


Brazilian researchers analyzed behavioral and physiological factors in animals whose mothers received a synthetic substance that activates the same receptors as marijuana during pregnancy. The consequences were different in males and females.
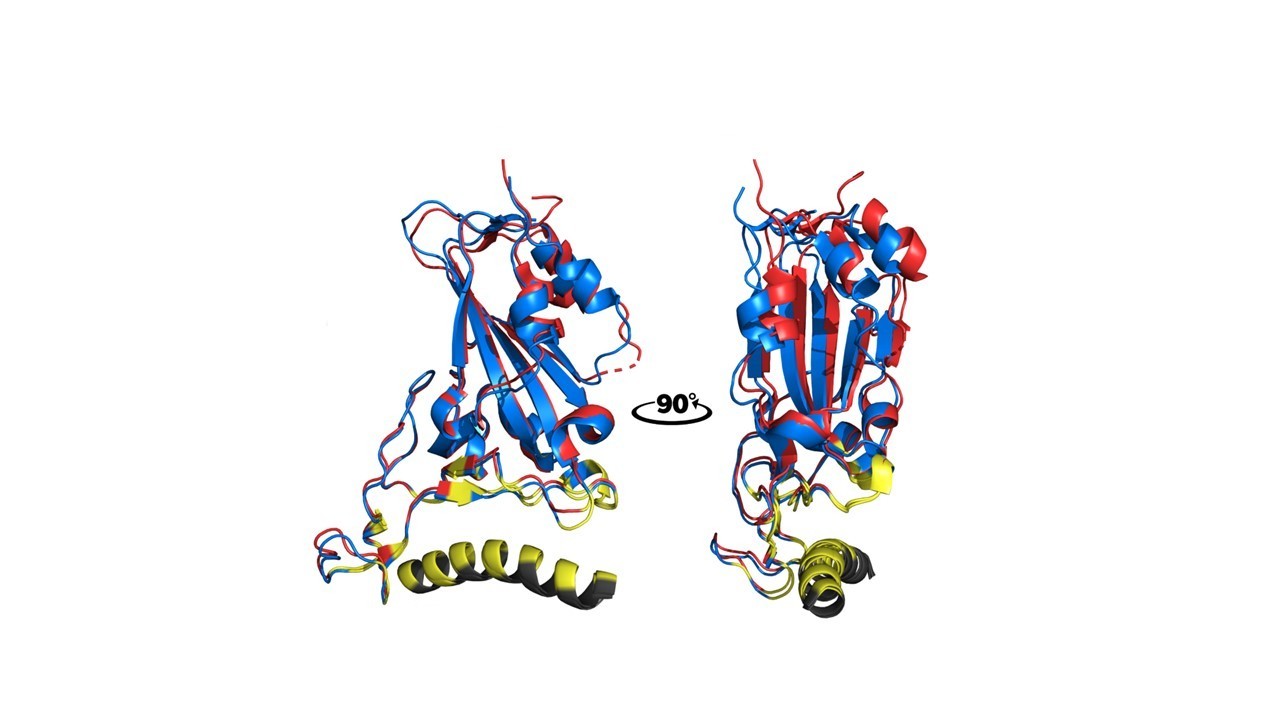
The synthetic peptide was inspired by ACE2, the protein to which the virus that causes COVID-19 binds to invade human cells. The results point to a route for the development of novel antivirals.
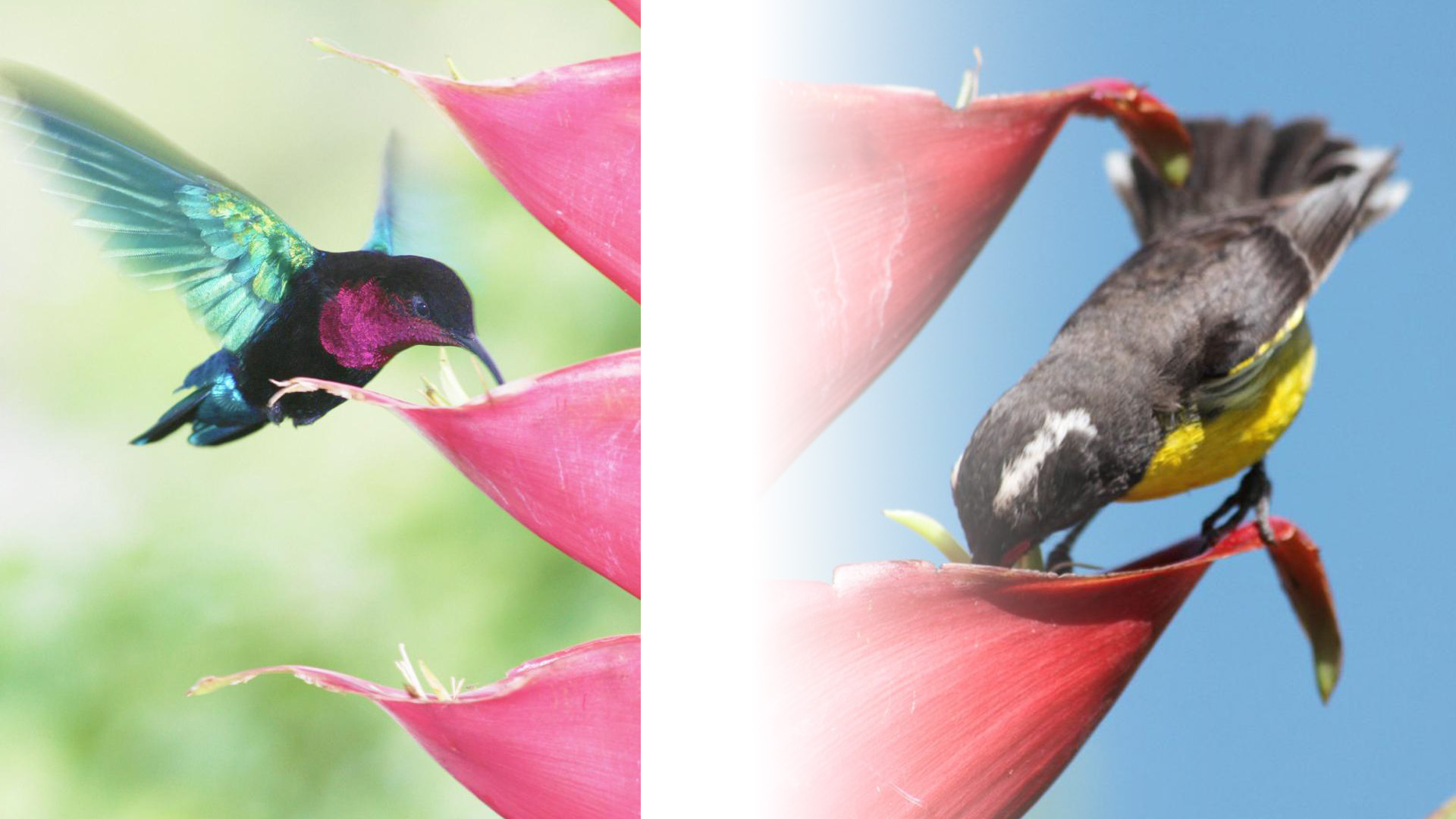

Hurricane Maria killed so many Purple-throated caribs, sole pollinator of two species of heliconia, that other birds were able to gain access to the plants, according to an article in New Phytologist, which concludes that species extinction is a far more complex process than is often thought.
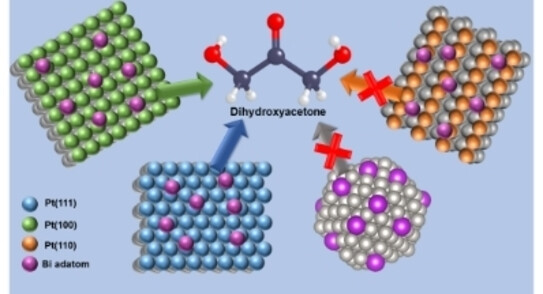
The experiment of the Center for Development of Functional Materials was described in an article in the journal ChemCatChem.
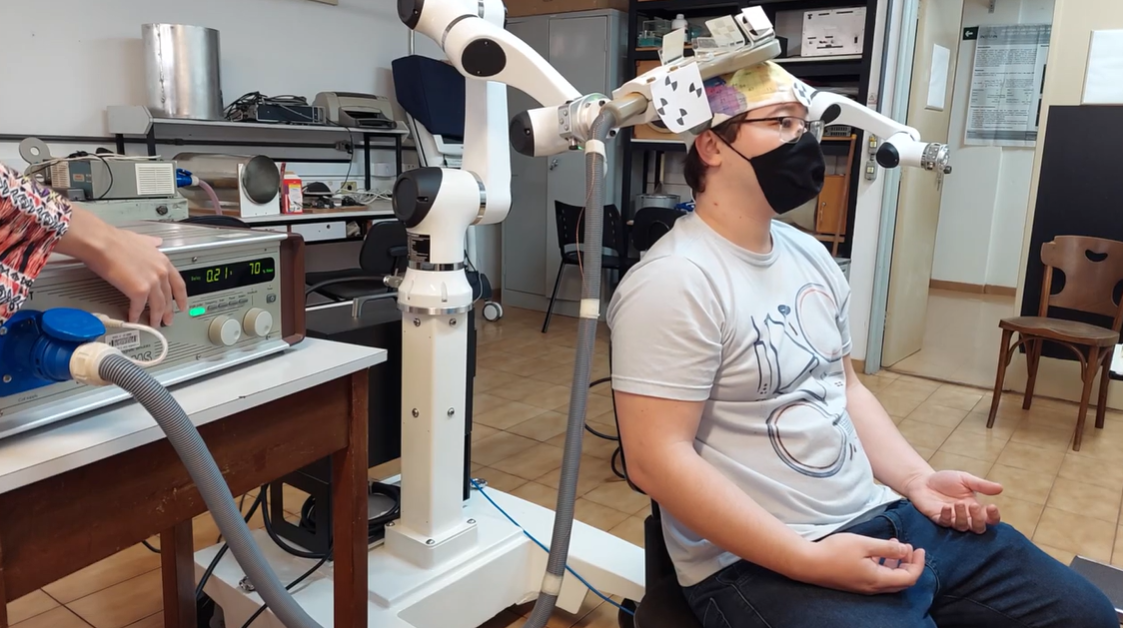

The technology was developed at the Research, Innovation, and Dissemination Center for Neuromathematics in collaboration with scientists from Finland.

The process designed by researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Brazil and collaborators in Chile and Mexico results in low-cost raw materials and reduced environmental damage.
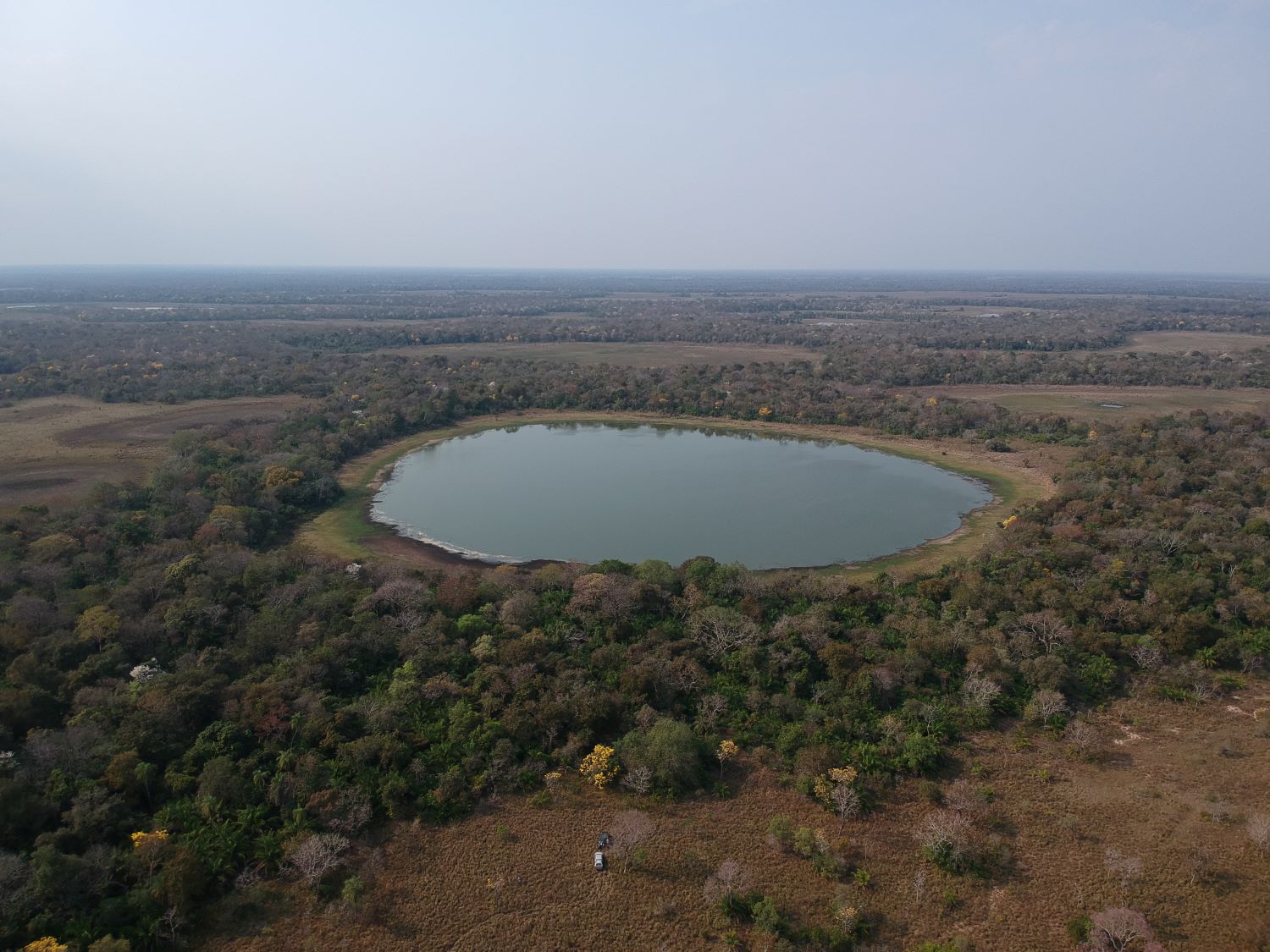

Characterized by high pH and salinity, these water bodies have practically dried up because of rising temperatures, changing rainfall patterns, and wildfires. The findings show how the local microbial community and other factors influence greenhouse gas emissions.
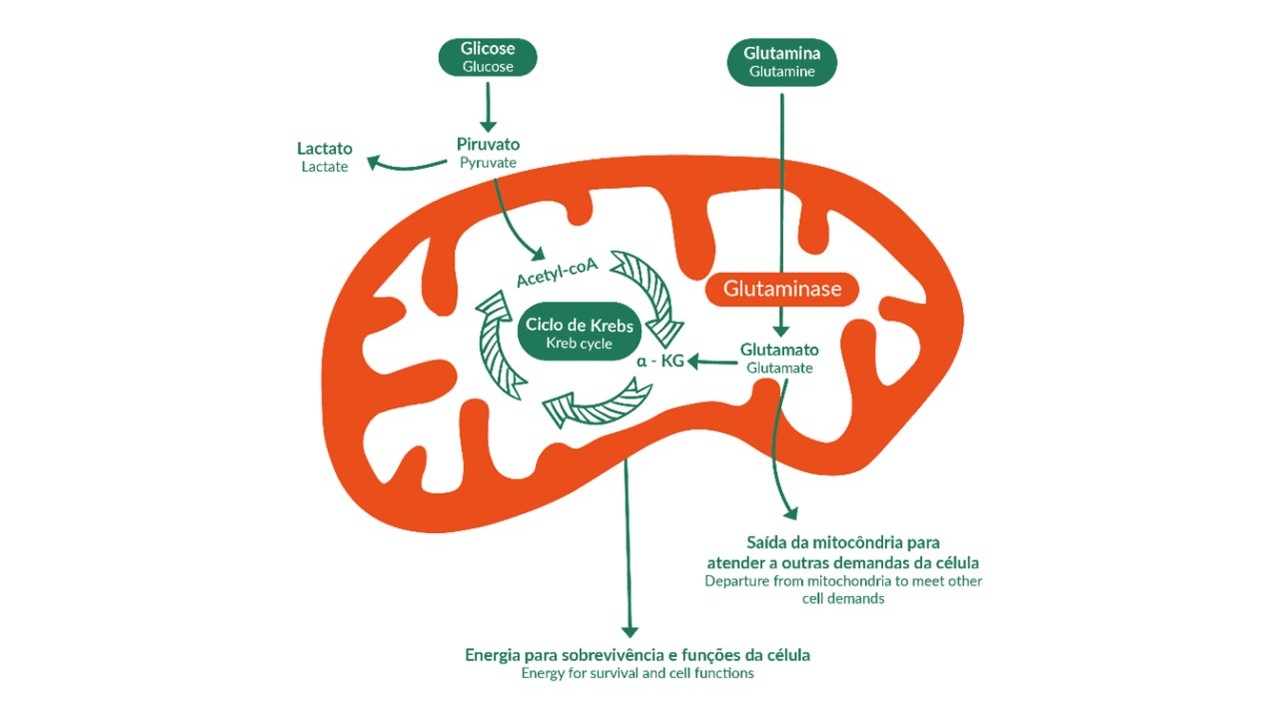
Promising results were obtained by a group at the Brazilian Center for Research on Energy and Materials (CNPEM), working with collaborators elsewhere. They combined inhibition of glutaminase, an enzyme that converts glutamine into nutrients for tumor cells, with inhibition of HuR, a protein that regulates the RNA of glutaminase.

Experiments conducted at the Federal University of the ABC showed that nitrogen-fixing bacteria play a key role in the reproduction of a legume native to Brazil.

Residents of the cities of Bauru and Belo Horizonte were challenged to identify the image and song of the main bird species that inhabit these places.

In an article published in Perspectives in Ecology and Conservation, researchers affiliated with the National Space Research Institute (INPE) and the National Disaster Surveillance and Early Warning Center (CEMADEN) in Brazil discuss CO2 emission reduction challenges and solutions.

A study by the University of São Paulo shows that expansion of cattle ranching to meet growing domestic demand has contributed more than any other driver to the elimination or degradation of the Amazon’s original vegetation, followed by expanding croplands and urbanization.
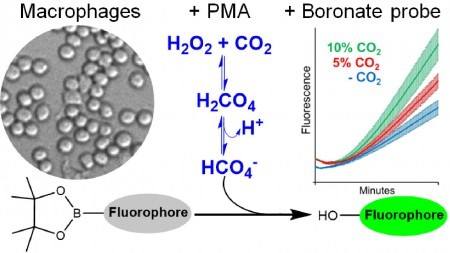
A study conducted at the University of São Paulo in Brazil helps elucidate the impact of high levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide on human health.
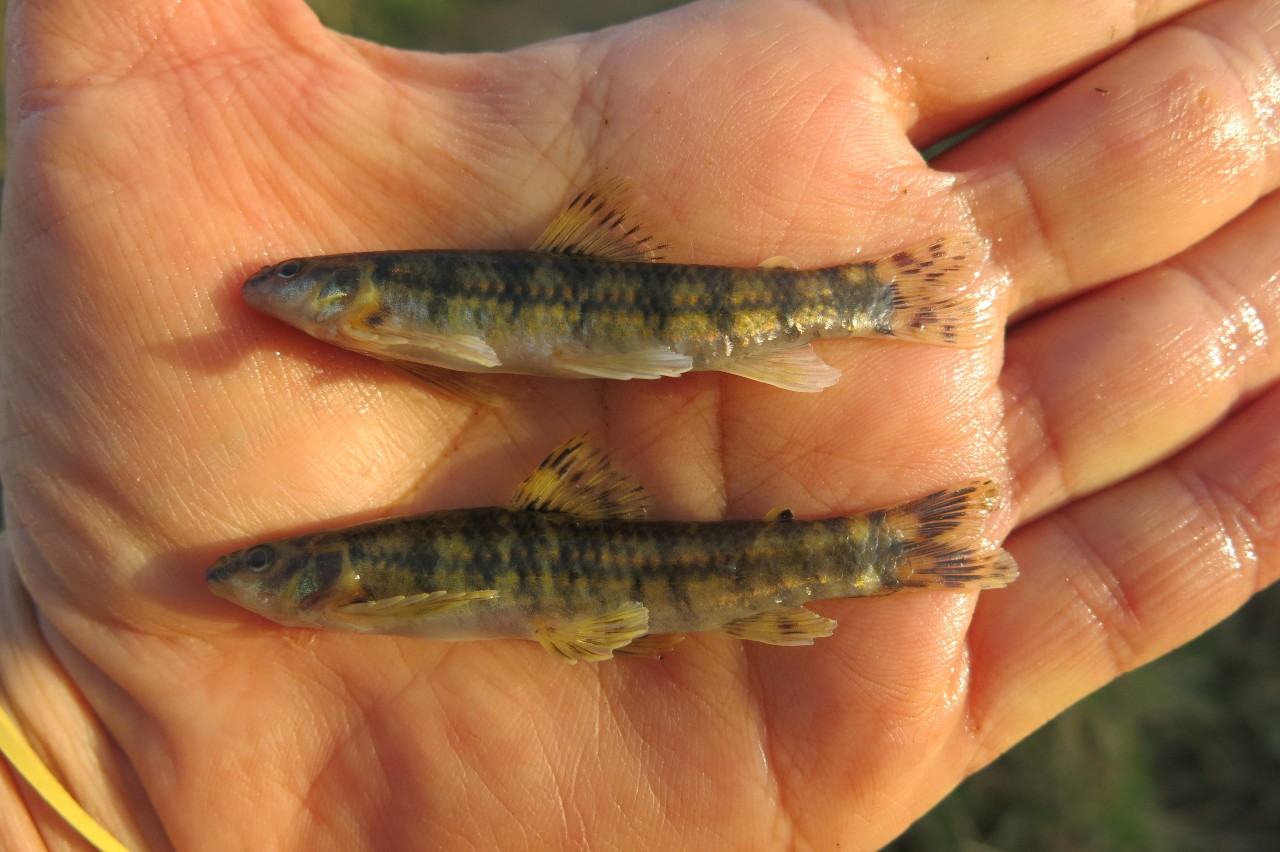

Through morphological and molecular analysis of material collected from rivers in Brazil's Northeast region, the researchers are extending their knowledge of the evolutionary history of South American darters in the genus Characidium.

The product, derived from sugarcane, is being developed by Dermbio Biotech, a startup incubated at the State University of Campinas.

The conclusion is from a study of 774 vegans conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo in Brazil. An article reporting its findings is published in JAMA Network Open.

Alex Ruane delivered the 7th FAPESP Lecture 2024 on “Climate Change and Food Security”
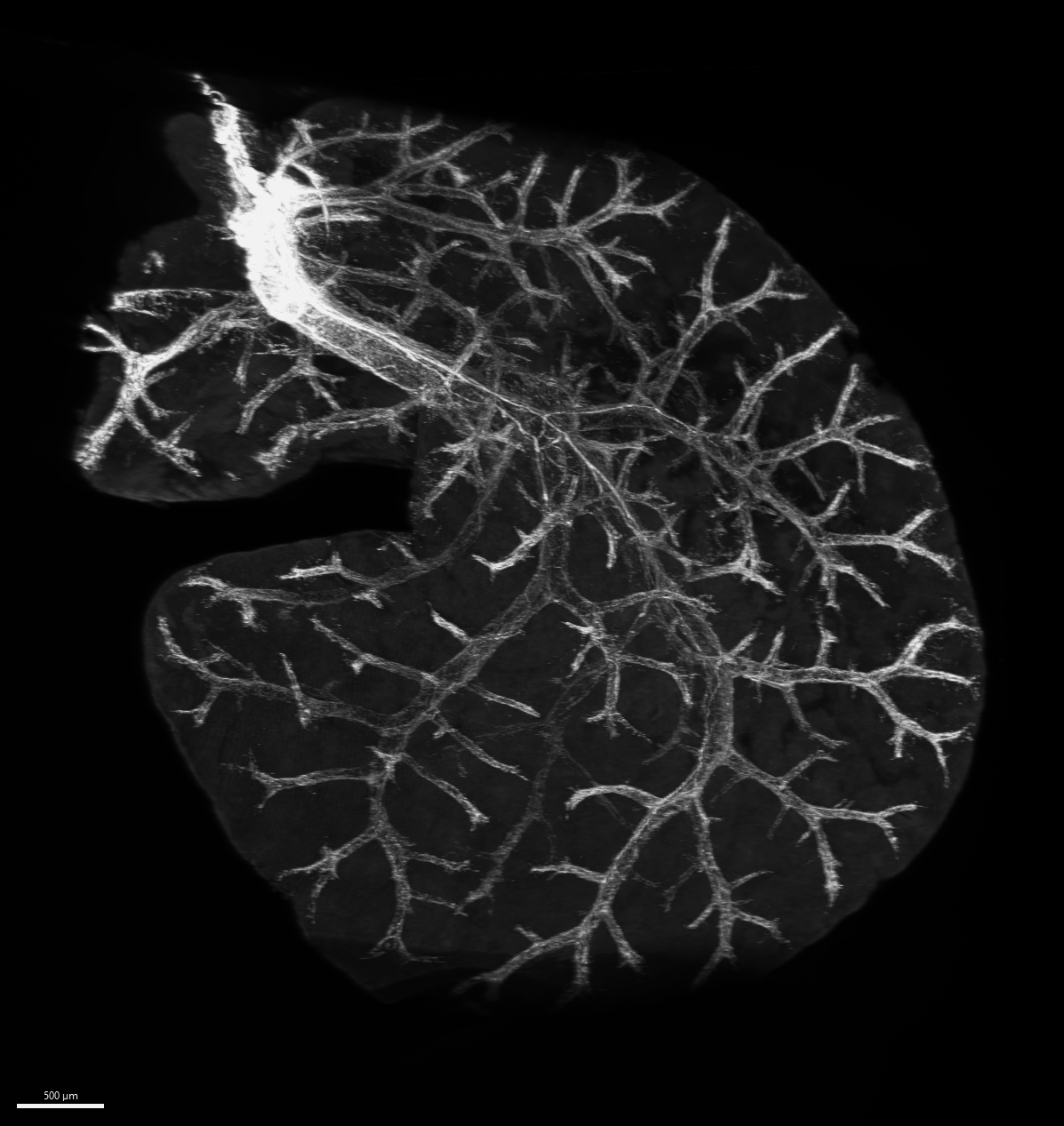
In addition to providing a detailed description of the morphology of hepatic nerves, the study led by Brazilians showed that the increase in blood sugar was activated by a protein called CREB.

Researchers affiliated with the FAPESP Research Program on Global Climate Change met at the State University of Campinas in Brazil to discuss current research priorities in the effort to understand and combat the consequences of the extreme events caused by global warming.

A study conducted by Brazilian scientists and colleagues in other countries shows that earthquakes, hurricanes, tsunamis and volcanic eruptions increase the risk of extinction for mammals, birds, reptiles and amphibians. The natural events may have synergies with hazards due to human activity.

Researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Brazil evaluated the effect of three different low-cost training programs on a group of socially vulnerable female volunteers. HIIT combined with muscle strength exercises was the most efficacious in terms of reducing blood pressure and arterial stiffness, the main risk factors for cardiovascular disease.

The solution, developed by a startup supported by FAPESP, enables farmers to forecast water availability for a six-month horizon.

A report by an international group of researchers including three Brazilians shows that climate change tripled the probability of weather conditions favoring unprecedented wildfires in Canada and multiplied it by a factor of 20 in western Amazonia between March 2023 and February 2024. Global carbon emissions were 16% above average.
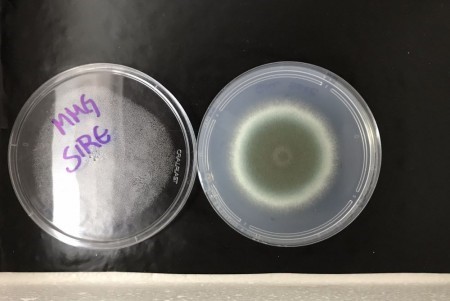
The researchers are now looking for a molecule that inactivates the protein expressed by the gene as a basis for a drug that could complement existing medications, which are not always effective and can have adverse side-effects.

The MoU is the first cooperation agreement between NIH and a foreign partner to cover a wide array of research areas.