


A study published in the journal Science shows for the first time the degree of threat to all tree species in the biome, classifying 65% as vulnerable or endangered to some extent. According to the authors, their findings are conservative – the actual situation could be even more alarming.
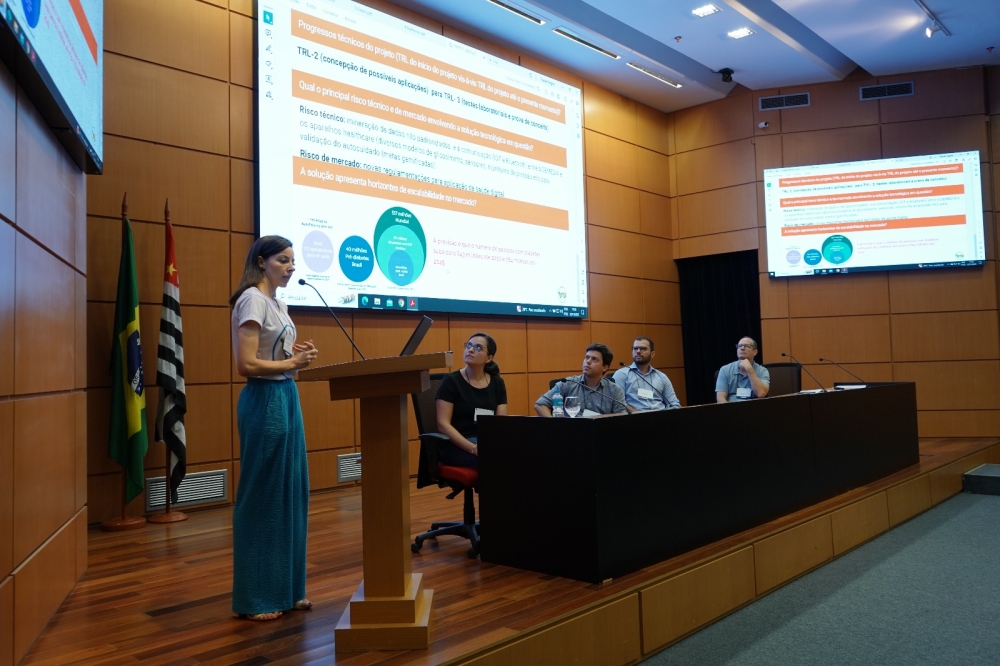

Representatives of 44 startups based in São Paulo received technical support for a year to develop products and business plans via in-person training, mentoring and workshops run by experts from FAPESP and associations that foster entrepreneurship.

A study involving 20 women with rheumatoid arthritis and high blood pressure demonstrates the benefits of walking at moderate speed for 30 minutes even after tests that simulate stressful situations and tend to raise blood pressure.

The International Panel for Ocean Sustainability (IPOS) will translate scientific information into policymaking decisions that help protect the world’s oceans.

The funding will be for scientific expeditions under the current call for proposals which is taking applications until April 29, 2024.

Agrosmart, a startup based in São Paulo state, presented its portfolio of solutions during COP28, the UN Climate Change Conference held in Dubai.
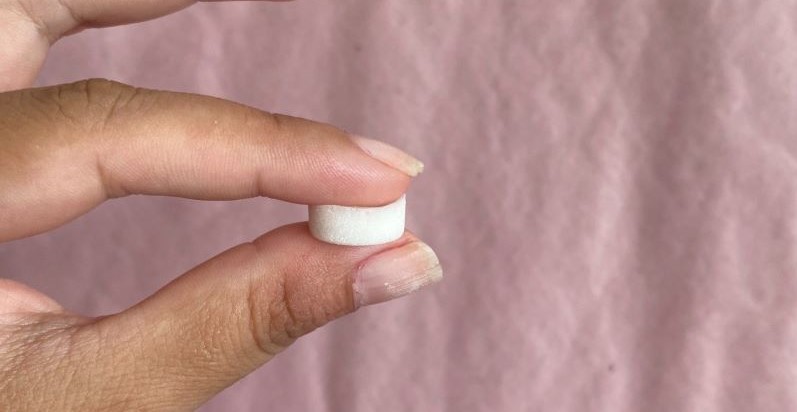
The device is under preclinical trials; the sponge is made of soft, biodegradable material and releases medication slowly into the organism.
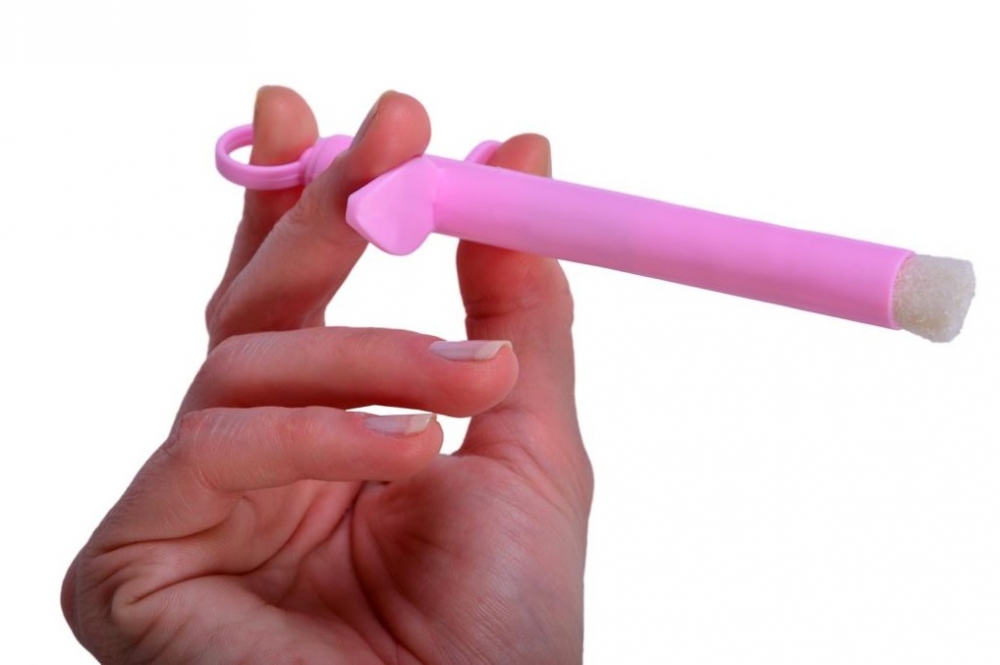

The kit is designed to be used for screening. If the result is negative, it should be repeated a year later. If positive, the individual should see a specialist.
Researchers at the University of São Paulo identified in mice the neurons associated with the anxiolytic effect of growth hormone. Their discovery paves the way for the development of novel classes of medications for neuropsychiatric disorders.
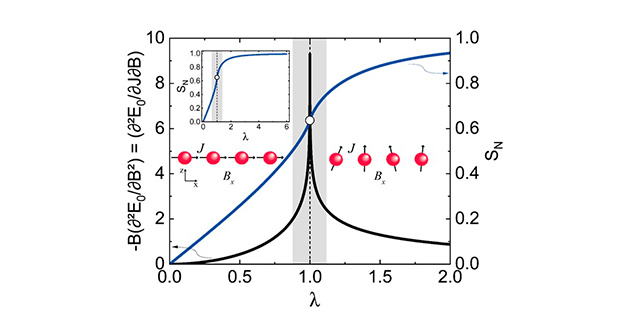
Entanglement is a key concept in quantum physics and a condition for the success of quantum computing.

Surveys conducted in the Cerrado since the 1990s show falling biodiversity as the agricultural frontier advances in the vicinity of Emas National Park. Species with biotechnological potential are dwindling and even disappearing.
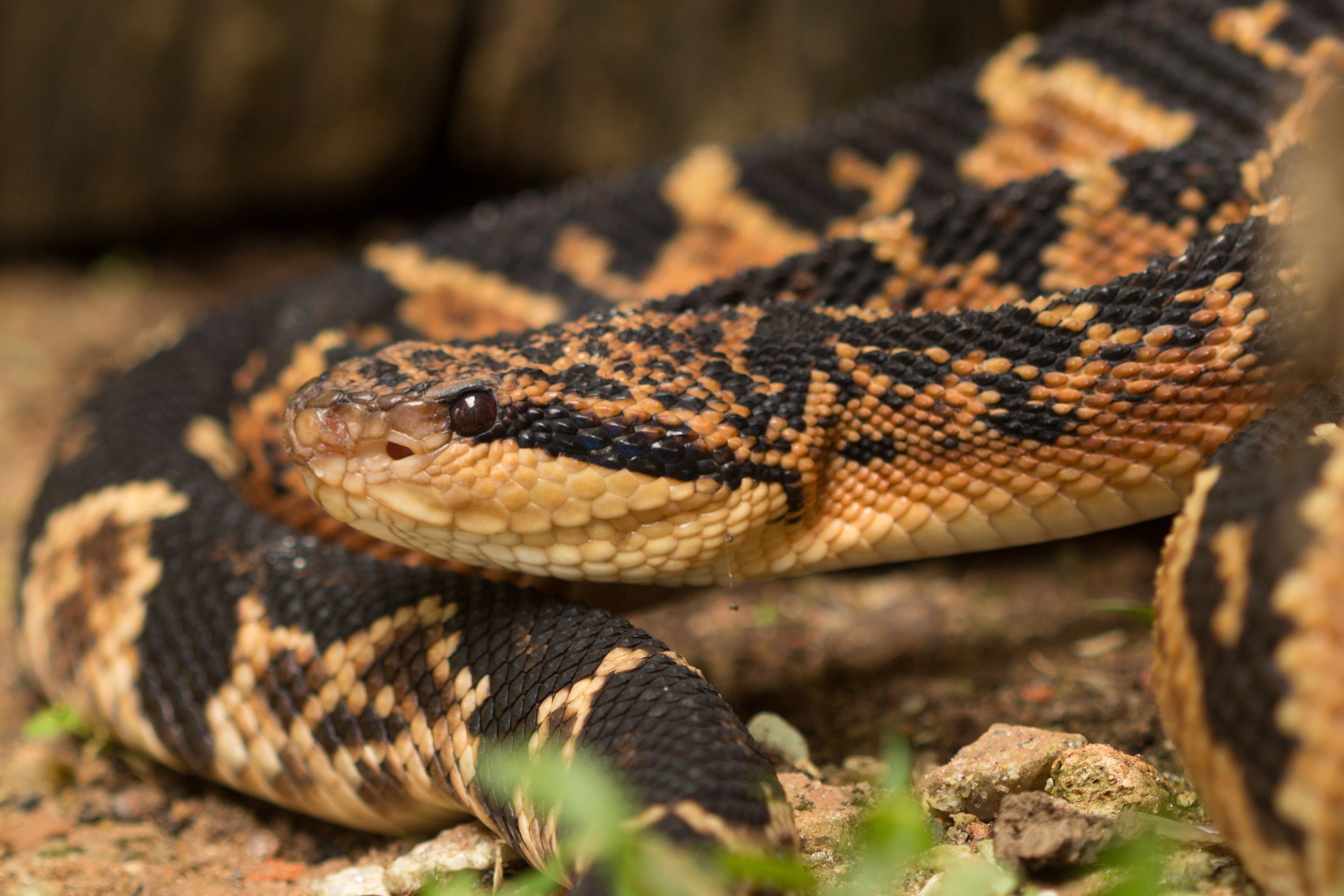

Fragments of hemorrhagic toxins that may help treat high blood pressure were found in the venom of the pit viper Cotiara, which inhabits the South of Brazil, and that of the South American bushmaster, a denizen of tropical rainforests. The molecules might one day be used in drugs with fewer adverse side effects.
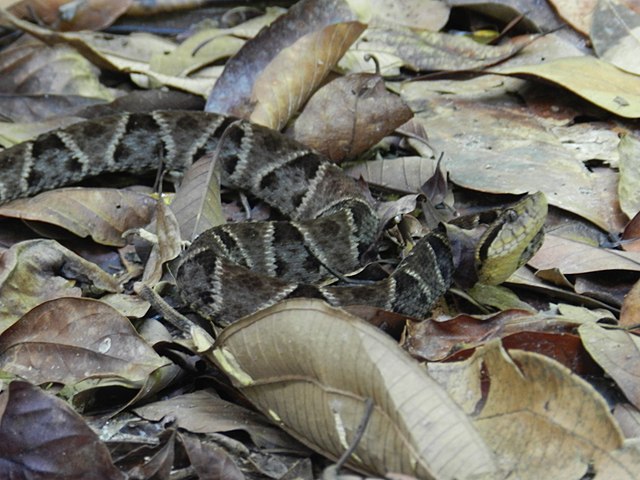

A survey conducted in a Brazilian state with the country’s second-highest number of ophidic accidents draws attention to the need to train health workers to complete notification forms correctly. Better data will help improve research and antivenom distribution.
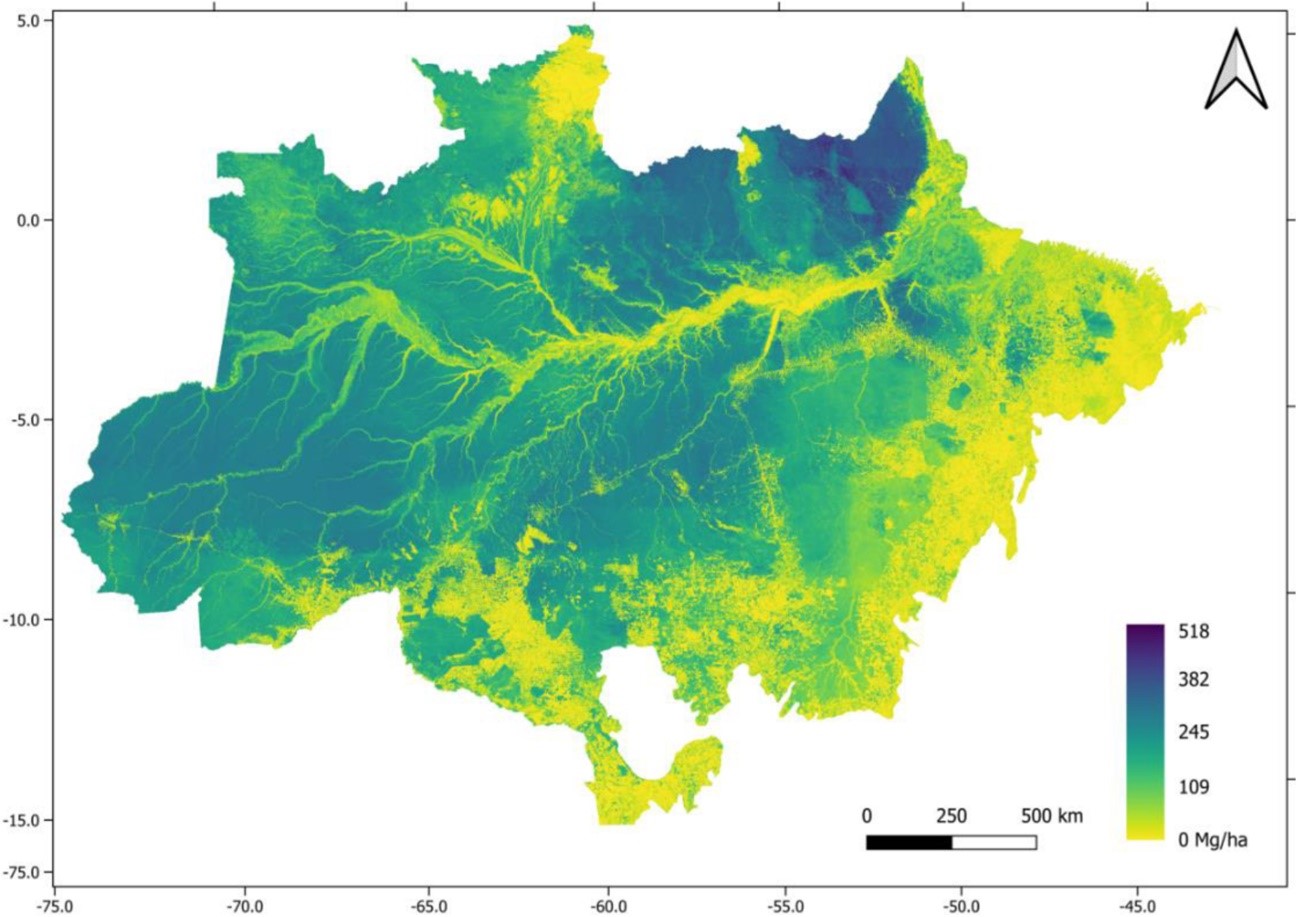
The map is derived from a study conducted by researchers at Brazil’s space research institute and collaborators, and combined airborne laser scanning, satellite imagery and forest inventories. The results will support planning, conservation and sustainable management decisions.

Brazilian researchers tested a photocatalyst based on zinc oxide and found it to perform well in degrading sertraline, an emerging pollutant.

The event took place in São Paulo on November 29-30 to foster interaction and promote center-to-center relations.
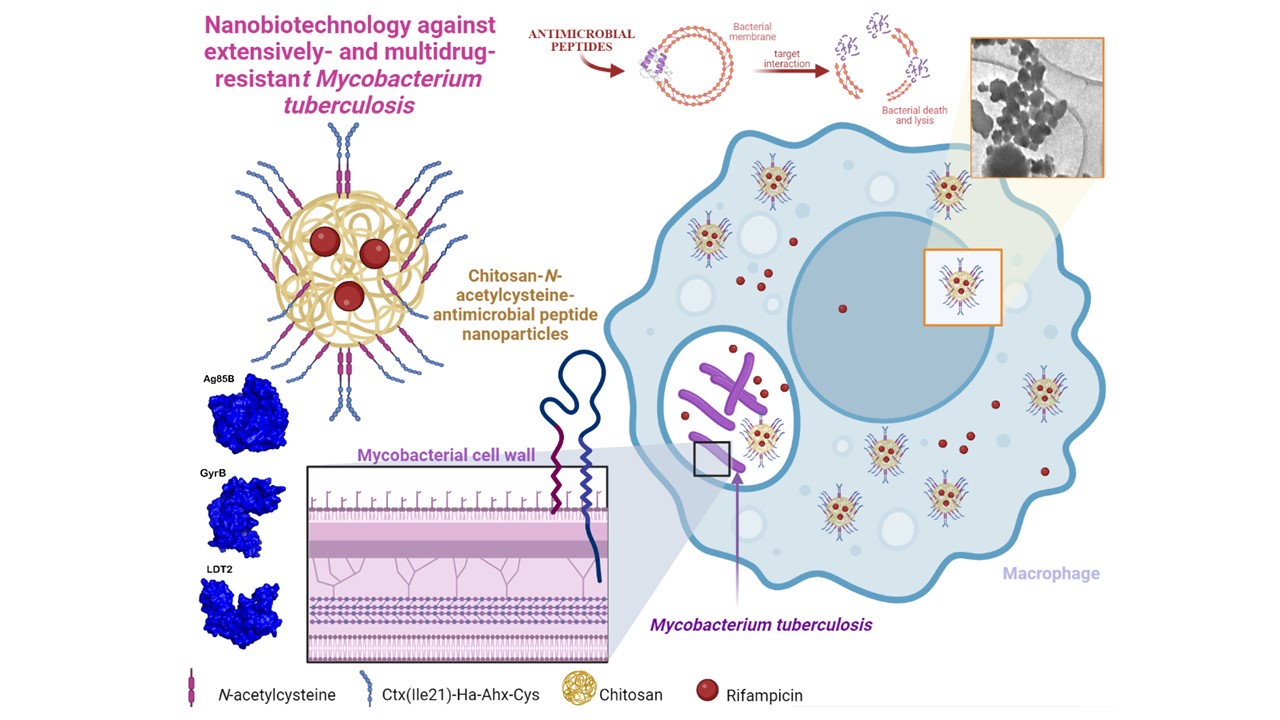
Researchers at São Paulo State University tested the action of nanoparticles loaded with antibiotics and other antimicrobial compounds on cells infected by the bacillus that causes tuberculosis. The results suggest the strategy can overcome multidrug bacterial resistance.
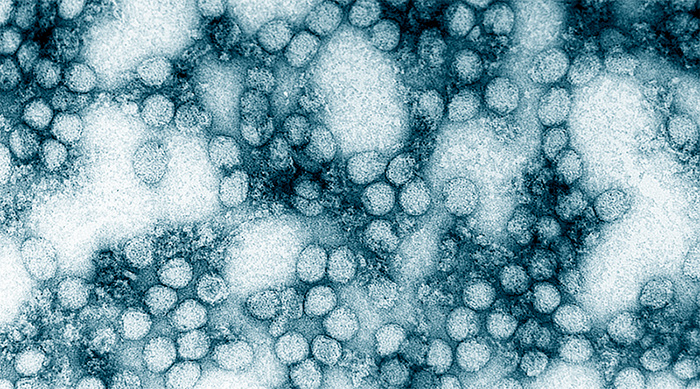
The study is the first-ever demonstration of the anatomical substrate for the cardiac arrhythmias that occur in human yellow fever.

Brazilian researchers analyzed air pollution in metropolitan São Paulo in 2019-20 when mobility restrictions and social distancing applied in the southern hemisphere’s largest city. Even so, the daily average exceeded the World Health Organization’s air quality standard on 75 days.
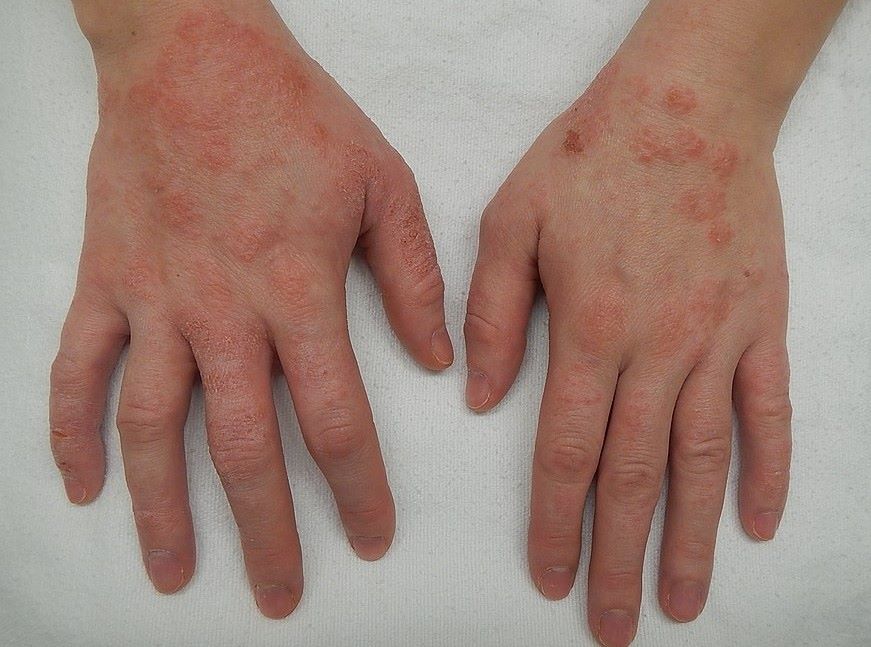
A review article by Brazilian researchers lists recent discoveries on this chronic inflammatory skin disease, which affects around 10% of adults and 25% of children.
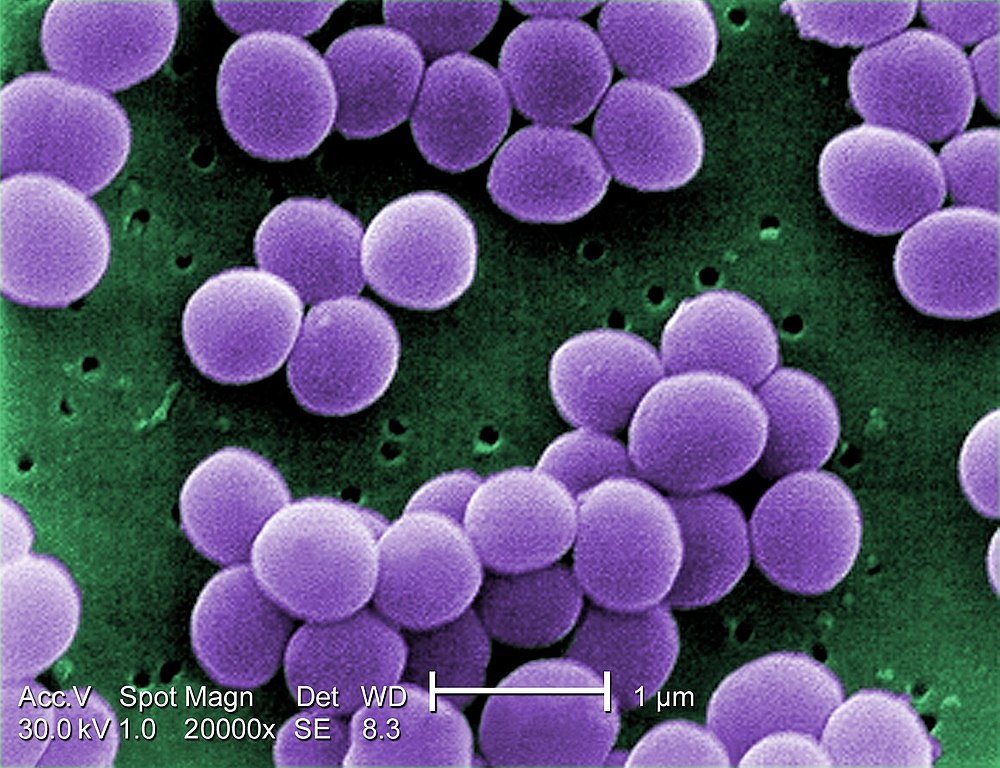
A study conducted at the University of São Paulo’s Optics and Photonics Research Center in Brazil showed a change in the bacterium’s sensitivity after five applications.
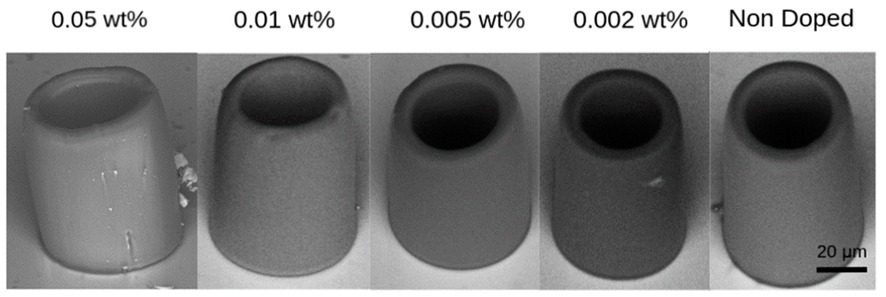
Researchers at the University of São Paulo’s São Carlos Institute of Physics developed the technique, which can be used in information processing and cell marking, among many other applications.

The artist outlined her life’s work in the Eighth FAPESP 2023 Lecture, which was entitled “Roots that emerge: interweavings of art and science”.
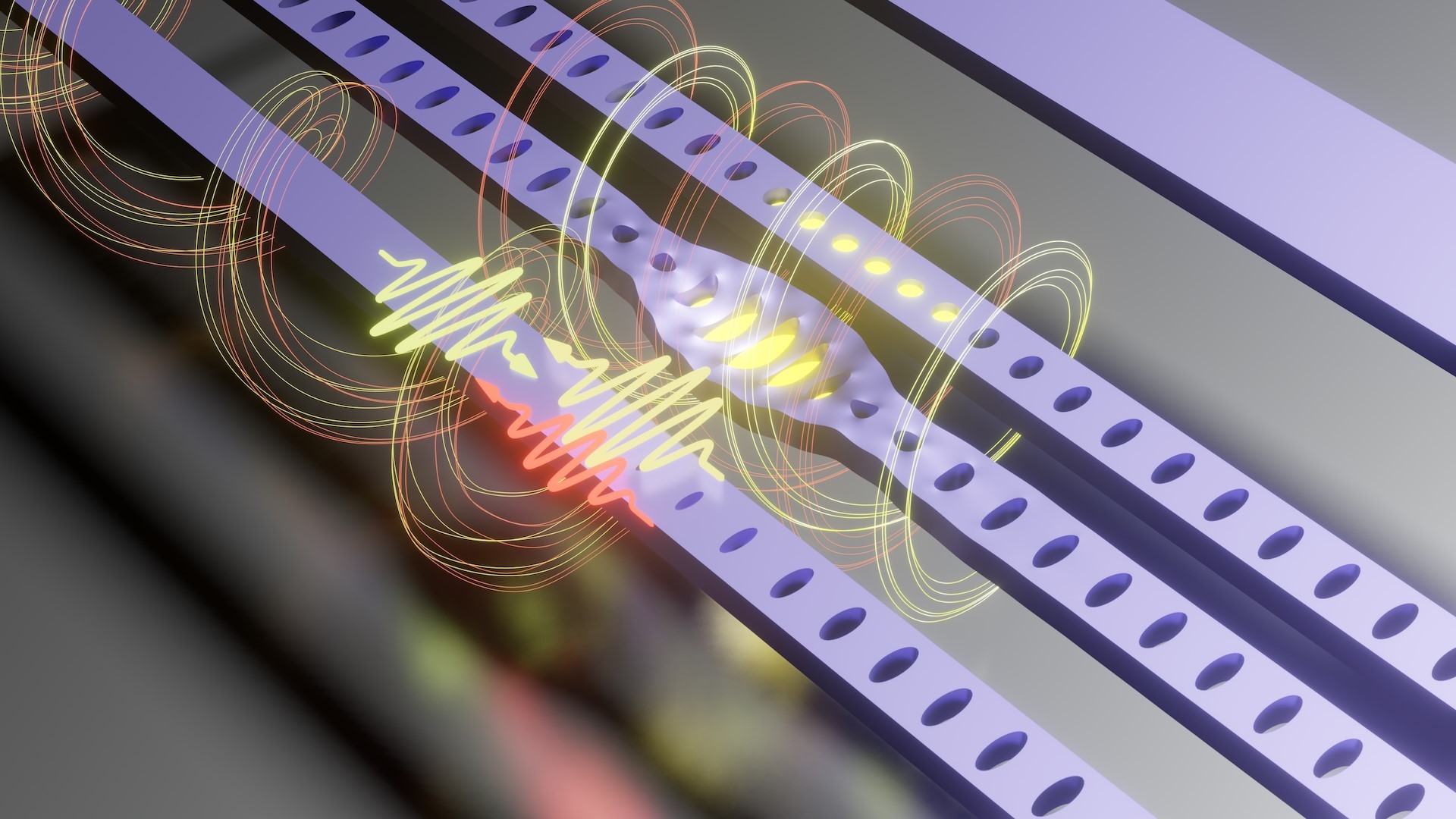
This research carried out at the State University of Campinas focused on the use of nanometric optomechanical cavities as bridges between superconducting circuits and optical fibers, with applications in computing and quantum communications.
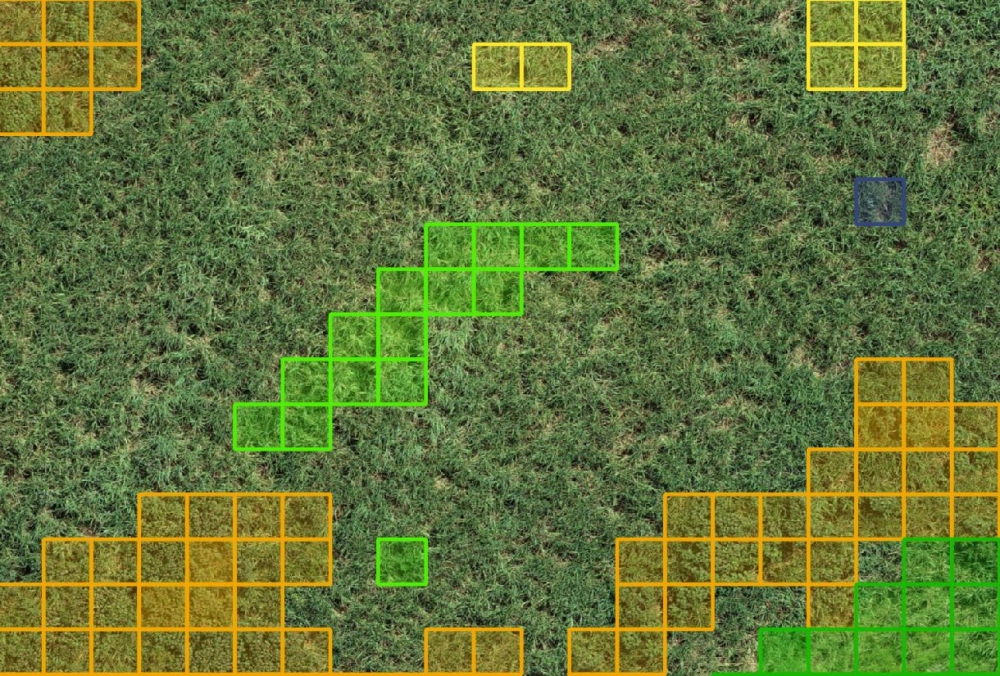

A Brazilian startup’s AI algorithms detect infestations, classify weeds and produce localized spraying files.