


A study conducted at the State University of Campinas provides a foundation for future research to confirm identification of the best candidate genes for biotech applications such as insertion into commercially valuable plants and development of sugarcane varieties resistant to environmental pressures.
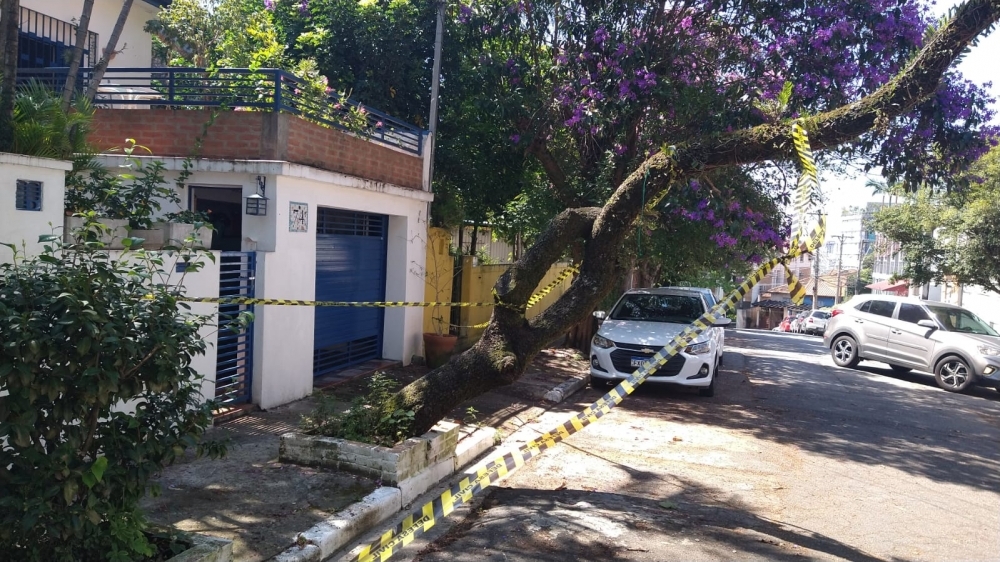

Research conducted in São Paulo, the largest city in the southern hemisphere, also found sidewalk width and tree height to be key factors. The results will be used in tree management and urban planning.
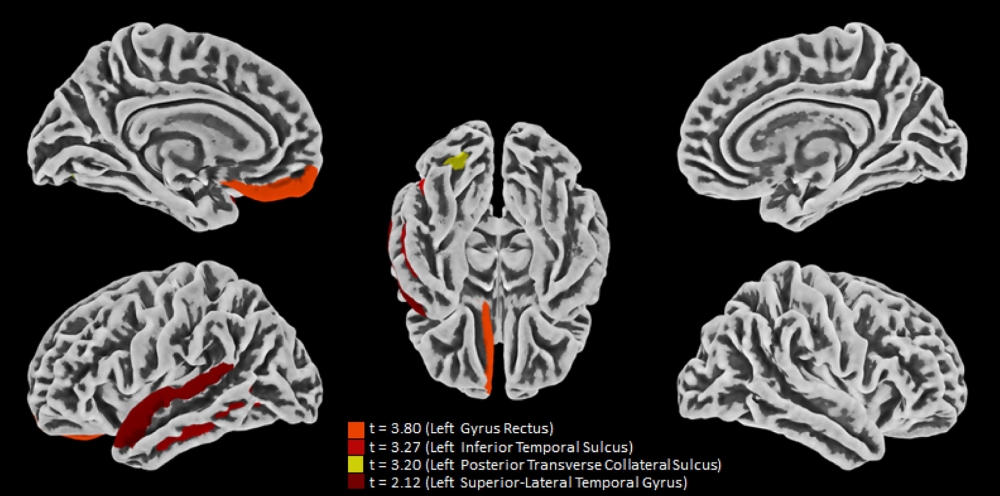
Research by groups at the University of São Paulo and the State University of Campinas combined MRI scans of the brains of mild COVID-19 patients, analysis of brain tissue from people who died of the disease and experiments on human nerve cells infected in the laboratory.
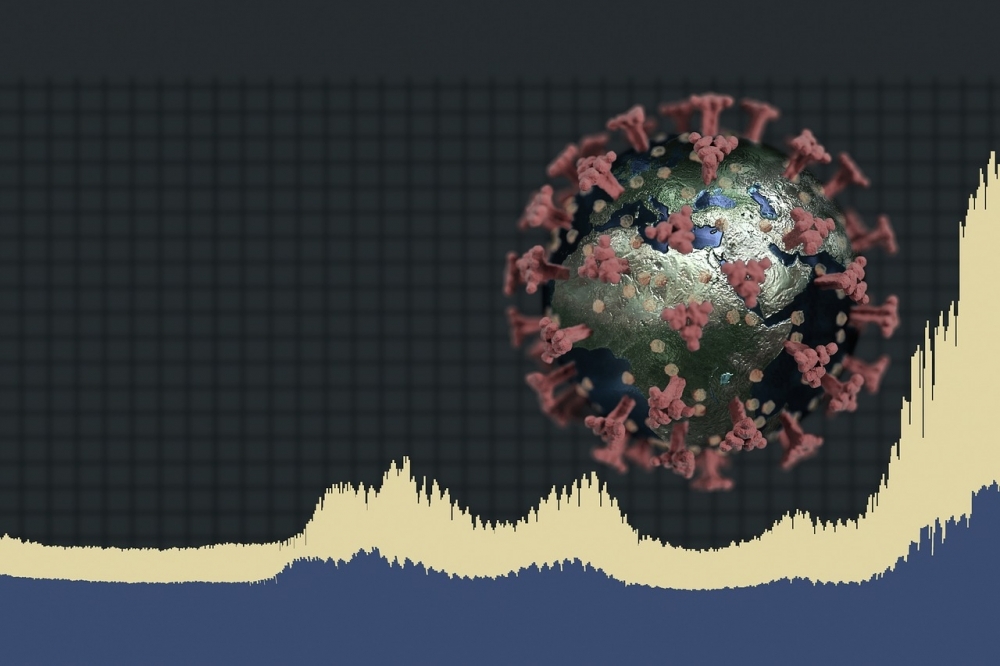
A study published in the journal Vaccines used samples from blood banks in seven Brazilian state capitals to measure levels of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and the extent to which vaccines afford protection against the delta variant.
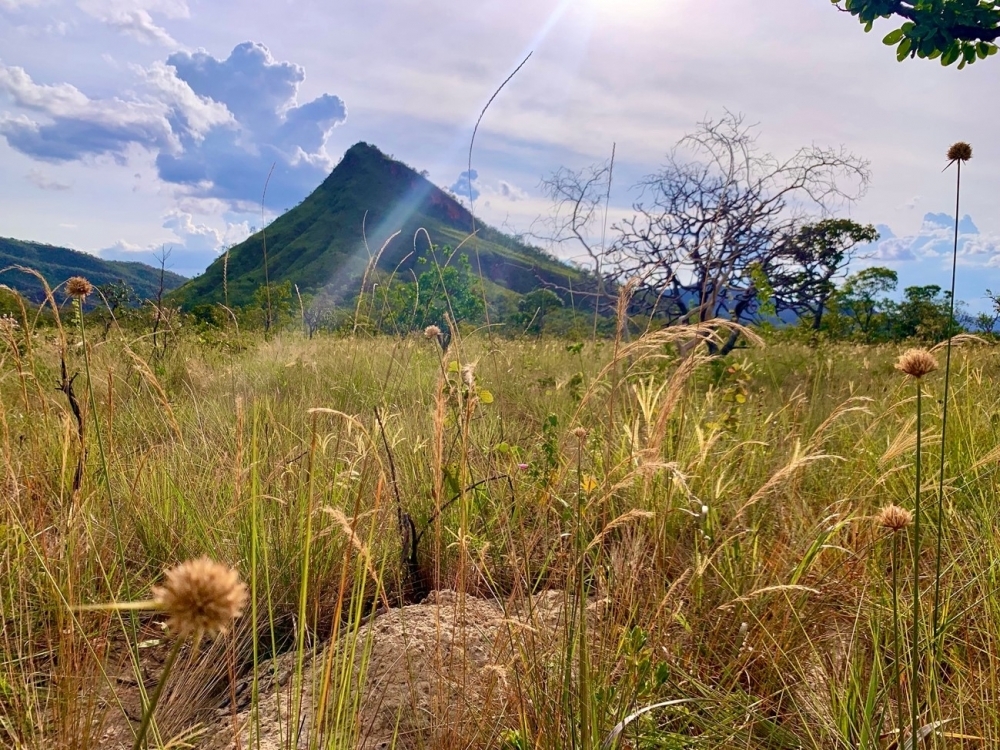

In a special issue of the journal Science, some of the leading experts on the subject argue that rehabilitating degraded areas requires more complex solutions that take the biome’s specificities into account.
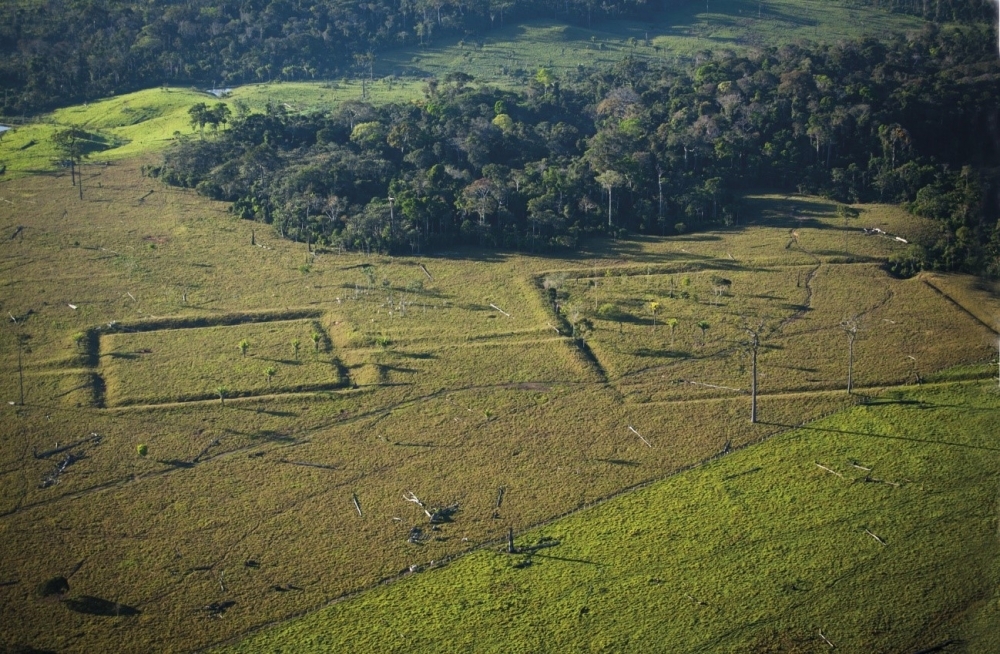

Eduardo Góes Neves, an archeologist at the University of São Paulo, sets out this and other findings of 15 years of research in a book for non-specialists.

Twenty-one patients with metabolic syndrome were given a calorie or protein restriction diet in a randomized clinical trial by Brazilian and Danish researchers. Weight loss, controlled blood pressure and improved blood sugar and lipid levels were observed in all participants.
A study by Brazilian researchers analyzed risk factors and found that reducing smoking prevented most deaths from cardiovascular disease, while high blood sugar had the most significant impact on mortality.
Proteomic analysis suggests zika virus causes alterations in the expression of proteins linked to the metabolism of developing neural cells, and proteins associated with the maturation of oligodendrocytes.
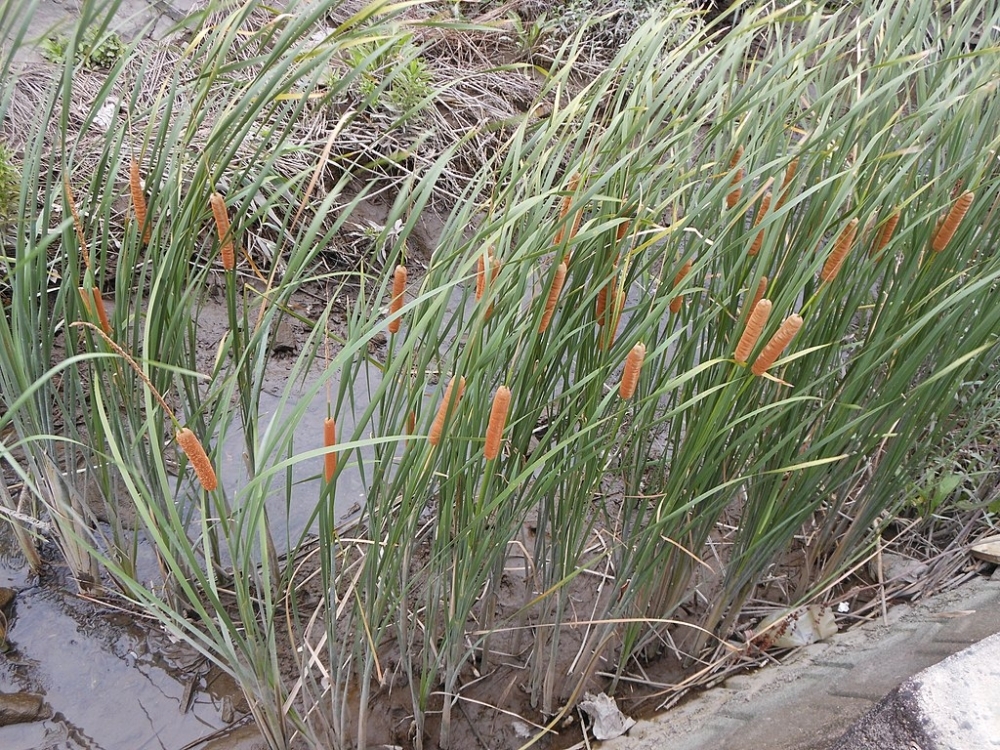

Researchers at the University of São Paulo and collaborators showed that the aquatic plant can scavenge up to 34 times more manganese from contaminated soil than other plants found in similar environments.
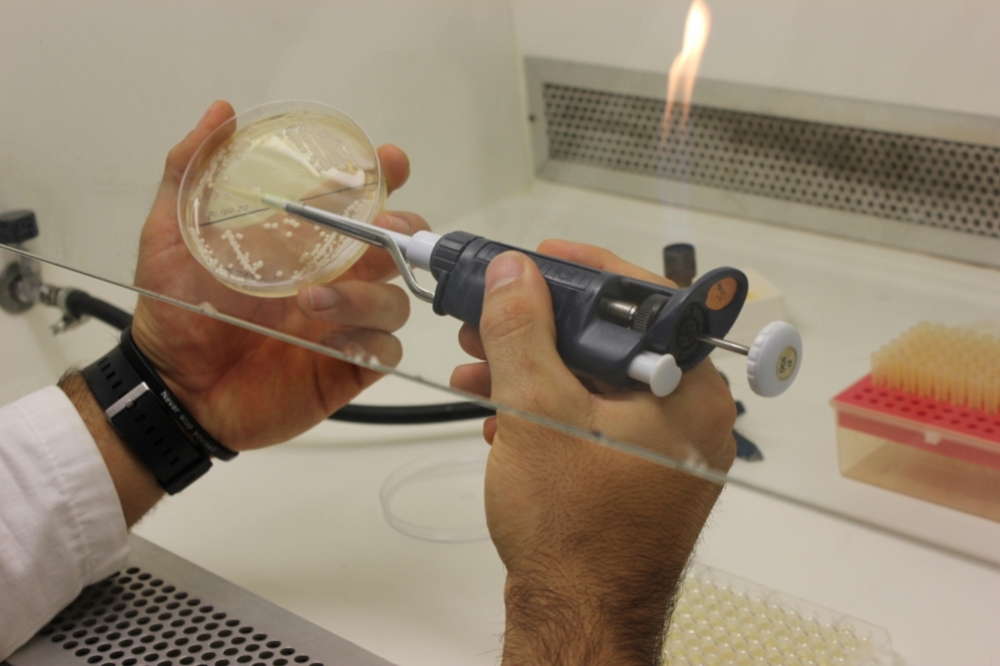

Researchers at the State University of Campinas have edited the genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the brewer’s yeast used to produce ethanol, so that it converts xylose into xylitol. The strategy can add value to the ethanol industry and meet demand for a healthier sweetener.
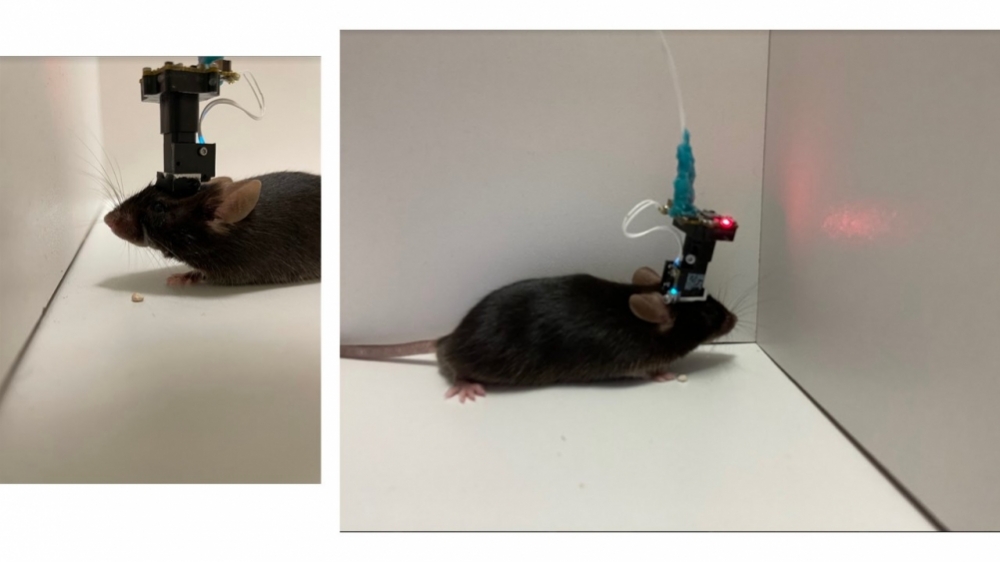
The study involved the use of biosensors, algorithms and open-source software to build a miniature microscope. The findings contribute to a better understanding of how our brains track and retain information about routes and learn new locations.

Conservation of CO2 stocks in the biome is highly affected by forest degradation, which could lead to at least 30% higher emissions than those produced by climate change. The warning comes from a paper by Brazilian scientists published in Science Advances.
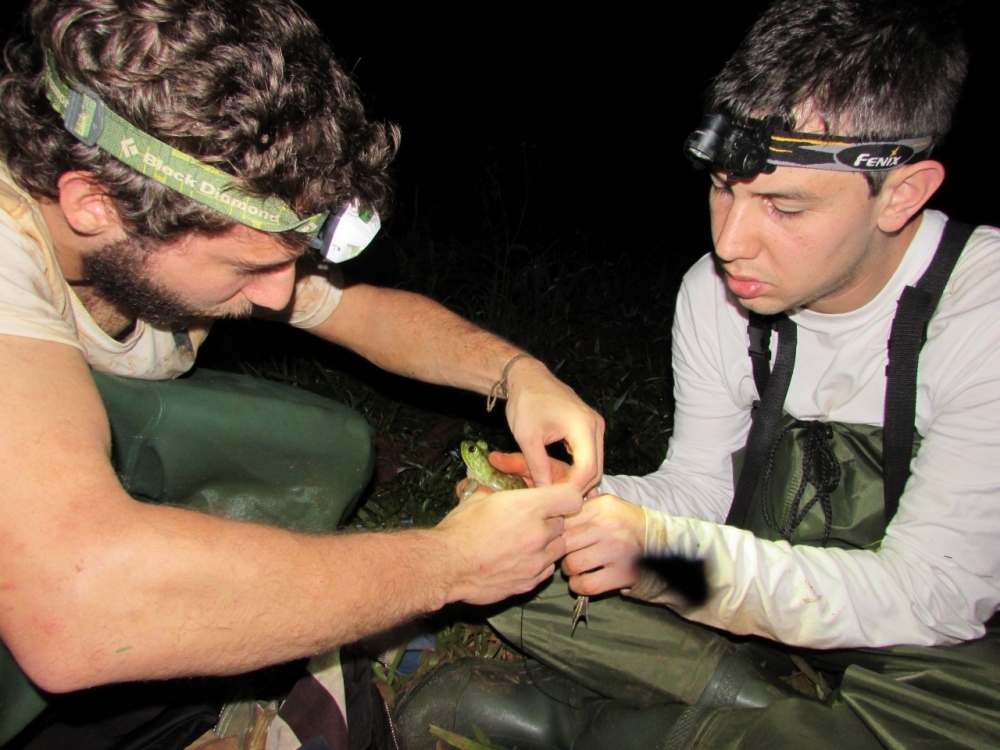

Genetic analysis of Aquarana catesbeiana, a species that originally came from North America and is now found in nine Brazilian states, shows that the lineage introduced in 1935 prevails in both captive and feral bullfrogs. Law enforcement to maintain sanitary standards is difficult. The invaders prey on native amphibians and transmit diseases to them.
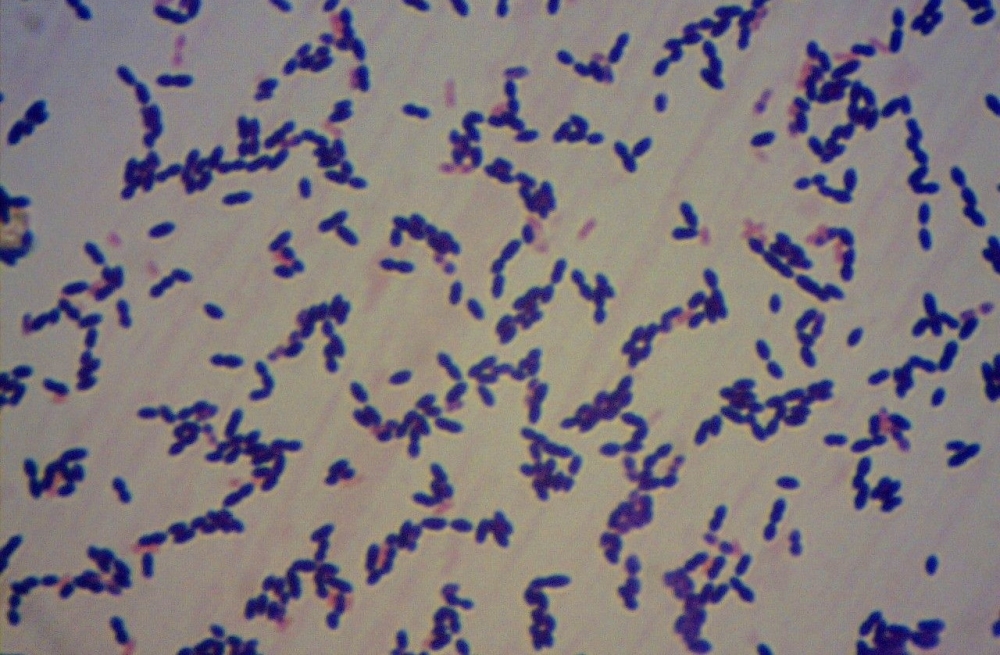
The results of a study conducted by Brazilian researchers will be useful both for epidemiological surveillance and to improve the treatment available to patients. An article on the study is published in PLOS ONE.

A startup supported by FAPESP has developed software to process legal cases, winning an important order from Brazil’s federal court of auditors.
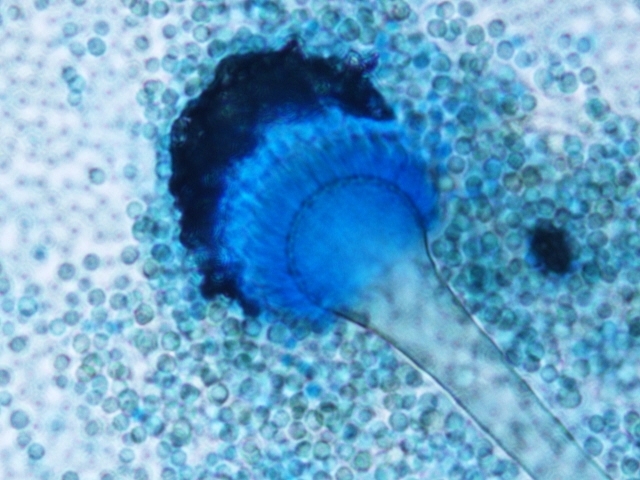
An international group of scientists presents this conclusion in an article in Nature Microbiology, warning that novel antifungal medications are urgently.
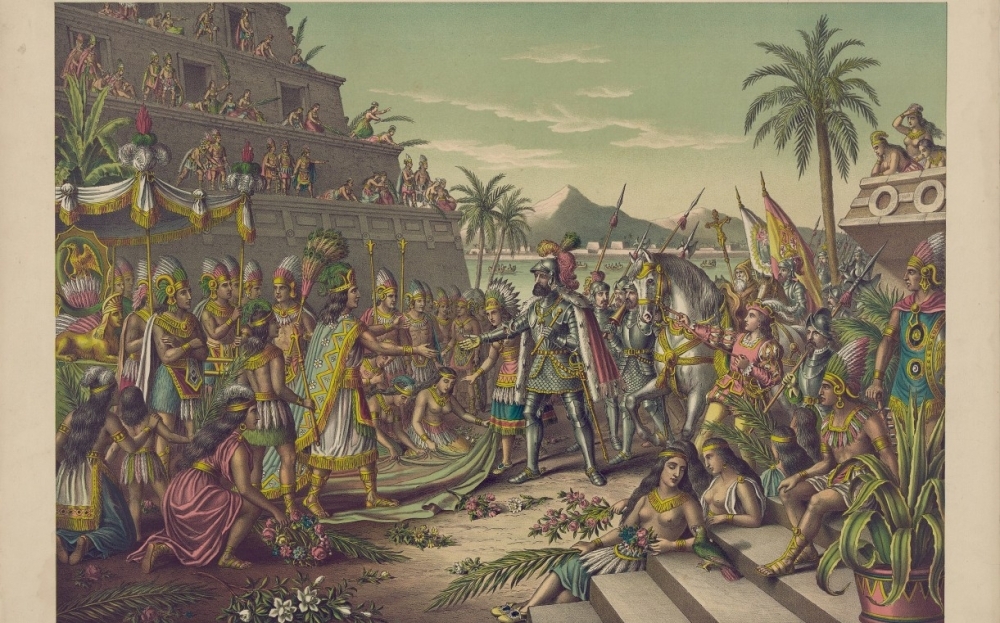

The topic was discussed by French historian Serge Gruzinski in a lecture delivered at the FAPESP 60 Years School in Humanities, Social Sciences and Arts.

This and related issues were discussed by Martin Ravallion from Georgetown University and Marcelo Medeiros from Columbia University (USA) during the 13th FAPESP 60 Years Conference.

The system is being developed by a Brazilian startup supported by FAPESP and can be used by biologists in scientific research, by NGOs to track endangered species, and by environmental consultants.

The topic was discussed on August 9 by Barry O’Keefe of the US National Cancer Institute during the FAPESP 60 Years School on Exact, Natural and Life Sciences. The other speakers on the second day of the event were José Nelson Onuchic of Rice University and Virgilio Almeida of the Federal University of Minas Gerais.

The combination is particularly dangerous for women, according to a study by researchers in Brazil and the UK who analyzed data for 5,310 people aged 50+ followed in a ten-year health survey.
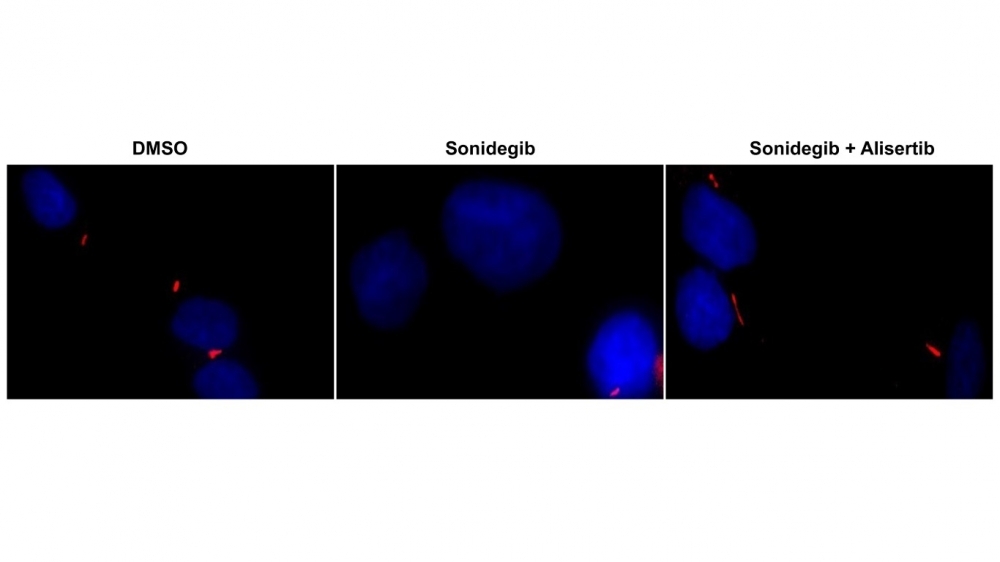
The type of ependymoma studied mainly affects children, has a low survival rate and has no specific chemotherapeutic treatment. A combination of two experimental drugs inhibited tumor growth in vitro.

The need to adapt was emphasized by Guy Brasseur, director of the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Nobel Peace Laureate in 2007, and keynote speaker on the last day of the FAPESP 60 Years School.
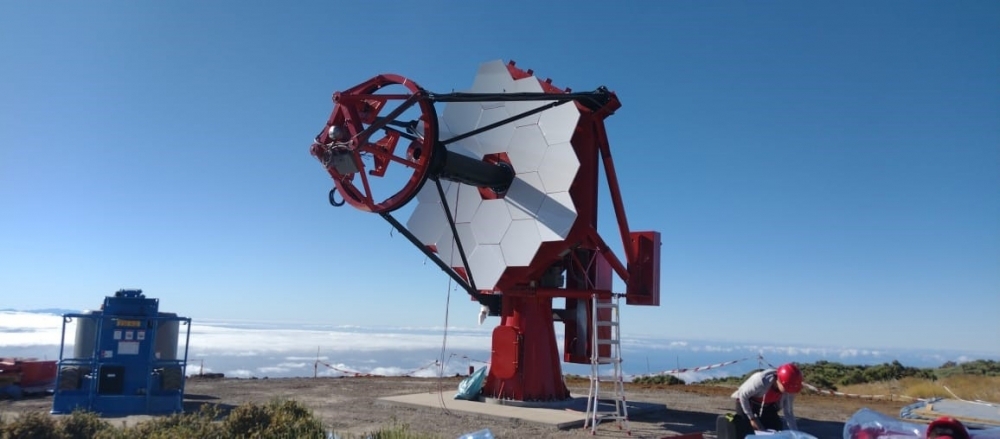

Astronomers from Brazil, Italy and South Africa have begun installing the first of nine telescopes sensitive to gamma rays on Tenerife in Spain’s Canary Islands.