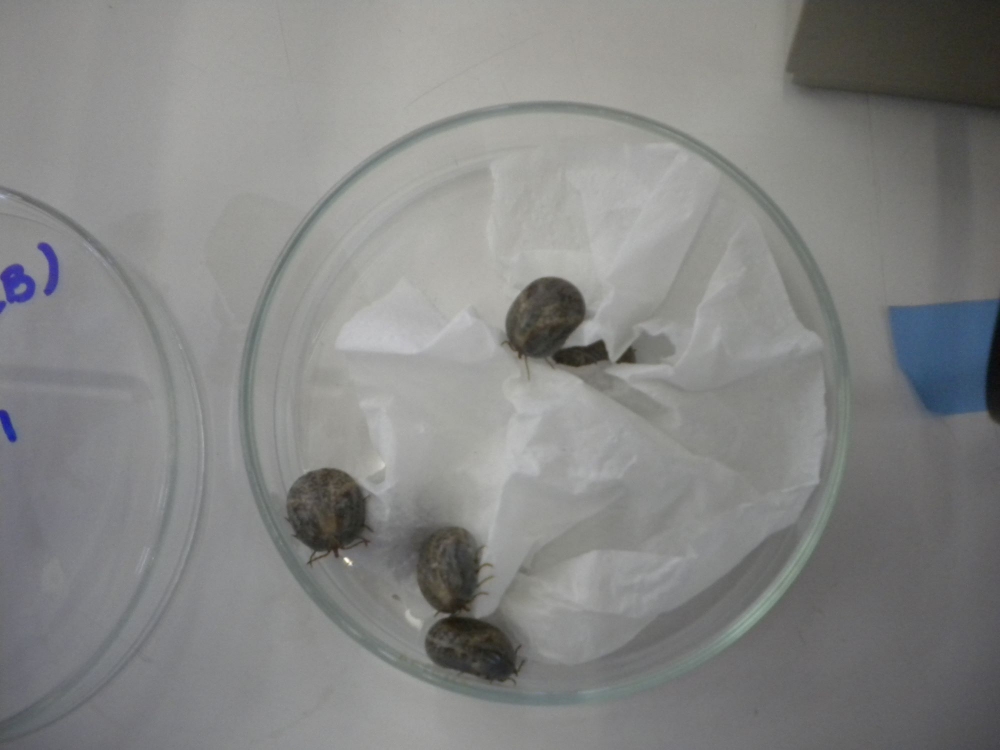



The molecule was identified by researchers at the University of São Paulo in cells of the Amblyomma tick that transmits the disease.
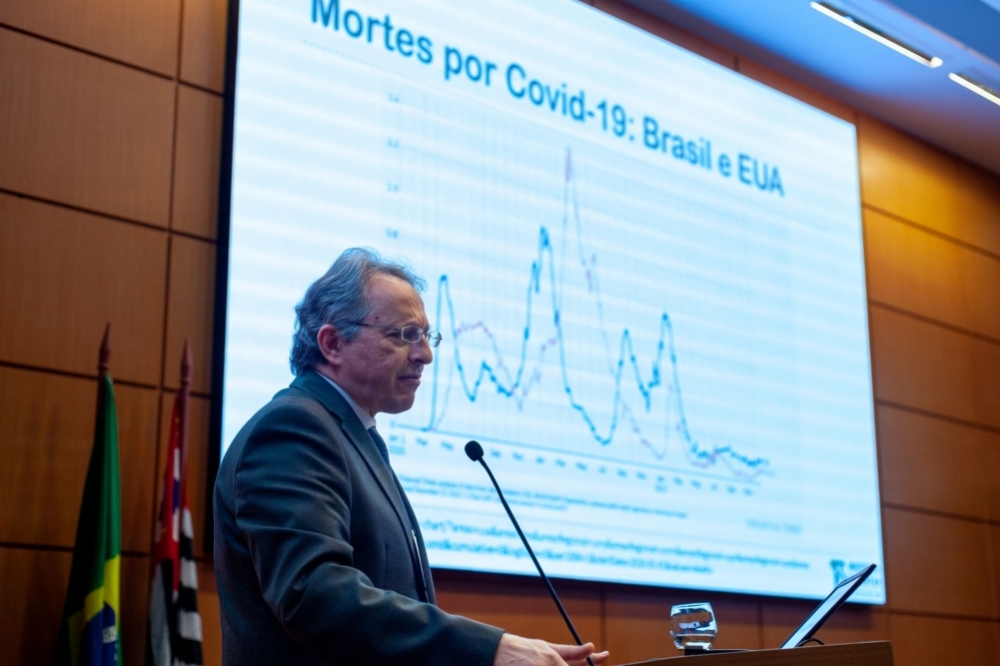

Esper Kallás, who heads Latin America’s leading producer of vaccines, delivered the Second 2023 FAPESP Lecture on “Viruses, pandemics and vaccines”. He spoke about the “100 Day Mission” to produce novel vaccines in just over three months.

The computer program was developed at the State University of Campinas to include more vegetation diversity in the analysis of climate change impacts.

The alert came from scientists who participated in the 10th German-Brazilian Dialogue on Science, Research and Innovation, organized by the German Center for Science and Innovation in São Paulo in partnership with FAPESP.
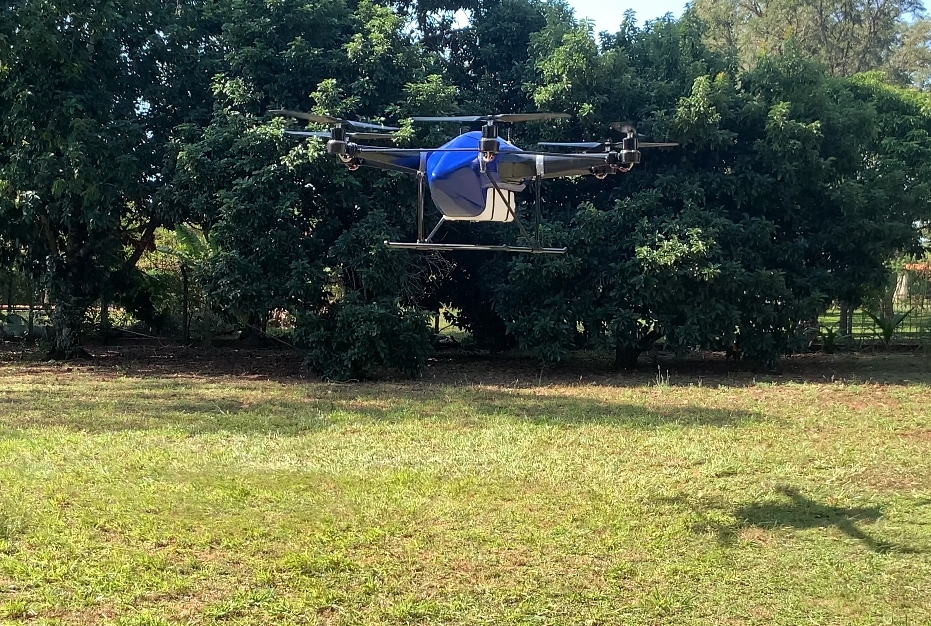

Brazilian technology developed with FAPESP’s support can be used to spray large or small areas, economizing inputs, lowering costs and mitigating environmental impacts.

First meeting was held last week in The Hague, Netherlands, during the Annual Meeting of the Global Research Council.

Initiatives developed by Elsevier, Royal Society of Chemistry, South Africa’s National Research Foundation and German Research Foundation were presented at event held in The Hague, Netherlands.

Debate was hosted by Swedish, American and Japanese research funding agencies at the Annual Meeting of the Global Research Council.
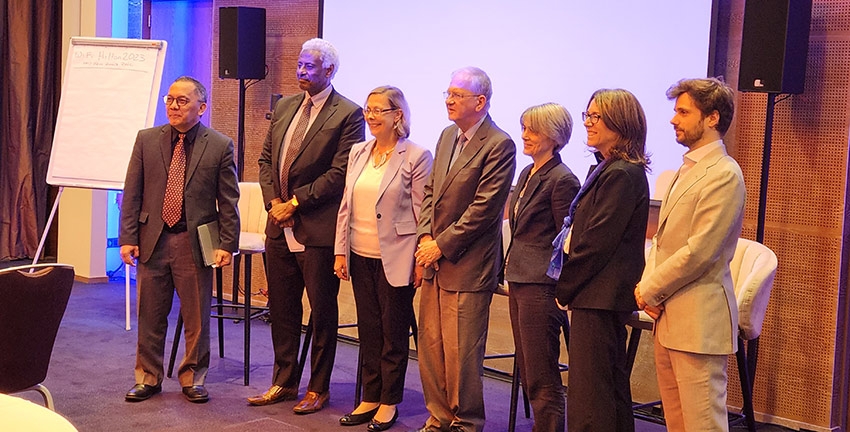

This assessment was made by participants of an event promoted on Tuesday by the Gender Working Group of the Global Research Council. One of the panelists was Marco Antonio Zago, president of FAPESP.
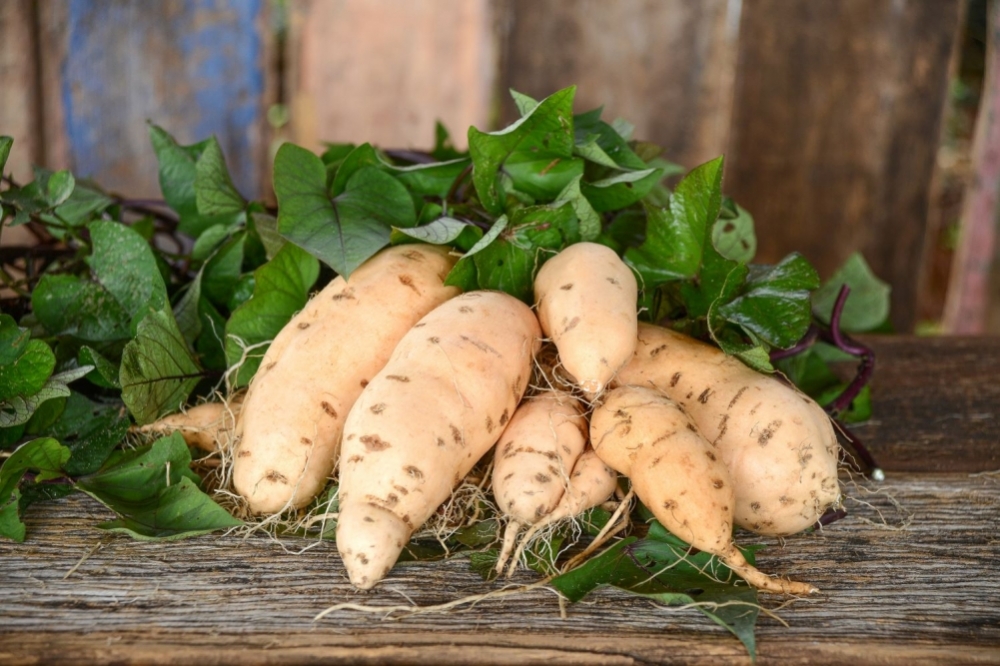

Research groups in São Paulo state and Mozambique analyzed carotenoids in over 1,000 sweet potatoes and found some with 88% more beta-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A.

Discovered by Uruguayan scientists in 2013, two psychrophilic (cold-adapted) species have been experimented with since 2018 by a partnership between IIBCE in Montevideo and the University of São Paulo in Brazil.

Researchers in São Paulo state analyzed data for over 1 million patients hospitalized for treatment by the public health service after contracting COVID-19. Lower levels of inflammatory cytokines and fewer ACE2 receptors for the virus to bind to may be the explanation.

In experiments involving rats, researchers at São Paulo State University found that periods of low oxygen levels in the first months of life can lead to dysregulation of the sympathetic autonomic nervous system, which controls functions such as heart rate and blood pressure. The discovery points to possible routes to the development of novel therapies.
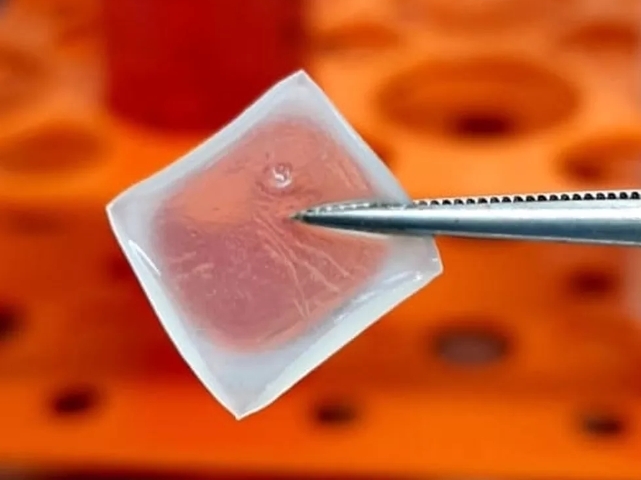
A biodressing containing human umbilical cord stem cells was produced in a 3D printer by the startup In Situ Cell Therapy. Researchers at the University of São Paulo found that when used on diabetic mice, the “smart” biodressing modulated the immune response, stimulated collagen synthesis and enhanced tissue repair.

FAPESP has funded more than 40,000 research projects linked to one or more SDGs, said Marco Antonio Zago.
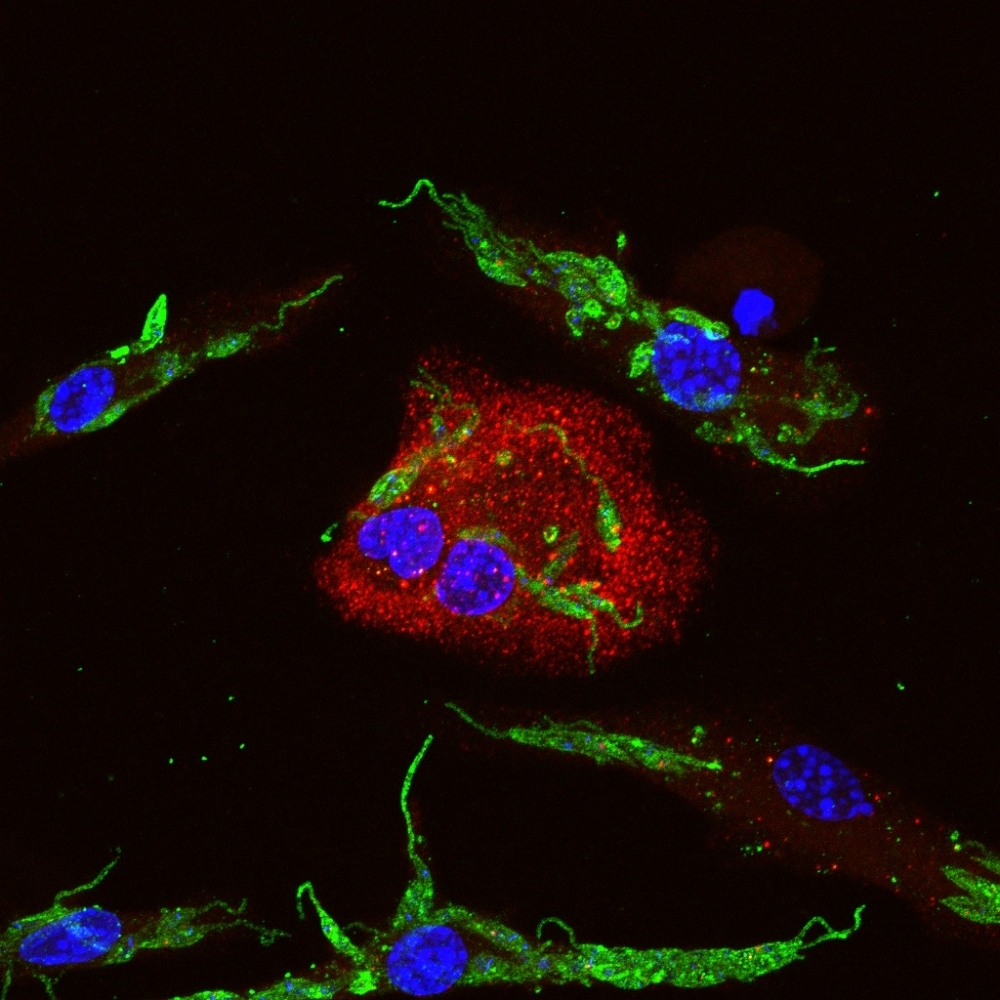
Leishmania alters the structure of the human protein that would normally induce the death of infected cells and weakens the inflammatory response. Reported in Nature Communications, the discovery could serve as a basis for better treatment.

An analysis conducted at the University of São Paulo showed that no sample exceeded the recommended limit for aflatoxin M1, a contaminant of fungal origin considered carcinogenic. Nevertheless, the researchers warn of the need to demand best practices in dairy production.
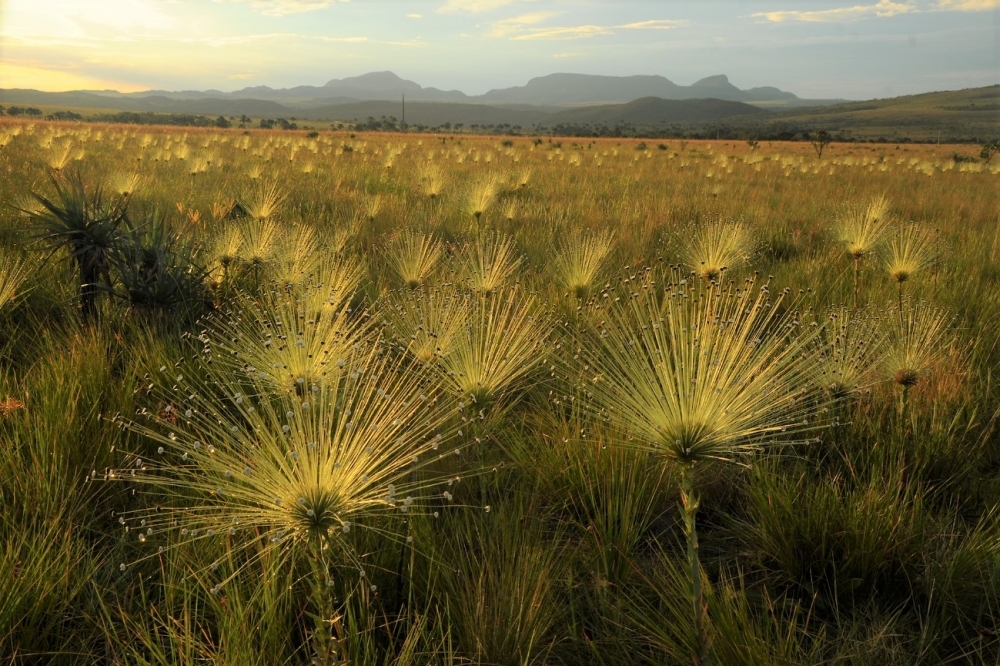

No fewer than eight important hydrographic basins depend on the ecosystems that make up the Cerrado, Brazil’s savanna-like biome, but ambiguities in the legislation have permitted the advance of soybean plantations in the region. The warning is in an article by Brazilian researchers in the journal Perspectives in Ecology and Conservation.

A study by researchers at the State University of Campinas showed that although the two types of training produce similar metabolic stress, muscle activation is different.
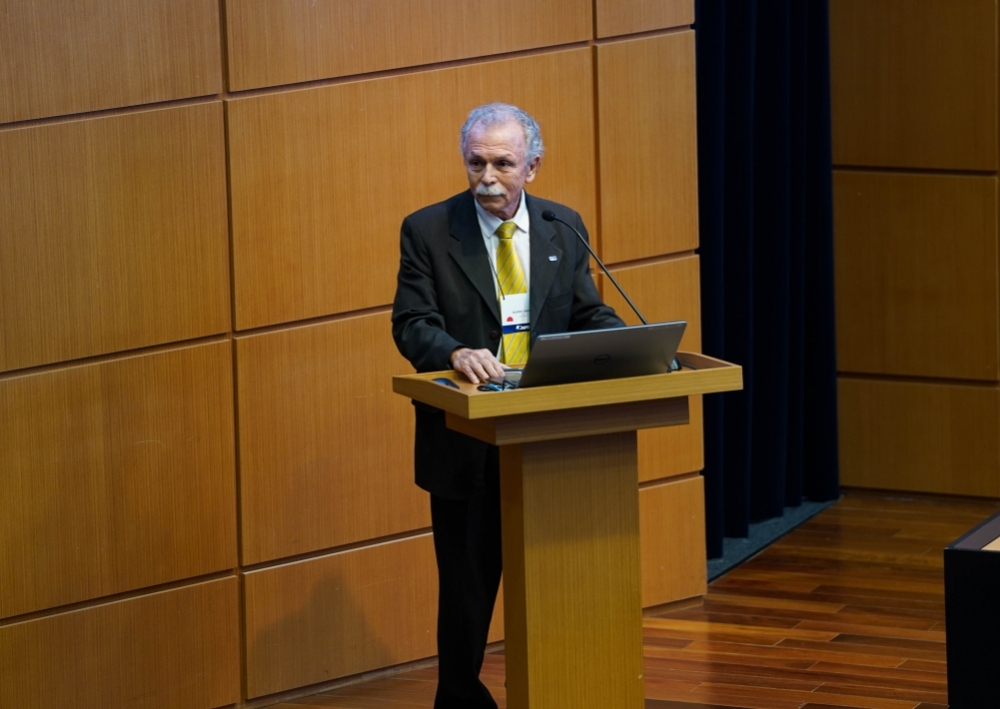

Ricardo Galvão, President of the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), discussed the status quo and outlook for Brazilian science in the first of the 2023 FAPESP Lectures.
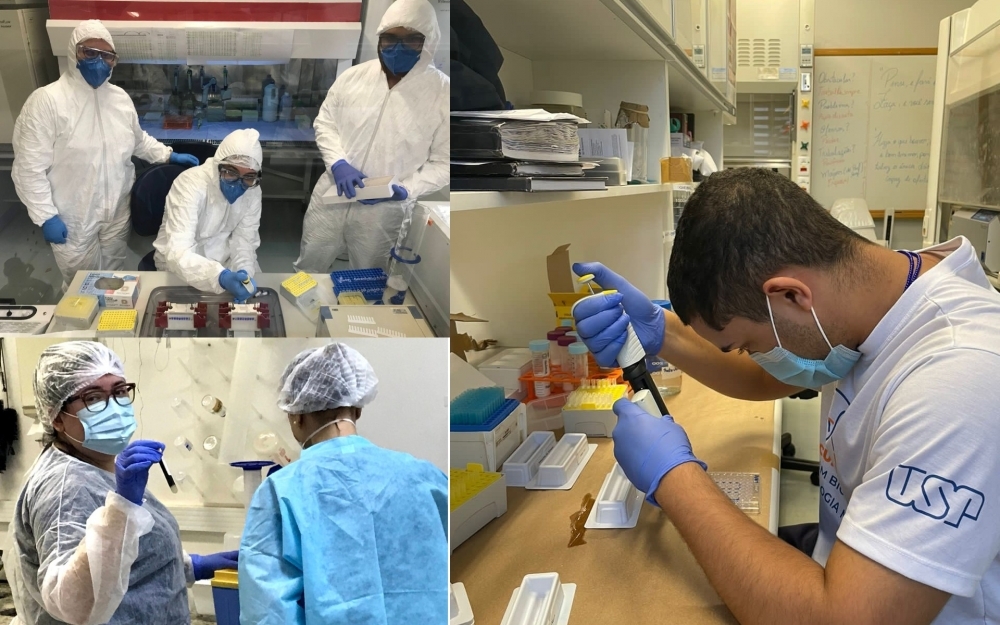

Brazilian researchers observed an increase in production of endocannabinoid, a natural anti-inflammatory neurotransmitter, in COVID-19 patients given glucocorticoids. The discovery points to possibilities of novel treatments for various inflammatory and neurological diseases.
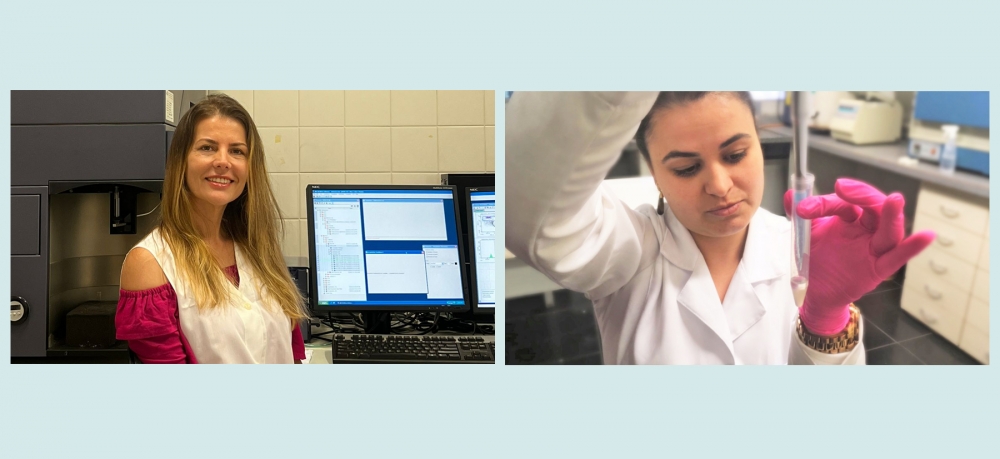

Scientists at São Paulo State University repurposed a device already used to analyze bovine reproductive cells to observe different characteristics of human sperm simultaneously.

A sprayable solution developed by researchers at the State University of Campinas does not spread rapidly over a surface and efficiently eliminates harmful microorganisms. The technology can be licensed from the university’s innovation agency.
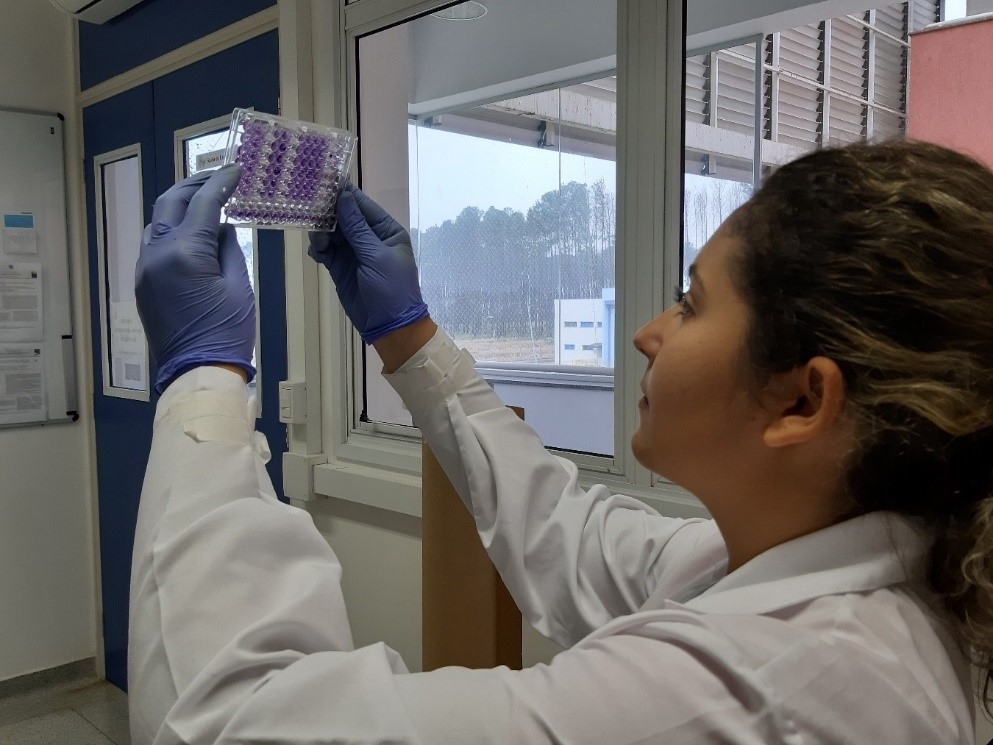

In vitro experiments were conducted at a FAPESP-supported research center with a synthetic peptide inspired by molecules secreted by the probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus plantarum.
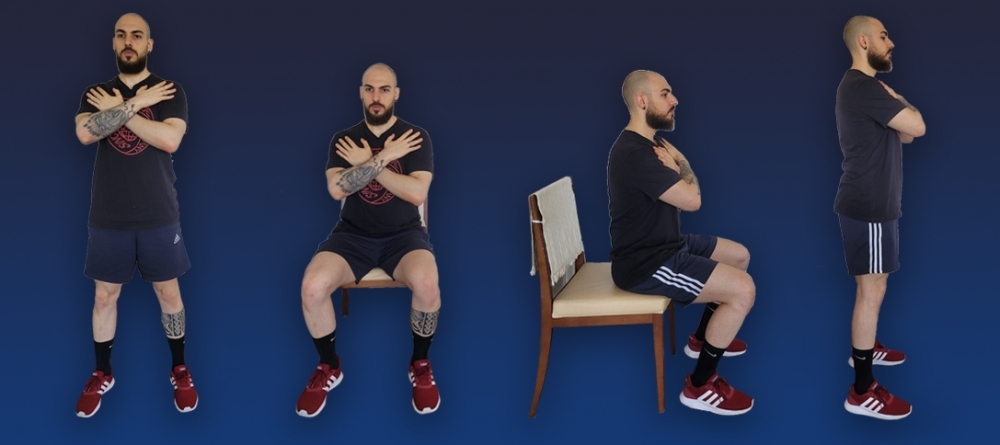

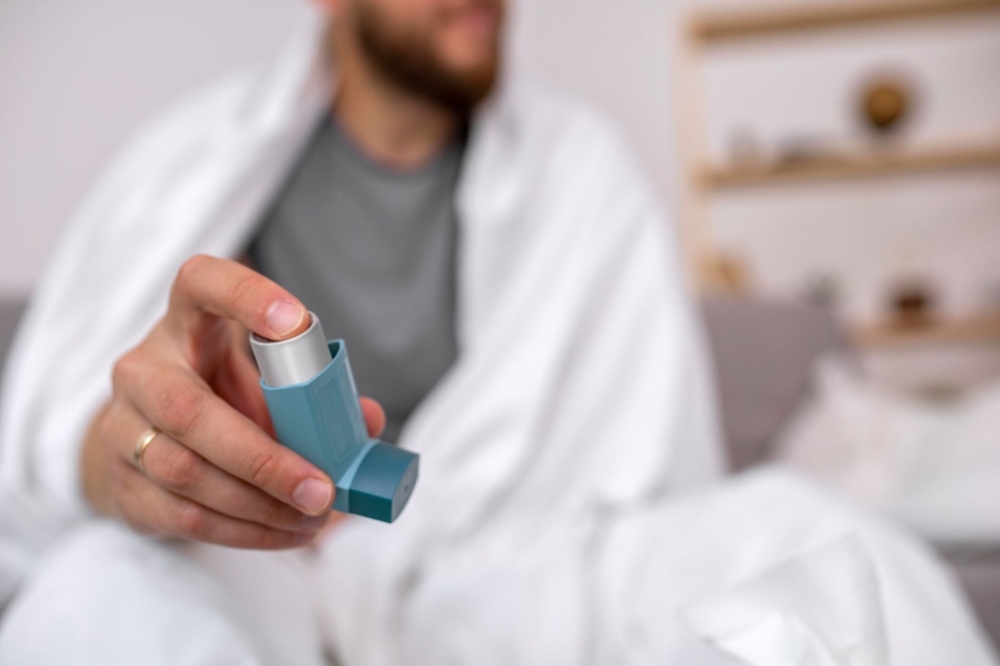
A program developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo included three weekly sessions of up to 80 minutes each for 16 weeks, with positive effects on cardiorespiratory fitness, lung function, functional capacity, body composition and persistent symptoms.