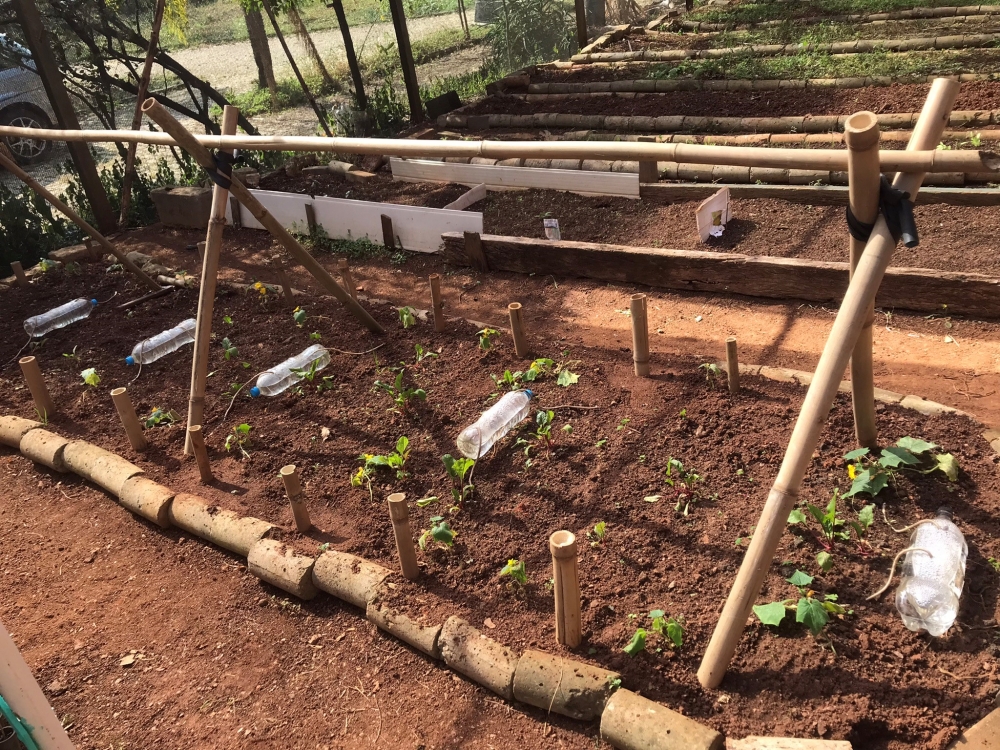



With the support of FAPESP, Santa Food Tech has developed a model to transform urban areas into laboratories of sustainability; the initiative is already implemented in four micro-regions of the state capital and in Guarulhos.
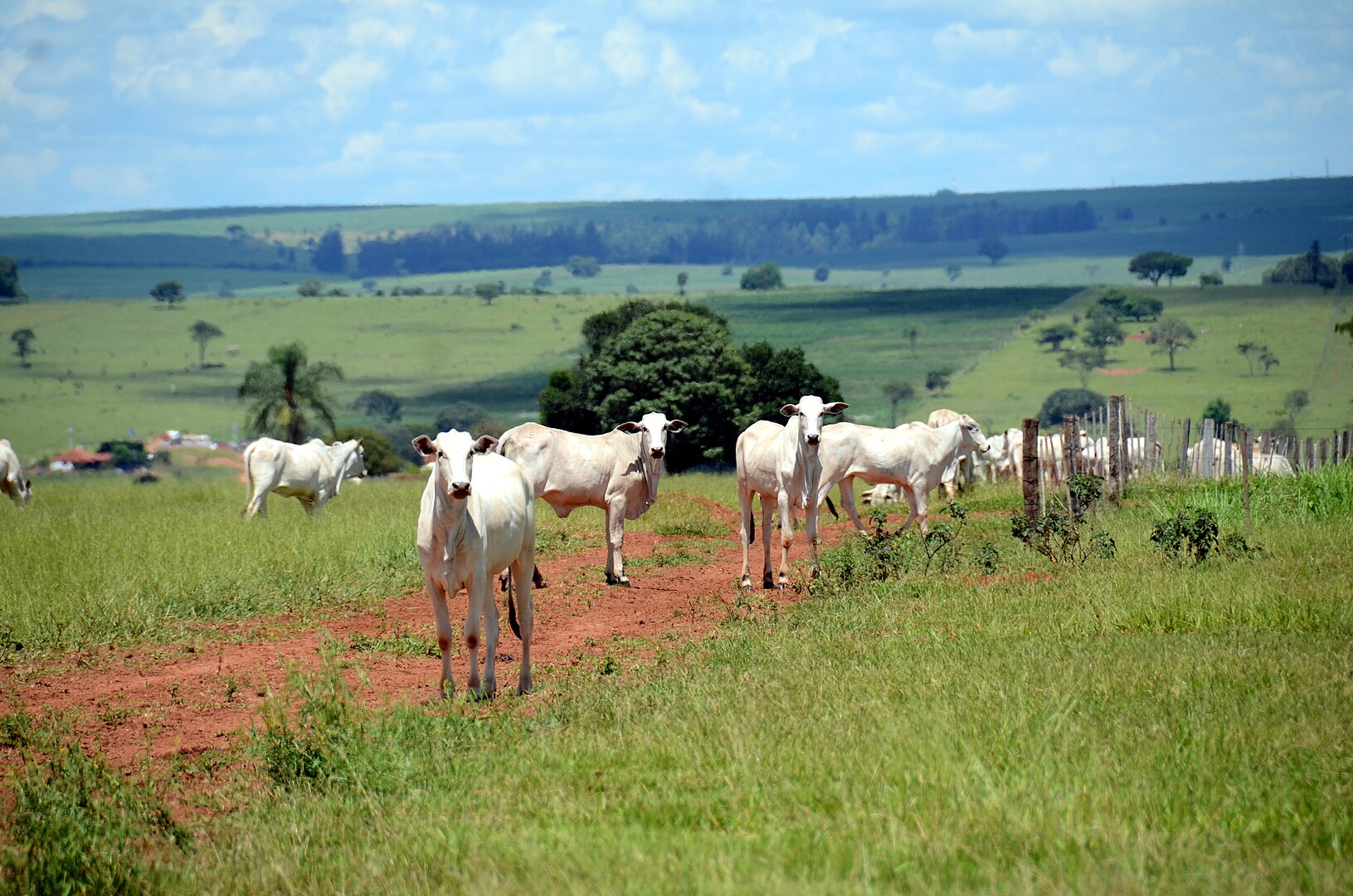

In an article published in Environmental Science and Pollution Research, researchers from the Federal University of São Paulo discuss the need for the production chain to adopt emission reduction practices.
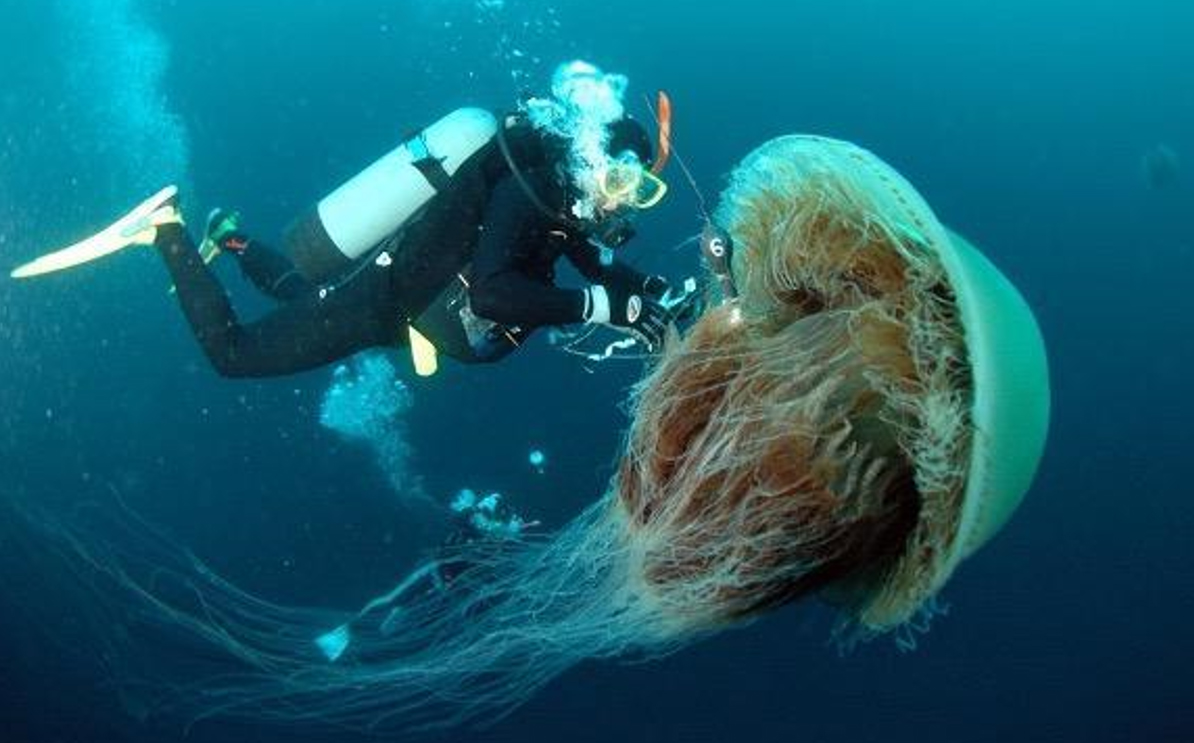

Among the 36 authors, André Morandini, director of the Center for Marine Biology of the University of São Paulo, presents the results of studies supported by FAPESP.
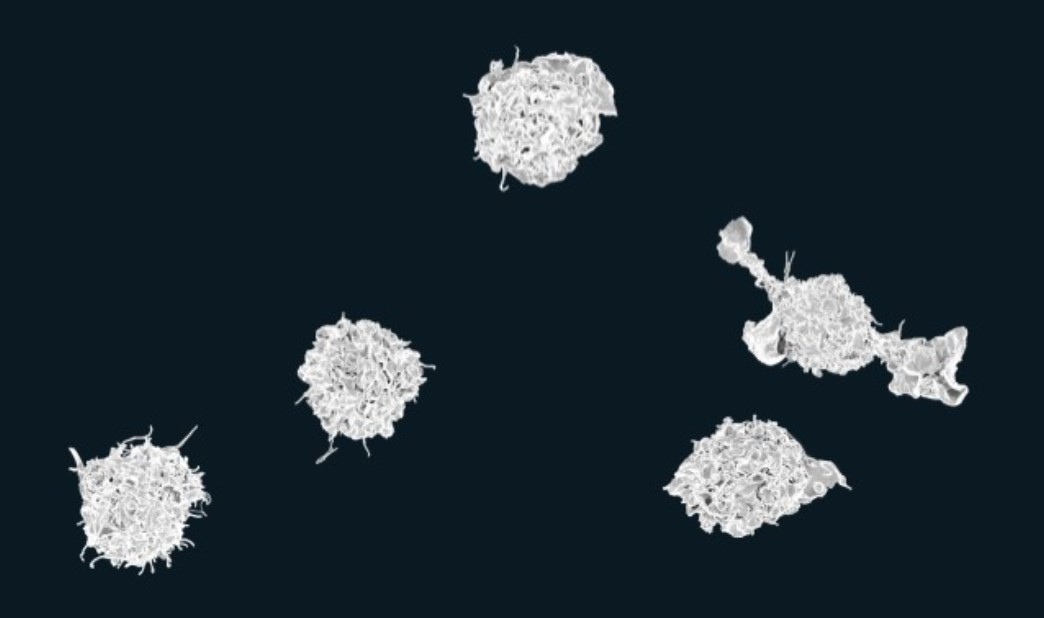
Through experiments with mice, scientists from the State University of Campinas have shown that physical activity induces immune cells involved in the inflammatory process to acquire an anti-inflammatory profile. The finding opens the way to new therapeutic approaches.

A study conducted at the Federal University of São Paulo compared the performance of people diagnosed with primary progressive aphasia and healthy individuals, identifying the main tasks that can signal the presence of the syndrome.

Analysis of the gut microbiota of more than 700 babies also showed that breastfeeding was a protective factor, mitigating the problem in those who consumed industrialized products. The study underscores the importance of breastfeeding and avoiding foods high in sugar, saturated fat, salt and chemical additives.

The samples were taken from the bottom of a lake in the Ipiranga Fountains State Park. The analysis showed a strong correlation between industrialization, population growth and increased concentrations of pollutants.

System integrated into a backpack is equipped with a camera and tactile signals that vibrate to warn of the presence of objects above the waist.

With the support of FAPESP, the CCDEP should incorporate new computational methodologies to improve the production of essential information in the state of São Paulo.

The center is a research unit dedicated to exploring and developing advanced data science and artificial intelligence solutions with a focus on improving the efficiency, innovation and competitiveness of industries.

The Governor of the state of São Paulo visited the site to learn about the FAPESP-supported pilot project, which is a global pioneer and could boost sustainable energy in Brazil.

Coordinators of the FAPESP Program for the South Atlantic and Antarctica begin mapping São Paulo’s ocean science at an event in Santos.

In an article in Nature Sustainability, researchers from Brazil and the United States point out the advantages of fish farming over livestock farming, but warn of the need for stricter environmental regulations to prevent the activity from becoming an additional pressure on the biome.

The most robust estimate ever made in the biome shows that hunting, predation by domestic dogs, livestock diseases and competition with wild boars are among the main anthropogenic influences. Scientists used an innovative method involving trained dogs and fecal DNA analysis.

This is the finding of a study that followed 352 pairs of newborns and their mothers in the cities of Guarulhos and São Paulo (Brazil). Changes observed in the first two months of life may increase future risk of obesity and diabetes.

A group of scientists supported by FAPESP is studying a new strain of bacteria in consortium with rhizobia, microorganisms that biologically fix nitrogen, an essential nutrient for crops.
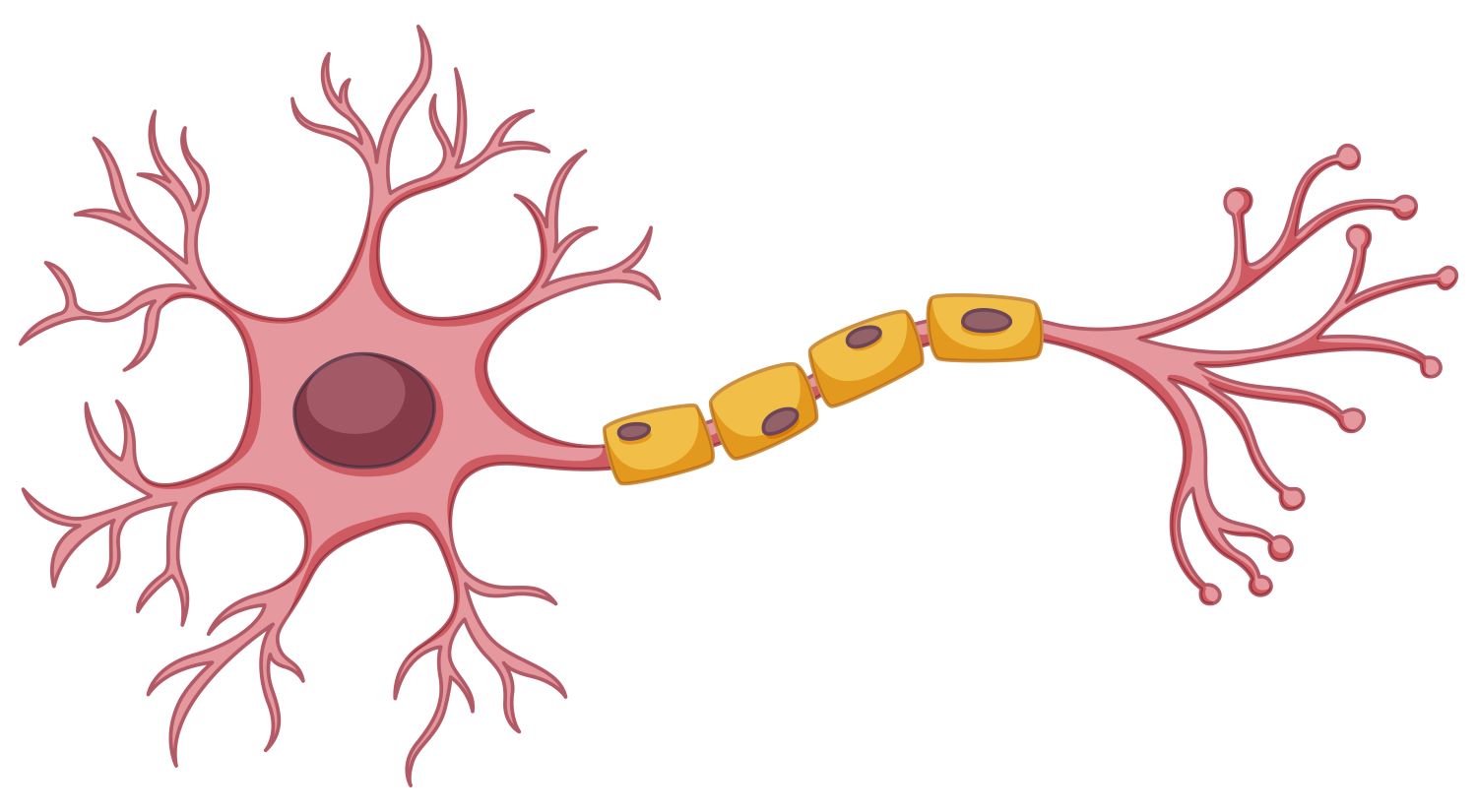
The rodent experiment, conducted at the State University of Campinas, highlighted the involvement of the hnRNP A1 molecule in maintaining the integrity of the myelin sheath – a fatty layer that protects neurons and facilitates communication between them. The findings pave the way for potential therapies.

The topic was discussed during the first event of the FAPESP Conferences 2025 series, with guest speaker Ane Alencar, Director of Science at the Amazon Environmental Research Institute.

Inaugurated at a ceremony held at the University of São Paulo on March 31st, the FAPESP-funded center aims to tackle complex problems such as climate urgency, inequality and deindustrialization.
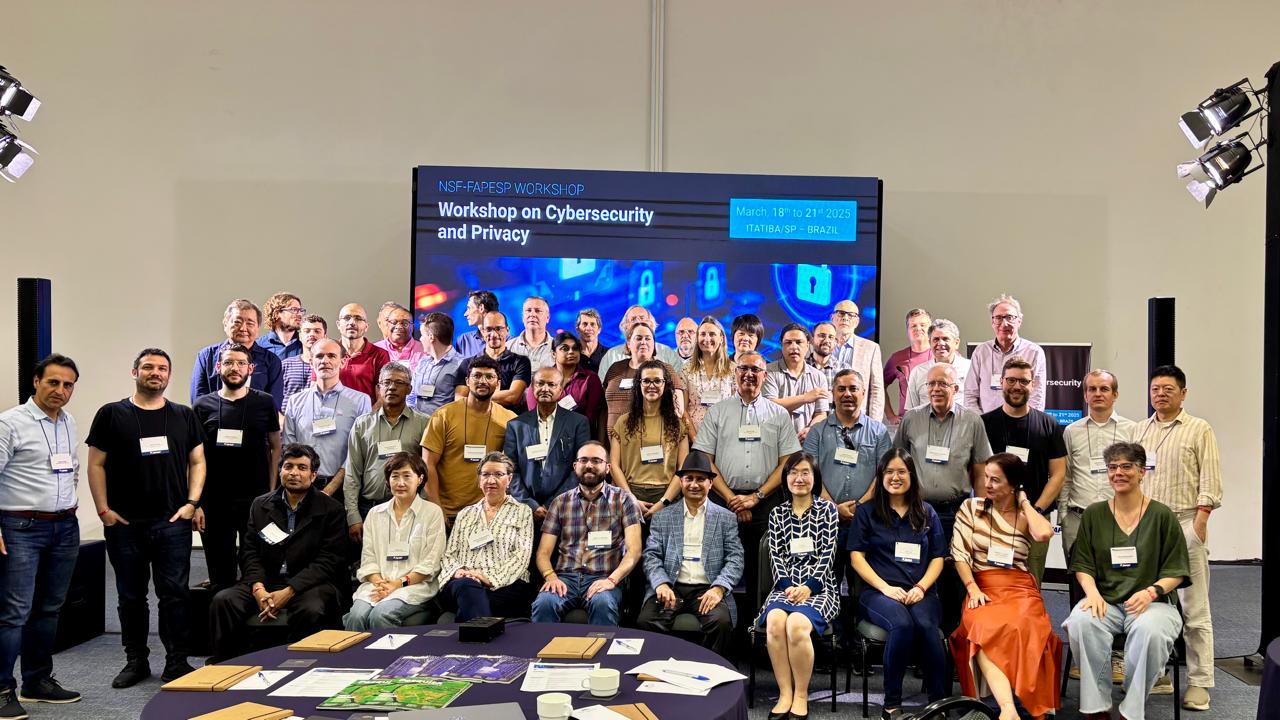

Workshop brought together Brazilian and American experts to discuss new opportunities for collaborative research in the face of increasing volumes of information, the rise of artificial intelligence, the imminent arrival of quantum computing, and the mass production of fake news.
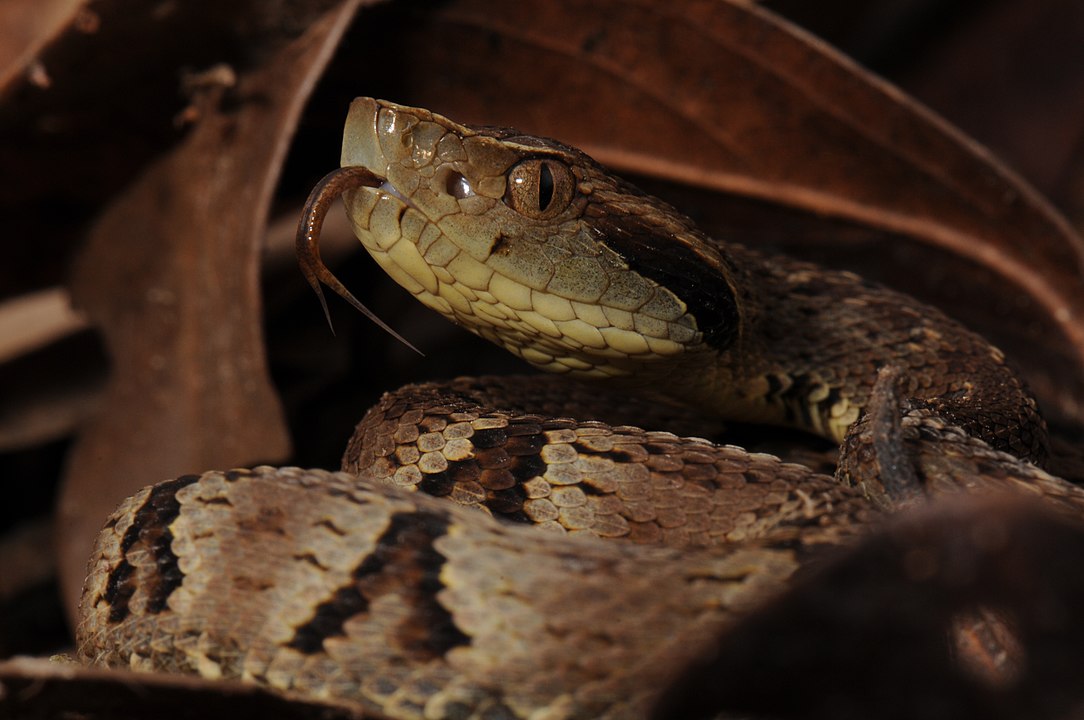

Researchers from the Federal University of São Paulo and the Butantan Institute are working on an improved version of the antibothropic serum, with more neutralizing antibodies and fewer proteins associated with side effects.
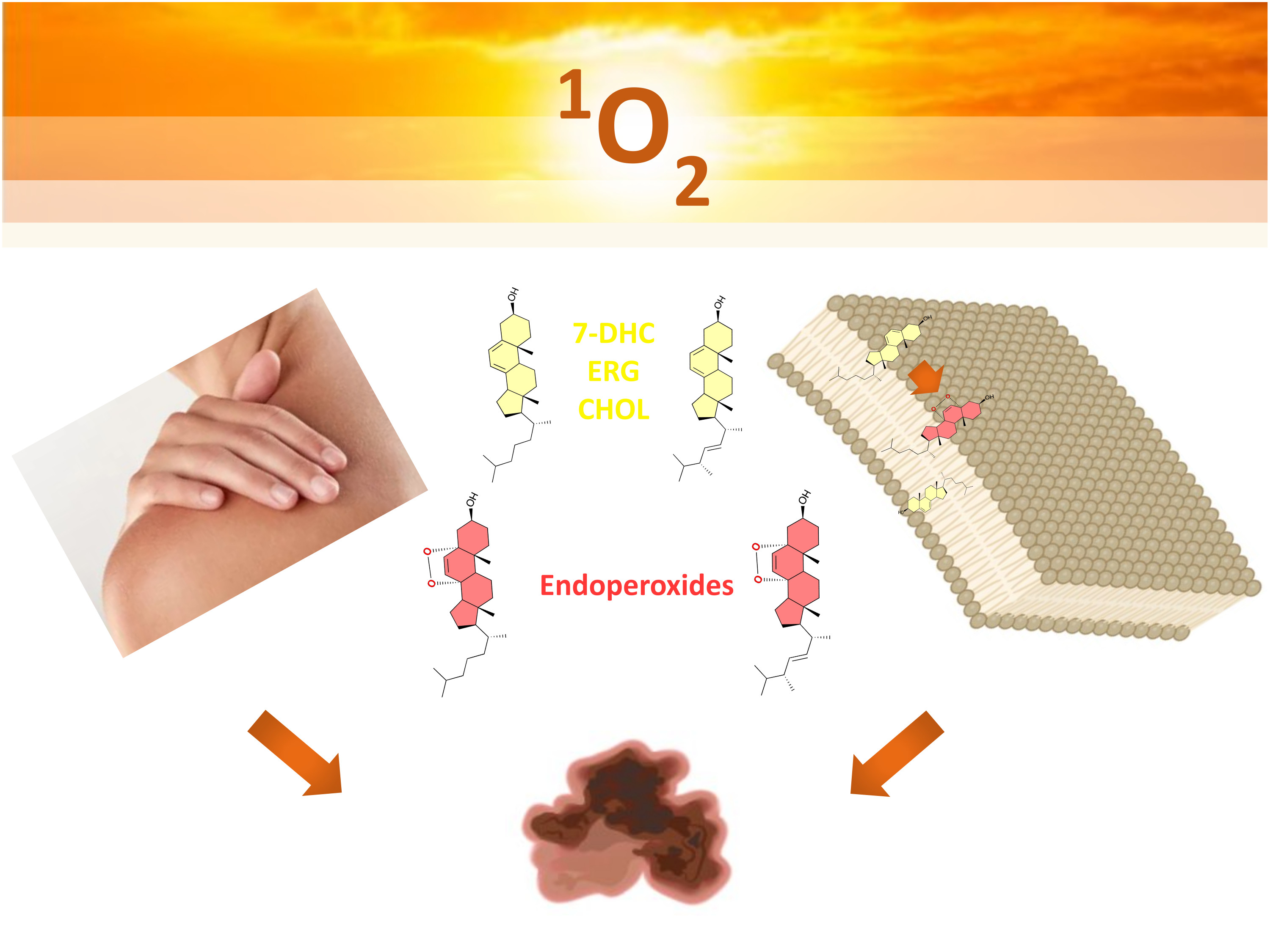
Results from a FAPESP-supported research center pave the way for expanding the use of photodynamic therapy in the fight against skin cancer.

Company developed with the support of FAPESP a process to transform by-products into high-tech materials for batteries.

While cognitive-behavioral therapy showed faster results, the effect of acceptance and commitment therapy was more lasting, shows a study conducted at the University of São Paulo with 227 volunteers.
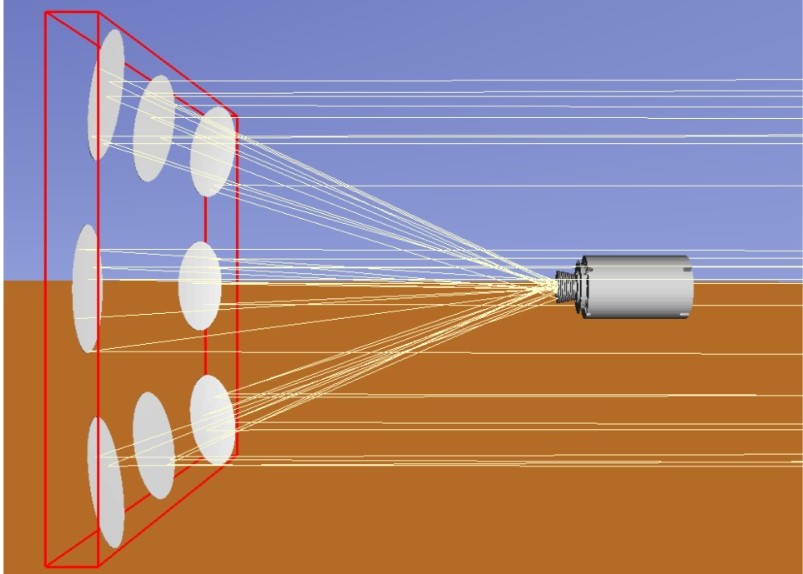
Produced at the Engineering School (POLI-USP), the equipment generates thermal radiation similar to that of the sun. It makes it possible to test devices and technologies in the laboratory without having to rely on ideal weather conditions.