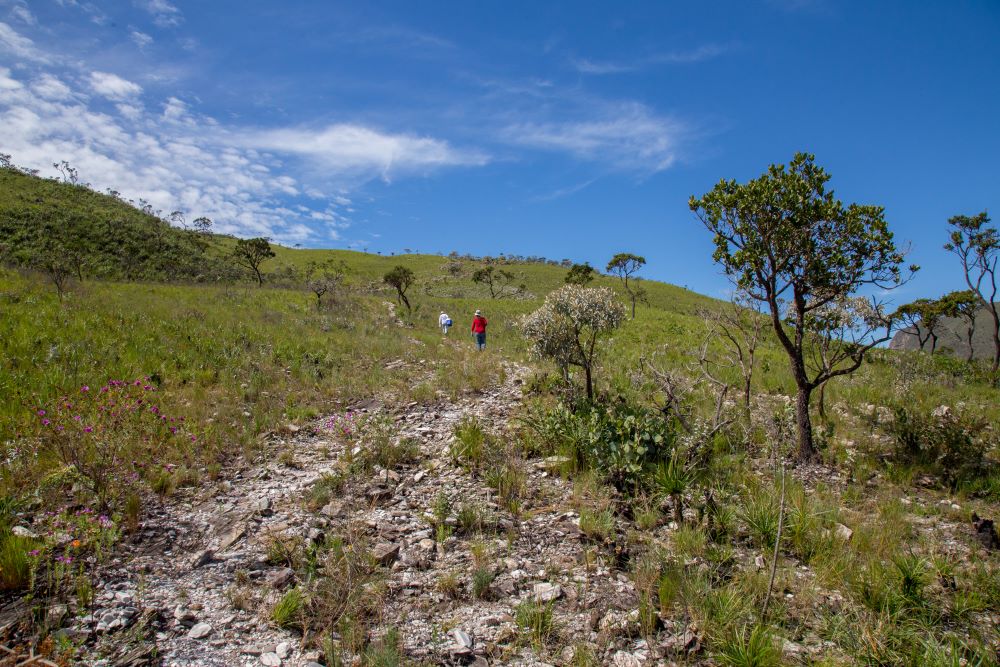

A study has identified more than 257,000 species of bacteria and archaea in velozias, which are plants that thrive in extreme environments of drought, heat, and poor soil, such as this mountainous savannah ecoregion. The results could guide conservation initiatives and biotechnological solutions for soil management in arid conditions.
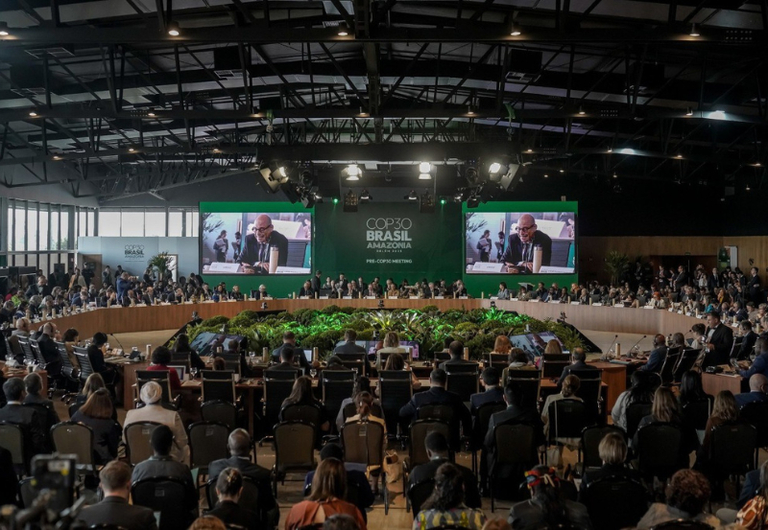

In an article published in a scientific journal, the group emphasizes that Brazil must align its domestic policies with international commitments.

In an article published in a scientific journal, the group emphasizes that Brazil must align its domestic policies with international commitments.
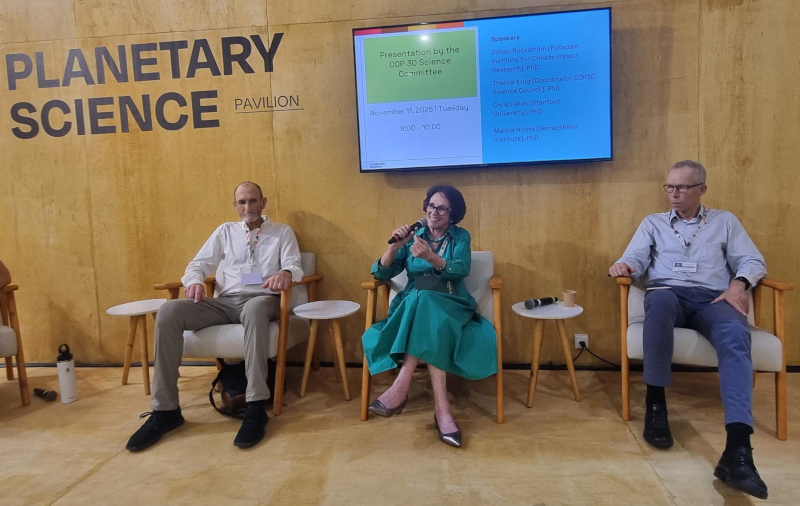

The margin must be defined as a reference point in the COP30 negotiations, assess members of the Scientific Council of the climate conference presidency.
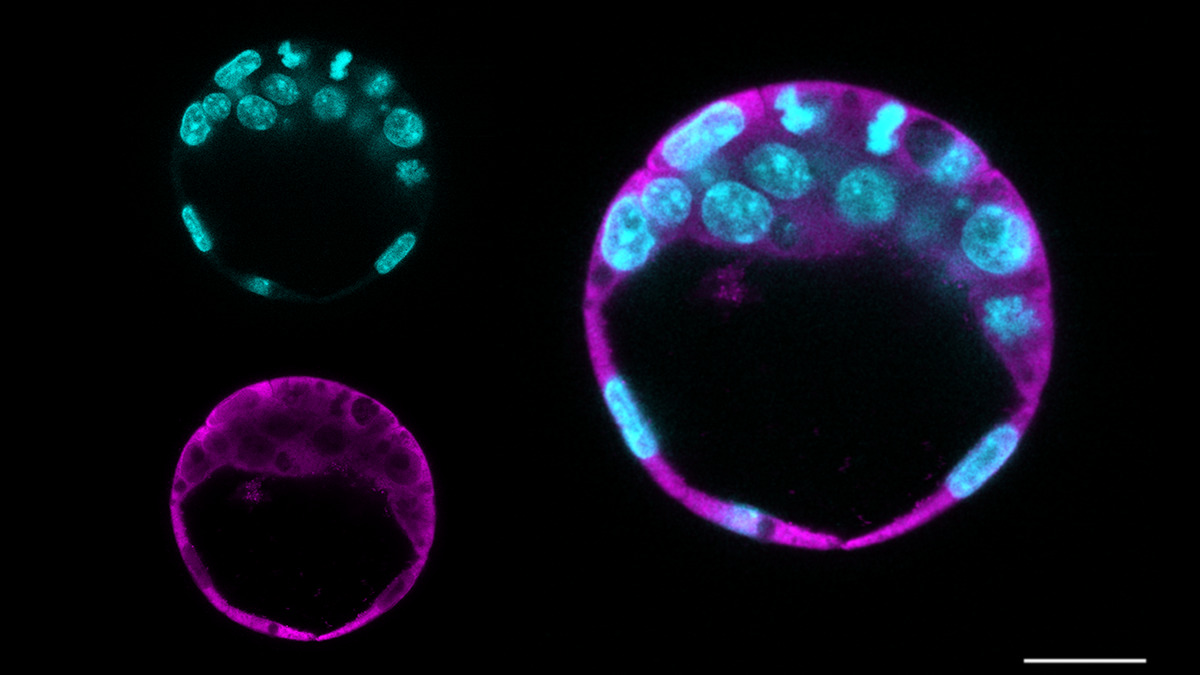
Led by scientists from the University of São Paulo, the studies help clarify the roles of STIP1 and Maspin in vital cell processes and pave the way for advances related to cancer and applications in regenerative medicine.

Led by scientists from the University of São Paulo, the studies help clarify the roles of STIP1 and Maspin in vital cell processes and pave the way for advances related to cancer and applications in regenerative medicine.
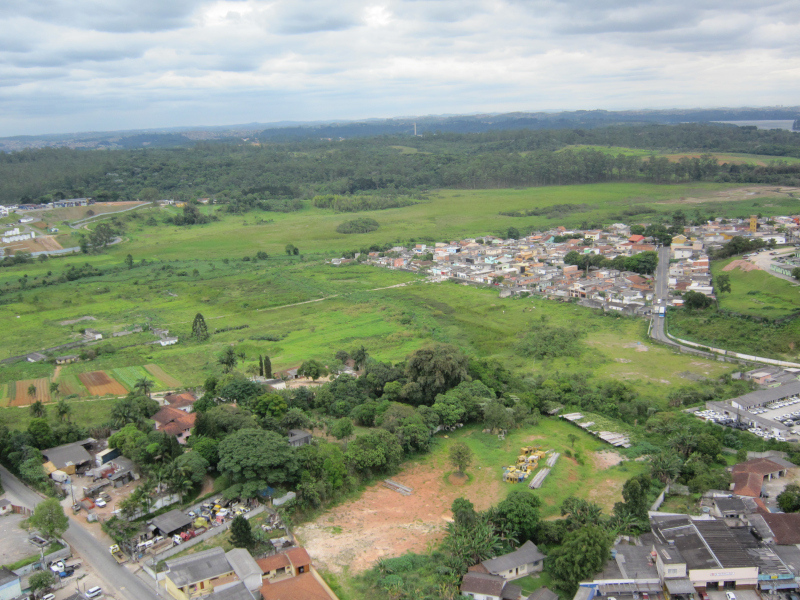

Researchers from a FAPESP-supported research center point to 410,000 hectares of land in cities that could be regenerated.

Researchers from a FAPESP-supported research center point to 410,000 hectares of land in cities that could be regenerated.
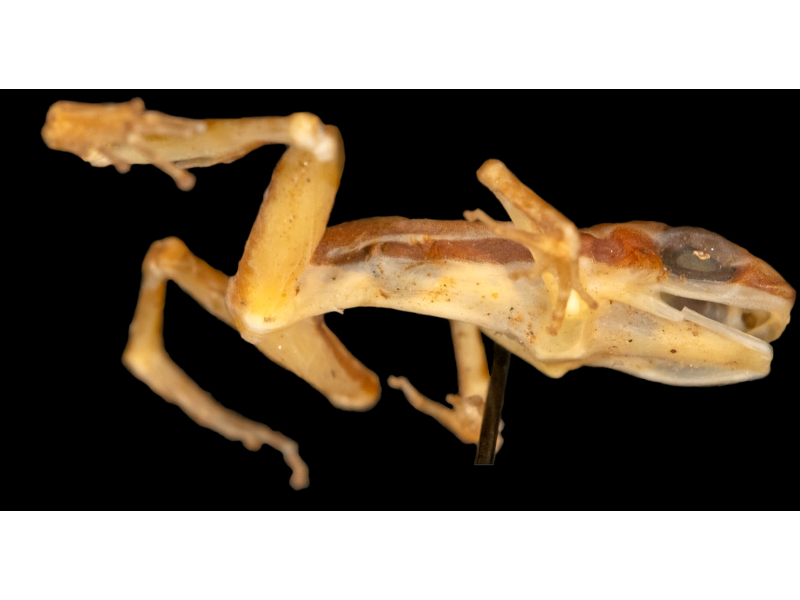

The dried specimen of the amphibian, collected by herpetologist Doris Cochran in 1963 in what is now a residential neighborhood of Curitiba, Brazil, is stored in the collection of the Smithsonian Institution’s National Museum of Natural History in the United States.

The dried specimen of the amphibian, collected by herpetologist Doris Cochran in 1963 in what is now a residential neighborhood of Curitiba, Brazil, is stored in the collection of the Smithsonian Institution’s National Museum of Natural History in the United States.
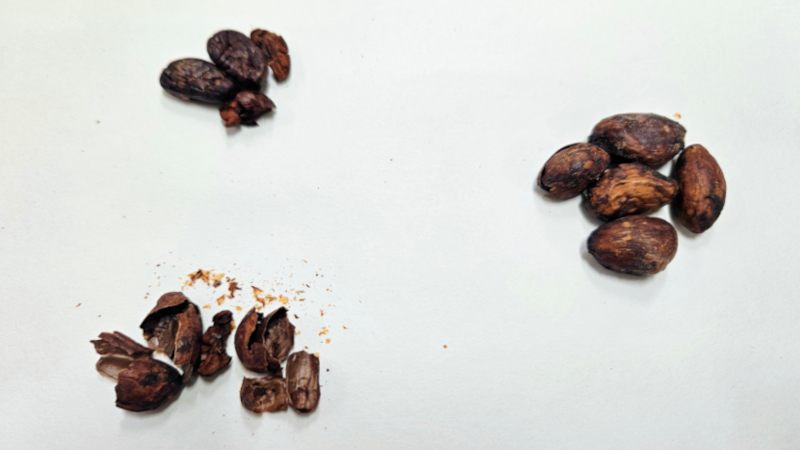

Researchers at the State University of Campinas used a product from native stingless bees to extract bioactive compounds, such as caffeine, from chocolate manufacturing waste. This process adds nutritional and commercial value to an ingredient that is usually discarded.

Researchers at the State University of Campinas used a product from native stingless bees to extract bioactive compounds, such as caffeine, from chocolate manufacturing waste. This process adds nutritional and commercial value to an ingredient that is usually discarded.