

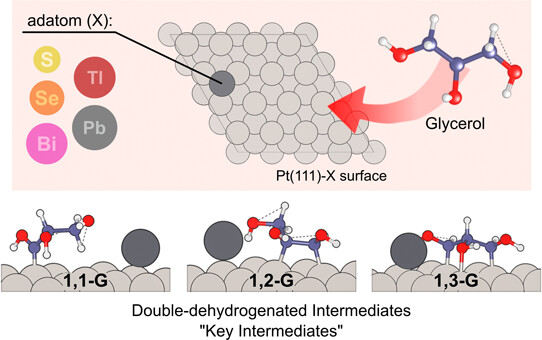
Research by the Center for the Development of Functional Materials and the State University of Campinas addresses an important process for generating energy and producing high value-added chemical products.

The assessment was made by participants in the opening session of FAPESP Week France in Toulouse.

With support from FAPESP, the São Paulo startup has developed a molecule that can stimulate the immune system to fight cancer caused by the human papillomavirus; the technology will be presented at the VivaTech fair in Paris.

Researchers affiliated with São Paulo’s universities, research institutions, companies, and science and technology-based startups participate in another edition of FAPESP Week in Toulouse and Paris.
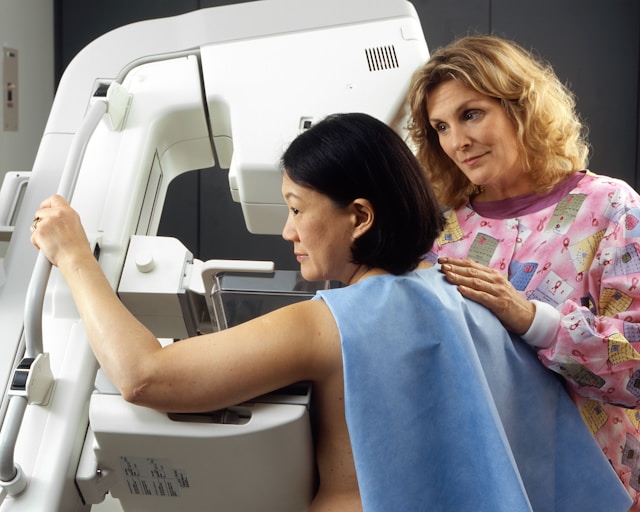

In a study conducted at São Paulo State University with 80 women over the age of 45, low-dose vitamin D supplementation nearly doubled the treatment response rate.
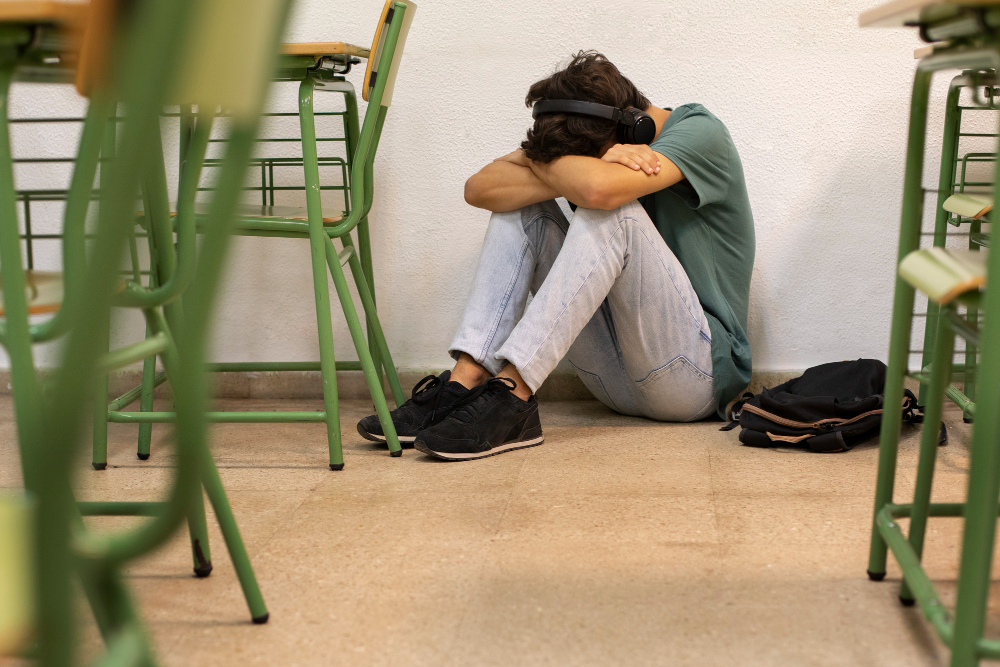

Based on individual interviews with adolescents and focus group discussions, researchers from São Paulo State University have created a classification of the coping strategies used by young people in situations of school bullying. The study also provides recommendations for educational institutions.
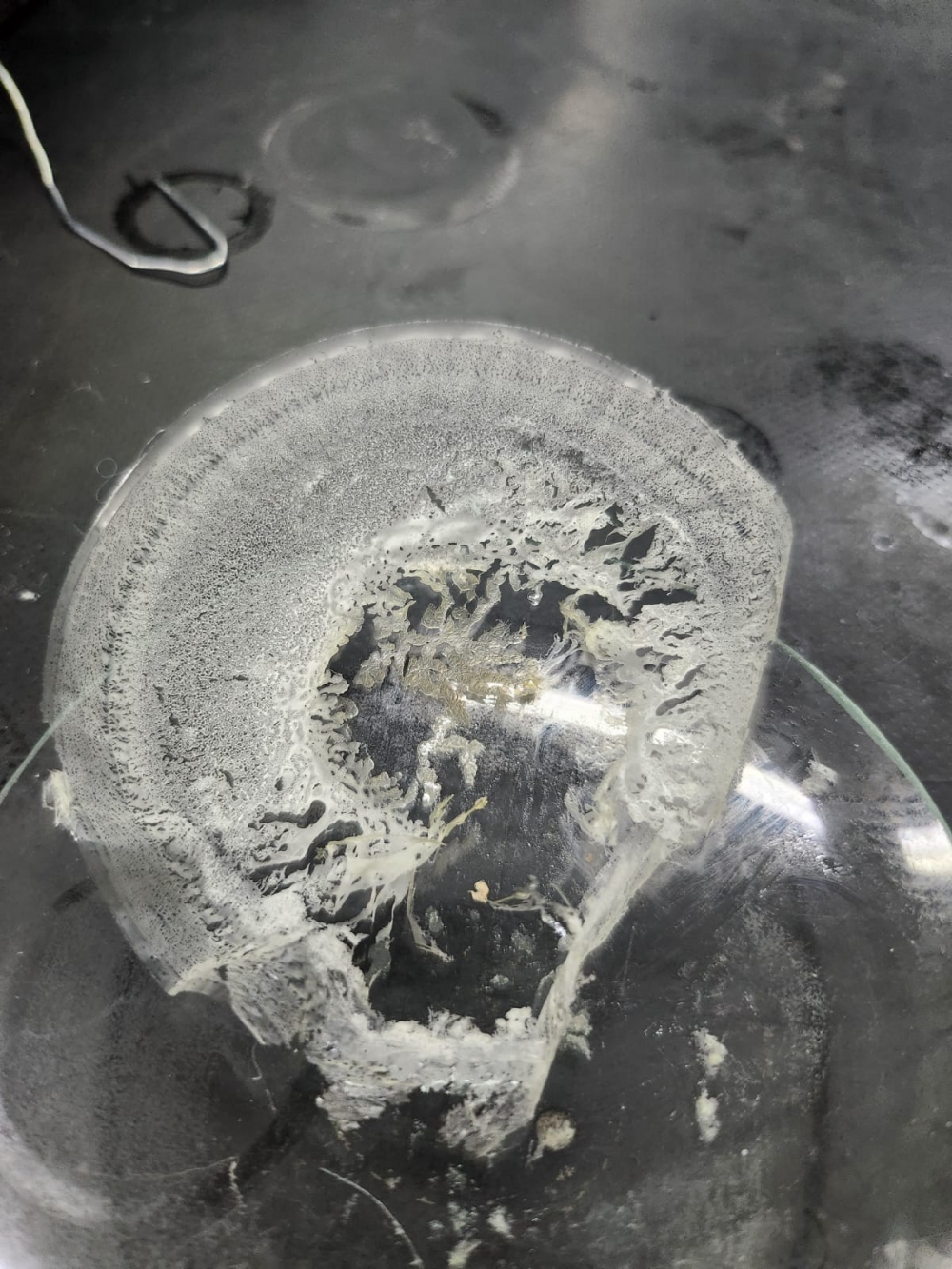

A startup supported by FAPESP has developed an alternative material using waste from the beer production process and used cooking oil.
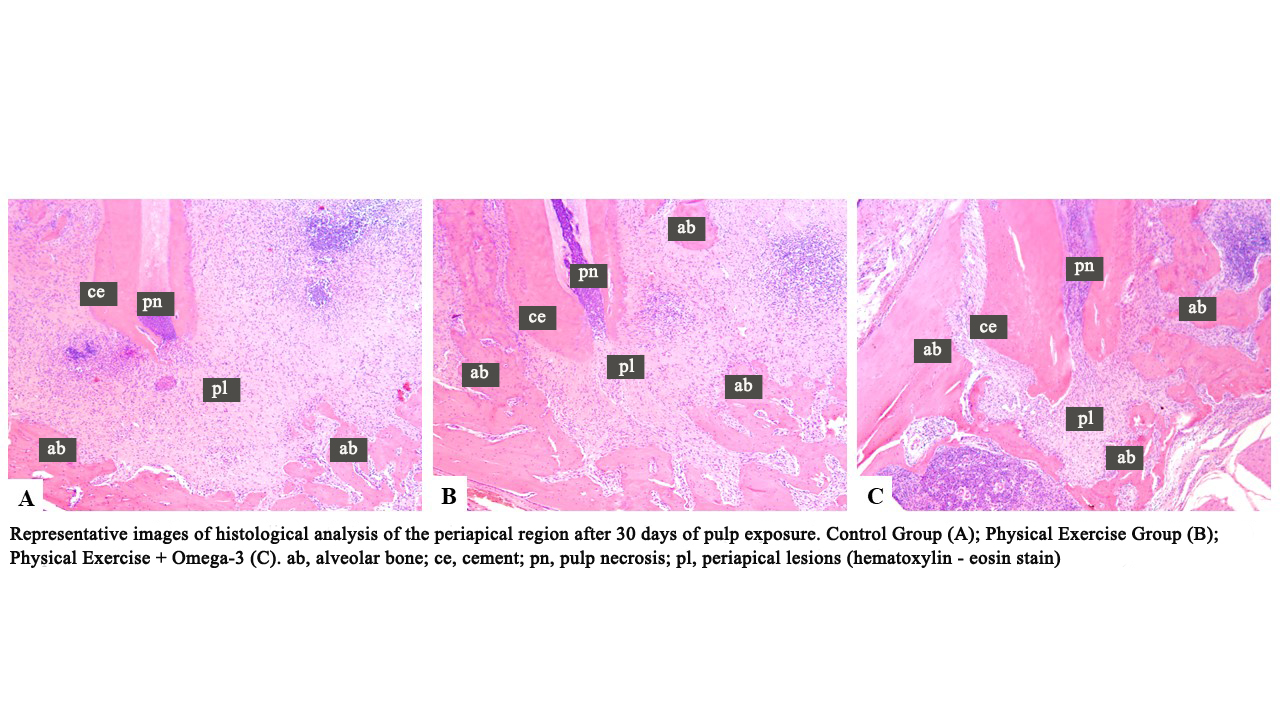
Rats that exercised and took fatty acid supplements responded better to bacteria and the inflammatory process of apical periodontitis, which can occur when caries reach the root canal and cause an infection.
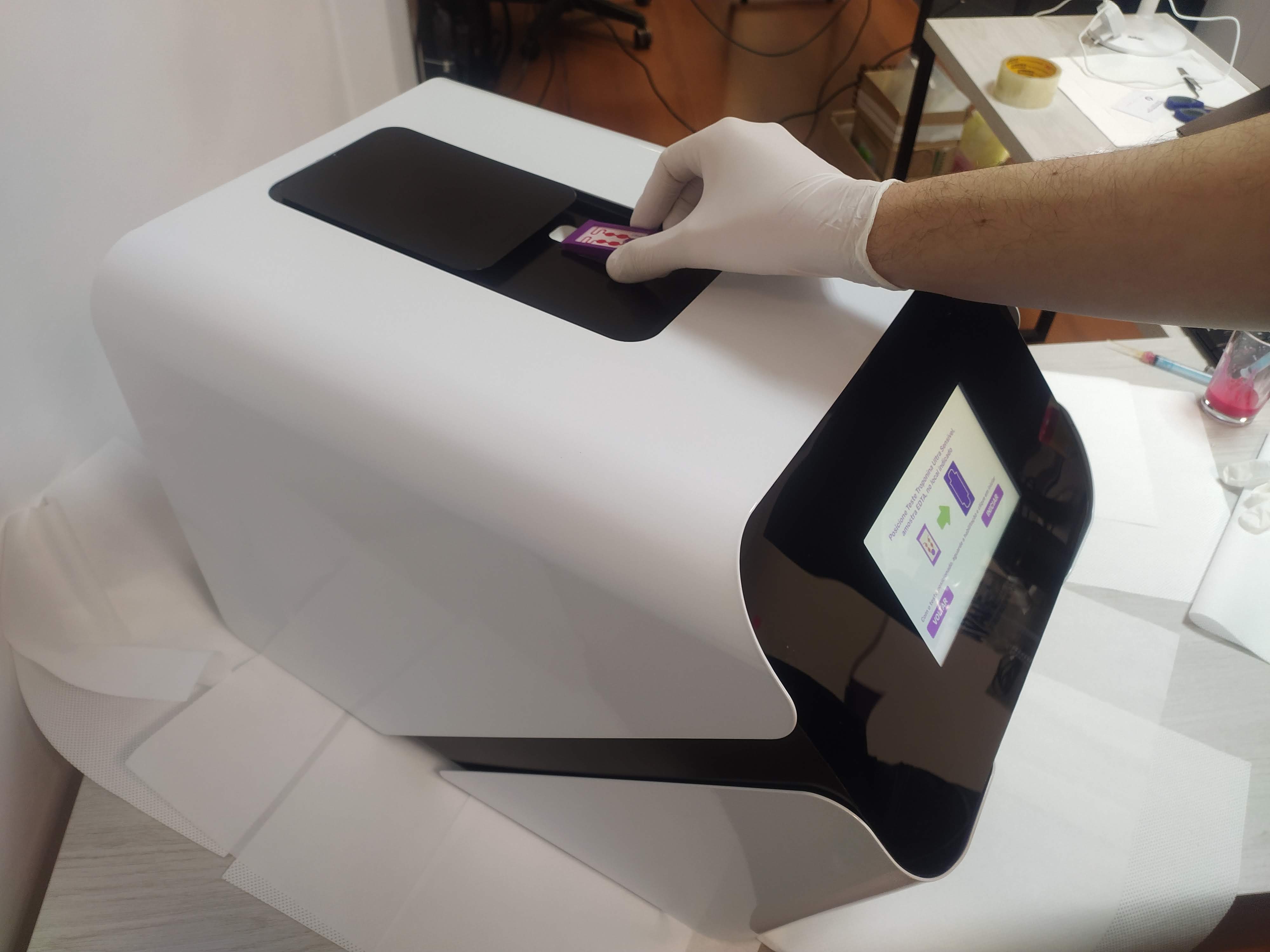

The system, developed by the FAPESP-supported startup, performs an assessment in eight minutes, drastically reducing the time needed to save lives; the technology will be presented at VivaTech in Paris.
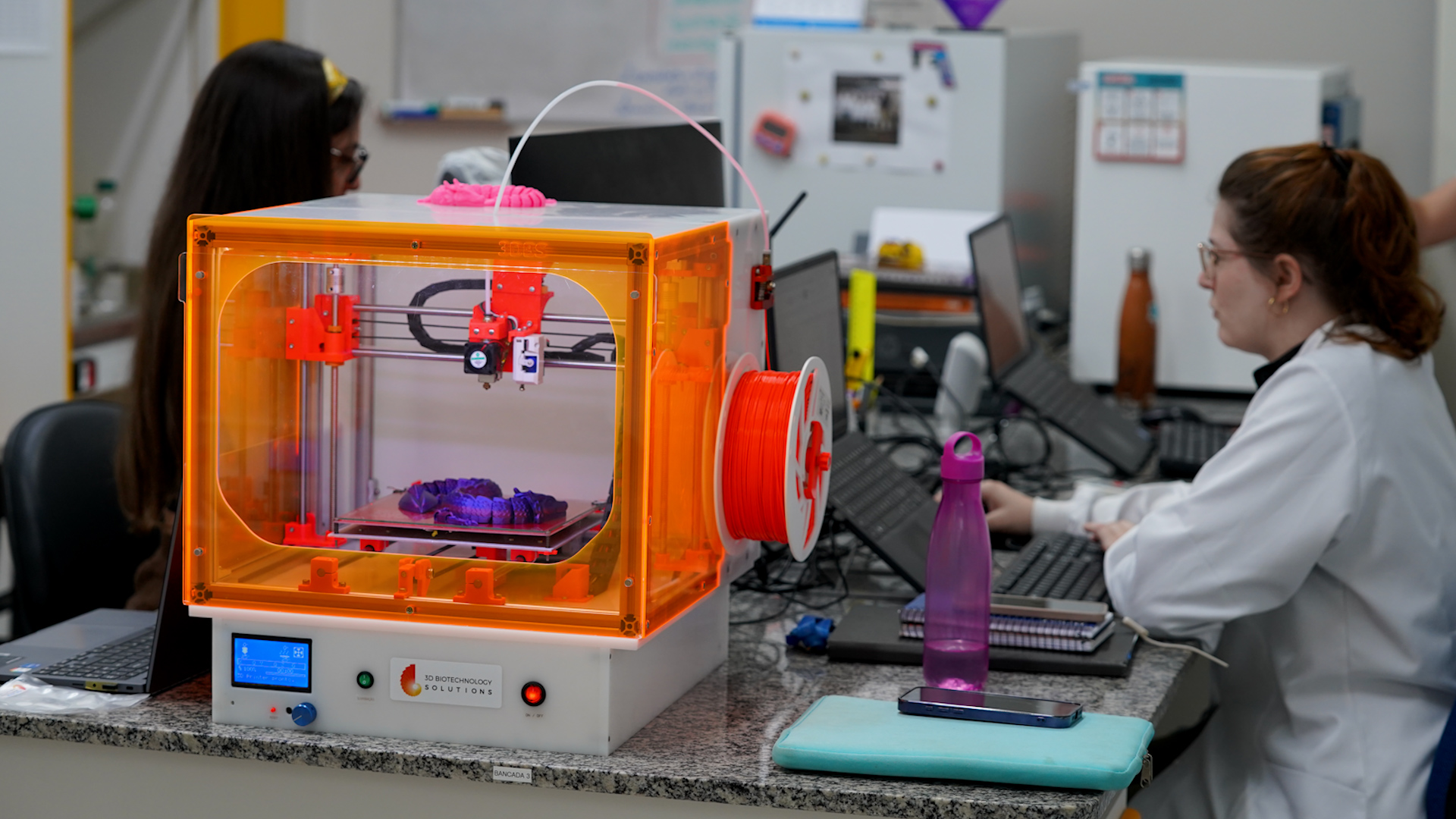

The Campinas-based startup has developed its own biofabrication and tissue engineering technologies with support from FAPESP; these solutions will be presented at Europe’s largest innovation fair in Paris.
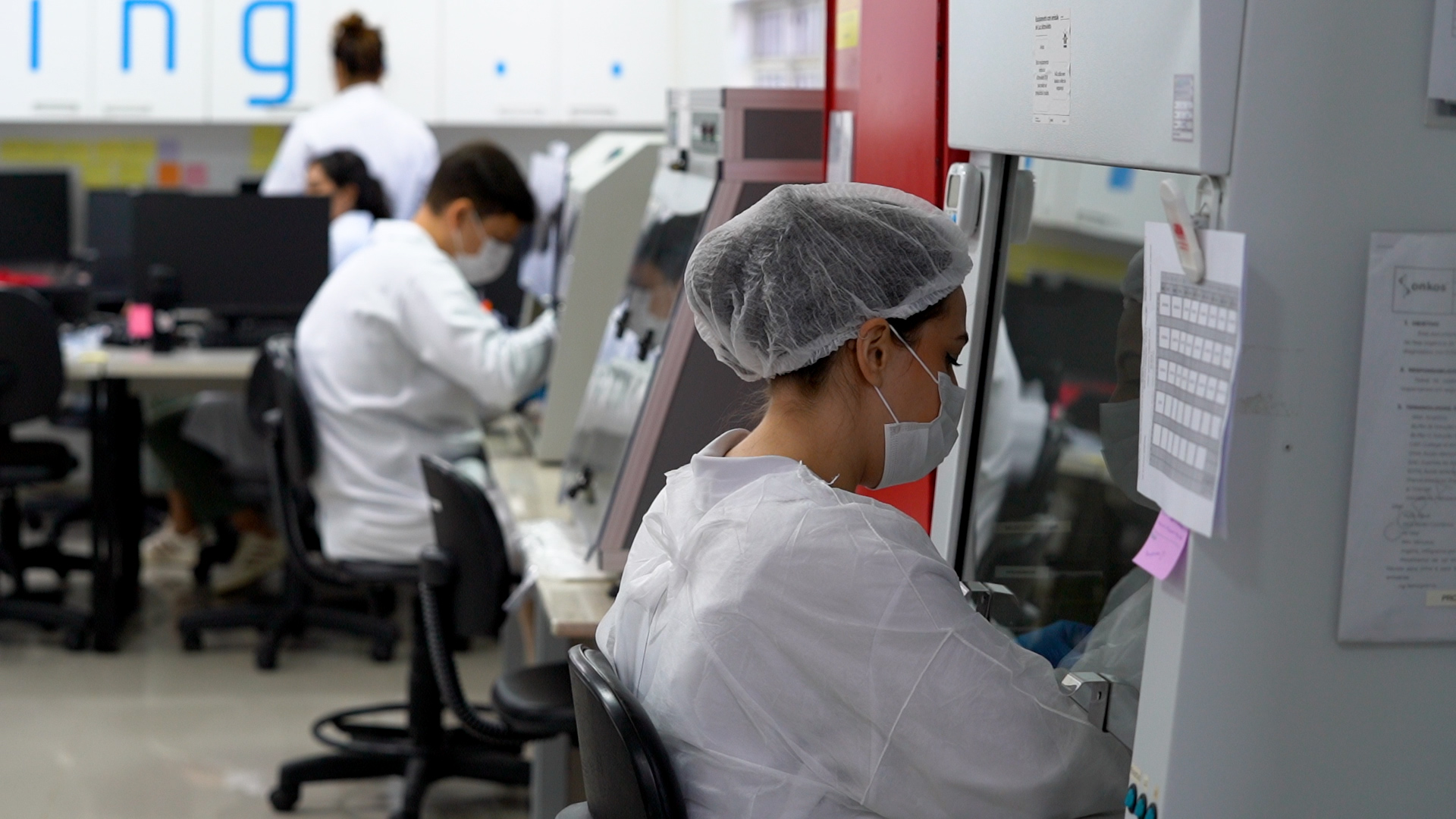

A test developed by the São Paulo state startup with support from FAPESP can distinguish benign nodules from malignant ones; the technology will be presented at one of the largest innovation events in France.

VivaTech is one of Europe's leading technology and startup events; USP and FAPESP will take researchers and disruptive technologies to the event in the areas of health, agriculture, sustainability, and artificial intelligence.

With support from FAPESP, the startup has developed a material containing human umbilical cord stem cells that speeds up the recovery of skin lesions; the technology will be presented at the VivaTech technology fair in France.
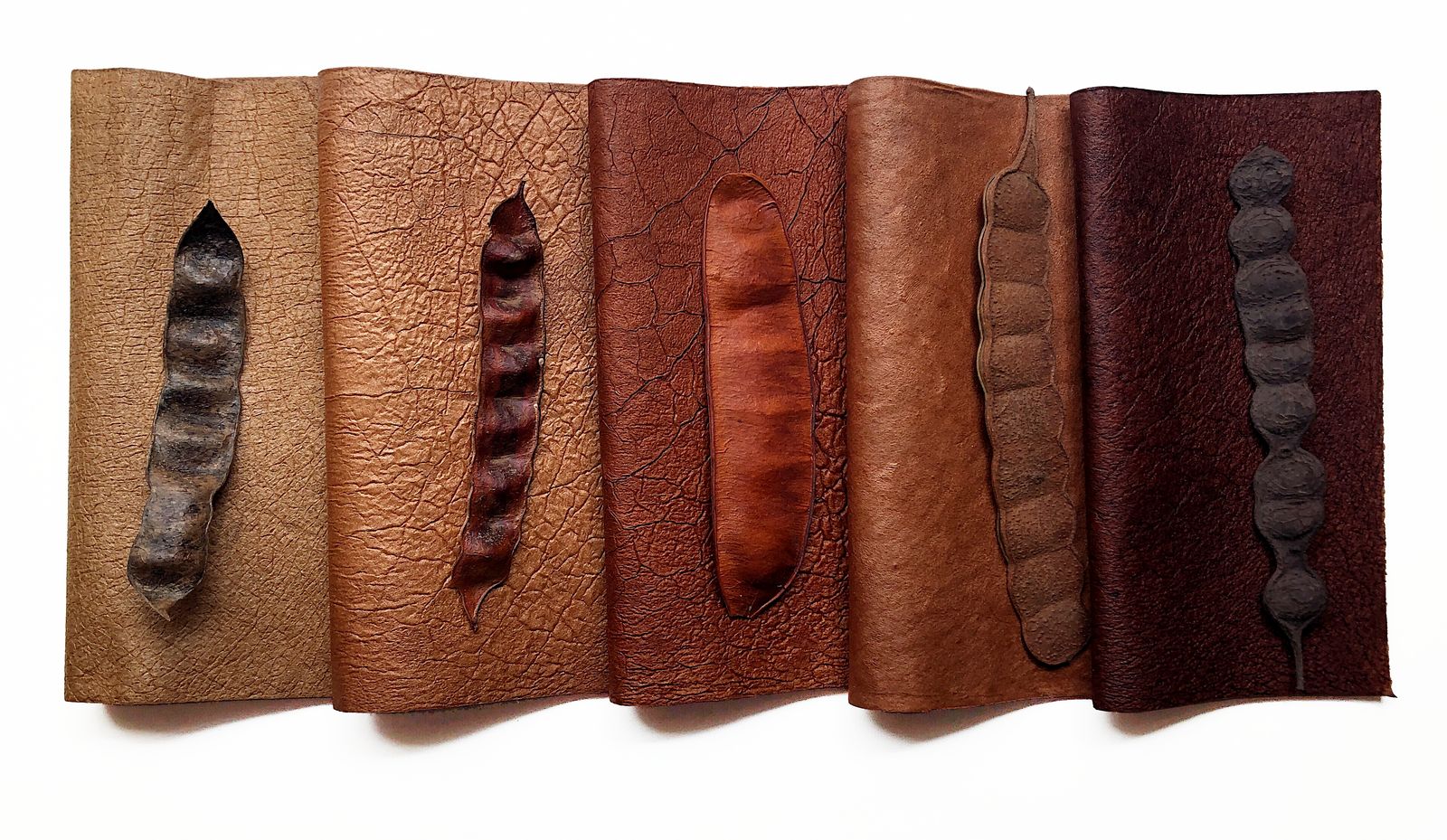

Startup supported by FAPESP develops promising sustainable solution from native flora; angico biotissue will be presented at VivaTech in France.

The FAPESP-supported company is developing critical equipment to make electric and hybrid aircraft models and eVTOLs viable; these technologies will be presented at VivaTech in France.
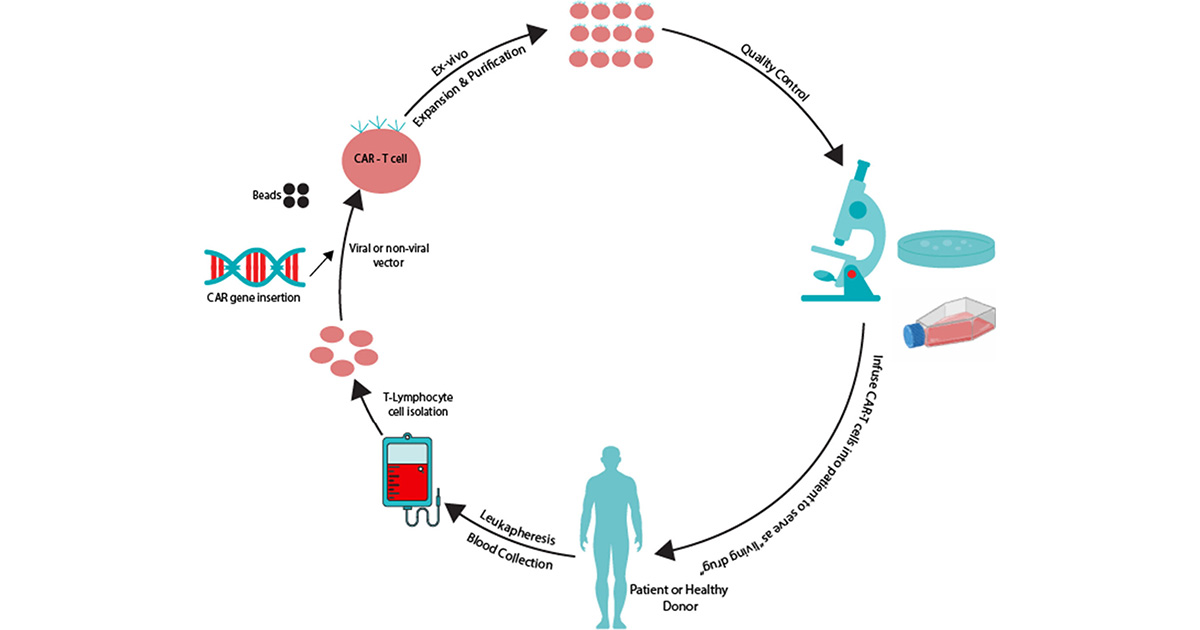
Researchers at a FAPESP-supported research center have discovered 14 proteins that could be targets for improving CAR-T cell-based therapies.
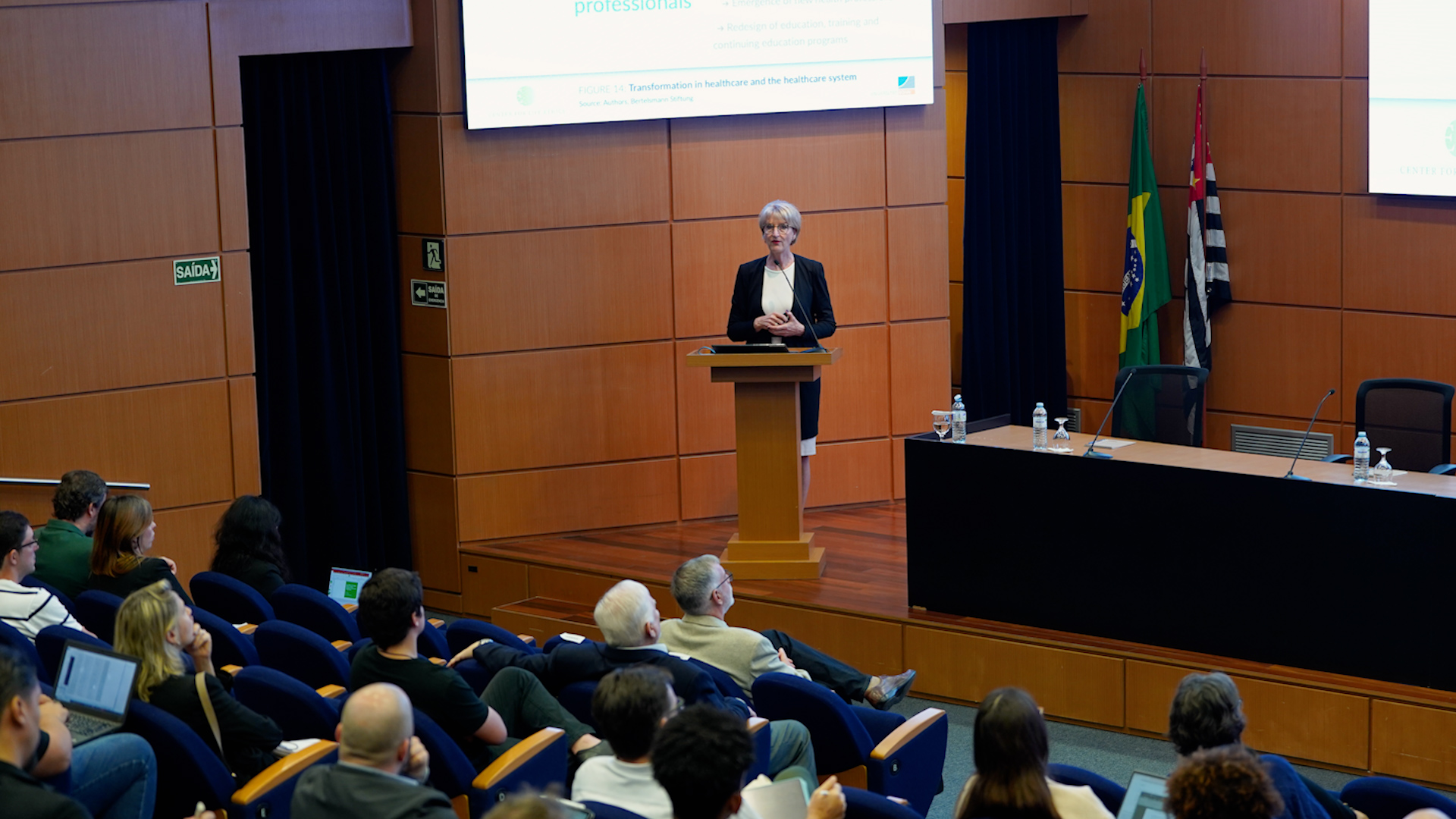

The assessment was made by researchers who participated in the 11th edition of the German-Brazilian Dialogue on Science, Research, and Innovation, held last month in the FAPESP auditorium.
Online event brought together leaders from the Foundation, the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM), and the French Embassy in Brazil, as well as researchers.

In addition to the scarcity and unequal distribution of water, quality is being strongly affected by agricultural pesticides, industrial waste, and the disposal of medicines and hygiene products.

The publication, which resulted from a project conducted at the Federal University of São Carlos, is available in Portuguese and English and has the potential to be an important, low-cost therapeutic and educational tool.
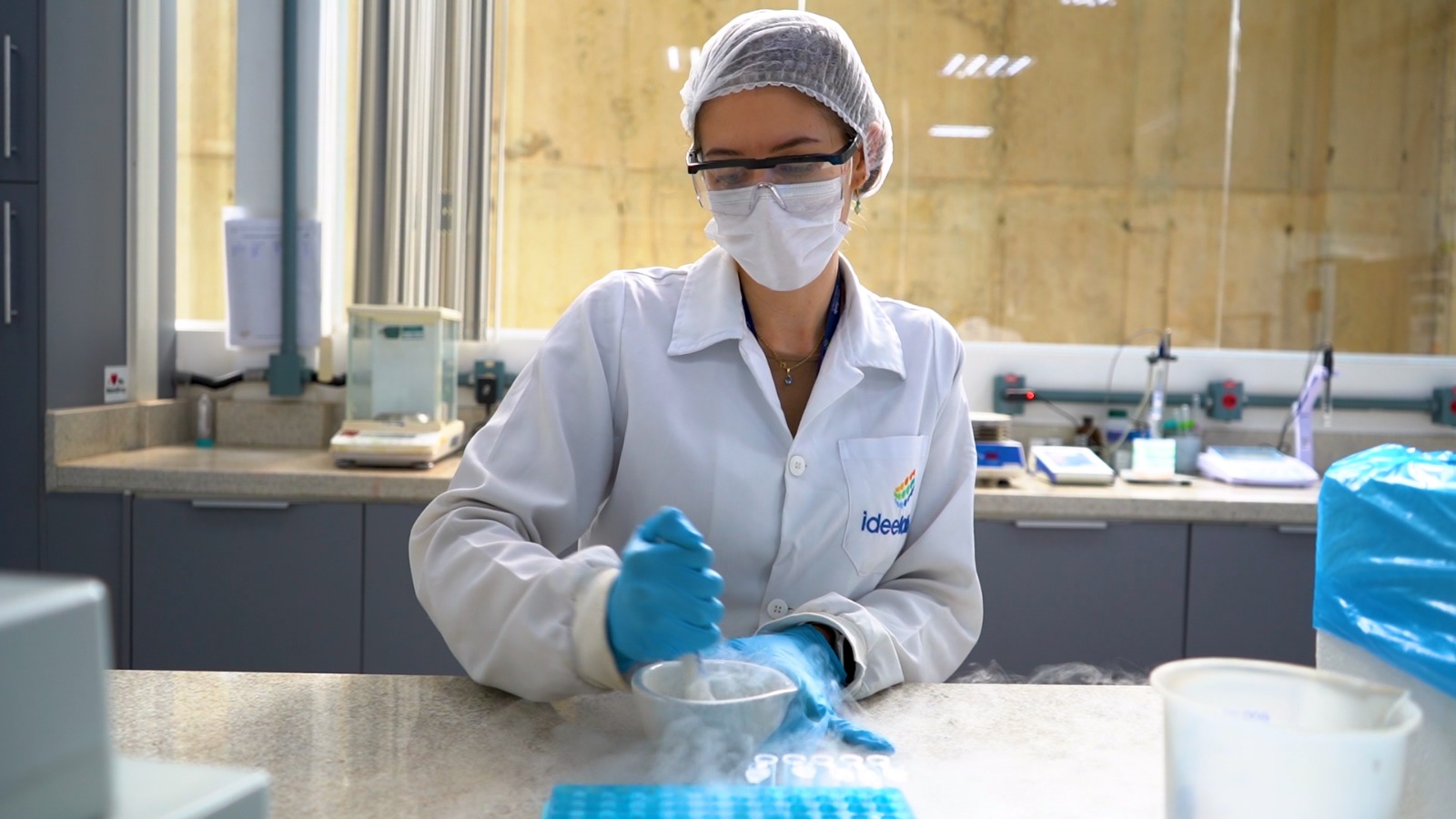

With support from FAPESP, the São Paulo startup is developing more efficient strategies to combat pathogens that threaten citrus farming; the technology will be presented at VivaTech in France.
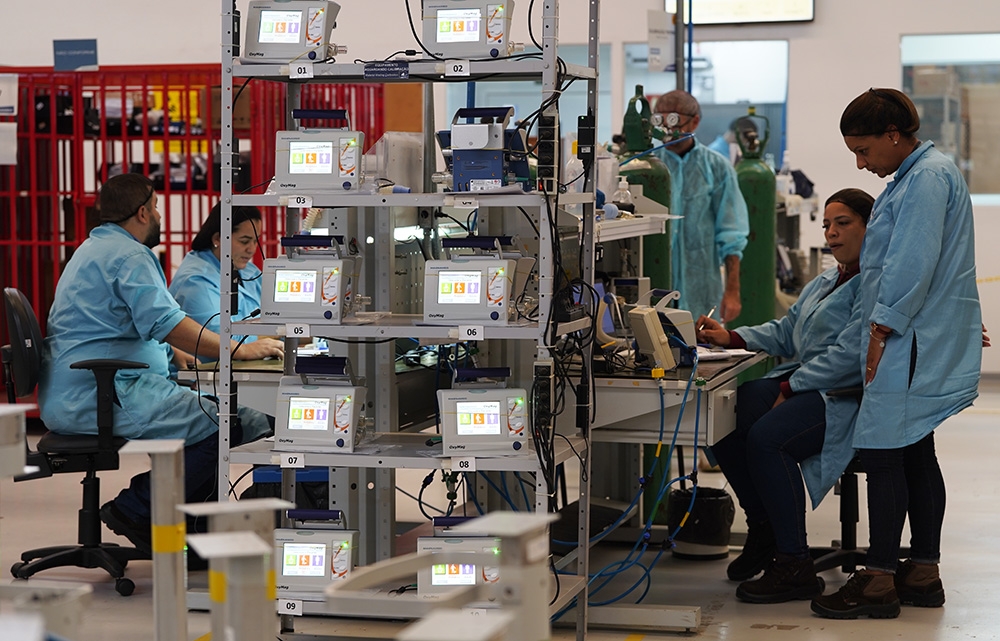

The FAPESP-supported company already exports one model and has applied for certification of two new devices in the United States.
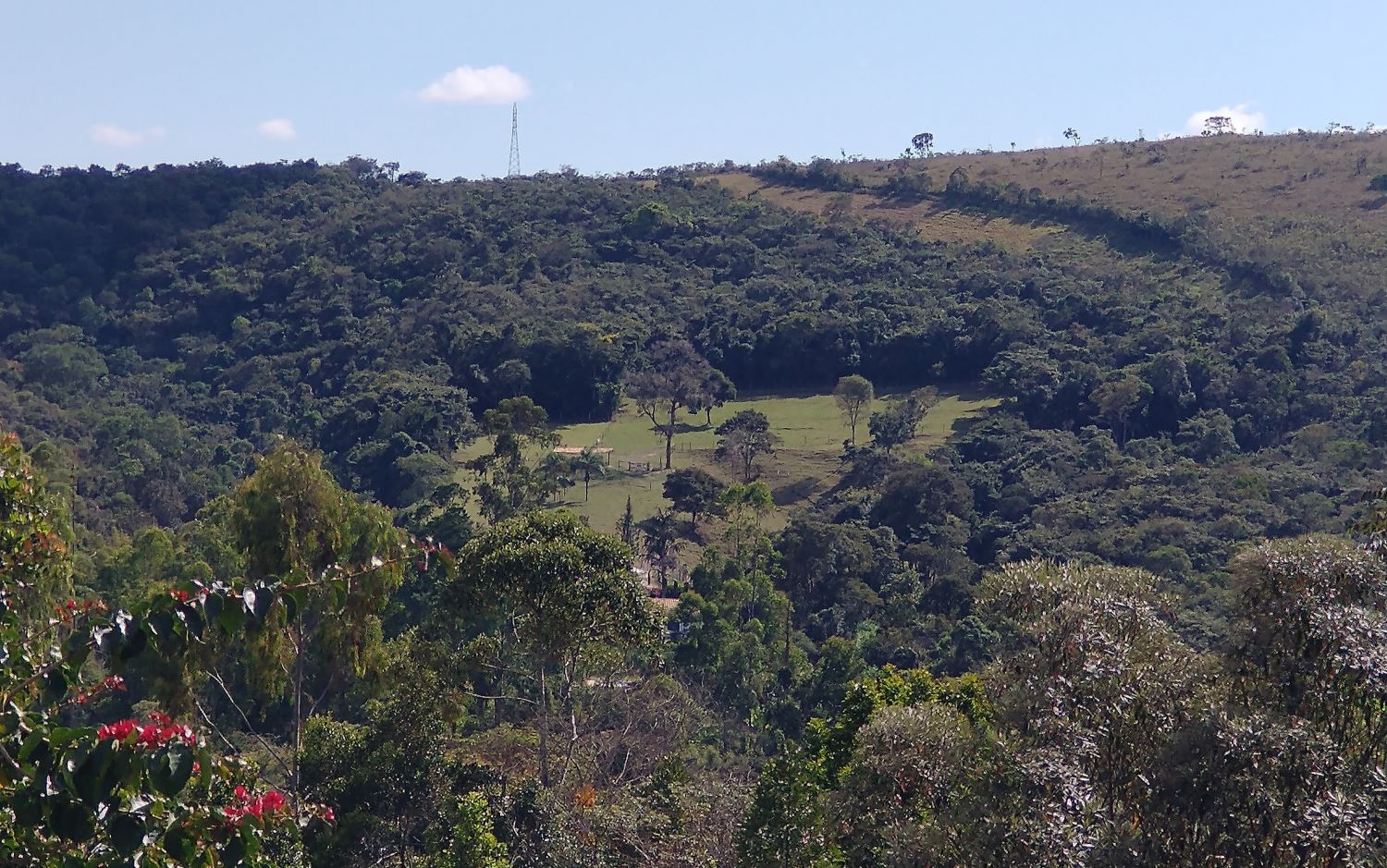

Model designed to comply with current legislation uses biodiversity, landscape, and ecosystem services data and could support public policies.
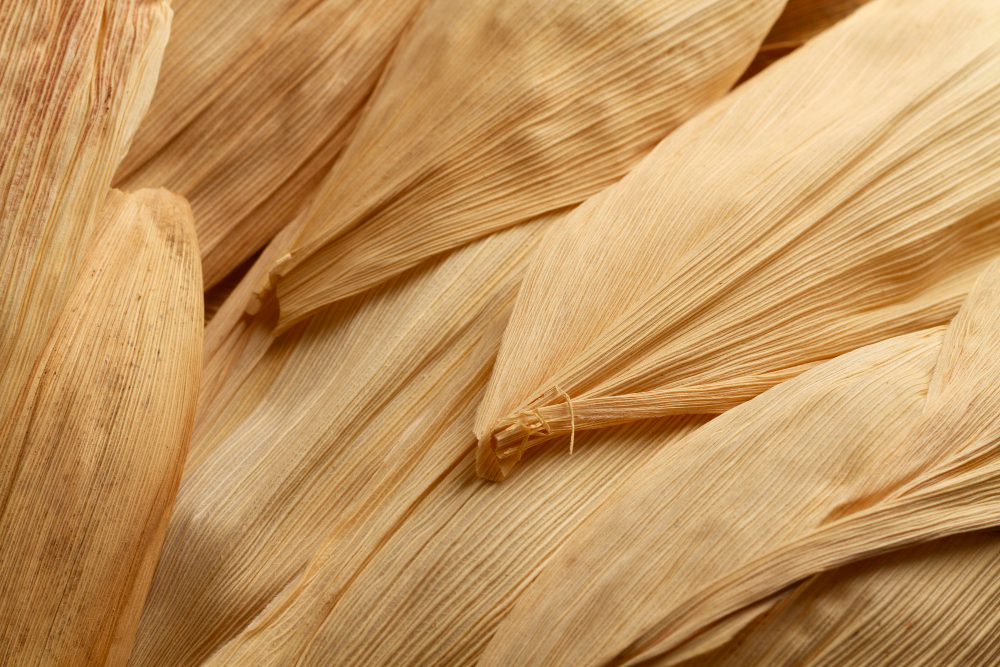

The optimized extraction of sugars, organic acids, and phenolic compounds with antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties uses only water, making it promising for applications in the biofuels, pharmaceutical, and food industries.
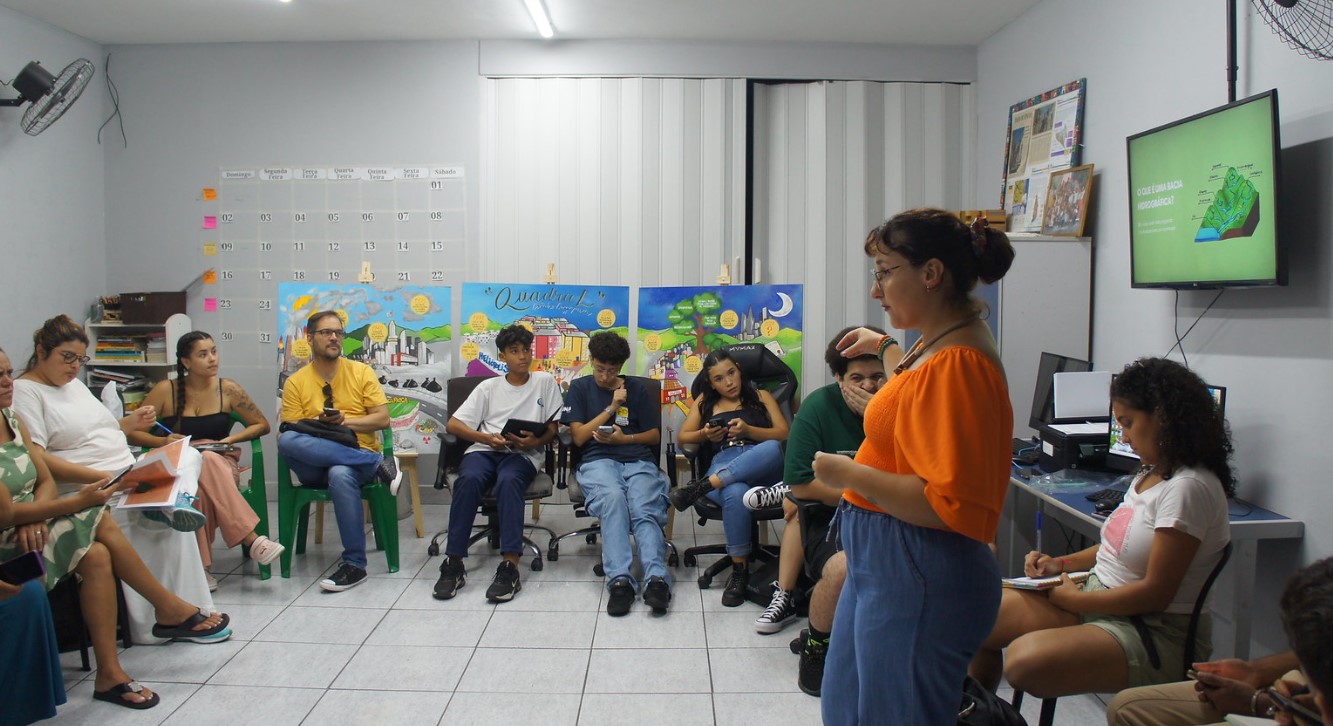

Booklet summarizes the results of a survey conducted by groups from the Center for Favela Studies and the Laboratory of Urban and Regional Studies and Projects of the Federal University of ABC; the material was presented to the community at a workshop held in February.