

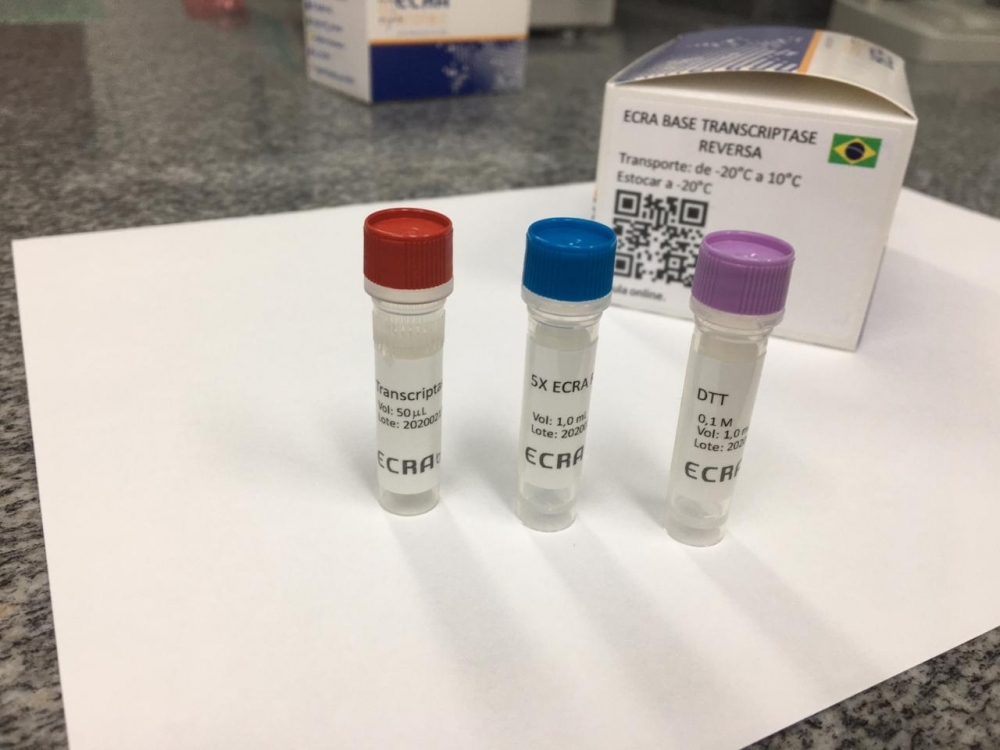
Researchers at the University of Campinas partner with biotech startups to promote local production of hitherto imported reagents. The goal is to increase Brazil’s capacity to perform RT-PCR tests, considered the gold standard for COVID-19 diagnosis.
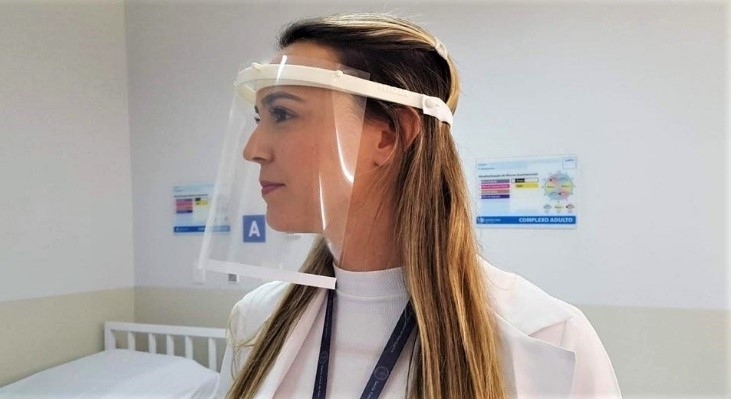
3D printed face shields are worn by frontline health workers over a conventional surgical mask.
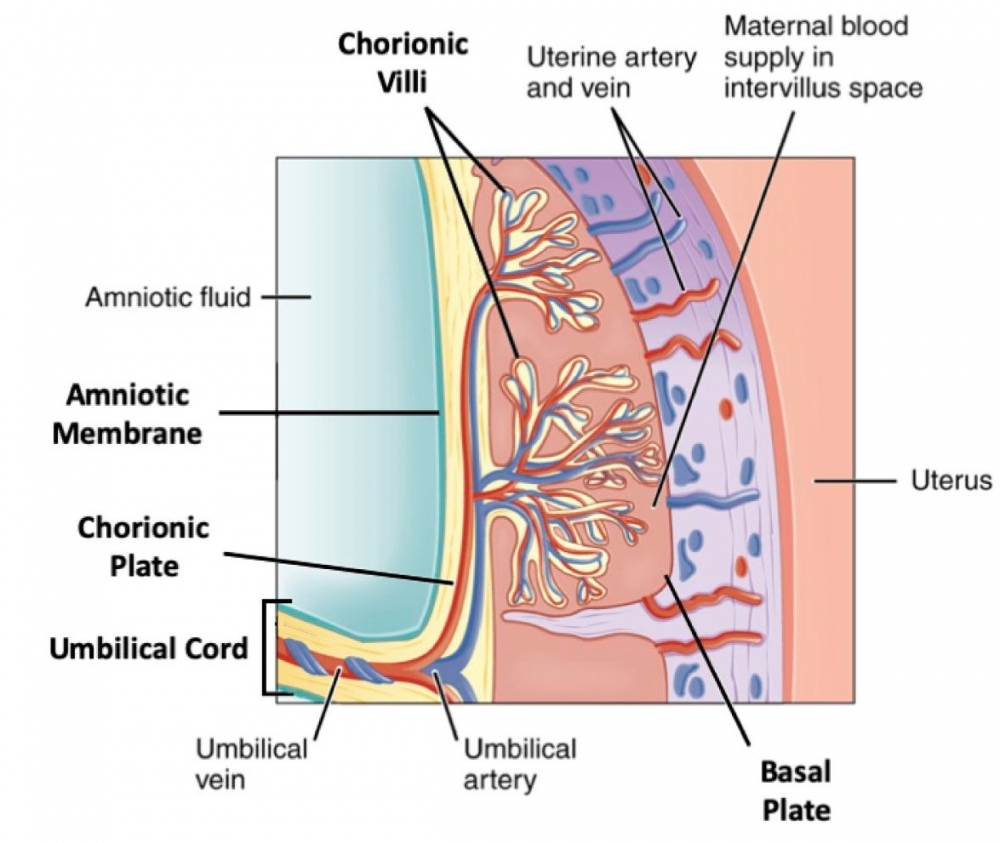
Brazilian researchers show that the virus can infect different placental regions and that collection and storage methods should be taken into consideration to ensure that the results are trustworthy and representative.
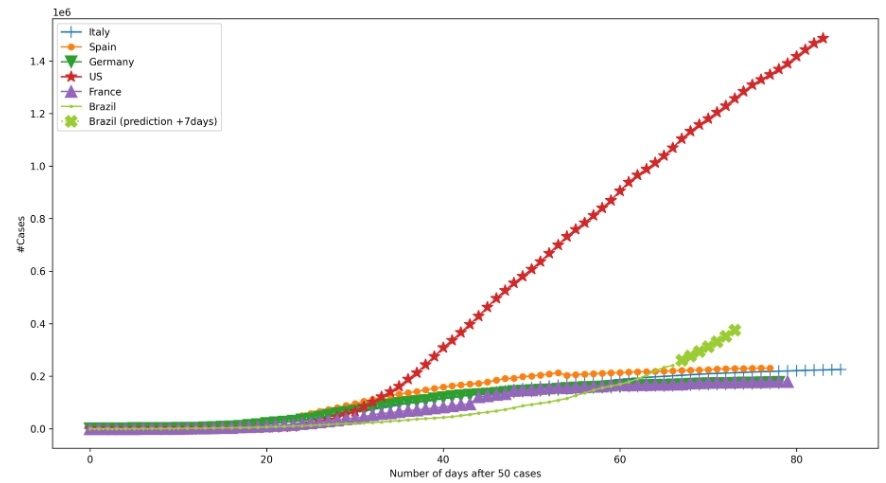
Digital tool developed at the University of São Paulo’s Mathematics and Computer Sciences Institute (ICMC-USP) in São Carlos refines projections for the spread of the pandemic.
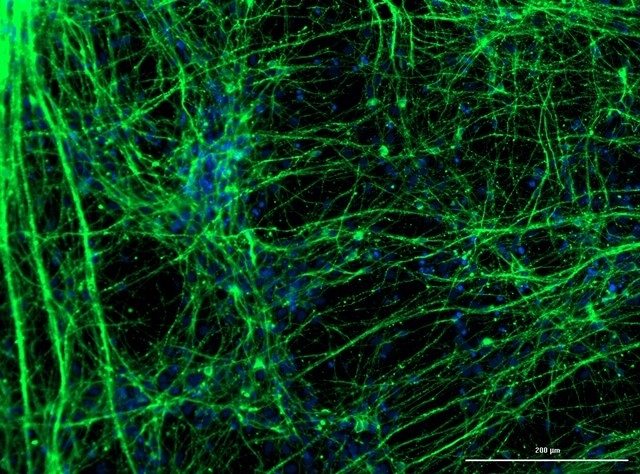
Brazilian researchers are conducting tests with cultured cells to find out how COVID-19 changes patterns of proteins and other metabolites present in samples.
Scientists in Butantan Institute’s Special Vaccine Development Laboratory will couple SARS-CoV-2 antigen to bacterial membrane in order to trigger defense against coronavirus.
Based on the Internet of Things, the system was developed in a project supported by FAPESP. Patients can be advised to seek hospital care if they detect a deterioration in clinical signs.
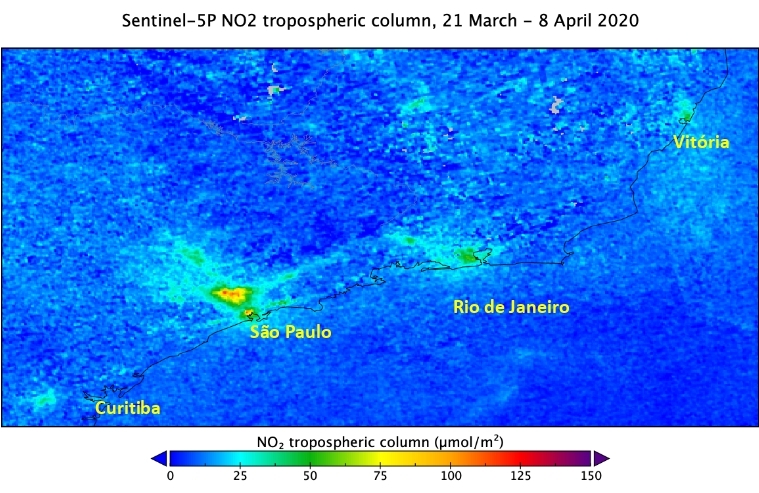
A drop of 33% in levels of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is associated with a reduction in diesel vehicle traffic and industrial production due to isolation measures taken to slow the spread of novel coronavirus.
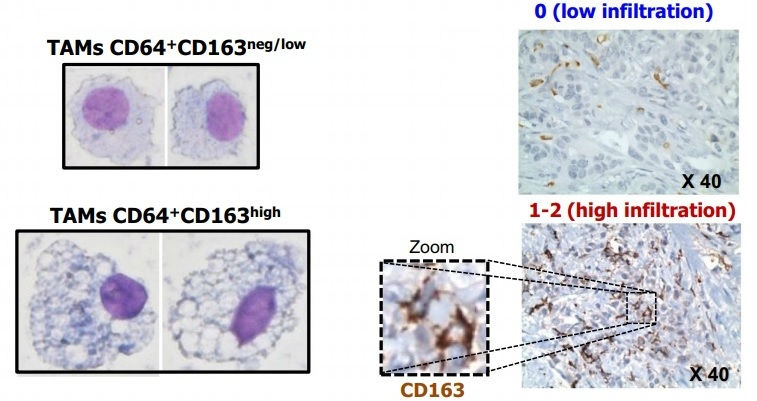
This study shows that patients develop alterations in a type of leukocyte at the initial stage of the disease. This discovery paves the way for the enhanced diagnosis and treatment of this type of tumor.
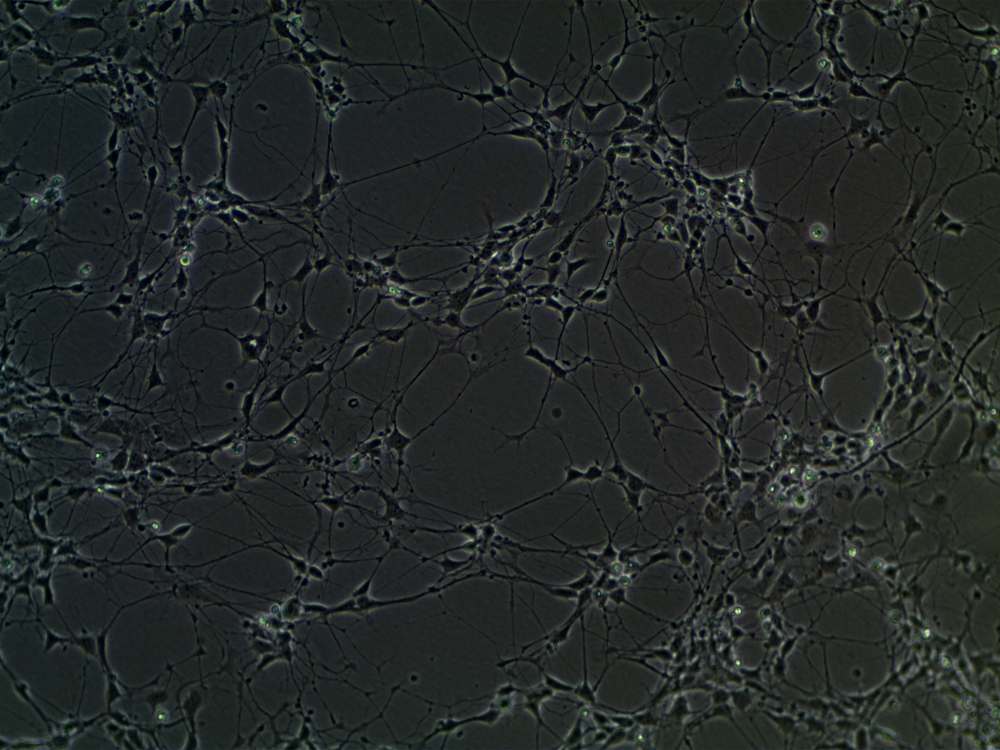
The dysregulation appeared to affect communication among neurons in the subjects of the study, which was conducted in Brazil. The discovery could improve diagnosis, which is currently based on the clinical analysis of symptoms.
Several initiatives are pursuing alternatives to increase the number of diagnostic tests performed in Brazil. Research groups who previously developed low-cost rapid tests for Zika fever and other viral diseases are adapting these models for use in detecting SARS-CoV-2.
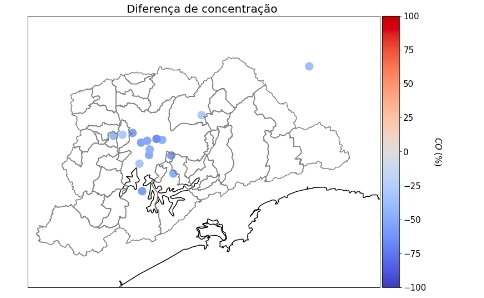
A drastic reduction in traffic due to the coronavirus lockdown resulted in a rapid decrease in airborne pollution: The levels of carbon monoxide fell by 50% in São Paulo City in a single week.
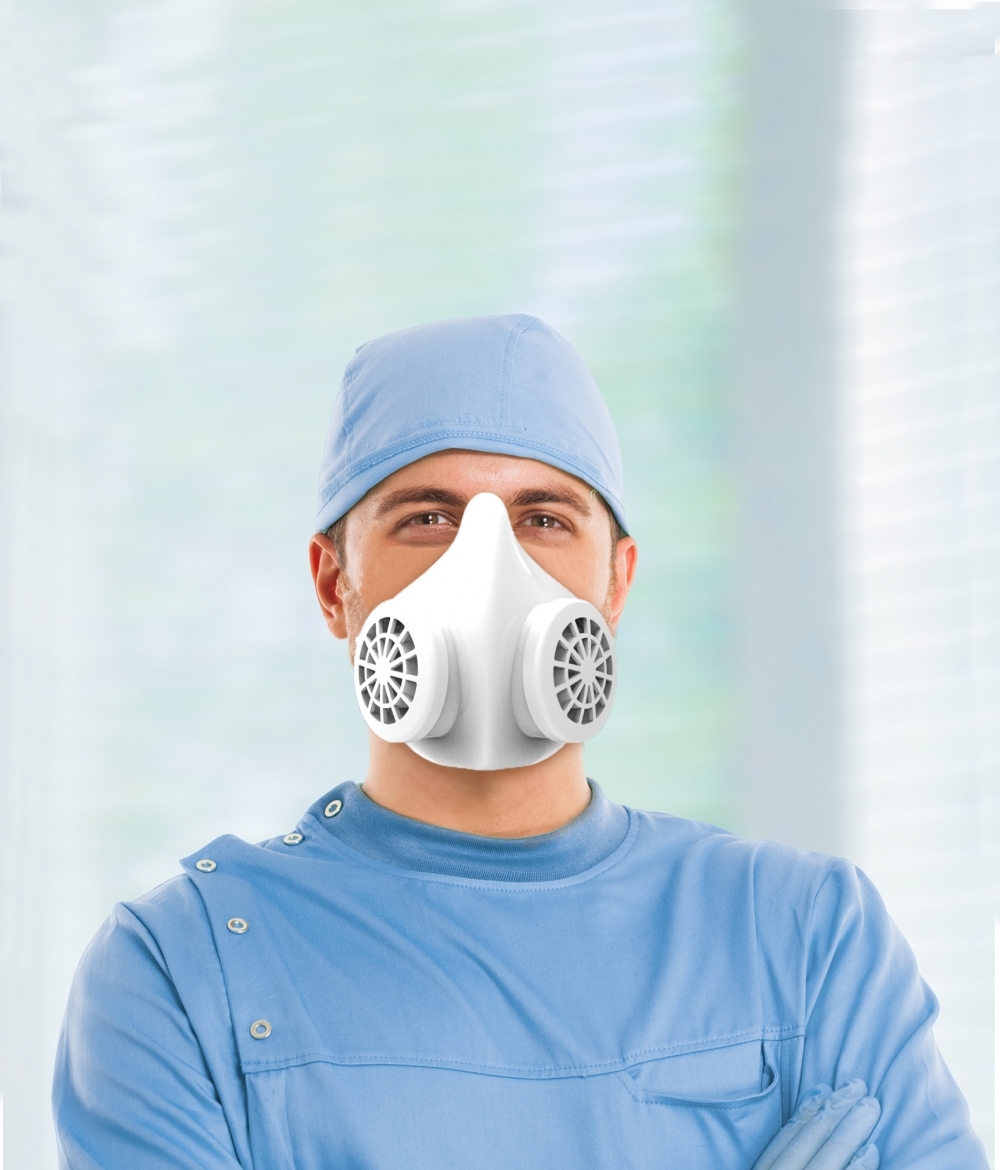

Developed with FAPESP’s support via its small business program, the N95-type respirator is made of material containing silica-silver microparticles with antimicrobial and antifungal properties that hinder surface adhesion by SARS-CoV-2.

Brazilian researchers show that proteins associated with diseases and key biological processes can be found in the blood plasma fraction usually discarded in proteomic analysis.
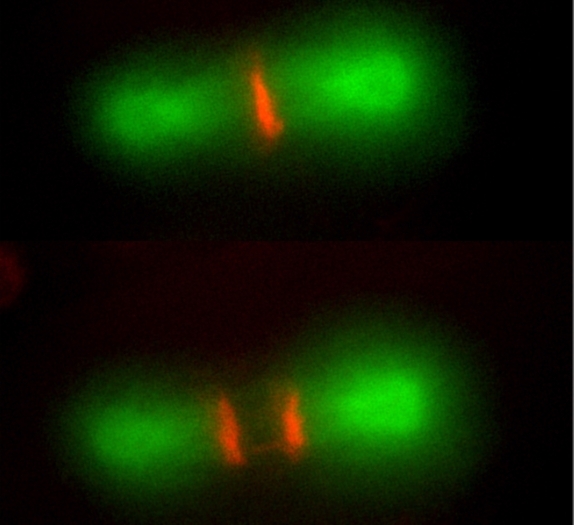
A study shows that administering coenzyme Q10 reverses damage done to germinative cells by BPA, a contaminant found in many kinds of plastic.
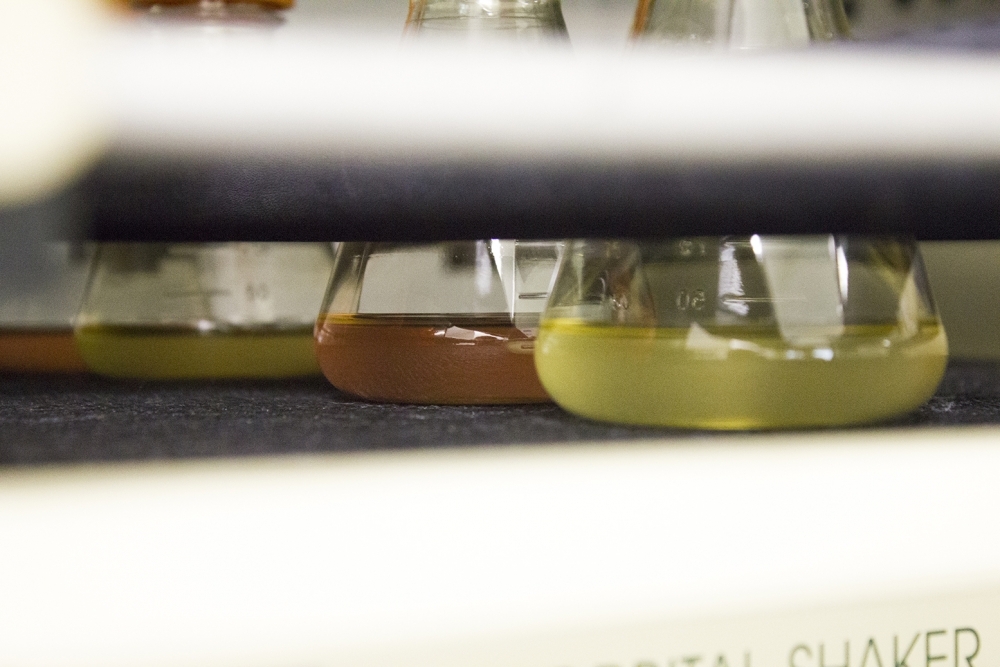

To develop a drug capable of treating the disease caused by the novel coronavirus, a research institution in São Paulo will deploy a platform used to produce monoclonal antibodies against tetanus and zika.
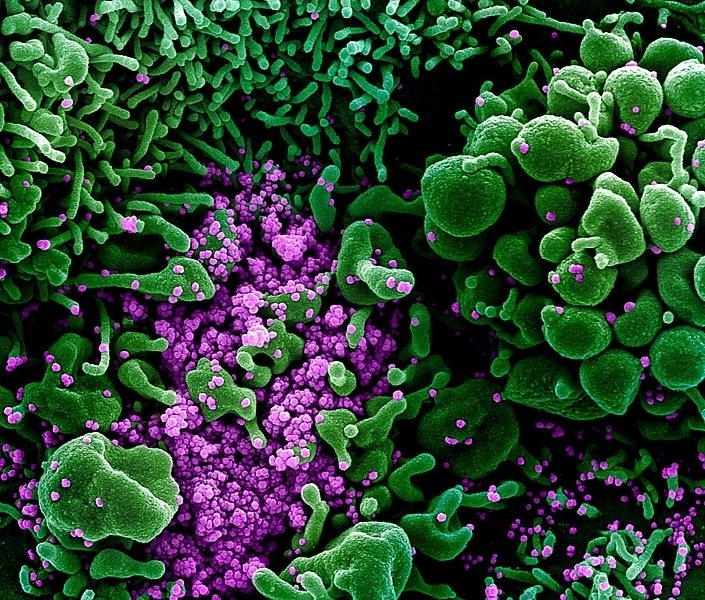
Brazilian researchers show that the activity of the gene TRIB3 in lung cells declines in men as they age. Compounds capable of reversing the process could be tested against the novel coronavirus.
Selected projects aim to repurpose existing drugs for treatment of COVID-19, find novel compounds with therapeutic potential and develop alternative diagnostic methods. The call remains open until June 22.

AI-based technology developed by a São Paulo startup supported by FAPESP is in use at Albert Einstein Jewish Hospital to reduce the risk of coronavirus transmission

The new Engineering Research Center will be hosted by São Paulo State University’s School of Agrarian and Veterinary Sciences in Jaboticabal. Its scientists will also research biotechnology and plant resistance.
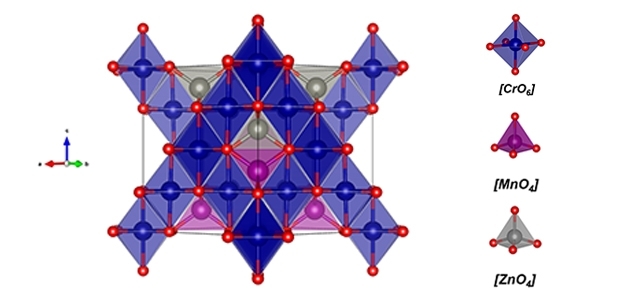
Thanks to its magnetic properties, the material – zinc-doped manganese chromite – can be used in a range of products, from gas sensors to data storage devices.
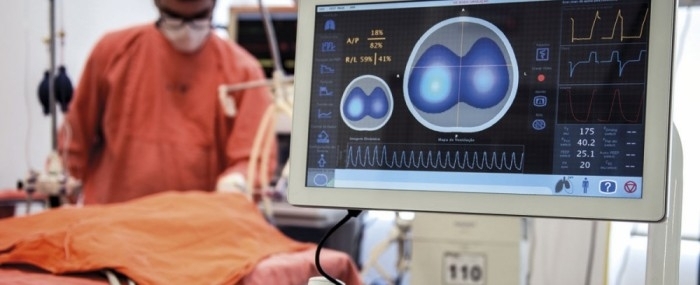
Electrical impedance tomography system developed by startup based in São Paulo minimizes complications associated with mechanical ventilation and is used in the treatment of COVID-19 by hospitals in Italy, Spain and the US.
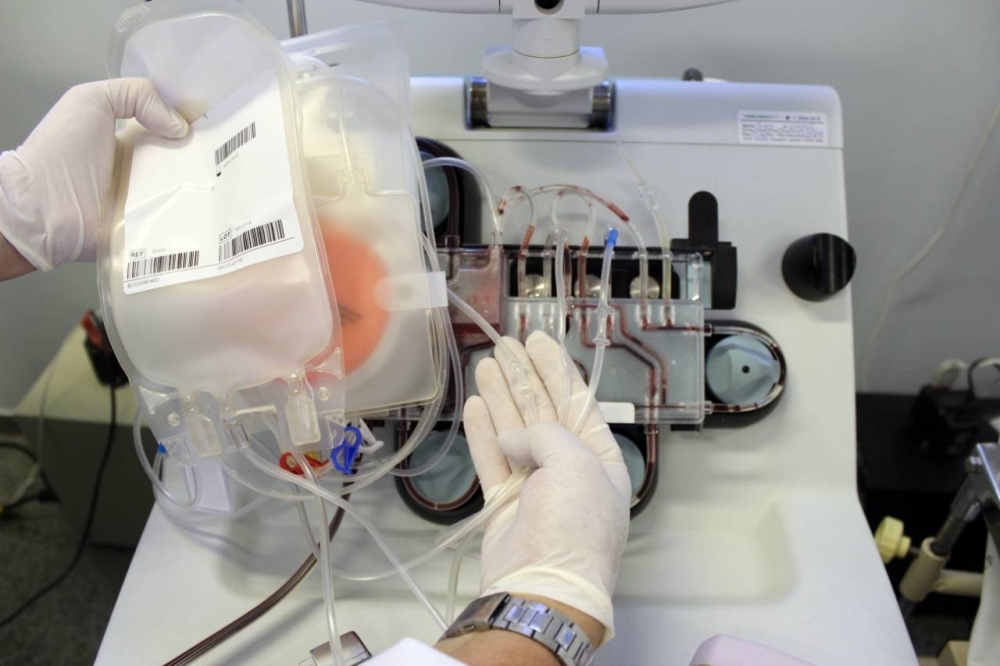
Scientists affiliated with the FAPESP-funded Center for Cell-Based Therapy have collected plasma from donors and are conducting a trial to check the safety and effectiveness of passive immunization.
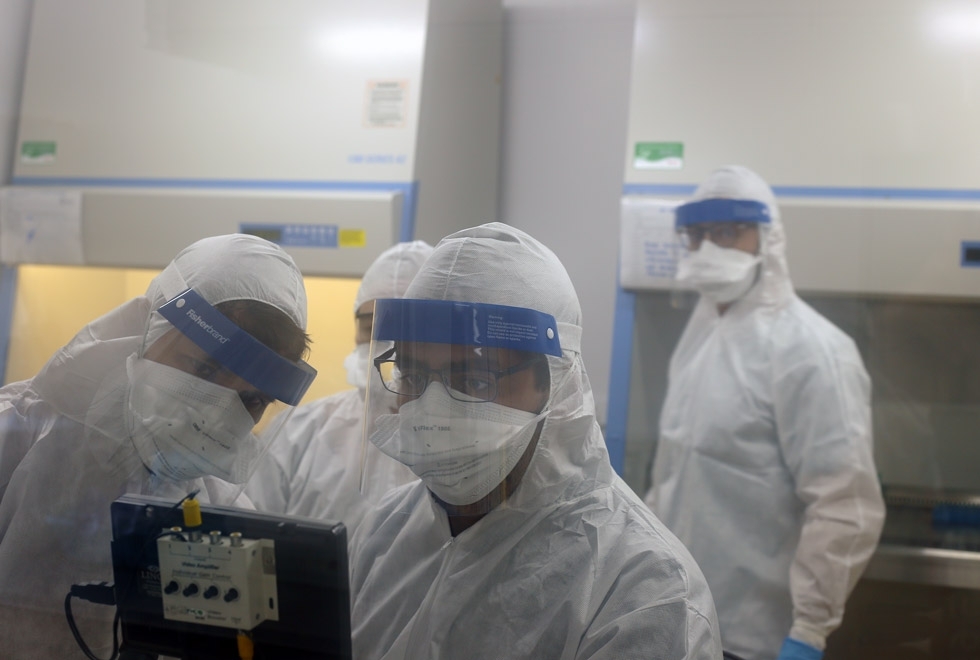

Researchers at the University of Campinas are organizing professionals, supplies and equipment to test for COVID-19, understand how the virus works, identify existing drugs that are effective against the disease, and use 3D printing to produce parts for ventilators and personal protective equipment.
The initiative is coordinated by Butantan Institute and includes units in several cities accredited by Adolfo Lutz Institute (IAL), the regional reference laboratory. Short supply is the main bottleneck delaying the expansion of testing in the state.