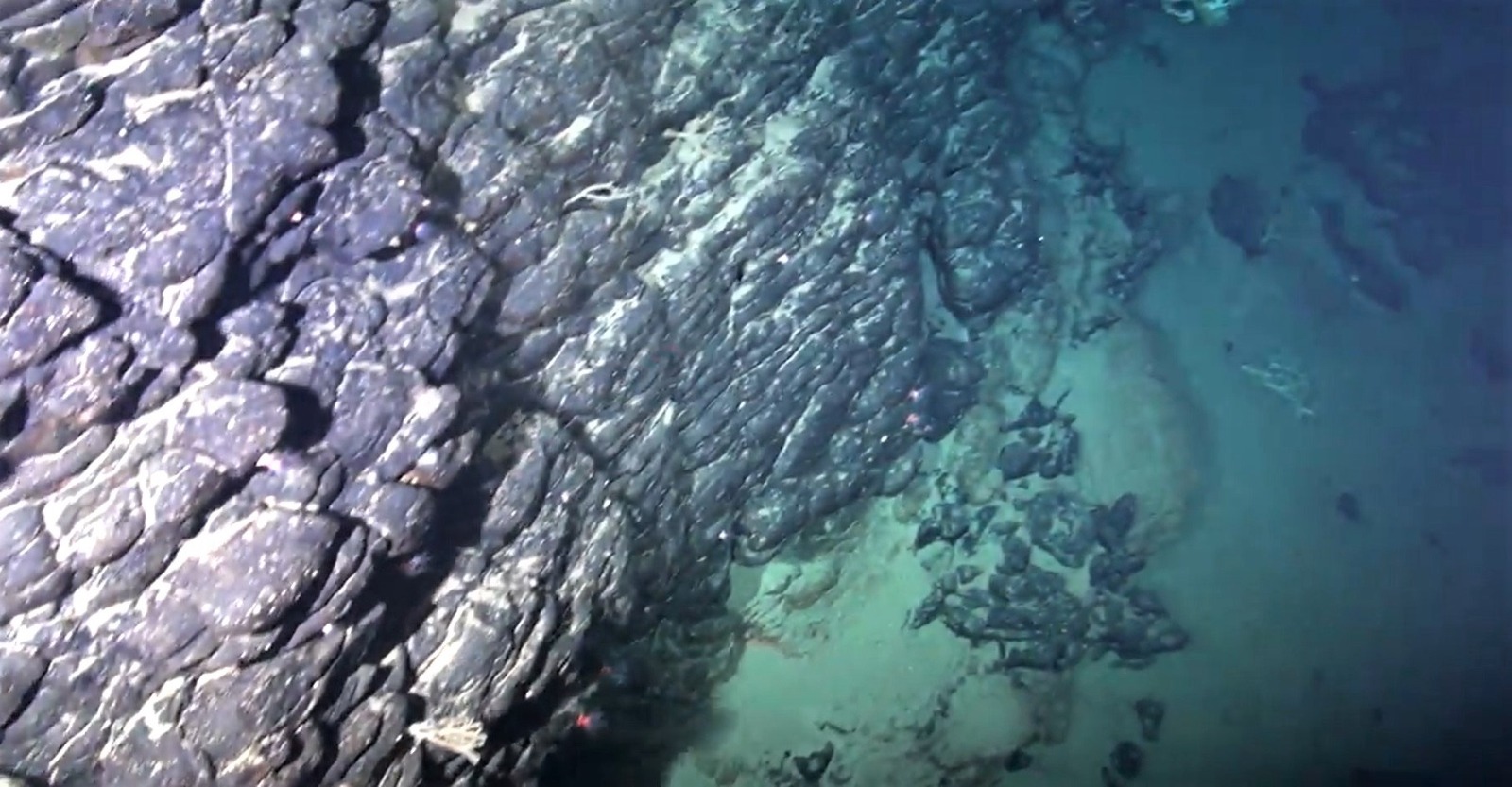



This part of the seafloor in the South Atlantic is rich in cobalt, nickel and lithium, as well as tellurium and other rare earths critical to the energy transition. The scientists plan to continue research on its natural processes as a contribution to prospecting efforts.

Developed by a team of Brazilian researchers, the device is made of plant-based material with little environmental impact, and detects pesticides in a few minutes, helping to certify food safety.

In 18 cities of the Barretos region, where the proportion of Black people in the population is smaller, cancer kills more members of this ethnic group, whereas in the capital of the same state, it kills more White people, according to a study that compares cancer mortality rates and points to ways of reducing inequalities in diagnosis and treatment.
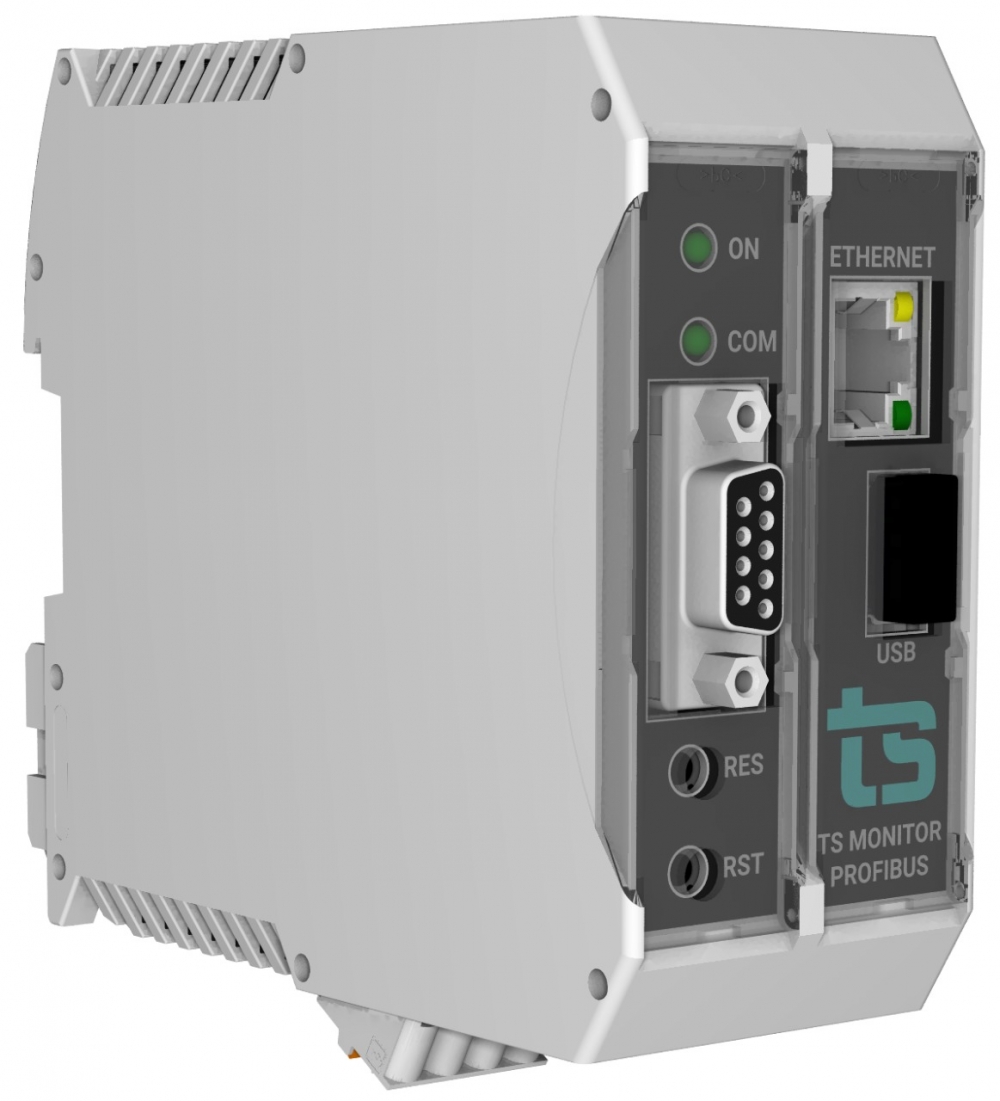

The platform, developed by a company based in São Carlos (São Paulo state, Brazil) and supported by FAPESP, is able to predict and permit correction of failures in order to avoid unplanned factory production line downtime.
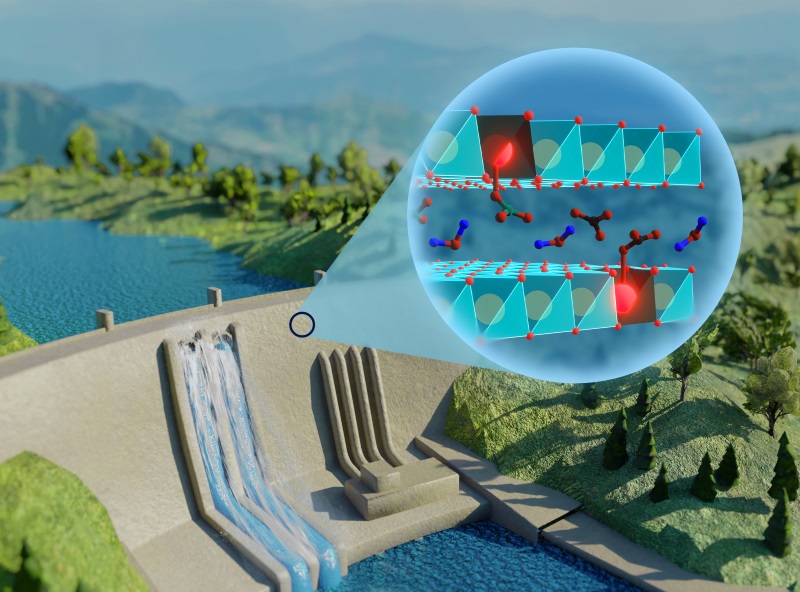
The material is a compound similar to clay and enables inspectors to carry out in-situ assessment of structural conditions in buildings, bridges, dams and other structures without having to drill for samples and analyze them in a laboratory.

The two parties are interested in collaborative research on sustainable use of biodiversity in the Amazon, prevention of transmissible and chronic diseases, and sustainable construction, among other subjects.

In experiments with rats, researchers at the University of São Paulo analyzed brain tissue and detected alterations in genes associated with energy metabolism.
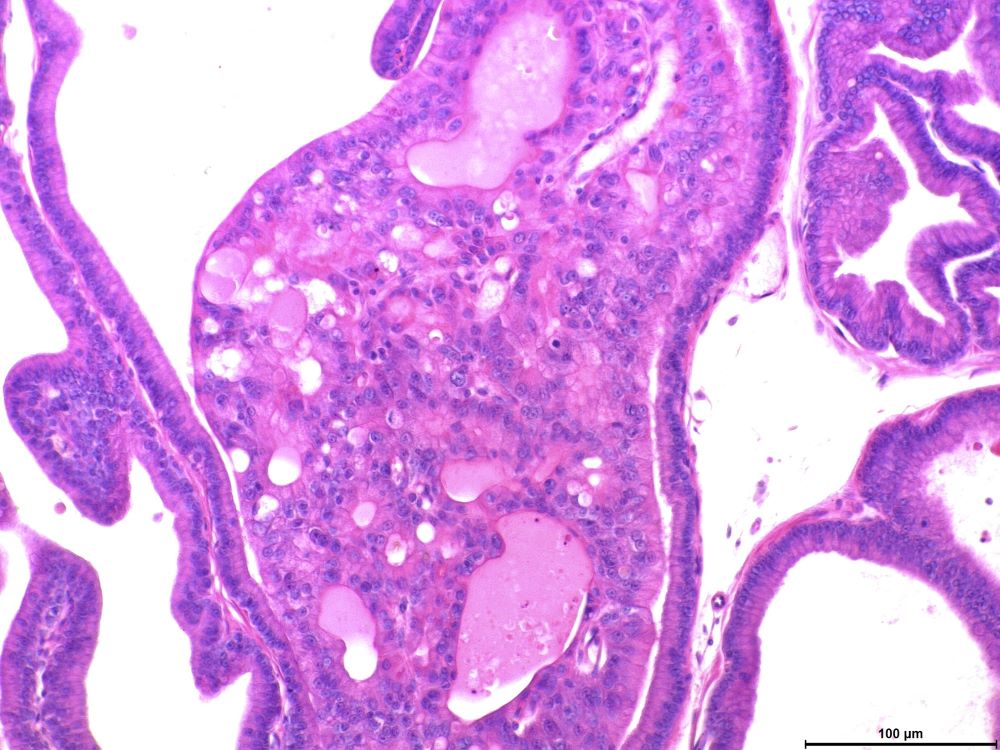
In experiments with rats, researchers at São Paulo State University detected changes in the expression of more than 700 genes in offspring. One of these genes is known to be associated with prostate cancer.

The solution, which was developed via a project supported by FAPESP, aims to help farmers assess risks and forecast future prices.
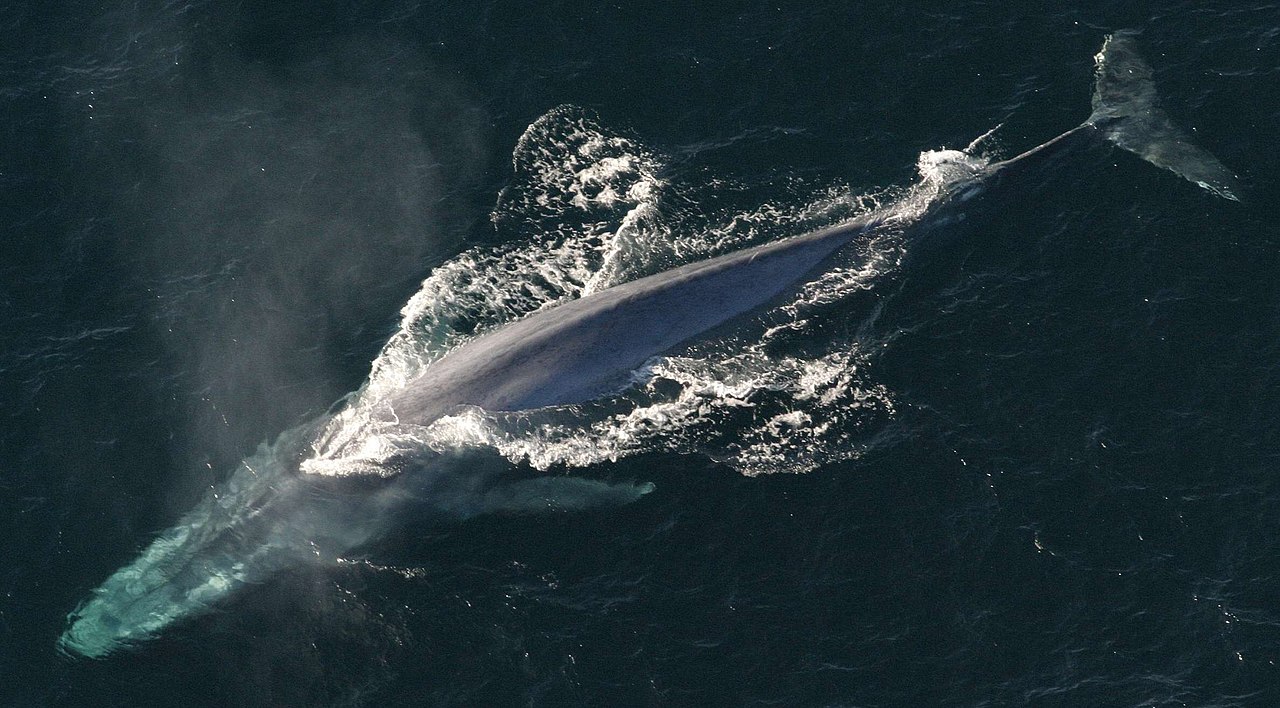

Some species of cetacean are up to 4 meters in length, while others reach 30 meters. According to researchers at the State University of Campinas, genes that favor the colossal growth of these mammals also inhibit the development of cancer.
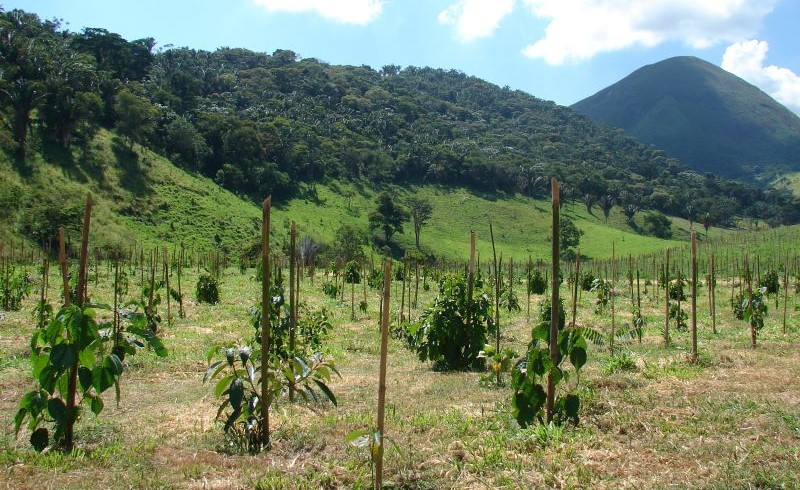

The study analyzed data for 13 Atlantic Rainforest restoration areas involving ten species of native trees that could be commercially useful to the timber industry. Publication of the findings comes during the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration.

Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore Thailand and Vietnam have dynamic economies and similarities with Brazil that make collaboration particularly relevant.

The purpose of the event was to build ties and foster collaboration between researchers in São Paulo state and the United Kingdom.
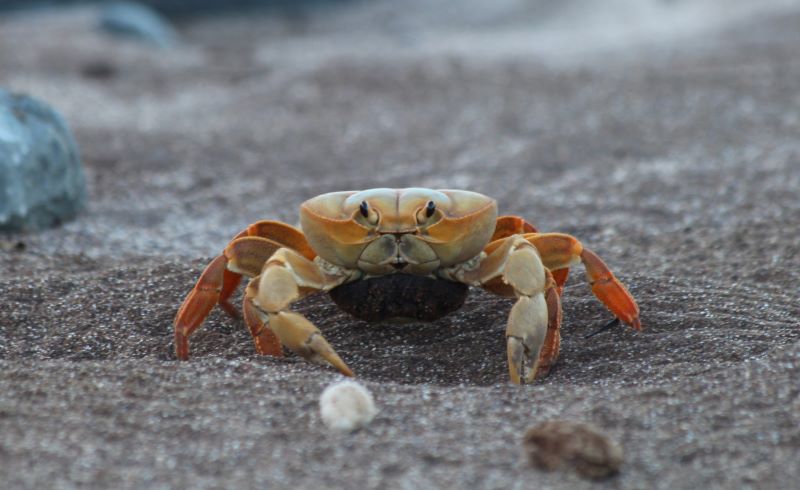

The land crab Johngarthia lagostoma occurs only on four ocean islands, three of which are in Brazil, but little is known of its natural history. Brazilian researchers discovered that a hill and beach on Trindade Island play a key role in the species’ reproductive cycle and survival.
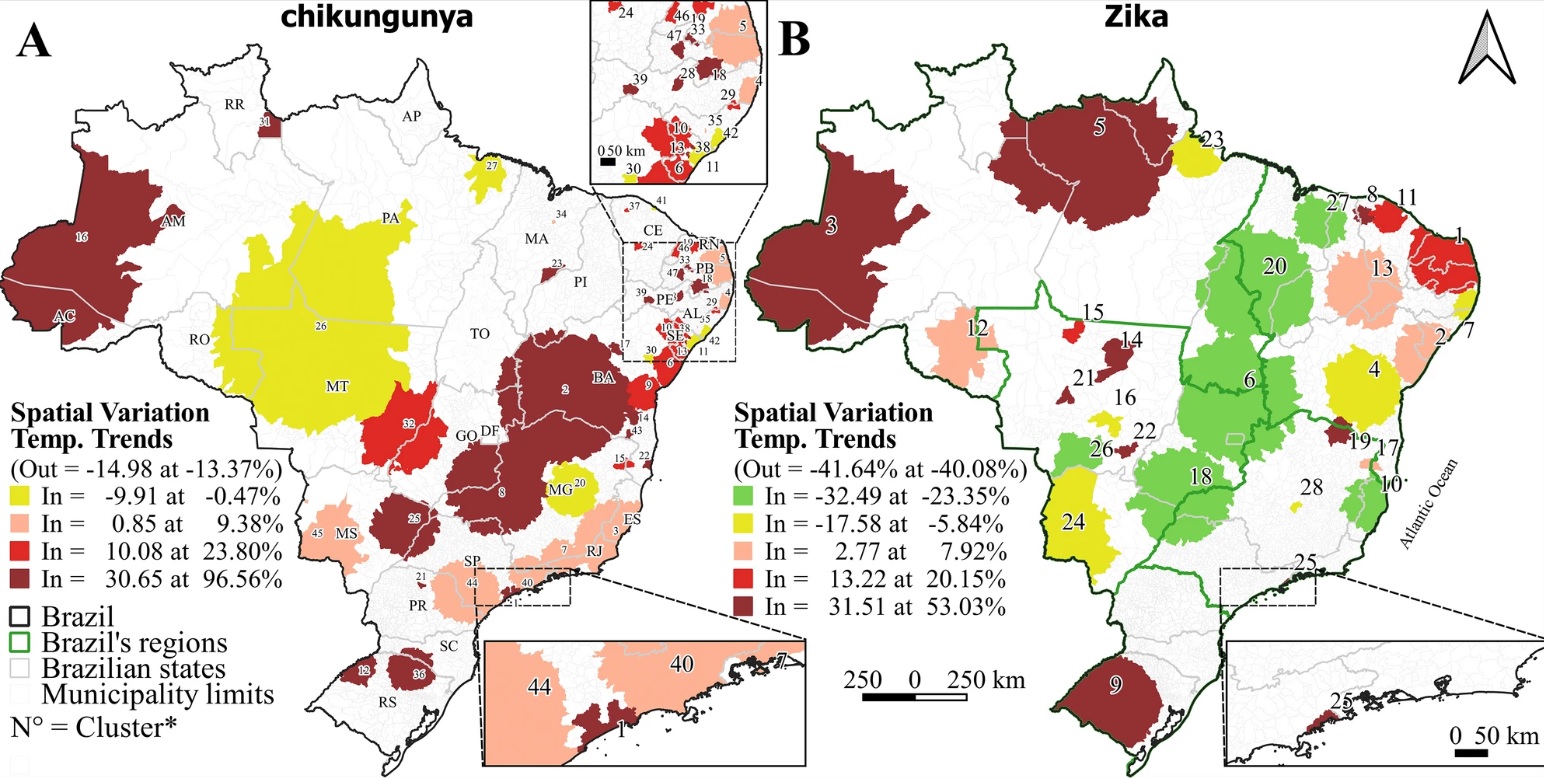
Researchers at the University of São Paulo and São Paulo state’s Center for Epidemiological Surveillance observed spatial and temporal patterns of occurrence and co-occurrence for the two arboviral diseases in all Brazilian municipalities, alongside the influence of environmental and socio-economic factors.
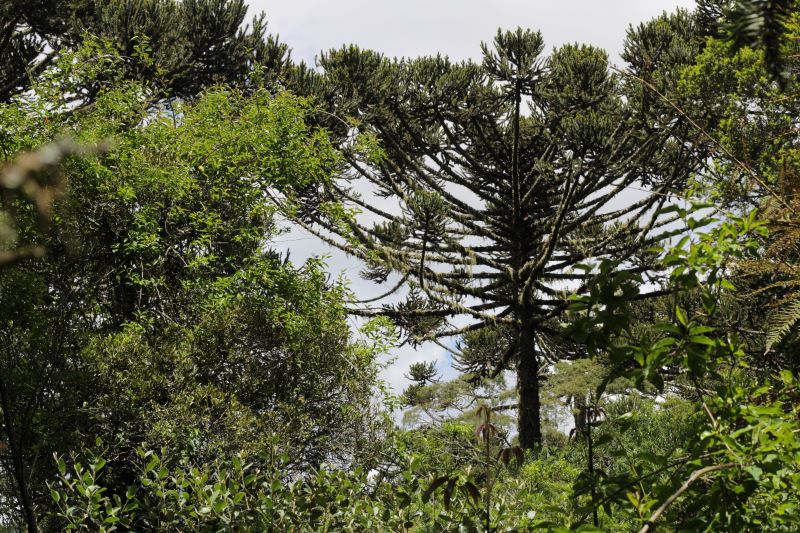

A study published in the journal Science shows for the first time the degree of threat to all tree species in the biome, classifying 65% as vulnerable or endangered to some extent. According to the authors, their findings are conservative – the actual situation could be even more alarming.
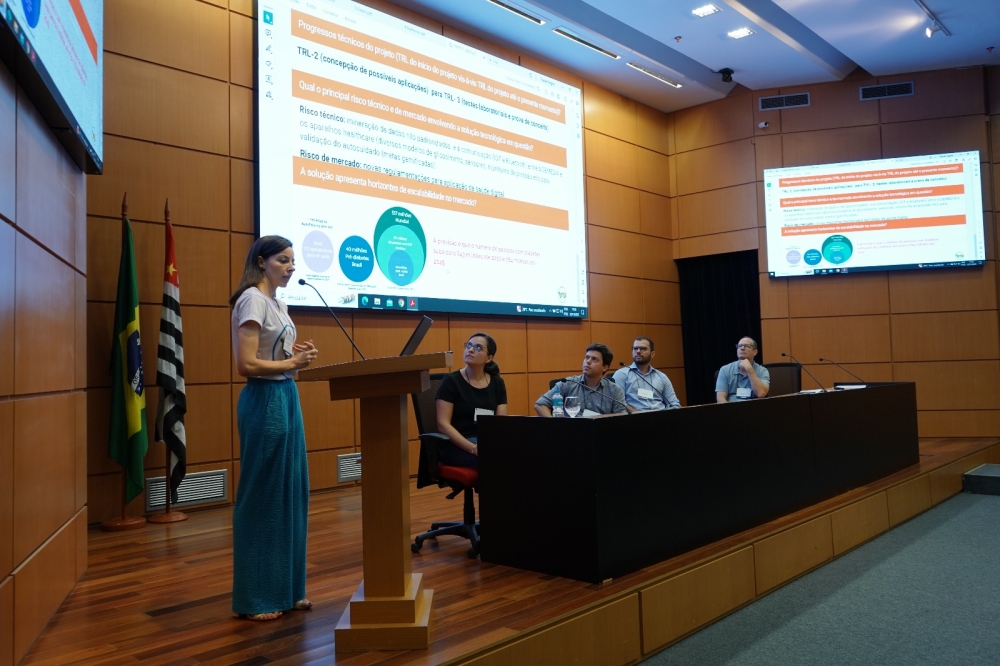

Representatives of 44 startups based in São Paulo received technical support for a year to develop products and business plans via in-person training, mentoring and workshops run by experts from FAPESP and associations that foster entrepreneurship.
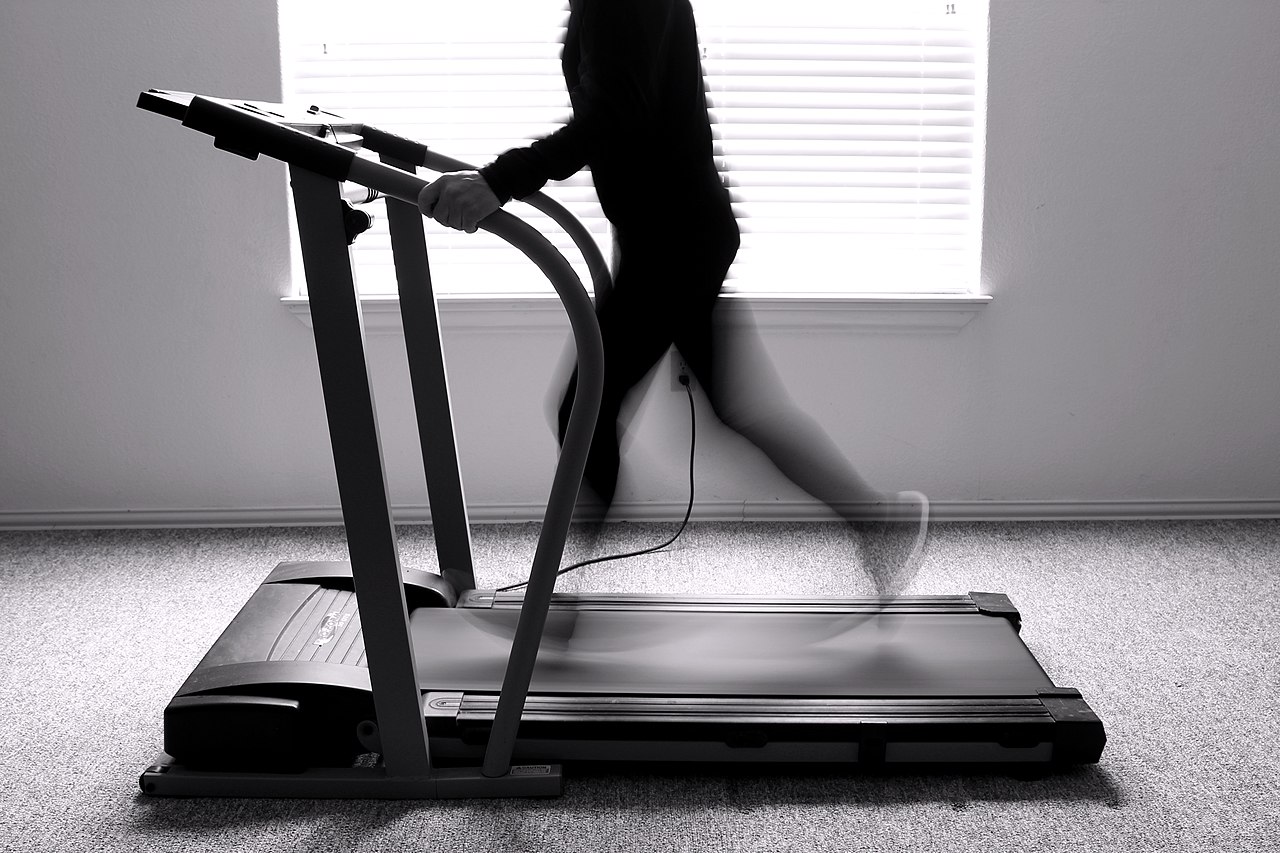

A study involving 20 women with rheumatoid arthritis and high blood pressure demonstrates the benefits of walking at moderate speed for 30 minutes even after tests that simulate stressful situations and tend to raise blood pressure.

The International Panel for Ocean Sustainability (IPOS) will translate scientific information into policymaking decisions that help protect the world’s oceans.

The funding will be for scientific expeditions under the current call for proposals which is taking applications until April 29, 2024.
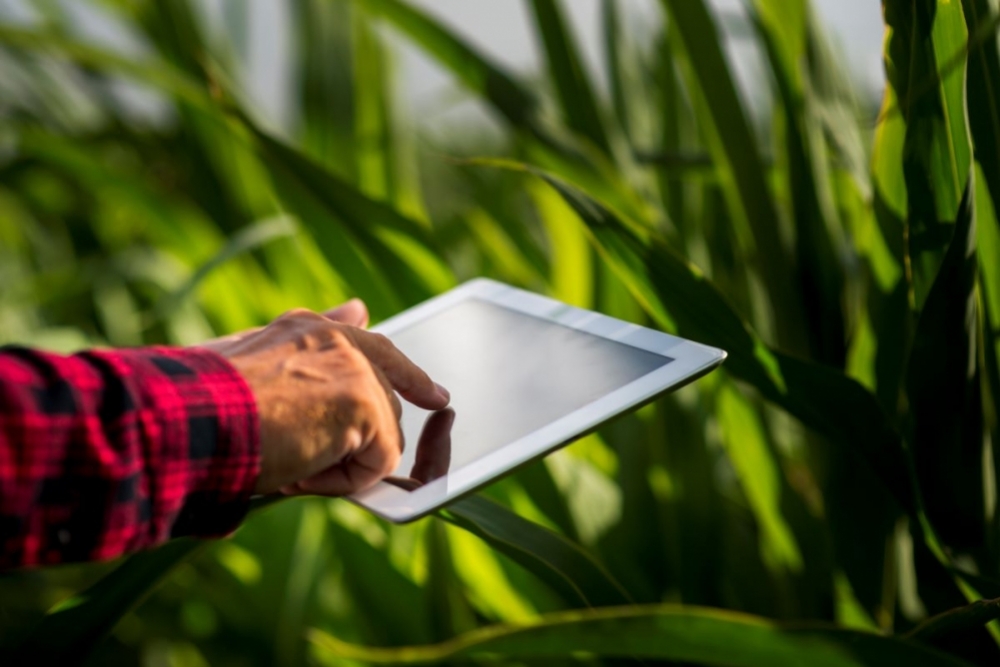

Agrosmart, a startup based in São Paulo state, presented its portfolio of solutions during COP28, the UN Climate Change Conference held in Dubai.
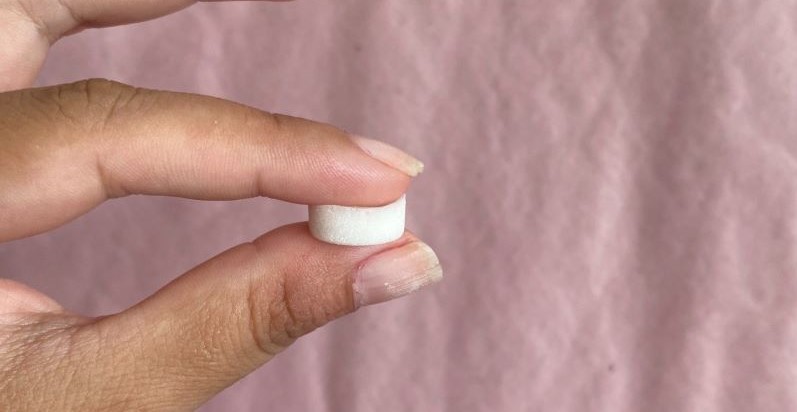
The device is under preclinical trials; the sponge is made of soft, biodegradable material and releases medication slowly into the organism.
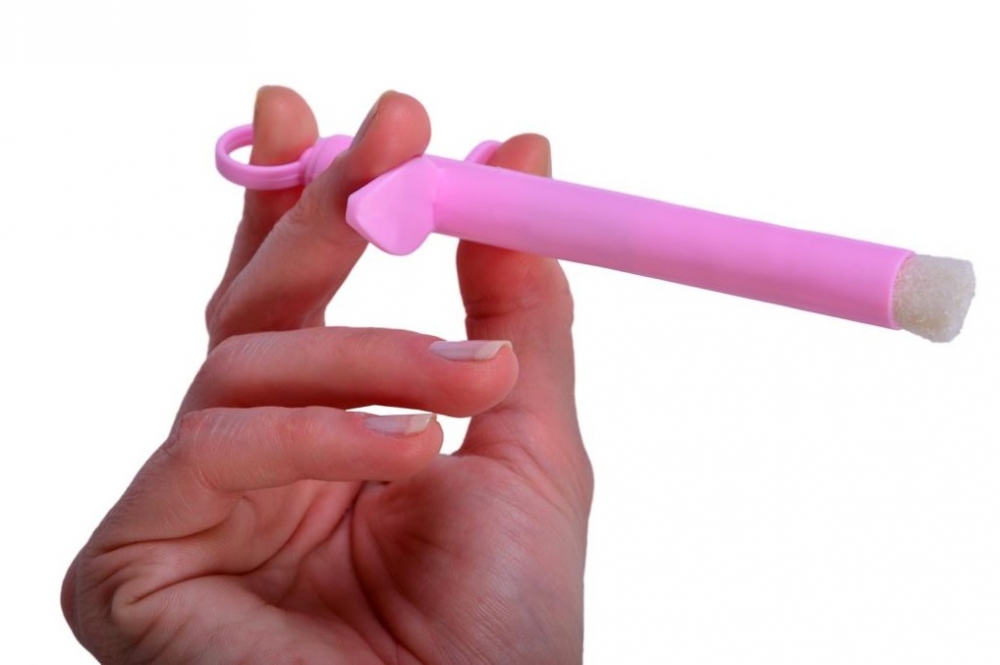

The kit is designed to be used for screening. If the result is negative, it should be repeated a year later. If positive, the individual should see a specialist.
Researchers at the University of São Paulo identified in mice the neurons associated with the anxiolytic effect of growth hormone. Their discovery paves the way for the development of novel classes of medications for neuropsychiatric disorders.
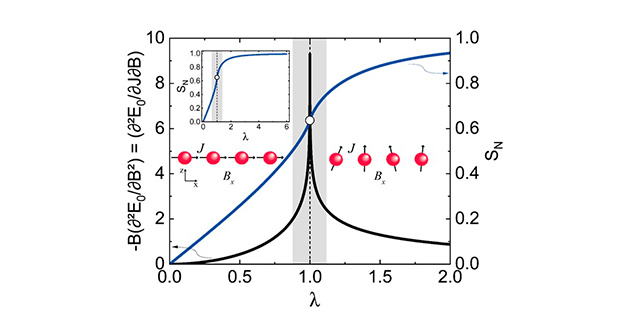
Entanglement is a key concept in quantum physics and a condition for the success of quantum computing.