


The finding was based on questionnaires applied to 313 Brazilian women in their 30s. The results indicate that, although the reported discomforts negatively affect the participants’ quality of life and sexual health, they tend to normalize them.
An international consortium of scientists presents an overview of the subject in an article published in the journal Science.

The study conducted at the University of São Paulo evaluated data from 54 women who were newly diagnosed with early-stage disease.
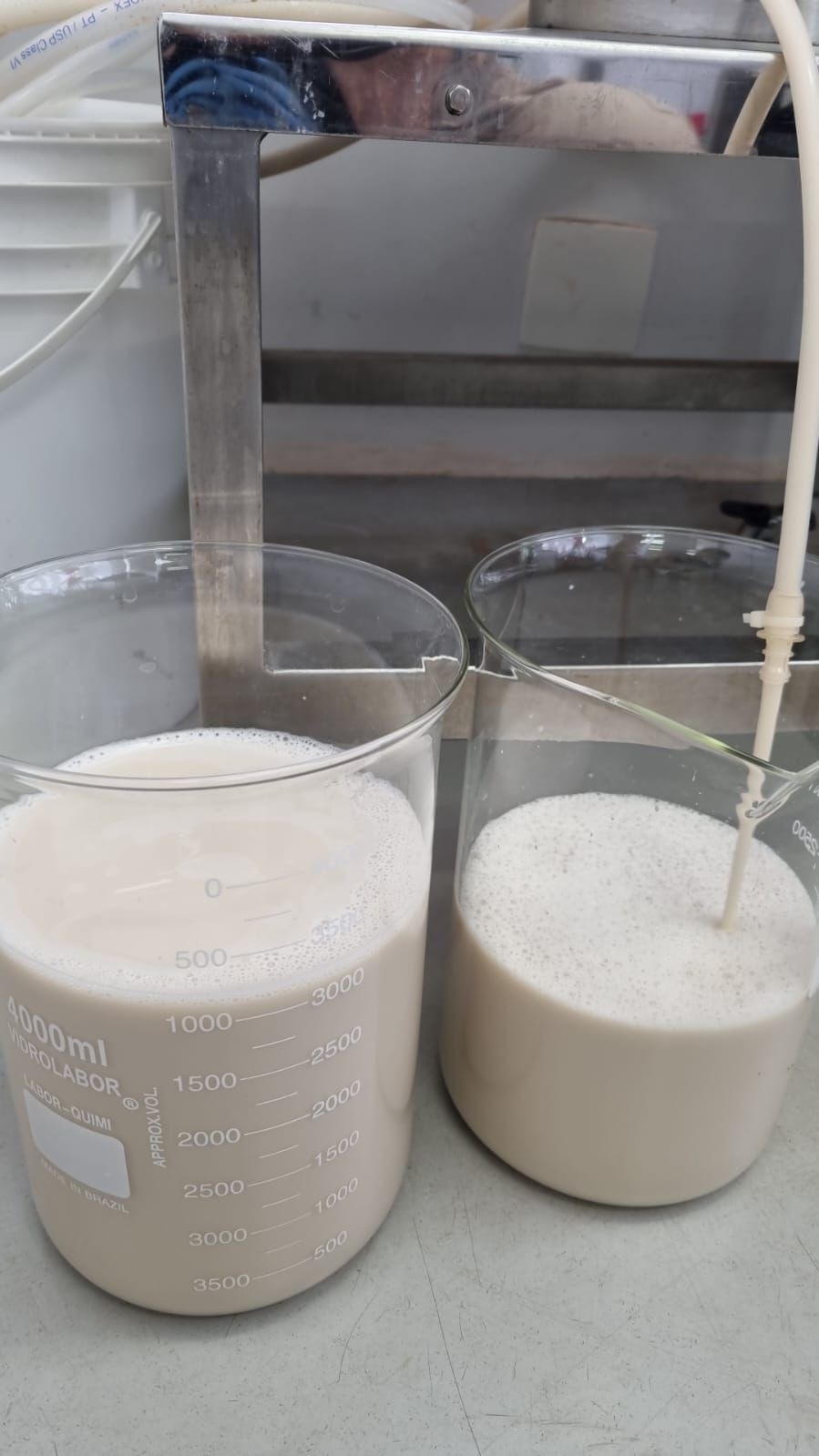

Future Cow uses precision fermentation to create dairy ingredients in a sustainable way; the startup, supported by FAPESP, was selected to participate in VivaTech, one of Europe’s largest innovation events.

Event will be promoted by the Institute of Marine Science of the Federal University of São Paulo between August 19th and September 1st.
In animal tests, researchers from the University of São Paulo observed that changes in insulin signaling in the brain affected both memory and the frequency and severity of seizures. The findings support clinical evidence and point the way to new therapeutic approaches.
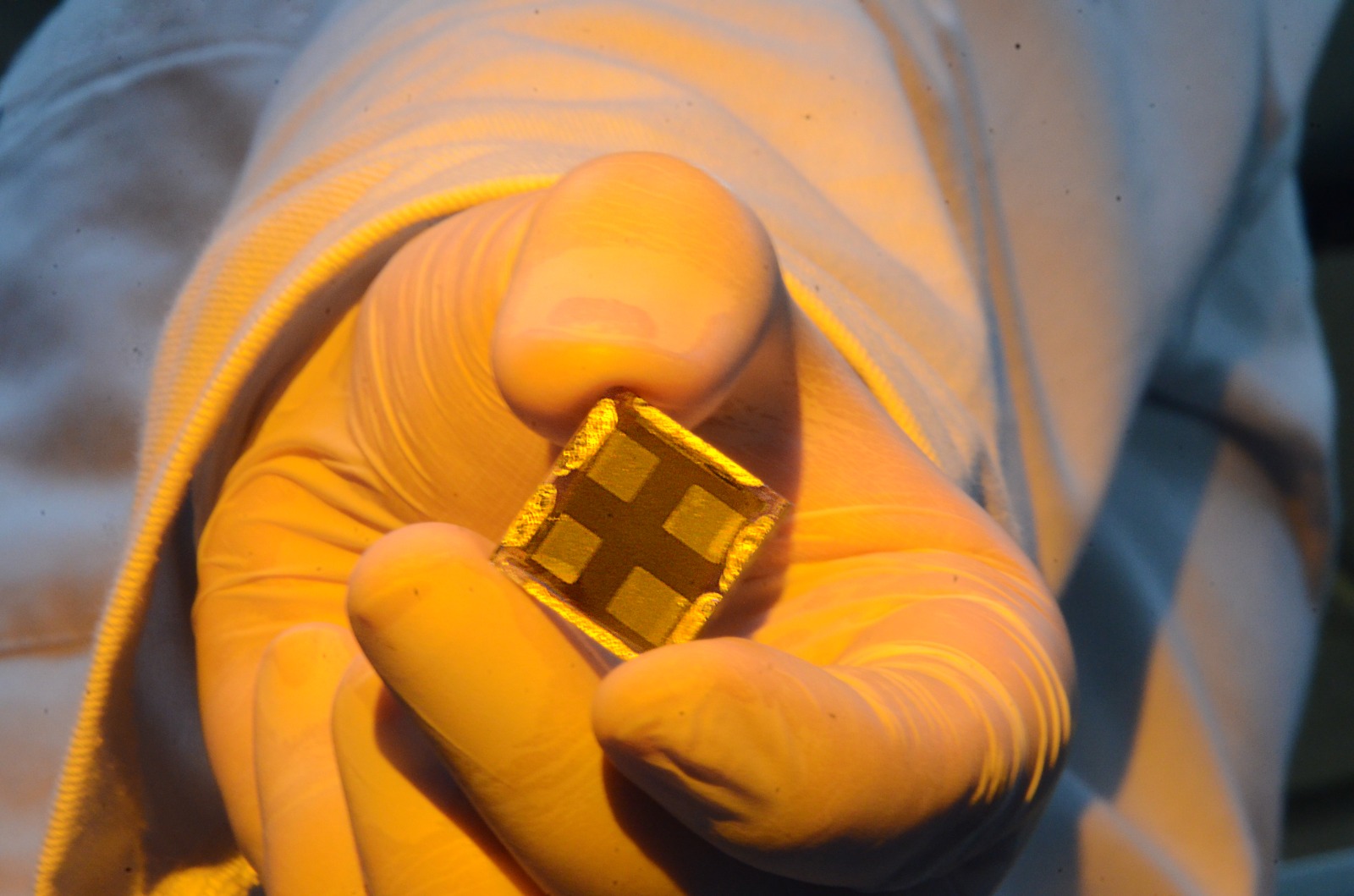
The material is as efficient as silicon in generating clean energy and has lower production costs, greater lightness and flexibility. Its rapid degradation is one of the main obstacles to overcome to make its use viable.

Researchers from the Federal University of São Paulo used oysters and mussels as sentinel organisms to assess the presence of these pollutants. The results show that even the most restrictive sites for human presence have significant contamination.

Created by Claro, FAPESP and the University of São Paulo, the initiative will involve more than one hundred researchers in the development of disruptive solutions in three areas: Smart Cities, Industry 4.0 and Agrotech.
A group led by researchers at the A.C.Camargo Cancer Center has succeeded in improving CAR-T cells, making them more effective in treating refractory types of lymphoma and leukemia.
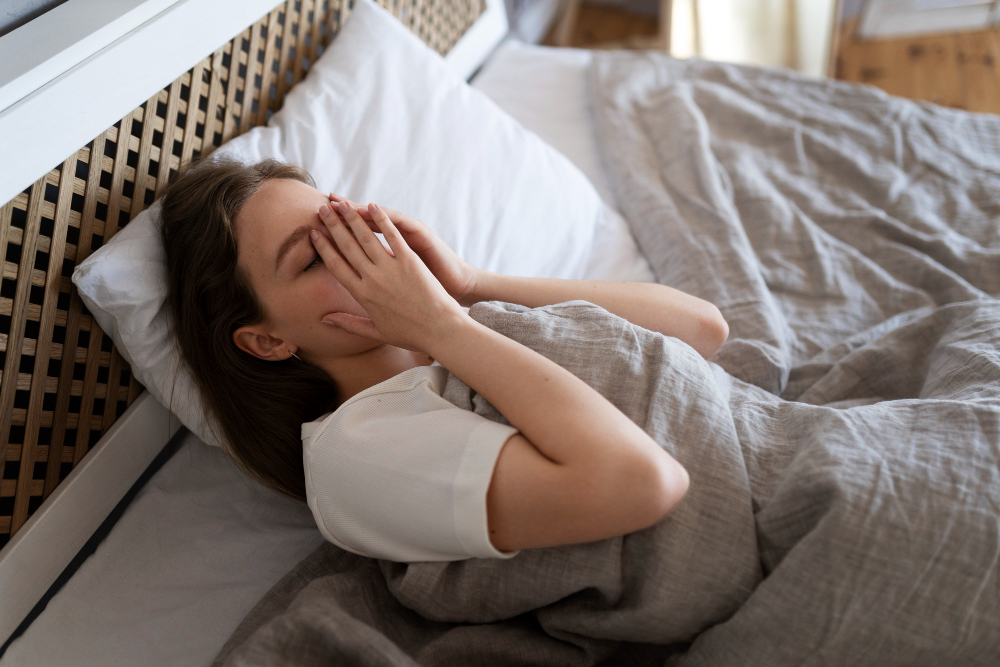

The conclusion comes from a study conducted at the University of São Paulo with 595 participants between the ages of 18 and 59. The analysis shows a link between insomnia and high levels of neuroticism, and points to anxiety as part of the problem.

Researchers from the University of São Paulo and collaborators conducted a comprehensive review of the available literature on the subject, which included more than 13,000 articles.

The project developed by Food Research Center takes into account the eating habits and biodiversity of each country in the region.
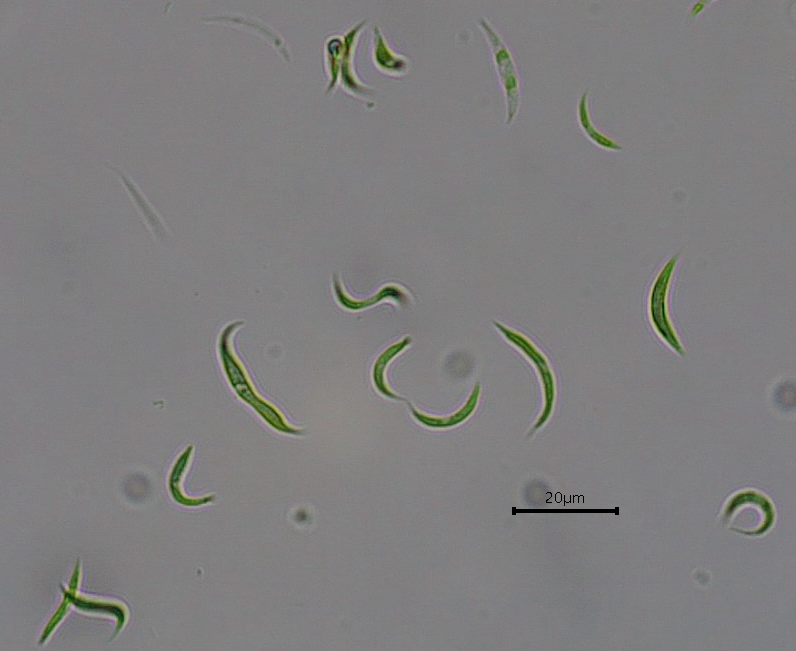
In the laboratory, the species Monoraphidium contortum removed some of the drugs added to the liquid and produced biomass with potential commercial value.

Praziquantel, usually administered in large tablets, is the only anthelmintic available on the market. New form of presentation uses nanotechnology and facilitates use by children and pets.
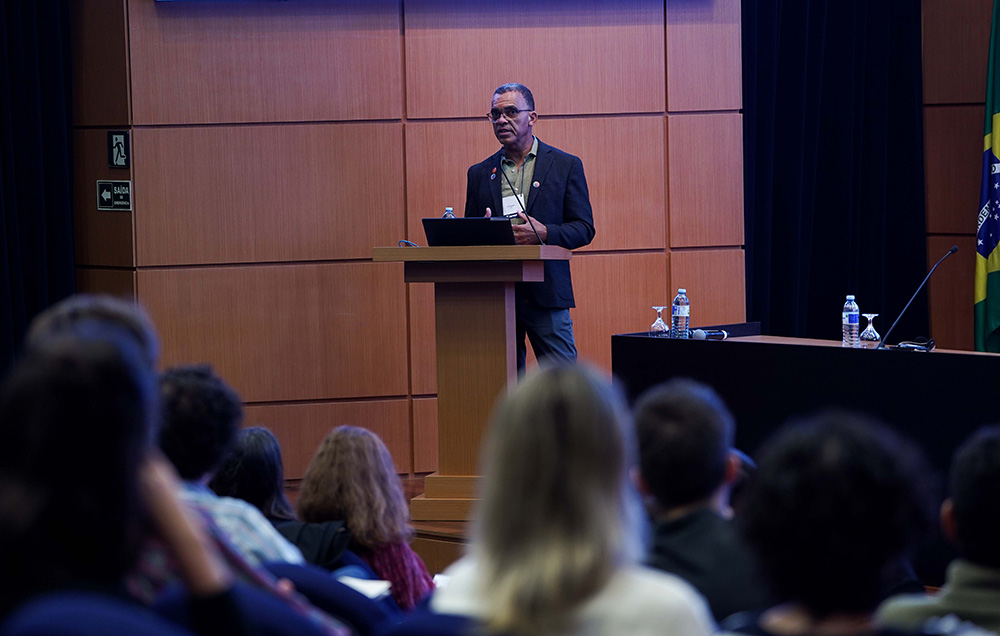

The topic was discussed by Kenyan marine ecologist David Obura, chairman of the Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services, and Brazilian researchers during the 3rd FAPESP 2025 Conference.
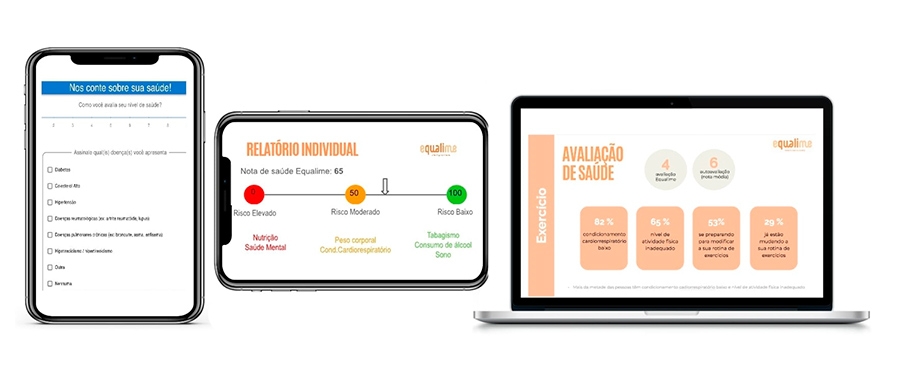
Digital tool developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo measures employee health indices and guides more efficient corporate actions for well-being at work.
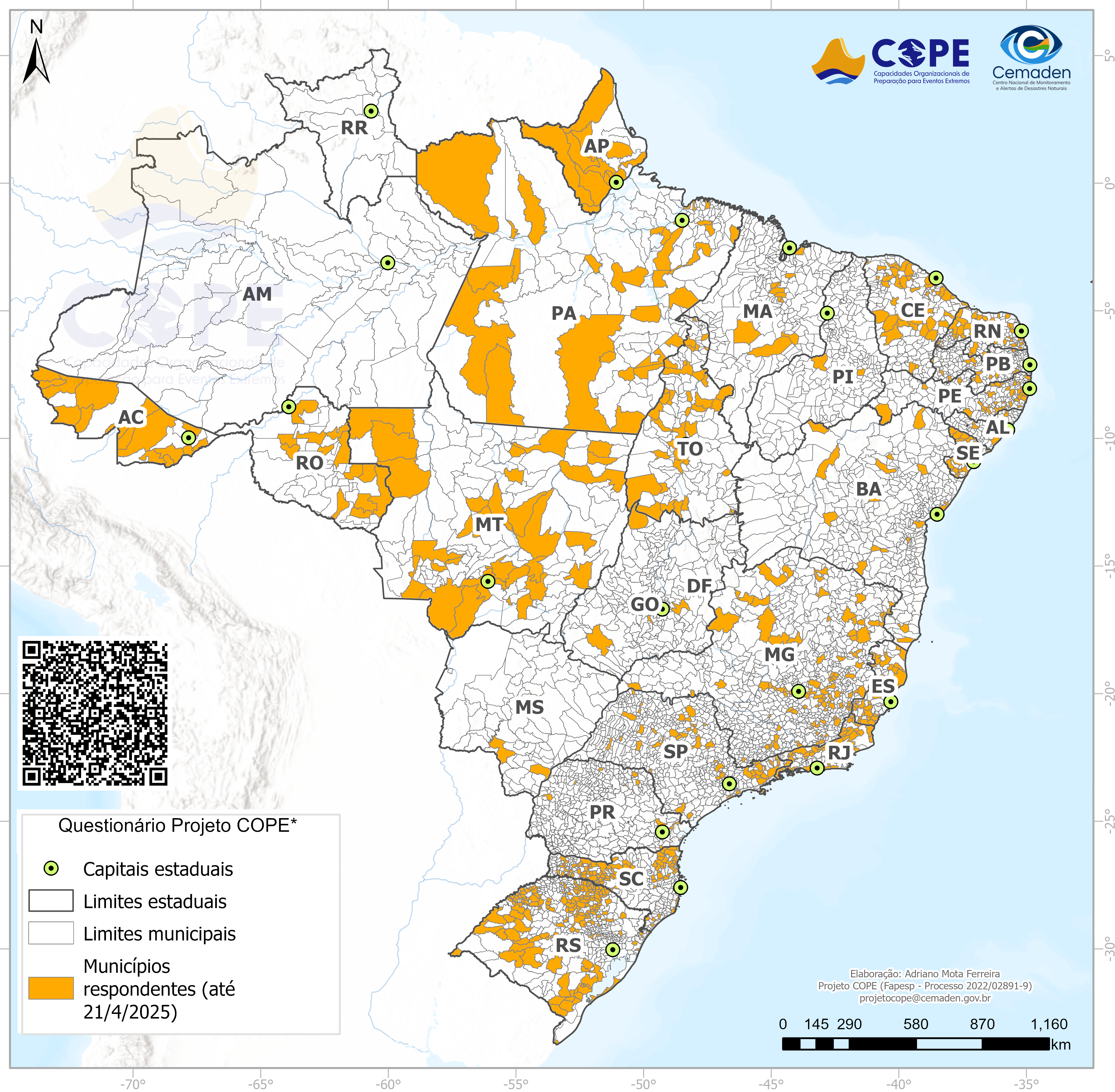
Research proposes action fronts to increase the organizational capacity of these units in municipalities; expanded coordination with other areas is one of the next steps for the sector.
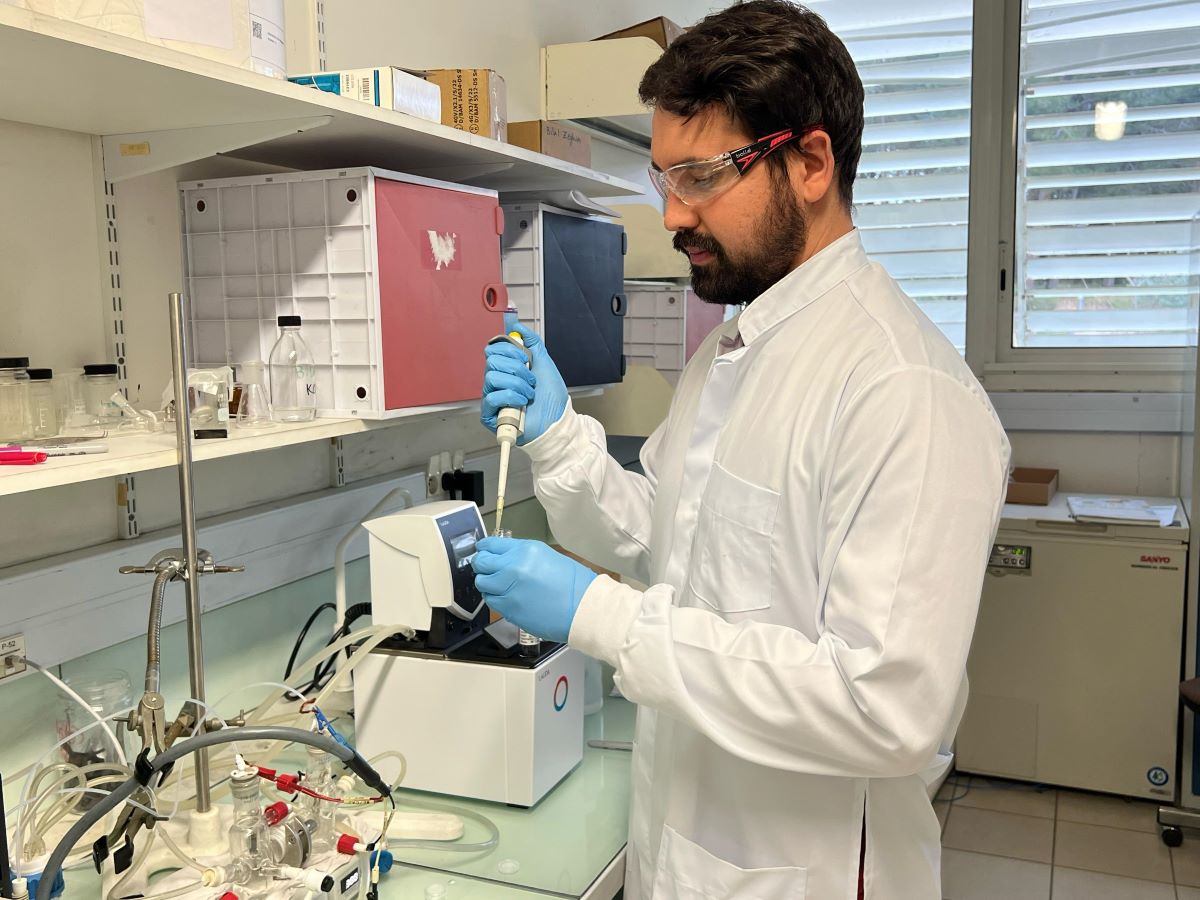

In order to improve the performance of photoelectrocatalysts that act in the “separation” of H2, work carried out at a FAPESP-supported research center uses light and glycerol to eliminate unwanted compounds resulting from the reaction of these materials with organic molecules.
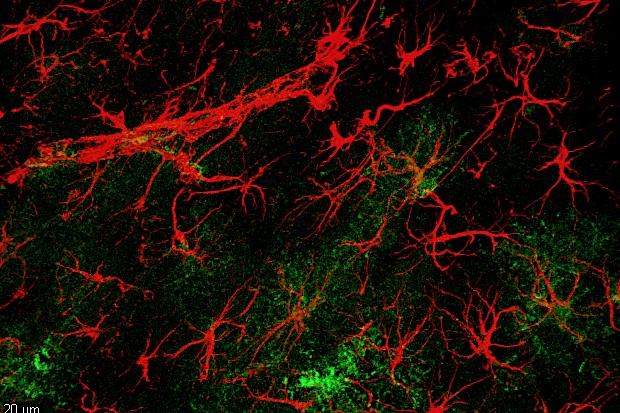
Brazilian researchers observed increased connections between neurons in rodents after inducing an increase in the synthesis of hevin – a glycoprotein naturally produced by astrocytes.
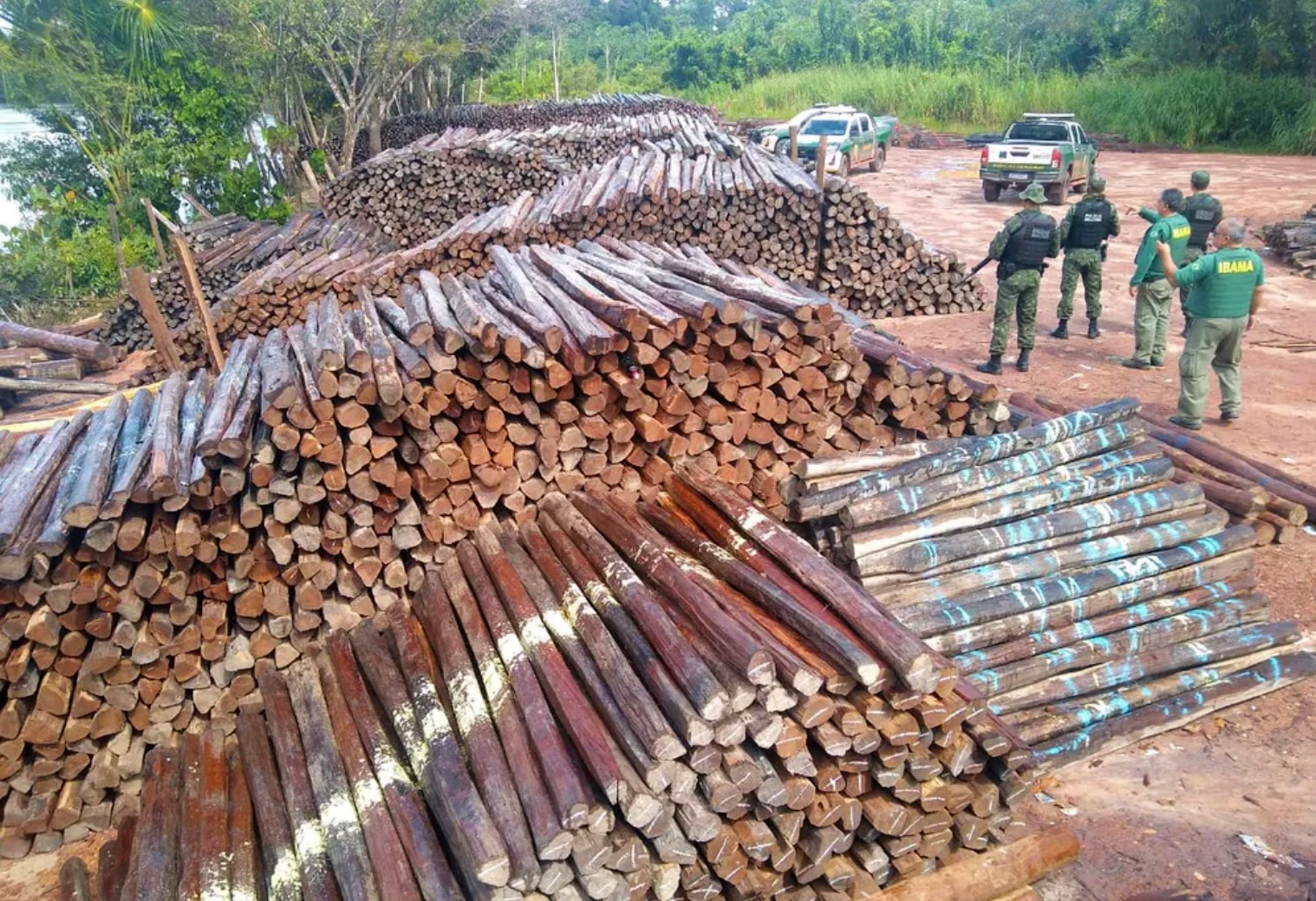

Solution developed at the Center for Research in Mathematical Sciences Applied to Industry is based on the analysis of the timber trade network.
This natural protein, called CelOCE, was obtained at the Brazilian Center for Research in Energy and Materials and can be immediately incorporated into the industrial process. The discovery was published in the journal Nature.
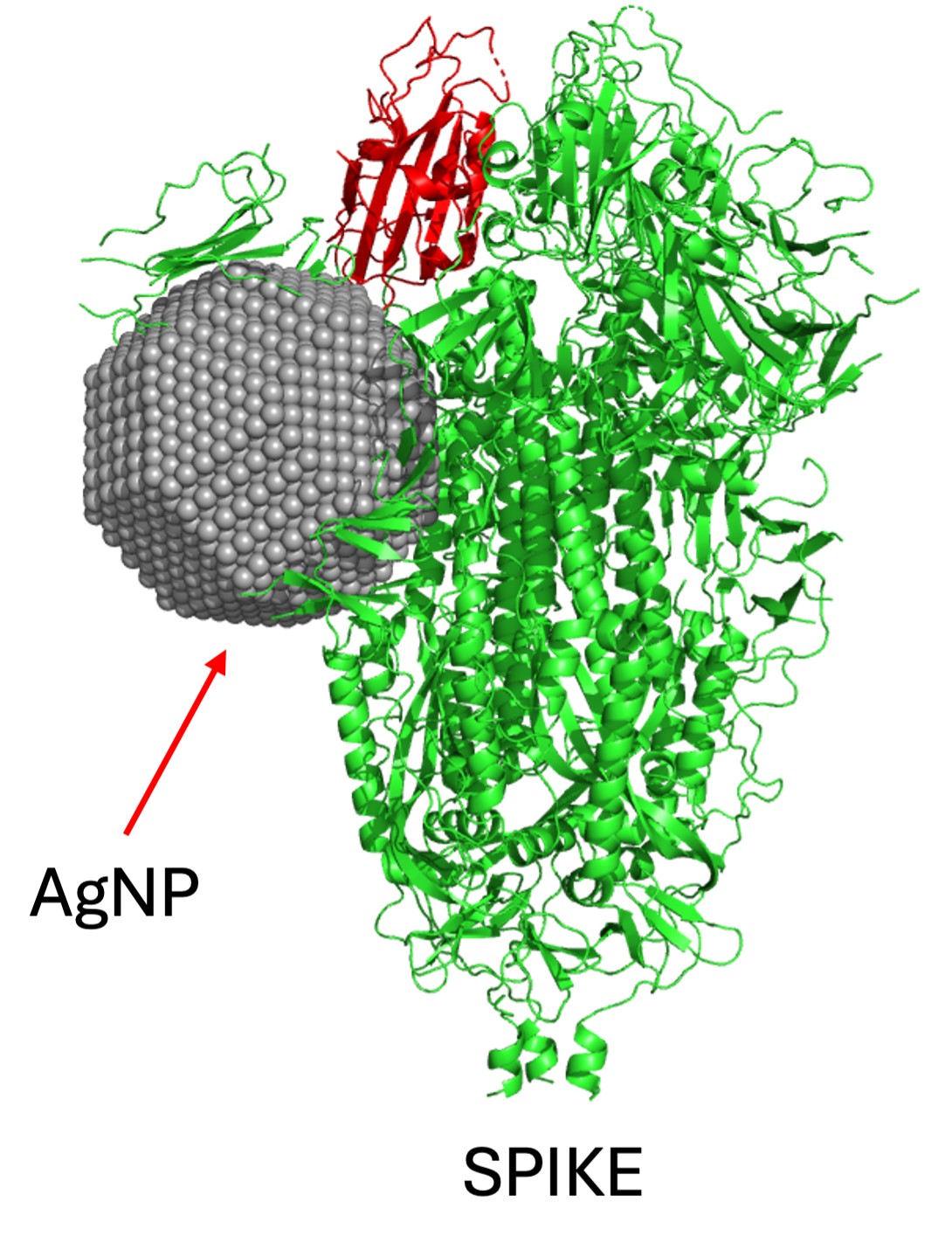
Study in hamsters paves way for development of nasal sprays and other products to fight several viral diseases, including HIV/AIDS, shingles and influenza.

The conclusion comes from a study that followed 805 Brazilians in their 50s for eight years. The results underscore the need for increased attention to hearing health as a way to prevent dementia.
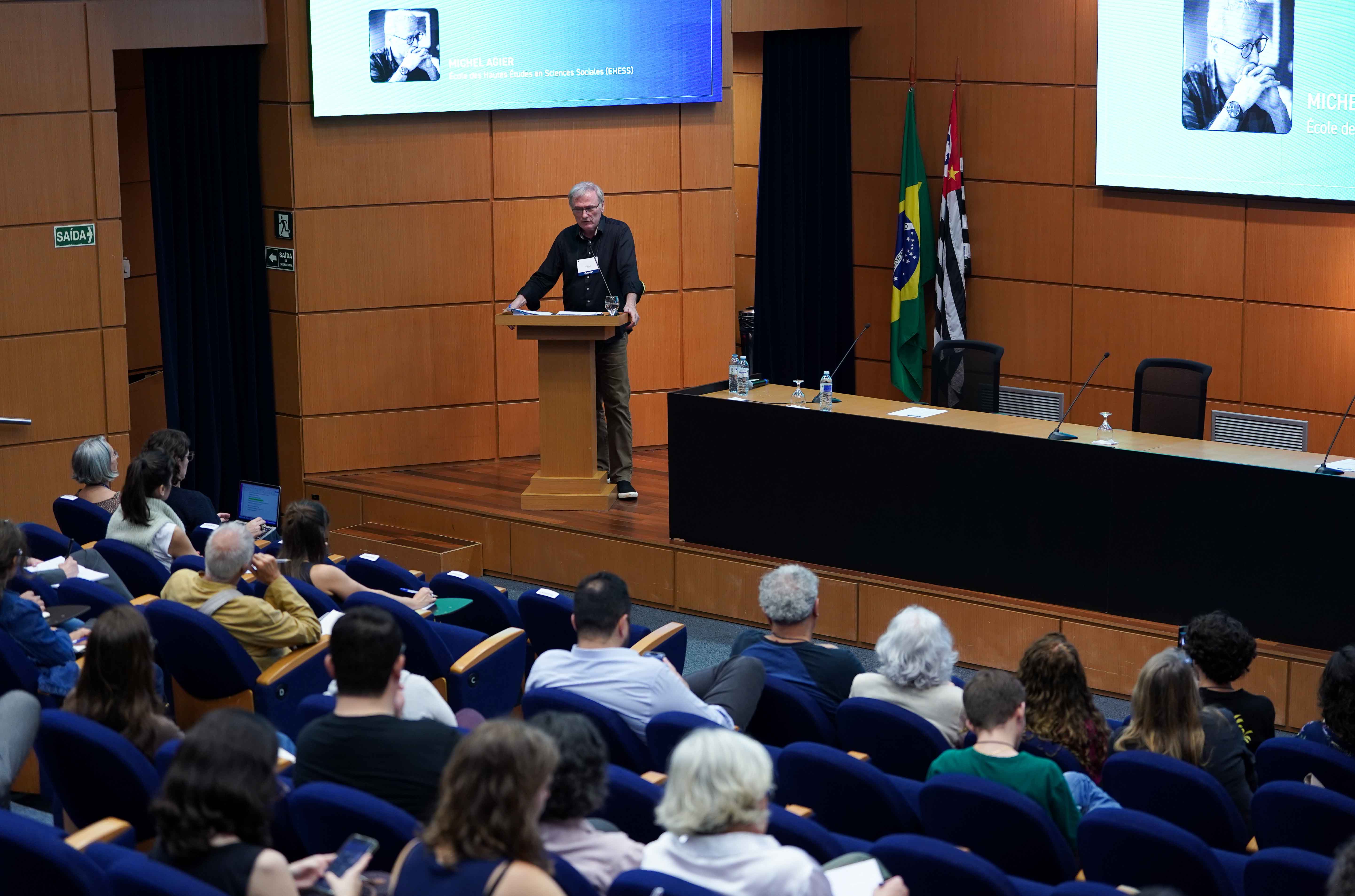

At the 2nd FAPESP 2025 Conference, the French anthropologist and ethnologist Michel Agier exposed the ethical and political limits of contemporary society. He proposed the African concepts of Zumunti, Teranga and Ubuntu as cosmopolitical horizons for a common life.