

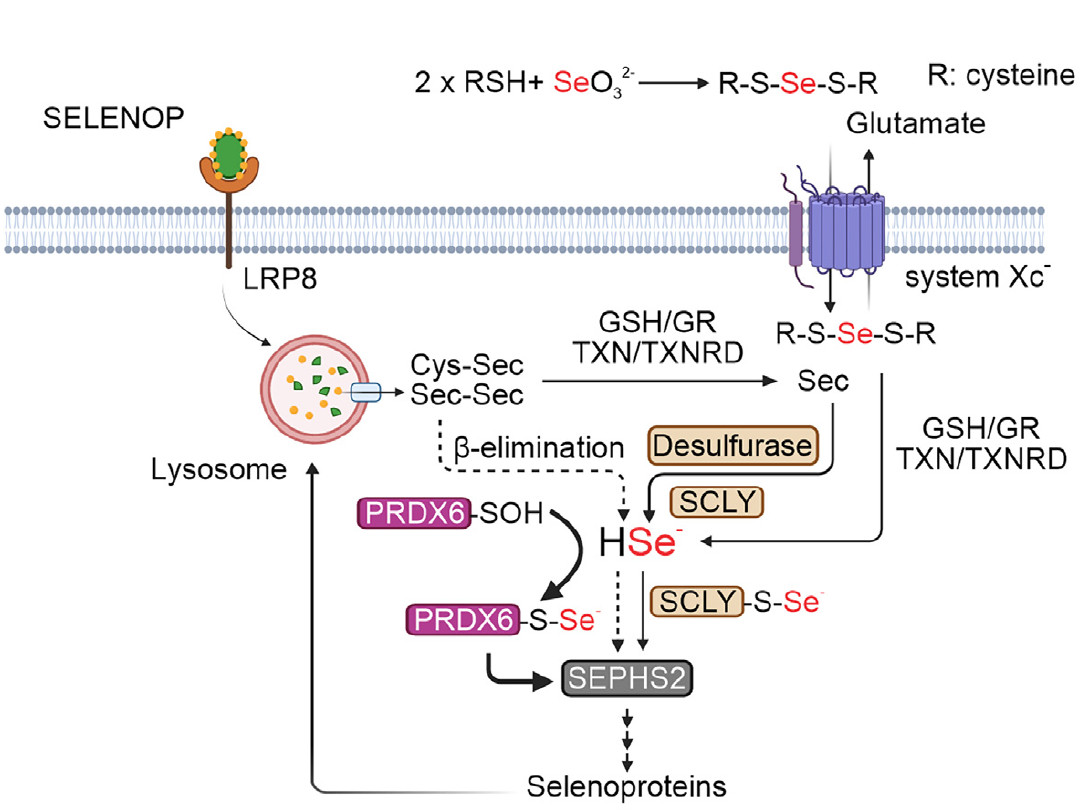
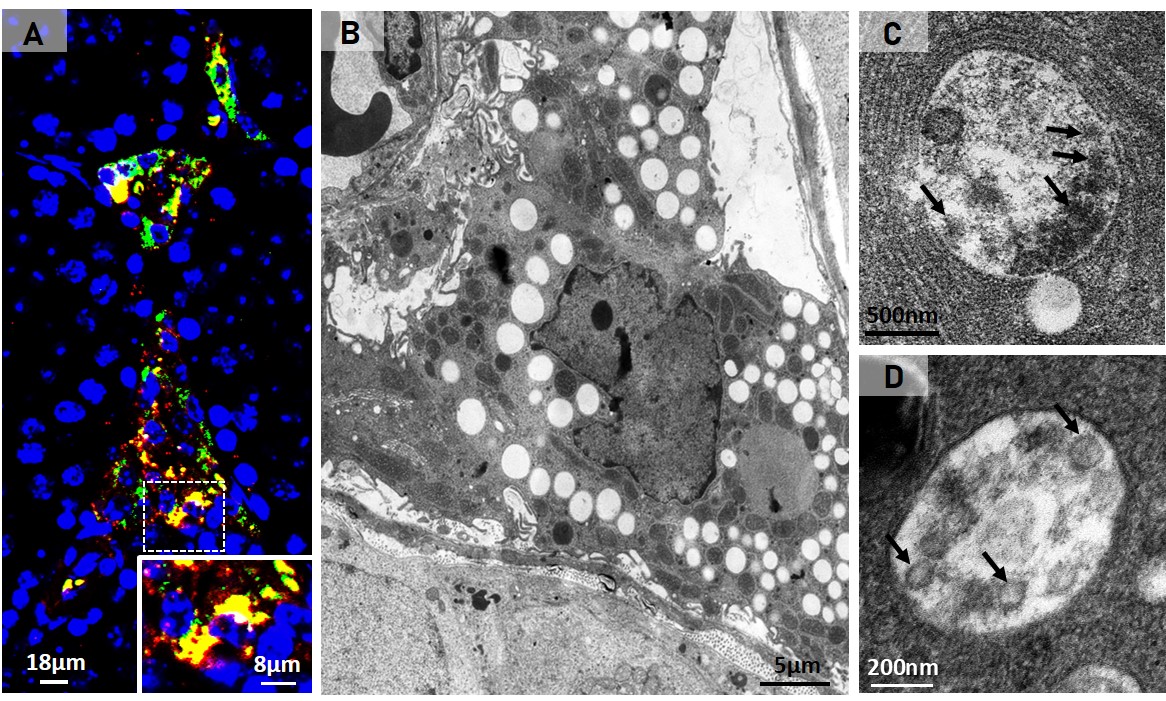
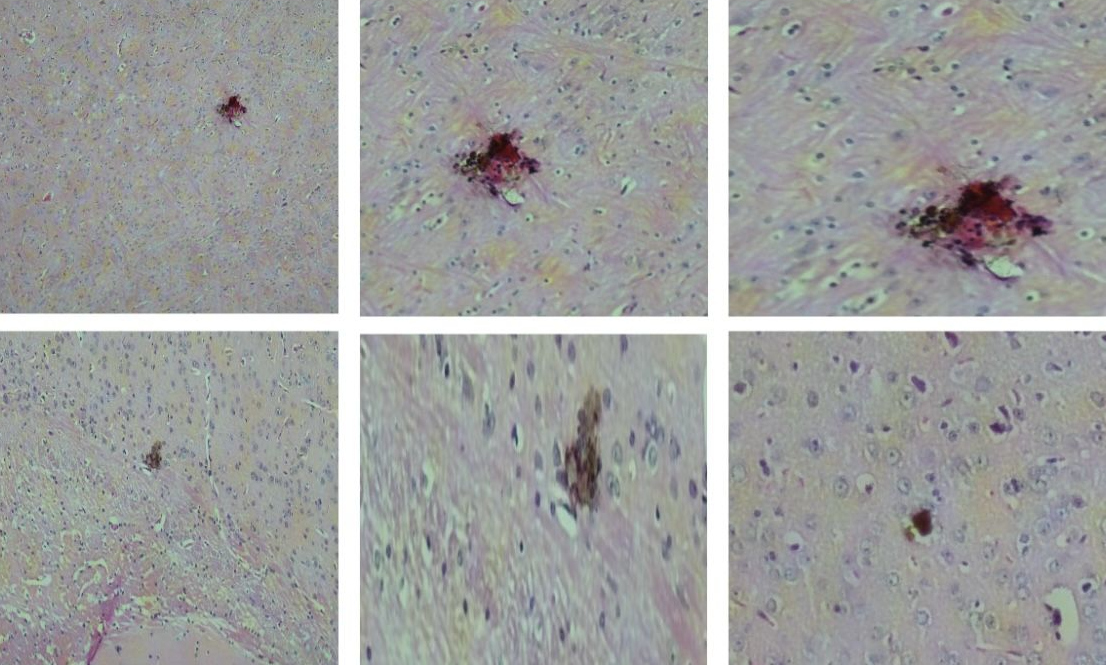
International team of researchers discovered that high levels of an enzyme called PRDX6 are associated with a subtype of neuroblastoma; animal studies showed that inhibiting the molecule caused a reduction in tumors.
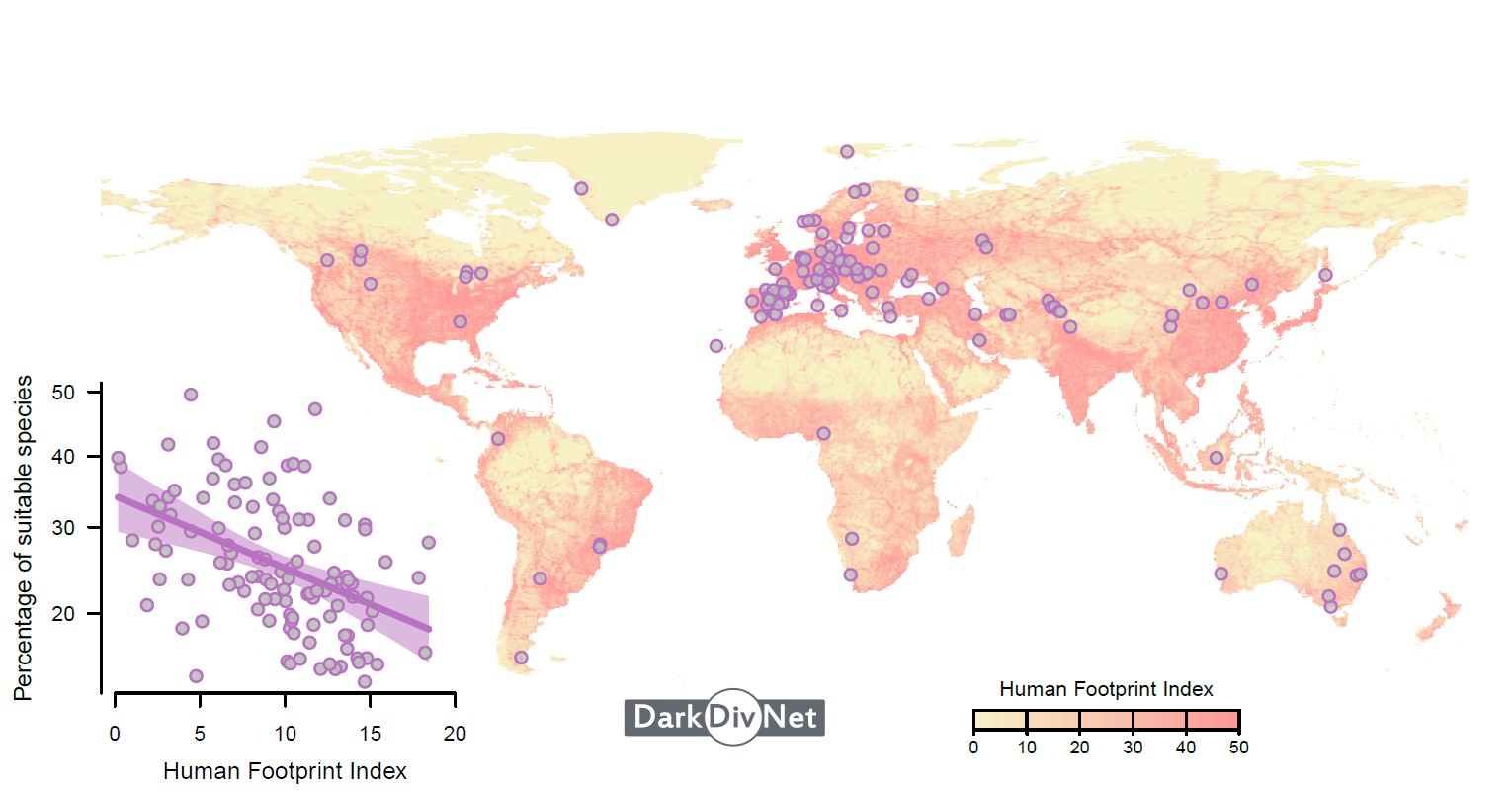
A survey of 119 regions around the world investigated “missing diversity,” or native species that could be present in a given area but were absent. The results were published in the journal Nature.
Research conducted on mice revealed that the COVID-19 virus uses cells responsible for testosterone production to replicate, thereby interfering with lipid metabolism. This helps explain the drop in testosterone and possibly cholesterol in patients with severe cases of the disease.
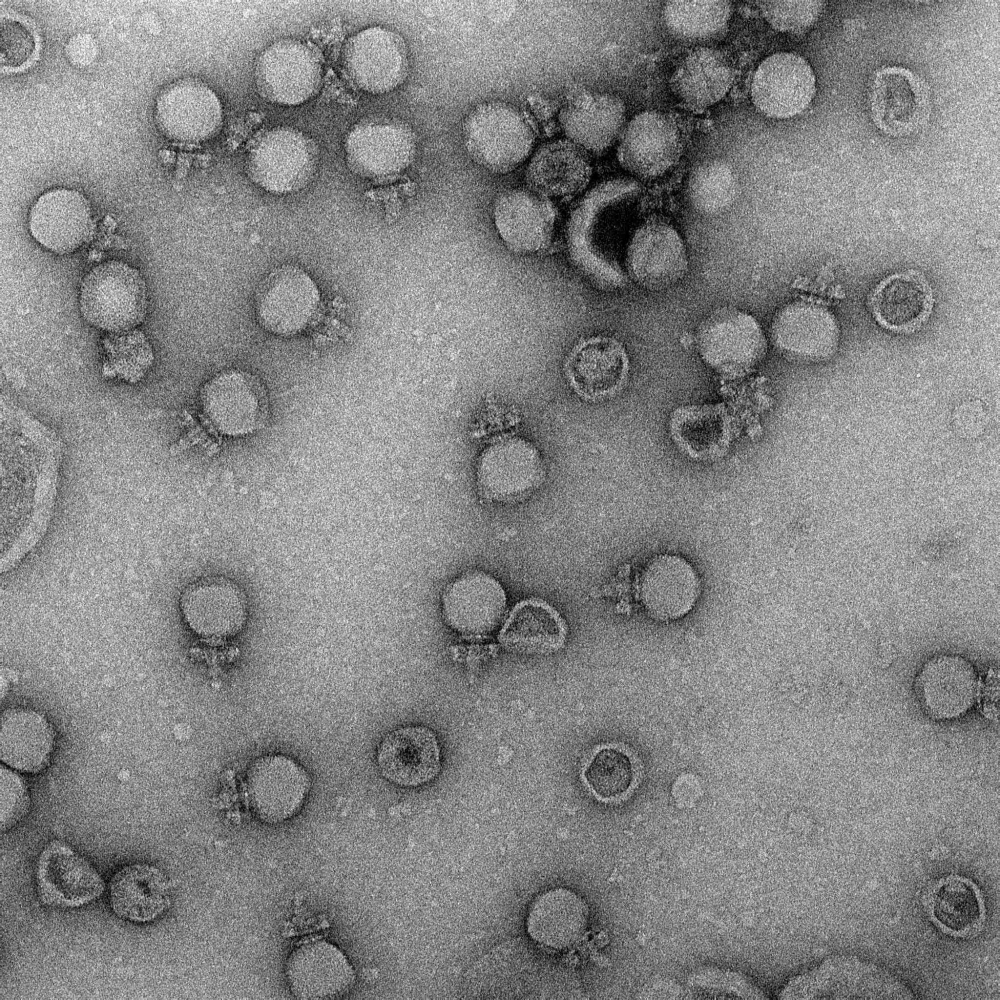
The vaccine is being developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo and is based on technology known as “virus-like particles” (VLPs), which does not use genetic material from the pathogen.

The compound is 100 times more effective than β-caryophyllene against the disease impacting orange groves in Florida and threatening citrus growers in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, the world’s largest orange producer.
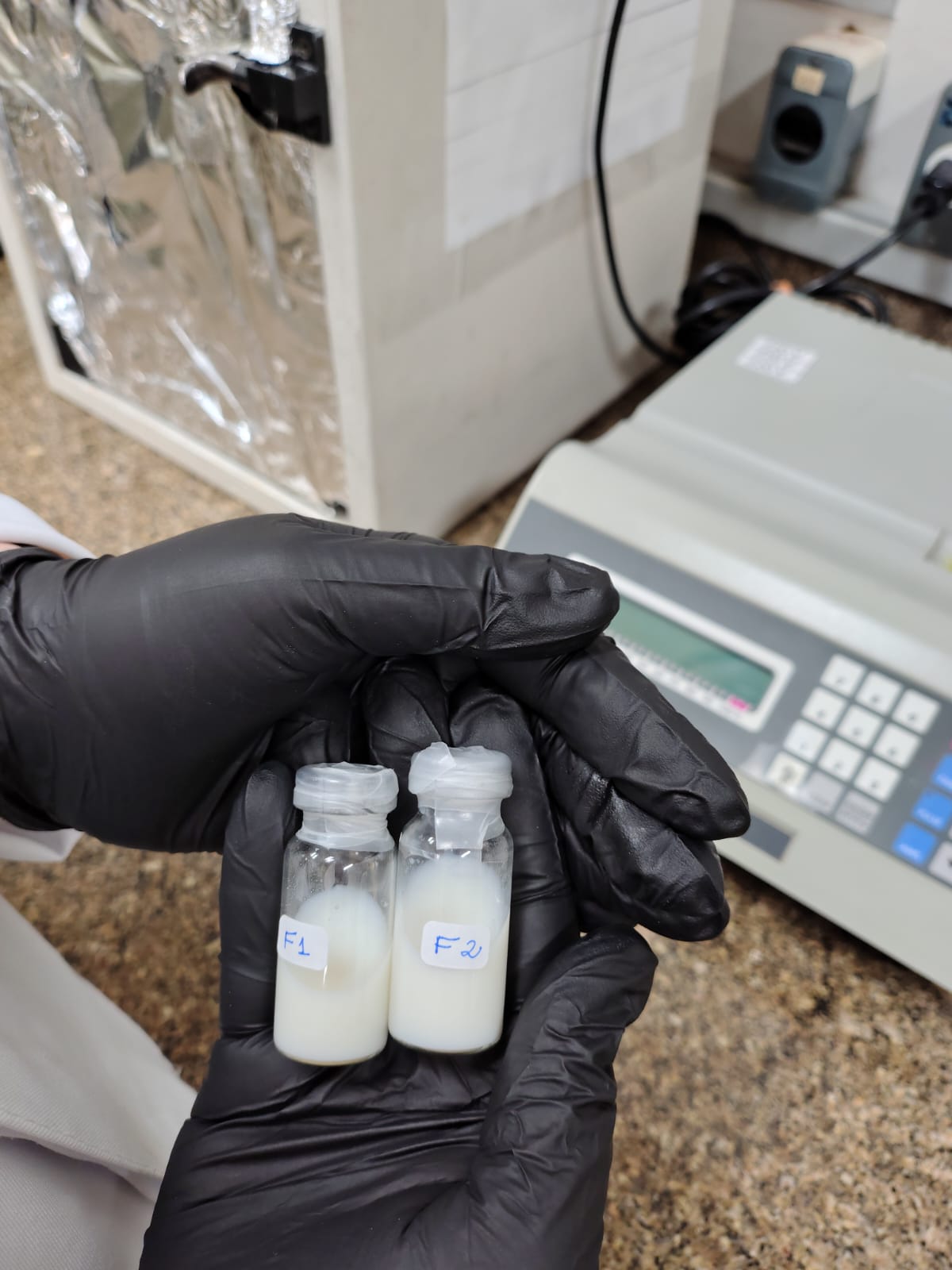

Solution created by Brazilian startup can treat pain and inflammation in pets.
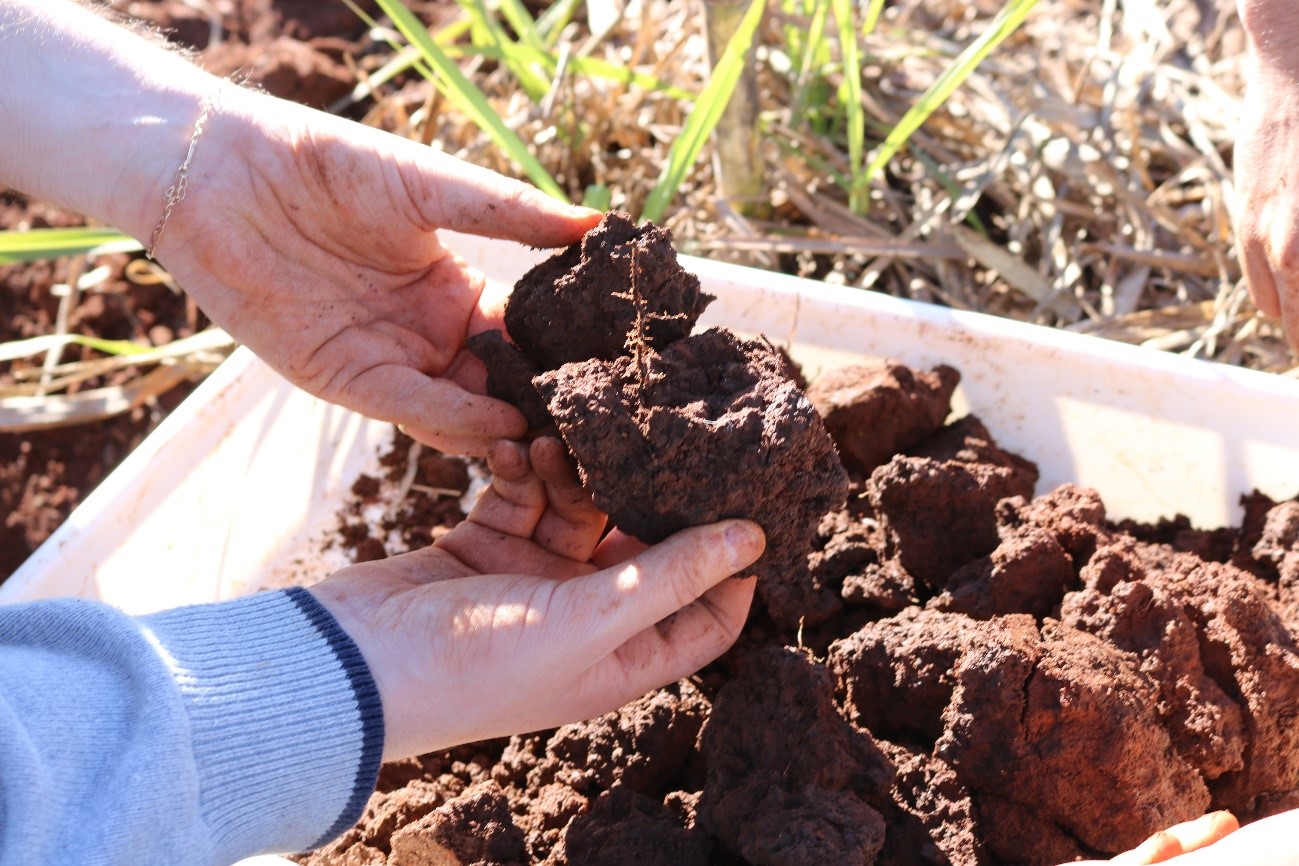

Countries such as Colombia and Venezuela lead the way in terms of the extent of healthy soils, while regions such as the Brazilian Northeast, northern Mexico and parts of Chile and Argentina face the greatest challenges. The data can guide public policies for conservation.
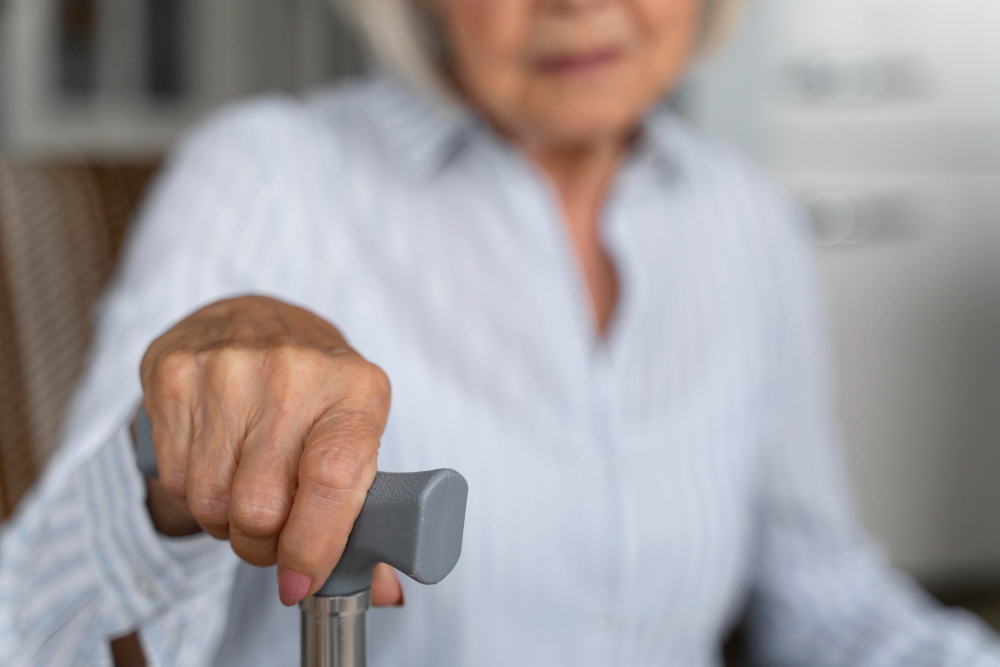

This is the conclusion of a study that evaluated data from 4,500 people who were followed for 14 years. The results are helpful in clinical practice and for screening patients at risk, eliminating the need for complicated tests.
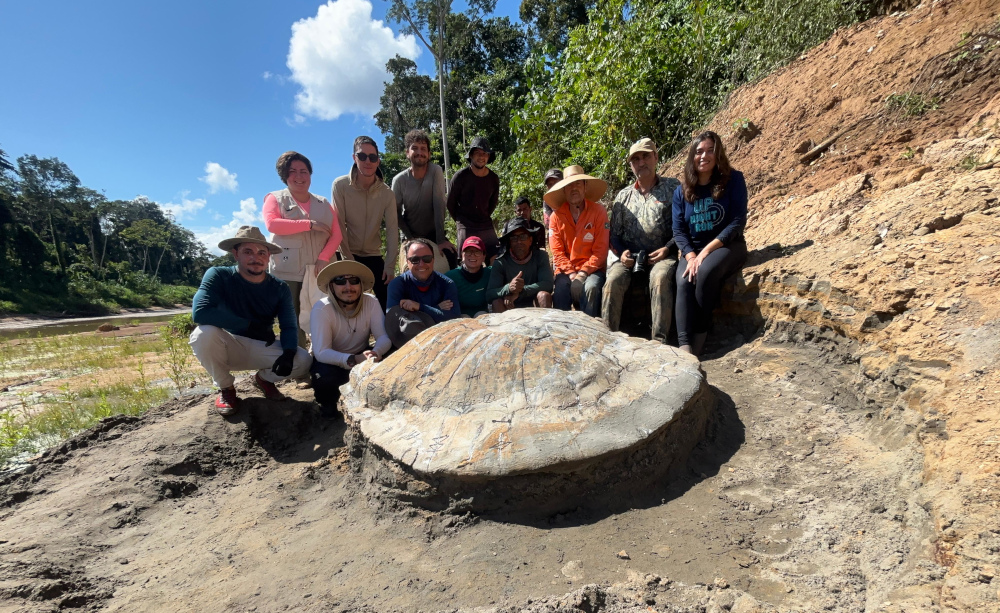

On its first expedition, a project funded by the Amazon+10 Initiative reveals clues about the Amazon millions of years ago.
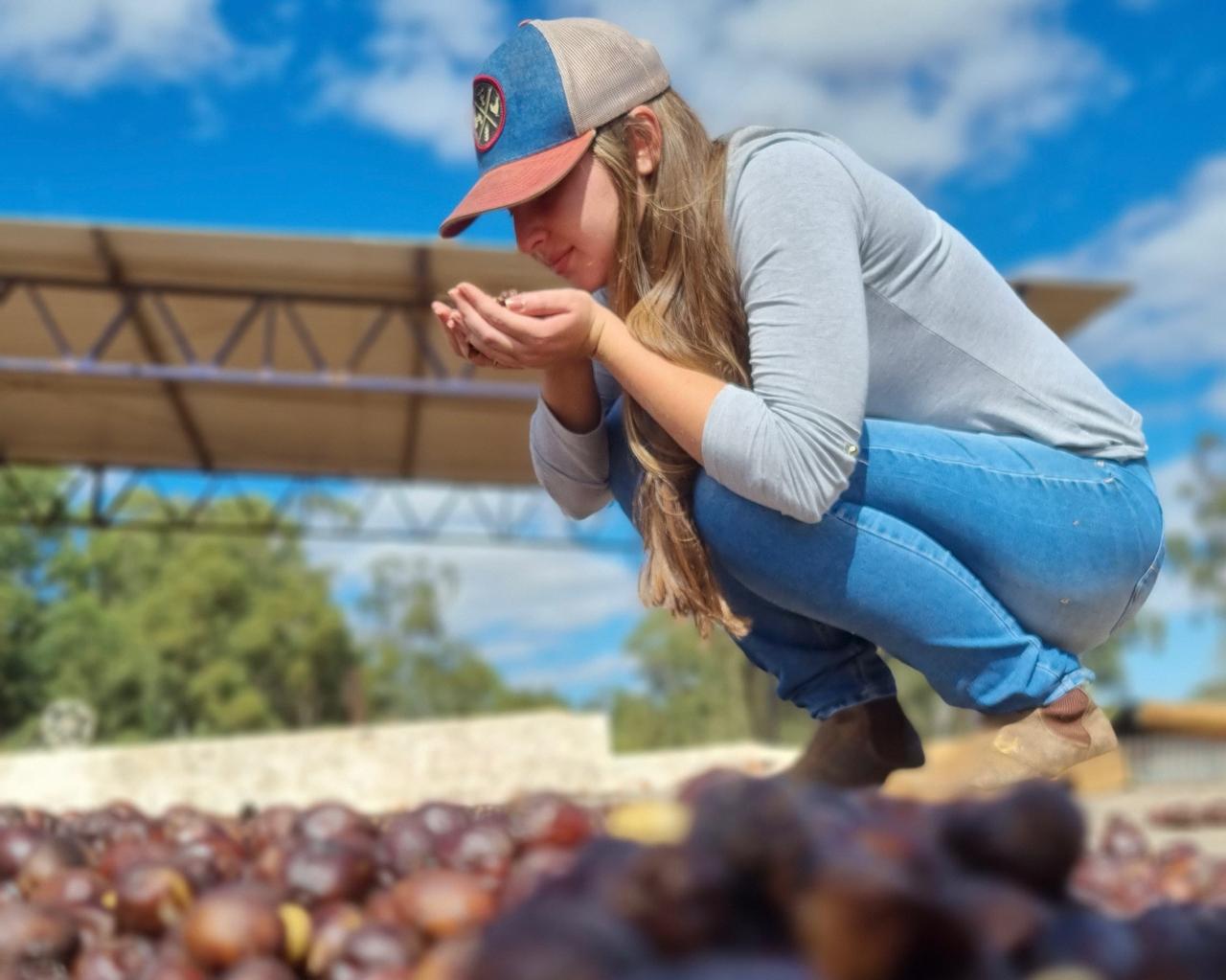

Normally discarded due to their astringent taste, green beans from the Arara cultivar were subjected to airless fermentation and produced high-quality beverages in blind tests. Brazilian researchers see potential for the product to be valued in domestic and foreign markets.
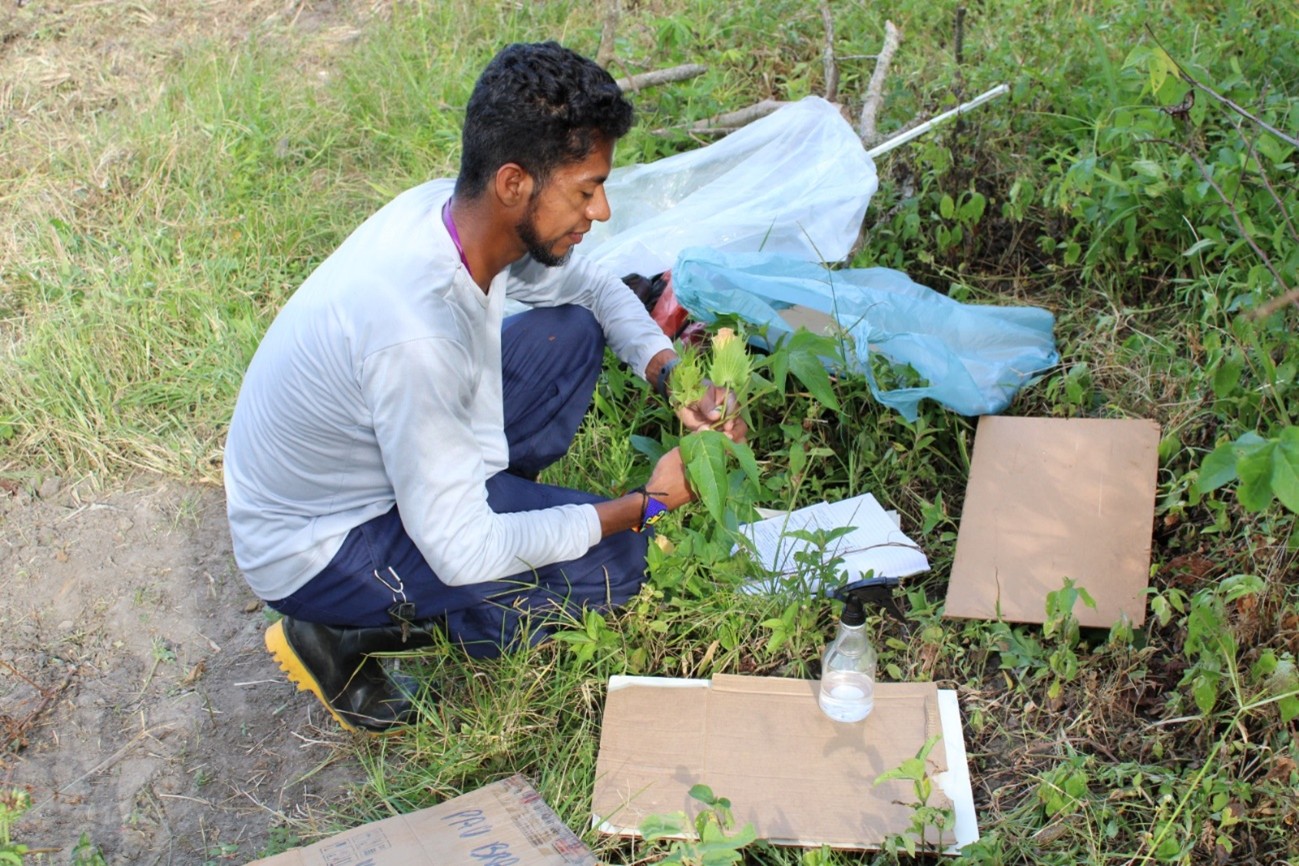

The study accessed ancestral knowledge and cataloged 175 medicinal plants used to treat diseases such as parasitic worms, diabetes, and hypertension. Community participation was central to all stages of the study.
The startup uses bacteriophages to prevent mastitis in dairy cows and reduce the use of conventional drugs.
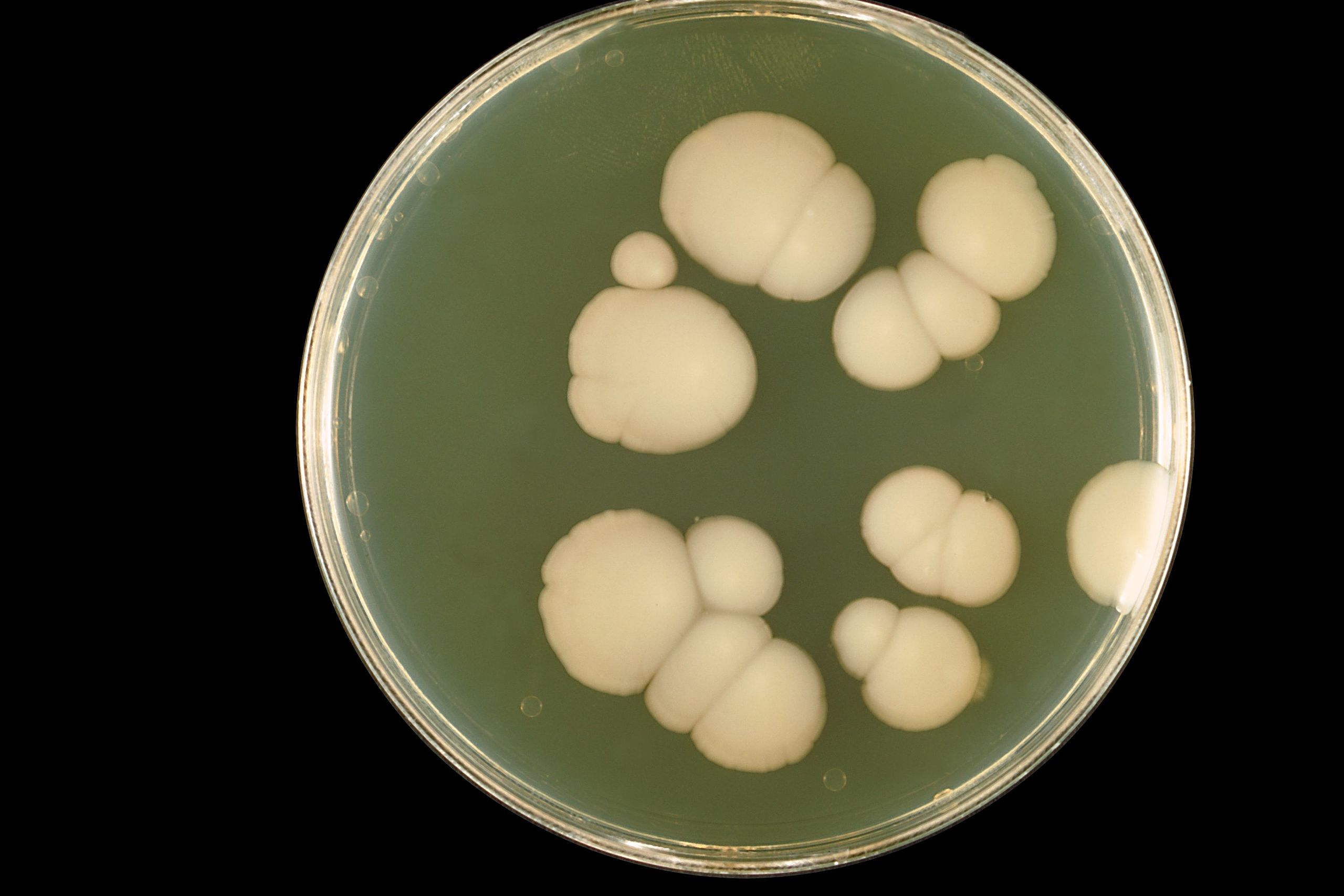
Researchers at a FAPESP-supported research center have managed to reduce Candida albicans’ resistance to fungicides by incorporating photodynamic inactivation techniques into the treatment. The results of the study indicate that the technology can be used in both human healthcare and the prevention of food contamination.
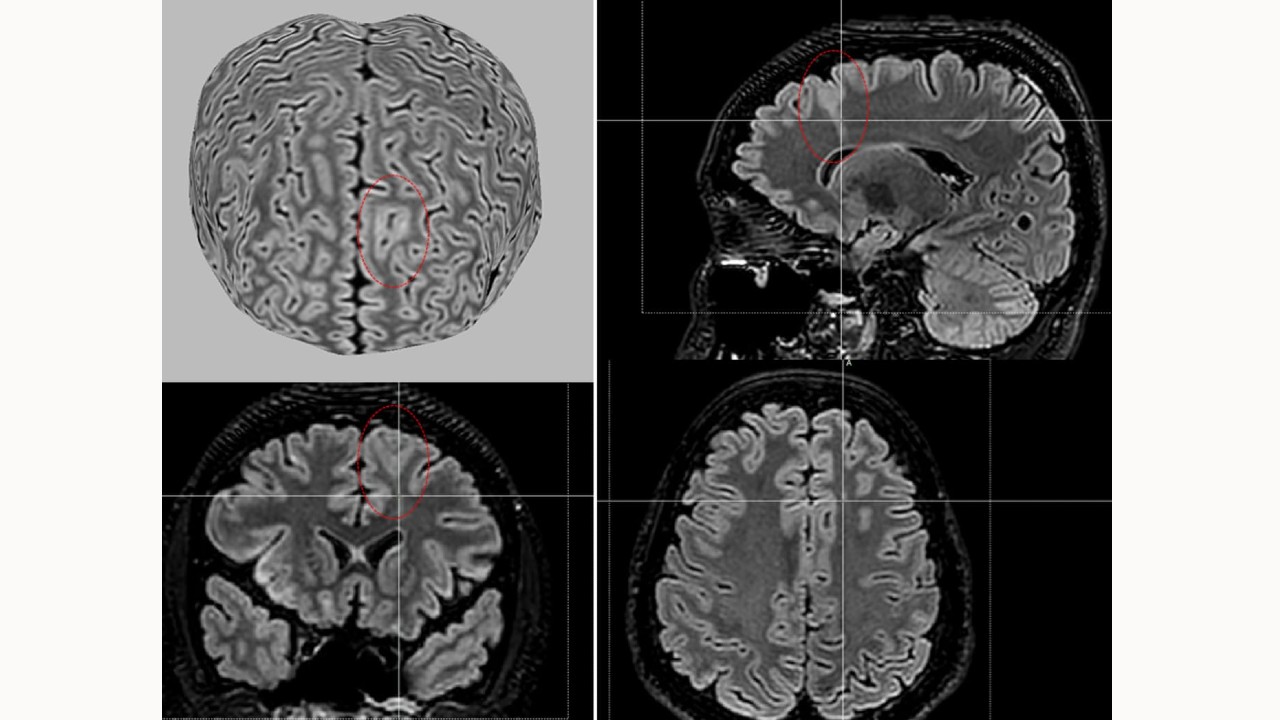
Publicly available algorithm facilitates lesion identification and surgical planning for patients with focal cortical dysplasia, a malformation associated with a drug-refractory form of the disease.

In a study of 141 patients, researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo and collaborators evaluated different models to predict which patients would benefit from risperidone treatment.

In mice, researchers observed increased intestinal stem cell proliferation and organ regeneration in the post-fasting period. However, depending on the diet and genetic profile, this can increase the risk of tumors.
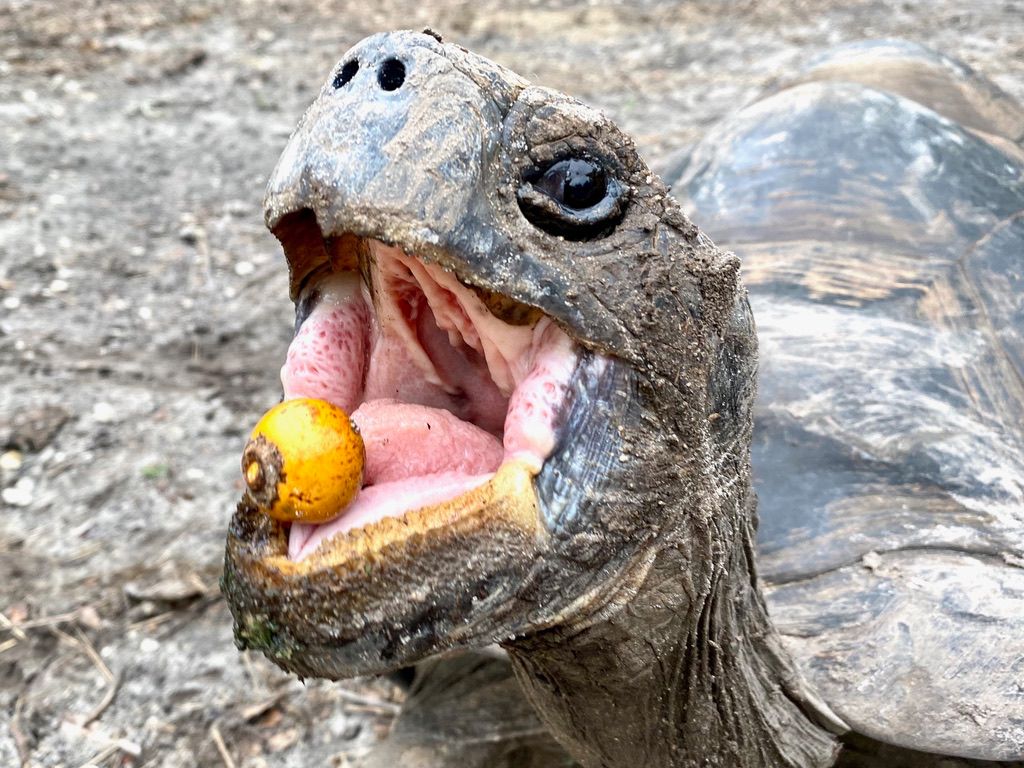

International team of researchers issues global warning about the need to include frugivores in conservation, forest restoration, and climate change mitigation strategies.
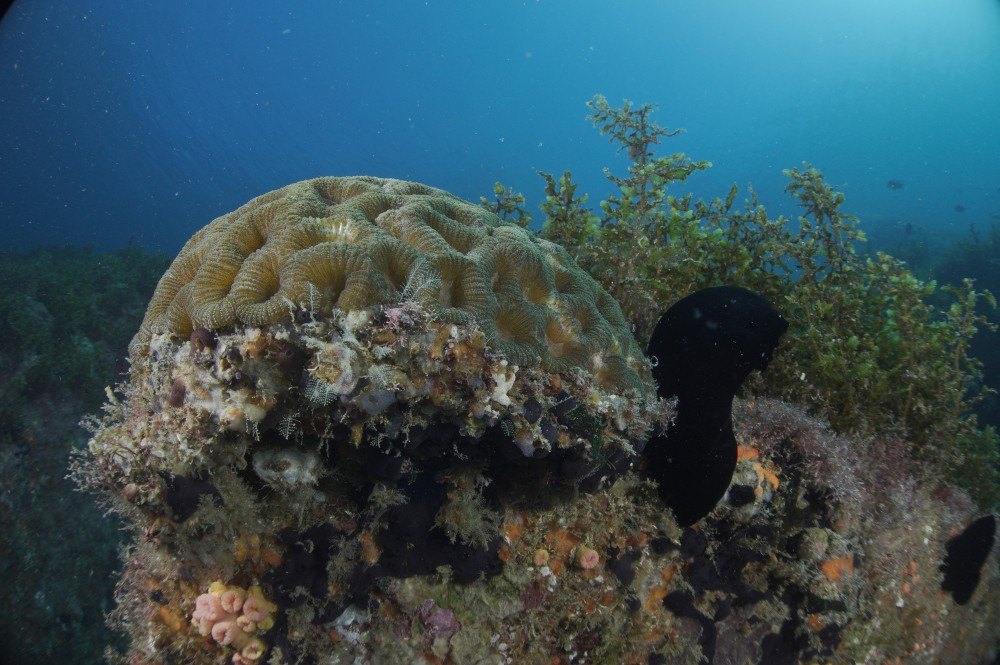

A single species found in the Alcatrazes Archipelago, brain coral, produces around 170 tons of calcium carbonate annually. This represents the retention of approximately 20 tons of carbon in mineral form, which can last for centuries or millennia. A study by the Federal University of São Paulo highlights the potential ecosystem services provided by subtropical corals.

Insper is holding an event supported by FAPESP that will explore key areas for sustainable transformation. Register by August 15.
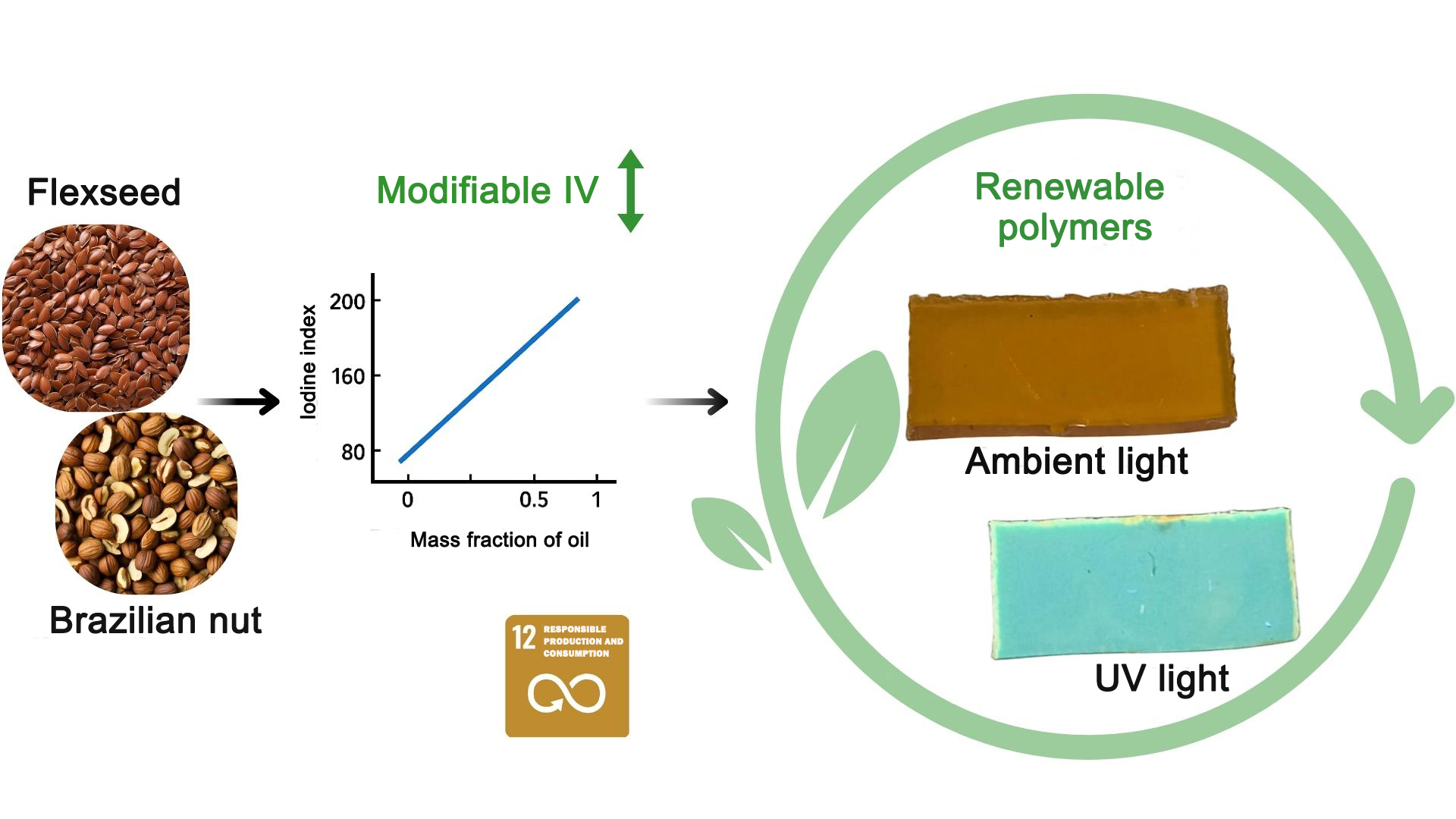
A study conducted at São Paulo State University characterized the properties of a formulation containing chemically modified flaxseed and Brazil nut oils.
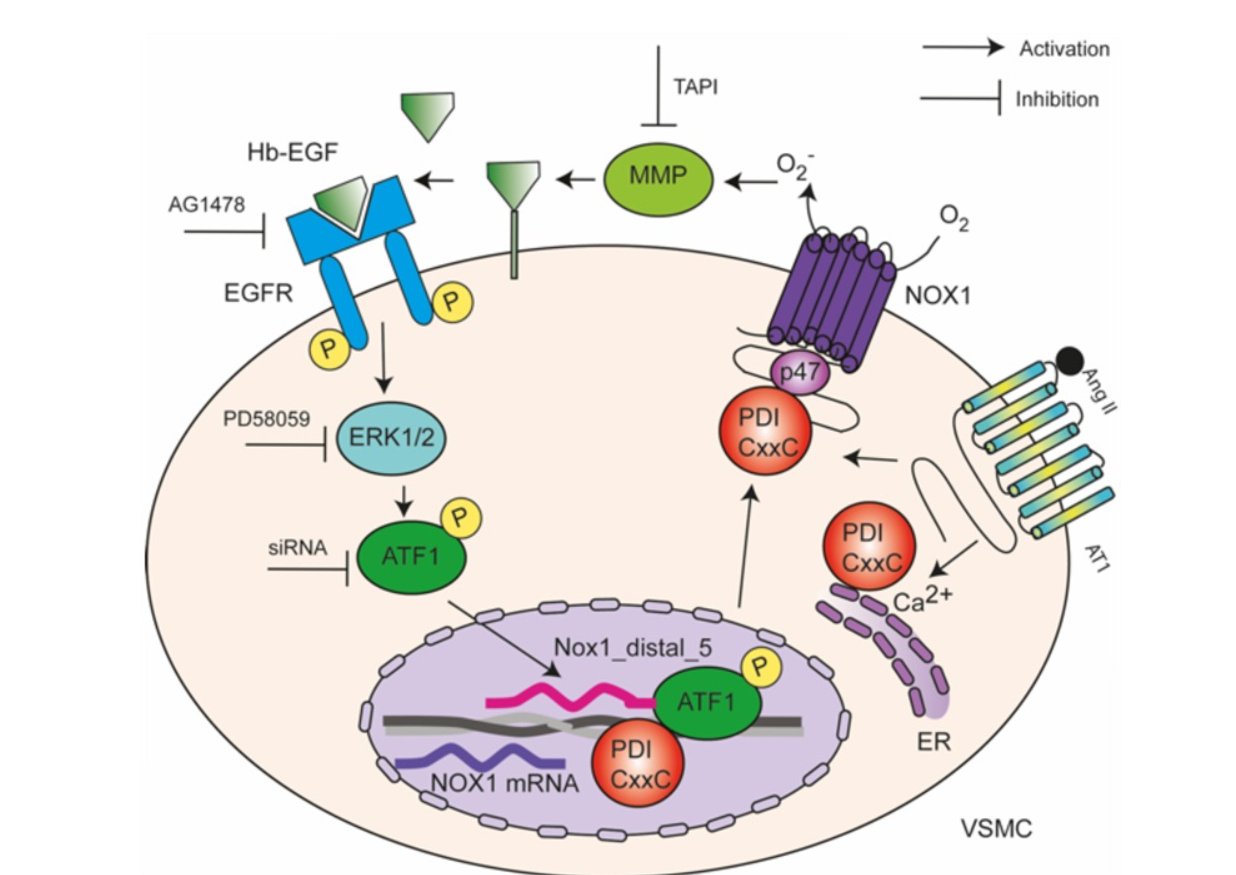
Discovery at the Center for Redox Processes in Biomedicine showed positive results in hypertensive rats and therapeutic potential.
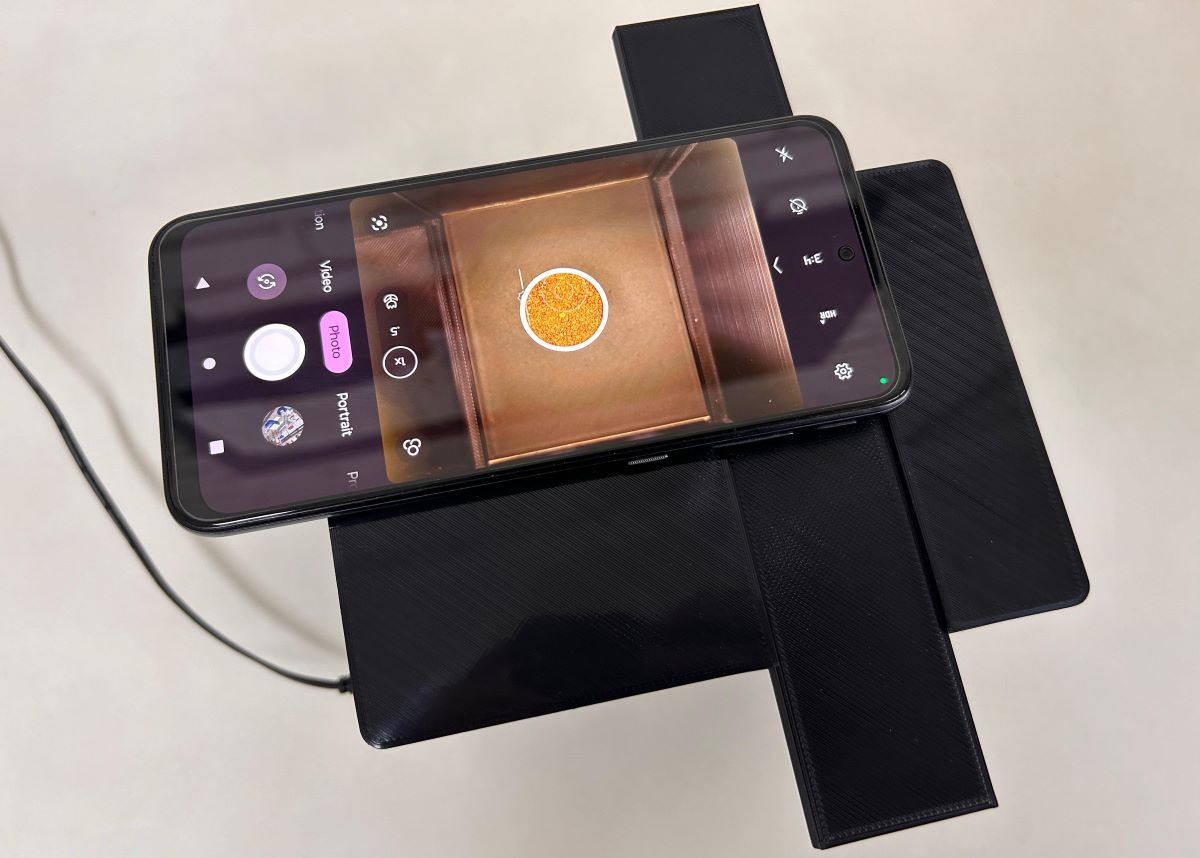

The method is part of a series of international studies on the Canephora species published by Brazilians and can be adapted to identify “fake coffees”.
Brazilian researchers develop precision tool that can predict immunotherapy treatment failure, with the potential to personalize therapies and reduce healthcare costs.
During the pandemic, a preference for domestic vaccines or those from countries such as the United States, Germany, and the United Kingdom was observed for the first time. This phenomenon, known in marketing as the country of origin effect, is usually associated with products that require consumer research before purchase or that have a long tradition in certain countries, such as Swiss chocolates. However, it had never been linked to free vaccines.
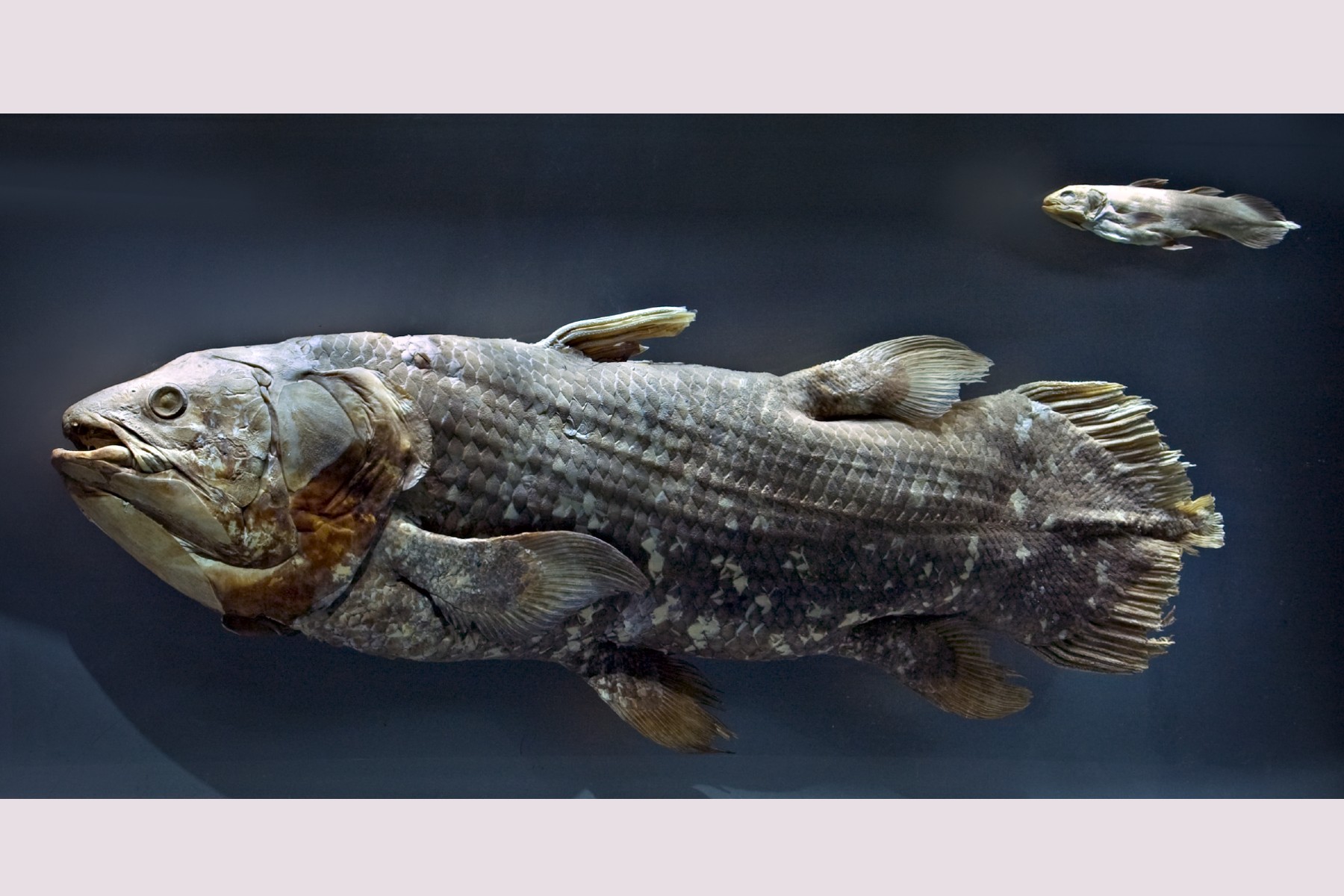

Researchers reanalyzed the skull musculature of coelacanths, a group of fish that has existed for 400 million years, and concluded that many structures had been incorrectly described. The study was published in Science Advances by researchers from the University of São Paulo and the Smithsonian Institution.