


The firm is supported by FAPESP and is developing an autonomous helicopter capable of spraying crops on steep hillsides.
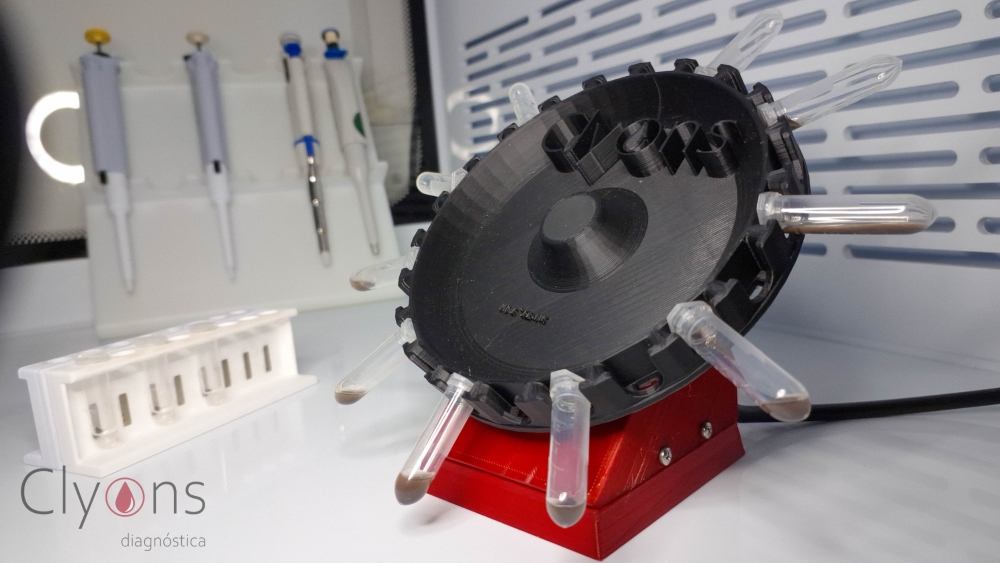

A Brazilian startup supported by FAPESP is developing a solution to detect a biomolecule linked to the presence of migratory oral cancer cells.
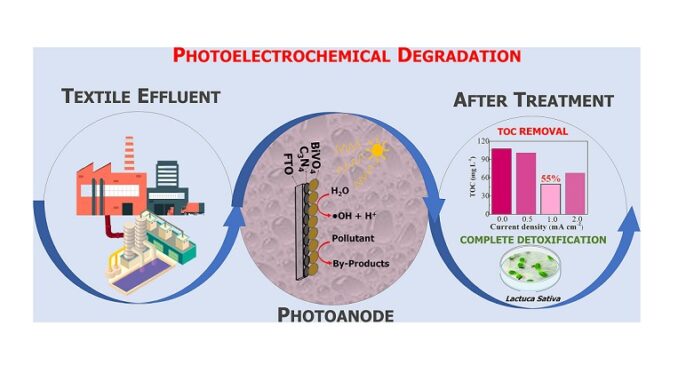
Investigators affiliated with two FAPESP-supported research centers conducted an experiment using actual effluent from the textile industry. The results are detailed in the journal Chemosphere.
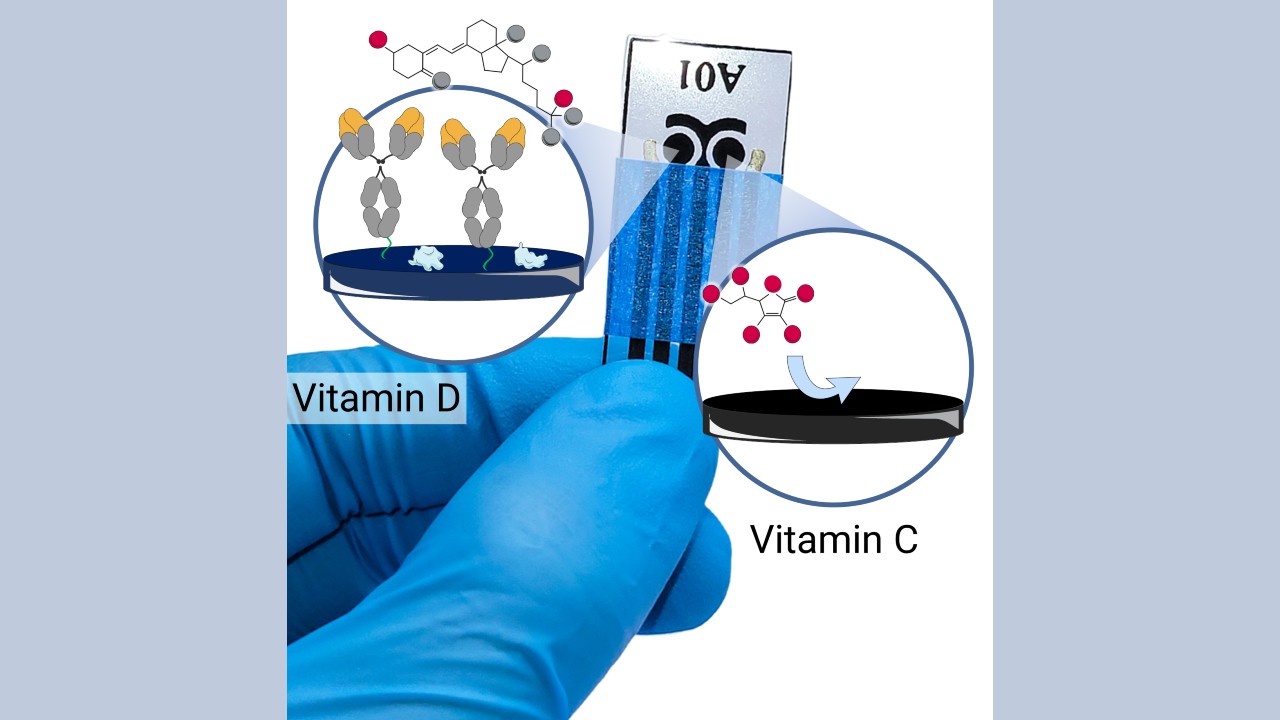
The device was developed at the University of São Paulo and can be used for self-monitoring of micronutrients, assistance with personalized diets, and prevention of deficiencies and toxicity.
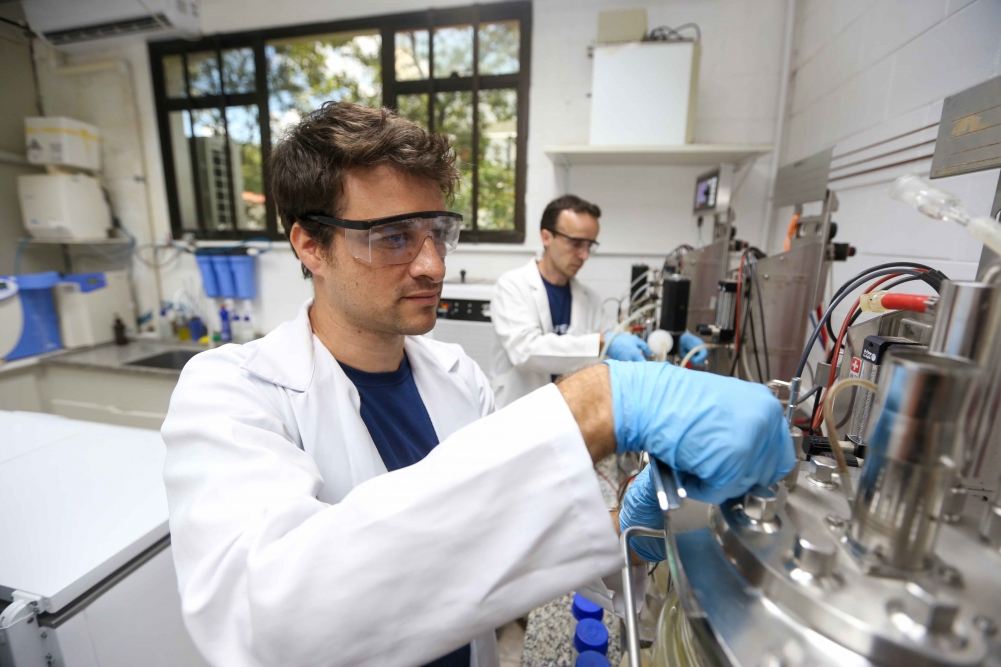

A startup supported by FAPESP is developing a platform that will enable local production of enzymes to act as catalysts for chemical reactions.
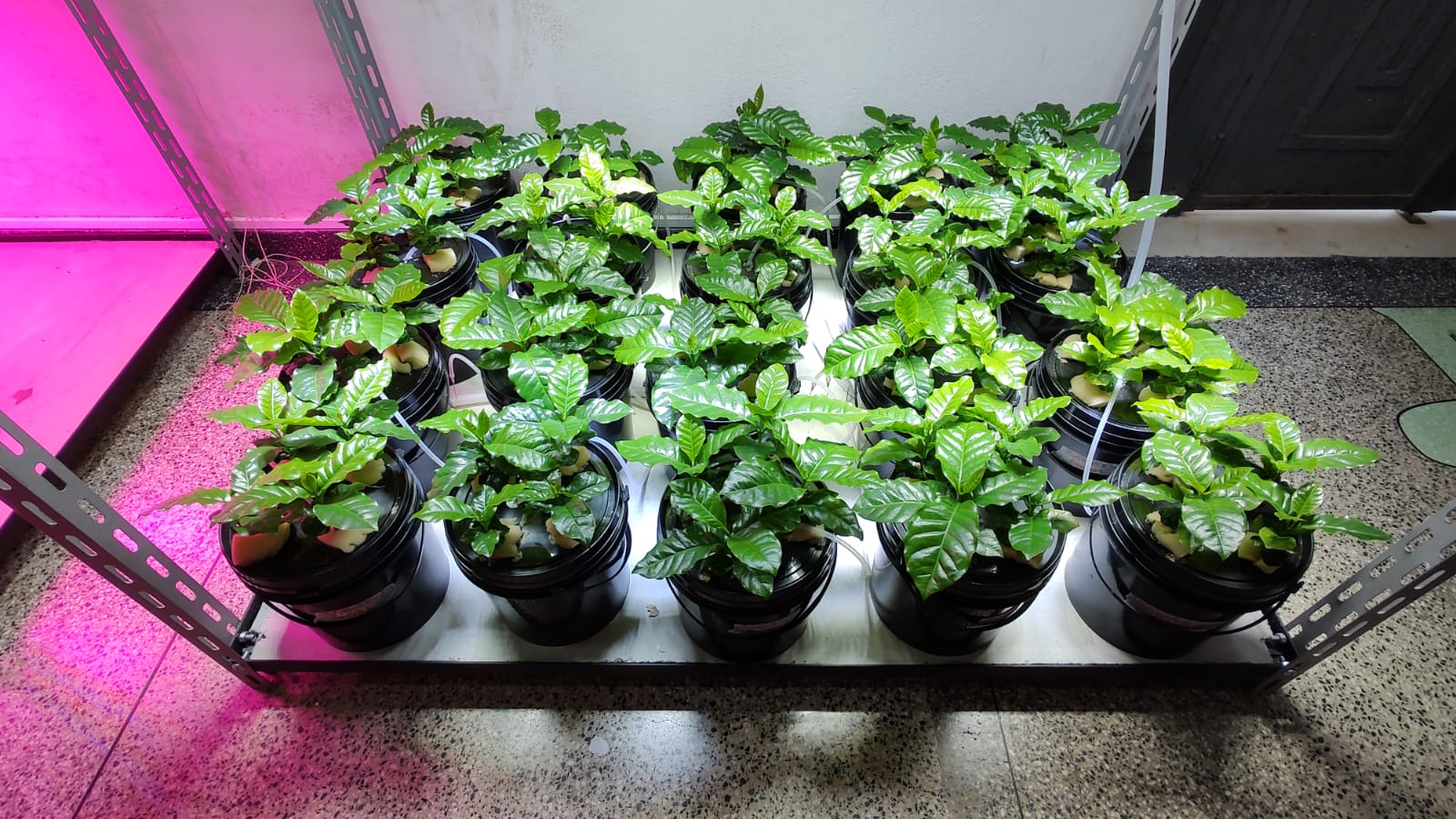

The work makes it possible to tell the story of the fusion of genomes that gave rise to the world’s most consumed species, as well as identifying genes responsible for resistance to rust and other diseases.
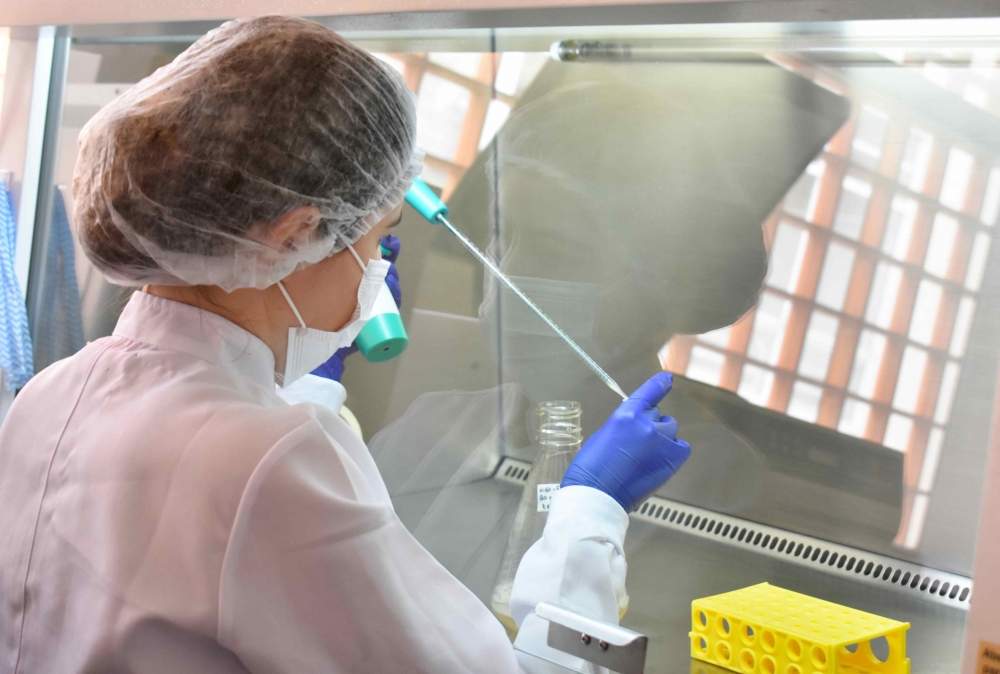

Researchers supported by FAPESP have created a drug using antibodies for direct application to the skin.
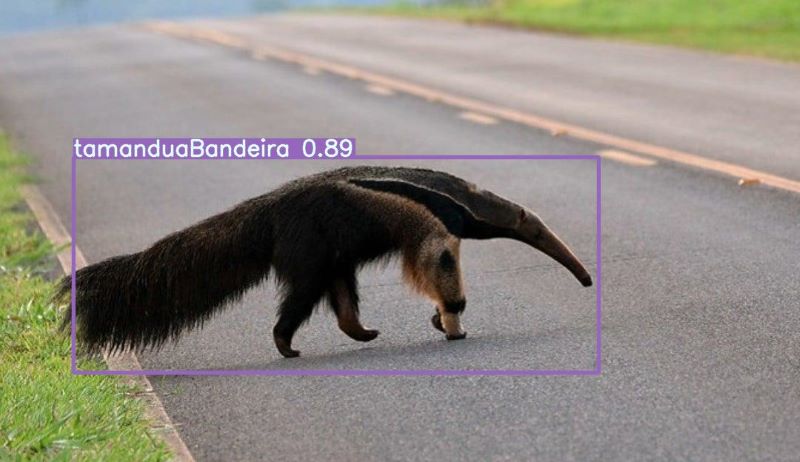

The researchers trained computer vision models to identify Brazilian mammals must susceptible to roadkill in real time and are partnering with toll road operators to test the system in real-world situations.
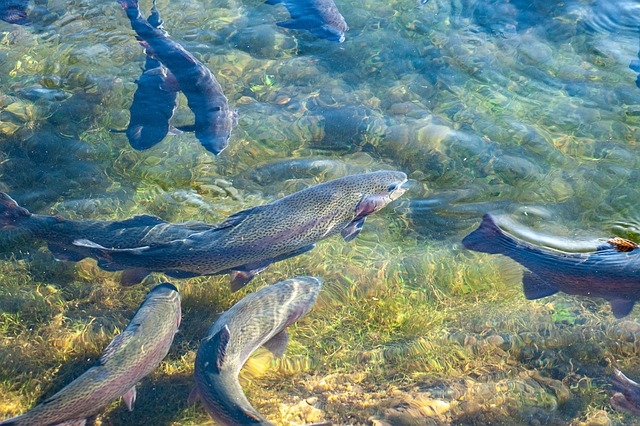

A startup supported by FAPESP has developed a solution to prevent disease in fish tanks by means of environmental monitoring.
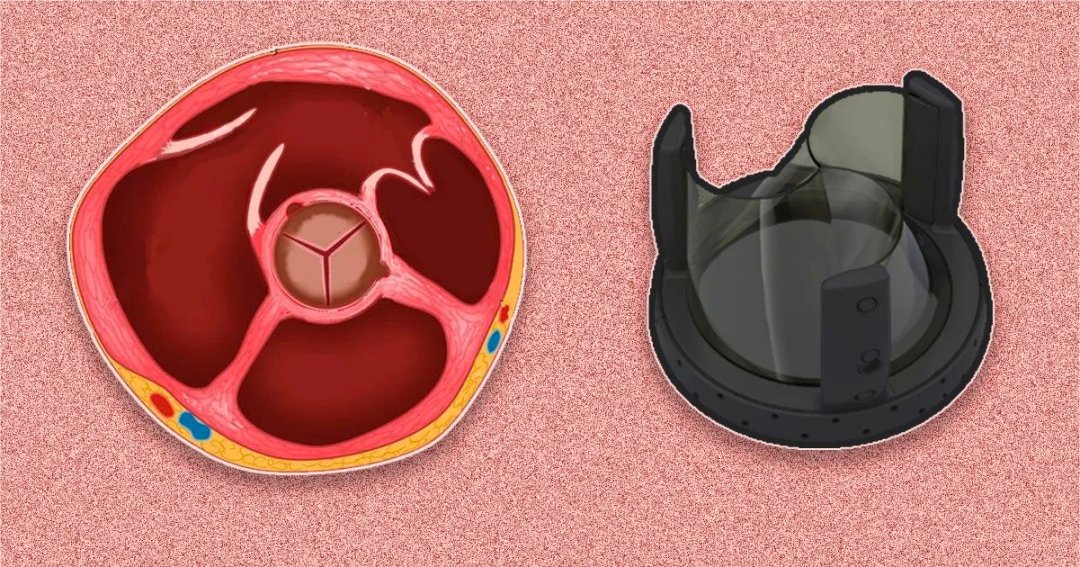
Study developed at Center for Mathematical Sciences Applied to Industry aims to perfect device for cardiovascular treatments.
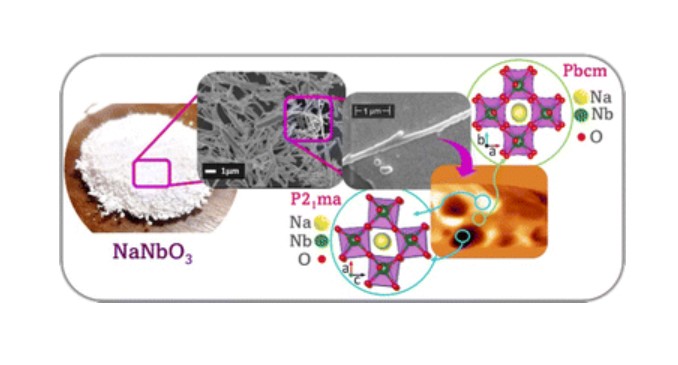
Sodium niobate is a type of ceramic with properties of interest to green chemistry; scientists from the Center for the Development of Functional Materials and collaborators have developed a new strategy for obtaining it.
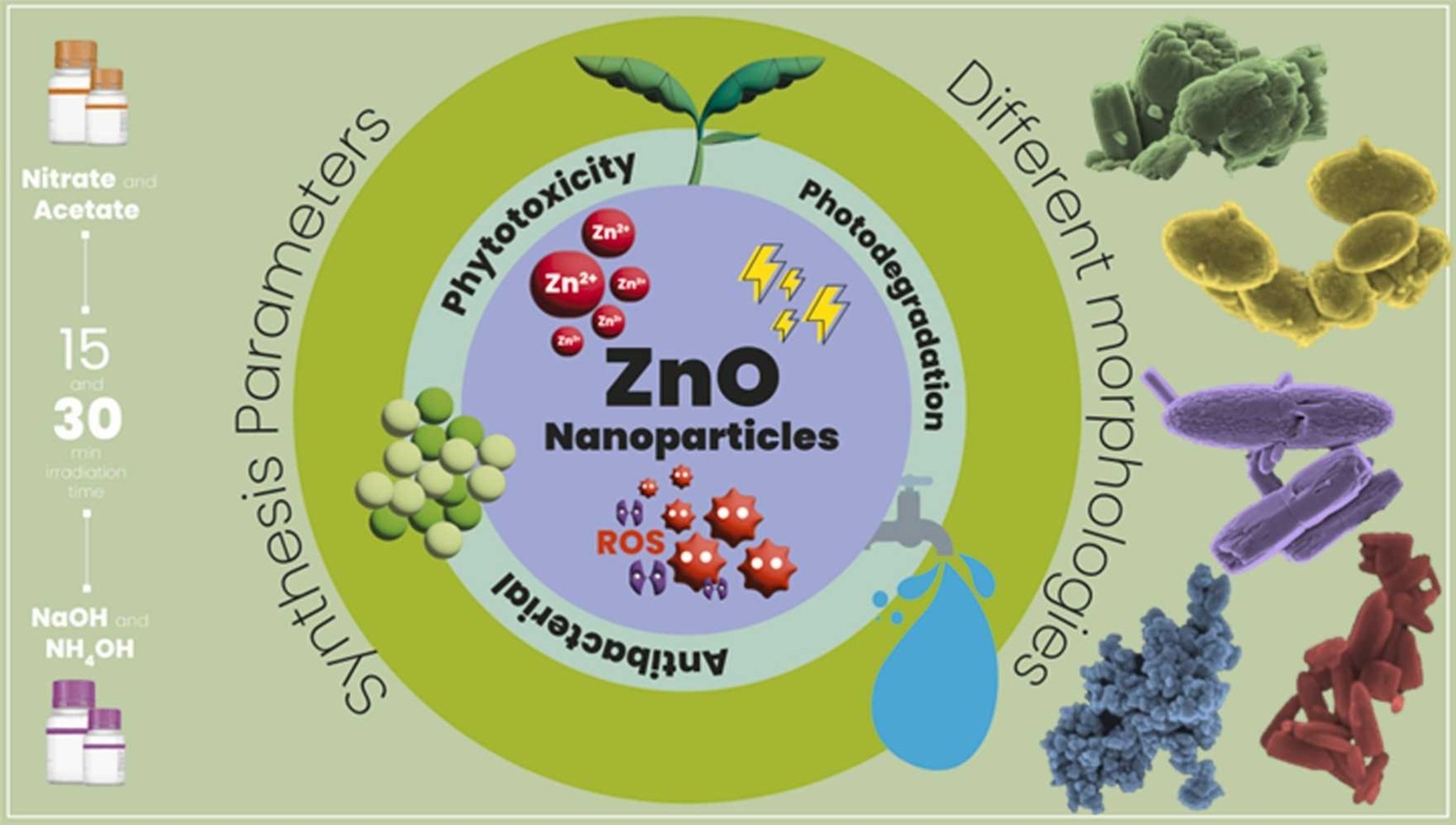
Zinc oxide nanoparticles with varying morphologies were tested against microorganisms isolated from patients. The results are reported in the Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.

A startup supported by FAPESP is developing novel cultivars to offer growers a high-value-added option.

Developed by ImunoTera as part of a project supported by FAPESP, the molecule triggers the immune system’s response to infected cells and helps combat the disease.

Developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo, the process proposes using silica particles coated with melanin in formulations to protect the skin not only from UVA and UVB rays, but also from visible light.

A paper by scientists from the Center for the Development of Functional Materials discusses the effects of femtosecond laser irradiation, which can create and functionalize new materials for the microelectronics industry.
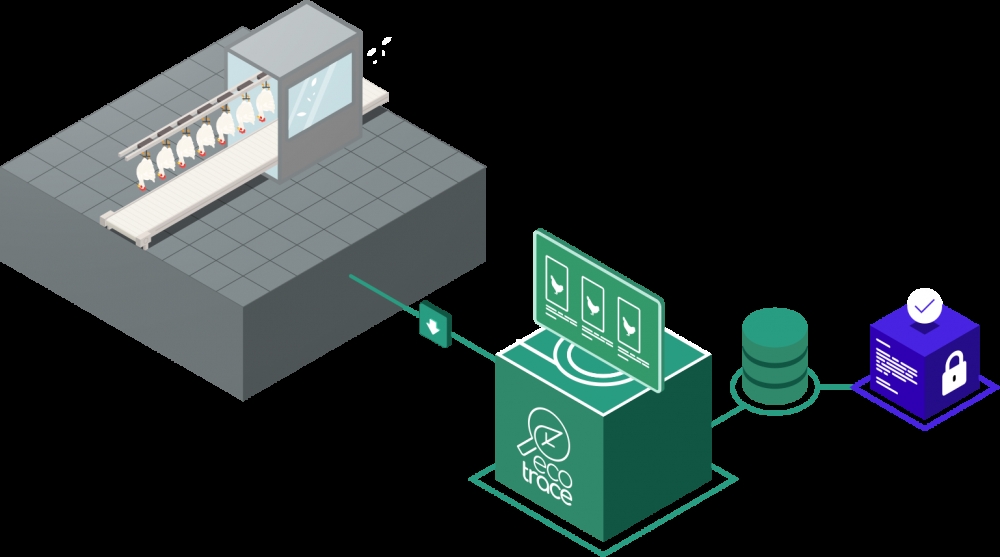
The system created by startup Ecotrace with FAPESP’s support is designed to help poultry processors detect carcass lesions in real time.
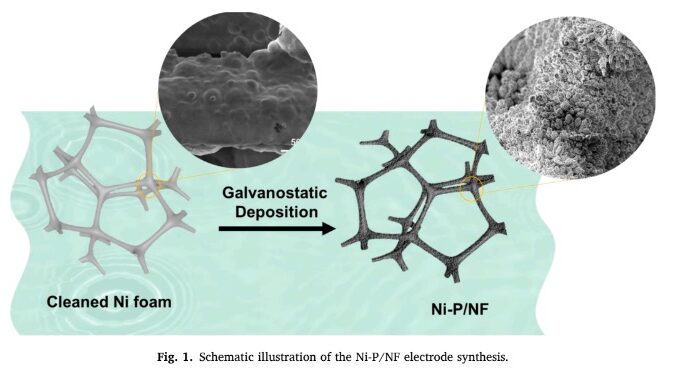
The nickel phosphide electrode proved effective and efficient as a catalyst in processes designed to produce H2 via water molecule breakdown.
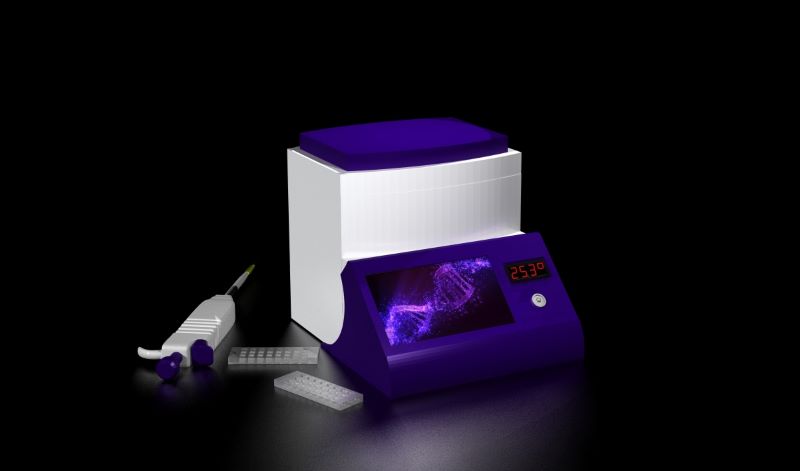

A startup supported by FAPESP is developing a solution to detect beer spoilage microorganisms, which affect flavor and aroma, both in the brewery and at the point of sale.
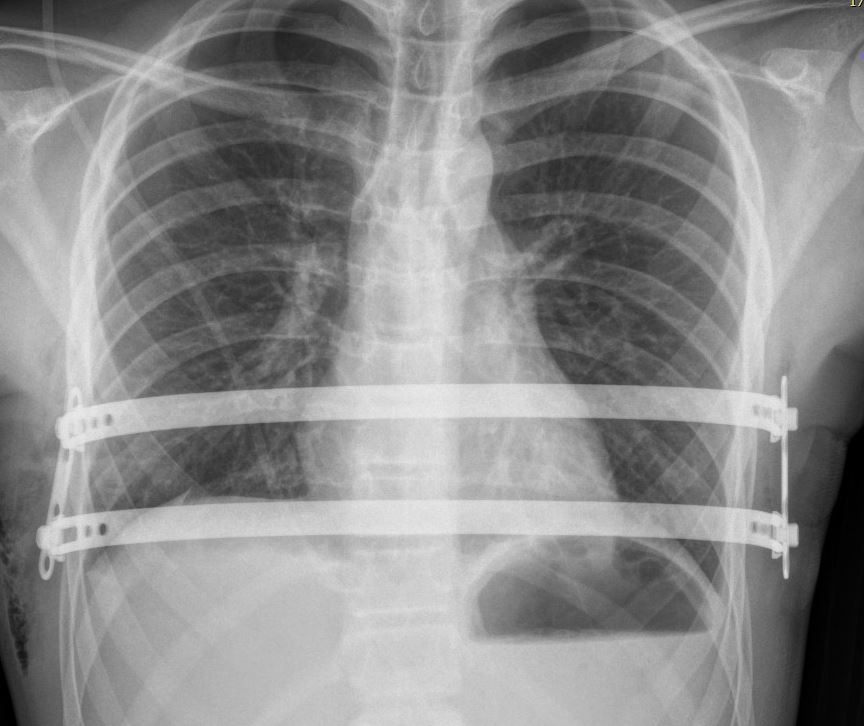
The device was developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo’s Heart Institute (INCOR) and a Brazilian company with FAPESP’s support. It is biocompatible and offers other advantages over the imported product used hitherto.
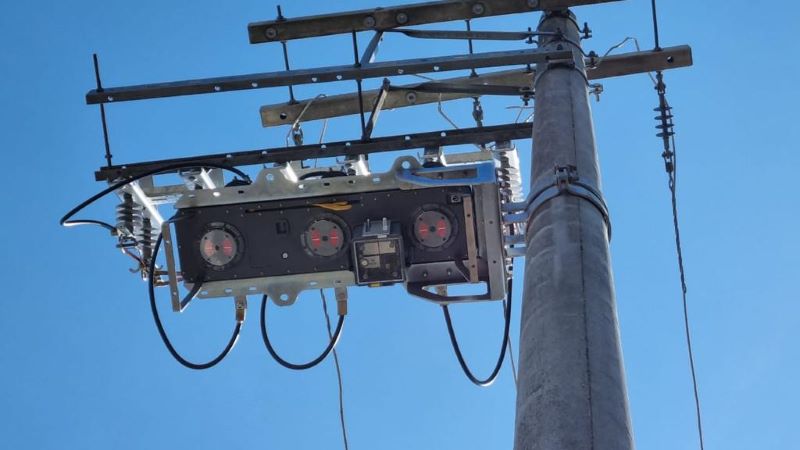

The producer is a company supported by FAPESP. It is developing an advanced three-phase recloser that isolates a section of the grid cut off by a tree fall and lets power be restored remotely.
The event will take place in São Carlos (São Paulo state, Brazil) with FAPESP’s support. Twenty participants from Brazil and 20 from other countries will be selected.
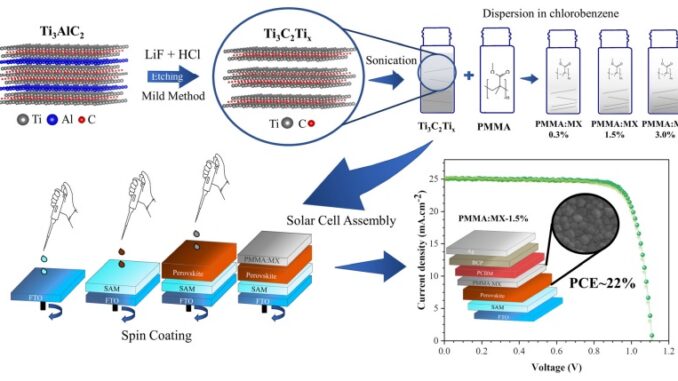
The results of a study conducted by researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) could be highly positive for the future of the solar power sector.
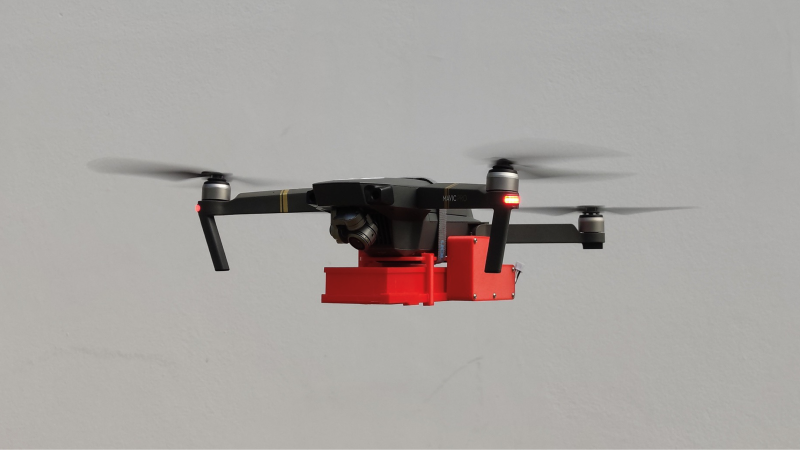

The solution developed by the firm, with FAPESP’s support, permits controlled release of sterile males of Aedes aegypti in urban areas with the aim of reducing the population of these mosquitoes.
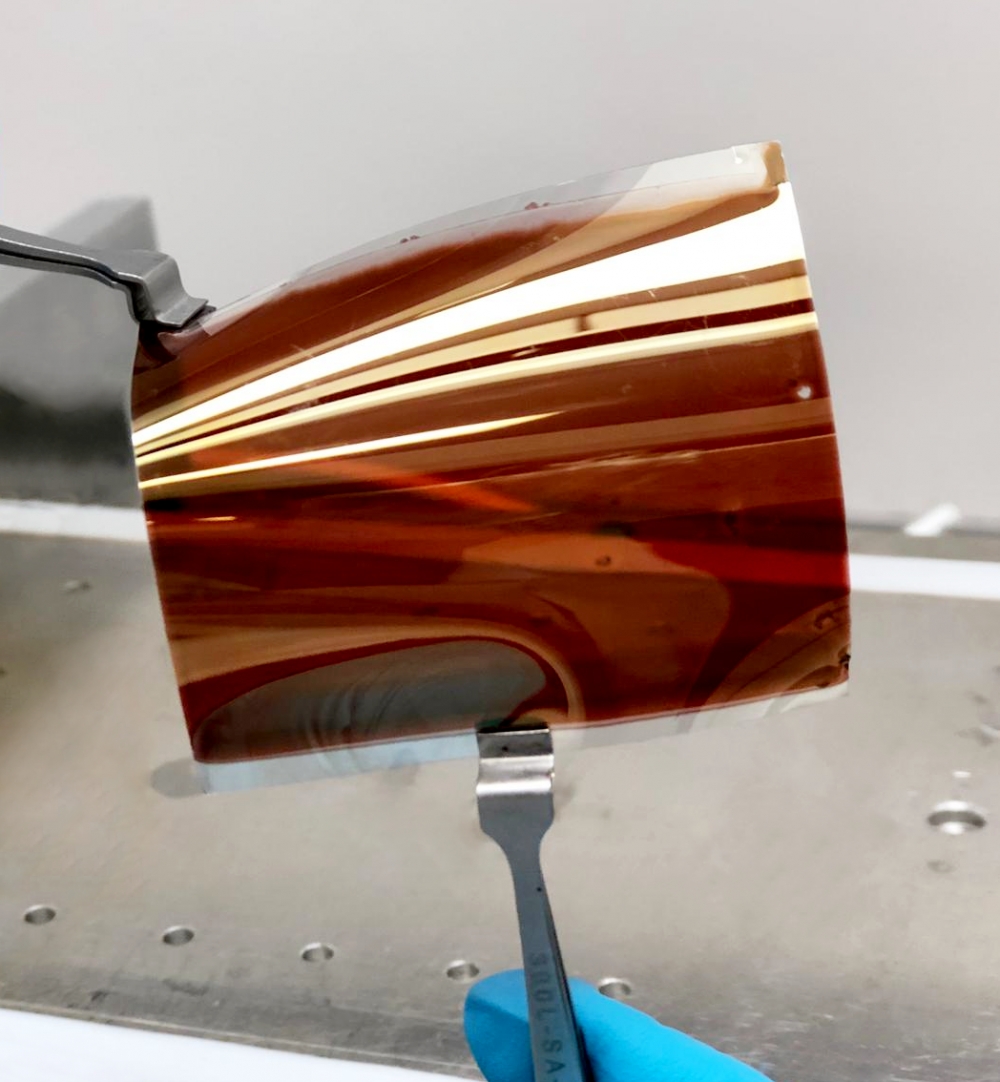
The startup has been supported by FAPESP since its foundation in 2020. The device can be used to make film for perovskite solar cells, biomaterials for wound dressings and tissue regeneration, and novel drug and cosmetic delivery systems.