


Written by two experts on biofuels, Luís Augusto Barbosa Cortez and Frank Rosillo-Calle, the book explores Brazil’s experience and how other countries can learn from it in the context of climate change.
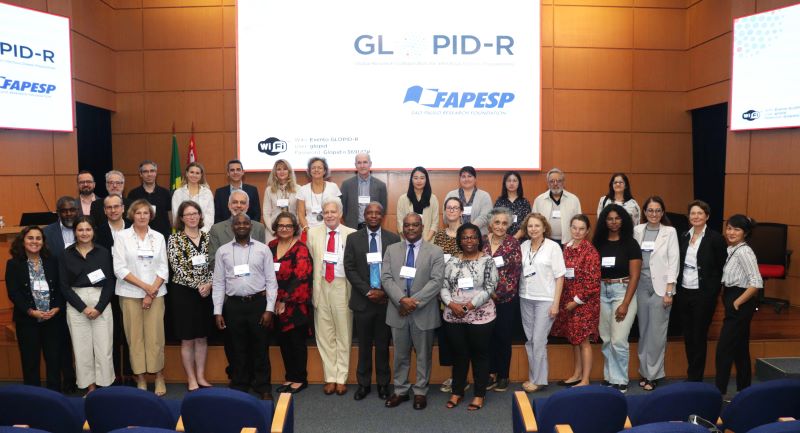

The Ninth General Assembly of the Global Research Collaboration for Infectious Disease Preparedness, representing funding agencies, research institutions and government bodies from around the world, was held at FAPESP in São Paulo, Brazil, on October 24-25.
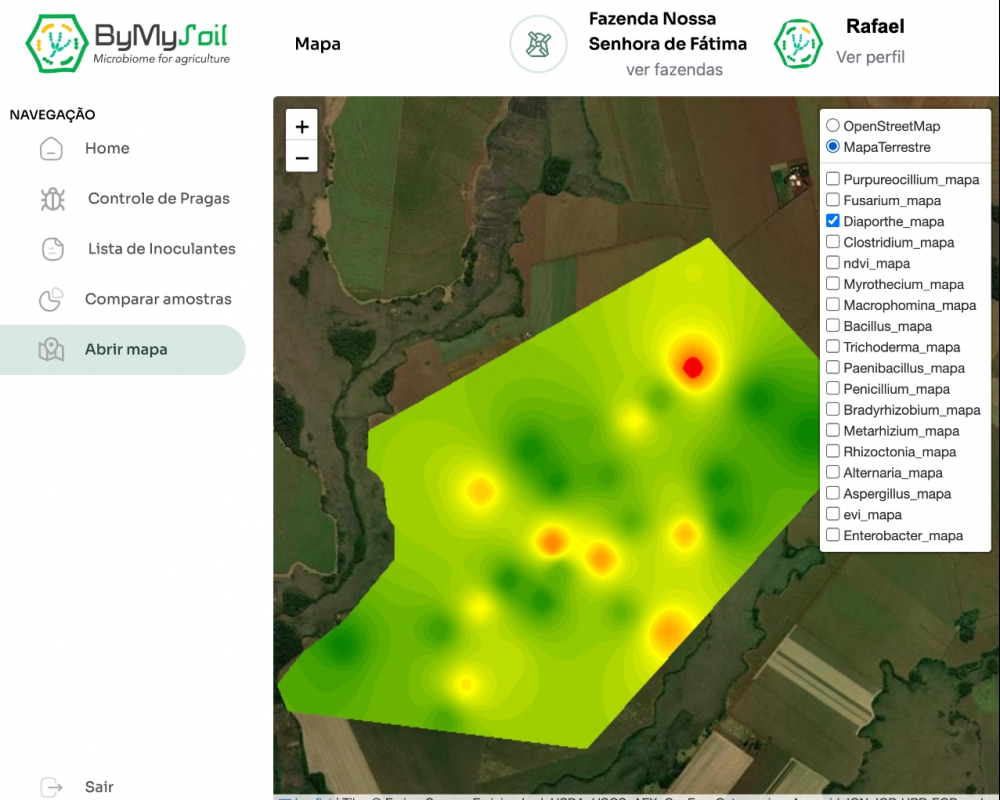
Technology developed by the startup ByMyCell with the support of FAPESP helps farmers make decisions that boost yields and reduce the use of agrochemicals.

Scientists at the University of São Paulo’s Center for Research on Redox Processes in Biomedicine used a novel technique they themselves developed to identify altered molecules in an animal model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
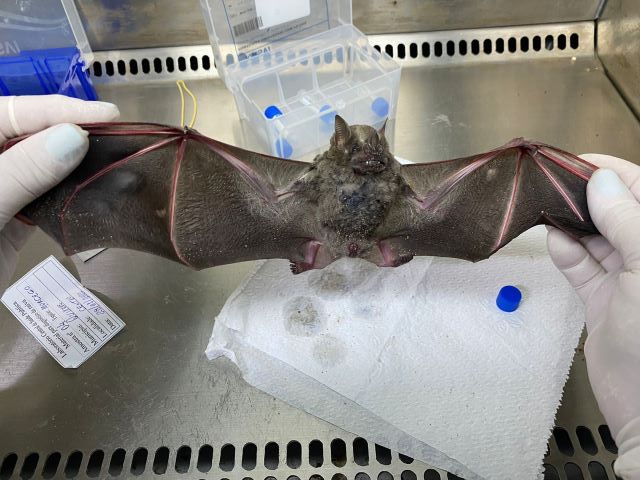
The emergence of rabies in distinct wildlife species is a potential source of human infection and poses life-threatening risks. As the researchers responsible for the discovery warn, anyone who comes into contact with these animals should alert the authorities. A 36-year-old farm worker died in May, only weeks after being bitten by a marmoset.
Results of trials involving animals, cell cultures and human heart tissue are reported in the European Heart Journal. The study was conducted by researchers at USP in partnership with a biopharmaceutical firm, offering hope to 2 million Brazilians who suffer from the disease.
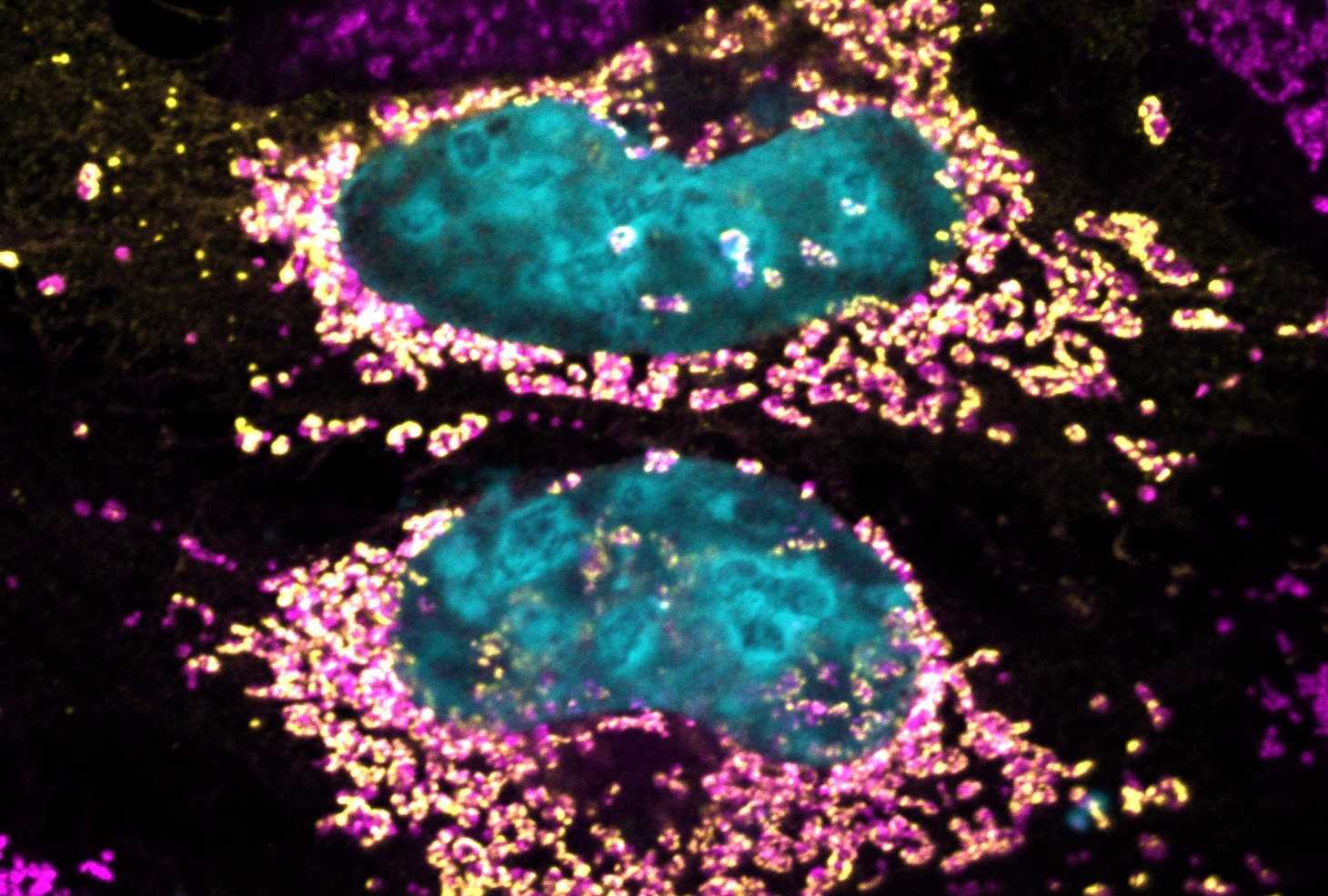
An article published in PNAS by Brazilian and Australian researchers describes a hitherto unknown protein with anti-oxidizing properties secreted by Coxiella burnetii, a Gram-negative intracellular bacterium, pointing to possible treatments for auto-immune diseases and even cancer.
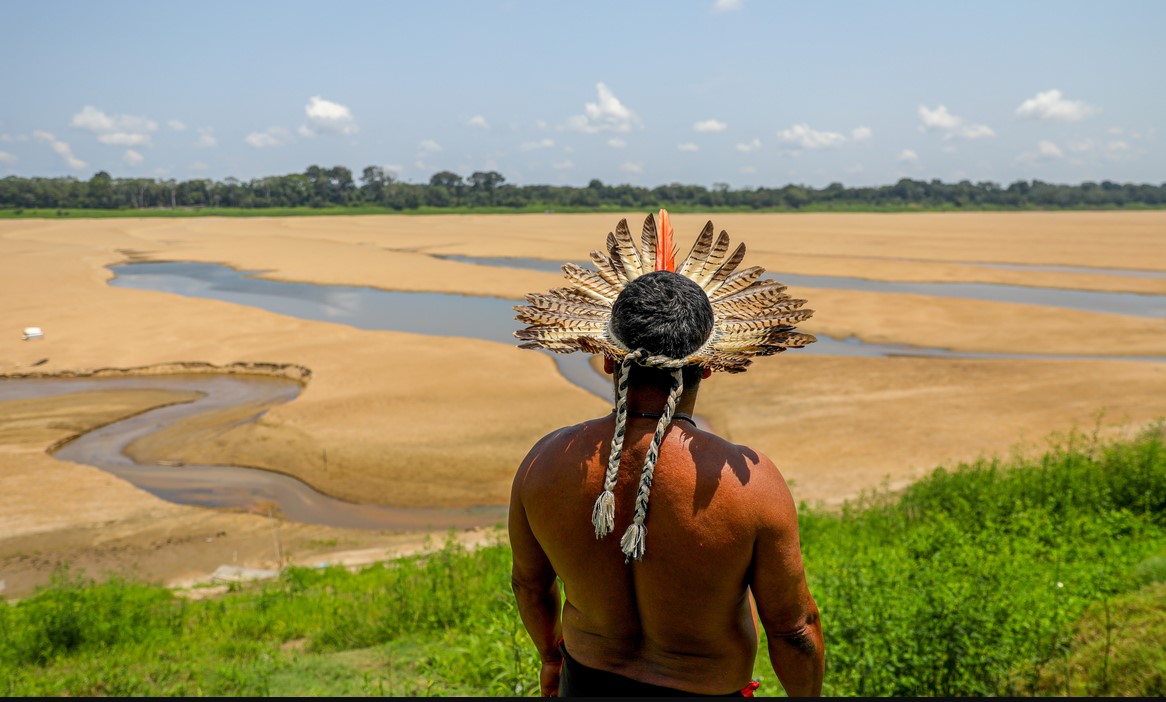

Brazil’s North region is experiencing the worst drought of the century, with severe social and economic impacts. The problem was discussed at an event hosted by FAPESP on October 17.

FGV Analytics is a partnership involving FAPESP, Getúlio Vargas Foundation, the University of São Paulo and the São Paulo State Department of Public Safety. Its mission includes fostering development of evaluation tools and evidence-based public policy.
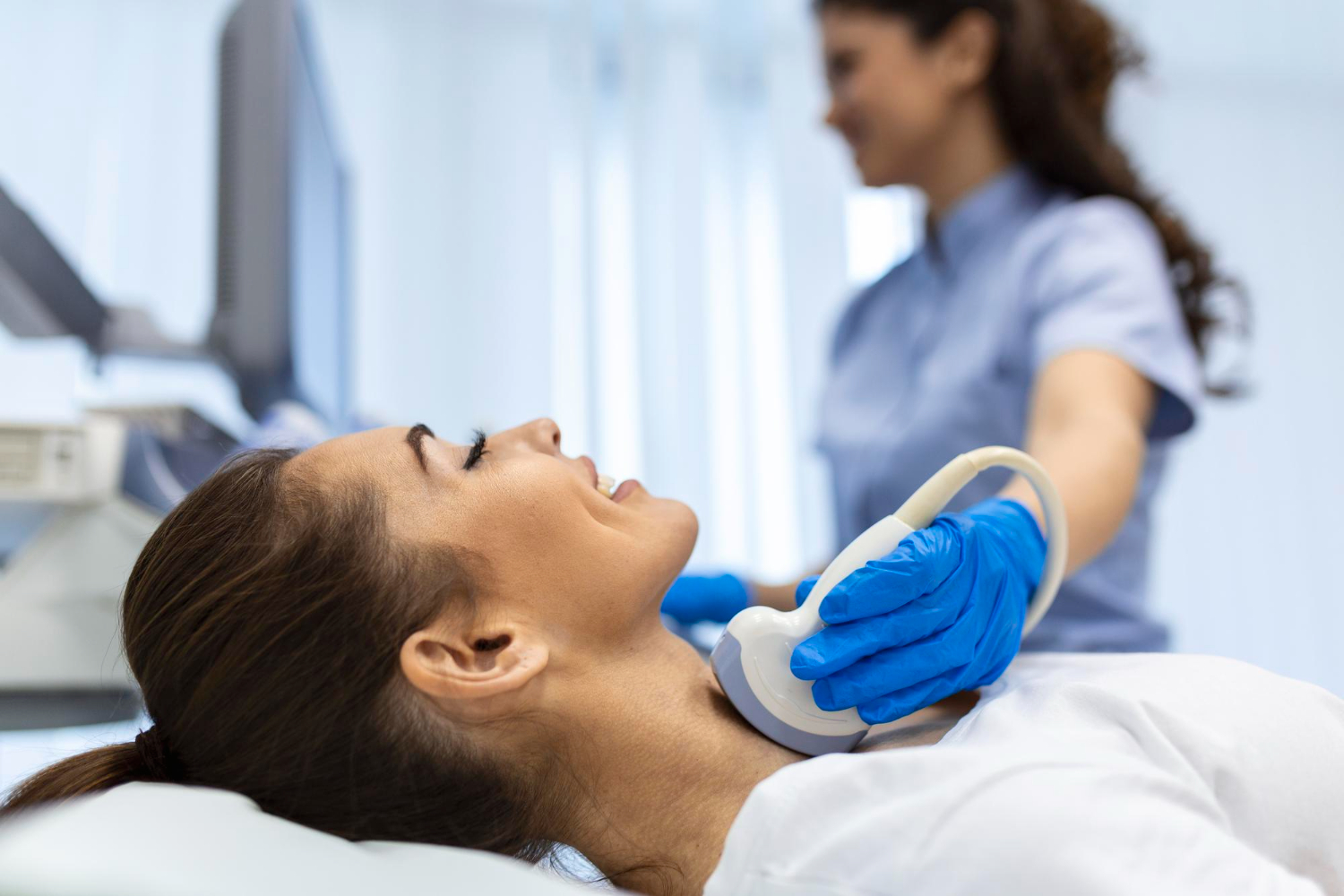
A study compared geographical and socioeconomic dimensions of the disease in São Paulo and the Barretos region. Incidence was far higher in the former but mortality rates were similar, suggesting overdiagnosis in specific areas and social groups.
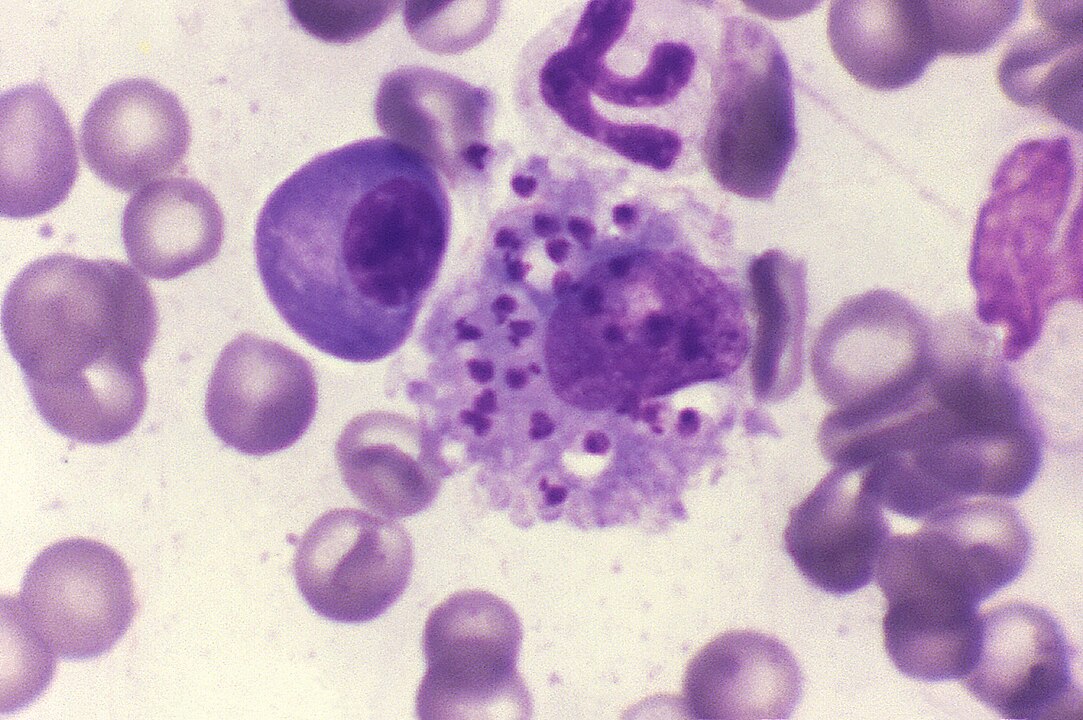
The test developed by Brazilian researchers accurately identifies the causative agent in less than two hours, so that treatment can be properly targeted. Brazil is seeing a growing number of cases of co-infection by protozoans Leishmania infantum and Crithidia.

High-precision maneuvering support system with integrated hardware and software developed by a startup supported by FAPESP transmits dynamic information in real-time via a smart platform.
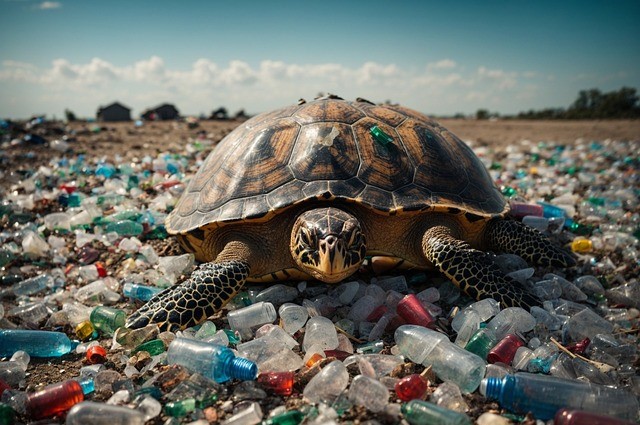

Researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo analyzed allegedly biodegradable plastic items sold by 40 supermarkets and found most to be oxo-degradables, banned in several countries because they contribute significantly to microplastic pollution. Bills currently before Brazil’s Congress would regulate the sale of such products.
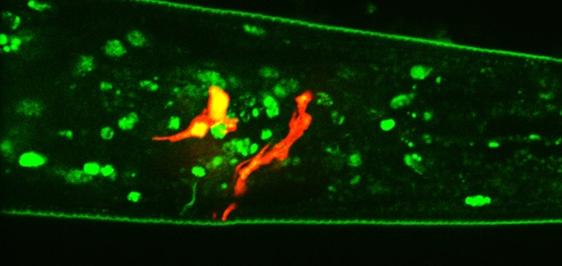
In nematode worms exposed to a compound secreted by pathogenic bacteria, researchers observed activation of a neural circuit resulting in a longer lifespan and less protein aggregation, one of the causes of neurodegenerative diseases. The discovery paves the way for the development of treatments for age-related diseases.
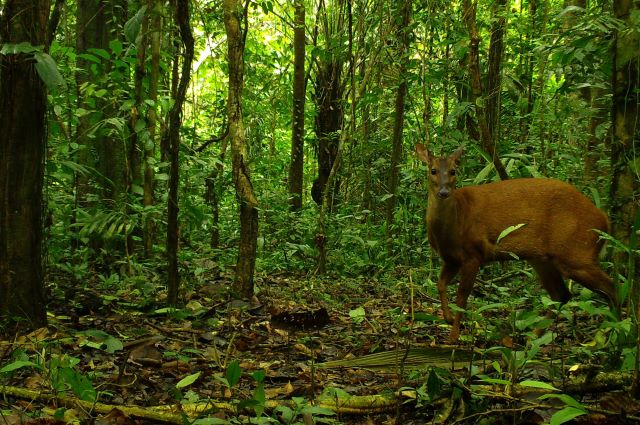

A study conducted in sustainable-use reserves shows that local game species become less abundant about 5 kilometers away from the nearest human community, but the negative effects of anthropic activity can be mitigated by appropriate management strategies.

A research project showed that mobilizing citizens in flood-prone areas improves data collection and increases resilience.
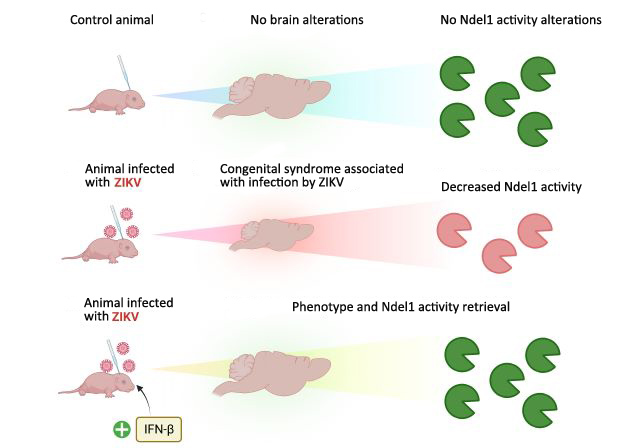
Brazilian researchers showed that brain activity of Ndel1, an enzyme that plays an important role in neuron differentiation and migration, decreased in mice infected by zika during pregnancy. The enzyme could become a biomarker for early diagnosis of the congenital syndrome associated with zika.
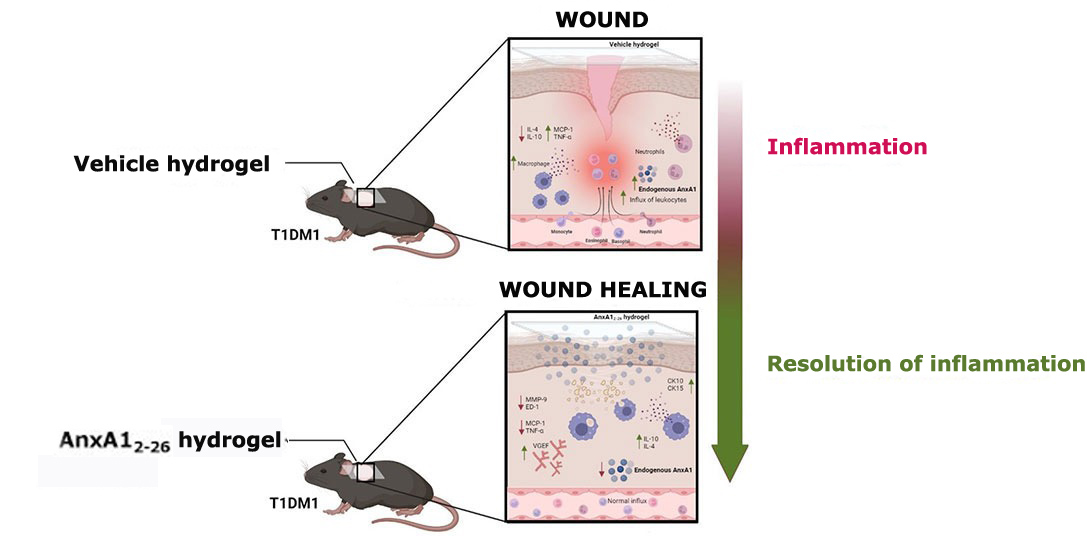
The product, which contains the anti-inflammatory protein annexin A1, accelerated complete skin wound healing in mice, and has the potential to become part of the arsenal of treatments for a disease that affects 17.7 million Brazilians.

Plant species native to the Brazilian savanna-like biome grow thick bark to protect their internal tissues and hide organs that assure resprouting below the ground, according to an article in Flora by researchers at São Paulo State University.
Opened in 2022 with FAPESP’s support, Nutera is Latin America’s first cellular product manufacturing plant. It is run by researchers from Butantan Institute and the University of São Paulo’s Ribeirão Preto Blood Center, and could become a supplier to the SUS, Brazil’s public healthcare network.

The calls offer opportunities for accelerators and agencies that provide services for startups under the aegis of Tecnova III, a program run by the Brazilian Innovation Agency which in São Paulo is operationalized in partnership with FAPESP.

Findings reported in the journal Antibiotics by scientists working in Brazil and the United States pave the way for the development of drugs against resistant bacteria.

This is one of the findings of a study led by Brazilian scientists and reported in the science journal Fire. The researchers built a model based on images from the SENTINEL-2 satellite and were able to detect burned areas much more accurately.
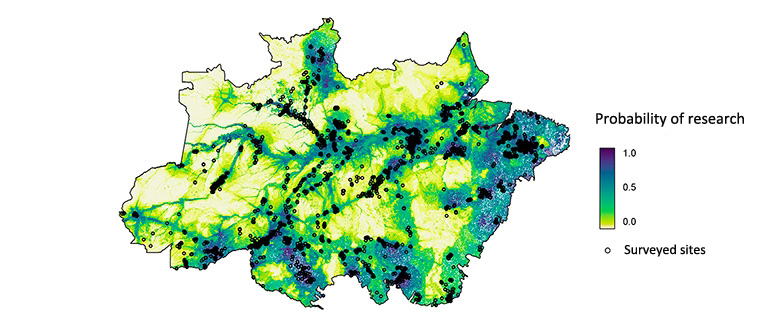
The findings evidenced high susceptibility to climate change by 2050 in 15%-18% of the areas with the most neglected biodiversity.

In addition to helping combat antimicrobial resistance, the bioparticle developed at the Federal University of São Paulo avoids the waste and pollution created by excessive amounts of drugs in water bodies. The strategy was tested on an ornamental fish species native to the Amazon and found to be safe.