

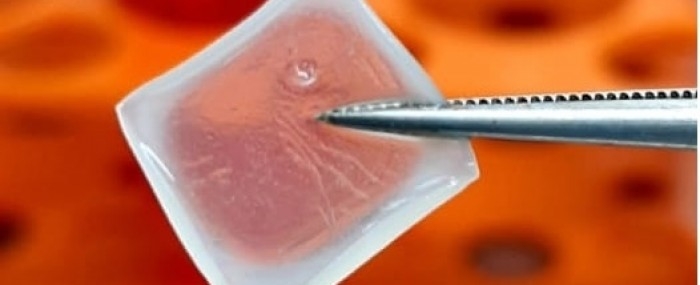
Developed by startup In Situ from stem cells and a hydrogel, the product is bioprinted and placed lightly on the skin.
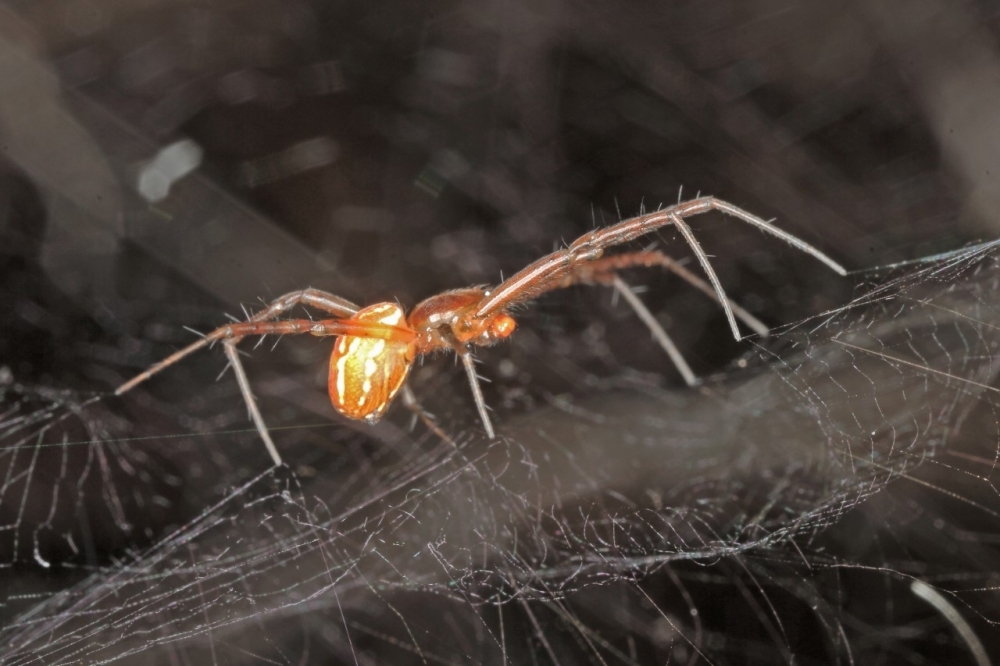

Study shows that males of the species Manogea porracea protect spiderlings and eggs against predators even if they cannot be sure of their paternity.

Non-invasive method uses samples of saliva or other body fluids. The diagnosis can be obtained by means of computational techniques for visualizing data and machine learning.
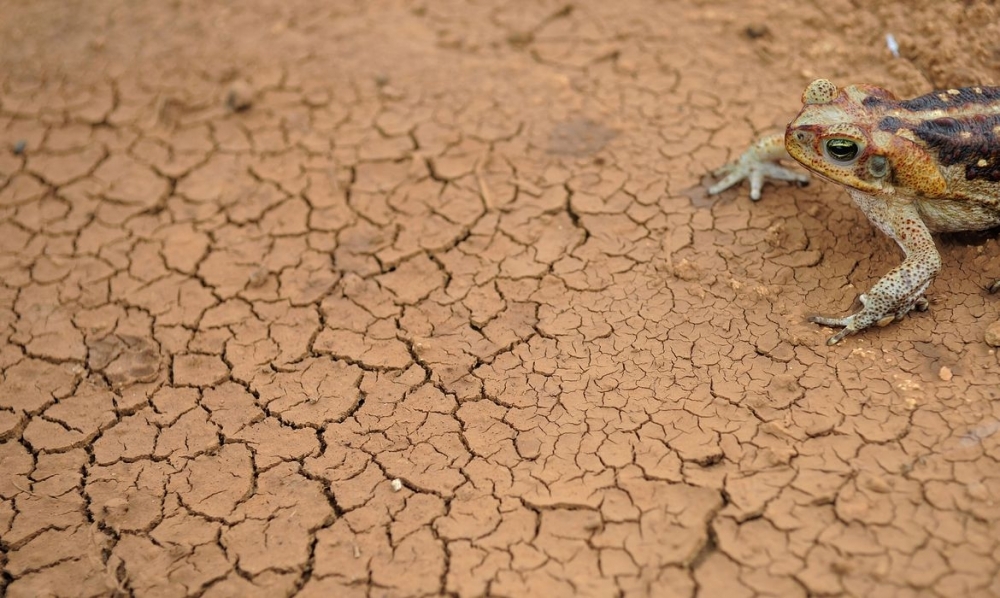

If greenhouse gas emissions continue at the current level, the average temperature will tend to rise by as much as 4 °C in some regions. Under this scenario, extreme weather events will be more intense and frequent, according to projections made using the IPCC’s new climate models.
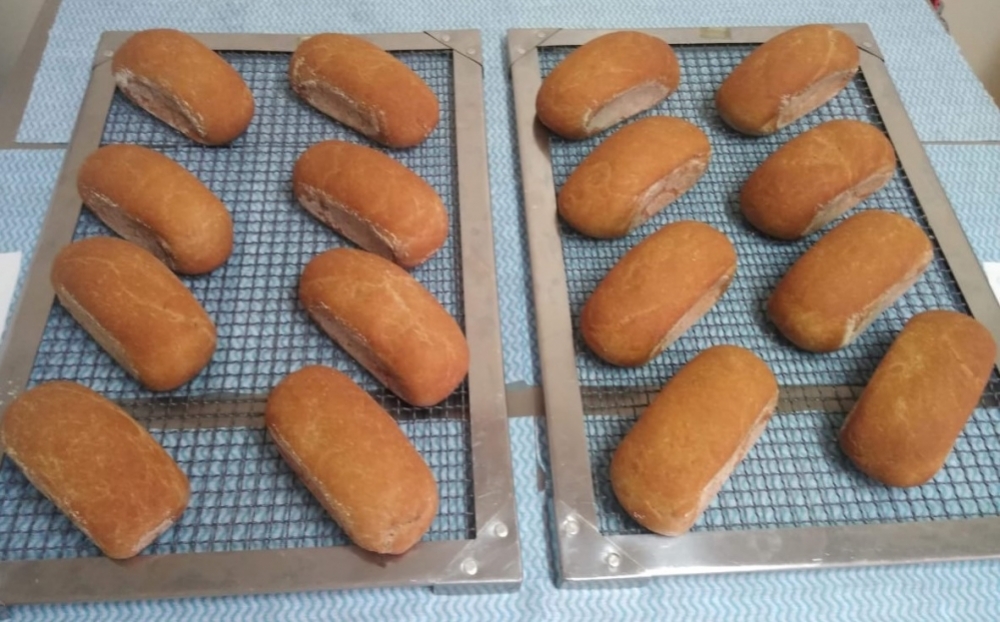

Study at the Federal University of São Paulo developed a recipe combining chickpea flour and psyllium, a plant-derived soluble fiber. The product is nourishing and rated highly by consumers in qualitative surveys.

Researchers compared data for pregnant women in Rio de Janeiro and Manaus who were infected by zika virus in 2015-16. Factors that influenced the risk of fetal malformation were the high zika attack rate in the area and being infected in the first trimester of pregnancy.

Based on data for 344 volunteers, Brazilian researchers compared the physical and mental health benefits of workouts led in person by a fitness instructor, unsupervised online sessions, and classes supervised remotely via video call. Gradually increasing intensity was associated with improvements in mental health.
A project led by researchers at Getúlio Vargas Foundation in Brazil and the University of Michigan in the US produced a detailed analysis of the effects of public policies and government decisions on the response to COVID-19, highlighting the factors that influenced its success or failure in many countries and regions around the world.

The study was conducted in the city of São Paulo, with over 2,000 participants who were active or retired staff of the University of São Paulo and enrolled in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brazil). The researchers say the city has one of the highest prevalence rates of psychiatric disorders in the world.
The initiative is being implemented as a partnership between local government, DASA Laboratories and FAPESP.
The platform holds more than 50 million datasets from 800,000 patients in Brazil and has registered some 4,000 downloads by users in 36 countries.

In an online seminar organized by FAPESP, researchers in Brazil and the United States presented preliminary results of studies on mental health and quality of life among survivors of COVID-19 up to six months after discharge from hospital.

Packaging paper and corrugated cardboard eliminate 99.99% of viral particles in up to 10 minutes of contact.

Simulations run by Brazilian scientists on a supercomputer at the National Space Research Institute (INPE) show that the direct impact of rising levels of carbon dioxide over the Amazon rainforest would be a reduction in rainfall equivalent to or even greater than the impact of complete substitution of the forest by pasture. The result calls attention to the need for regional and global action to mitigate the adverse effects of climate change.

Tests performed by Brazilian researchers after the first 16 weeks of COVID-19-induced confinement showed loss of muscle strength and diminished aerobic capacity, as well as an increase in cholesterol and glycated hemoglobin, both of which are risk factors for metabolic disorders.
Butantan Institute produces CoronaVac and is testing two new vaccines. Four projects are under way at the University of São Paulo, and two at startups supported by FAPESP’s PIPE innovation funding program.
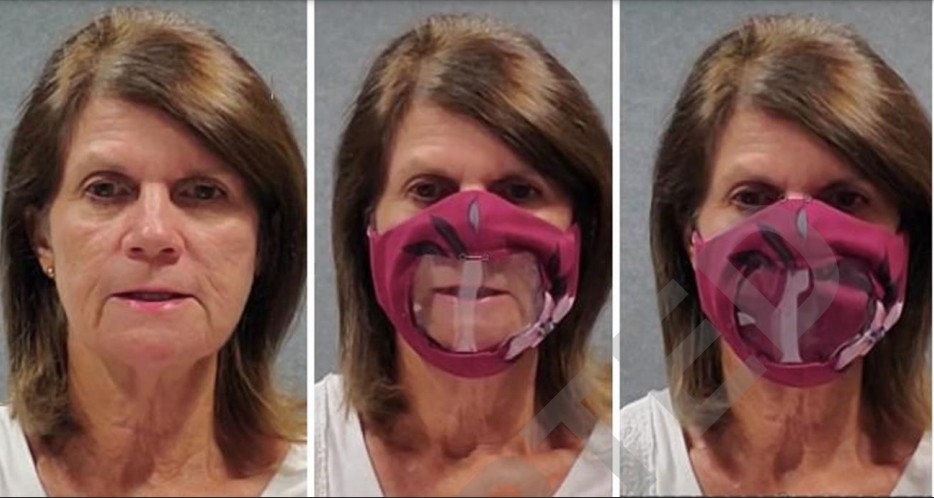
An online study involving 154 volunteers measured the importance of visual cues to communication for people with normal hearing and hearing loss.

In the run-up to the 26th UN Climate Change Conference of the Parties (COP26), experts participating in a webinar hosted by FAPESP showed that the 2020 revision of Brazil’s nationally determined contribution failed to improve targets and allows in practice for a higher level of greenhouse gas emissions.

A solution developed by a startup based in São Paulo state combines fungicidal action and delayed ripening. The researchers who founded the startup took part in the 17th edition of the PIPE High-Tech Entrepreneurial Training Program.

Researchers have completed the first stage of a technical study on the creation of environments designed to foster the development of innovative solutions and creativity in the cities of São Paulo and Campinas.
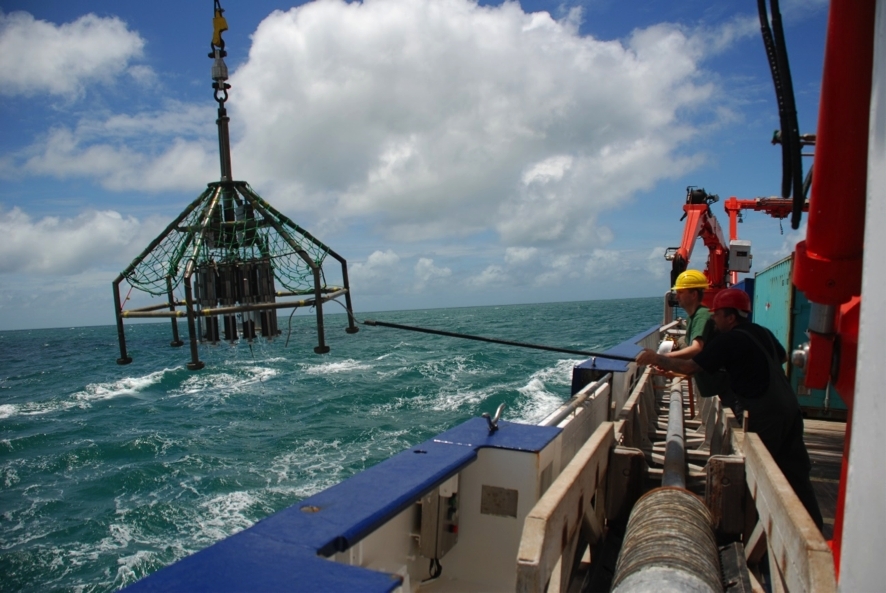

The phenomenon is linked to gradual contraction of the tropical rain belt over the last 5,000 years, according to a study conducted at the University of São Paulo. Its findings can help predict the region’s future climate.
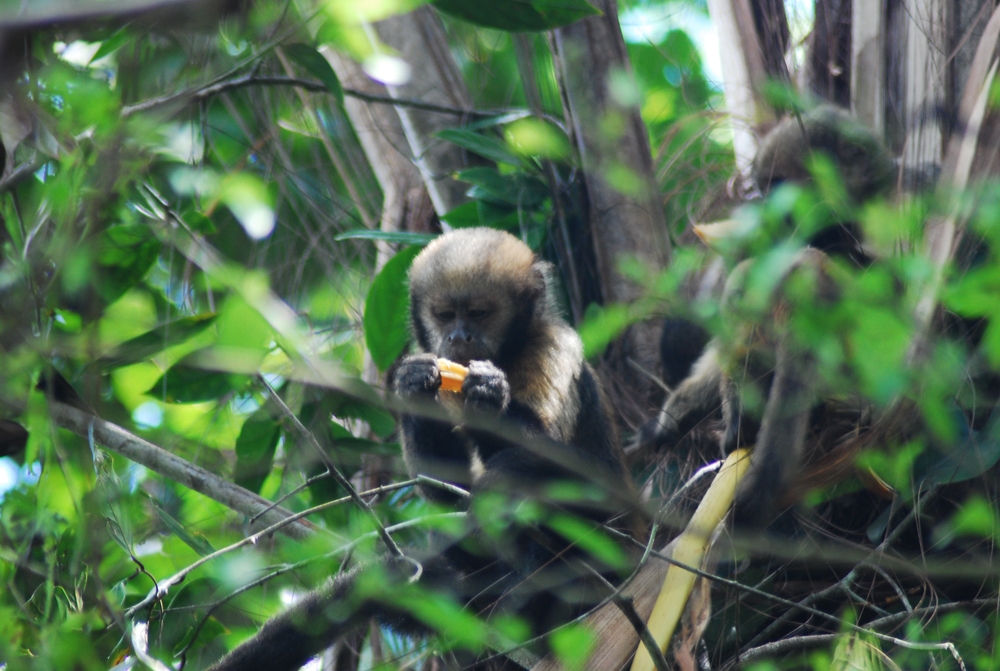

Contradicting theories of primatologists, a study led by Brazilian scientists shows that in a habitat with high hunting pressure, the risk of predation influences the habits of these monkeys more than the availability of food. They spend less time in areas they perceive as ‘more dangerous’ even if plant biomass and invertebrates are more abundant there.
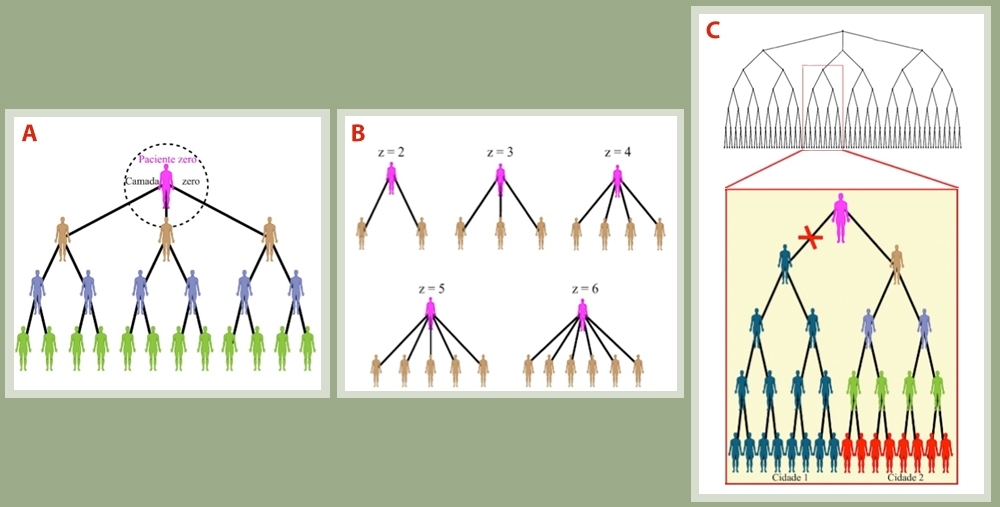
A study conducted at São Paulo State University shows that mathematical models used to describe the physical behavior of magnetic materials can also be used to describe the spread of the disease.
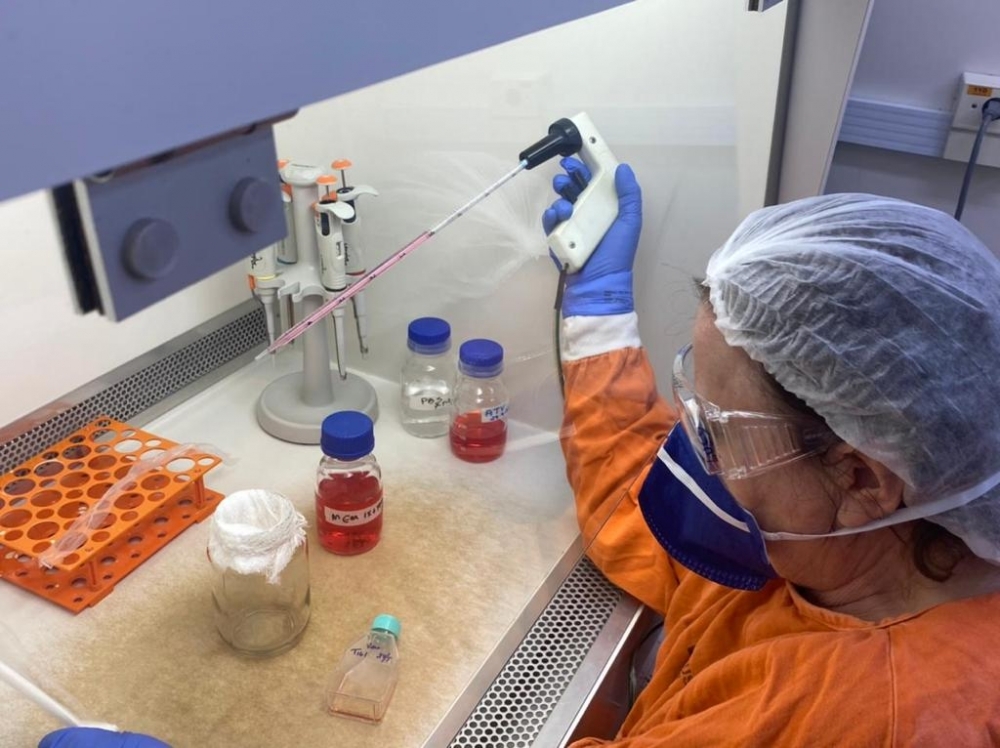

Researchers at the University of São Paulo conducted experiments with blood plasma from 60 volunteers infected in 2020 by SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.28. In 84% of cases, antibodies in the samples neutralized the Gamma variant in cultured cells.
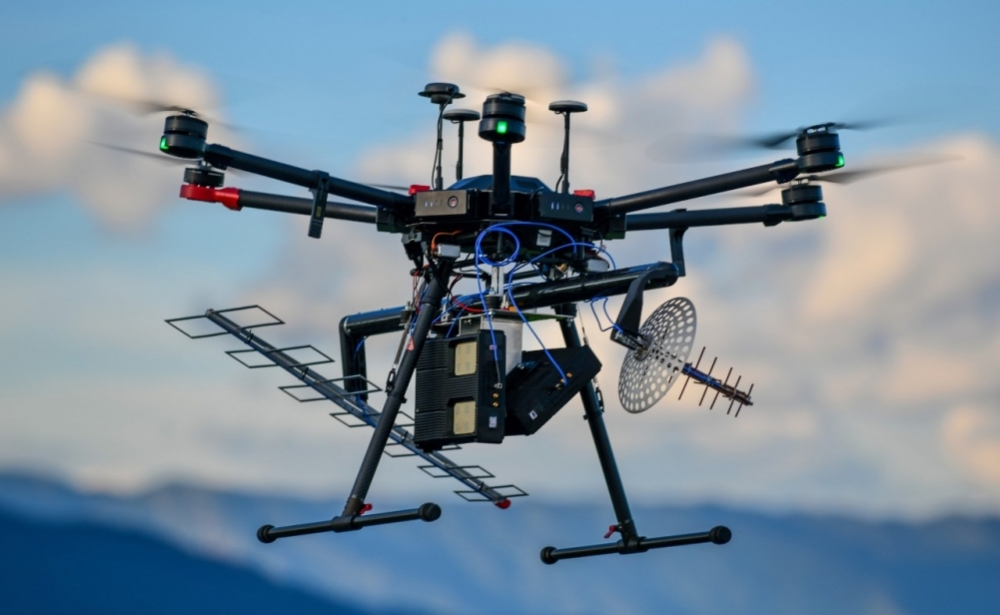

The system, developed by a startup supported by FAPESP, in partnership with researchers at the University of Campinas, helps plantation managers choose the optimal time to harvest the crop.