

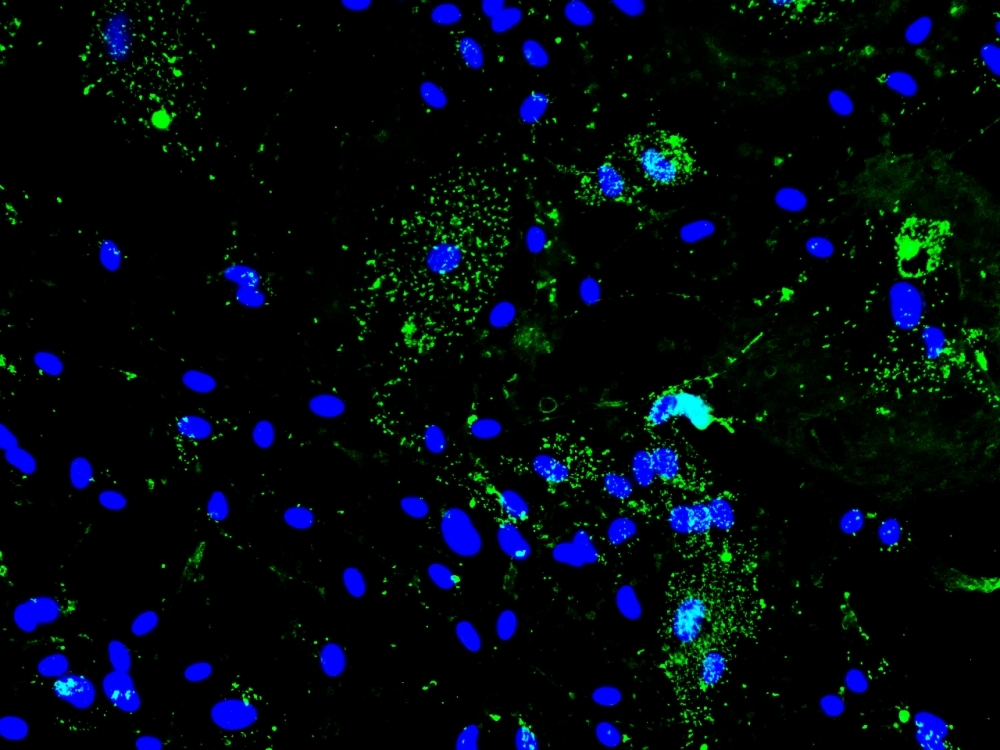
Experiments with hamsters and cultured astrocytes point to possible causes of neurological complications in COVID-19 survivors.
Collaboration between business and academia in the state of São Paulo proves the virucidal action of iron phthalocyanine and develops a mouthwash containing the compound. In a clinical trial involving patients in the initial stage of infection, the product reduces symptoms and hospital stay.
The event was the first of a series of three online seminars organized by FAPESP in partnership with sister agencies in Paraguay and Argentina, under the aegis of the Global Research Council (GRC), with the aim of providing opportunities for an exchange of experiences and cross-border collaboration.

The findings, published in Gynecologic Oncology, pave the way to the development of a blood test that can be performed by a physician at the time of diagnosis to help personalize treatment.
Models capable of predicting the spread of pathogens, algorithms that monitor health complaints on social media, and the use of big data and machine learning to speed up drug development were some of the issues discussed by experts who took part in a webinar organized by FAPESP and the Global Research Council.
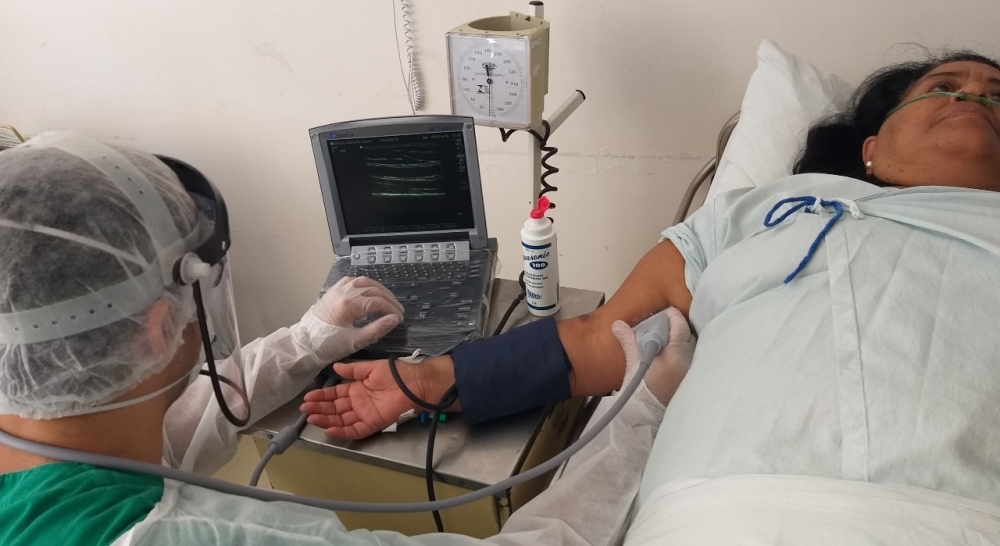
Brazilian researchers conducted a study of 109 hospitalized volunteers in search of the factors that determine endothelial dysfunction, a condition in which the blood vessels become unable to contract and relax adequately, increasing the risk of heart attack, thrombosis and stroke.
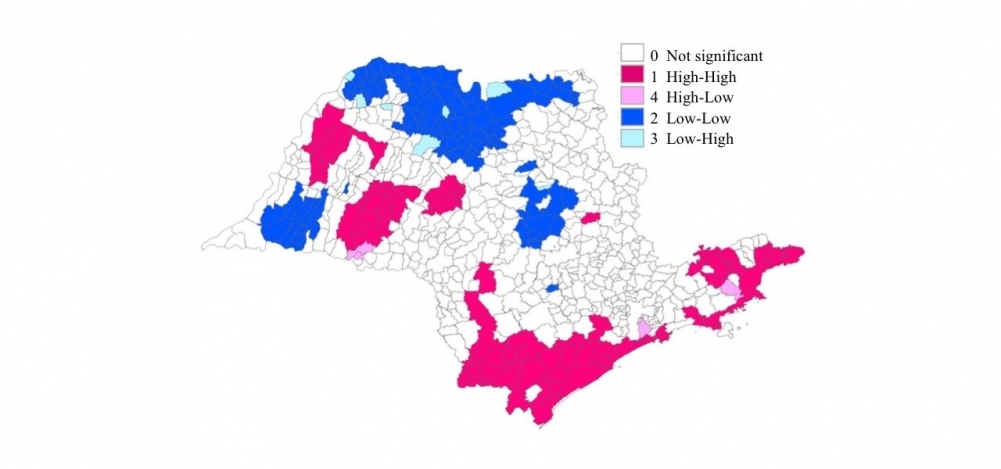
The methodology used in the study, which is published in PLOS ONE, can help policymakers plan strategies for preventing deaths of babies under 28 days old.
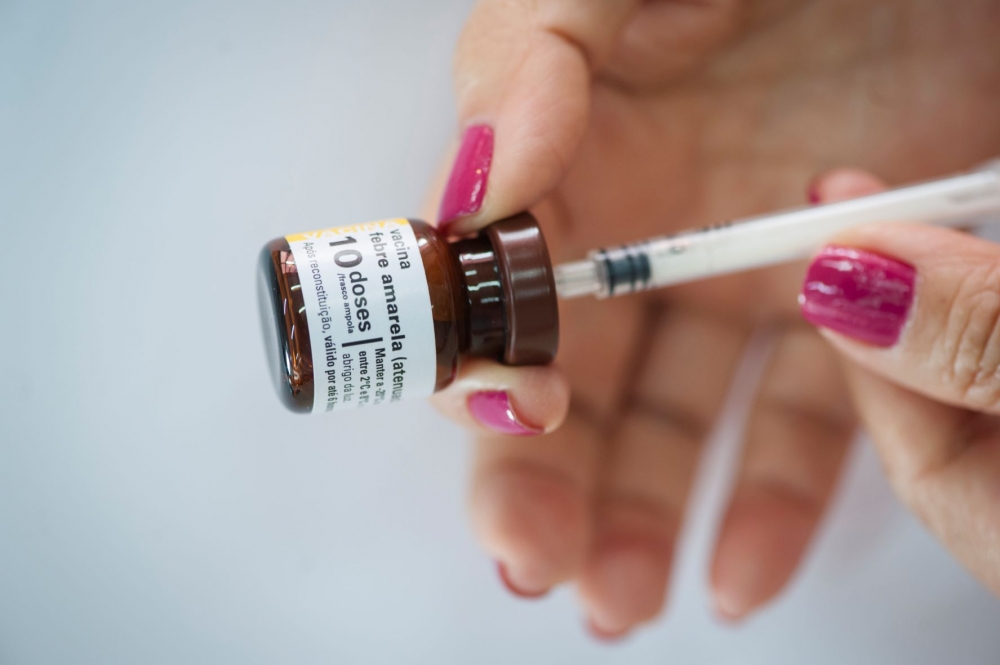
An article in Scientific Reports shows that the virus spread at a speed of 1 km per day in the latest sylvatic outbreaks in the state, between 2016 and 2019, reaching cities never affected before. The authors warn that the situation could recur.
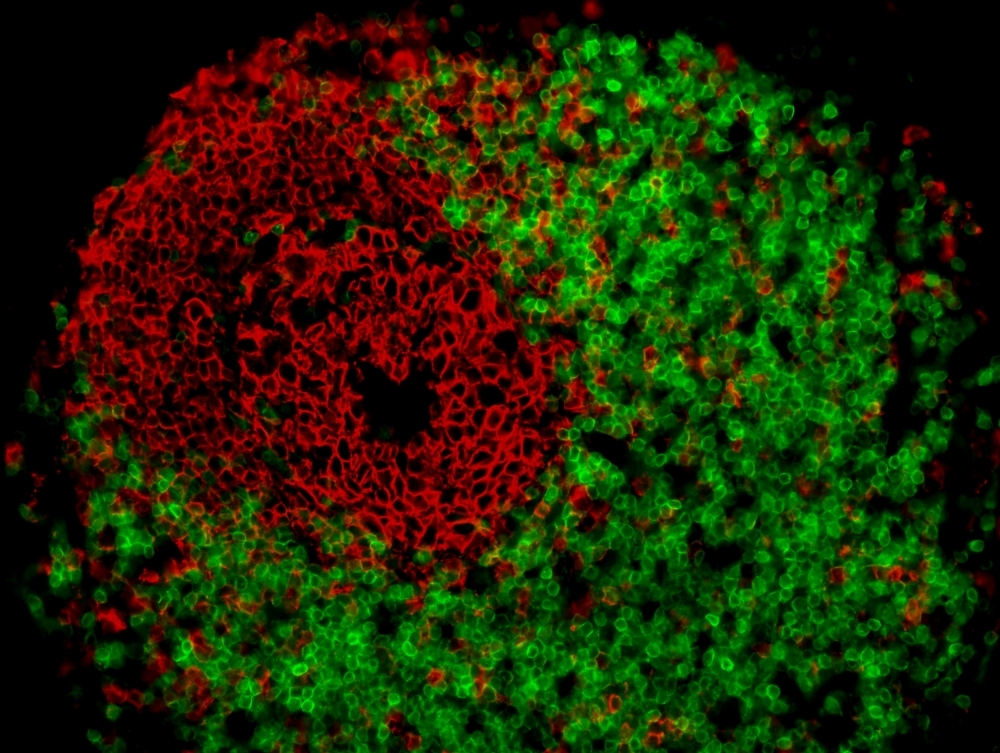
Analysis of tissue samples showed the presence of cells that can trigger the inflammatory process typical of Crohn’s. The study paves the way for the detection of biomarkers that can help predict evolution to the severe form of the disease, and for more precise diagnosis.

A study conducted at the University of São Paulo shows that levels of TTV, an apparently inoffensive virus considered an indicator of immunodepression, tend to be higher in people infected by SARS-CoV-2. TTV load declines as the symptoms of COVID-19 disappear, the researchers write in PLOS ONE.
This is one of the main findings of a clinical trial involving 465 patients at 28 hospitals in six countries, including Brazil. The likelihood of dying was 78% lower for the group given a therapeutic dose of the anti-coagulant.
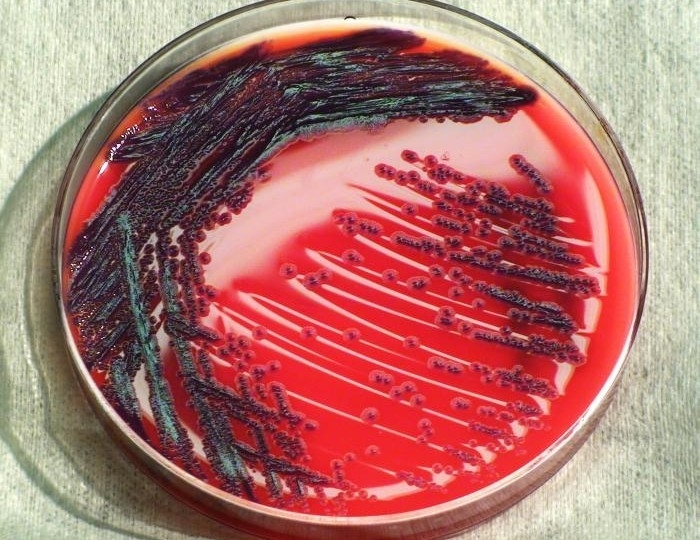
Researchers at the University of São Paulo have unraveled the strategy used by Chromobacterium violaceum, a pathogen found in water and soil in tropical and subtropical regions, to increase its capacity to replicate and infect host organisms. The discovery offers a route for the development of novel therapies.
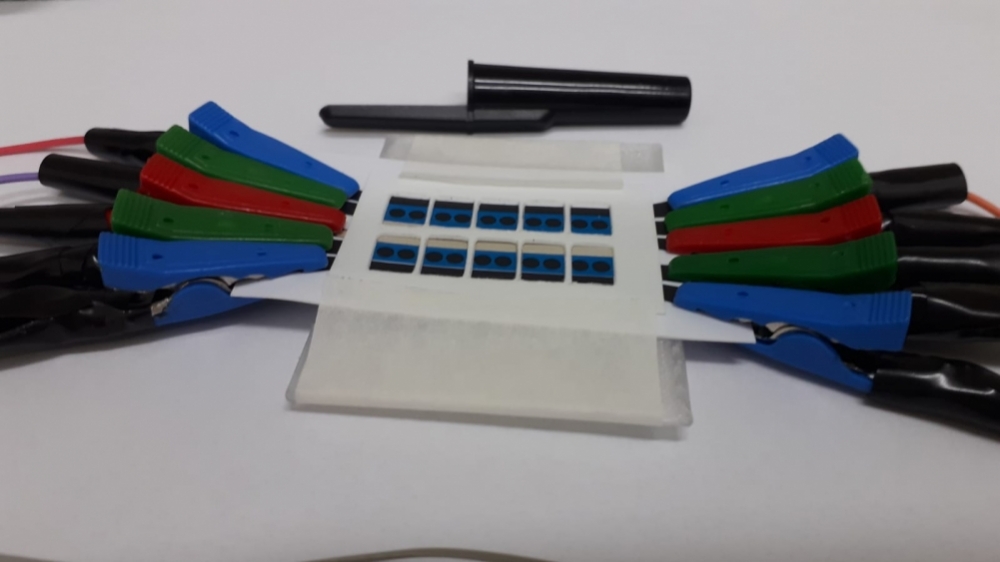

The portable device developed at the Federal University of São Carlos is as accurate as RT-PCR, the gold standard for diagnosing COVID-19, and can analyze up to 20 samples at the same time.
A study in rats by researchers at institutions in Brazil, the US and Norway investigated the effects of physical exercise on cancer cachexia. The analysis suggested that exercise training can be an ancillary treatment for cancer patients.

Researchers recombined extracts from this fruit industry waste to produce a mini-emulsion that can be used as the basis for an anti-aging skin complex.

For scientists gathered at this FAPESP-hosted webinar, projects like the Belo Monte dam and the Transamazon highway have had few local benefits and led to a rise in poverty, violence, deforestation and disease.

The conclusion was published by Brazilian researchers in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. They followed 1,539 children in a part of Amazonia that accounts for 18% of infections by Plasmodium vivax in Brazil.
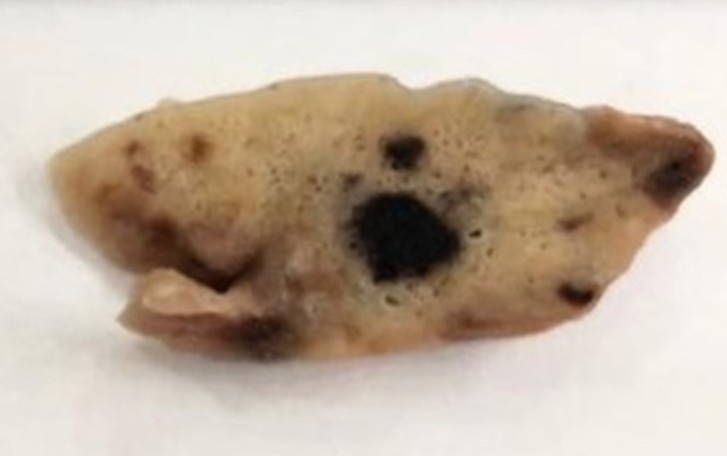
Lung tissue samples from 47 people who died as a result of severe acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by the novel coronavirus were analyzed by Brazilian researchers. The findings can be used to improve treatment of the disease.
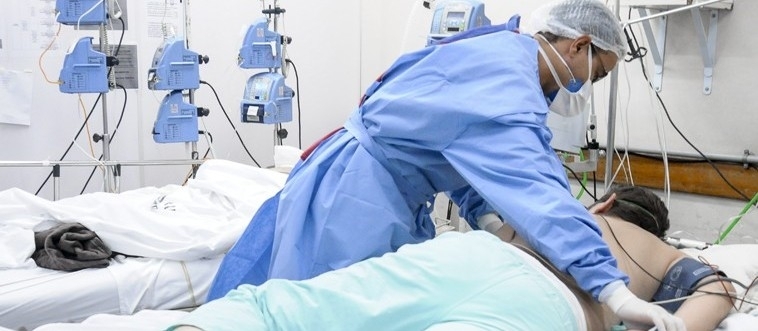
Liver recipients who contracted SARS-CoV-2 recovered faster and with less inflammation than heart or kidney recipients, according to researchers at the University of São Paulo. The reason may have to do with differing amounts and types of immunosuppressants, the drugs used to prevent organ rejection.

Experts who took part in the fourth FAPESP 60 Years Conference discussed the challenges of diagnosing and combating emerging pathogens and the need to integrate multidisciplinary teams and governments if outbreaks of infectious disease are to be prevented.
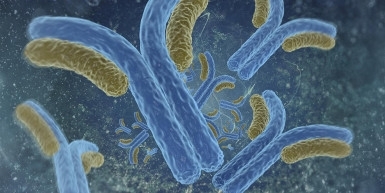
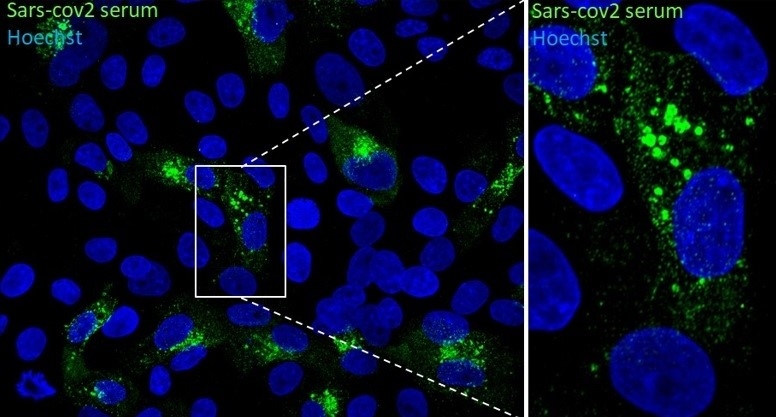
Molecules that attack cells and tissues in the patient’s own organism were detected in blood serum from volunteers infected by SARS-CoV-2, who progressed to moderate or severe COVID-19 after the samples were collected. The discovery could lead to novel therapeutic approaches.
A study by Brazilian researchers evidenced a correlation between post-zika neurological complications and high levels of Gas6, a protein that facilitates viral replication. The findings are published in Brain, Behavior, and Immunity.
In an online seminar held by FAPESP, experts stressed that deforestation favors pathogen spillover from wild animals to humans, and that zoonotic disease surveillance urgently needs to be upgraded.
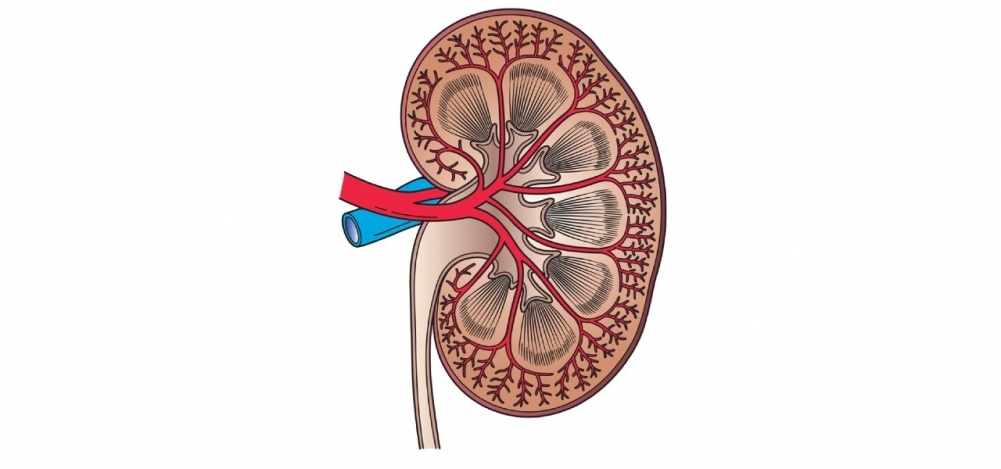
Loss of ACE2, the protein used by the novel coronavirus to invade human cells, leads to an imbalance in systems that regulate essential metabolic functions, impairing blood filtration and causing kidney injuries that can become permanent.

To achieve a deeper understanding of the links between the nervous and immune systems, researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo inhibited the REM stage of sleep in mice to see how this affected the progress of infectious diseases, allergic processes and cancer treatment.