


An agreement to this end was signed in Belém in the Brazilian Amazon during the visit of French President Emmanuel Macron and Laurent Linguet, President of the University of French Guiana. The aim is to foster international cooperation that furthers the development of the Amazon region.

FAPESP signed a memorandum of understanding to fund projects that will be conducted at the IRC.

The new member of the Pasteur Network, which comprises 33 laboratories in 25 countries, is being equipped with the support of FAPESP, which is also funding several young researchers associated with the institute.

Brazilian researchers analyzed more than 200 articles on the subject and identified the types of training most indicated for these cases. Their findings are reported in the journal Psychiatry Research.

In Brazil, researchers analyzed data for 8,384 clinical appointments that took place in a two-year period at Hospital de Base in São José do Rio Preto (São Paulo state) and found the situation to be similar to those in publicly-funded psychiatric outpatient clinics elsewhere in the country. The results, reported in Frontiers in Psychiatry, list the most common mental health problems and most frequently prescribed drugs.
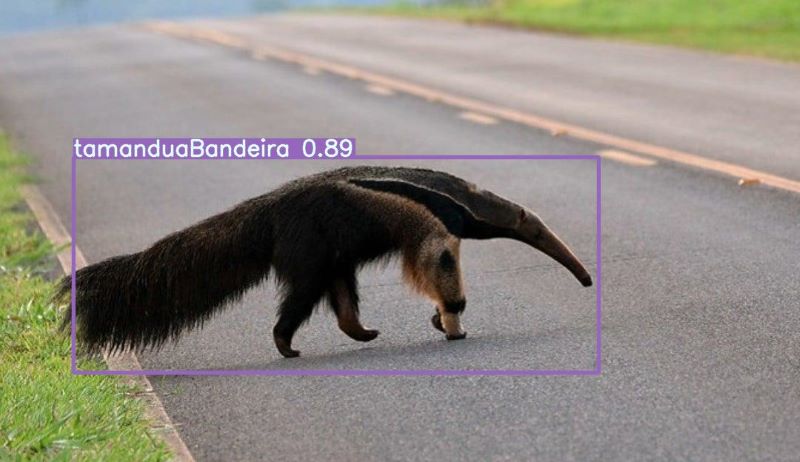

The researchers trained computer vision models to identify Brazilian mammals must susceptible to roadkill in real time and are partnering with toll road operators to test the system in real-world situations.
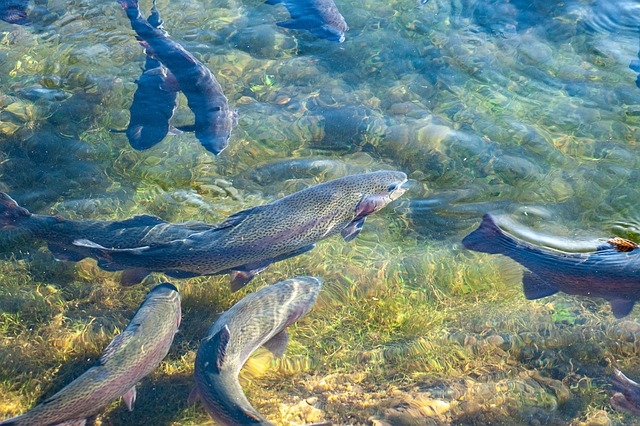

A startup supported by FAPESP has developed a solution to prevent disease in fish tanks by means of environmental monitoring.
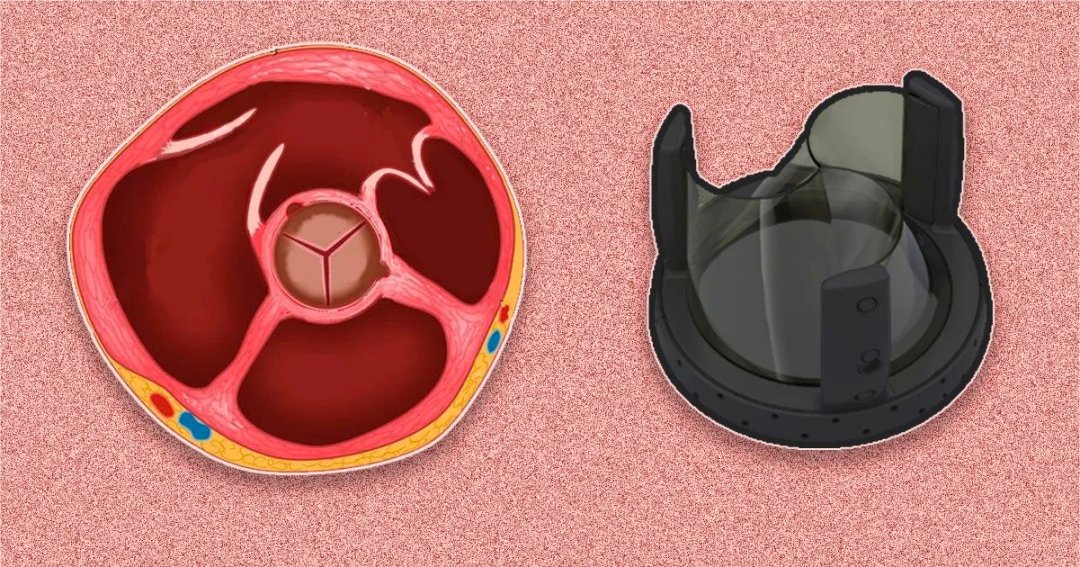
Study developed at Center for Mathematical Sciences Applied to Industry aims to perfect device for cardiovascular treatments.
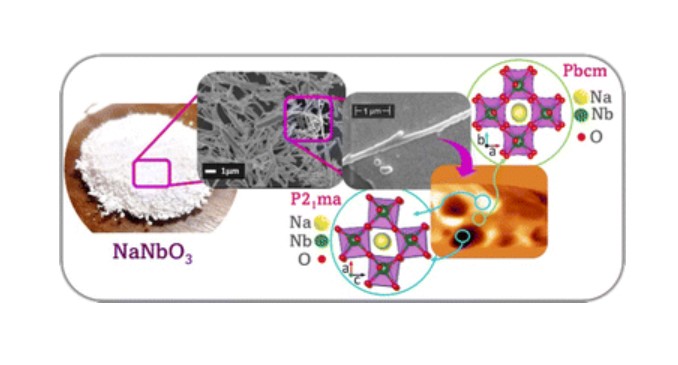
Sodium niobate is a type of ceramic with properties of interest to green chemistry; scientists from the Center for the Development of Functional Materials and collaborators have developed a new strategy for obtaining it.

The Brasillinois program, which will be launched this month during FAPESP Week Illinois in the United States, aims to promote student and faculty mobility and foster connections in areas such as climate and sustainability, medicine, public health, and social inclusion.

For the first time in South America, researchers recorded the use of ultrasound by a frog endemic to the Atlantic Rainforest in Brazil, which has more species of amphibians than any other country. Other frogs may use very high-frequency calls for the same purpose.
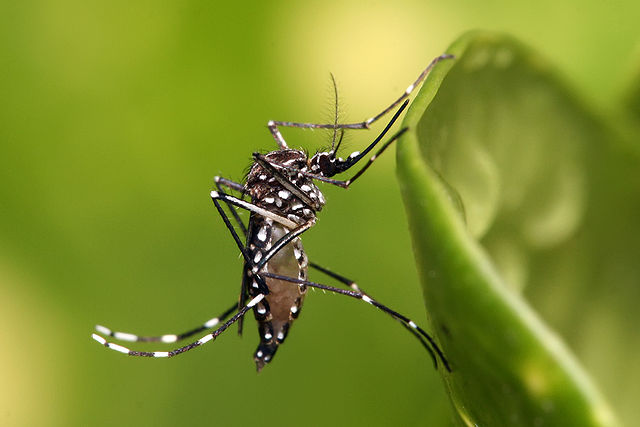

The number may be an underestimate in light of gaps in studies of the problem, according to the authors of a report issued by the Brazilian Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services.
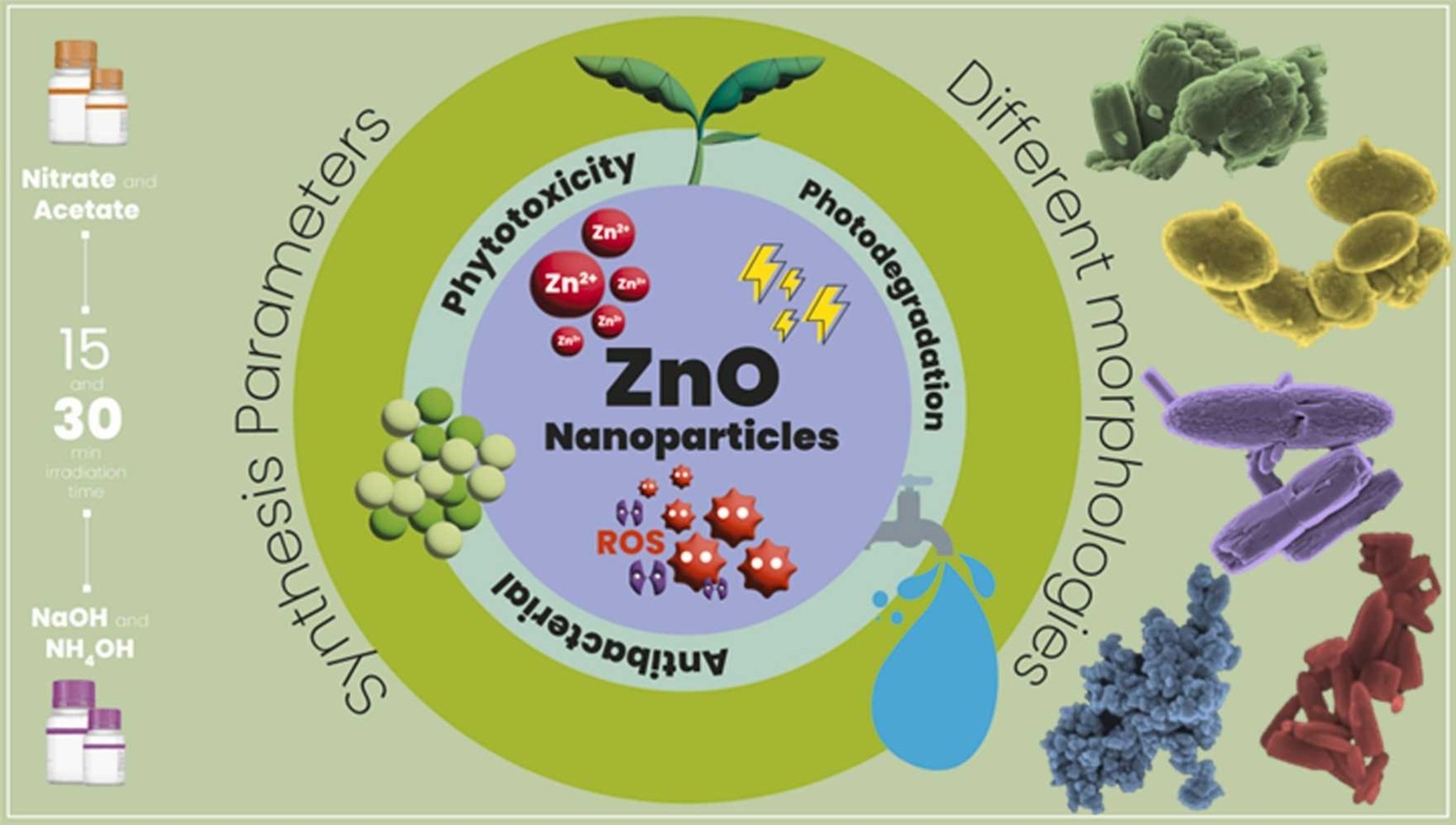
Zinc oxide nanoparticles with varying morphologies were tested against microorganisms isolated from patients. The results are reported in the Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.
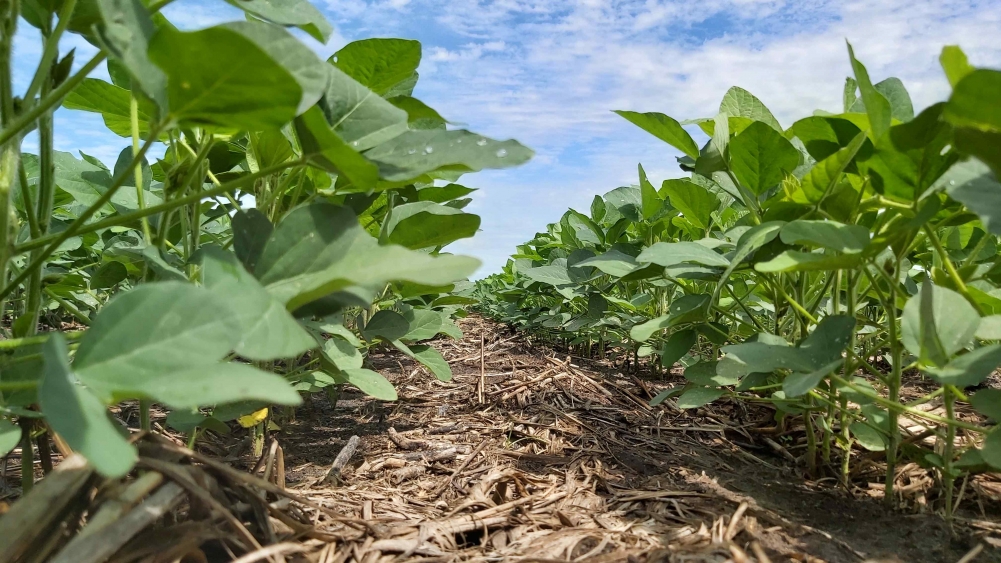

A startup supported by FAPESP is developing novel cultivars to offer growers a high-value-added option.
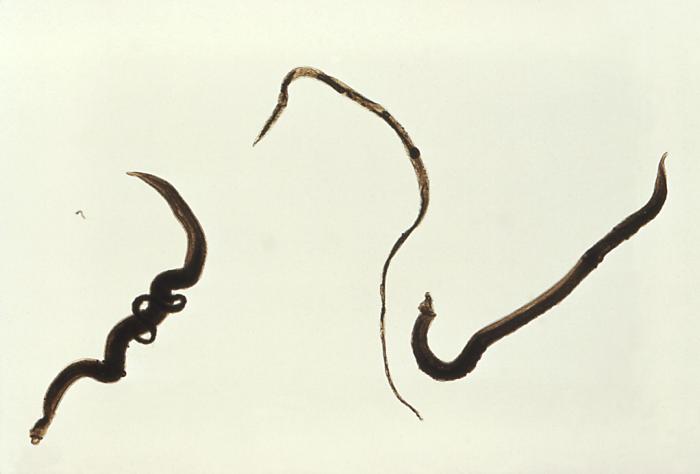

Experiments conducted at Butantan Institute in São Paulo used phage display to screen 12,000 proteins found in Schistosoma mansoni, the worm that causes the disease. The method deployed bacteriophages, viruses that infect bacteria, to identify key parasite peptides.
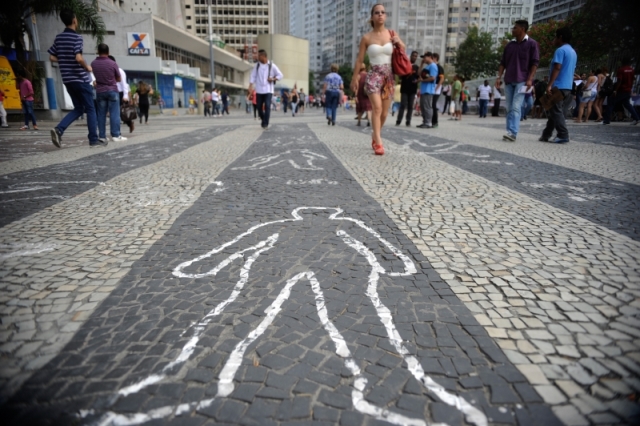

With the support of FAPESP, the research is developing mathematical and computational tools that will address issues related to public safety in an innovative way.
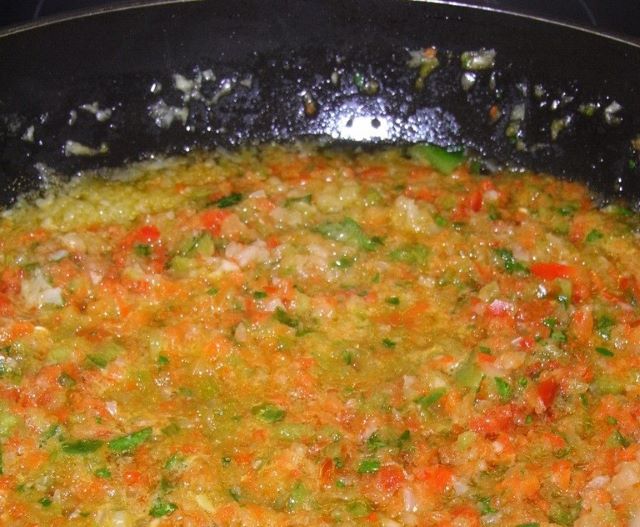

The health benefits of the so-called “sofrito” were observed in experiments with rats conducted by scientists from the Food Research Center and collaborators. The effect may be linked to a compound identified in the animals’ livers called butanediol.
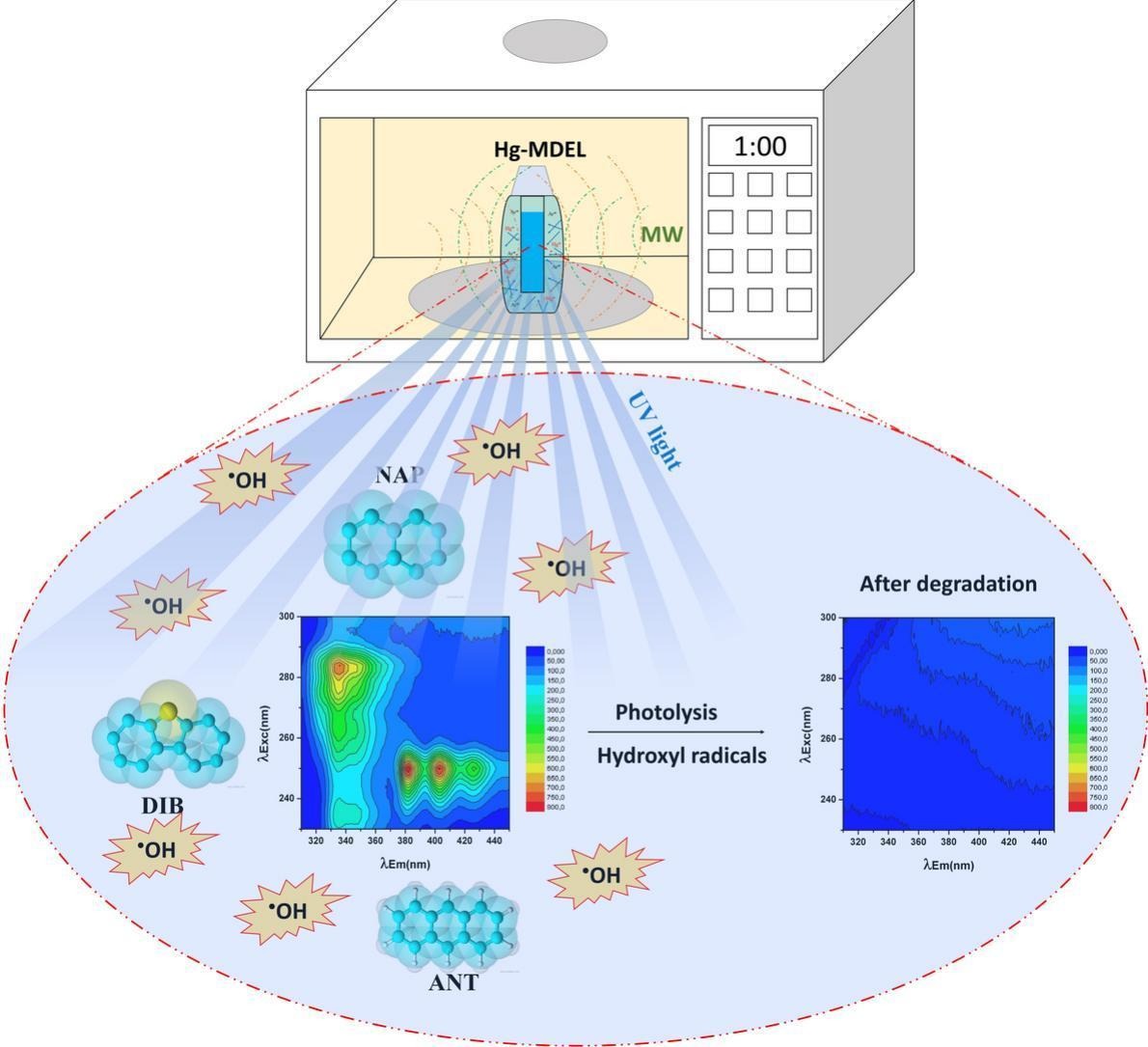
Brazilian scientists tested a simple and sustainable method for monitoring and degrading a mixture of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, compounds present in fossil fuels and industrial waste.
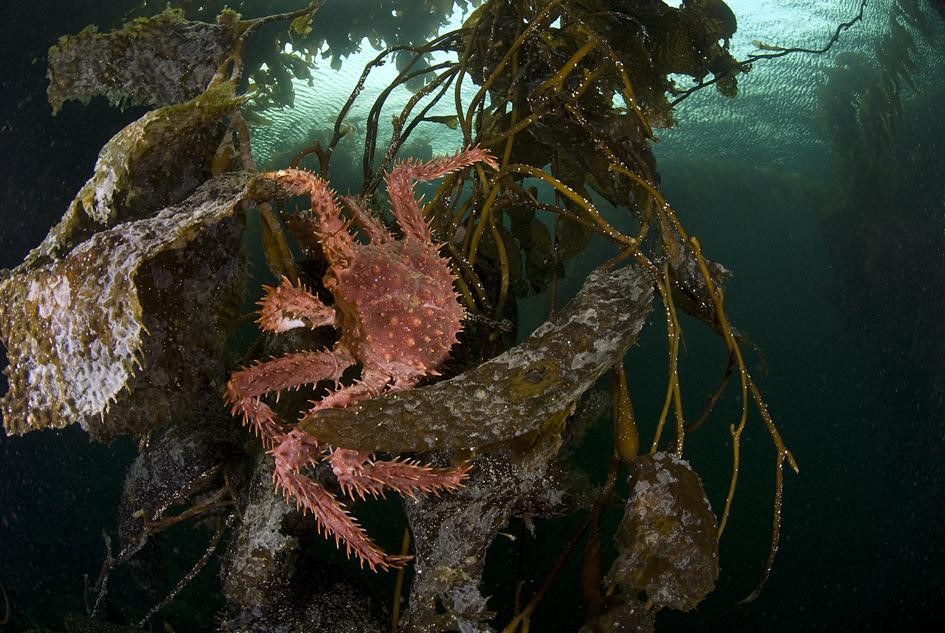

Working in partnership with scientists at the University of Magallanes in Chile, Brazilian researchers are conducting studies of the Chilean subantarctic region.
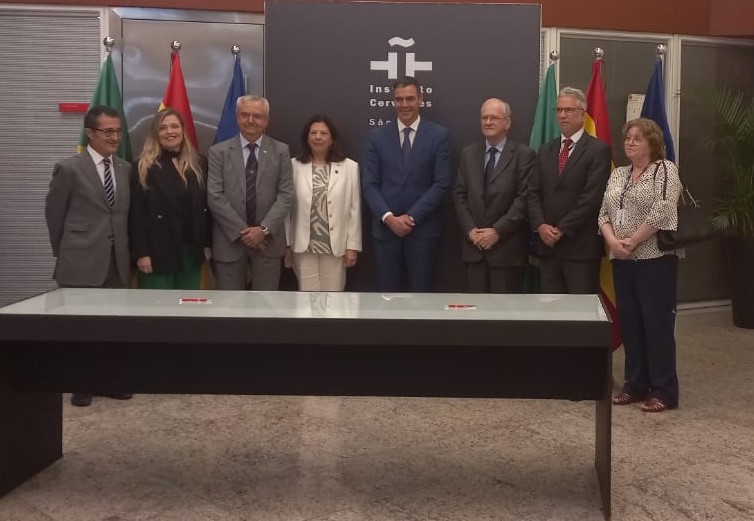

Pedro Sánchez, Prime Minister of Spain, was present at the ceremony in São Paulo where the MoU was signed by the Spanish ambassador to Brazil and the President of FAPESP.
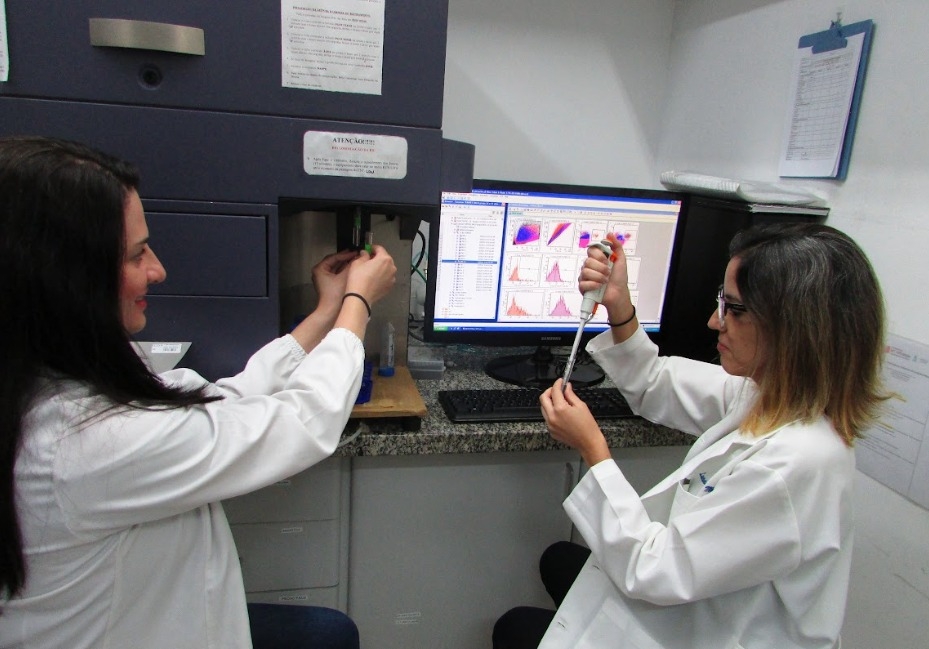

Developed by ImunoTera as part of a project supported by FAPESP, the molecule triggers the immune system’s response to infected cells and helps combat the disease.
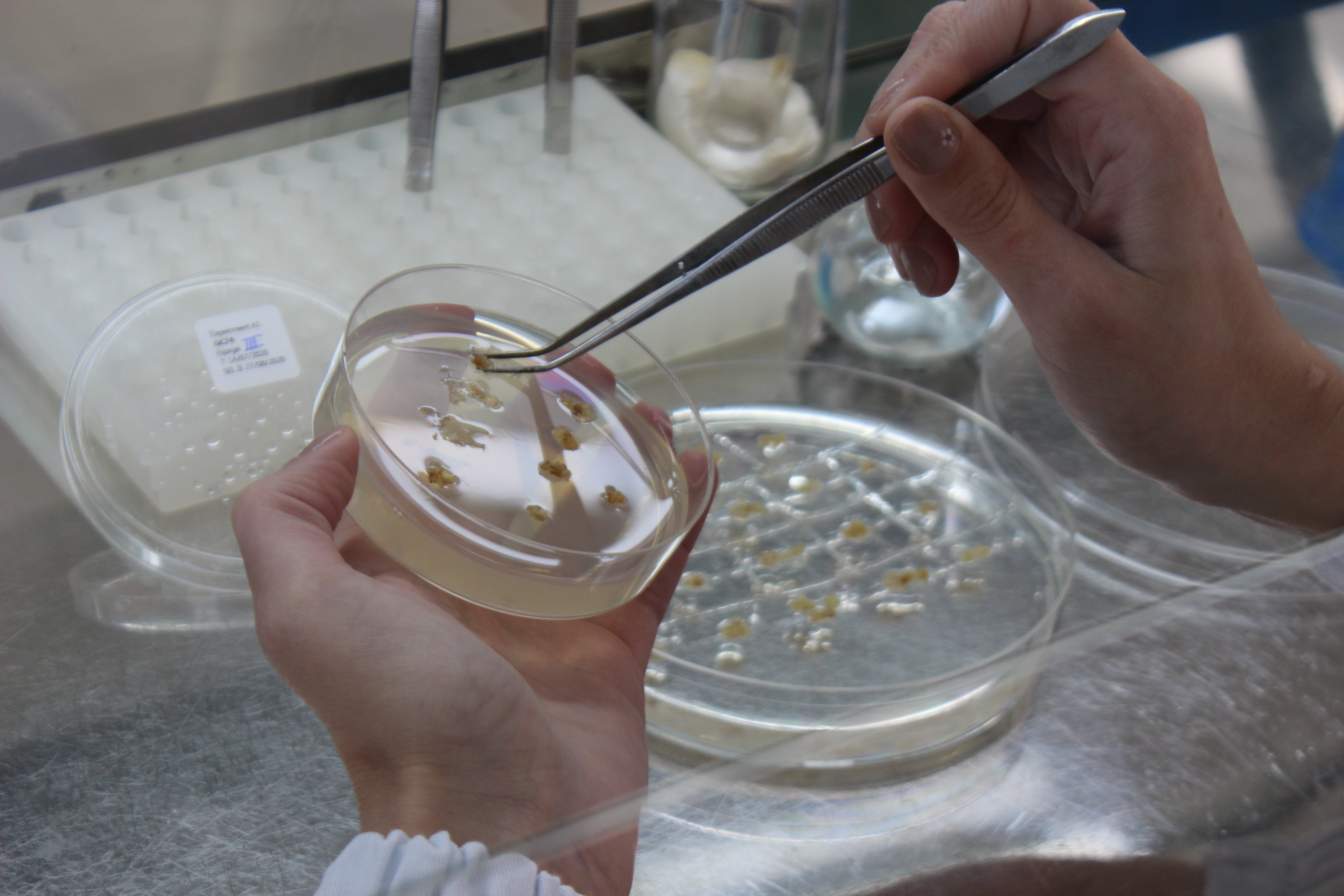

Three of the five tropical strains were successfully transformed using the morphogenic gene expression strategy, achieving efficiency rates three times higher than the average of the protocols.
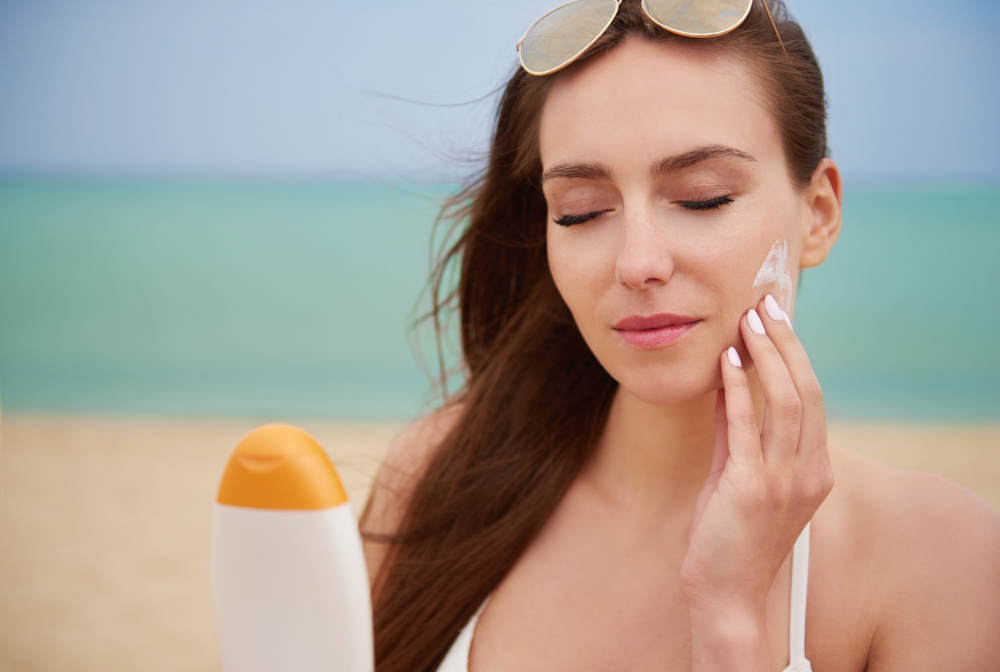

Developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo, the process proposes using silica particles coated with melanin in formulations to protect the skin not only from UVA and UVB rays, but also from visible light.
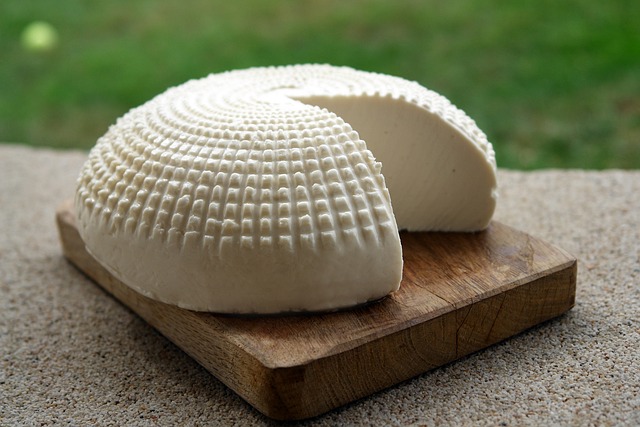

The proposal is being analyzed by an inspection body in the state of São Paulo. In this region alone, there are more than 1,200 informal producers of milk and dairy products with the potential to be regularized.

The Global Technology Hub, launched at COP28, will promote decarbonization projects and financing. The goal is to enable developing countries to achieve net-zero emissions.