

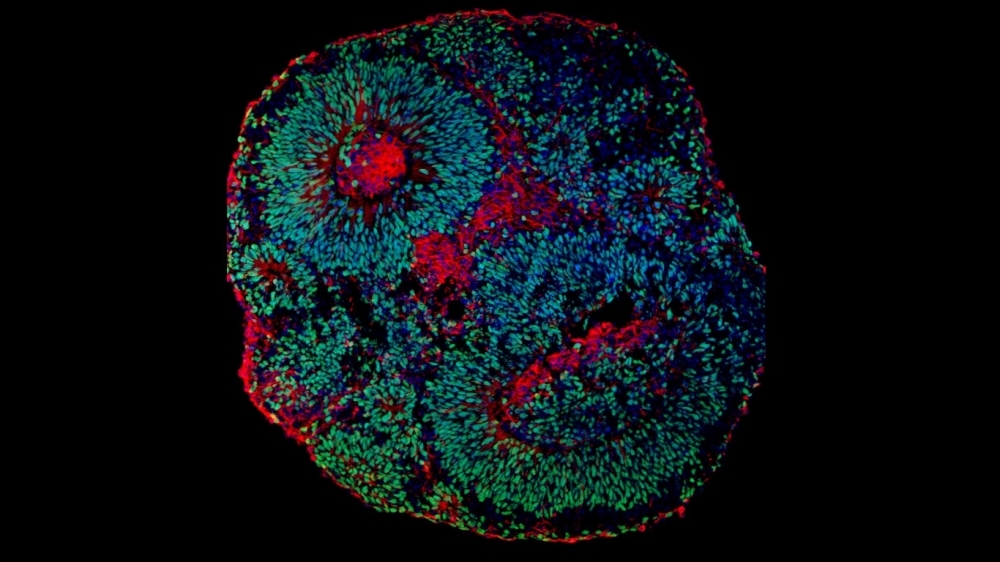
Researchers at the State University of Campinas and the University of California San Diego have discovered the mechanism that causes this rare but severe autism spectrum disorder. They reversed progression of the syndrome in laboratory models, opening up new possibilities for treatment using drugs and gene therapy.
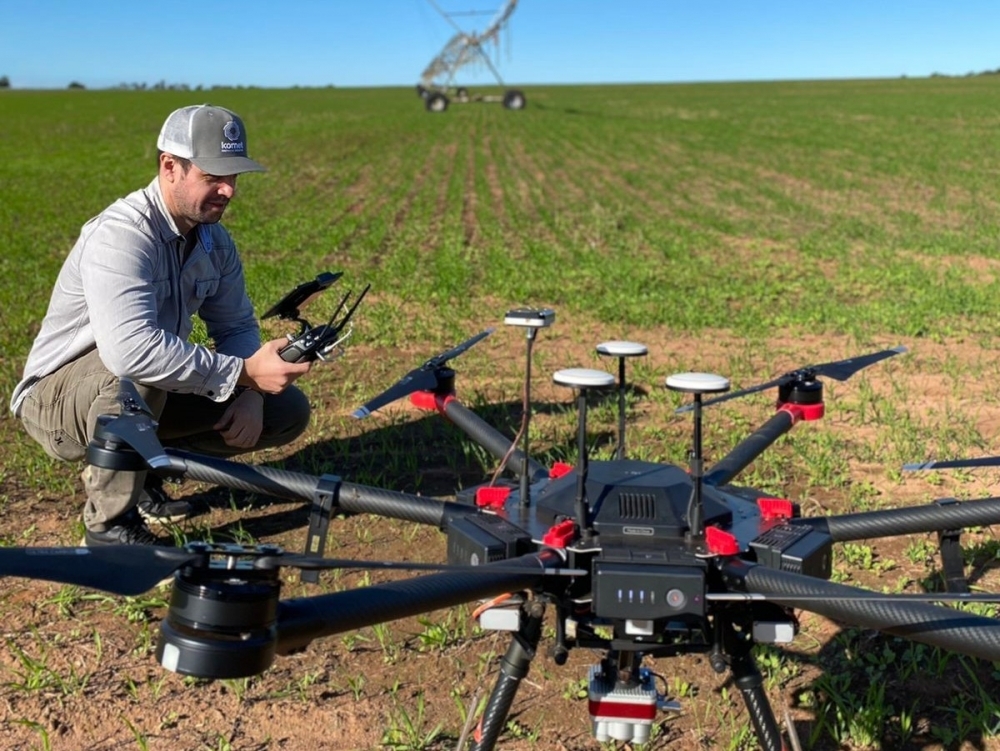

A study conducted at the University of São Paulo showed that management of irrigation with the aid of the algorithm, adjusted on the basis of field data, reduced water and power consumption by 31%. The researchers are now pursuing market validation of the technology.
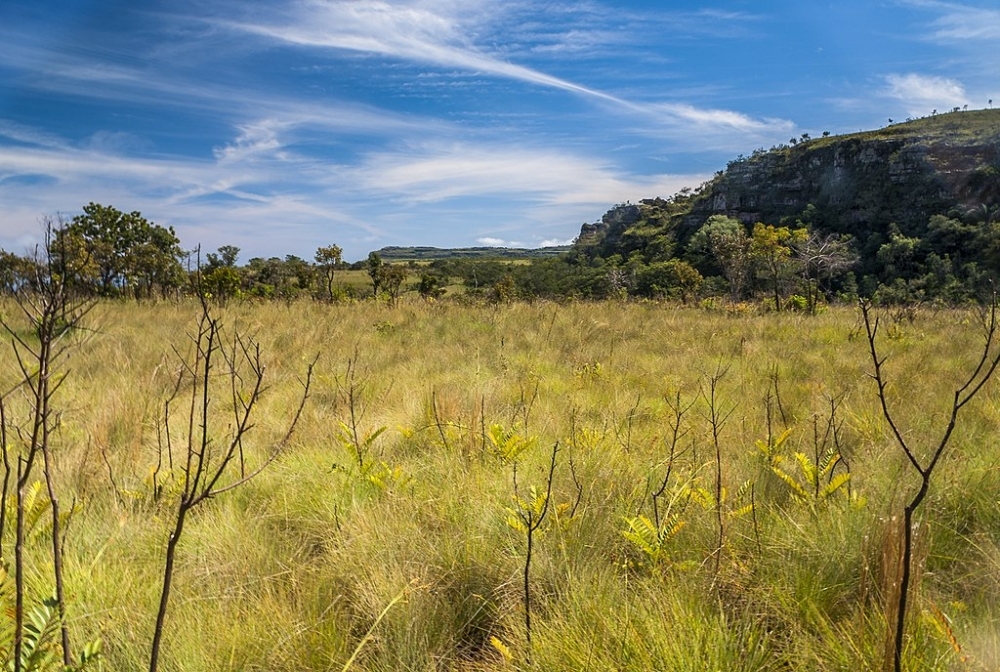

Grasslands are endangered everywhere on Earth, warns a group of researchers from several countries in Nature Reviews Earth & Environment. The solution involves restoration and the pursuit of sustainable economic development alternatives.
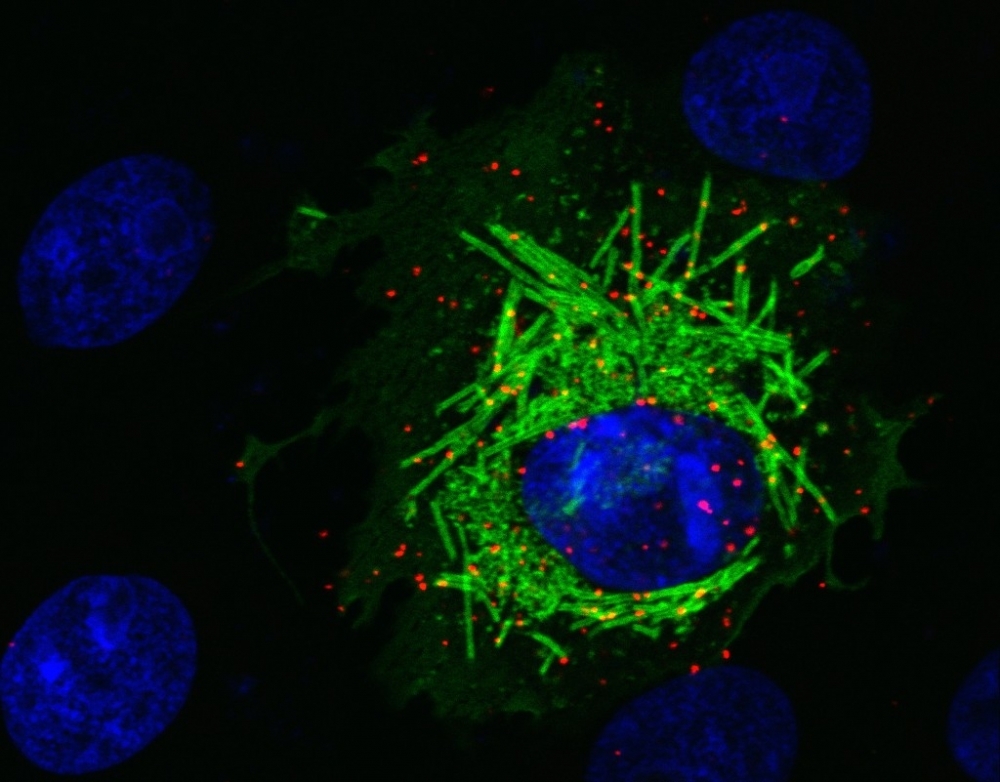
Brazilian researchers have discovered that PCNA, a protein present in the nuclei of human cells, interacts with the SARS-CoV-2 membrane matrix protein M. In laboratory tests, inhibition of this mechanism using a drug reduced viral replication by 15%-20%.
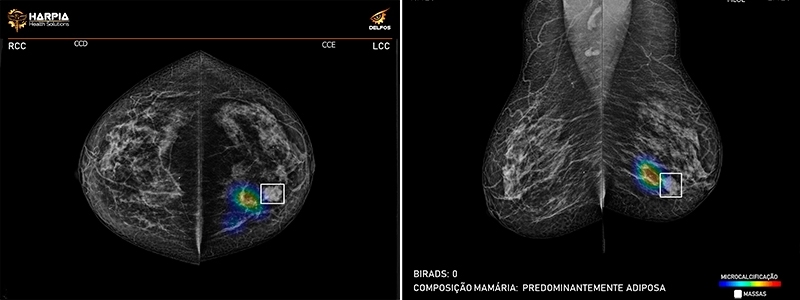
A startup supported by FAPESP has developed a technology based on artificial intelligence that can reduce the time to produce a diagnosis by 40%.
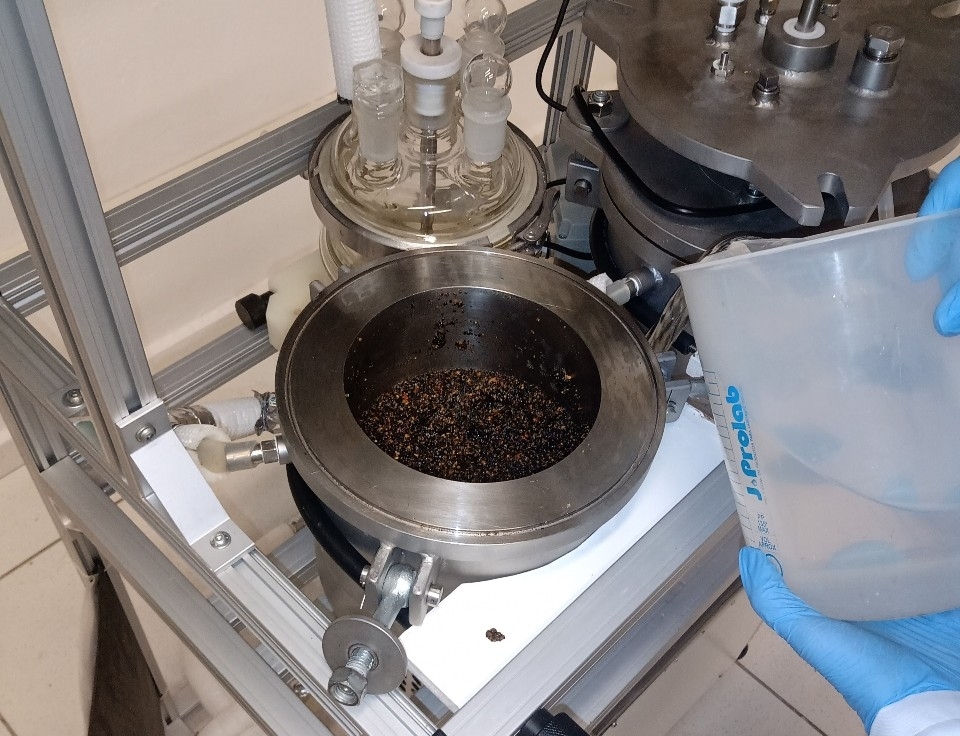

A research group at the State University of Campinas proposes treating the solid waste produced by breweries with ultrasound before submitting it to the process of digestion by microorganisms. The strategy obtains larger amounts of methane, which can be used by the brewery itself to generate electricity and heat. The final waste can be used as crop fertilizer.

Several substances that killed antibiotic-resistant bacteria were found by Brazilian researchers in a marine sponge native to Fernando de Noronha, an archipelago off the coast of the Northeast.

Results of studies conducted at the Research Center for Greenhouse Gas Innovation (RCGI) have fed into a bill before the Senate to set up a legal framework on carbon capture and storage as an economic activity.
The São Paulo State Academy of Sciences presented the first chapter of a book on FAPESP’s 60 years of contributing to science for national development at the first in a series of online events that will continue until December and can be watched on Agência FAPESP’s YouTube channel.

The latest in the FAPESP 60 Years lecture series featured an assessment of the current social and political conditions in Brazil by Maria Hermínia Tavares de Almeida, a professor at the University of São Paulo. The event focused on the erosion of liberal democracy. Oscar Vilhena, Dean of Getúlio Vargas Foundation’s São Paulo Law School, also took part.

Researchers at the University of São Paulo analyzed 43 scientific articles with data for some 11,500 athletes. The findings point to the need for carefully personalized assessment of athletes and sports players before a resumption of training is allowed, they warn.
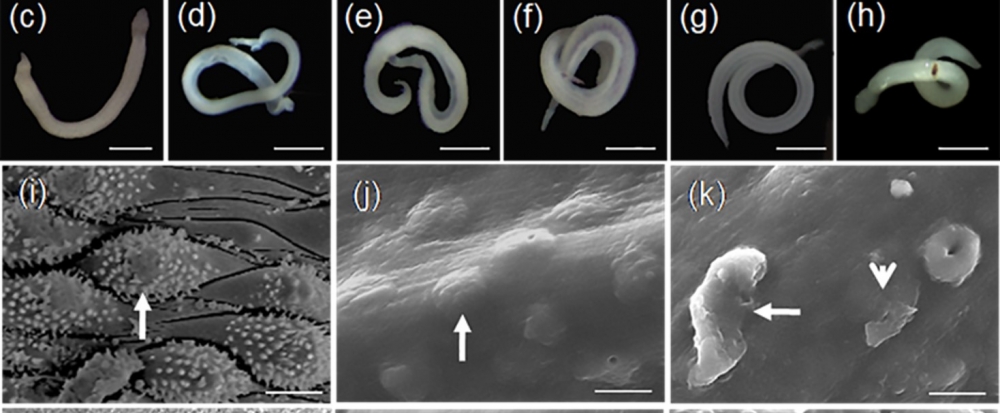
Advanced drug discovery methods have led to advances in the search for treatments for some neglected tropical diseases, including leishmaniasis and Chagas, but research on schistosomiasis and other diseases caused by worms remains at an early stage, according to an article in Drug Discovery Today by Brazilian researchers.
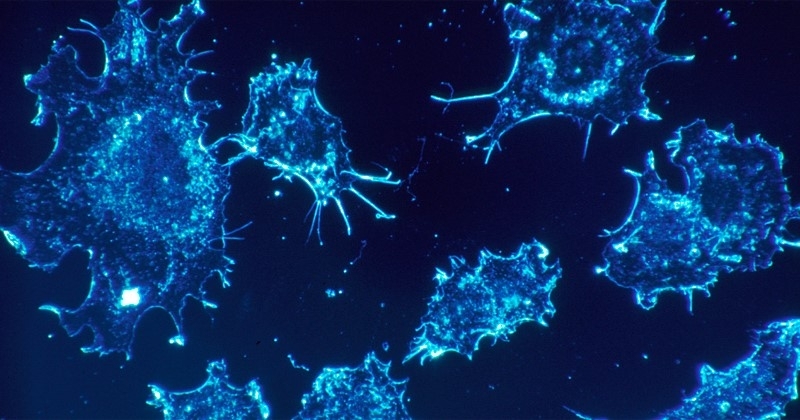
Research that can increase Brazil’s access to CAR T-cell therapy, an increasingly important strategy for treating cancer, is under way at the University of São Paulo’s Center for Cell-Based Therapy (CTC) in Ribeirão Preto, and the Butantan Institute.

In mice fed a high-fat diet, the molecule mitigated weight gain while reducing insulin resistance and liver fattiness. An article describing the results of the study by researchers at the University of São Paulo and collaborators is published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
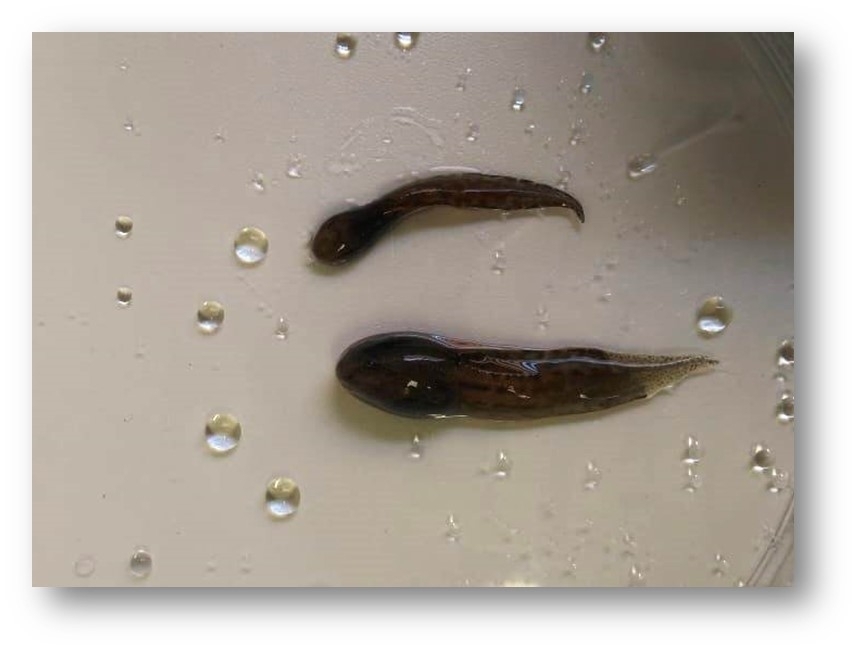

In the laboratory, tadpoles of the species B. ibitiguara kept in water 3 °C warmer than the highest temperature recorded in their habitat were unable to complete metamorphosis, indicating a threat to the species from climate change.

Brazilian researchers surveyed 900 volunteers via an online platform for five months. Most reported feeling that time passed more slowly during home confinement in the early months of the pandemic, associating this perception with feelings of loneliness and a lack of positive experiences in the period.

FAPESP and 19 other research foundations will invest BRL 50 million in collaborative science projects aiming at sustainable development in the Amazon.

The material can be used for diagnostic testing, research on the evolution of the monkeypox virus, and development of novel treatments and vaccines.

A delegation from New Zealand led by Education Minister Chris Hipkins visited FAPESP to discuss new partnerships and areas of interest shared by the two countries.
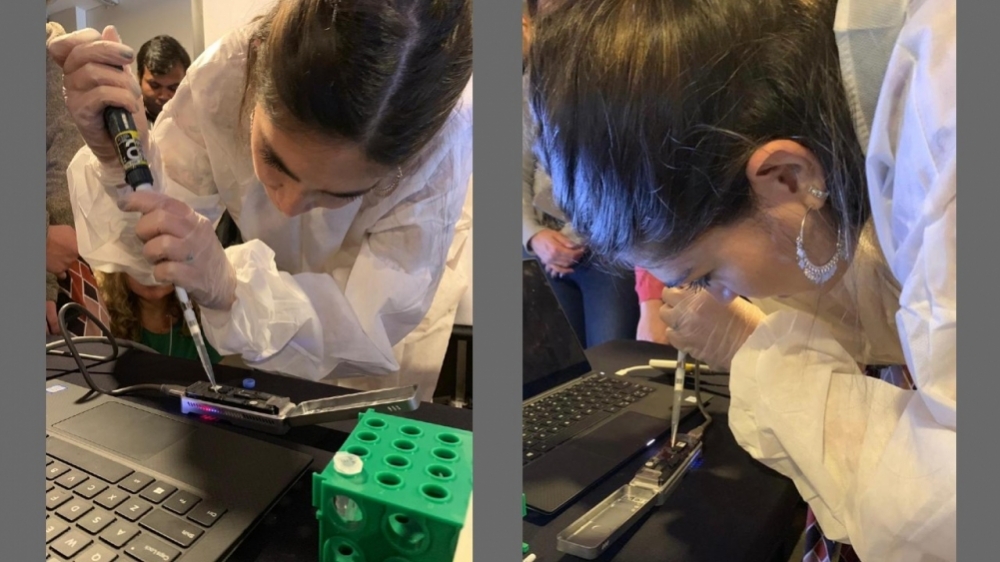

A protocol developed by the Brazil-UK Center for Arbovirus Discovery, Diagnosis, Genomics and Epidemiology (CADDE) was used to analyze a sample from the first Brazilian patient with a confirmed diagnosis. The technology can also be used to detect unknown emerging viruses.
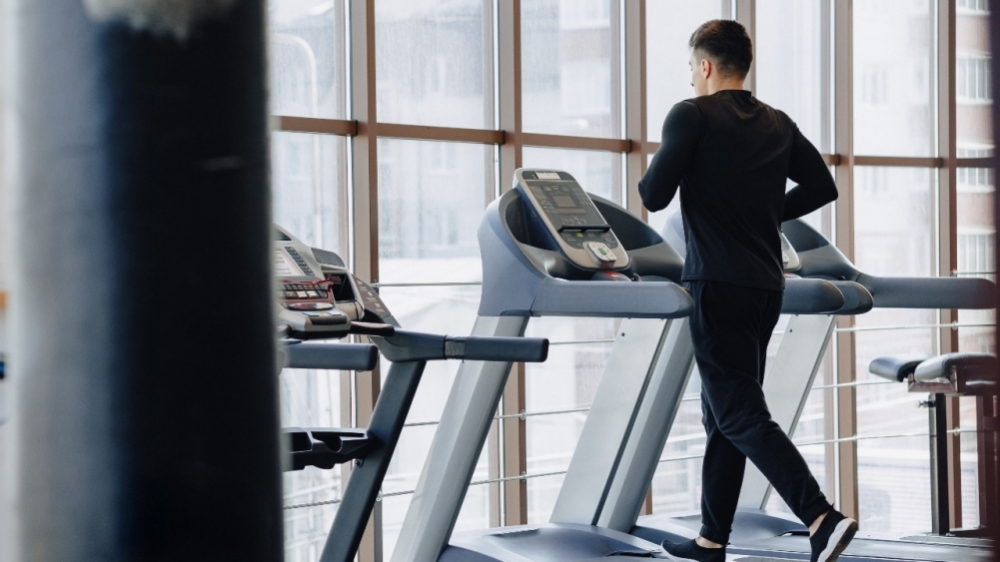

The finding comes from a clinical trial by researchers at the University of São Paulo who recruited 32 male volunteers and have now published the results in Clinical and Experimental Hypertension.
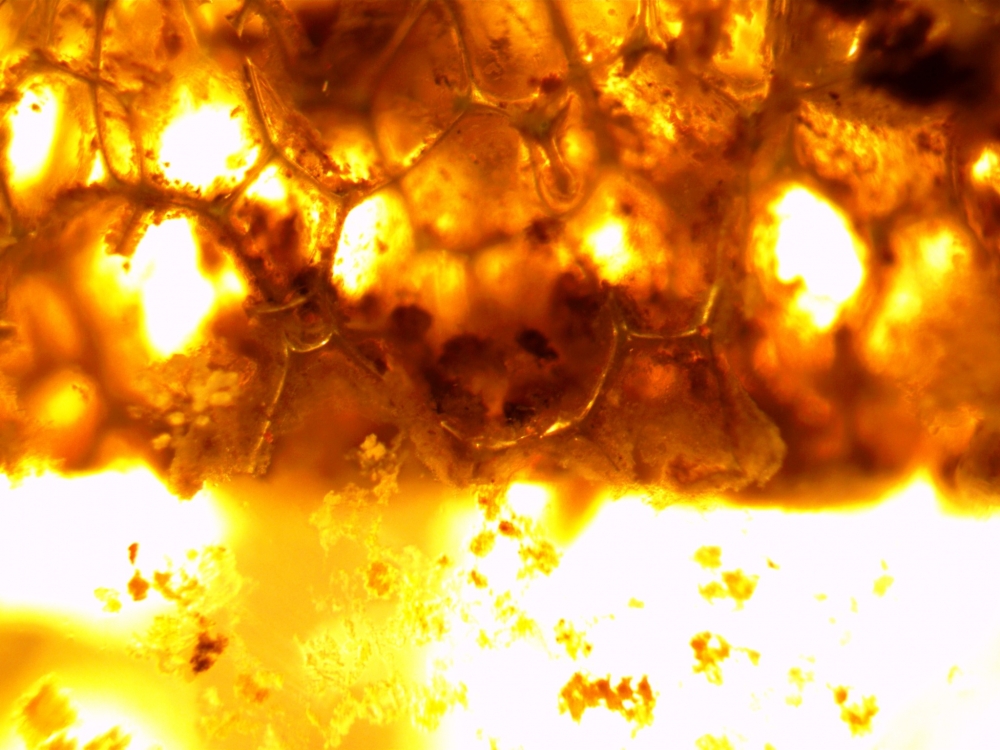
Brazilian researchers have designed a new low-cost anaerobic reactor that uses a bacterial biofilm on a sheet of polyurethane foam. The goal is to enable more wastewater treatment plants in Brazil to achieve nitrogen removal and reduce water body contamination.
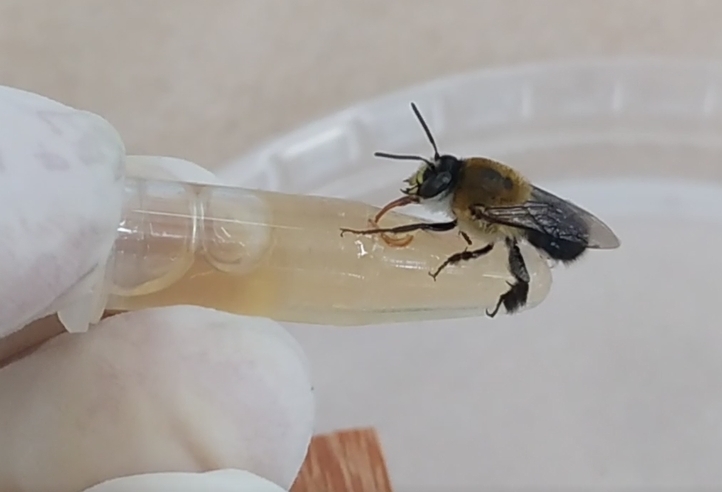

Preliminary results of trials conducted by Brazilian scientists show that the existing regulatory framework based on a protocol referenced to the Western honeybee, Apis mellifera, is too Eurocentric and may not be sufficient to guarantee the protection of native bees, which are important pollinators.
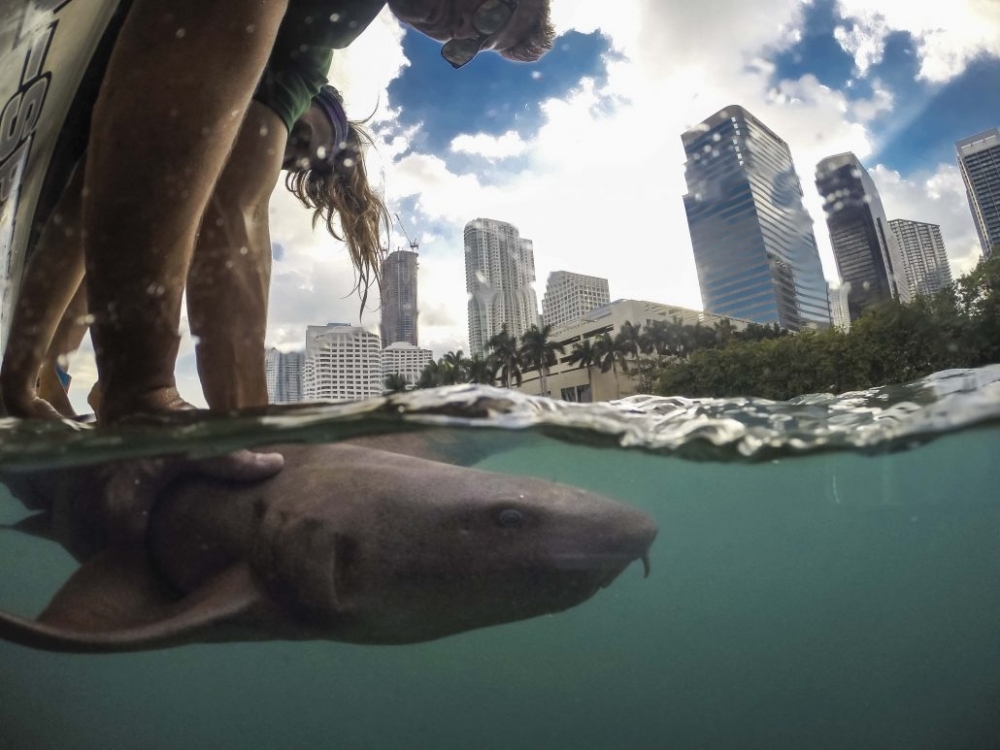

Analysis of blood samples showed that sharks living near urban areas have a lower-quality diet than those living in wilderness areas. Dietary imbalances can impair important physiological processes, such as cardiovascular tone, inflammatory response and reproduction.
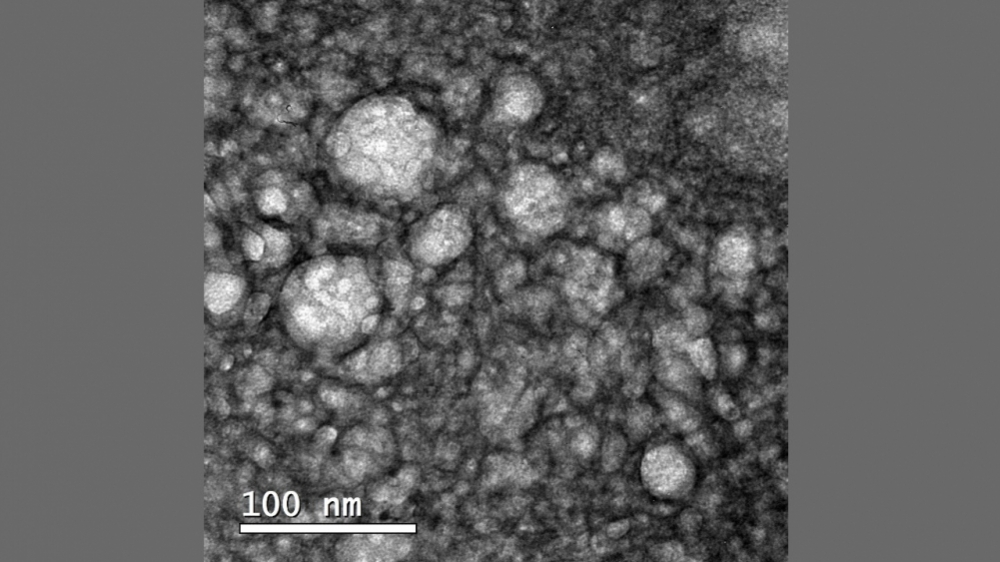
The approach combined nanotechnology, chemotherapy and monoclonal antibodies. It produced promising in vitro and in vivo results against glioblastoma multiforme.