


The warning came from a FAPESP-held webinar in which researchers discussed the present-day and historical factors that explain the inadequate response to the pandemic in Brazil’s North region.

The Brazilian startup Crop Biotecnologia has developed a peptide that inhibits bad cholesterol receptors in the liver. The researchers who founded it took part in the 18th edition of the PIPE High Tech Entrepreneurial Training Program.
Scientists at a FAPESP-funded research center investigated the mechanism that produces the main enzyme involved in the virus’s replication in cells. The findings are reported in the Journal of Molecular Biology.

Researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos in Brazil in partnership with University College London (UCL) in the UK analyzed data for 2,294 individuals aged 60 or more who were monitored for eight years. Results were published in the journal Age and Aging.
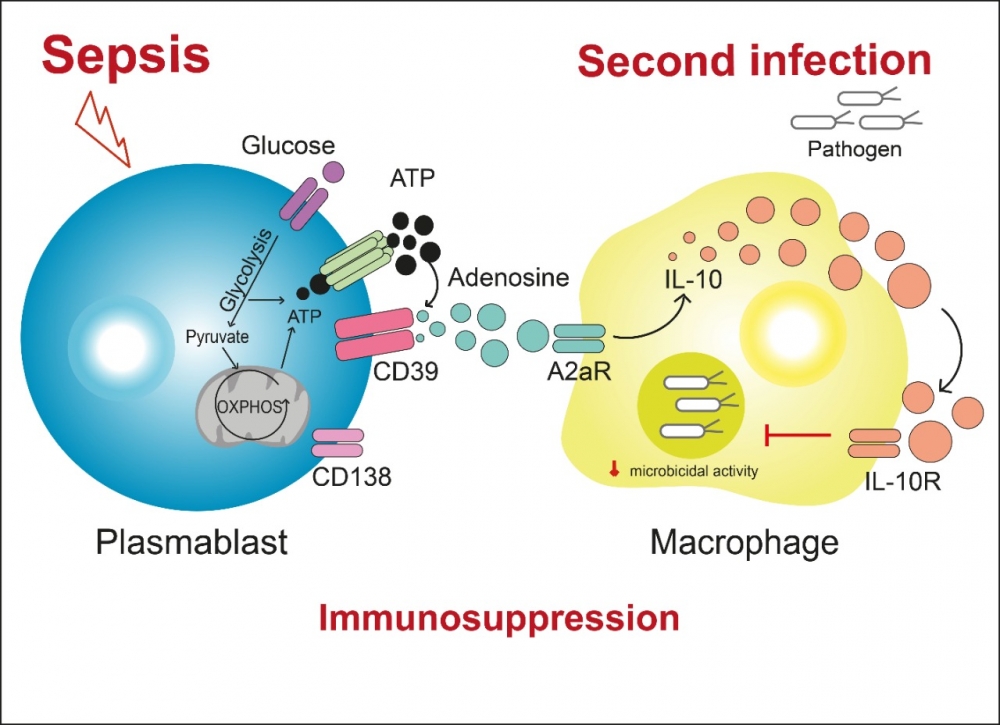
Many patients suffer from a significant decline in immunity lasting for years after they are discharged from hospital. In an article published in the journal Immunity, Brazilian researchers reveal why this happens.
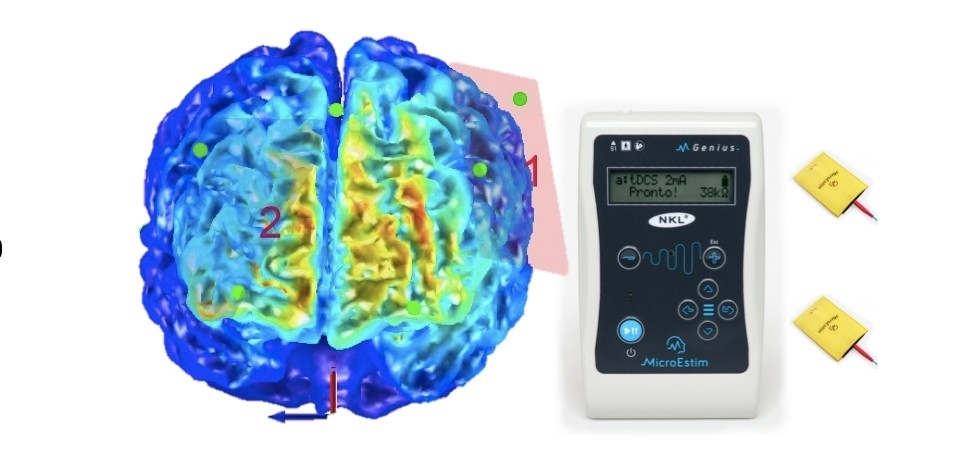
The result was obtained in a study of 20 volunteers by researchers at São Paulo State University. The treatment is painless and uses a weak current delivered by electrodes placed over specific brain regions.
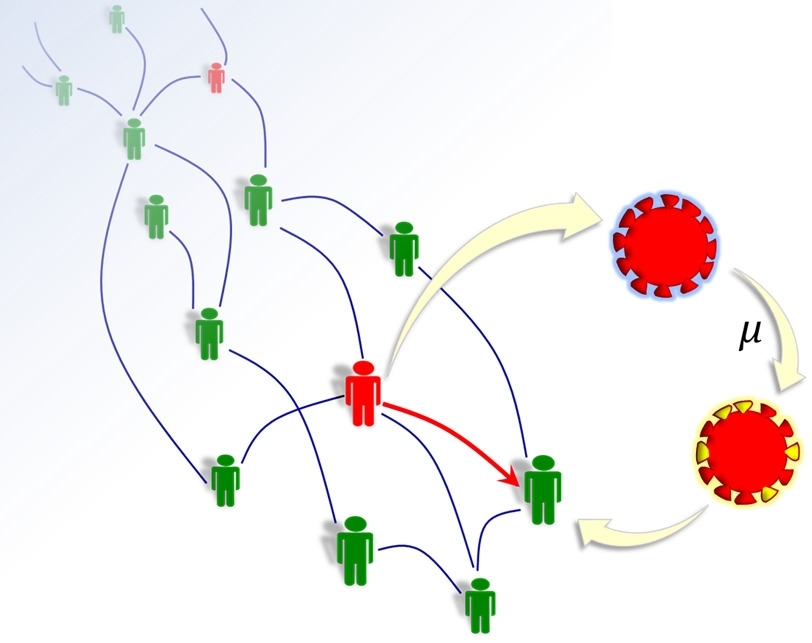
The study is published in PLOS ONE. Equations suggest viral population variability can be estimated on the basis of epidemiological data.
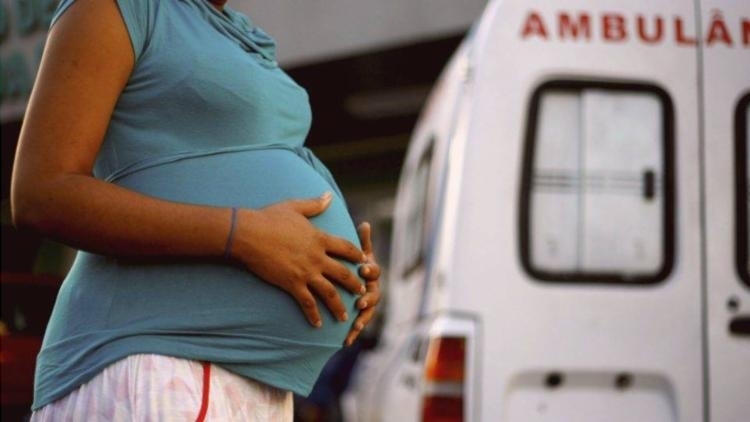

In a review of the scientific literature, researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo concluded that infection by SARS-CoV-2 during pregnancy can reduce the availability of ACE2, a protein that plays an important part in placental development, control of blood pressure, and the circulatory adaptations required for fetal development.
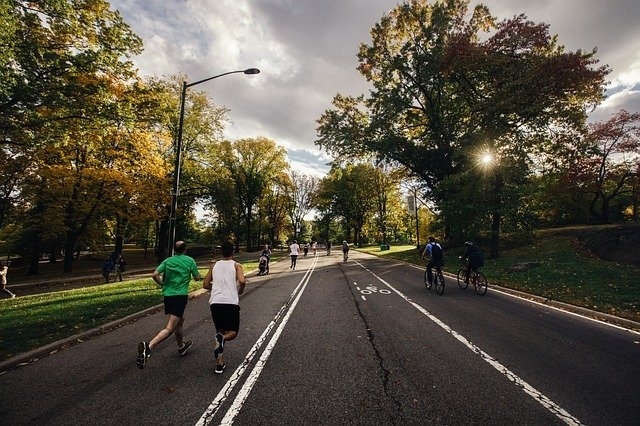

More than 1,000 Brazilian volunteers immunized with the CoronaVac vaccine were assessed by researchers at the University of São Paulo. Those who were active for at least 150 minutes per week without long sedentary periods produced more antibodies against SARS-CoV-2.
The platform is used by several hospitals, has more than 2,500 users, and performs 800 care processes per month on average.
A study conducted by researchers at the Center for Cell-Based Therapy in São Paulo state, Brazil, identified a genetic signature that can be used to predict whether patients should be submitted to radiation therapy.
Correlating whole-genome sequencing with epidemiological data for the city of São José do Rio Preto in Brazil, researchers show that severe COVID-19 and deaths from the disease rose sharply when the variant became prevalent in the region. A two-week lockdown and vaccination of the elderly averted a collapse of the health system.
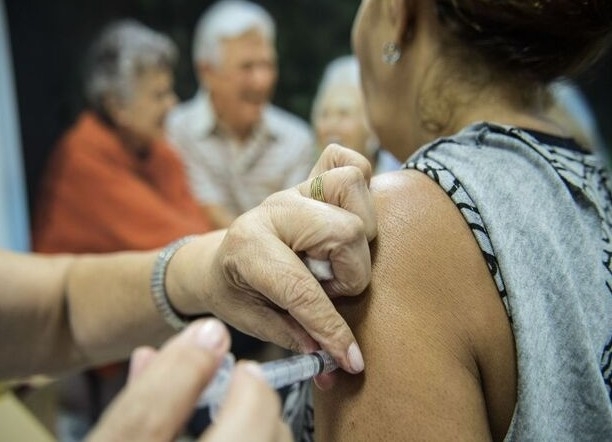

A study published in Nature Medicine evaluated individuals before and after taking CoronaVac. Based on the results, researchers at the University of São Paulo’s Medical School are testing novel strategies such as suspending treatment one or two weeks before vaccination.
Outbreaks at two care homes in São Paulo state (Brazil) show that even people who have been vaccinated with one dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine or two doses of CoronaVac can transmit the virus. The cases were asymptomatic or mild and did not require hospitalization, but underscore the importance of rapidly vaccinating the entire population while continuing to require face coverings and social distancing even for those who have been vaccinated.
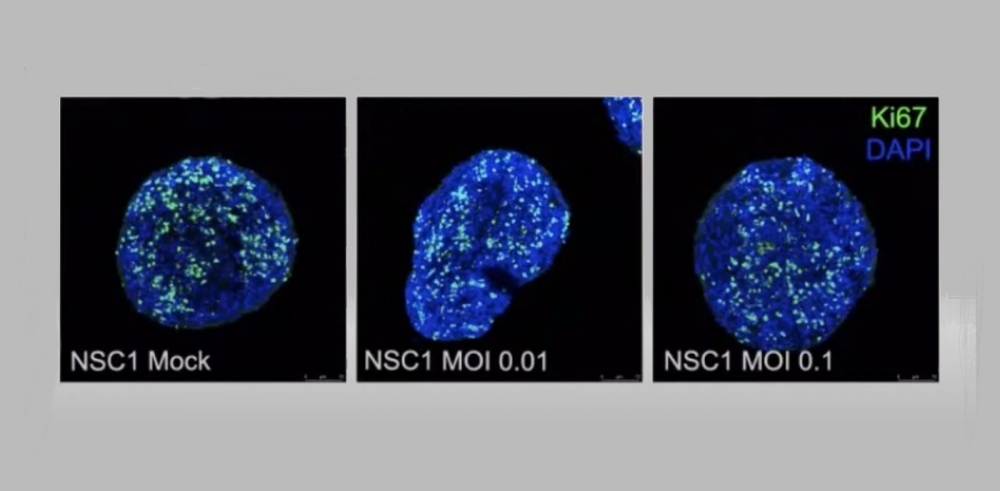
A webinar held by FAPESP featured researchers from Brazil and Germany whose findings offer clues as to how SARS-CoV-2 invades the central nervous system and which cells are most affected.
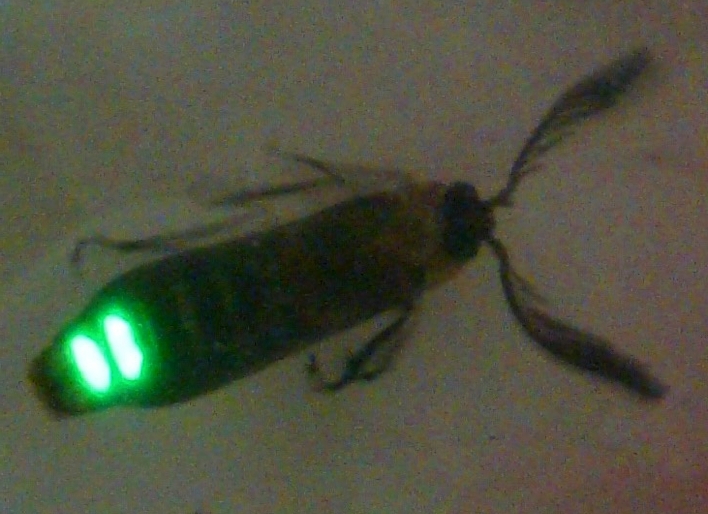

Brazilian researchers coupled the molecule with a protein that binds to SARS-CoV-2. The presence of antibodies against the virus in the sample is confirmed by light emission.
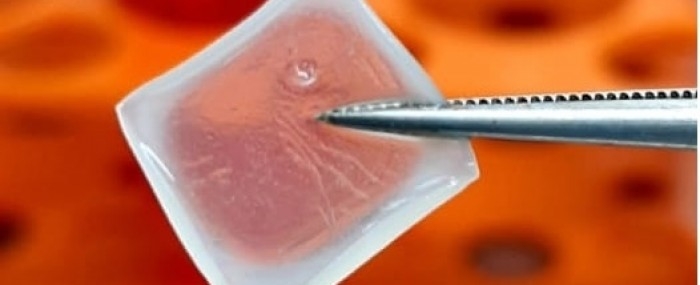
Developed by startup In Situ from stem cells and a hydrogel, the product is bioprinted and placed lightly on the skin.

Non-invasive method uses samples of saliva or other body fluids. The diagnosis can be obtained by means of computational techniques for visualizing data and machine learning.
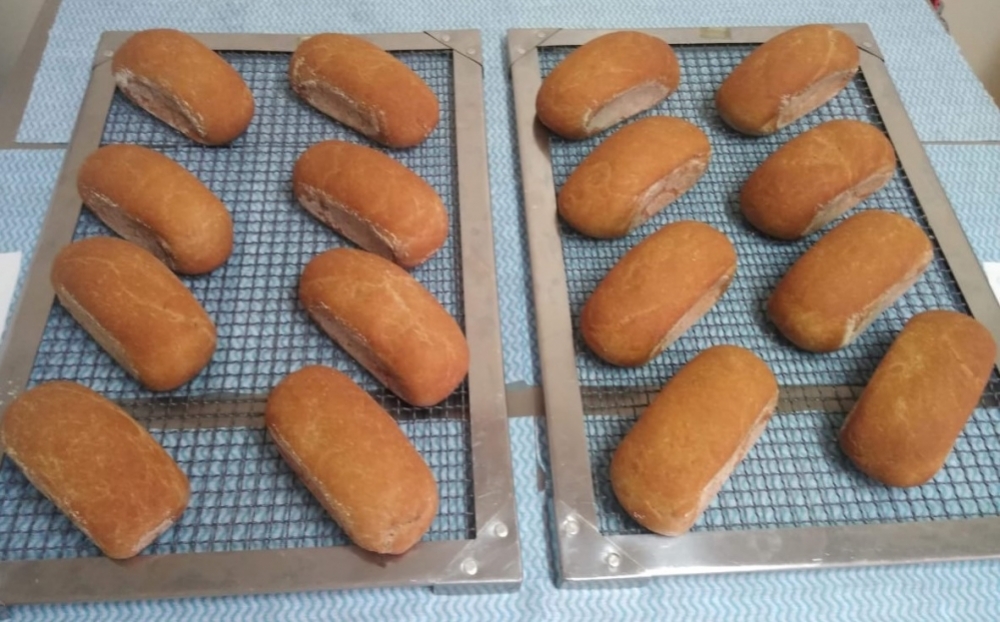

Study at the Federal University of São Paulo developed a recipe combining chickpea flour and psyllium, a plant-derived soluble fiber. The product is nourishing and rated highly by consumers in qualitative surveys.

Researchers compared data for pregnant women in Rio de Janeiro and Manaus who were infected by zika virus in 2015-16. Factors that influenced the risk of fetal malformation were the high zika attack rate in the area and being infected in the first trimester of pregnancy.

Based on data for 344 volunteers, Brazilian researchers compared the physical and mental health benefits of workouts led in person by a fitness instructor, unsupervised online sessions, and classes supervised remotely via video call. Gradually increasing intensity was associated with improvements in mental health.
A project led by researchers at Getúlio Vargas Foundation in Brazil and the University of Michigan in the US produced a detailed analysis of the effects of public policies and government decisions on the response to COVID-19, highlighting the factors that influenced its success or failure in many countries and regions around the world.

The study was conducted in the city of São Paulo, with over 2,000 participants who were active or retired staff of the University of São Paulo and enrolled in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brazil). The researchers say the city has one of the highest prevalence rates of psychiatric disorders in the world.
The initiative is being implemented as a partnership between local government, DASA Laboratories and FAPESP.
The platform holds more than 50 million datasets from 800,000 patients in Brazil and has registered some 4,000 downloads by users in 36 countries.