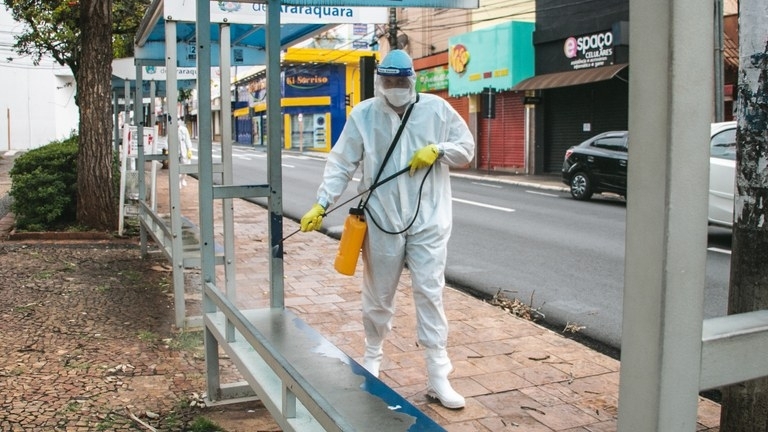



In Araraquara, state of São Paulo, researchers detected the P.1 variant in 93% of samples from patients diagnosed at a primary healthcare facility in the first two months of the year.
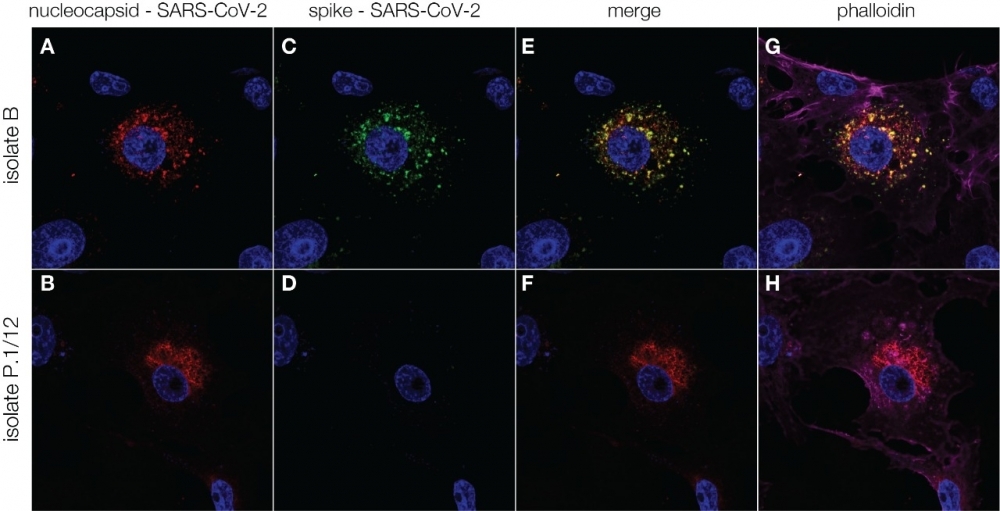
Blood plasma from COVID-19 convalescents was tested against Brazilian variant isolates obtained from patients diagnosed in Manaus. The study also assessed the effectiveness of plasma from volunteers immunized with CoronaVac.

Published by an Anglo-Brazilian epidemiological research center, the study revealed that in only seven weeks SARS-CoV-2 lineage P.1 became the most prevalent strain of the virus in Manaus. Analysis of more than 900 samples from patients diagnosed in the period pointed to a higher viral load.

In a study conducted at the University of São Paulo, researchers used infrared laser irradiation to accelerate the activity of enzymes immobilized on gold nanoparticles. The technique could have biomedical and industrial applications.
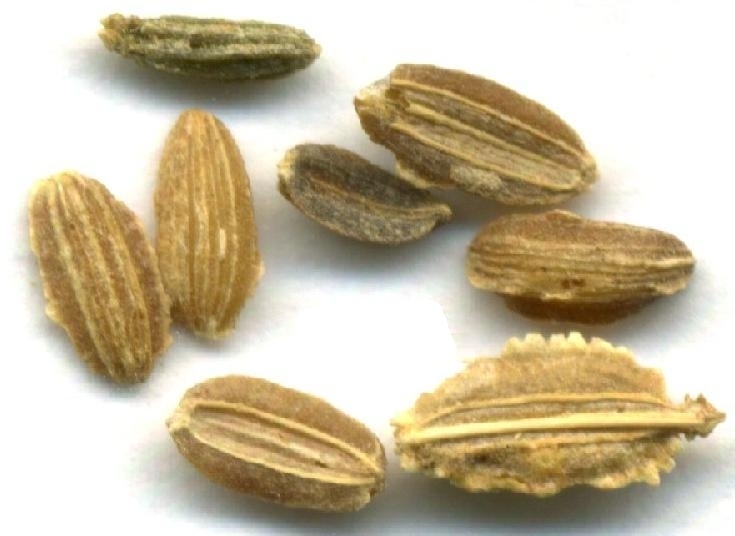

Developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo, the non-invasive methodology facilitates identification of immature or poor-quality seeds without destroying them or creating residues.
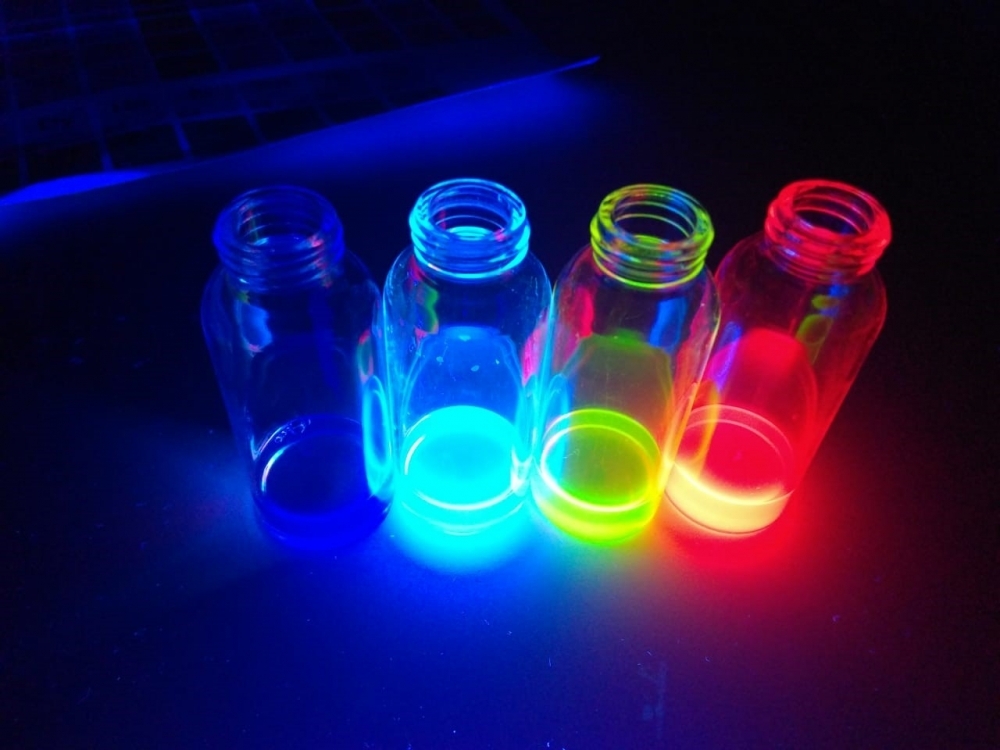

Study conducted at University of Campinas in collaboration with University of Michigan explains nanoscale physics of this manmade material in article published in Science Advances.

Agricultural residues already produce 25% of the electricity used by households in the state. The proportion could jump to 70%, according to researchers who took part in an online seminar on the topic.

Open-access repository established to facilitate research on the disease holds anonymized data including clinical examinations and laboratory test results from 485,000 patients processed by five institutions.
Study conducted at a FAPESP-supported research center shows that anti-inflammatory peptide TnP could lead to drug development.

Study suggests that replacing native vegetation with pasture or crops increases competition among microorganisms, favoring those with antimicrobial resistance genes. Brazilian scientists advocate more research to find out whether bacteria can migrate to food and reach humans.

Operating in the São José dos Campos Technology Park, Autaza’s RIC has an optical system for automotive paint quality inspection using computer vision and artificial intelligence.

In October the CDC recommended ten instead of 14 days of isolation for patients with mild or moderate symptoms, but Brazilian researchers found viable viral particles in 25% of samples collected from patients on the tenth day of symptoms.
There is no universally adopted system or standard for collecting, documenting and sharing the massive amount of data from research on the disease, noted an expert who took part in the Second Latin American and Caribbean Scientific Data Management Workshop.
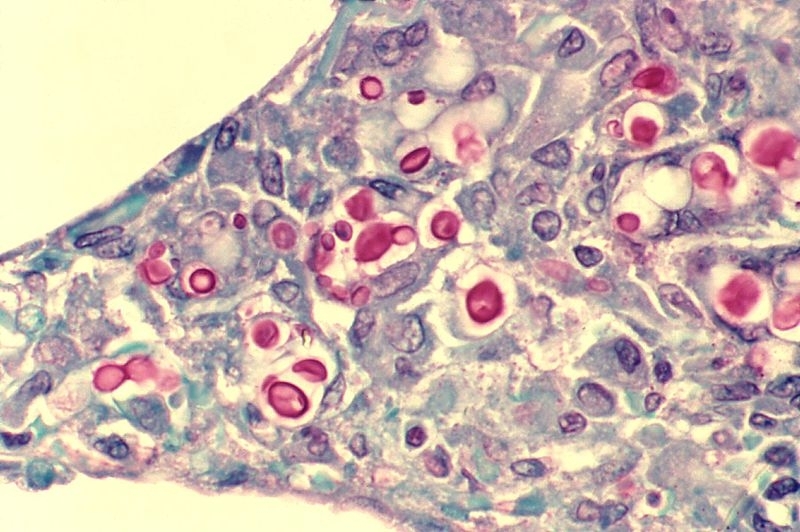
The use of CAR T-cells reprogrammed to “recognize” Cryptococcus spp. proved effective to combat the infection in vitro and in mice.
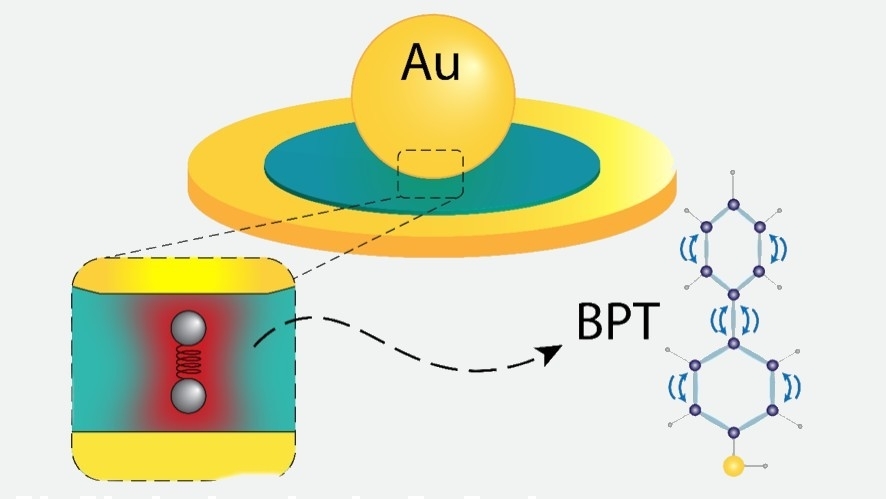
Study by researchers at the University of Campinas published in Physical Review Letters discusses both light dispersion by vibrations inside the device and light dissipation to the exterior, an aspect rarely studied hitherto.

Researchers in Brazil, Argentina, Chile, and the UK are participating in the initiative. Results are published in the journal BioScience.
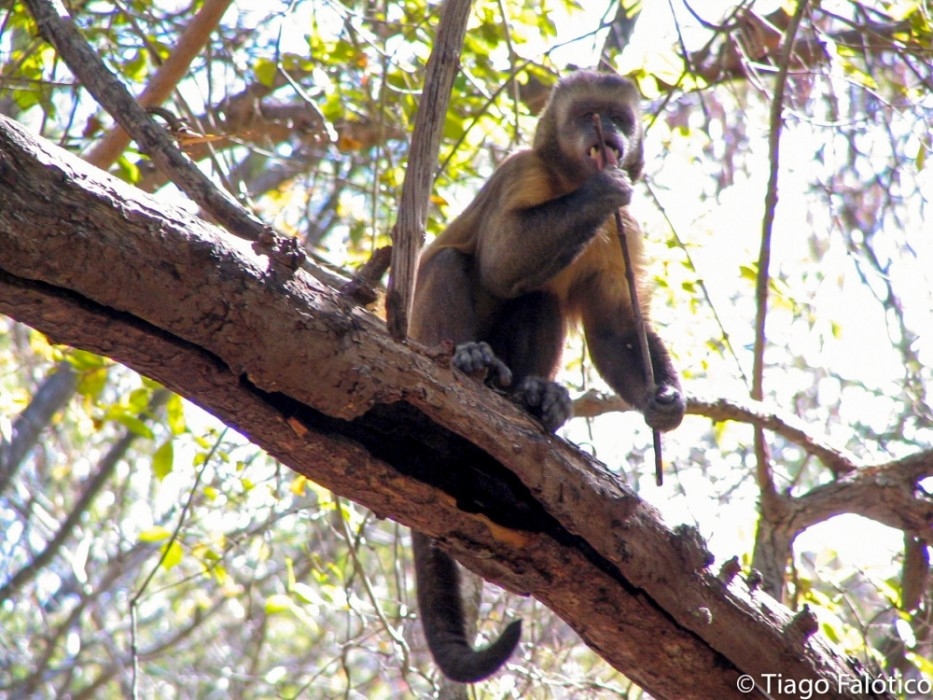

Scientists who study capuchin monkeys on a nature reserve in Brazil found that stone tools are used for digging, seed pounding, and stone-on-stone percussion. The monkeys can serve as a model to help understand how humans evolved to use tools.
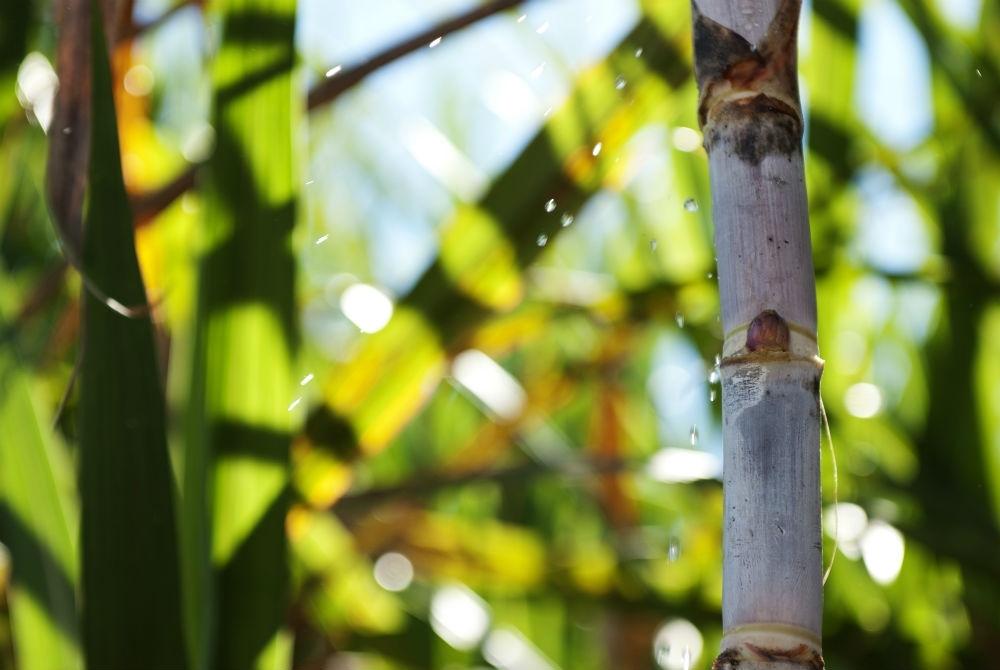

With FAPESP’s support, PangeiaBiotech develops genetically modified varieties of sugarcane that are protected against attacking insects and glyphosate-tolerant.
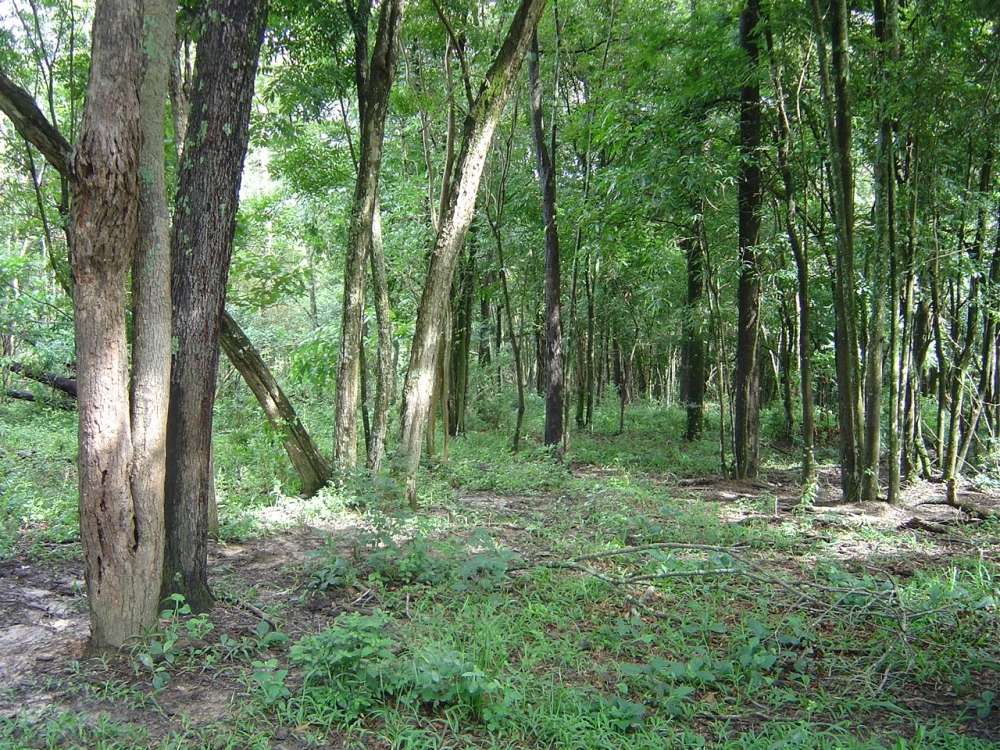

Researchers at the University of São Paulo estimated biodiversity and biomass losses in the biome using data from 1,819 forest inventories. In terms of carbon storage, the losses correspond to the destruction of 70,000 km² of forest, representing some USD 2.6 billion in carbon credits.
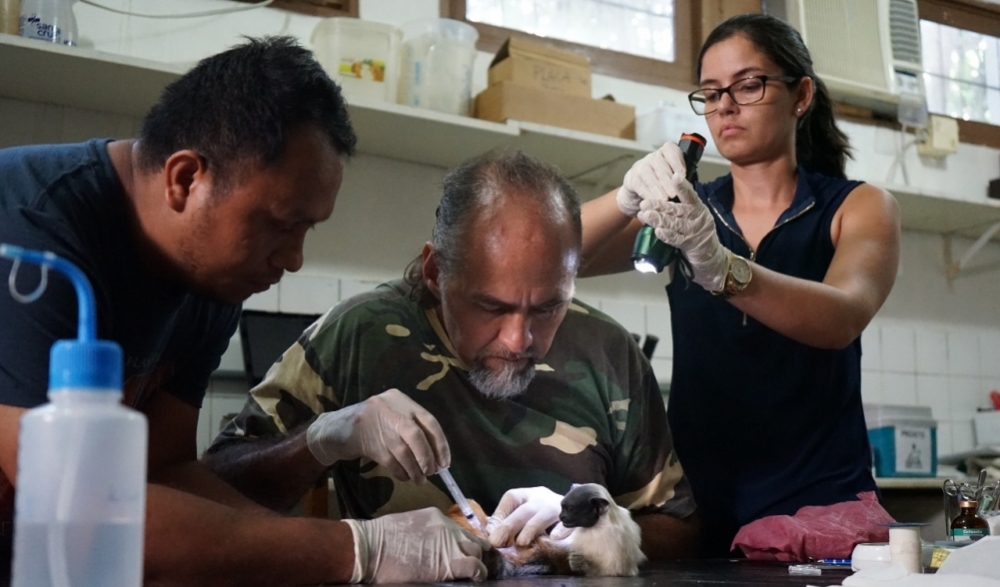

Scientists will monitor areas in which these diseases are endemic, such as São Paulo, the Amazon, the Pantanal and Panama, to investigate the factors that trigger outbreaks.

According to a paper by Brazilian researchers published in Nano Today, the spatial arrangement of proteins on the surface of SARS-CoV-2 assures highly efficient interaction with target receptors on human cells.
The different criteria used in Phase 3 clinical trials of the vaccines approved so far were explained by scientists in a webinar hosted by FAPESP. The impact of delays in vaccinating Brazilians was one of the topics discussed.

An analysis conducted in the Brazilian state of São Paulo detected seven proteins in plasma from hospitalized patients that could be used in novel treatments and methods of identifying potentially severe or critical cases.

The new Applied Research Center’s mission is to conduct research that can provide input for public policies. FAPESP is partnering with the Maria Cecilia Souto Vidigal Foundation and INSPER to mount the initiative.

In an article published in Scientific Reports, Brazilian researchers show that besides simplifying operational logistics and improving production, fertilization of the grass used as a cover crop can reduce fertilizer use in the long run.