


Scientists from Brazil and Spain use sensors embedded in drones and agricultural machinery, as well as satellite imagery, to predict the ideal time to harvest, reduce CO2 emissions, and manage water use in plantations; work was presented at FAPESP Week Spain.

Using a mathematical model, researchers at the Research Center for Greenhouse Gas Innovation demonstrated a potential reduction of more than 15% in polluting gases.

Researchers at the University of São Paulo analyzed data from 89 mother-father-baby triads and concluded that the higher the father’s body mass index, the smaller the baby, and that this can influence the baby’s health far into adulthood.

The strategy developed at the State University of Campinas consists of submitting the ingredient to heat treatment and combining it with guarana extract and vitamin D. The result could become an alternative to animal products.

WHO advisory group publishes first article in scientific journal outlining challenges and actions that can help make the field more equitable and promote progress in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of various diseases, including rare ones.

The Guarani Aquifer is the source of drinking water for some 90 million people and is being overused in several areas of São Paulo state (Brazil). The researchers deployed stable isotopes to estimate the relative contributions of rainwater and groundwater to the maintenance of springs in the region.
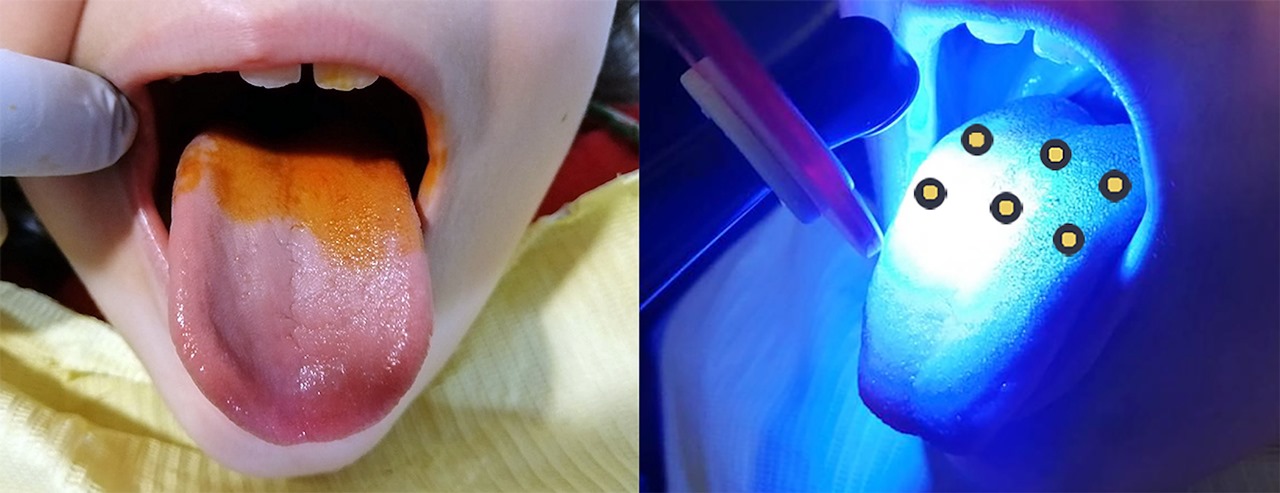
The study involved 52 mouth-breathing children aged 6-12 with halitosis. The results are published in PLOS ONE.
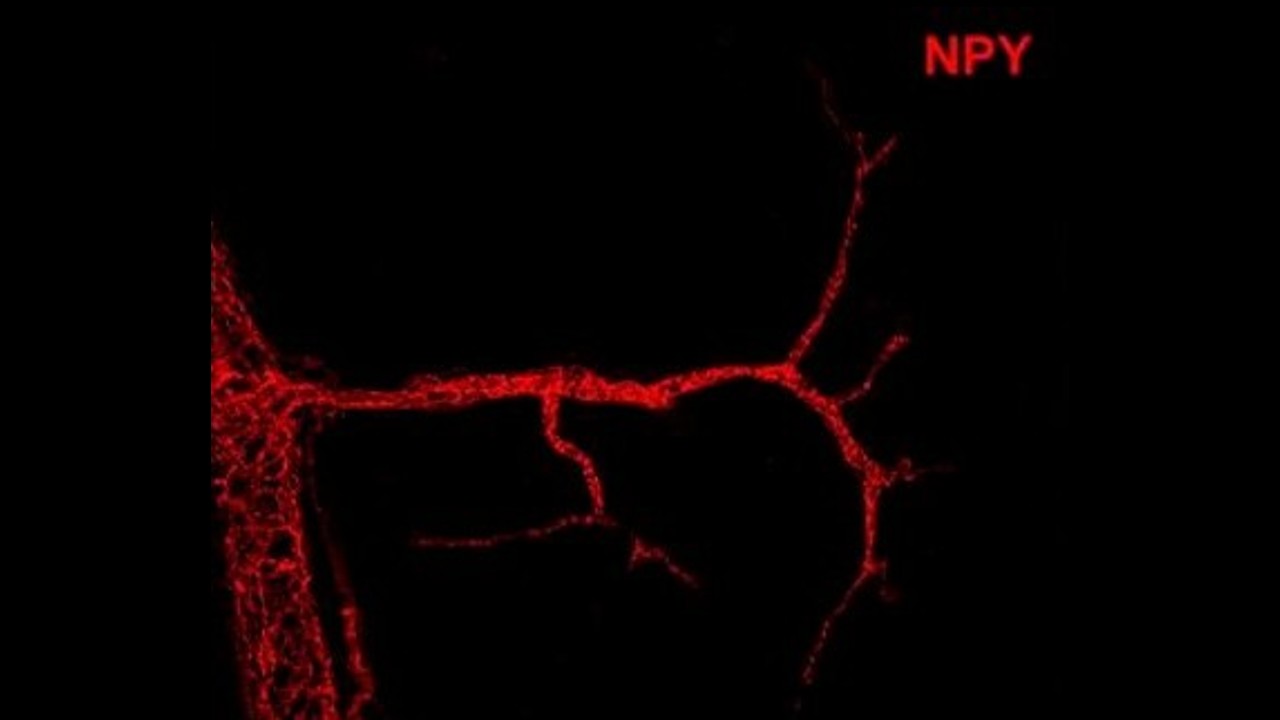
Researchers from the University of Oxford and the State University of Campinas have discovered a neuropeptide that acts on the peripheral nervous system, outside the brain, to speed up metabolism. The finding opens the way to more efficient and cheaper treatments for obesity.
While studying a region of vineyards in the interior of the state of São Paulo, researchers observed that the most preserved sites had a greater diversity of birds and the ecological functions they perform.
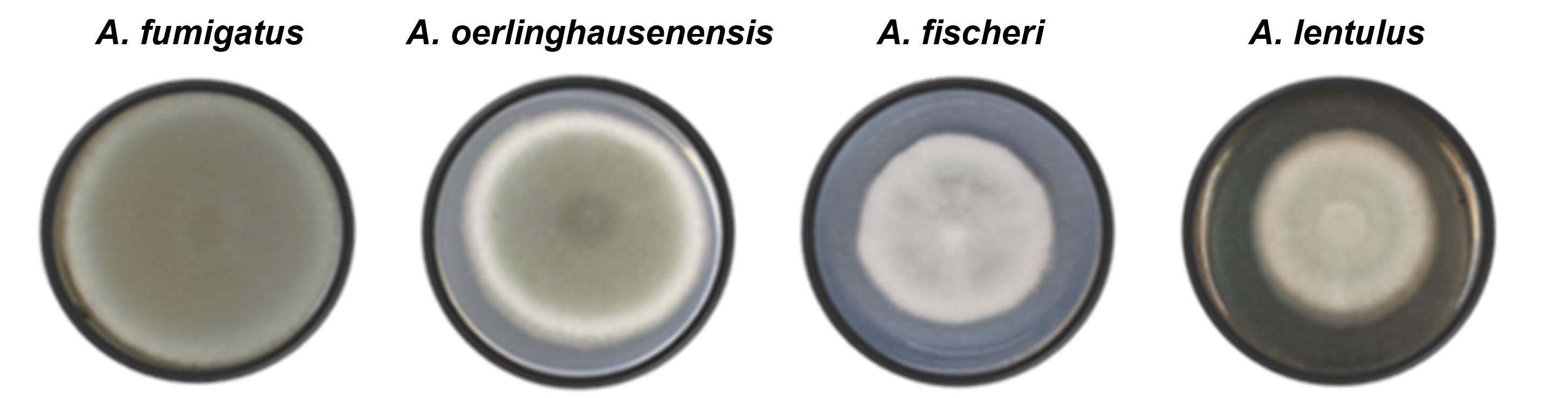
Researchers at the University of São Paulo found 62 proteins specific to spores of Aspergillus fumigatus, a fungal species that causes lung disease. The study, published in Nature Microbiology, showed that at least one of these proteins inhibits human defense mechanisms.

The use of biofuels in Brazil and other developing countries can avoid some 400 million metric tons of greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector by 2030, according to a report produced by an International Energy Agency task force led by researchers affiliated with the FAPESP Bioenergy Research Program.

São Paulo-based startup supported by FAPESP develops cheaper and more sensitive alternative to imported test kits.

An analysis of 429 specimens belonging to 39 species representative of the diversity of Polistes in the Americas confirmed the inverse of Bergmann’s rule by pointing to larger body size for species occurring in or near the tropics compared with species inhabiting higher latitudes.

The fuel produced at the experimental station will power three city buses that will circulate around the university campus, as well as a bus that can drive 450 Km on a to and fro travel between São Paulo and Piracicaba.

Conclusion comes from study that followed more than 4,000 people aged 50 or older for 12 years; damage is mainly in brain areas associated with memory.
Discovery contributes to advances in understanding of the disorder; study is one of the most comprehensive on the subject, with samples from 1,600 patients, including Brazilians.

Researchers partnering with the City of Guarujá (São Paulo state) conducted a study that found a high level of contamination on Perequê Beach, with plastics and cigarette butts predominating. The results will be useful for policymakers to implement measures that can mitigate the problem.

This particular strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae had previously been detected in the United States. The bacterium frequently causes infections in hospitals, is not eliminated by any existing antibiotic, and is especially dangerous for people with low immunity.

The inventory identified some 1,000 landslide points in São Sebastião (São Paulo state, Brazil). The research group is now using airborne laser scanning and other data inputs to create a methodology capable of more precise results.
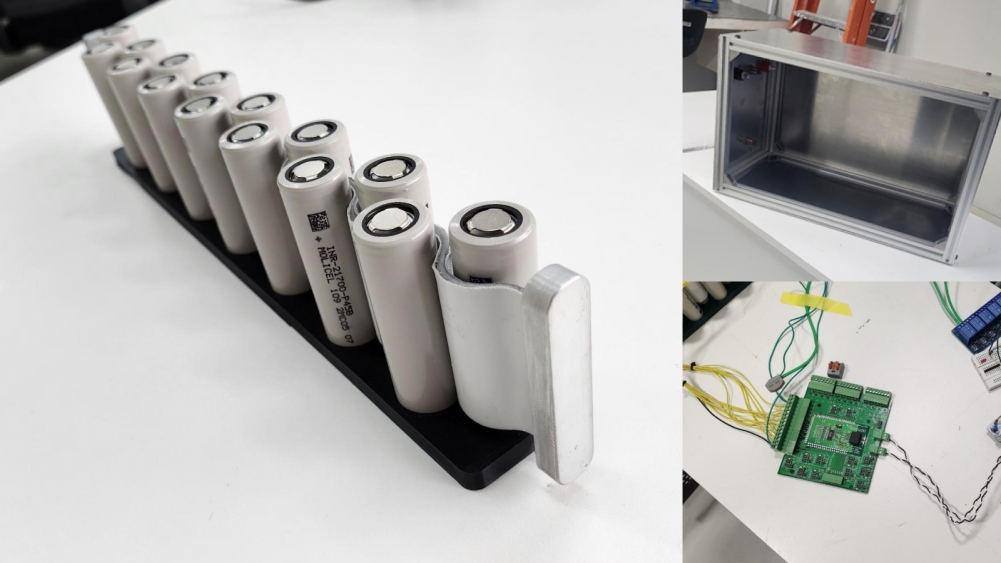

The FAPESP-supported deep tech aims to supply batteries to manufacturers of electric vertical takeoff and landing vehicles and operators of transportation services.

The study was conducted at the Federal University of São Paulo and involved 144 diabetic patients, who were treated with monochromatic infrared light and physical therapy.
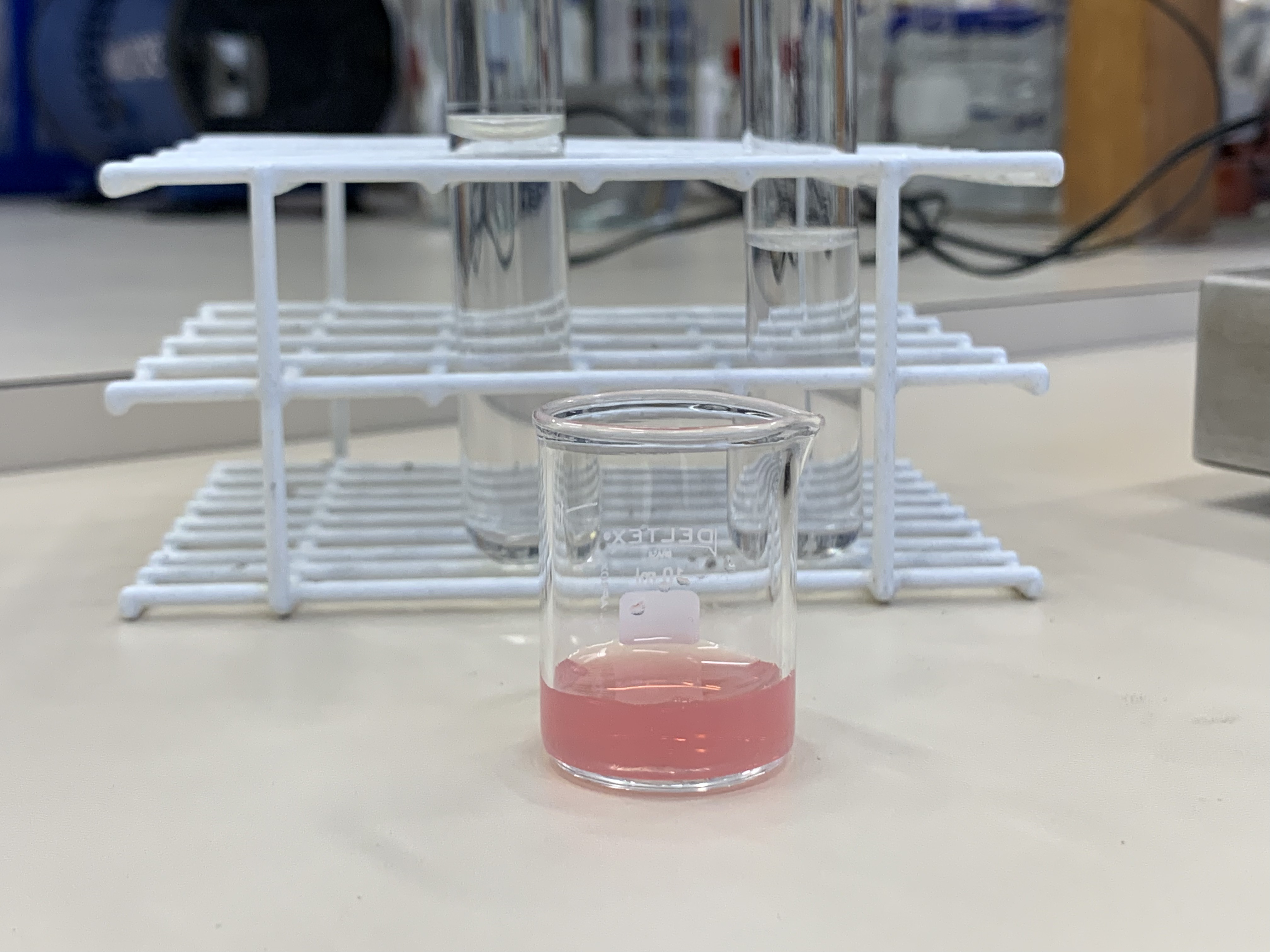

Plant-based pigment with antioxidant and anticancer properties breaks down easily in the gastrointestinal tract and under adverse environmental conditions. To avoid the problem, researchers at the University of São Paulo inserted the compound into pectin-coated nanoparticles, enhancing its bioavailability.
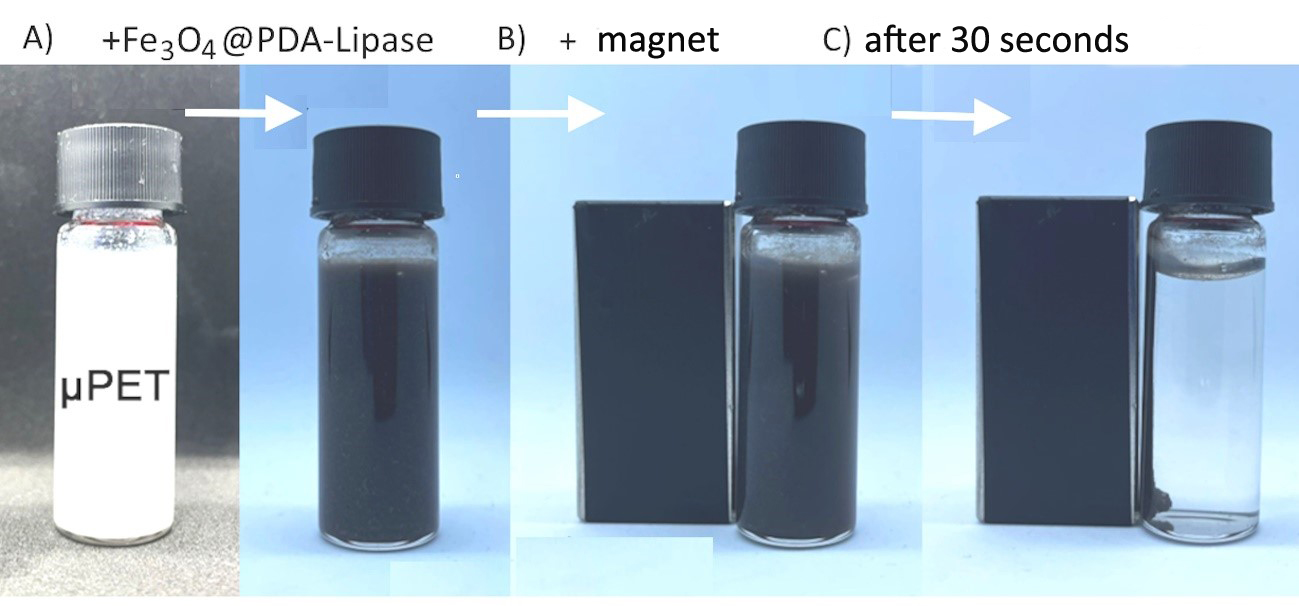
The strategy developed at the University of São Paulo uses magnetic nanoparticles that bind to tiny plastic particles and permit their removal with the aid of a magnet.

International event will be held on May 3-16, 2025, at the University of São Paulo’s campus in São Carlos.
Discoveries by Brazilian researchers belonging to a FAPESP-supported research center could lead to strategies to prevent cardiovascular disease associated with diabetes.