


An analysis of scientific papers published in a 15-year period on molecular methods to identify elasmobranch species shows that better detection of illegal trade has not enhanced protection.

A study conducted in a medium-sized city in São Paulo state (Brazil) found that chikungunya, which has caused major epidemics in several countries, can also circulate silently in a community, with few infections for years. The researchers produced a new profile of this arbovirus, underscoring the importance of disease surveillance to predict and prepare efficiently for epidemics.

With simple audio messages and images, the Viva Vida program produced significant improvements in over-sixties living in a major city in metropolitan São Paulo (Brazil). An article on the study is published in Nature Medicine.
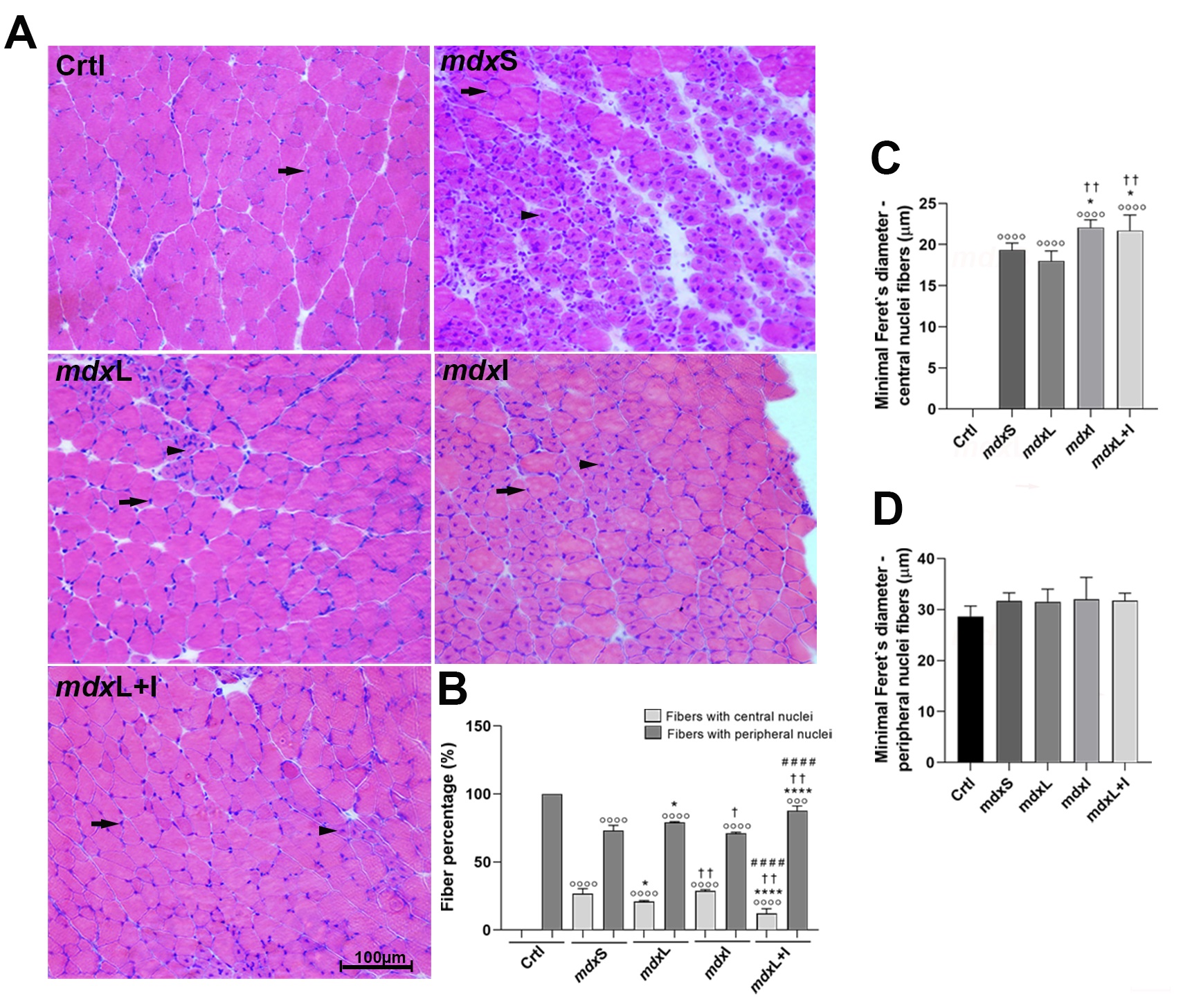
The use of photobiomodulation and an antioxidant drug called idebenone strengthened the regenerative capacity of muscle fibers in an experimental model, a study conducted at the State University of Campinas shows.
A startup supported by FAPESP is using AI to detect chronic diseases by analyzing ordinary blood tests.
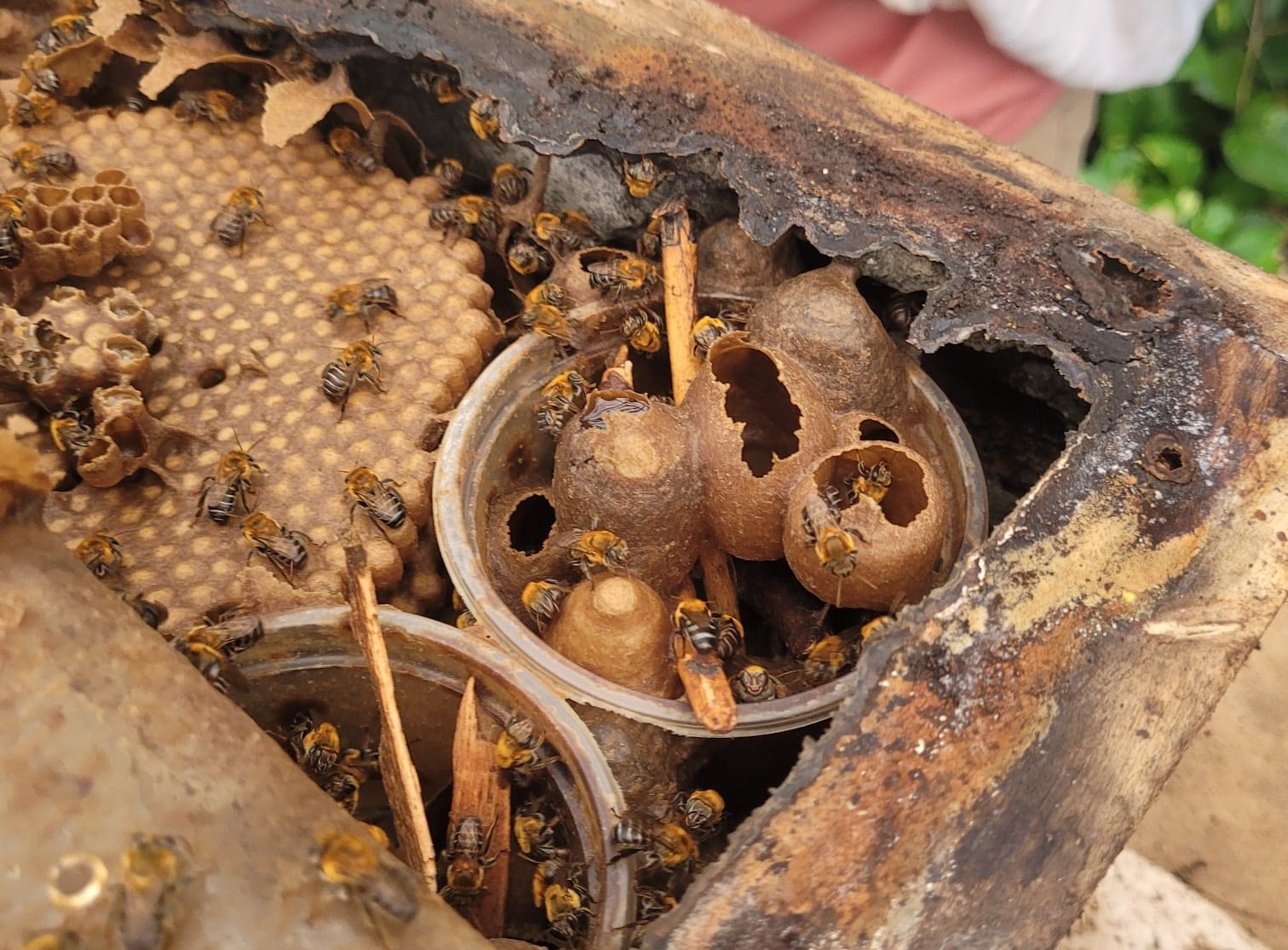

After 48 hours of exposure to the pesticides imidacloprid, pyraclostrobin and glyphosate, stingless bees of the species Melipona scutellaris exhibited morphological and behavioral alterations that could weaken colonies, impair pollination and adversely affect food security.

One of the fishing methods used to collect electric fish in the DEGy Negro River Expedition was employed for the first time on a large scale in freshwater during the Calhamazon project, which brought together researchers from Brazil and the United States between 1993 and 1996.
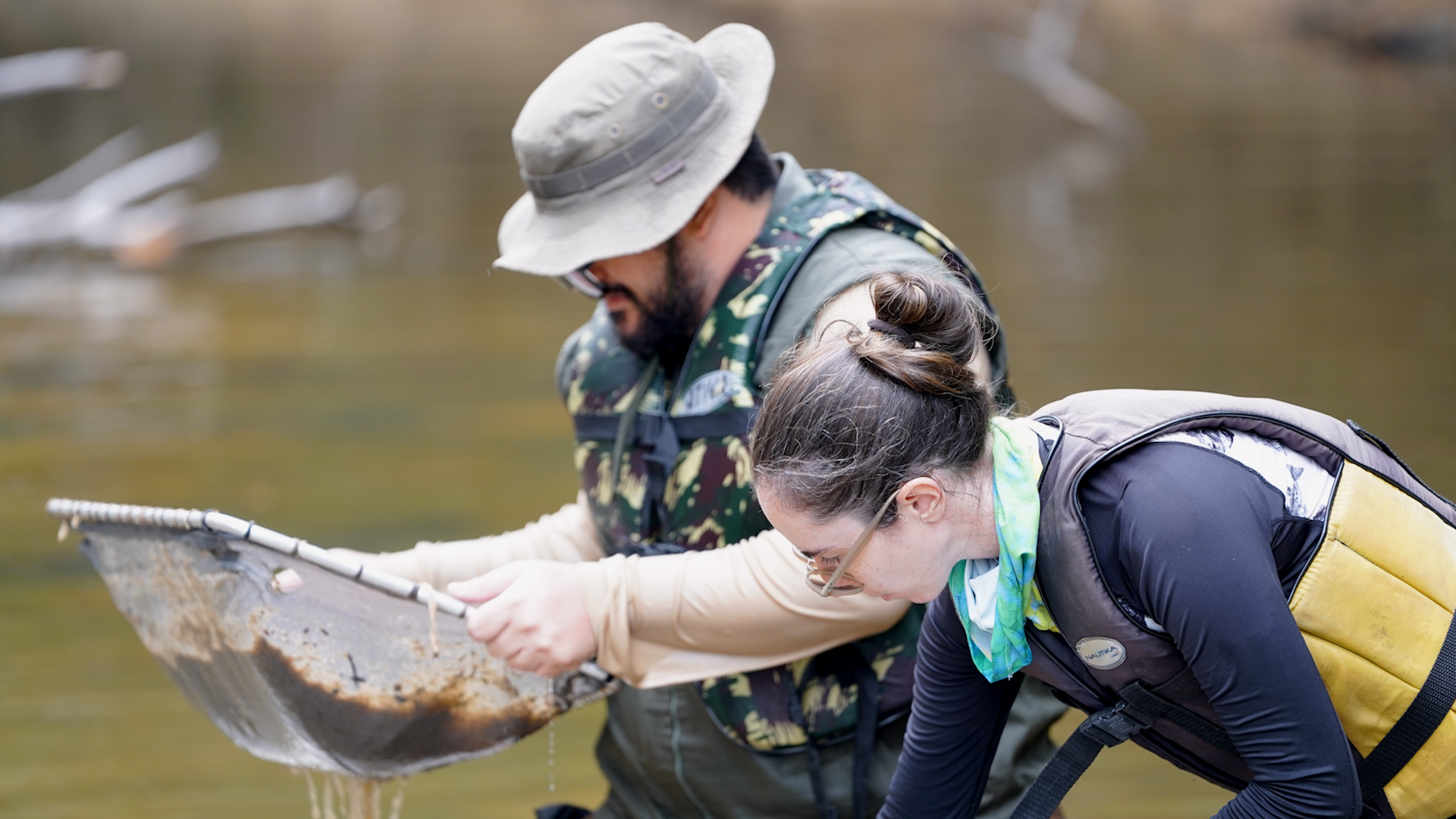

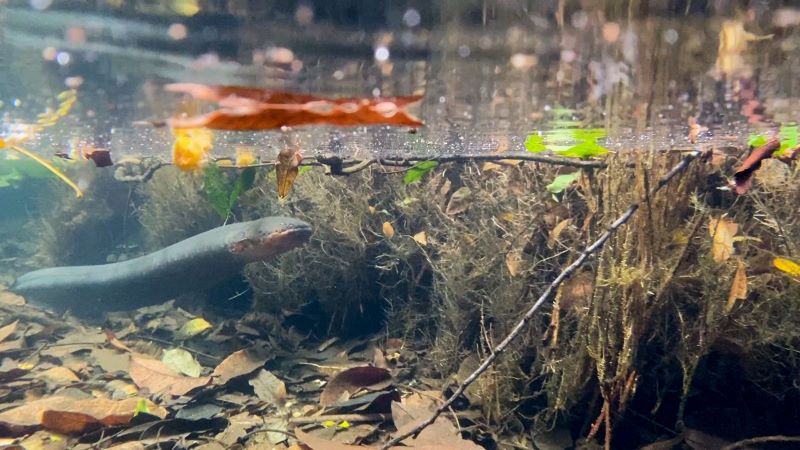
The most abundant electric fish are found from the bottom of large rivers to igarapés, where they can bury themselves in the sand or blend into the leaf litter. In two weeks, an expedition in the Negro River basin collected 27 species of the group.

A species from the Negro River basin uses the spaces between the roots and hollows of trees to build nests and care for its young for four to six months, leaving only at night to hunt.
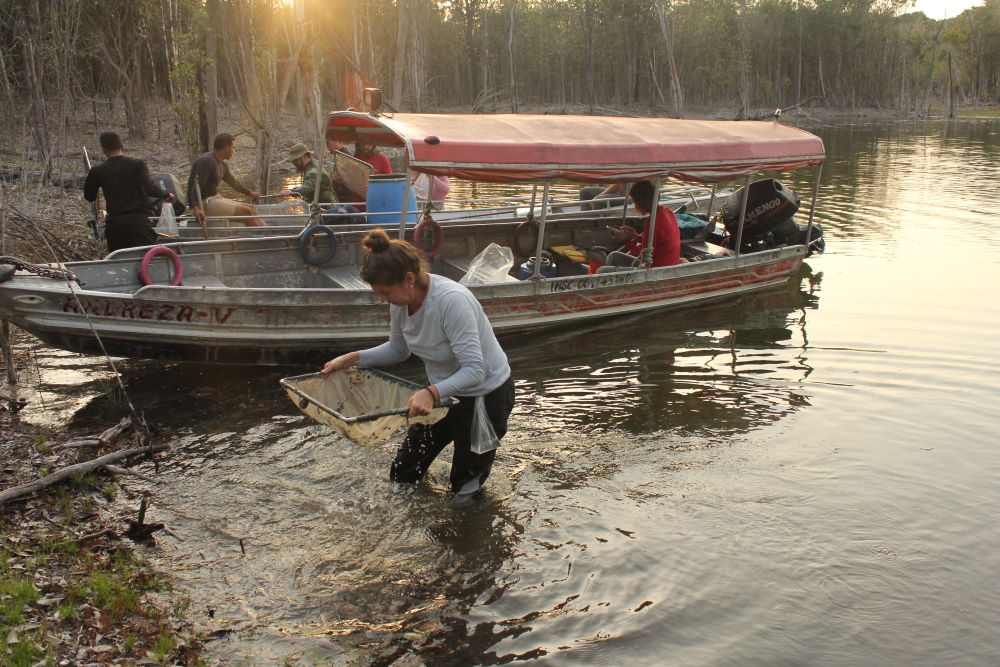

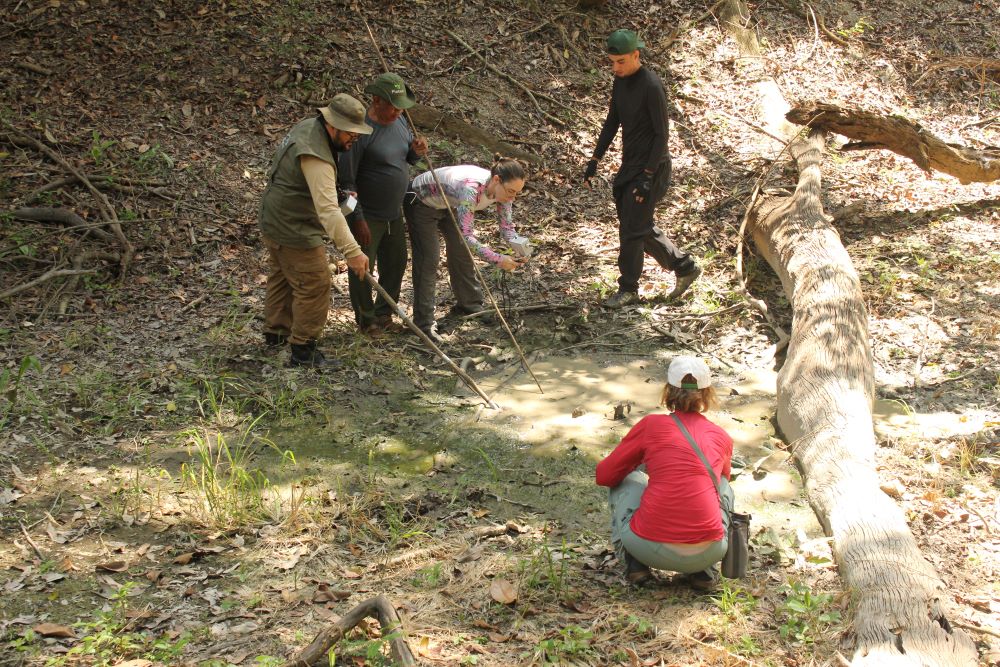
Historic drought in the Negro River basin and a possible inaccurate description of the distribution of Iracema caiana may be reasons why the species was not found by the DEGy Negro River Expedition. The episode describes the first collections.

In preparation for the expedition down the Negro River in search of fish of the order Gymnotiformes, researchers gather more than 200 kilos of equipment and supplies for detecting, collecting and storing specimens.

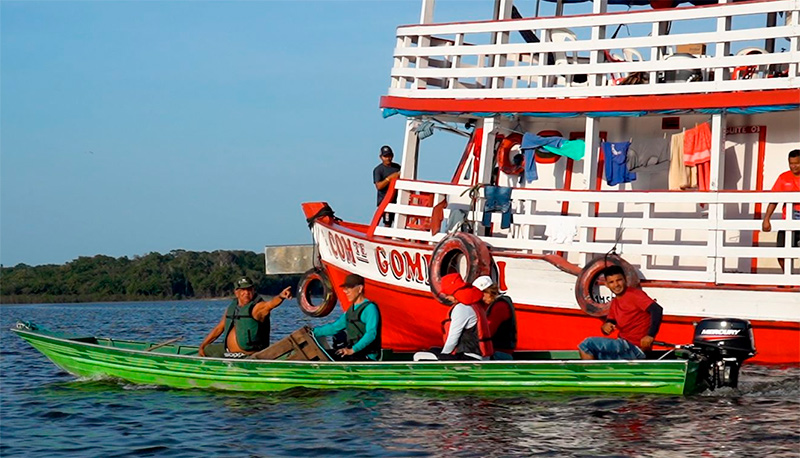
For two weeks, scientists from the University of São Paulo collected specimens of poraquês and other fish of the order Gymnotiformes aboard the vessel Comandante Gomes. The Agência FAPESP report followed the work in the field.
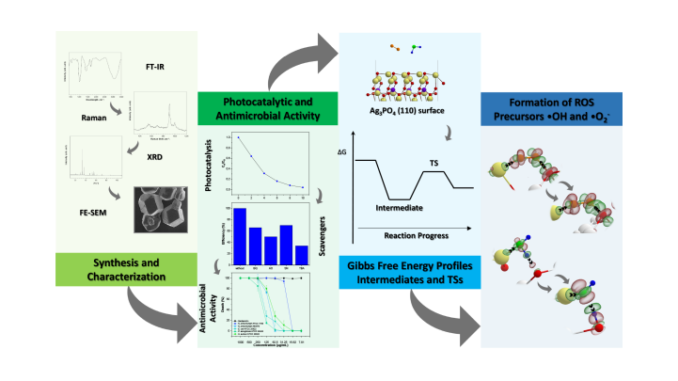
Experiment with the semiconductor silver phosphate revealed an unprecedented mechanism for the formation of reactive oxygen species – toxic molecules that can cause the death of pathogens.
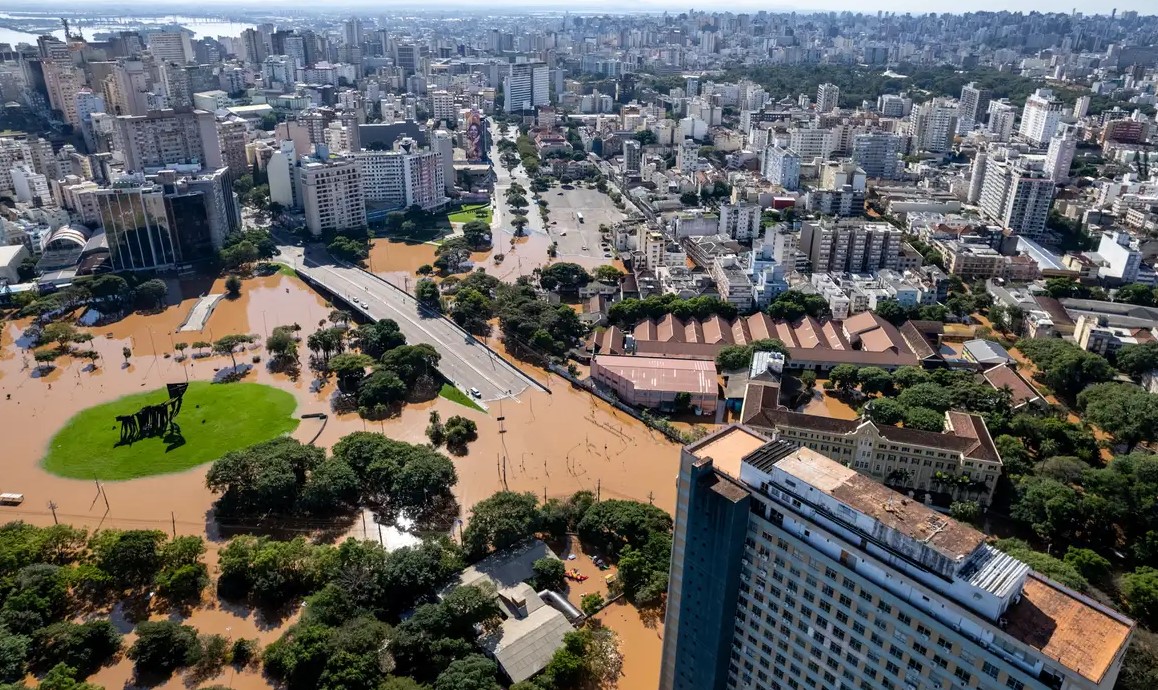

An analysis of data from weather stations shows that large contiguous areas of the region have seen more days of extremely heavy rain in the past seven decades.
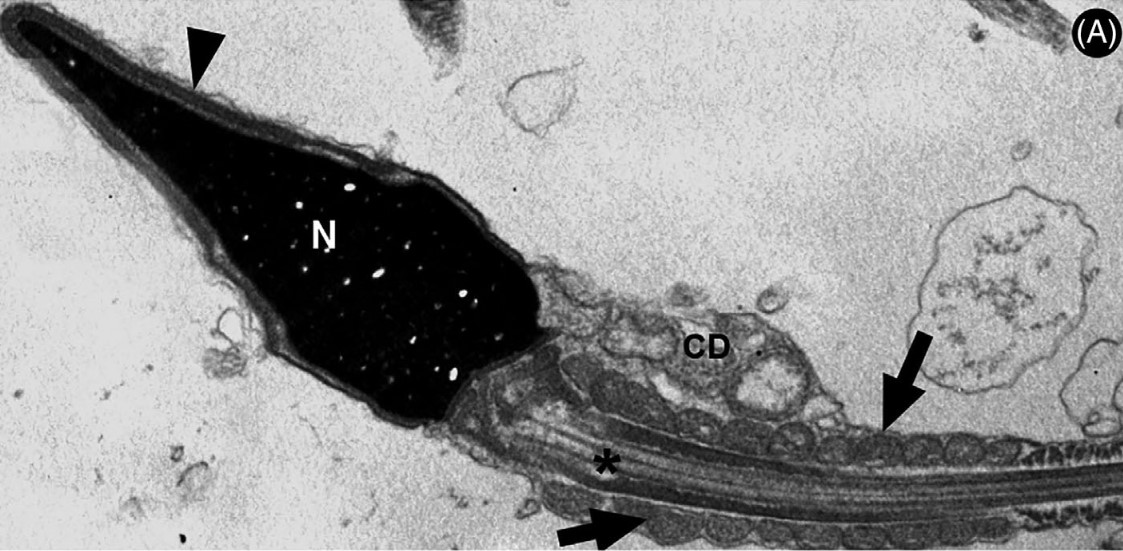
Researchers detected SARS-CoV-2 in male reproductive cells under the microscope even when PCR testing failed to detect the virus in semen. The discovery serves as a warning of possible implications for natural conception and particularly for assisted reproduction.
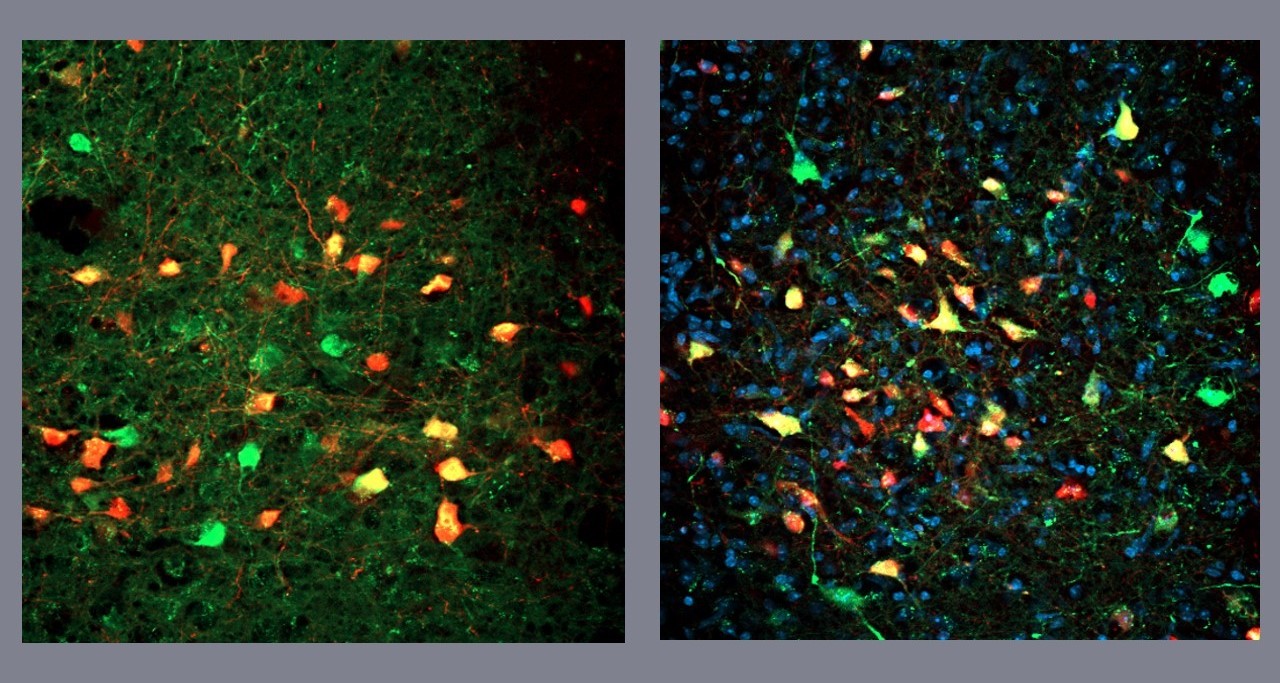
In a study involving mice, scientists used a technique that combines light stimulation and bioengineering to activate a cluster of nerve cells deep inside the brain. The discovery could pave the way to future treatment of eating disorders.
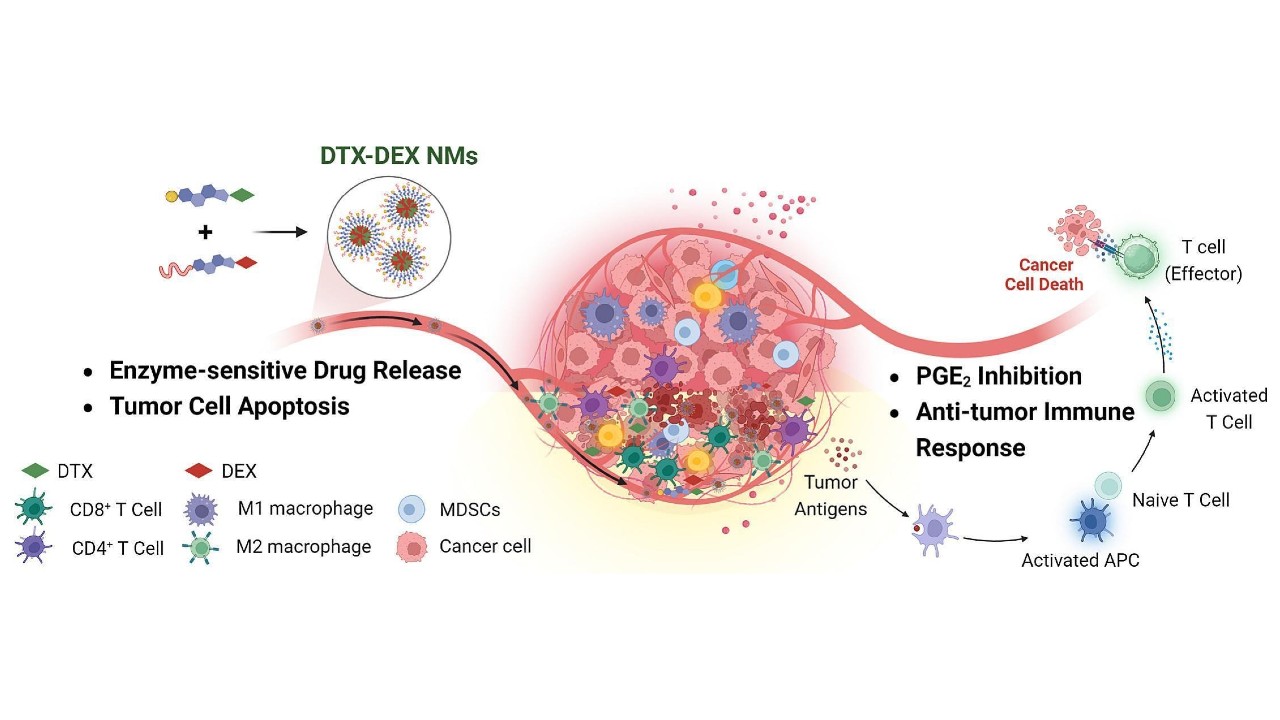
In tests involving animals, nanoparticles containing substances already approved for human use reduced inflammation in the biological microenvironment where malignant tumors flourish and facilitated the action of the immune system.
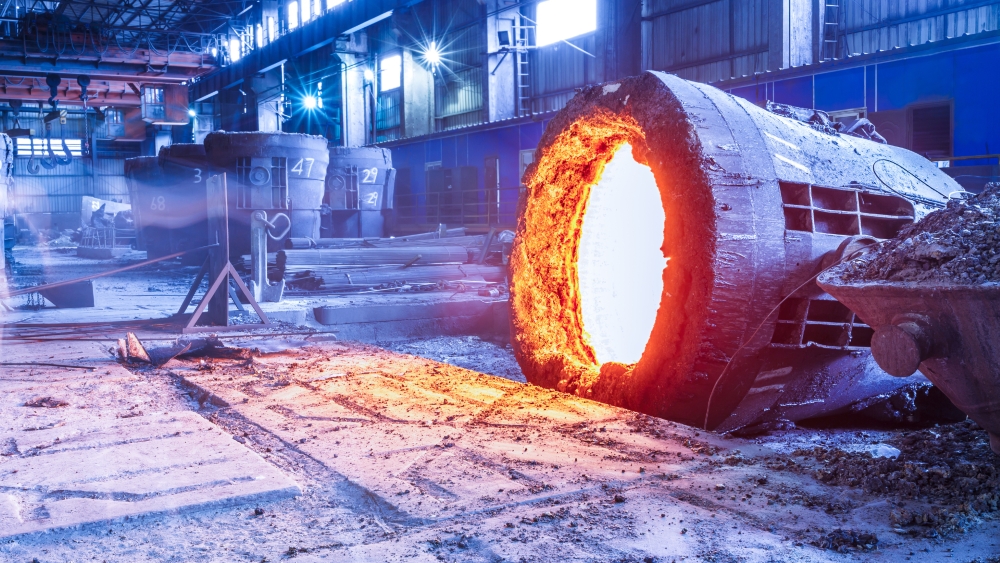

A startup supported by FAPESP is developing a system to assure the proper use of elements capable of guaranteeing structural integrity at high temperatures while reducing heat transfer from machinery and equipment to the environment.
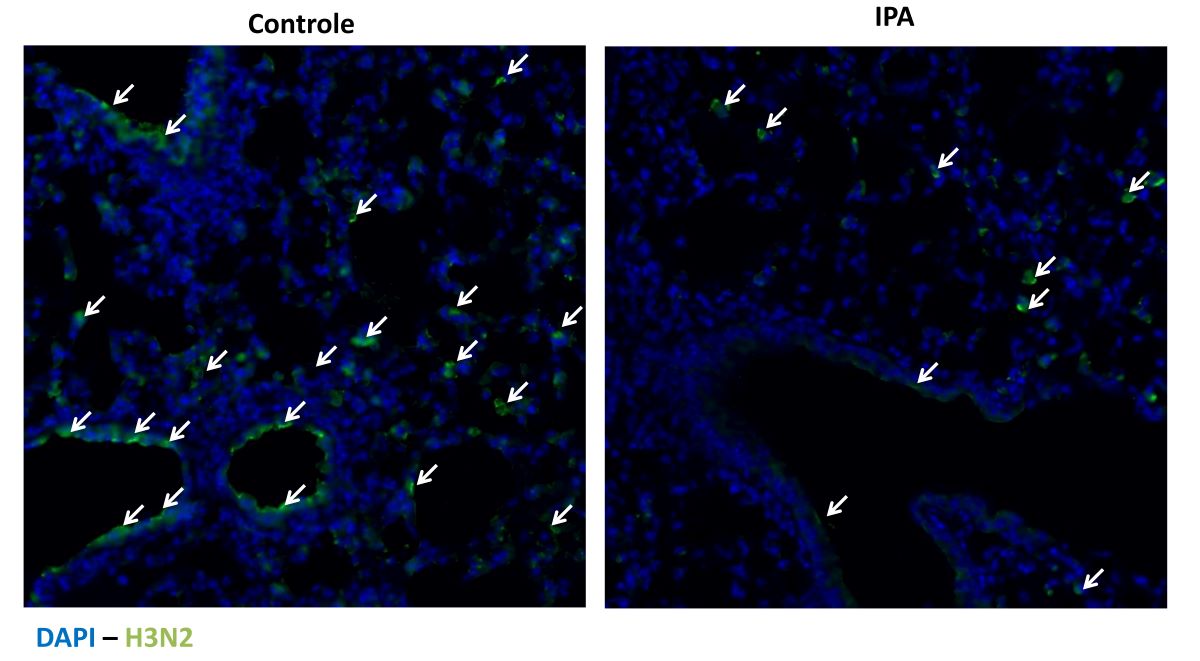
In experiments with mice, researchers at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in Brazil and the Pasteur Institute in Lille (France) found that viral load and inflammation decreased in animals infected by influenza virus when they were given the substance.
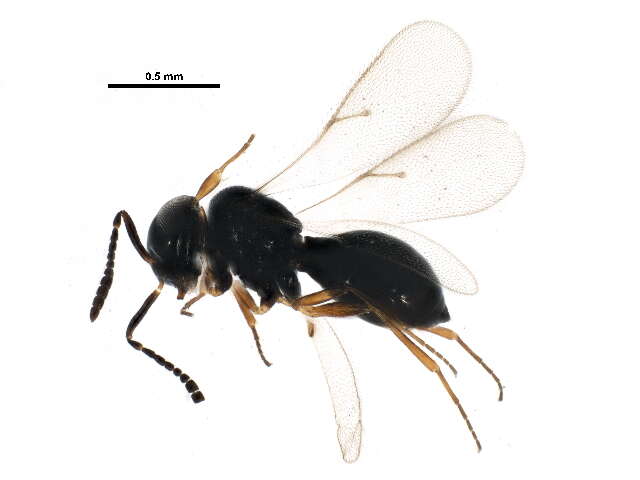

Scientists at São Paulo State University (UNESP) and Oklahoma State University (OSU) verified in the field that a parasitoid wasp that neutralizes the Brown stink bug should ideally be released at intervals of 30 m.
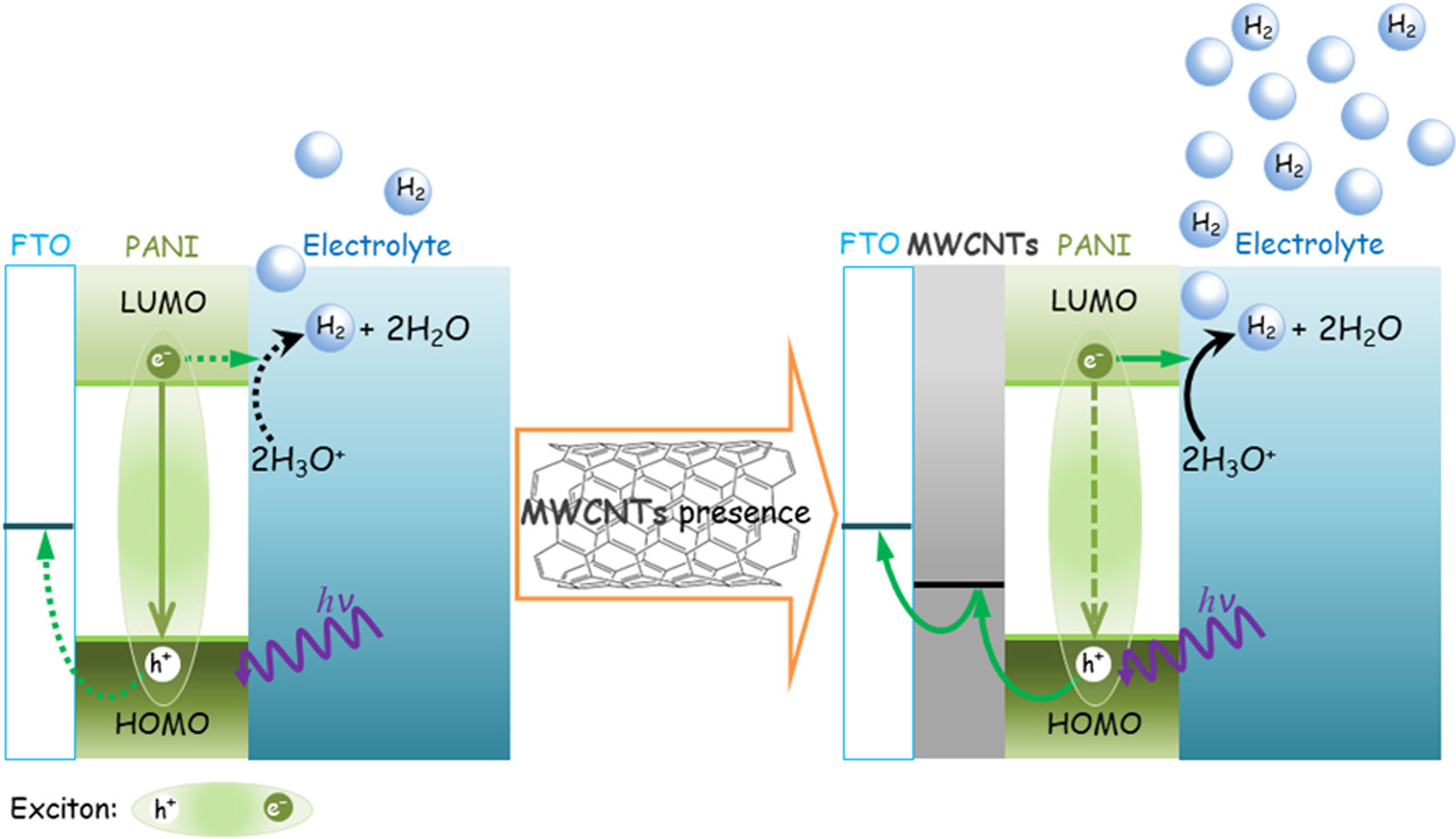
A study supported by FAPESP produced films comprising polyaniline nanostructures with a carbon nanotube underlayer.

The first Research, Innovation and Dissemination Center (RIDC) hosted by São Paulo State University (UNESP) will promote innovation focusing on sustainable solutions and accelerated knowledge dissemination.

In an article published in Nature Metabolism, researchers based in Brazil and Mexico analyze the Latin American obesity epidemic from a broad perspective that includes socioeconomic, cultural and epigenetic factors. For the authors, solutions must focus on collective action rather than individualization of the problem.
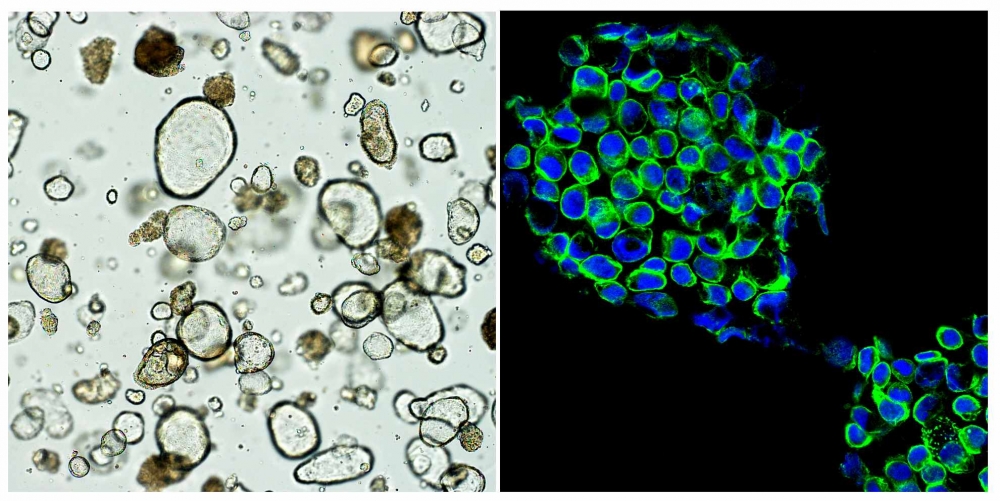
A startup supported by FAPESP is developing a methodology that will give oncologists more precise information to help them choose the best therapeutic approach.

A delegation from INRAE visited FAPESP to discuss common areas of interest in scientific collaboration.