

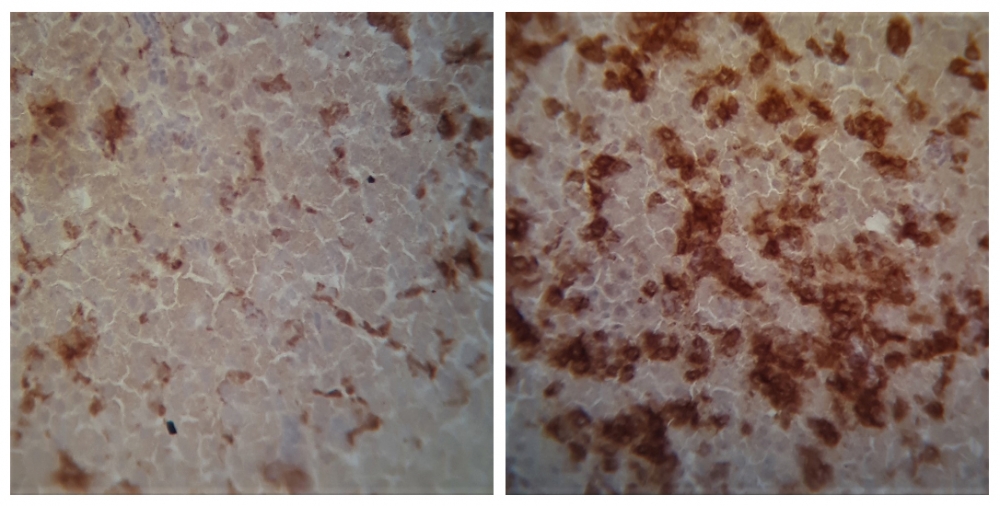
Deletion of two genes, which in mice attenuated the action of the bacteria, made the immune response more exacerbated in broiler chicks. The findings reinforce the need for animal health and hygiene measures throughout the poultry production chain.

The finding is from a longitudinal study conducted in Brazil. Analyzing data for high school students aged 13-18, it concluded that the problem affects girls more than boys and is associated with physical inactivity and low academic achievement.
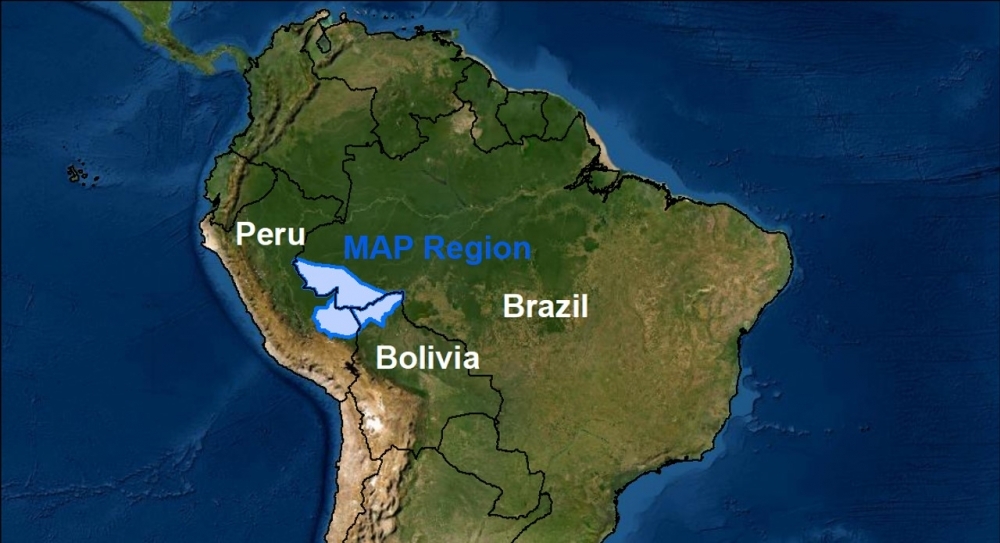
A lack of community involvement impairs fire control programs in the region known as MAP, between Madre de Dios (Peru), Acre (Brazil) and Pando (Bolivia).

The center will be hosted by the Federal University of Ceará and will focus on the use of the Internet of Things, big data, digital transformation and cutting-edge technology in prevention, diagnosis and low-cost therapies.

Addition of rosmarinic acid at a mere 0.1% reduced the amount of sunscreen needed to protect the skin, increased the sun protection factor by more than 41% and combined photoprotection with antioxidant activity. The innovation would reduce the volume of chemical substances discharged into the environment.
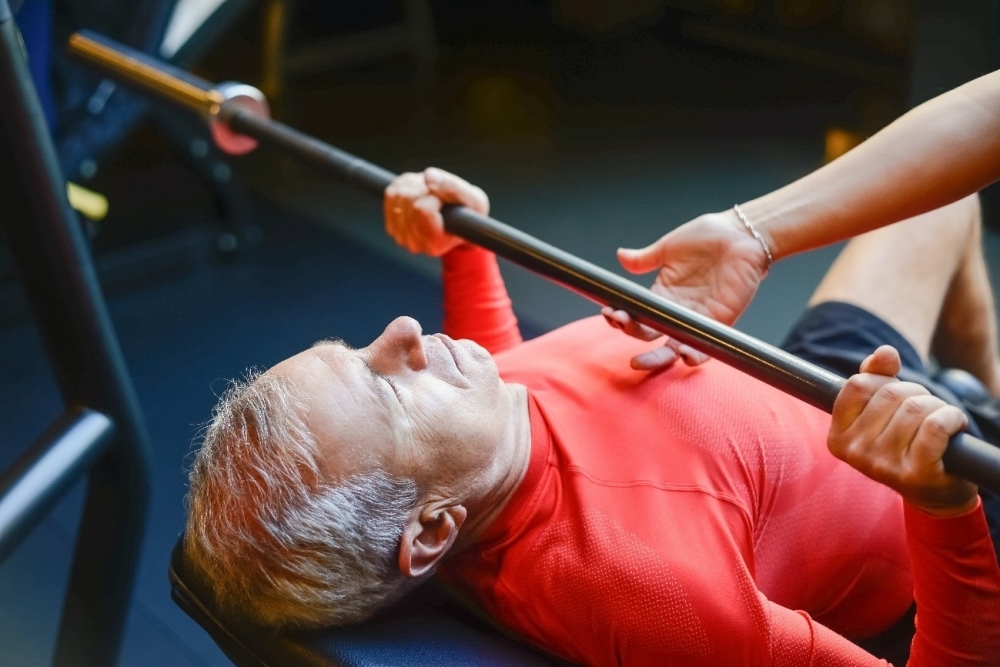

This conclusion, presented by Brazilian researchers in the journal Scientific Reports, is based on a systematic review of clinical trials held to investigate the effect of strength training on blood pressure in hypertensive patients. All age groups benefited, but the positive effects were most evident in patients aged 50 or less.

A review of the literature shows that 15% of articles published between 1960 and 2021 focused on only ten species, while no articles at all were published on almost 40% of all species. Research efforts tend to be biased toward large-bodied animals and species native to wealthier countries, among other factors that should be taken into consideration when planning future studies, according to the authors.

Established by FAPESP and Embraer at the Aeronautical Technology Institute (ITA), ERC-AMF will conduct research on innovative topics with the potential to contribute to the competitiveness of Brazil’s aerospace industry.

With the support of FAPESP and Banco Industrial do Brasil, the National Center for Research and Innovation in Mental Health (CISM) was launched at an event held on March 15.

Experiments involving nematode worms conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo showed that the benefits of physical activity to muscles are directly linked to processes occurring in mitochondria, the organelles that make energy for cells. Their findings offer possible routes for drug development.
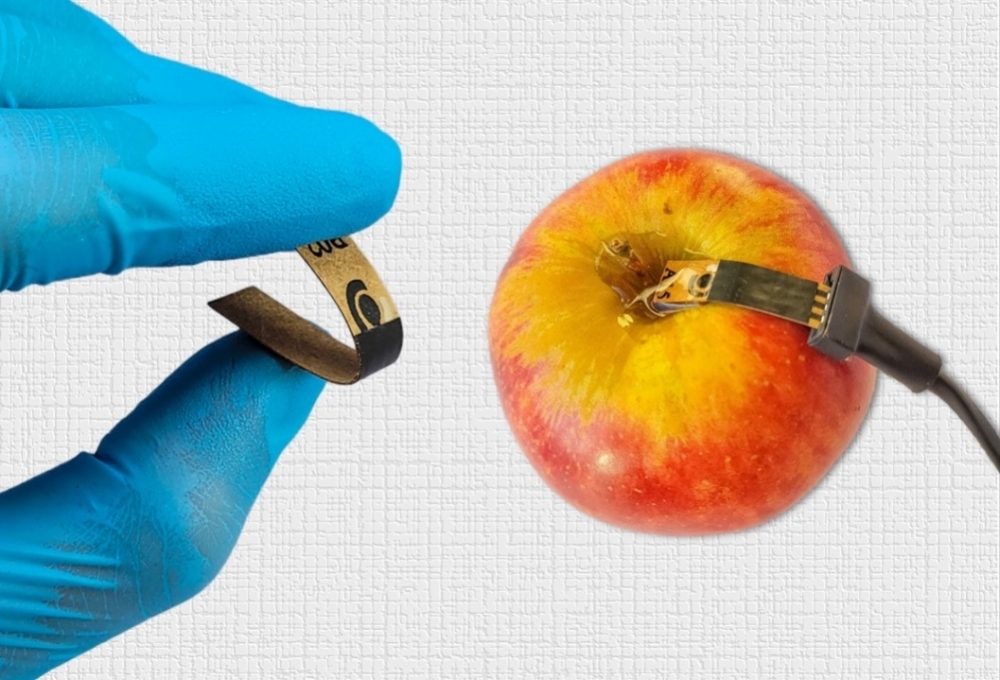

A device developed at the University of São Paulo resembles the glucometer used by diabetics to measure blood sugar: when it comes into contact with the surface of a fruit or vegetable, it detects and quantifies any traces of carbendazim, a fungicide in widespread use in Brazil despite being banned.
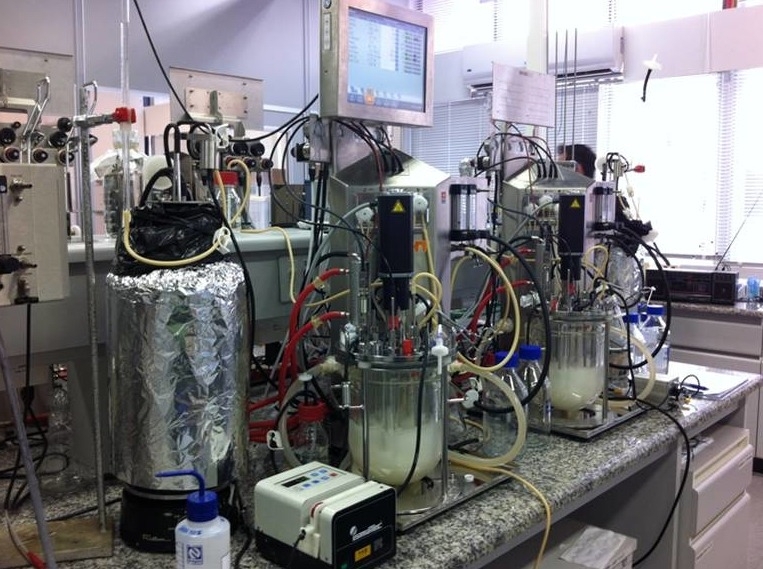

Brazilian researchers identified the genes that make the industrial yeast strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae SA-1 resistant to fermentation inhibitors generated during sugarcane bagasse preprocessing. The discovery will be useful as a basis for metabolic engineering of the microorganism.
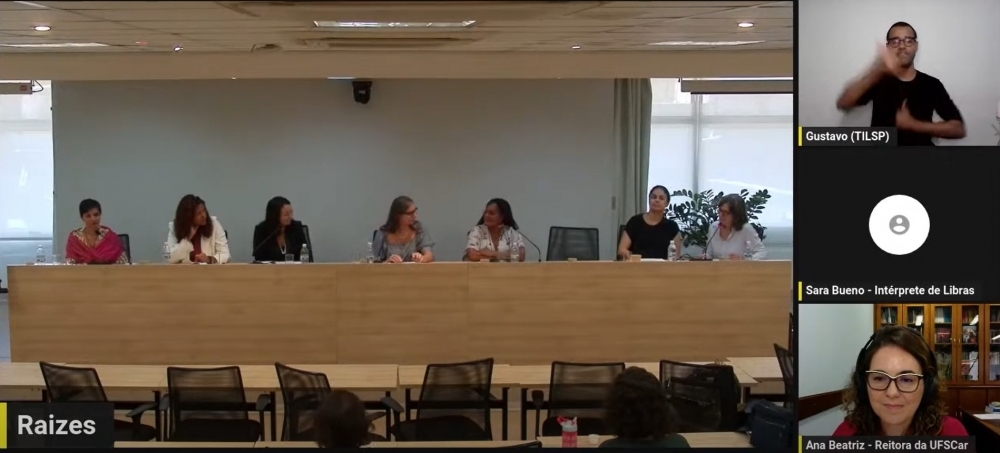

Rectors, vice-rectors, pro-rectors and heads of department at universities in São Paulo state established Rede Equidade as a force for formulating and promoting equity programs that take into account the links between gender and other differences and inequalities.

Annual production of NH3, the world’s most synthesized molecule, totals 1.2 million metric tons. Its successful use in fuel cells will boost demand.
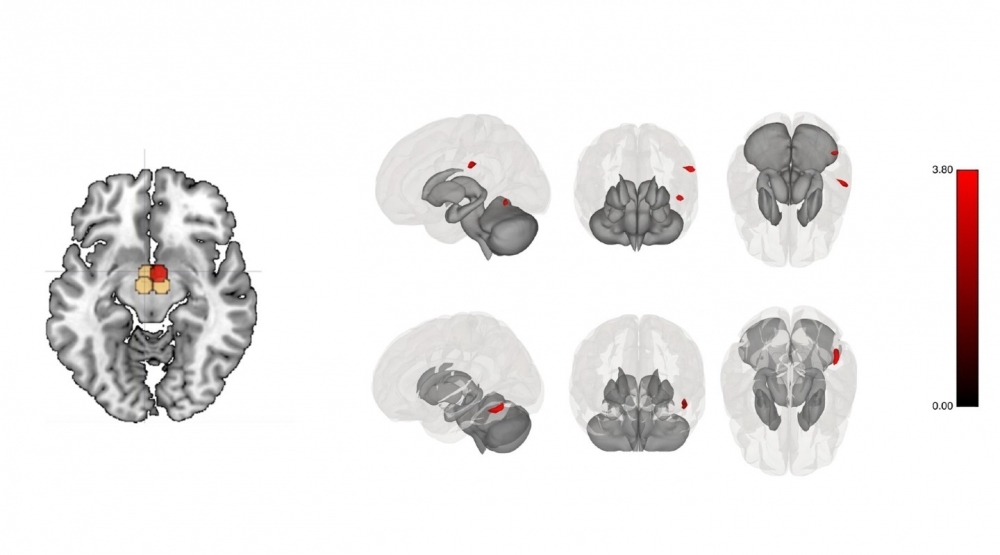
In a study conducted in São Paulo, Brazil, exercise training increased connectivity between the hypothalamus and sensory regions, accelerating satiety, for example.

France’s leading public-sector scientific research organization already has similar partnerships in the US, UK and Japan. FAPESP President Marco Antonio Zago expressed interest in supporting projects conducted at the center to be set up in São Paulo, Brazil, focusing on areas such as oceanography, biodiversity, and sustainability.
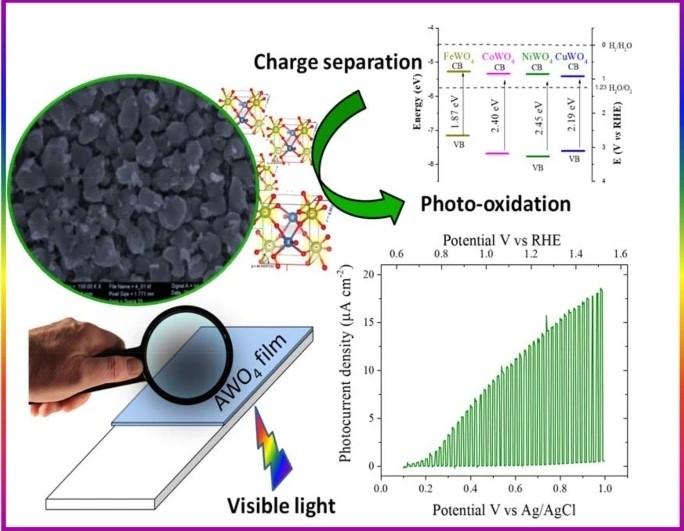
Thin films of transition metal tungstate showed potential for use in water splitting reactions and other photoelectrocatalytic applications.
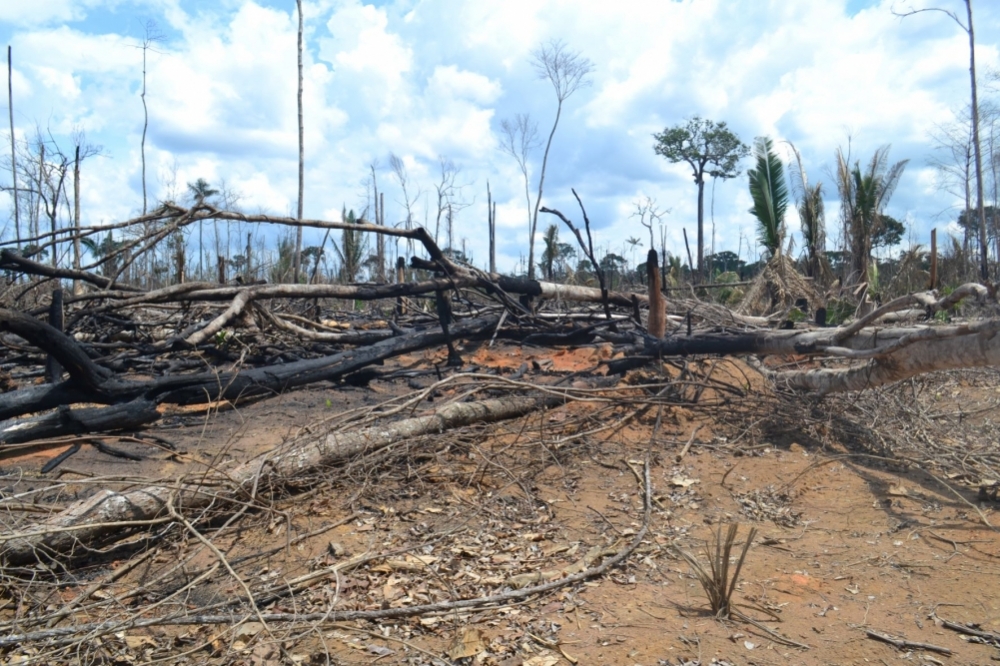

Fire destroyed 4,141 km² of forest and 6,484 km² of pasture and cropland between 2003 and 2019 in the area of Boca do Acre, Amazonas state, North Brazil, according to a recently published report. A year-by-year breakdown shows that the area affected by fire ranged from a low of 33 km² in 2011 to a high of 681 km² in 2019.

Researchers discuss 17 case studies conducted in the Americas, Asia-Pacific and Africa involving ways to implement integrated management of water, energy and food.

Analysis conducted in Spain used a methodology developed by researchers at the State University of Campinas to detect many toxins simultaneously.

A survey of news items on Brazilian deer published between 2011 and 2021 shows that most referred to habitat loss and poaching, but diseases transmitted by cattle and low reproductive efficiency were ignored as factors that can lead to species extinction. Lack of the right information can hinder conservation efforts.
A study in rats analyzed neural rhythm in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus with machine learning techniques. The results could guide future personalized treatments for psychiatric disorders.

Machine learning tool measures how environmental variables such as humidity and solar radiation affect the amount of carbon captured in a given area.

The researchers analyzed data for more than 500 coffee farms in areas of Atlantic Rainforest and Cerrado, Brazil’s savanna-type biome, in 84 municipalities in the states of São Paulo and Minas Gerais.
The aim of the study was to analyze the virulence and antimicrobial resistance profile of the main agent of urinary tract infections.