

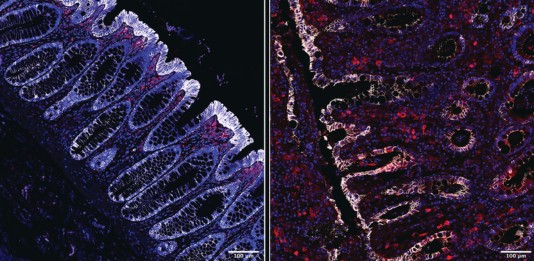
Rodents fed a diet rich in soluble fiber coped better with a microorganism that causes diarrhea and can lead to death in debilitated patients. Researchers observed that acetate – a compound produced by the gut microbiota when fiber is digested – helps modulate the immune response.
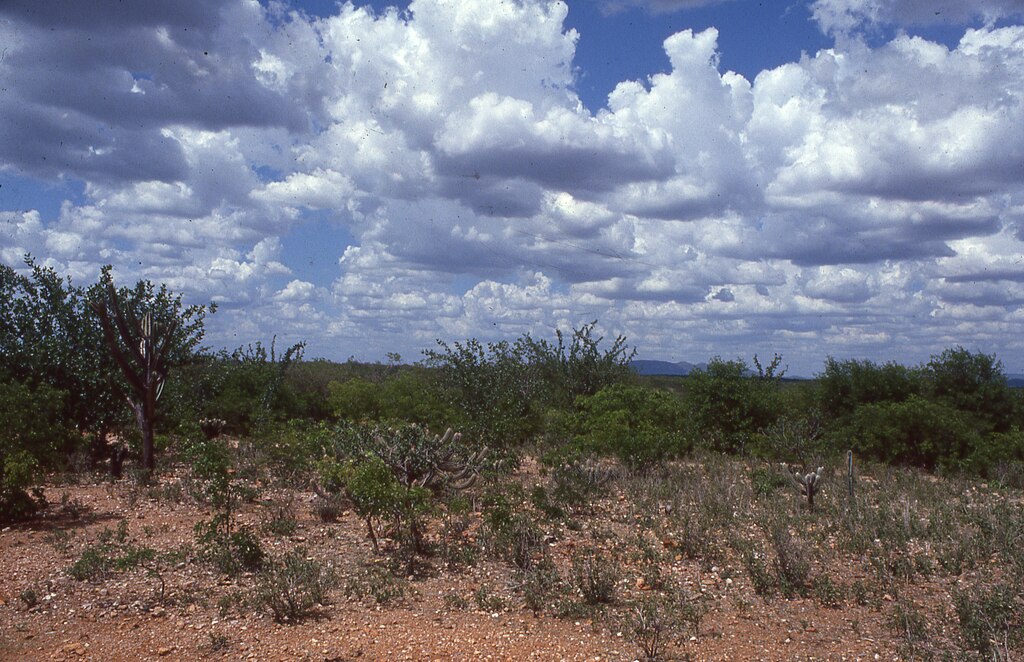

Study carried out in Brazil’s semi-arid biome found that removing animals did not lead to significant improvements, even after three years of spontaneous soil recovery. Researchers suggest complementary measures such as green manure and strategic tree planting.
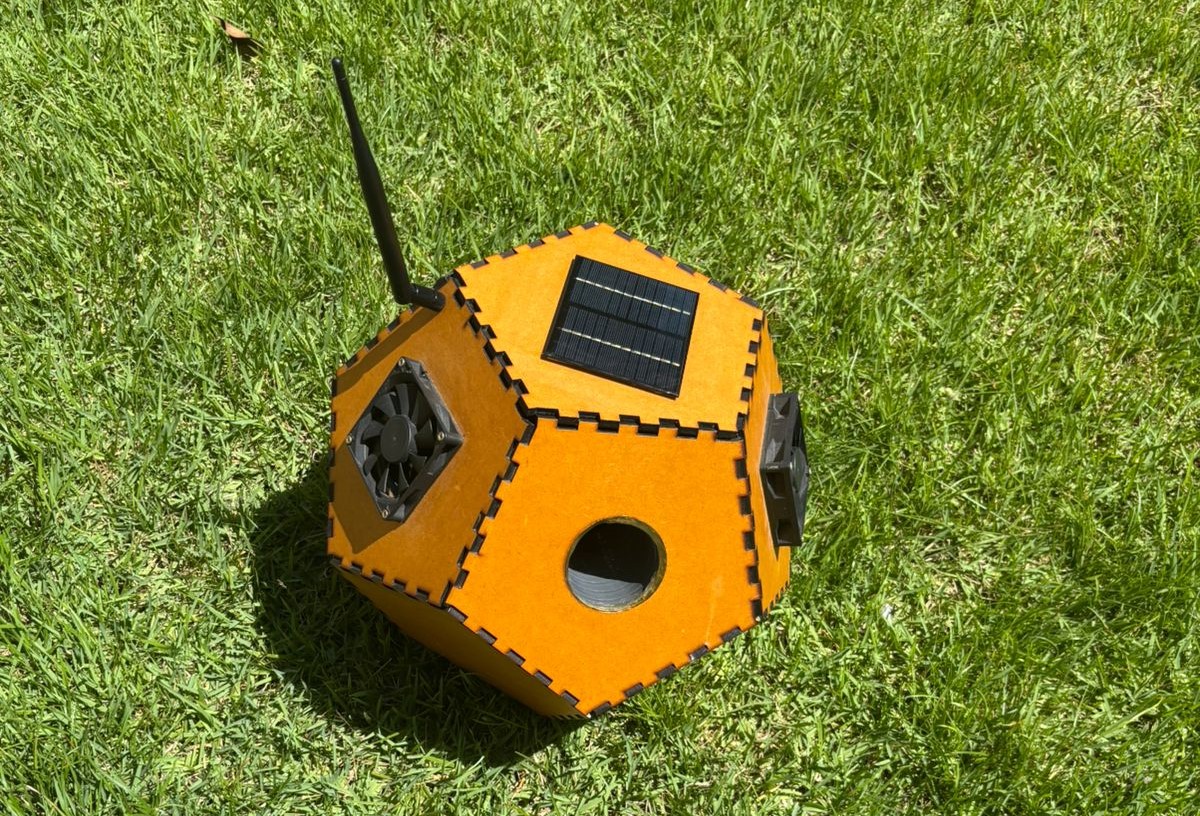

Equipment developed in Brazil by researchers at the National Telecommunications Institute combines Internet of Things devices, high-resolution cameras, and artificial intelligence algorithms to capture and identify female Aedes aegypti without harming other insects.

Device developed with the support of FAPESP is more accurate than assessments made by doctors using a dermatoscope.

Researchers from São Paulo State University and collaborators studied 50 young people with an average age of between 26 and 27. The goal was to find biomarkers that allow early detection of health changes.

Images taken from an unmanned aerial vehicle, processed with free software, help assess water stress parameters in corn experiments and select varieties that are better adapted to water shortages.
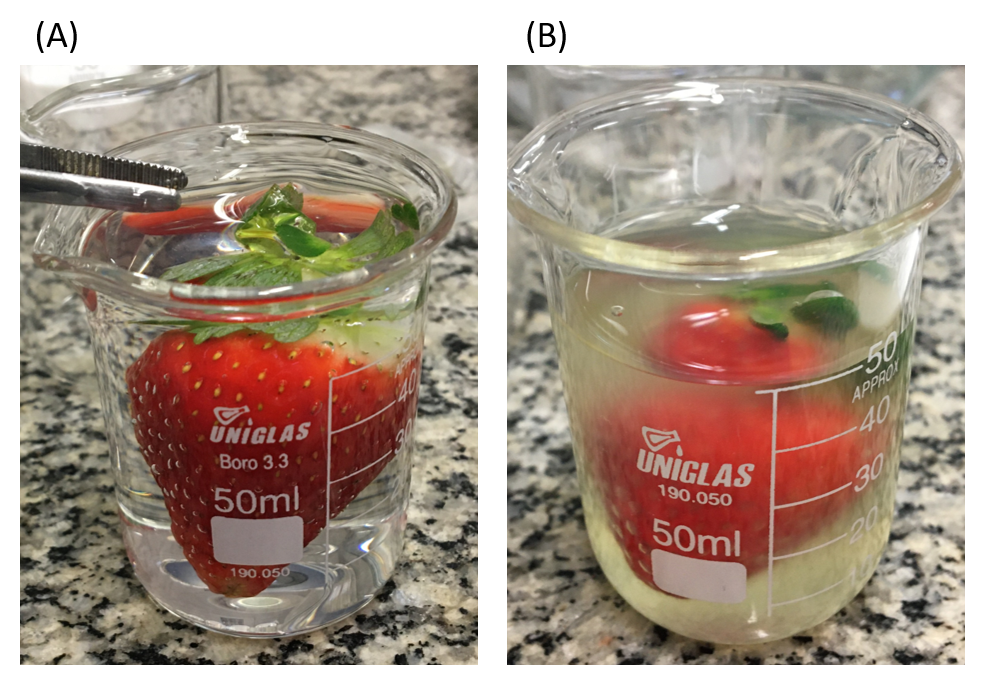
Fruit coated with the material developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo showed 11% less weight loss during storage and took longer to start becoming contaminated by fungi.

An enzyme cloned from an insect found by Brazilian researchers – and genetically modified – makes it possible to monitor intracellular acidity and could be used to study diseases and drugs.

The study, conducted at the State University of Campinas, involved 44 people with mild cognitive impairment. After six months, the volunteers who practiced strength training showed improvements in memory and brain anatomy, while the others showed a decline in the parameters evaluated.

Tool allows issues such as harassment to be identified before they become critical, enabling companies to take preventive action.

The Albert Einstein Jewish Brazilian Hospital, in São Paulo, creates research group to evaluate potential uses of the technology; the project was presented during FAPESP Week Germany.

Researchers from Brazil and Germany study the mechanism of action of phytochemicals from papaya, passion fruit and medicinal plant extracts; results were presented at FAPESP Week Germany.

Illiberal and authoritarian governments, economic power and digital media are some of the problems facing scientists, says São Paulo State University professor Murilo Gaspardo in a lecture during FAPESP Week Germany.

The assessment was made by participants at the opening ceremony of FAPESP Week in the country.

This assessment was made by the Brazilian Ambassador to Germany, Roberto Jaguaribe, during a reception for the participants of FAPESP Week Germany.

German researchers are increasingly interested in topics studied in Brazilian academia, such as indigenous and black feminist thought, said Brazilian researcher Sérgio Costa, Chair of Sociology at the Institute for Latin American Studies of the Free University of Berlin, in an interview with Agência FAPESP. He was one of the speakers at FAPESP Week Germany.
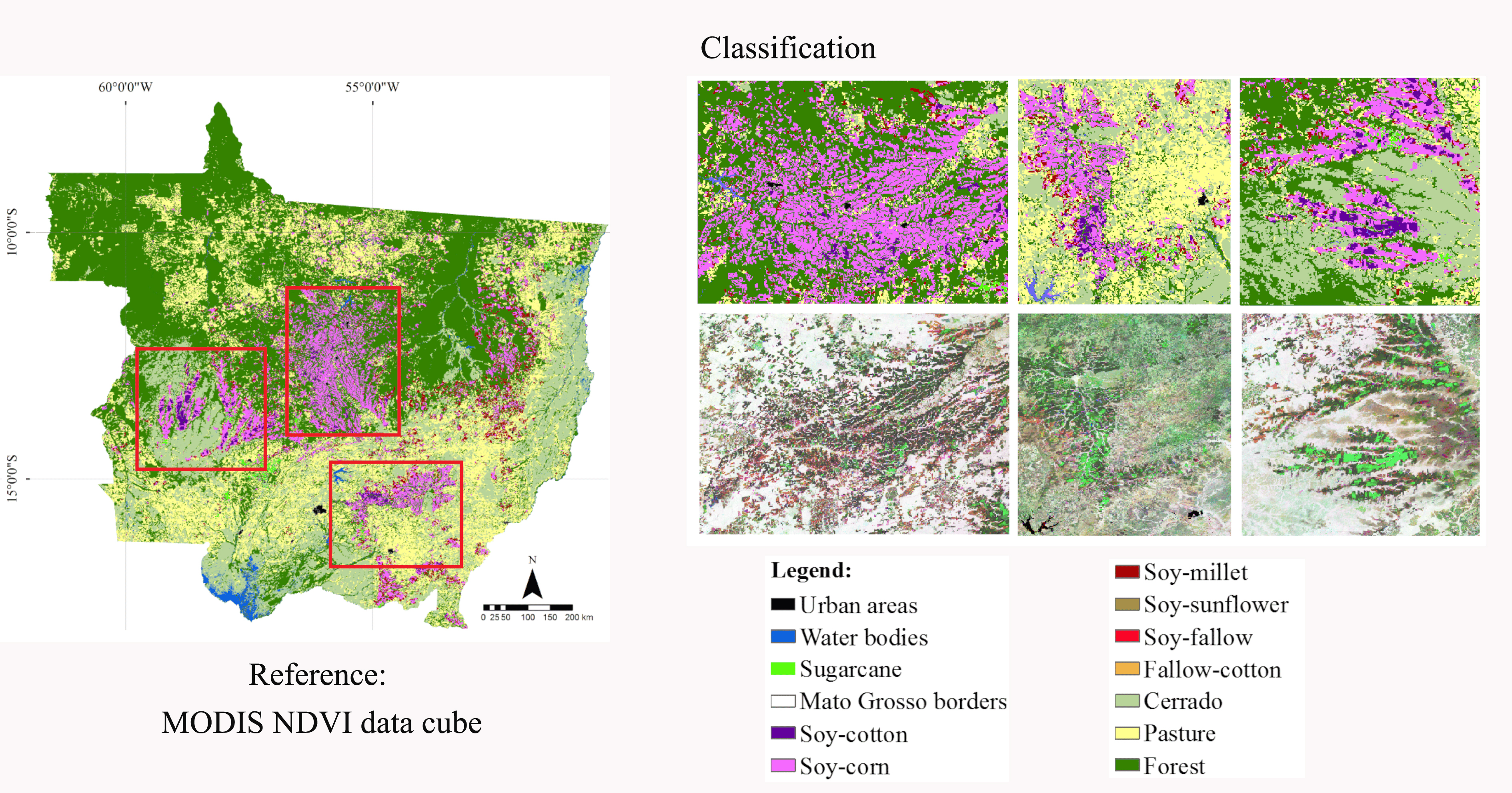
A technique developed by researchers at São Paulo State University was tested in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso and more accurately delineated areas of natural vegetation and agricultural production by crop type; the results showed 95% accuracy in mapping.

A study by Brazilian and Swiss researchers predicts that even in an optimistic greenhouse gas emissions scenario, 99% of the area of the Upper Paraguay River Basin will be lost.

Foundation launches new program to promote the creation of international research centers (CIPs) in universities and institutes in São Paulo.
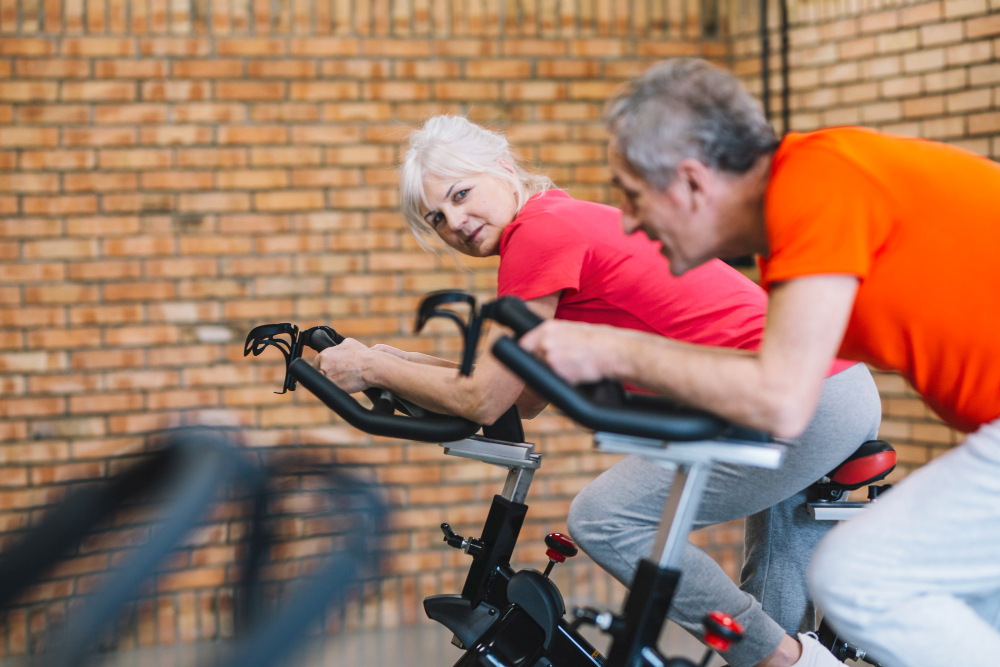

This is the conclusion of a study conducted at the University of São Paulo with 23 volunteers. The data show that only evening workouts regulated so-called baroreflex sensitivity – a mechanism that compensates for sudden changes in blood pressure.
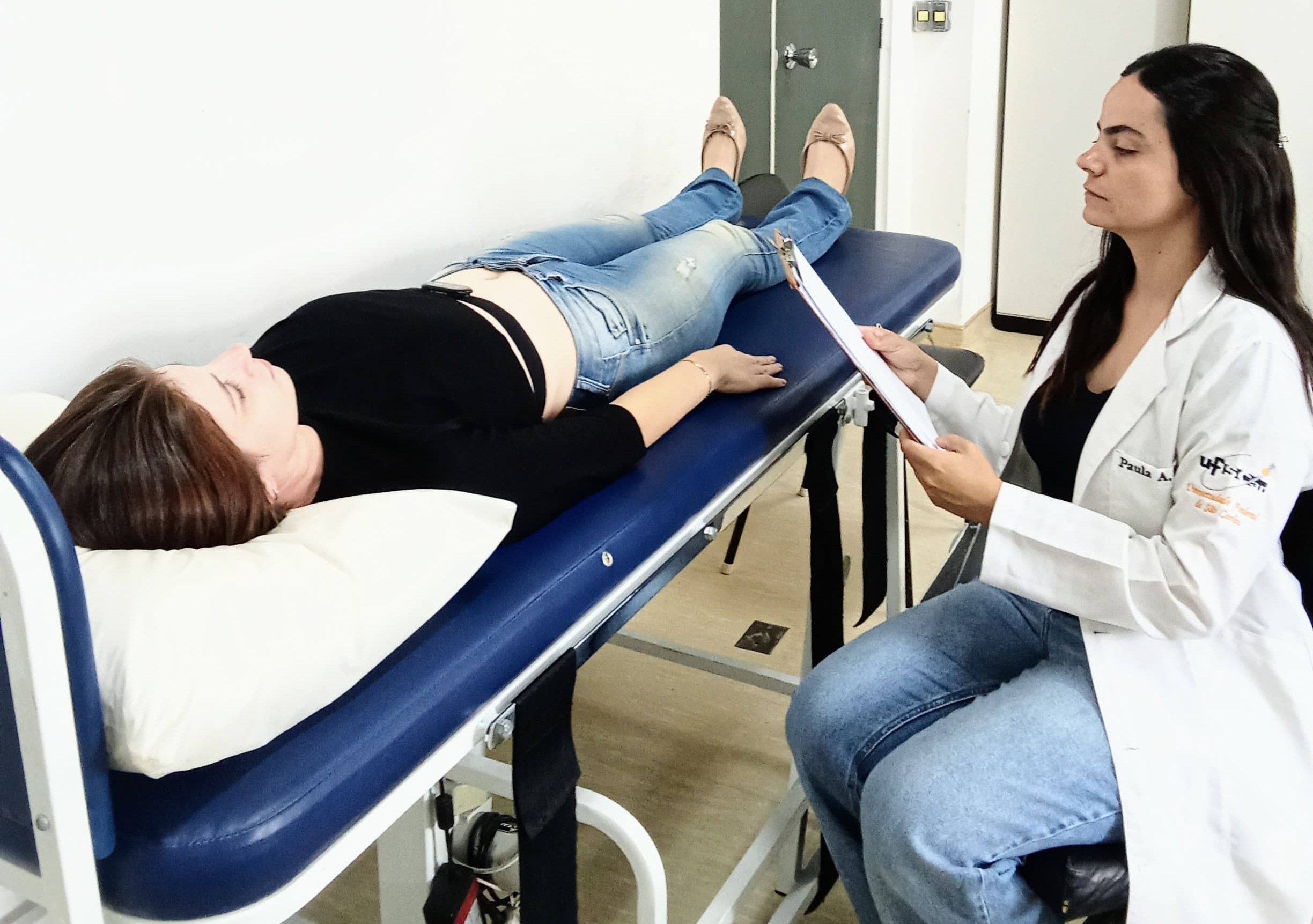
In a study of 130 volunteers conducted at the Federal University of São Carlos, a drastic decrease in heart rate variability, i.e. the heart’s ability to adapt to environmental and physiological demands, was observed – up to six weeks after infection.

Tool developed by startup with support from FAPESP works like a supermarket in the metaverse.

Practical guide prepared by researchers from the University of São Paulo gets extended version, accessible for free on the Internet.
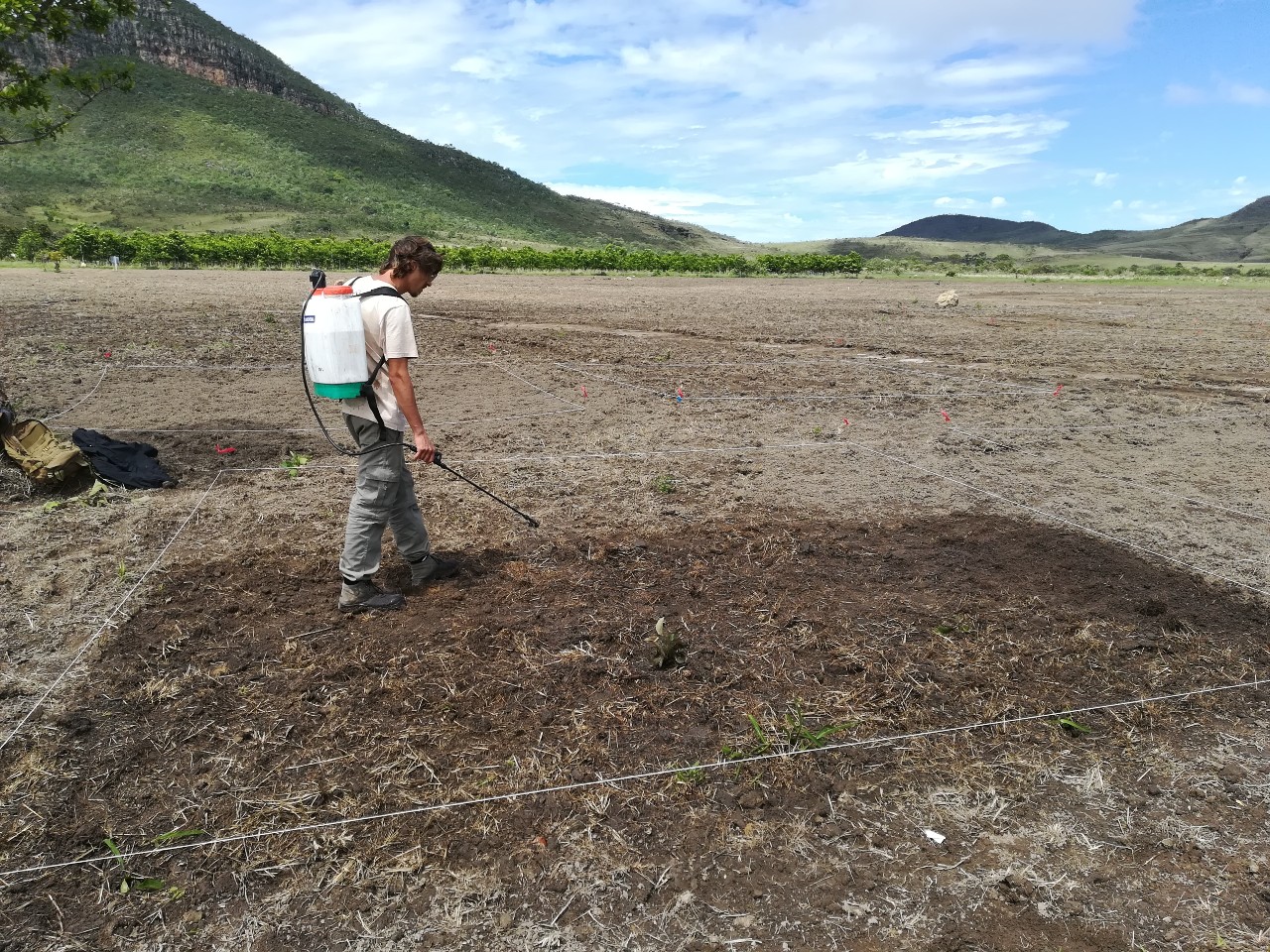

Application of iron sulfate in a degraded area of the Chapada dos Veadeiros National Park, in central Brazil, reduced nutrient availability and contained exotic species, allowing grasses typical of the Cerrado biome, adapted to poor soils, to regrow.
In rodent experiments, a cellulose product with silver nanoparticles was able to reduce microbial colonies in skin lesions, speeding up healing; treatment could benefit people with diabetic foot, burns, and bedridden patients with pressure ulcers.