


Research carried out at the Carbon Neutral Cities CCD, launched by FAPESP and the Technological Research Institute, will develop and apply technologies inspired by nature to increase urban resilience and mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
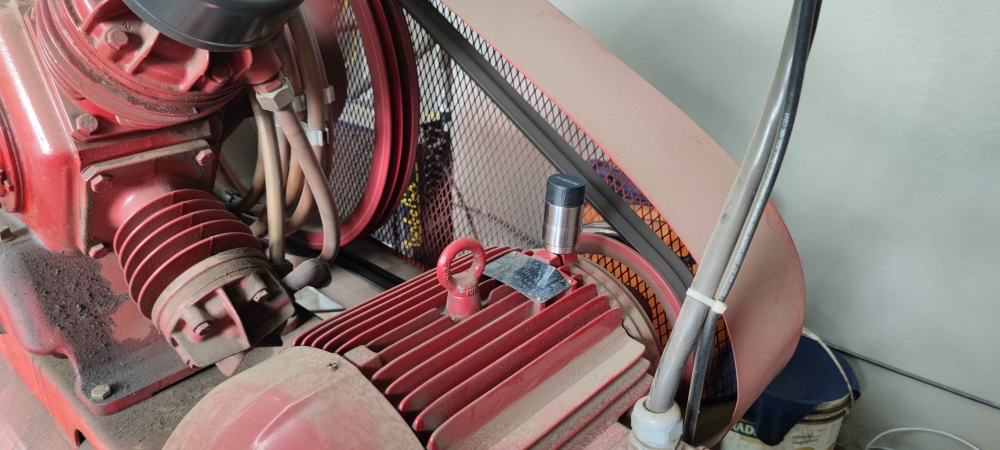

A combination of wireless sensors and artificial intelligence, developed by a FAPESP-supported company, can help companies of different sizes avoid losses due to production interruptions; the startup took part in a business mission during FAPESP Week Spain.
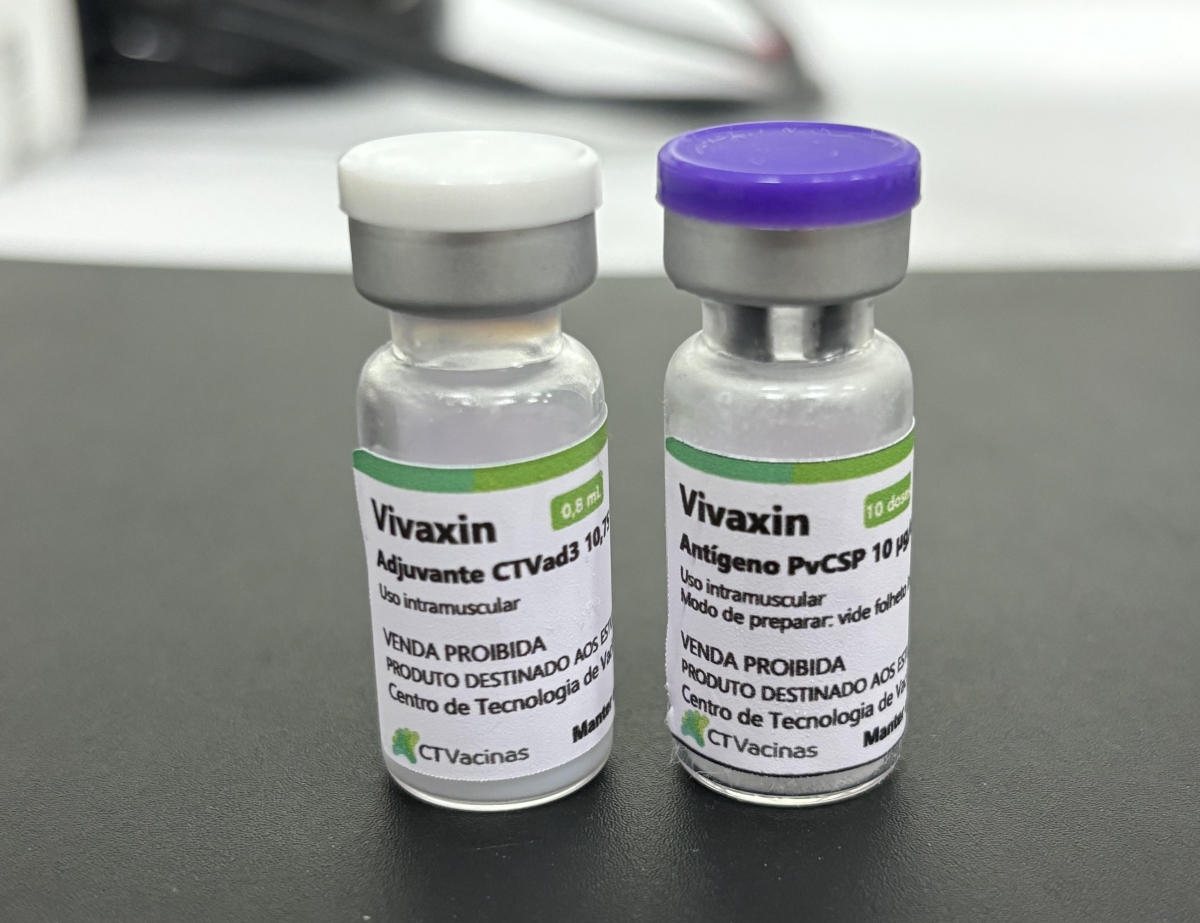
USP is developing the vaccine in partnership with the Vaccine Technology Center at the Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG). Permission to conduct a clinical trial is due before the end of this month.

In a ceremony at the University of São Paulo, which hosts the Center of Excellence in Ocean Innovation and Transformative Technologies, researchers and high officials celebrated a partnership set to foster research on ocean sustainability and fuel public policy.
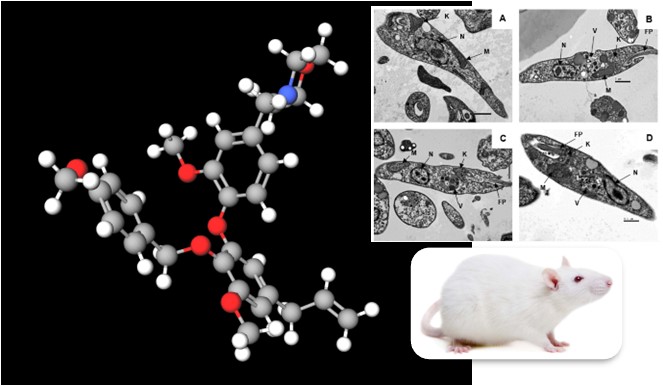
The researchers synthesized a molecule inspired by a substance present in Nectandra leucantha (canela-seca or canela-branca). Animal trials have produced promising results.
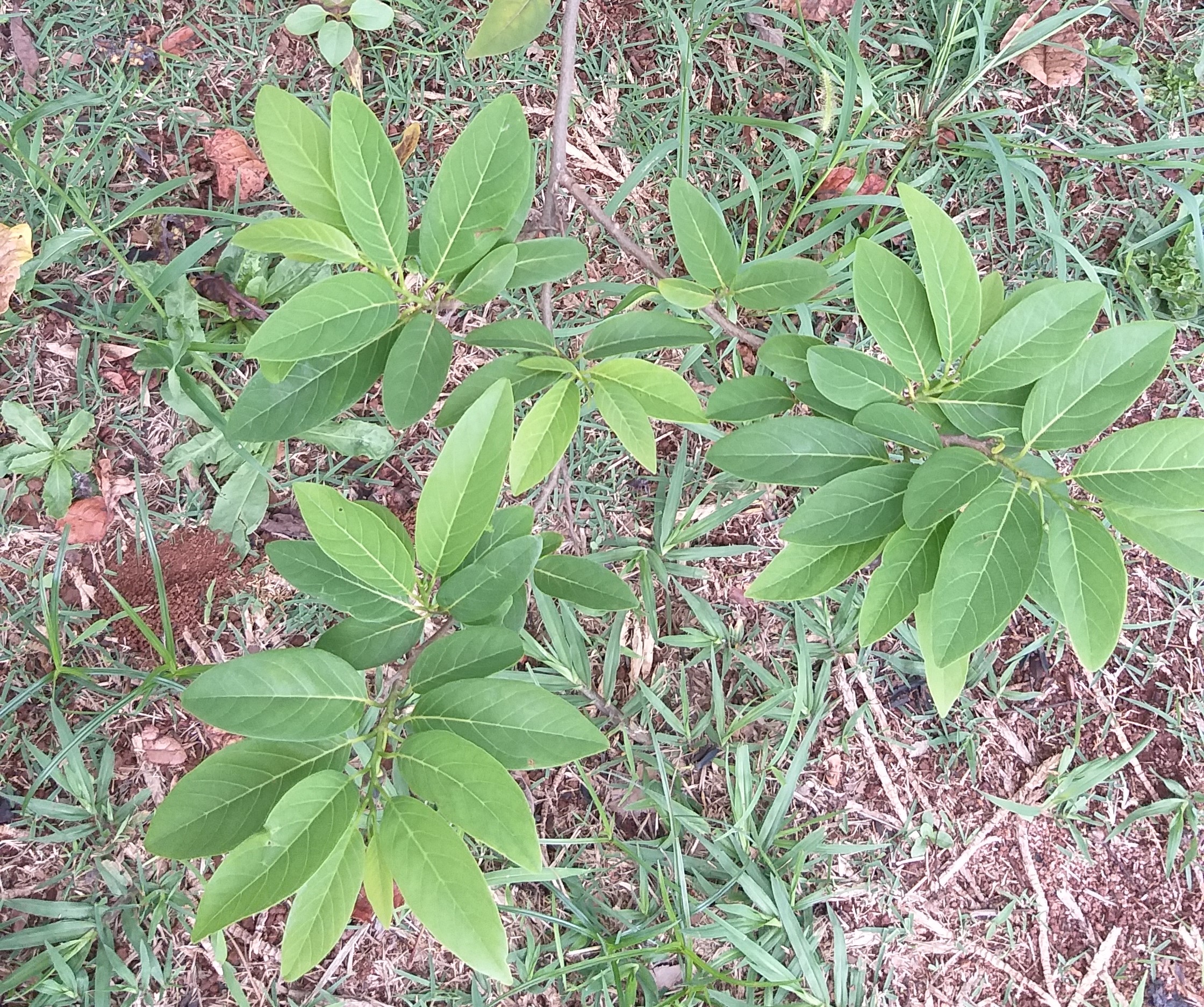

Researchers tested the effects of the plant’s methanolic extract and an isolated alkaloid substance, palmatine, on mice. The results were promising.

Researchers from the University of São Paulo (USP) and collaborators analyzed samples from mining areas in four Brazilian biomes, including the Amazon.

The study was conducted at the University of São Paulo. As the pregnant women were treated and their symptoms of depression improved, the proportion of “good” bacteria in their gut microbiome increased.
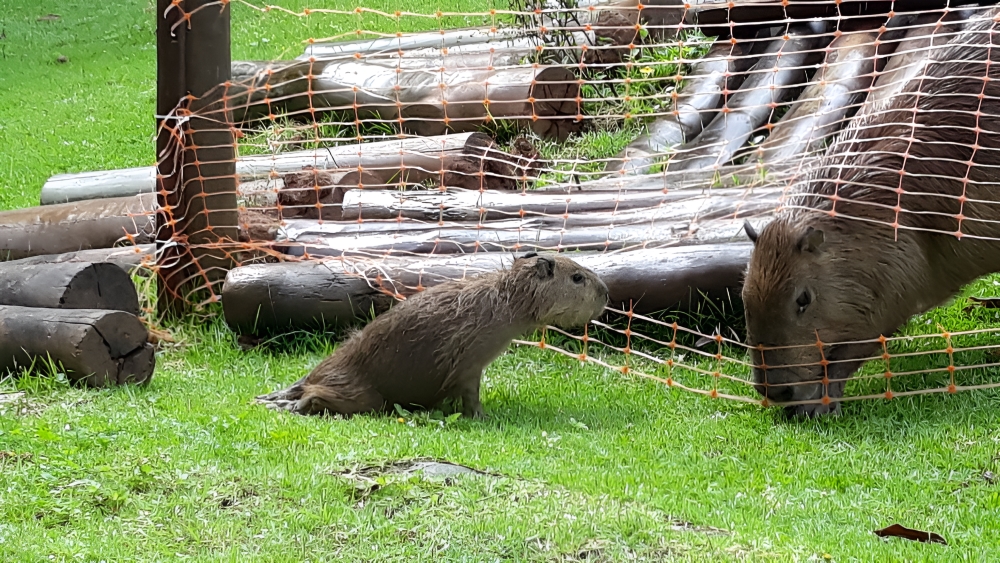

The viral strain found in the dead animals on Anchieta Island in Ubatuba was the variant transmitted by vampire bats, which probably fed on the capybaras’ blood at a time of habitat disturbance.

In the 10th FAPESP Lecture 2024, researcher Luiz Augusto Horta Nogueira highlighted the virtues of hybrid vehicles, which combine electricity and biofuels, stressing Brazil’s strategic role in the process.

The Applied Research Center for Innovation and Sustainability in Citrus Farming was inaugurated on December 12th in a ceremony at the Palácio dos Bandeirantes, seat of the São Paulo state government.
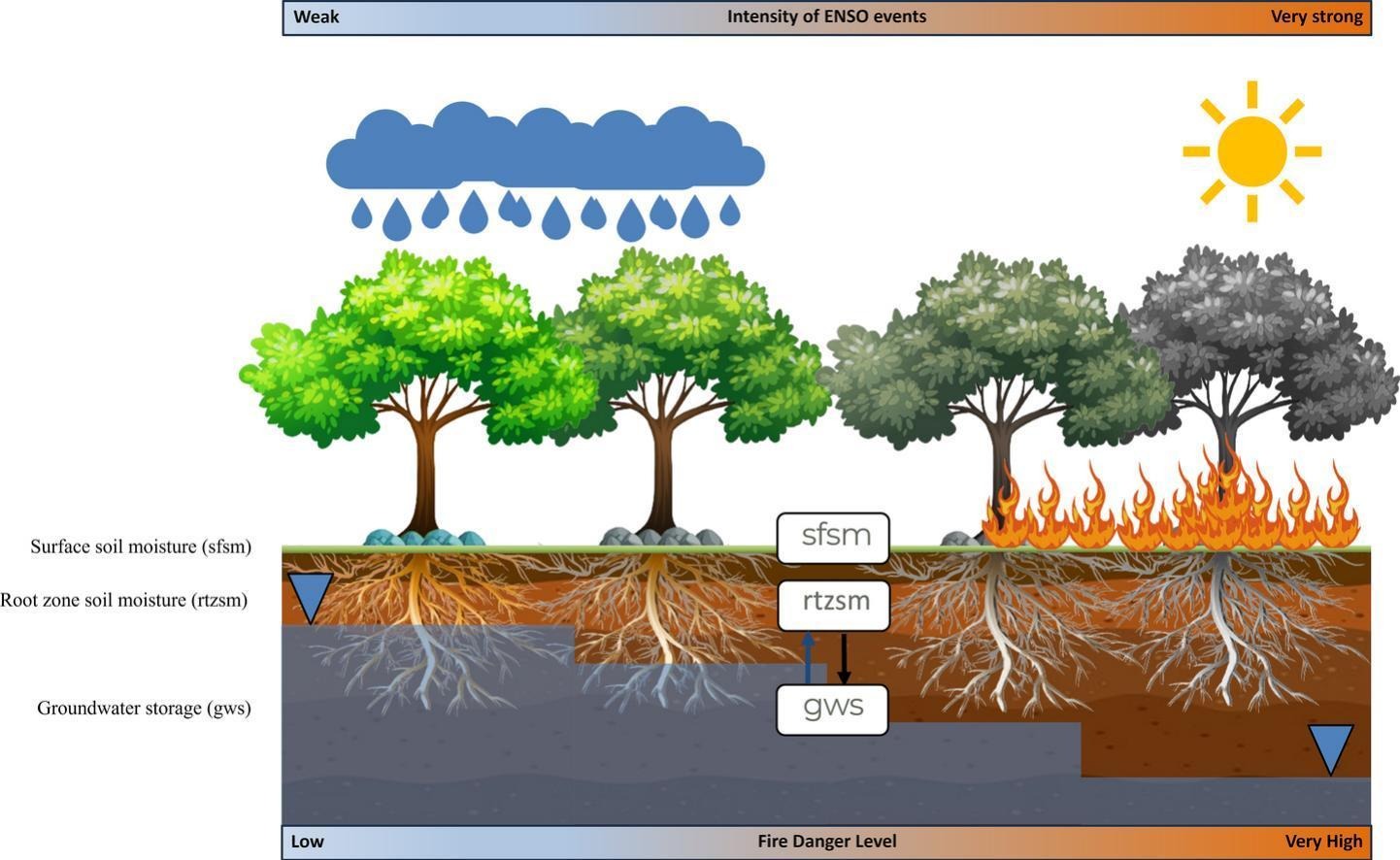
Researchers have been able to demonstrate a link between the climatic phenomenon and the propensity for fires, creating a tool that could help with future prevention efforts.

Portable device developed by a FAPESP-supported startup allows for the preventive detection of changes and the treatment of the material so that it remains suitable for use; company participated in business mission during FAPESP Week Spain.
A study conducted by a Brazilian researcher at Harvard shows that serotonin – a hormone known for regulating mood – plays a central role in the development of postprandial hypoglycemia in up to 30% of people who have undergone surgery; the findings suggest avenues for possible treatments.

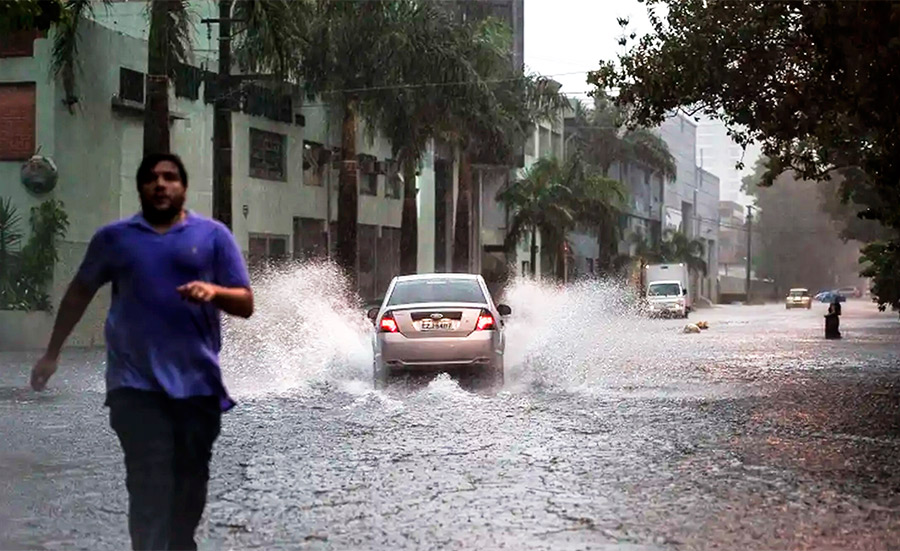
A study by a group of scientists shows that larval infestations of Aedes aegypti in open-air disused containers increased in response to the effects of the weather phenomenon, especially mean seasonal temperature and rainfall above 23.3 °C and 153 mm respectively.
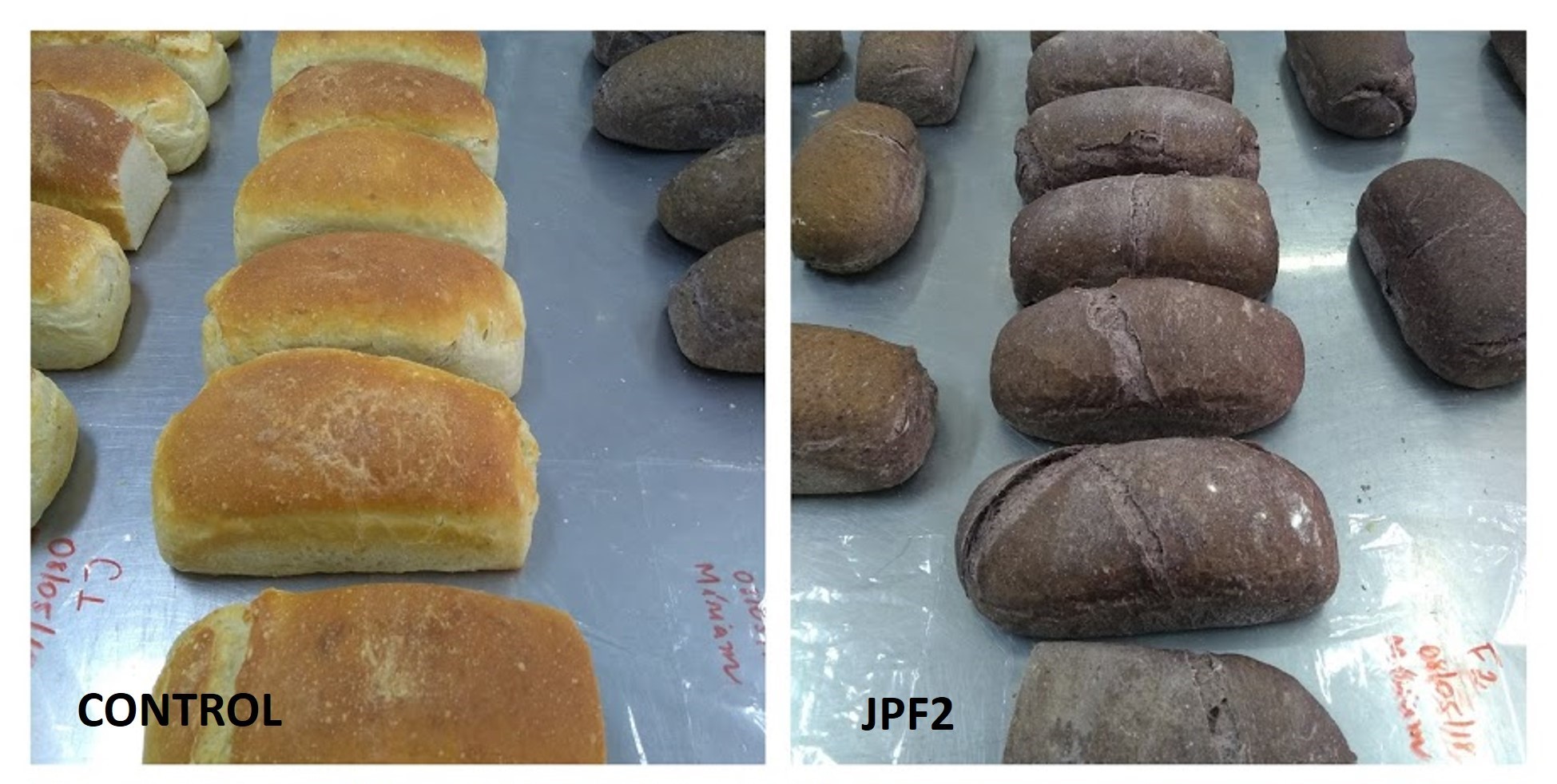

Consumption of bread supplemented with jabuticaba peel flour, which is rich in fiber and antioxidants, lowers glycemic peaks and prolongs satiety.
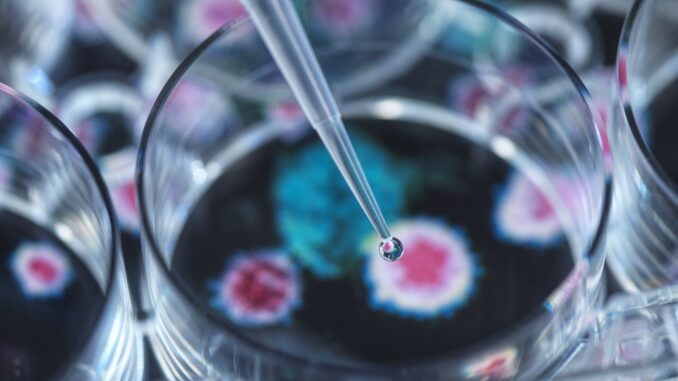
The result of collaboration between groups from the Federal University of São Carlos (Brazil) and Jaume I University (Spain), the innovation has already been patented.

For Elena Fernandez de la Iglesia, from the Faculty of Law at the Complutense University of Madrid, taxing producers and consumers according to the amount and type of material used is one of the best tools for promoting the circular economy. The topic was discussed during FAPESP Week Spain.
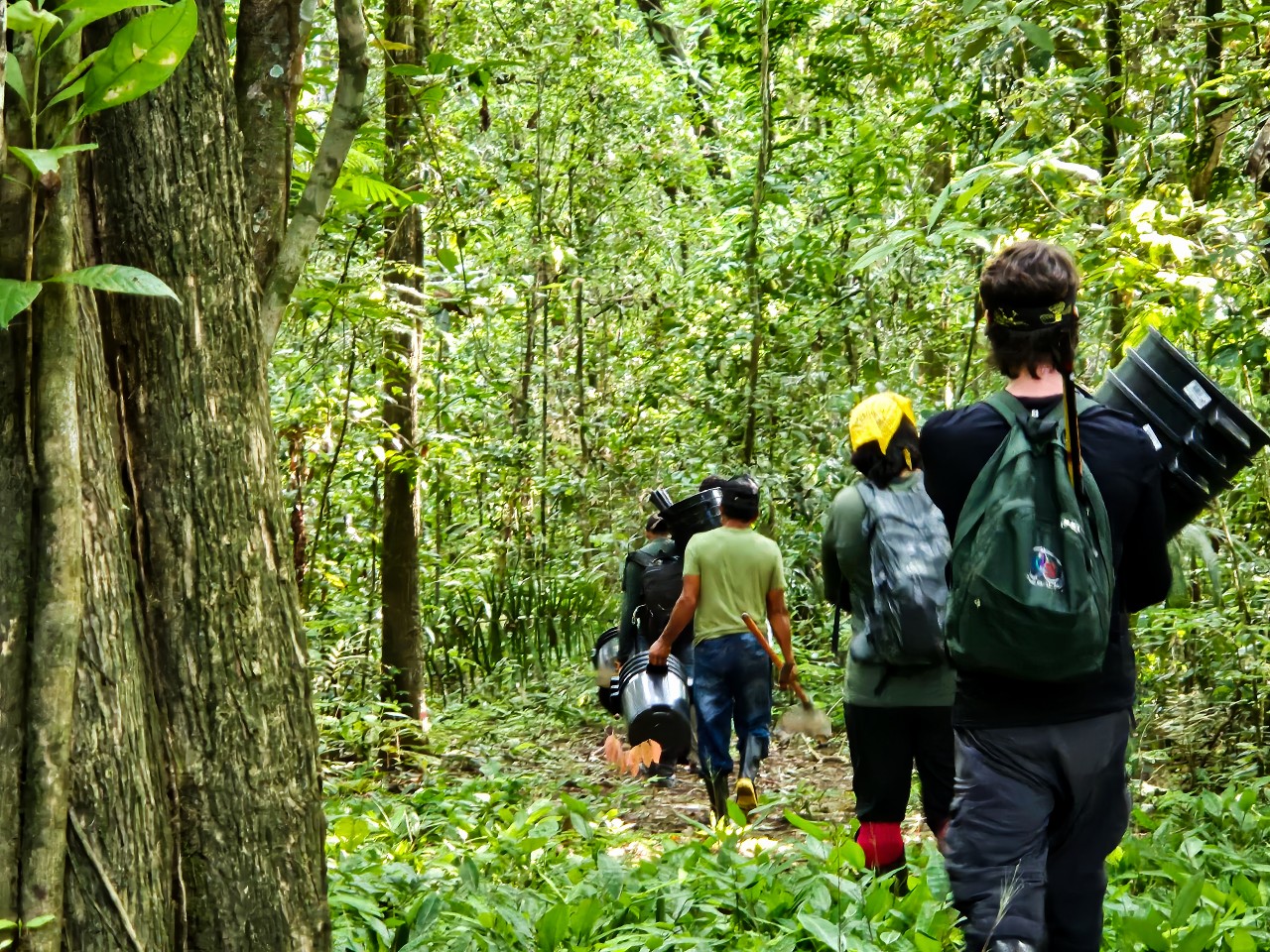

An expedition to the Maracá Ecological Station, about 130 kilometers from the capital Boa Vista, collected more than 400 specimens to study how these animals are coping with the temperature increases predicted for the coming decades. The work is part of the Amazon+10 Initiative.
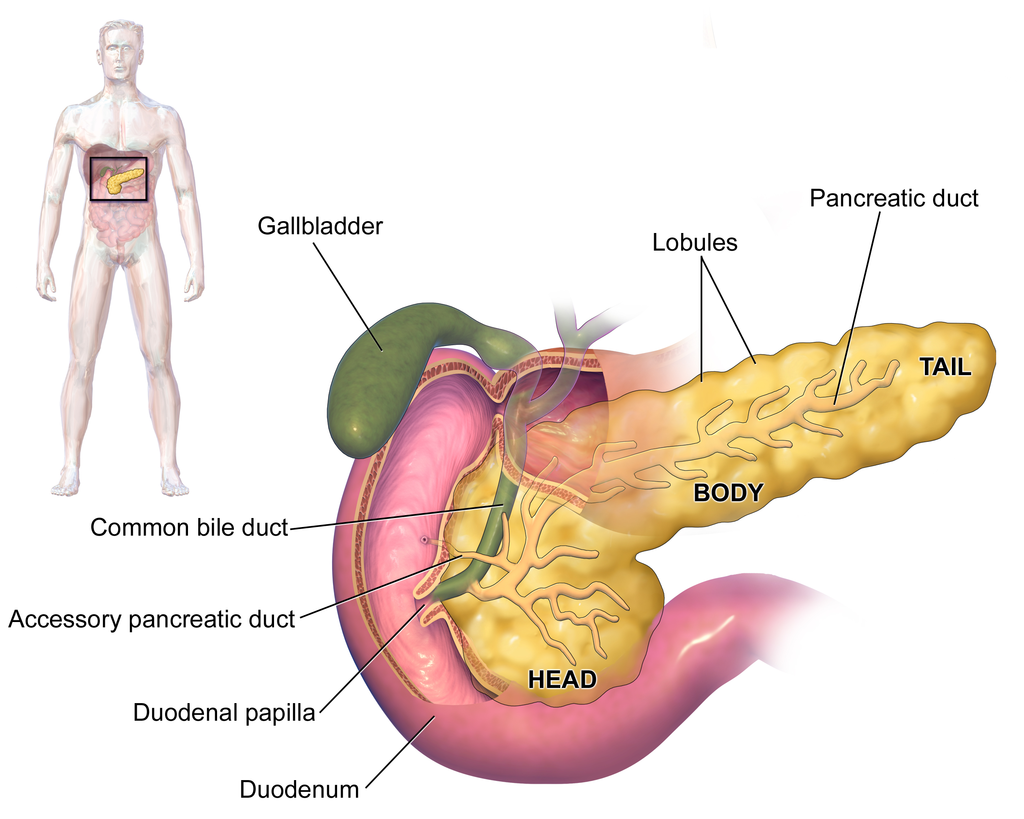
The pioneering initiative by scientists at the University of São Paulo aimed to promote early diagnosis and improve treatment of the disease, which is relatively infrequent but one of the leading causes of death from cancer in Brazil.
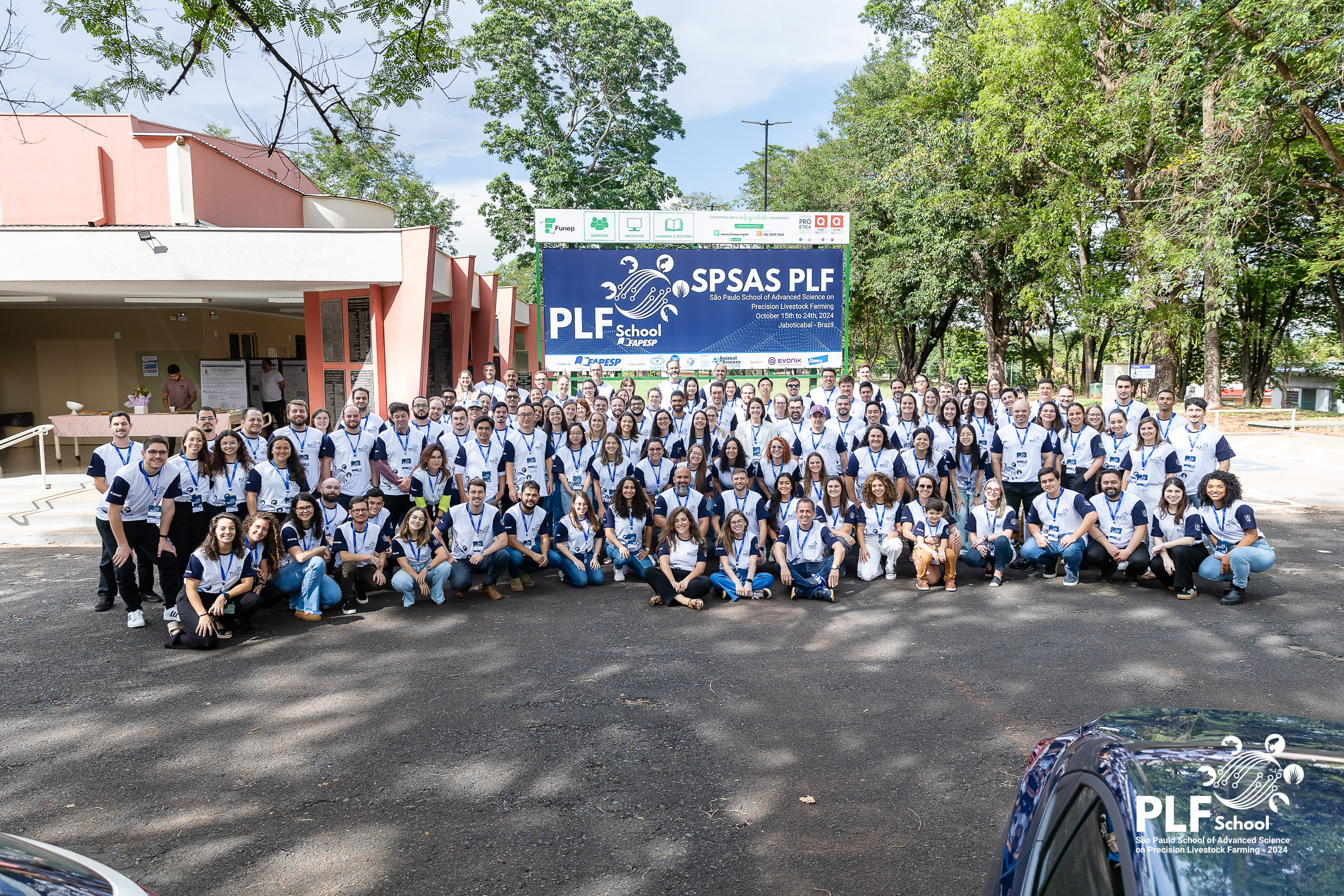

Cutting-edge technologies and systems promise to contribute to more sustainable practices but need academics, scientists, processors and farmers to join forces, according to speakers at the São Paulo School of Advanced Science held on the Jaboticabal campus of São Paulo State University.
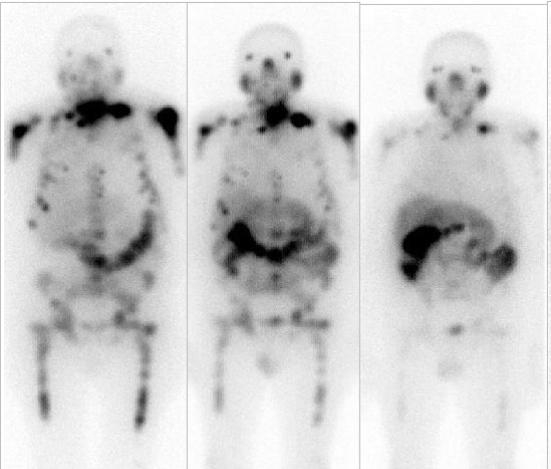
The formula developed by a startup supported by FAPESP is used to treat patients without therapeutic possibilities.
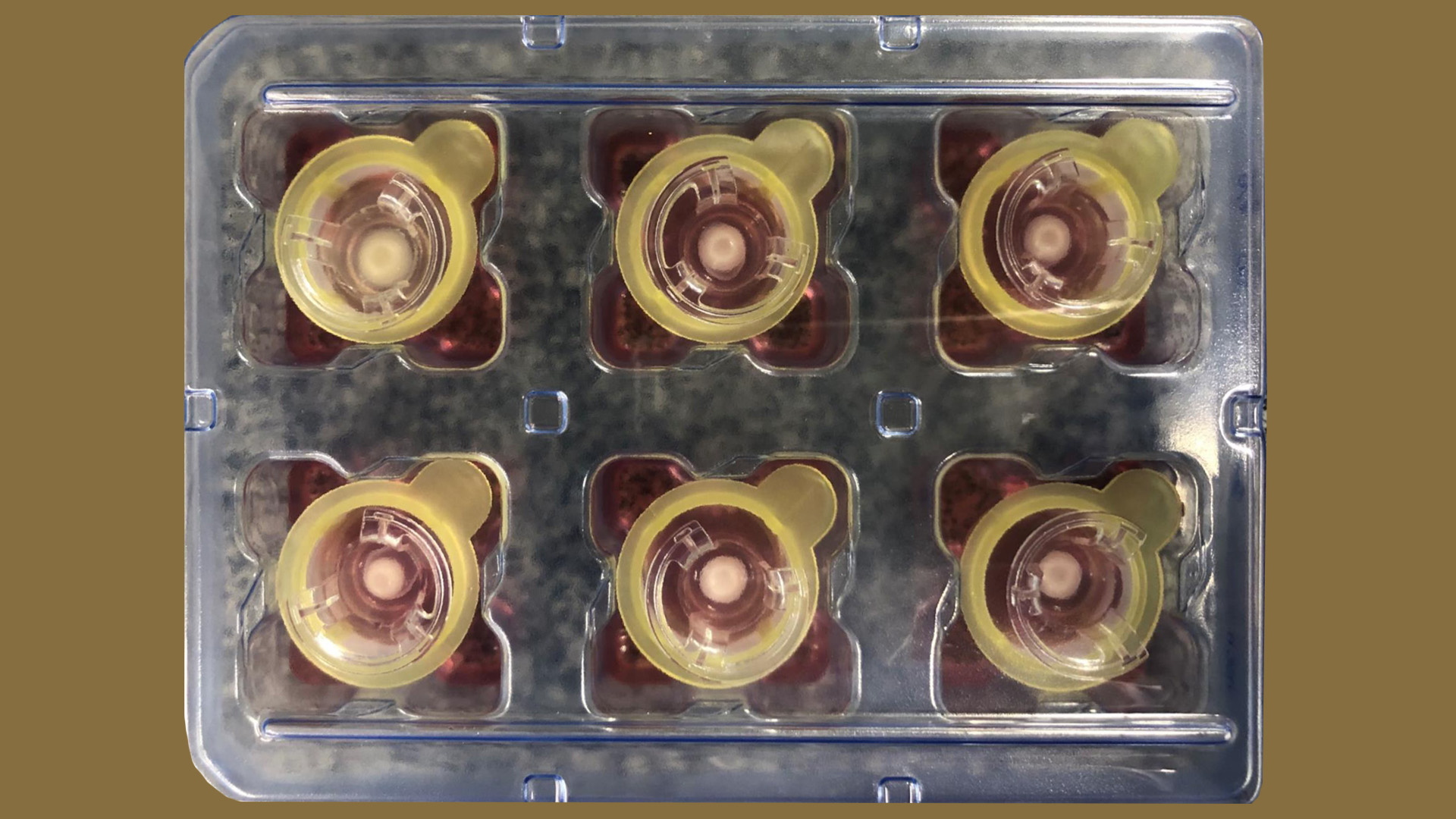

In vitro model has all three layers of the organ, simulates diseases and injuries more accurately, and could replace animals in toxicological studies of medicines and cosmetics; innovation was presented at FAPESP Week Spain.
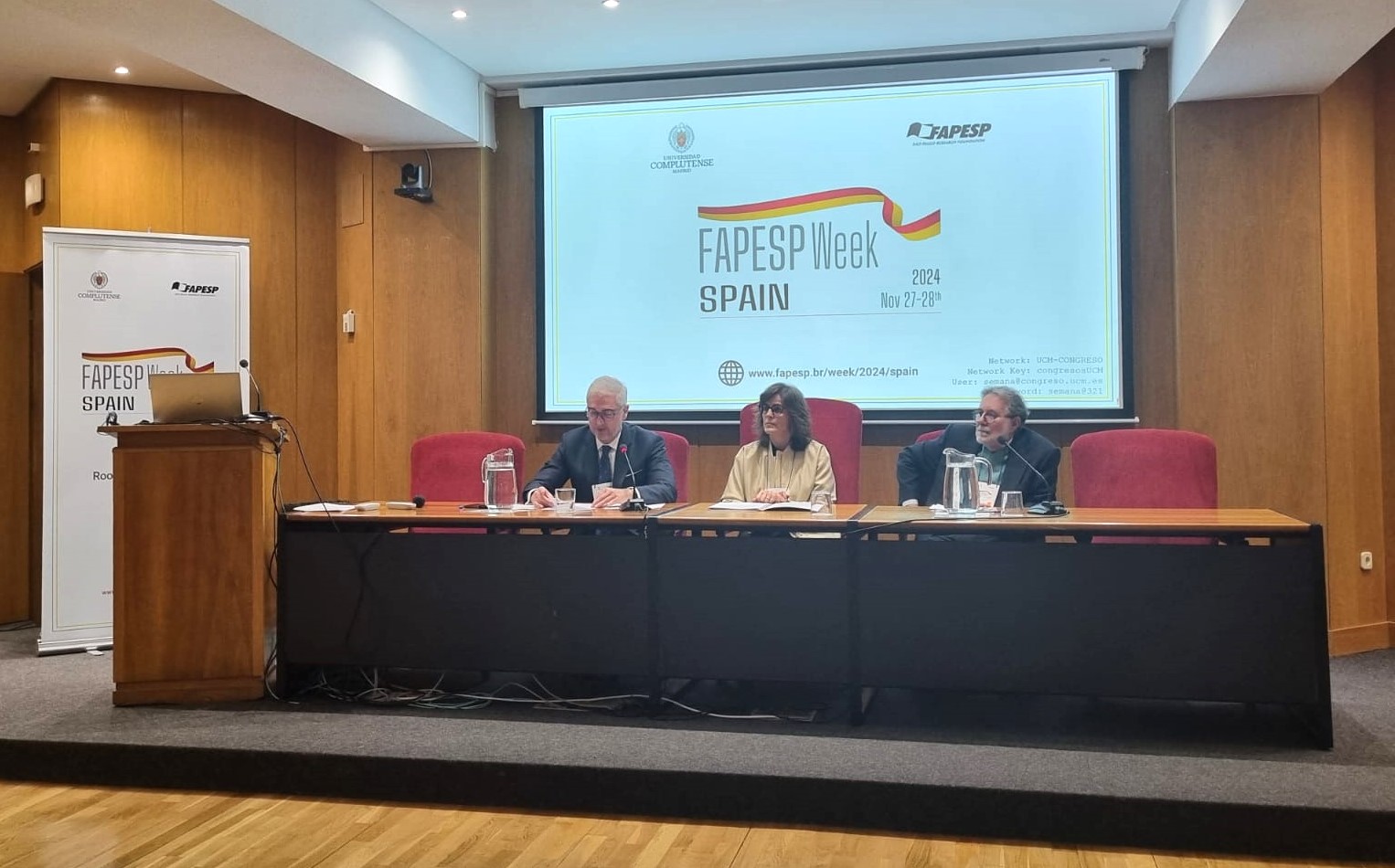

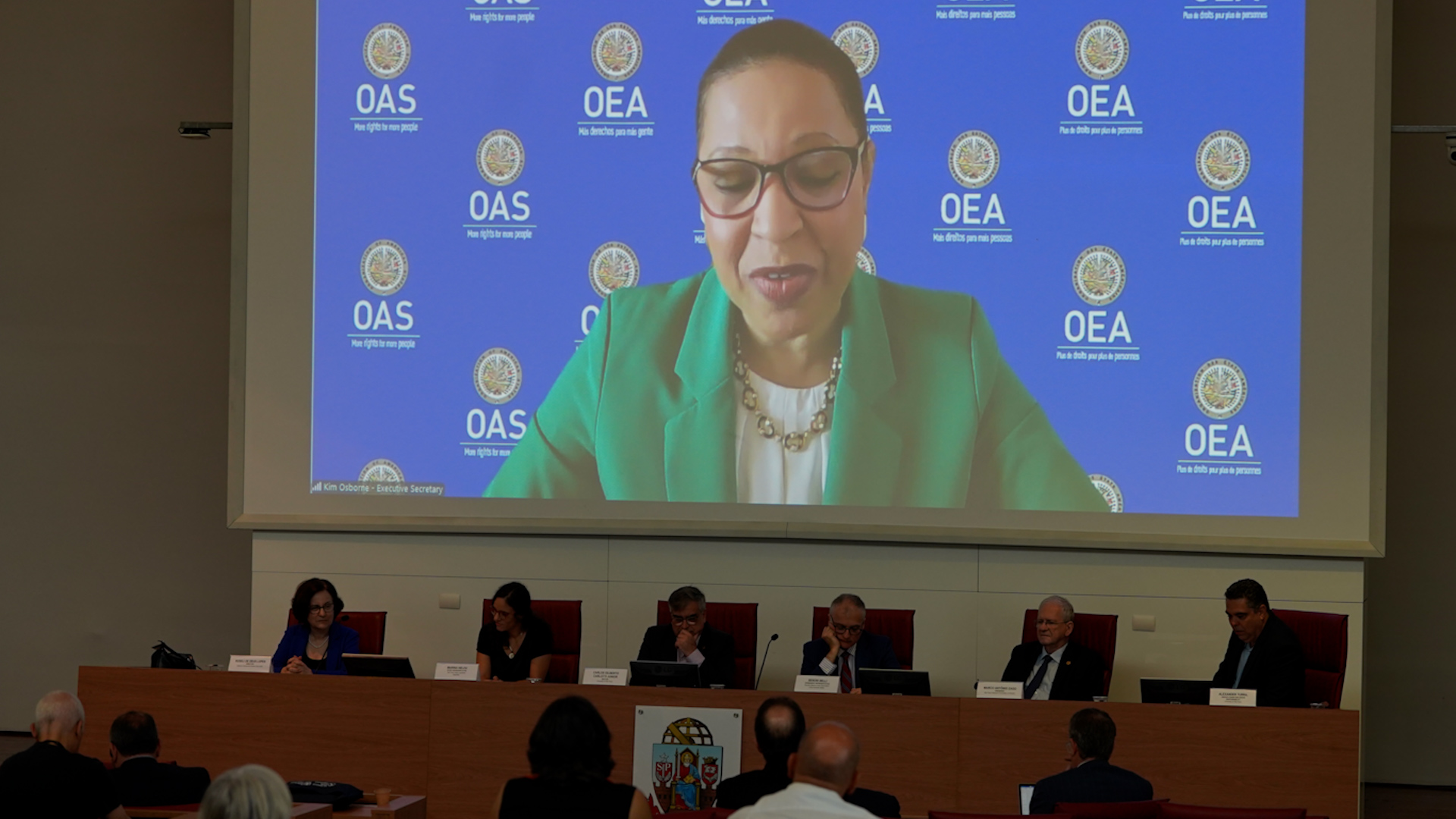
According to participants at the opening session of FAPESP Week Spain in Madrid, there is still a lot of room for increased collaboration between the two countries in these areas.

Deep techs supported by the Foundation’s innovative research program and that participated in FAPESP Week Spain are looking for partnership opportunities and potential investors in the European market.