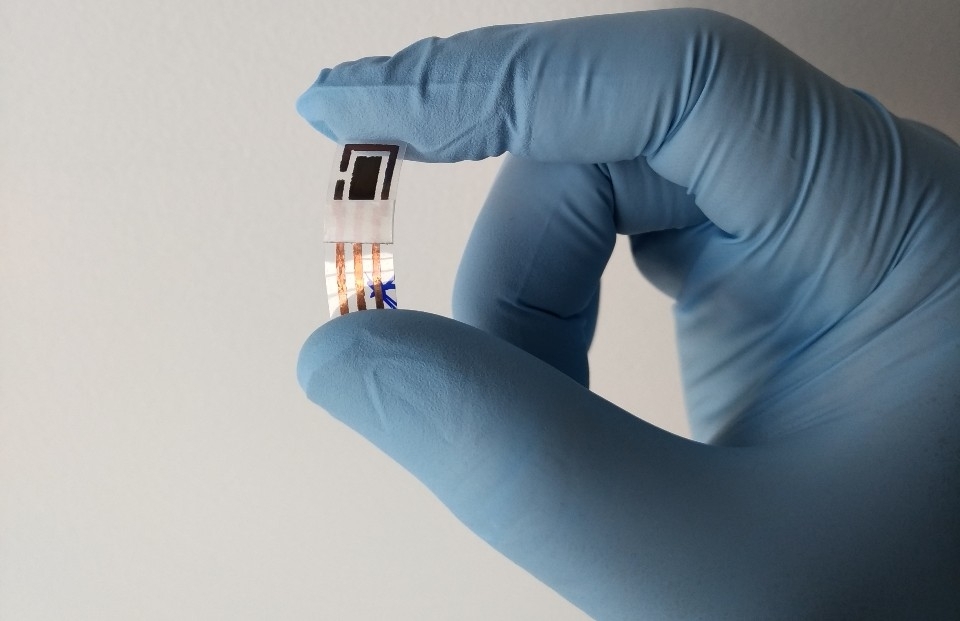



Flexible copper device identifies lead and cadmium in sweat and can be used by untrained personnel to monitor exposure to toxic materials.
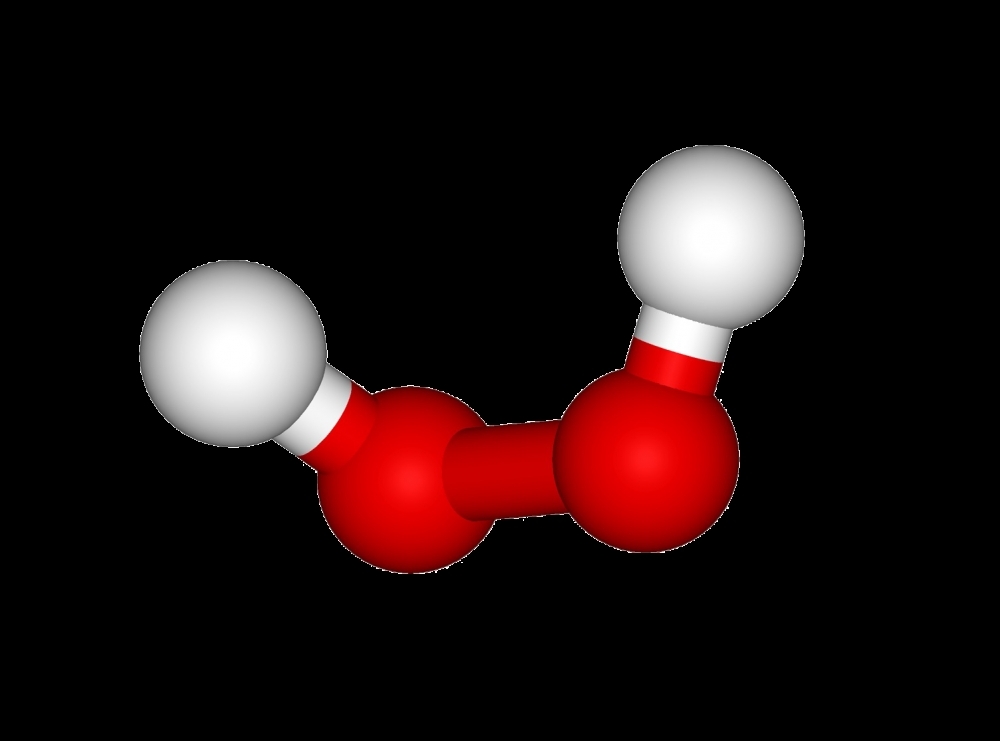
Hydrogen peroxide is used to sterilize medical equipment, to bleach fabric, pulp and paper, and whiten teeth, among other applications.
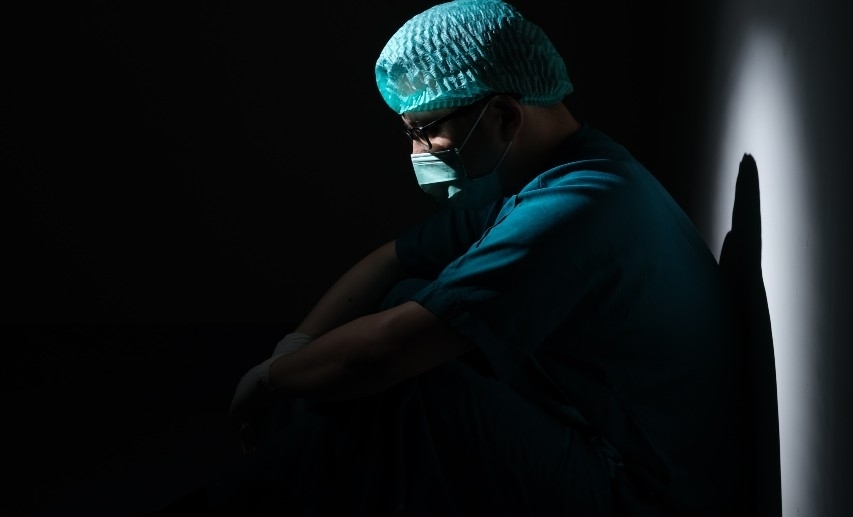
Stress, burnout, pain and poor sleep were some of the most frequent symptoms reported by nursing and other staff who care for patients in a study conducted by researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos in São Paulo state, Brazil.
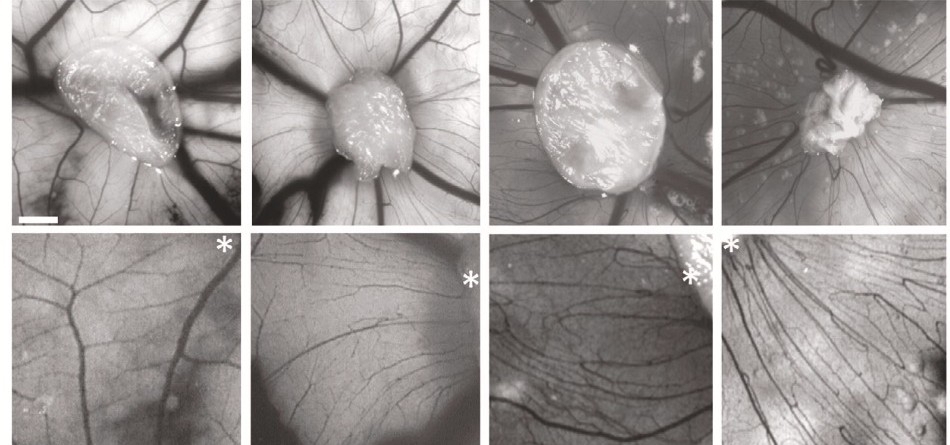
Brazilian researchers have discovered that central nervous system cells from patients with schizophrenia secrete substances that reduce the thickness of blood vessels in the brain, possibly leading to diminished metabolic flux in some parts of the CNS.
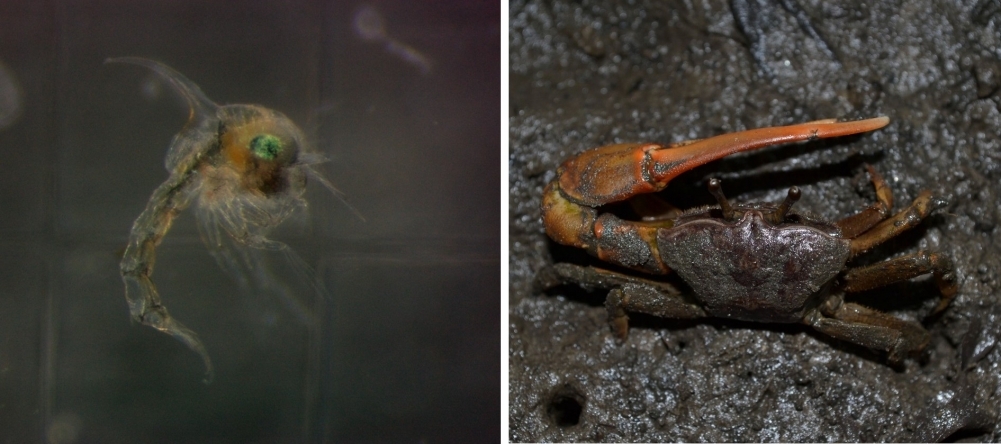

In an experiment, the survival and physiology of crab larvae on which other species feed were affected by rising sea surface temperatures. Events of this kind will be up to 35% more frequent between now and the end of the century in the study area.

Deep techs established in São Paulo have flourished in recent years, particularly in 2017-19, according to a survey led by the Brazilian Small Business Support Service.
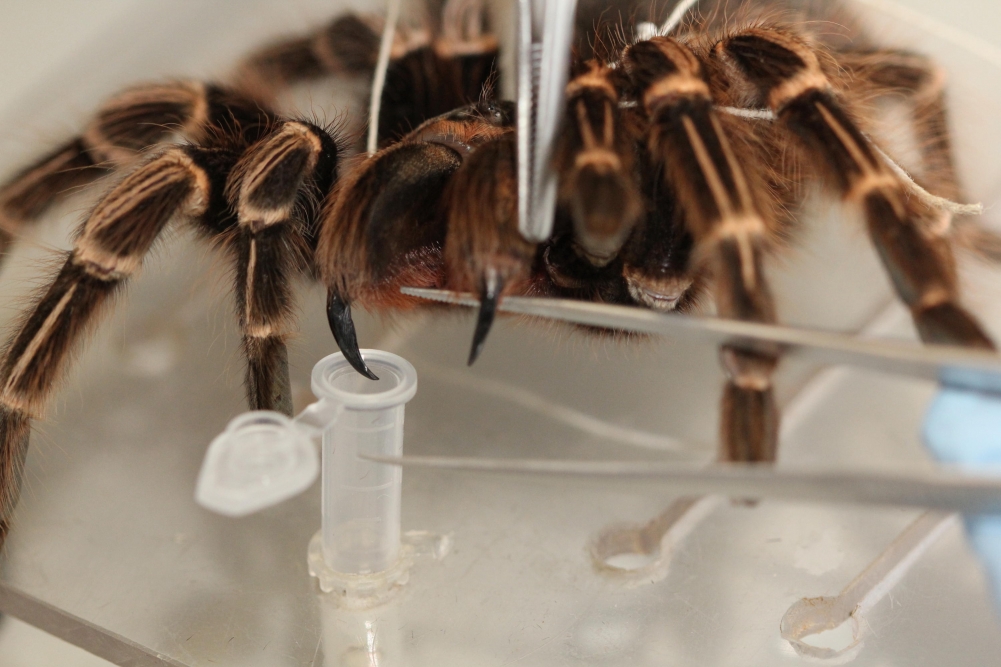

Researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo and Butantan Institute used several advanced techniques to analyze the venom of the Orange banded tarantula Acanthoscurria juruenicola and tested its capacity to paralyze crickets. The findings could contribute to the development of biodiversity-based solutions.

Neuropathic pain is chronic and caused by injury to the nervous system, affecting between 3% and 15% of the population. The only treatment options currently available are drugs originally developed for other conditions, such as epilepsy or depression.
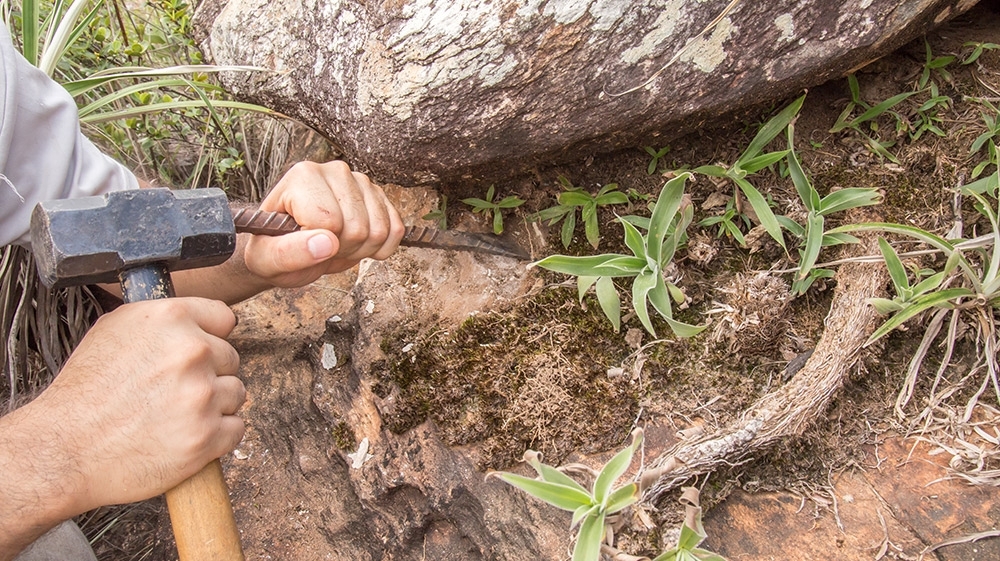

A study shows that archaea, bacteria and fungi found in campos rupestres, a Brazilian ecoregion with low-fertility soil, are essential sources of plant nutrients. Products originating in the discovery could be used in future as substitutes for chemical phosphate fertilizer.

The study involved 146 patients, 74 of whom were treated with an antivenom produced by Butantan Institute in São Paulo. The results showed the antivenom to be safe and effective, especially if it is administered within 48 hours.

In a survey of 3,021 people conducted in a Brazilian city, the proportion was 26% higher than for white women, 19% higher than for White men and 14% higher than for Black men. The findings are reported in PLOS ONE.

A review of 300 projects funded by FAPESP since 1972 highlights its contributions to the understanding of marine life, especially after the launch of BIOTA, its biodiversity program, in 1999. One of the challenges for the future is expanding deep-sea research.

Researchers who lectured at the São Paulo School of Advanced Science on a Sustainable and Inclusive Amazon insisted that a new bioeconomy is urgently needed for the region.
Online workshops involving 11 member organizations of the Global Research Council discussed mechanisms and tools to stimulate research partnerships across the continent.
The initiative was one of the few advances achieved at the 27th United Nations Climate Change Conference held in November, according to the participants in a webinar hosted by FAPESP.
This kind of phenomenon can have applications in encryption, communications and quantum computing.

One of the aims of the telecommunications excellence hub hosted by the State University of Campinas is to build a new platform capable of deploying advanced 5G and 6G networks.

The participants included Hernan Chaimovich and Carlos Henrique de Brito Cruz. The book A Ciência no Desenvolvimento Nacional, edited by the São Paulo State Academy of Sciences, was launched during the event.

Experts discussed violence and radicalization at an online seminar held by the São Paulo State Academy of Sciences. The topic is the title of the seventh and last chapter of FAPESP 60 Anos: A Ciência no Desenvolvimento Nacional.

A presentation to the 16th edition of the series of FAPESP 60 Years Conferences emphasized the importance of giving users of digital communications technology a minimum of means to defend themselves from fake news.
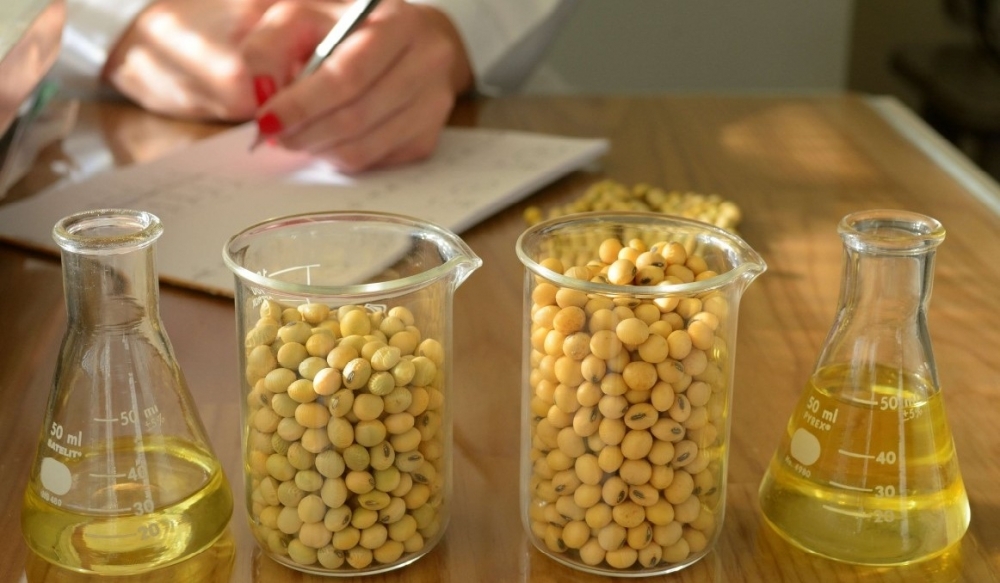

Brazilian and Dutch researchers have developed a technique for early identification of soybean genotypes that are unlikely to form green seeds, which cannot be used to produce oil.
The dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 variant substitution in the town where a clinical trial of vaccination effectiveness was conducted matched the pattern seen elsewhere in the country, but most cases were mild. The researchers analyzed 4,375 whole genomes of the virus.
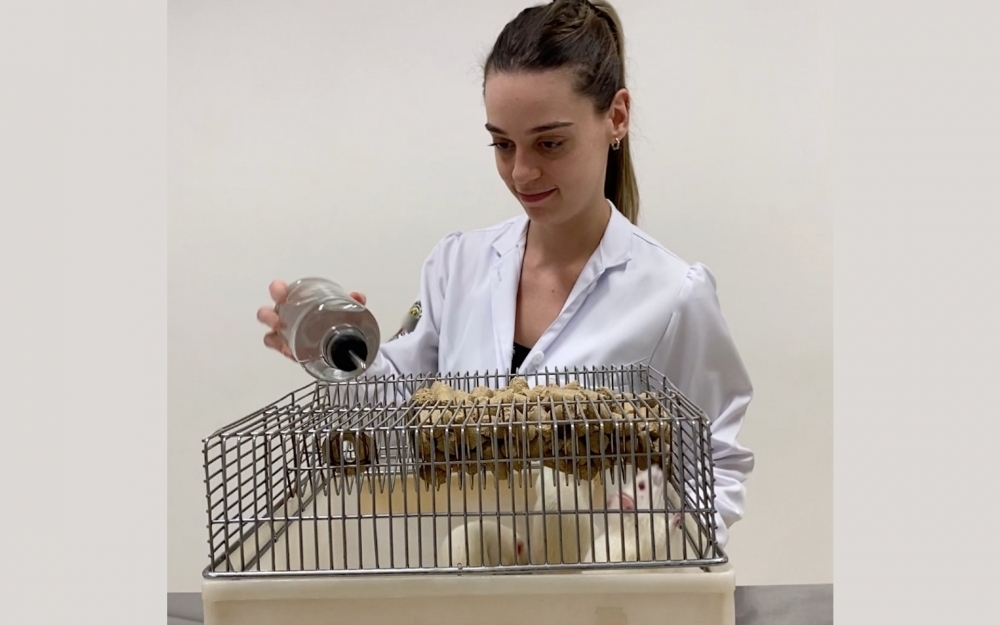

In experiments involving rats, researchers at the University of São Paulo analyzed the effects of celecoxib and indomethacin. The results are published in Scientific Reports.
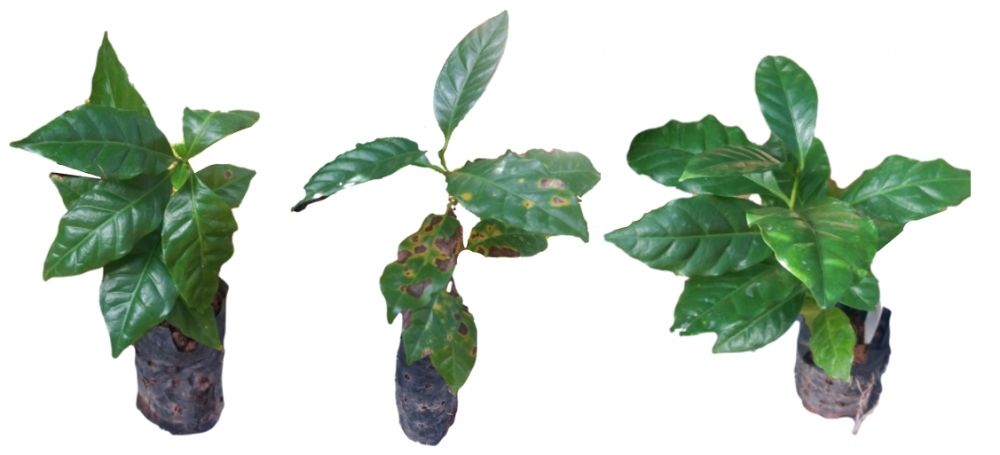

Their research is part basic science, investigating the bacterium’s resilience in a hostile environment – coffee leaves – and part biotech, seeing whether the bacterium inhibits the development of a pathogen that causes severe losses to coffee growers.
A group of researchers in Brazil and the UK have developed a method to track seroprevalence in real time. An article in the journal eLife shows how this was done in the case of SARS-CoV-2, providing a “portrait” of the first year of COVID-19 in Brazil.